Quantitative evaluation of hydrocarbon generation, expulsion, and retention potential in deep Permian Wujiaping Formation shale gas reservoir, southeastern Sichuan Basin
-
摘要:
高−过成熟页岩气藏生排滞烃强度的定量表征是深层资源评价的关键科学问题。四川盆地东南部红星地区二叠系吴家坪组二段页岩气藏(探明储量>1011 m3)具有薄层分布、强非均质性及多期构造改造等复杂地质特征,导致传统静态资源评价方法难以精确刻画其烃类生成−排出−滞留的时空演化规律。本研究构建热模拟实验、生烃潜力法与生烃动力学法相互验证的多维评价体系,系统重构了吴二段页岩气藏从成烃到保存的全过程演化模式,实现了资源潜力的定量表征与空间预测。半封闭体系热模拟结果表明,研究样品总烃产率达456 mg/g,其中总气产率为349.68 mg/g(占比76.7%),总油产率为106.59 mg/g(占比23.3%);油相产物以排出为主(103.35 mg/g),滞留量较低(3.24 mg/g)。生烃潜力法评价显示,吴二段页岩在镜质体反射率(
R o)为0.5%和0.8%分别进入生烃和排烃门限,原始生烃潜力指数高达550 mg/g,川东红星区及周缘地区现今生烃、排烃与滞留烃强度最高值分别达90×108,68×108,28×108 m3/km2,三者中心呈高度空间耦合,主要集中于万州−红星−恩施3个关键区域。生烃动力学模拟进一步揭示,研究区生气强度峰值可达50×108 m3/km2,滞留气强度最高为16×108 m3/km2。通过综合埋深、构造稳定性及封闭性等关键保存条件因素分析,定量确定了现今残余气强度分布格局,证实红星−万州地区为最优勘探靶区。研究结果不仅阐明了四川盆地二叠系页岩气藏生排滞烃的时空演化规律,也为深层−超深层页岩气精细勘探提供了理论依据和实践指导。Abstract:Objective Quantitative characterization of hydrocarbon generation, expulsion, and retention intensity in high to over-mature shale gas reservoirs remains a critical challenge for deep resource evaluation. The Permian Wujiaping Formation (Wu Second Member) shale gas reservoir in the Hongxing area of the southeastern Sichuan Basin (with proven reserves exceeding
1011 m3) exhibits thin-layer distribution, strong heterogeneity, and multi-stage tectonic modification. These characteristics complicate precise reconstruction of the spatiotemporal evolution of generation-expulsion-retention processes using traditional evaluation methods.Methods This study established a multi-dimensional evaluation framework that integrates thermal simulation experiments, hydrocarbon potential methods, and generation kinetic modeling with mutual verification. This framework systematically reconstructs the complete evolutionary model of the Wu Second Member shale gas reservoir from generation to preservation, enabling quantitative characterization and spatial prediction of resource potential.
Results Thermal simulation results show a total hydrocarbon generation rate of 456 mg/g, comprising total gas generation of 349.68 mg/g (76.7%) and total oil generation of 106.59 mg/g (23.3%); oil-phase products were primarily expelled (103.35 mg/g) with limited retention (3.24 mg/g). Hydrocarbon potential evaluation indicates that the Wu Second Member shale entered the hydrocarbon generation threshold at
R o=0.5% and the expulsion threshold atR o=0.8%, with an original hydrocarbon generation potential index reaching 550 mg/g. Present-day generation, expulsion, and retention intensities in the Hongxing area and surrounding regions reached maximum values of 90×108, 68×108, 28×108 m3/km2, respectively, with their centers highly spatially coupled in three key areas: Wanzhou-Hongxing-Enshi. Generation-kinetics modeling indicates that peak gas-generation intensity in the study area can reach 50 × 108 m3/km2, with a maximum gas-retention intensity of 16 × 108 m3/km2. Through a comprehensive analysis of crucial preservation factors (burial depth, structural stability, and sealing capacity), we quantitatively determine the present-day residual-gas intensity distribution, identifying the Hongxing-Wanzhou region as the optimal exploration target.Conclusion This study not only elucidates the spatiotemporal evolution patterns of hydrocarbon generation, expulsion, and retention in the Permian shale gas reservoir of the Sichuan Basin but also provides a theoretical foundation and practical guidance for the refined exploration of deep to ultra-deep shale gas reservoirs.
