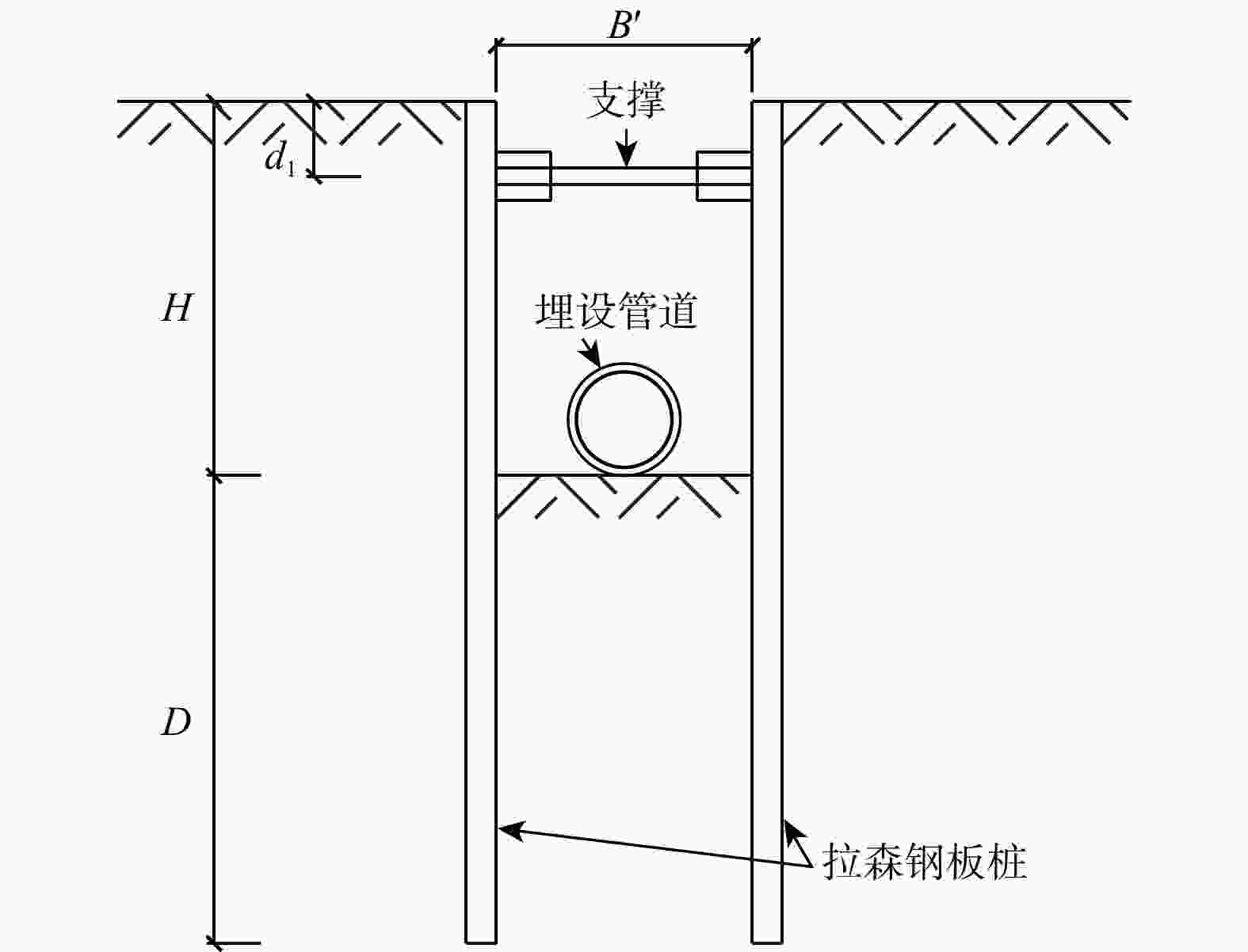
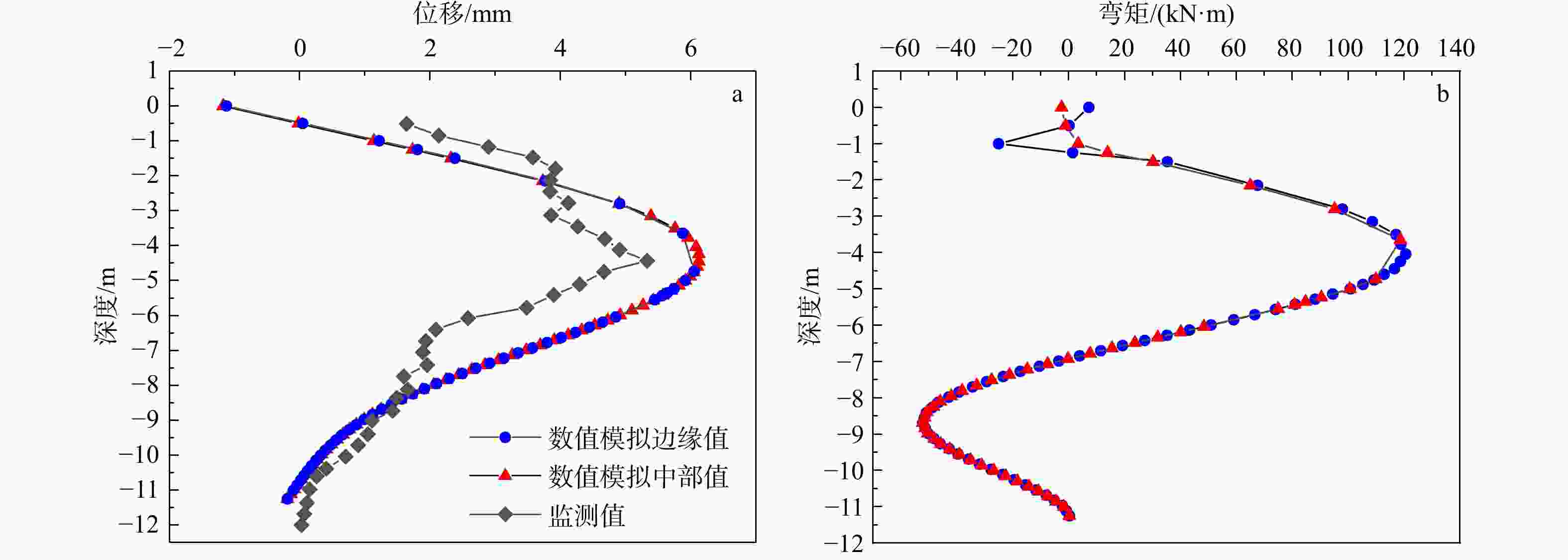
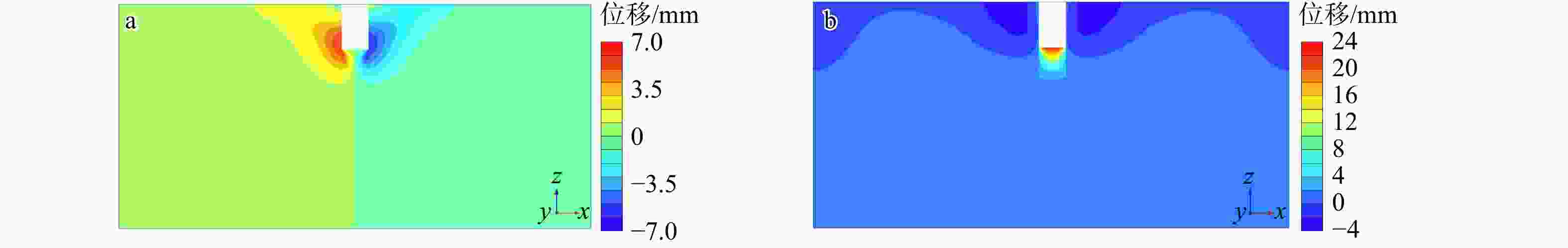
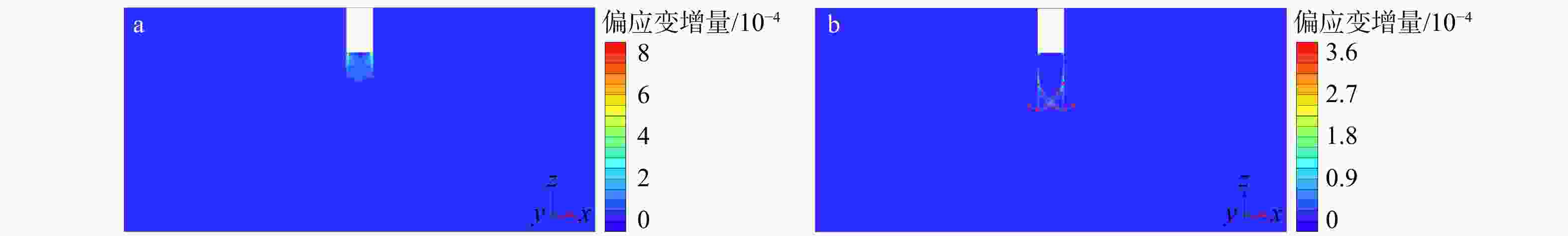
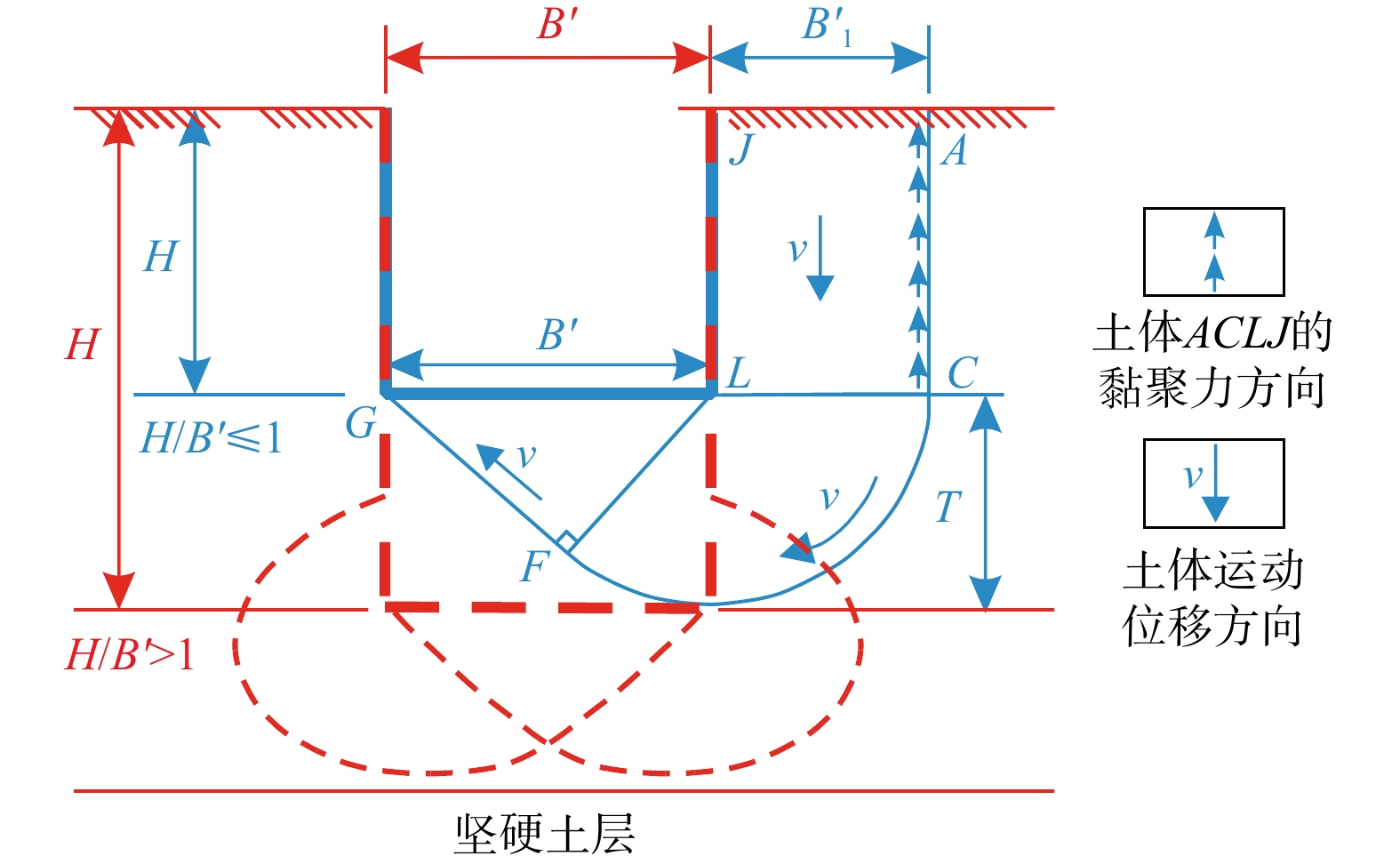
Basal-heave stability of narrow foundation pit in soft soil foundation based on hardening soil with small-strain stiffness (HSS) model
-
摘要:
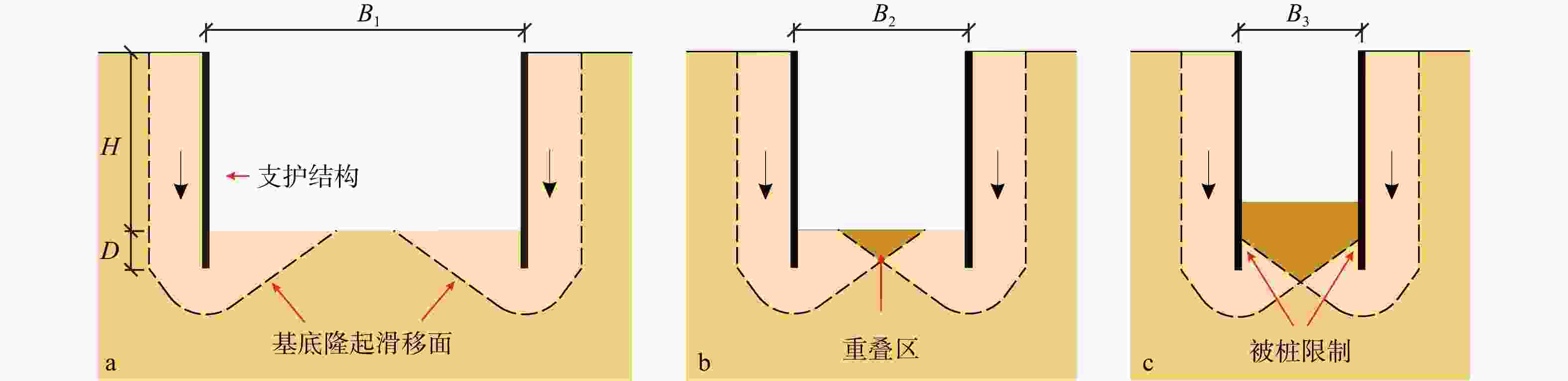
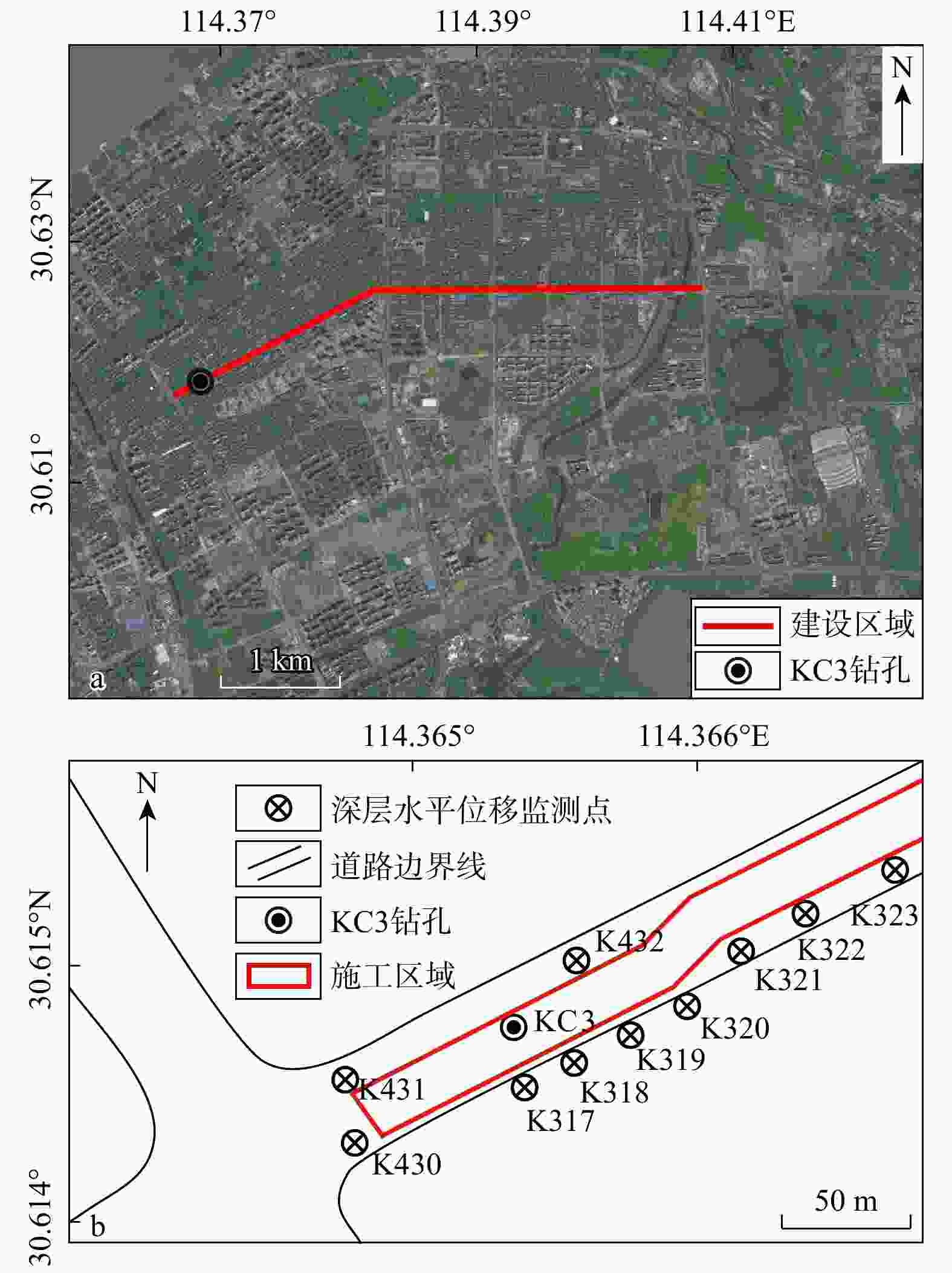