-
Key words:
- Sichuan Basin /
- Permian /
- Hongxing area /
- shale gas /
- generation intensity /
- expulsion intensity /
- retention intensity
-
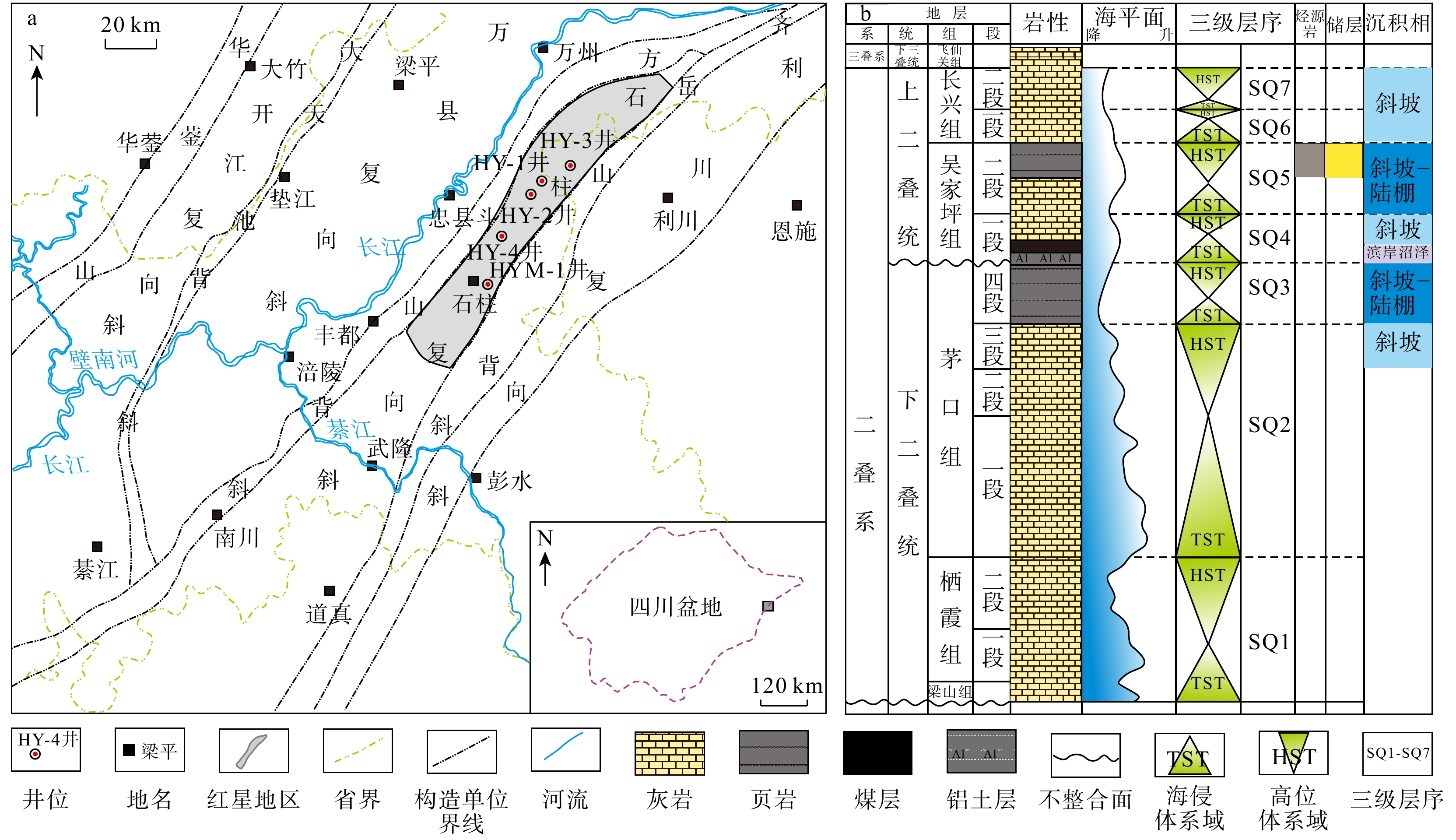
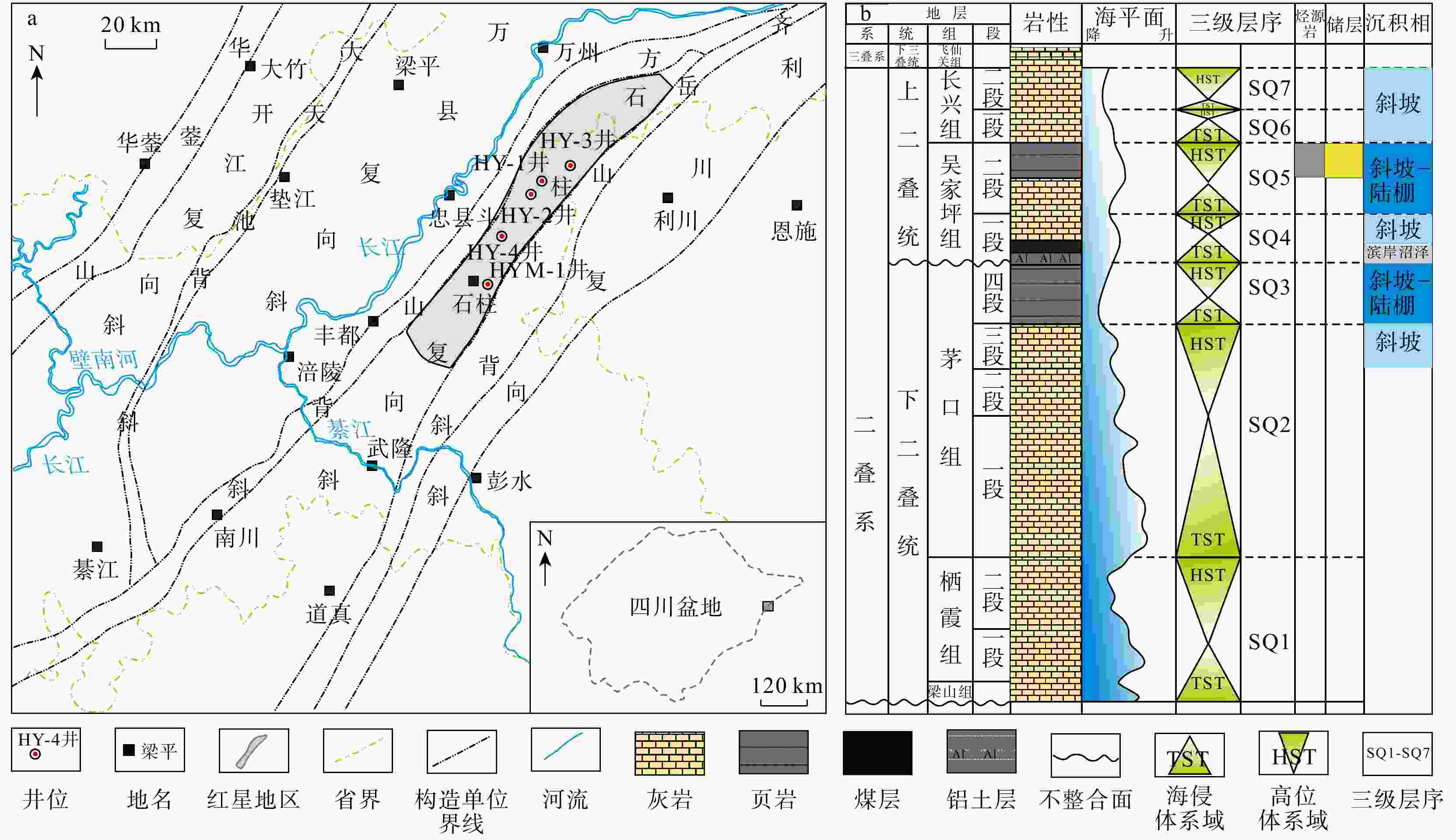
图 1 四川盆地东南部红星地区的地理位置(a)和二叠系综合柱状图(b)[7]
Figure 1. Geographic location (a) and comprehensive stratigraphic column of the Permian (b) in the Hongxing area, southeastern Sichuan Basin
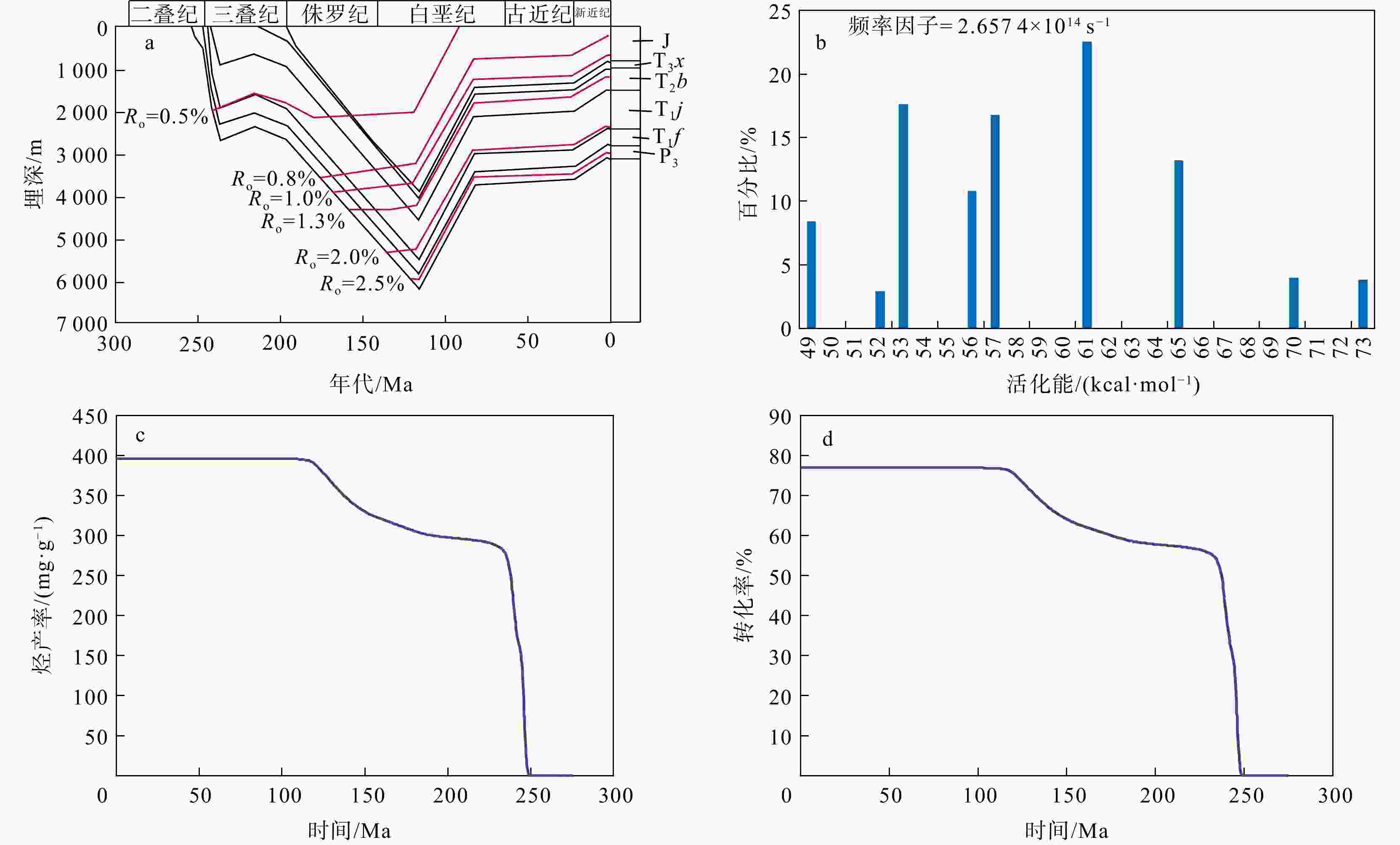