随着城市化和综合管廊的发展,狭窄型基坑工况日益增多。其支护形式、抗隆起计算方法及破坏模式与宽大基坑差异显著,在软土地层中坑底隆起尤为明显。为了进一步探究软土地基狭窄基坑支护结构的受力变形规律,抗隆起稳定性及其影响因素之间的敏感性关系,以武汉友谊大道快速化改造工程为实例,基于有限元计算和现场监测,采用小应变硬化土(HSS)土体本构模型和强度折减法研究基坑宽度、支护结构插入比、周边荷载和支护结构刚度等对狭窄基坑抗隆起稳定性的影响。结果表明:在支护结构刚度大、支撑间距小的情况下,狭窄基坑在支撑处和两道支撑中点处的受力变形差异不明显。狭窄基坑的变形土体可以分为地表至地表以下一定深度的基坑外侧土体和基坑底部土体,分别引起坑底隆起和坑外地表沉降;狭窄基坑土体塑性区会在坑底和结构底部处形成,随着塑性区发展,逐渐形成交叉的塑性区,并向两侧土体发展直至整个塑性区贯通,狭窄基坑最终破坏。敏感性分析表明,支护结构插入比和支护结构刚度对狭窄基坑抗隆起稳定性有显著的正面影响,基坑宽度和周边荷载则为负相关,且支护结构插入比的相关性最强。研究成果为软土地基狭窄基坑的支护结构设计和稳定性分析提供科学依据。
Abstract:Objective As urbanization accelerates and utility tunnel projects develop, narrow foundation pits are becoming increasingly prevalent. However, the supporting systems, basal-heave calculation methods, and failure modes of narrow foundation pits differ substantially from those of wider ones, and basal heave is more pronounced in soft soil strata.