图 5 红星地区HY-1井埋藏−热演化史(a)、活化能和频率因子(b)、烃产率演化史(c)和转化率演化史(d)
P3. 上二叠统;T1f. 下三叠统飞仙关组;T1j. 下三叠统嘉陵江组;T2b. 中三叠统巴东组;T3x. 上三叠统须家河组;J. 侏罗系
Figure 5. Burial and thermal evolution history of Well HY-1 (a), activation energy and frequency factor (b), evolution history of hydrocarbon generation rate (c), evolution history of conversion rate (d) in the Hongxing area
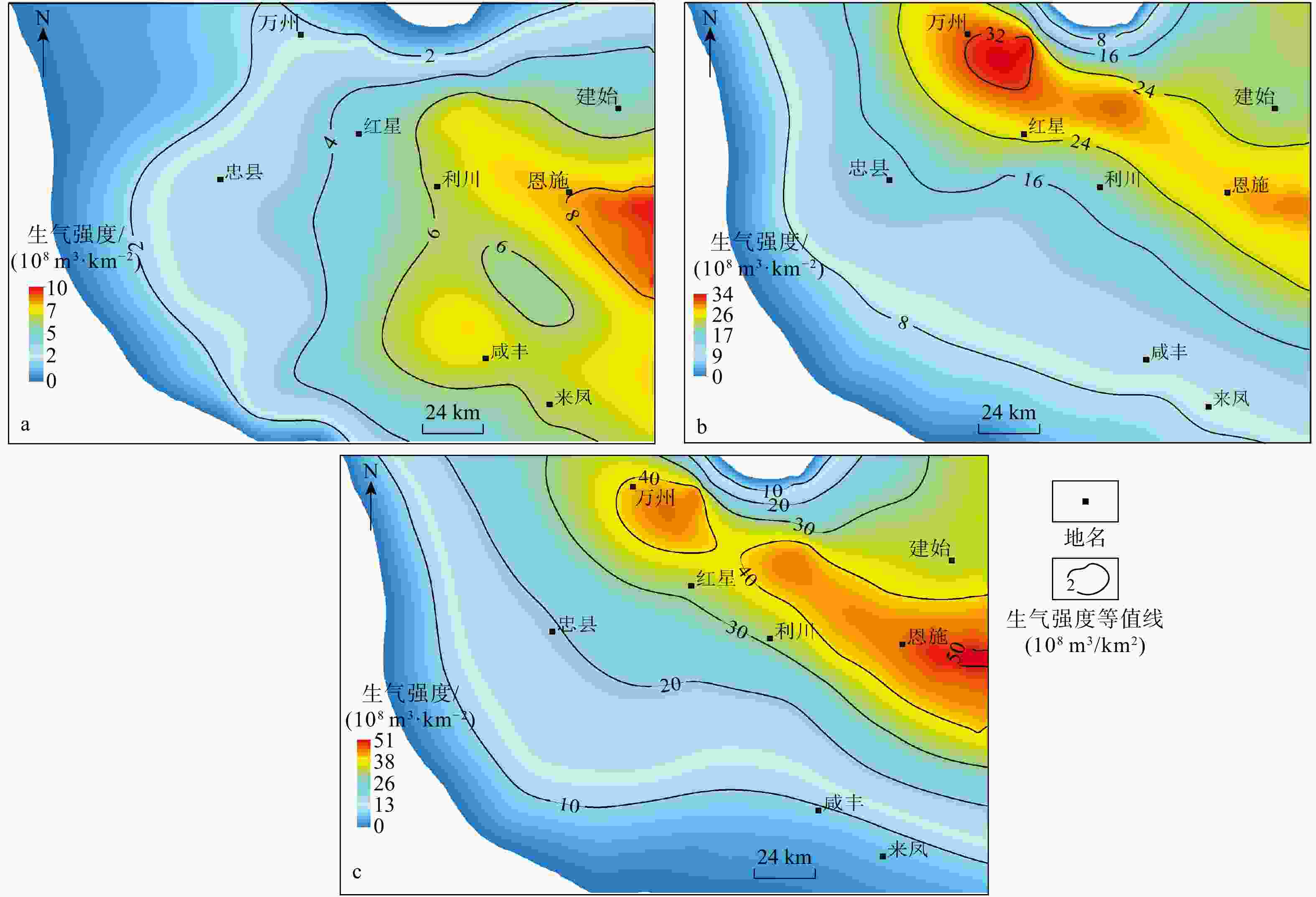
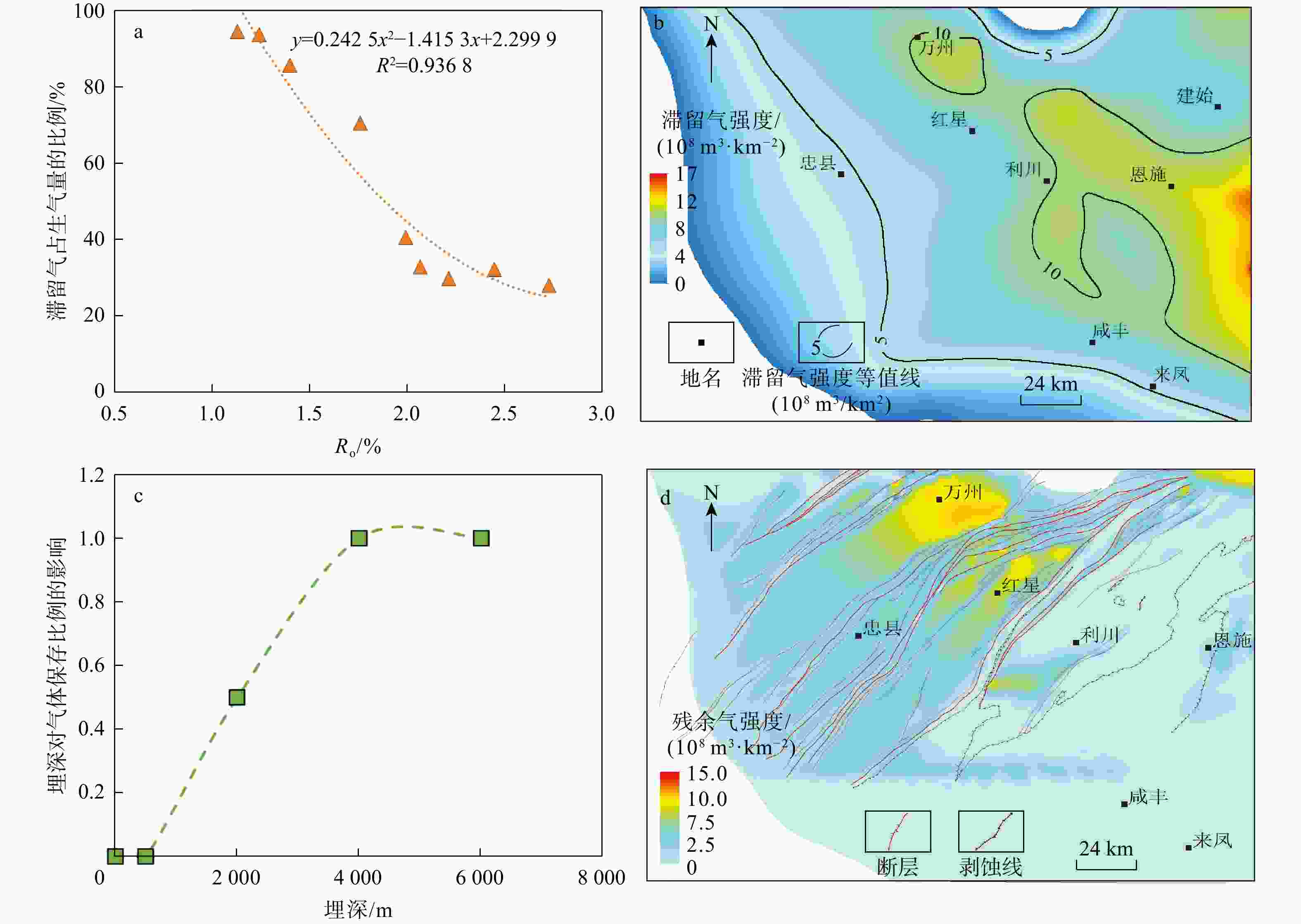
图 7 滞留气占总生气量的比例(a)、红星地区及周缘页岩滞留气强度平面图(b)、埋深对气体保存条件的影响(c)以及残余气强度平面图(d)
Figure 7. Ratio of retained gas to total gas generation(a), plan view of shale gas retention intensity in the Hongxing area and its periphery(b), effect of burial depth on gas preservation conditions(c) and plan view of residual gas intensity(d)
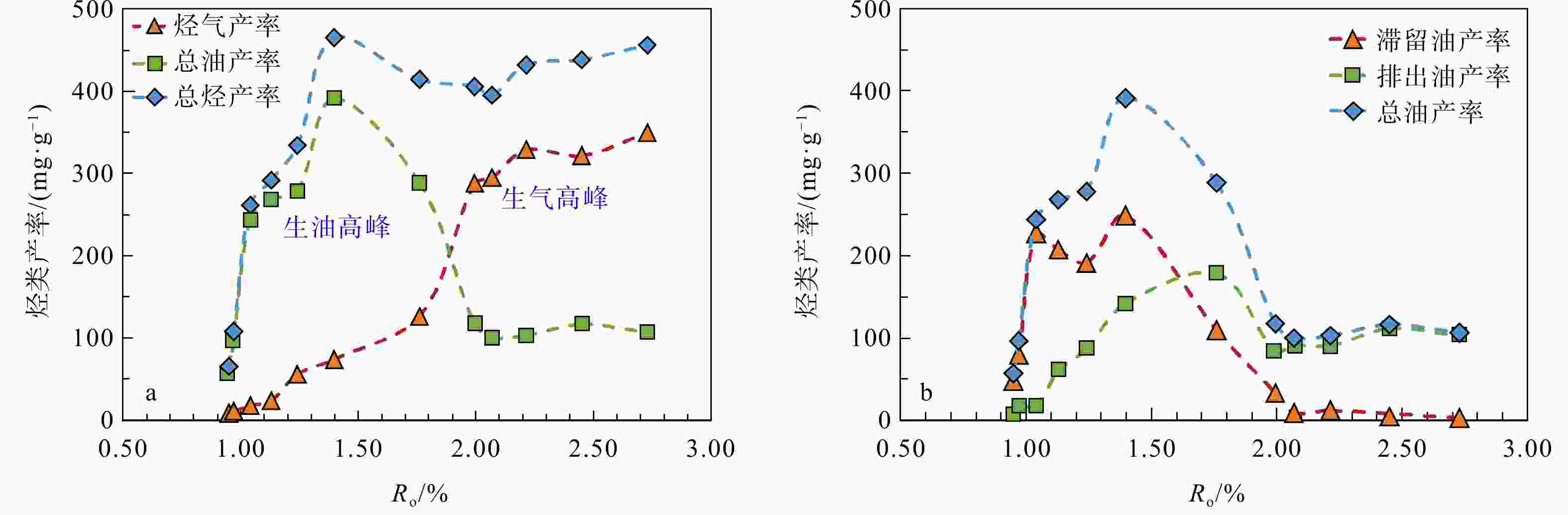
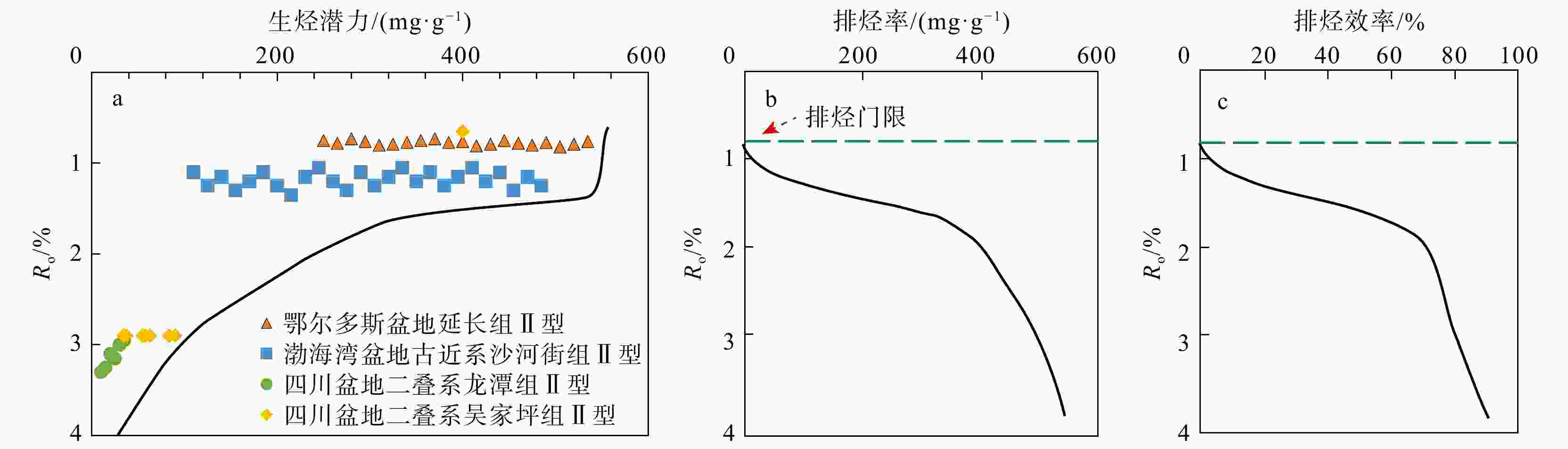
图 8 红星地区吴二段页岩生排烃模式[19](a)、排烃率(b)以及排烃效率(c)