Methods To further investigate the force-deformation behavior, basal-heave stability, and the sensitivity relationships among influencing factors of support structures for narrow foundation pits in soft soil foundations, finite element analysis and field monitoring were conducted using the Wuhan Youyi Avenue rapid reconstruction project as a case study. The hardening soil with small-strain stiffness (HSS) soil constitutive model, and the strength reduction method were employed to study the effects of excavation width, support structure embedment ratio, surcharge loads, and support structure stiffness on the basal-heave stability of narrow foundation pits.
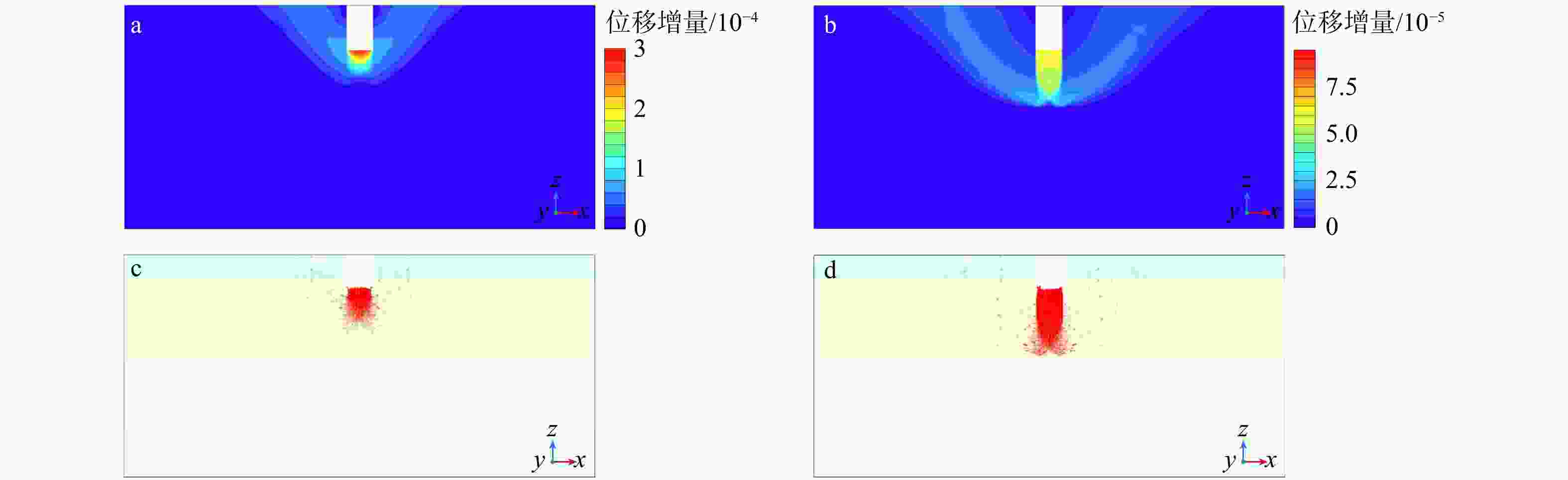
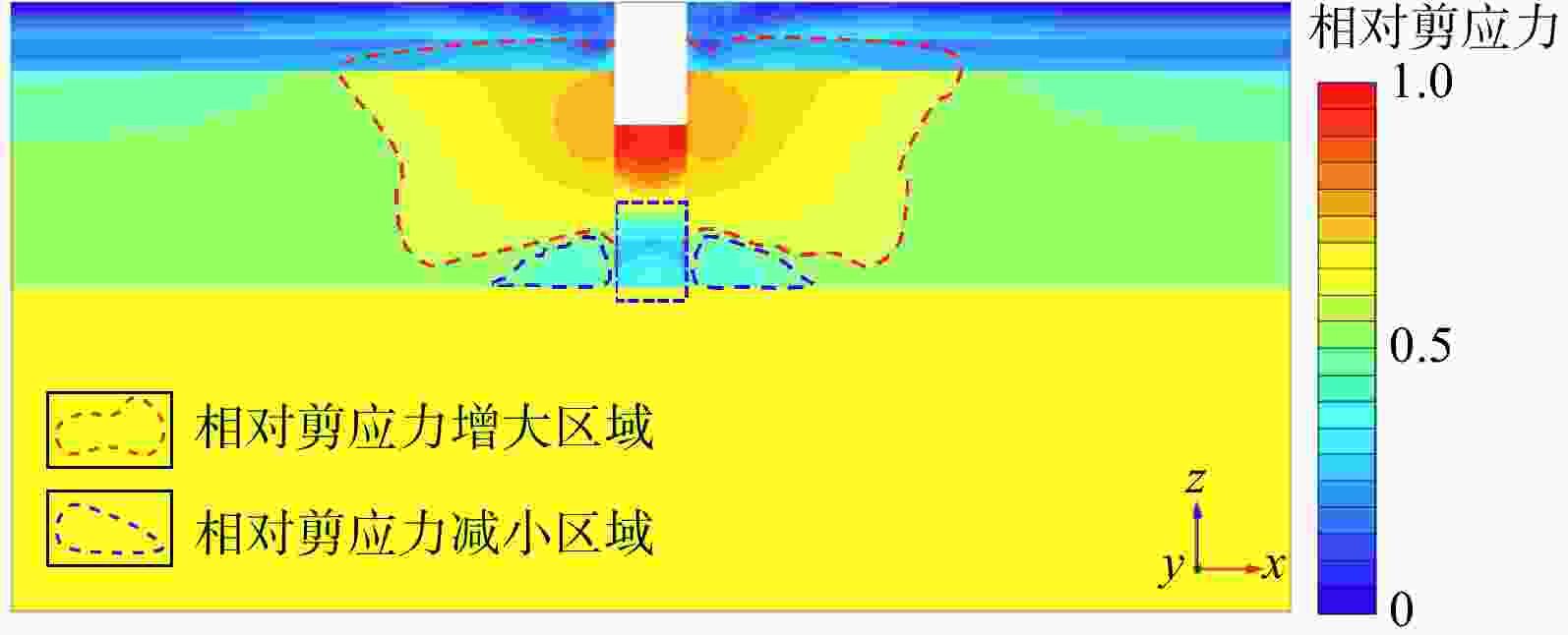
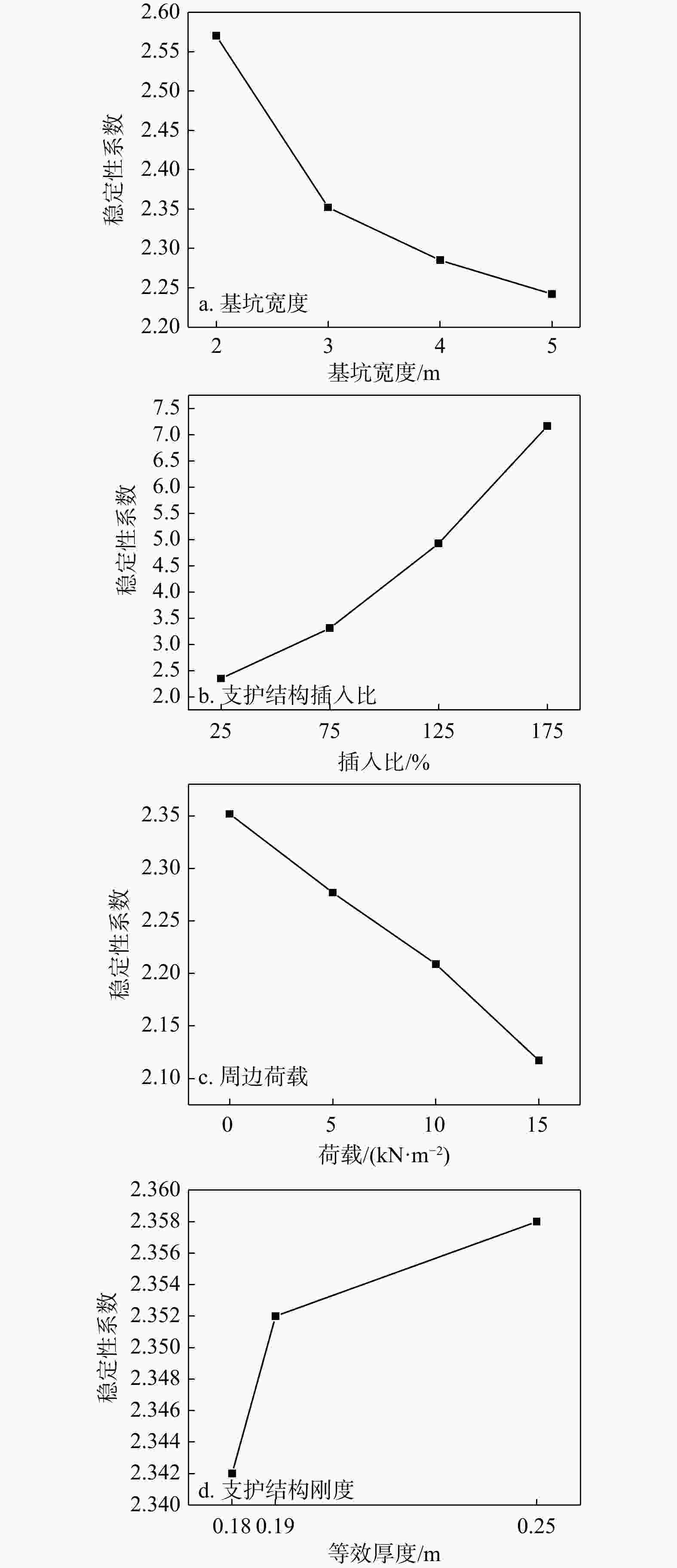
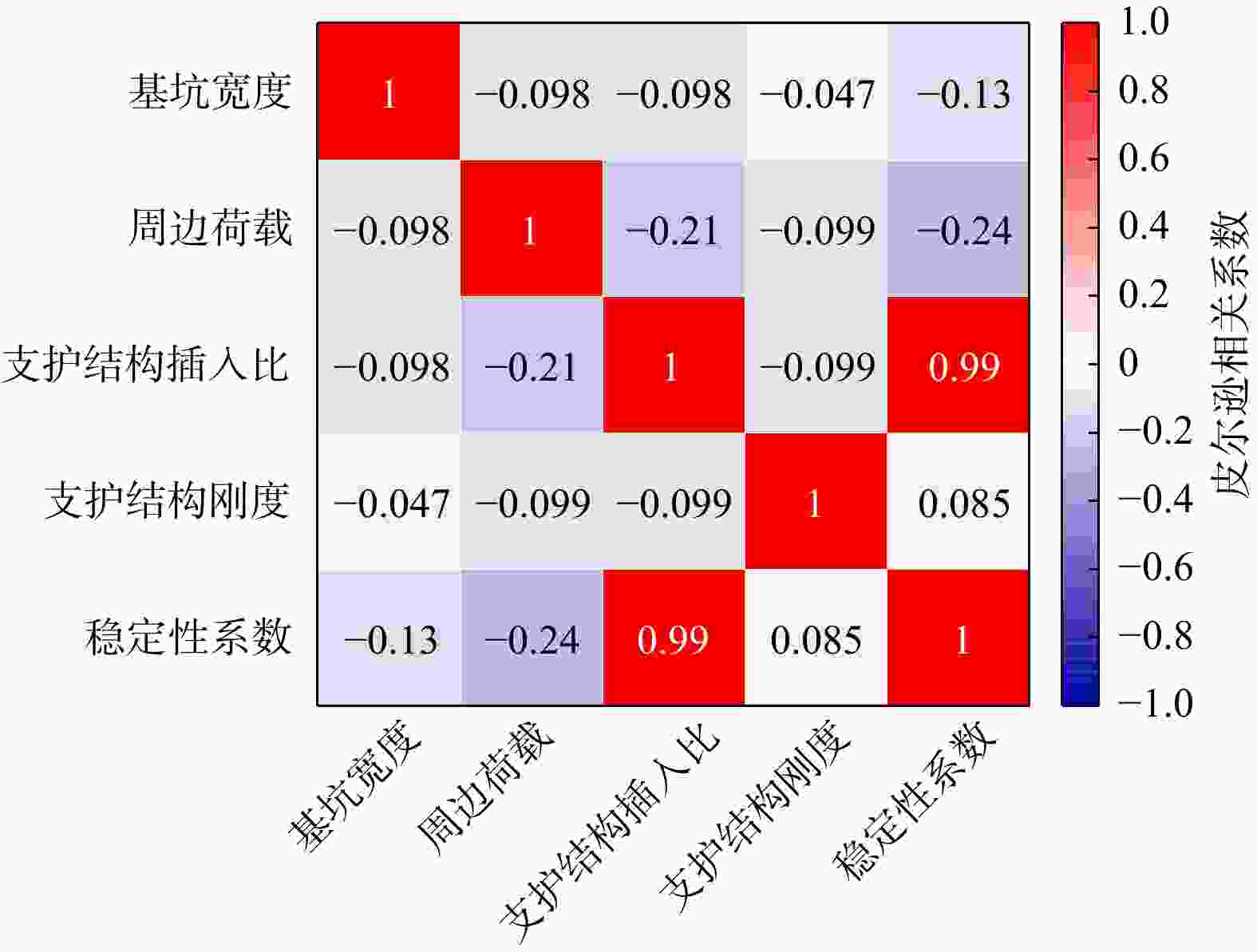
Results The results indicated that with higher support stiffness and smaller support spacing, the differences in stress and deformation between the supports and the midpoint between two adjacent supports were minimal. Soil deformation in narrow foundation pits was divided into the soil outside the pit from the ground surface to a certain depth below the surface and the soil at the pit bottom, which induced basal heave and ground surface subsidence outside the pit, respectively. In narrow foundation pits, plastic zones developed at the pit bottom and the base of the structure, with further development, intersecting plastic zones gradually formed and extended into the soil on both sides until the plastic zones coalesced throughout, ultimately leading to failure of the narrow foundation pit. Sensitivity analysis revealed that the embedment ratio and stiffness of the support structure had a significant positive effect on the basal-heave stability of narrow foundation pits, whereas excavation width and surcharge loads exhibited a negative correlation, with the embedment ratio displaying the strongest correlation.