Figure 8. Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion model (a), hydrocarbon expulsion rate (b), and hydrocarbon expulsion efficiency (c) of Wu Second Member shale in the Hongxing area
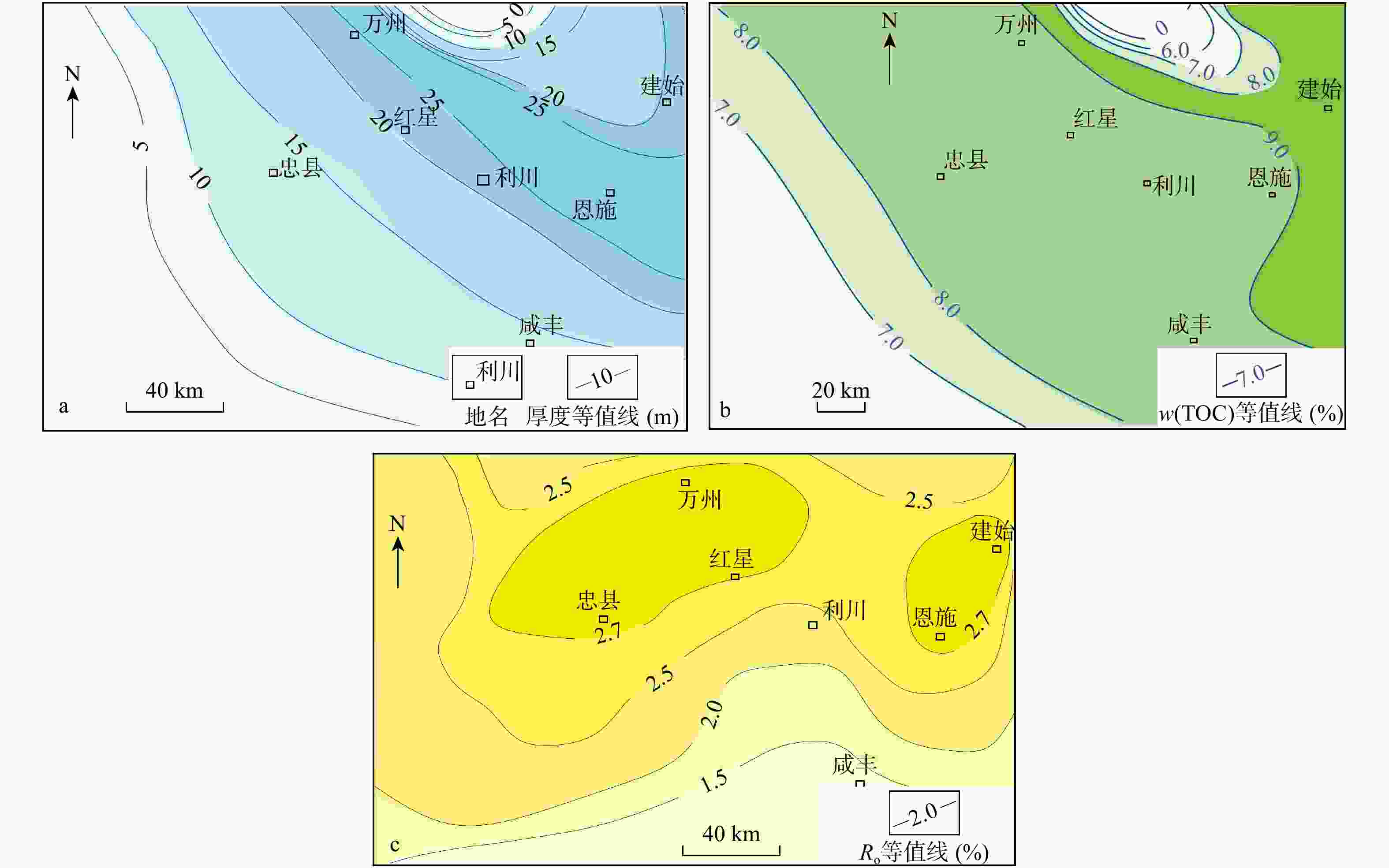