Conclusion These findings provide a scientific basis for the design of support systems and stability assessment of narrow foundation pits in soft soil foundations.
-
图 12 基坑宽度(a)、支护结构插入比(b)、周边荷载(c)和支护结构刚度(d)对狭窄基坑抗隆起稳定性的影响
通过调整模拟钢板桩的板单元的等效厚度,来反映不同型号钢板桩的规格变化,进而改变支护结构刚度,即等效厚度等效替代支护结构刚度
Figure 12. Effect of excavation width(a), embedment ratio of the support structure(b), surcharge loads(c) and stiffness of the support structure(d) on basal-heave stability of narrow foundation pit
表 1 土体物理力学参数
Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of soil
土层 杂填土 素填土 互层土 粉砂 粉细砂 z/m 1.5 2.8 11.7 20 51.8 γ/(kN·m−3) 18.5 18.2 18.2 18.6 18.8 γsat/(kN·m−3) 19 18.7 18.7 19.1 19.3 $E_{50}^{\mathrm{ref}} $/MPa 6.346 5.389 7.5 18.0 28.0 $E_{{\mathrm{oed}}}^{\mathrm{ref}} $/MPa 6.346 5.389 7.5 18.0 28.0 $E_{{\mathrm{ur}}}^{\mathrm{ref}} $/MPa 19.04 16.17 22.5 54.0 84.0 $G_{0}^{\mathrm{ref}} $/MPa 7.933 6.737 62.4 70.94 70.94 γ0.7 7.51×10−4 1.07×10−3 1.80×10−4 4.20×10−4 1.00×10−3 c/kPa 10 12 5 0 0 φ/(°) 18 10 15 33 31 ψ/(°) 0 0 0 3 1 注:z. 土层底面埋深;γ. 天然重度;γsat. 饱和重度;$E_{50}^{{\mathrm{ref}}} $. 参考割线刚度;$E_{{\mathrm{oed}}}^{{\mathrm{ref}}} $. 参考压缩模量;$E_{{\mathrm{ur}}}^{{\mathrm{ref}}} $. 参考卸载-再加载模量;$G_{0}^{{\mathrm{ref}}} $. 参考初始剪切模量;γ0.7. 阈值剪应变;c. 黏聚力;φ. 内摩擦角;ψ. 剪胀角 表 2 支护结构物理力学参数
Table 2. Physical and mechanical parameters of support structure
支护结构 型号 等效厚度/m 直径/m 壁厚/m 弹性模量/GPa 钢管 − − 0.325 0.012 30 拉森钢板桩 400×160 0.18 − − 200 400×170 0.19 − − 200 500×200 0.25 − − 200 表 3 基于不同计算方法的稳定性系数计算结果
Table 3. Stability coefficient calculation results by different methods
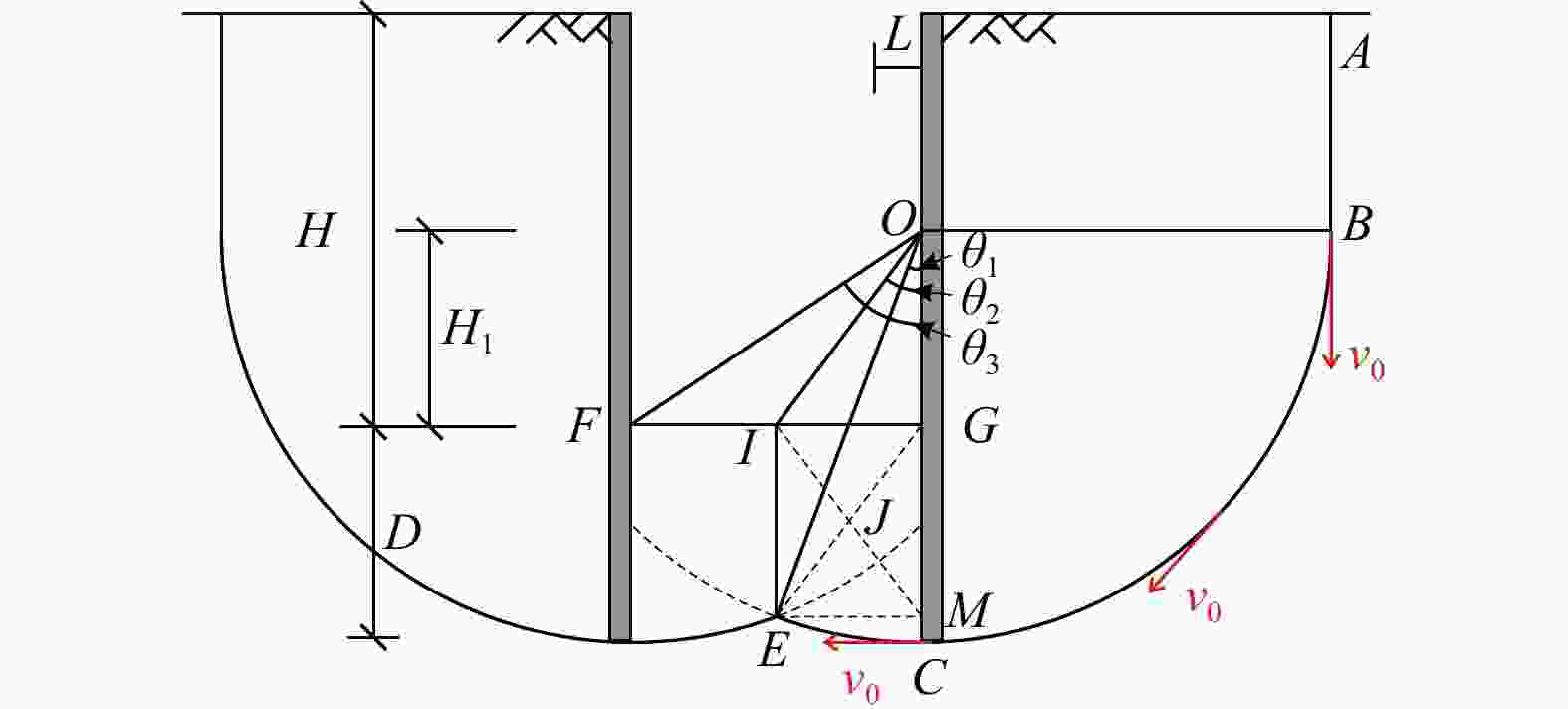
计算方法 规范法 本研究改进
公式法数值
模拟法整体稳定性 坑底抗隆起稳定性 稳定性系数 1.596 1.600 1.772 4.926 表 4 影响因素的重要程度及其排序
Table 4. Importance and ranking of influencing factors
影响因素 皮尔逊相关系数 重要程度 排列顺序 基坑宽度 −0.13 3 周边荷载 −0.24 2 支护结构插入比 0.99 1 支护结构刚度 0.085 4 -
[1] 姜晨光, 贺勇, 朱烨昕. 基坑形状与基坑稳定性关系的实测与分析[J]. 岩土工程技术, 2007, 21(5): 246-249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2007.05.008JIANG C G, HE Y, ZHU Y X. Relationship between the plane shape of foundation pit and its stability[J]. Geotechnical Engineering Technique, 2007, 21(5): 246-249. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2993.2007.05.008 [2] 洪春欣. 基坑形状与基坑稳定性关系实测研究[J]. 居舍, 2022(8): 175-177.HONG C X. Empirical research on the relationship between foundation pit shape and stability[J]. Dwelling House, 2022(8): 175-177. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 梁艳, 刘新根, 邓朝辉, 等. 开挖尺寸效应对基坑稳定性的影响分析[J]. 铁道建筑技术, 2022(2): 57-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4539.2022.02.013LIANG Y, LIU X G, DENG Z H, et al. Analysis on the influence of excavation size effects on foundation pit stability[J]. Railway Construction Technology, 2022(2): 57-61. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4539.2022.02.013 [4] 王洪新. 考虑二维和三维尺寸效应的基坑抗隆起稳定安全系数[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(11): 2144-2152.WANG H X. Safety factor of heave-resistant stability considering two- and three-dimensional size effects of foundation pits[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(11): 2144-2152. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] HUANG P, DANG K X, SHI H L, et al. Influence and mechanism of the excavation width on excavation deformations in Shanghai soft clay[J]. Buildings, 2024, 14(5): 1450. doi: 10.3390/buildings14051450 [6] 庄海洋, 张艳书, 薛栩超, 等. 深软场地地铁狭长深基坑变形特征实测与已有统计结果的对比分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(增刊2): 561-570. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2016.S2.071ZHUANG H Y, ZHANG Y S, XUE X C, et al. Deformation characteristics of narrow-long deep foundation pit for a subway station in soft ground and compared with existing statistical results[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(S2): 561-570. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2016.S2.071 [7] 胡敏云, 苟长飞, 严昱翔, 等. 基坑宽度效应对基坑稳定性影响的有限元分析[J]. 地基处理, 2020, 2(1): 1-8.HU M Y, GOU C F, YAN Y X, et al. Finite element analysis of the effect of foundation pit width on its stability[J]. Chinese Journal of Ground Improvement, 2020, 2(1): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] FAHEEM H, CAI F, UGAI K. Three-dimensional base stability of rectangular excavations in soft soils using FEM[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2004, 31(2): 67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2004.02.005 [9] 潘静杰, 朱春柏, 刘伟, 等. 外基坑宽度对坑中坑条件下被动土压力的影响[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 62-69. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0167PAN J J, ZHU C B, LIU W, et al. Influence of external pit width on passive earth pressure under pit-in-pit condition[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 62-69. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0167 [10] KARL T. Theoretical soil mechanics[M]. Hoboken: Wiley, 1943. [11] BJERRUM L, EIDE O. Stability of strutted excavations in clay[J]. Géotechnique, 1956, 6(1): 32-47. doi: 10.1680/geot.1956.6.1.32 [12] PRANDTL L. Theory of lifting surfaces. Part 2[J]. Technical Report Archive & Image Library, 1920: 1-10. [13] BOSE S K, SOM N N. Parametric study of a braced cut by finite element method[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 1998, 22(2): 91-107. doi: 10.1016/S0266-352X(97)00033-5 [14] ZHENG G, ZHEN J, CHENG X S, et al. Basal heave stability analysis of excavations considering the soil strength increasing with depth[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2024, 166: 106026. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2023.106026 [15] 施广焕. 关于基坑整体稳定性分析的探讨[C]//全国建筑工程勘察科技情报网, 内蒙古自治区勘察设计协会岩土分会, 全国建筑工程勘察科技情报网华北情报站, 等. 2014全国工程勘察学术大会论文集. [出版地不详]: [出版者不详], 2014: 322-325.SHI G H. Discussion on the overall stability analysis of the excavations[C]//National Engineering Survey Technology Information Network, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Survey and Design Association Geotechnical Engineering Branch, National Engineering Survey Technology Information North China Information Station, et al. Proceedings of the 2014 National Engineering Survey Academic Conference. [S. l. ]: [s. n. ], 2014: 322-325. (in Chinese) [16] 施琦. 考虑空间效应的狭长型沟槽基坑稳定性计算方法研究[J]. 城市道桥与防洪, 2021(8): 283-285. doi: 10.16799/j.cnki.csdqyfh.2021.08.073SHI Q. Research on stability calculation method of long-narrow groove foundation pit considering spatial effect[J]. Urban Roads Bridges & Flood Control, 2021(8): 283-285. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.16799/j.cnki.csdqyfh.2021.08.073 [17] 卢瀚. 淤泥区狭长基坑抗隆起稳定性分析[J]. 城市道桥与防洪, 2022(12): 248-251.LU H. Study on anti-heave stability of narrow-long foundation pit in silt area[J]. Urban Roads Bridges & Flood Control, 2022(12): 248-251. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] 应宏伟, 王小刚, 张金红. 考虑基坑宽度影响的基坑抗隆起稳定分析[J]. 工程力学, 2018, 35(5): 118-124. doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.01.0054YING H W, WANG X G, ZHANG J H. Analysis on heave-resistant stability considering the effect of excavation width[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2018, 35(5): 118-124. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6052/j.issn.1000-4750.2017.01.0054 [19] 阳吉宝, 黄星. 窄基坑隆起破坏模式及抗隆起稳定性验算研究[J]. 建筑结构, 2021, 51(增刊2): 1495-1503.YANG J B, HUANG X. Research on uplift failure mode and anti-uplift stability checking calculation of narrow excavation[J]. Building Structure, 2021, 51(S2): 1495-1503. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 俞建霖, 龙岩, 夏霄, 等. 狭长型基坑工程坑底抗隆起稳定性分析[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2017, 51(11): 2165-2174. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2017.11.010YU J L, LONG Y, XIA X, et al. Basal stability for narrow foundation pit[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2017, 51(11): 2165-2174. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-973X.2017.11.010 [21] 宋二祥, 付浩, 李贤杰, 等. 饱和黏性地层中基坑坑底抗隆起稳定验算方法[J]. 土木工程学报, 2021, 54(10): 97-105.SONG E X, FU H, LI X J, et al. Checking method for basal heave stability of deep excavation in saturated cohesive soil[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2021, 54(10): 97-105. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] JIN Z X, ZHANG C P, LI W, et al. Stability analysis for excavation in frictional soils based on upper bound method[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2024, 165: 105916. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2023.105916 [23] HE C H, LU Y, YANG Y L. Effect of size on the stability of narrow foundation pits[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2022, 2022(1): 7391622. doi: 10.1155/2022/7391622 [24] KE W H, WANG X, YAN C Z, et al. Numerical study of rock damage mechanism induced by blasting excavation using finite discrete element method[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(15): 7517. doi: 10.3390/app12157517 [25] KUNG G T, OU C Y, JUANG C H. Modeling small-strain behavior of Taipei clays for finite element analysis of braced excavations[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2009, 36(1/2): 304-319. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2008.01.007 [26] CAO M M, ZHANG Z, DU Z B, et al. Experimental study of hardening small strain model parameters for strata typical of Zhengzhou and their application in foundation pit engineering[J]. Buildings, 2023, 13(11): 2784. doi: 10.3390/buildings13112784 [27] 居尚威, 李雄威, 刘正明, 等. 基于HSS模型预测基坑开挖影响下的管线安全性分析[J]. 常州工学院学报, 2017, 30(1): 7-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0436.2017.01.002JU S W, LI X W, LIU Z M, et al. Safety analysis for excavation-induced impact on surrounding pipelines based on an HSS model[J]. Journal of Changzhou Institute of Technology, 2017, 30(1): 7-12. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0436.2017.01.002 [28] 何亮, 刘涛, 郭严伟. HSS模型在常州轨道交通基坑工程中的应用研究[J]. 江苏建筑, 2022(6): 117-121. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6270.2022.06.027HE L, LIU T, GUO Y W. Application research of HSS model in Changzhou rail transit foundation pit engineering[J]. Jiangsu Construction, 2022(6): 117-121. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6270.2022.06.027 [29] 吴小斌, 罗元喜, 何亮, 等. 土体小应变硬化模型的深基坑变形特性数值分析[J]. 科技创新导报, 2019, 16(3): 53-55. doi: 10.16660/j.cnki.1674-098X.2019.03.053WU X B, LUO Y X, HE L, et al. Numerical analysis of deformation characteristics of deep foundation pit with small strain hardening model of soil[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2019, 16(3): 53-55. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.16660/j.cnki.1674-098X.2019.03.053 [30] 林德周. 小应变土体硬化模型参数试验研究及工程应用: 以杭州某基坑工程为例[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2022.LIN D Z. Experimental study on parameters of small strain soil hardening model and its engineering application: A case study of a foundation pit project in Hangzhou[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 温科伟, 刘树亚, 杨红坡. 基于小应变硬化土模型的基坑开挖对下穿地铁隧道影响的三维数值模拟分析[J]. 工程力学, 2018, 35(增刊1): 80-87.WEN K W, LIU S Y, YANG H P. Three-dimensional numerical simulation analysis of the influence of pit excavation based on hardening soil-small strain model for metro tunnel[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2018, 35(S1): 80-87. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] MU L L, HUANG M S. Small strain based method for predicting three-dimensional soil displacements induced by braced excavation[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2016, 52: 12-22. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2015.11.001 [33] ZIENKIEWICZ O C, HUMPHESON C, LEWIS R W. Associated and non-associated visco-plasticity and plasticity in soil mechanics[J]. Géotechnique, 1975, 25(4): 671-689. doi: 10.1680/geot.1975.25.4.671 [34] MILLÁN M A, MENCÍAS-CARRIZOSA D, CALLE A. Sustainability of discontinuously supported slopes in temporary shallow excavations for building construction: A stability analysis procedure[J]. Sustainability, 2024, 16(23): 10393. doi: 10.3390/su162310393 [35] 程昊, 陈辉, 张抒, 等. 基于响应面试验设计的深基坑降水开挖地表沉降特性[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(5): 181-196. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230294CHENG H, CHEN H, ZHANG S, et al. Investigations into ground surface settlement characteristics of excavation under dewatering and excavating conditions using the response surface experimental design method[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(5): 181-196. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230294 [36] 高旭, 晏鄂川, 尹晓萌, 等. 武汉地区某基坑二元结构地层渗透系数反演[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(3): 218-224. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2017.0329GAO X, YAN E C, YIN X M, et al. Permeability inversion of dual structure formation of a foundation pit in Wuhan[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(3): 218-224. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2017.0329 [37] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑基坑支护技术规程: JGJ120−2012[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Technical specification for retaining and protection of building foundation excavations: JGJ120−2012[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Industry Press, 2012. (in Chinese) [38] BENZ T, VERMEER P A, SCHWAB R. A small-strain overlay model[J]. International Journal for Numerical & Analytical Methods in Geomechanics, 2010, 33(1): 25-44. [39] 寇海磊, 周超, 闫正余, 等. 基于小应变硬化土模型的黏性土本构参数研究及其工程应用[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2023, 45(4): 16-22. doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2023.04.003KOU H L, ZHOU C, YAN Z Y, et al. Research and engineering application of constitutive parameters of cohesive soil based on small strain hardening soil model[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2023, 45(4): 16-22. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.13984/j.cnki.cn37-1141.2023.04.003 [40] GOH A T C, ZHANG F, ZHANG W G, et al. A simple estimation model for 3D braced excavation wall deflection[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2017, 83: 106-113. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.10.022 [41] 李广. 拉森钢板桩在深大基坑支护中的应用以及土压力分布规律研究[D]. 江西抚州: 东华理工大学, 2022.LI G. Application and study on earth pressure distribution law of larsen steel sheet pile in deep and large foundation pit support[D]. Fuzhou Jiangxi: East China Institute of Technology, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] ZHANG X, WANG L B, MA M S, et al. Stability analysis of the foundation pit and the twin shield tunnels during adjacent construction[J]. Buildings, 2023, 13(4): 1000. doi: 10.3390/buildings13041000 [43] WANG J C, CUI D S, CHEN Q, et al. Morphological damage and strength deterioration of red sandstone under freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2025, 17(2): 671-687. [44] SUN Y Y, ZHOU S H, LUO Z. Basal-heave analysis of pit-in-pit braced excavations in soft clays[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2017, 81: 294-306. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.09.003 -




 下载:
下载: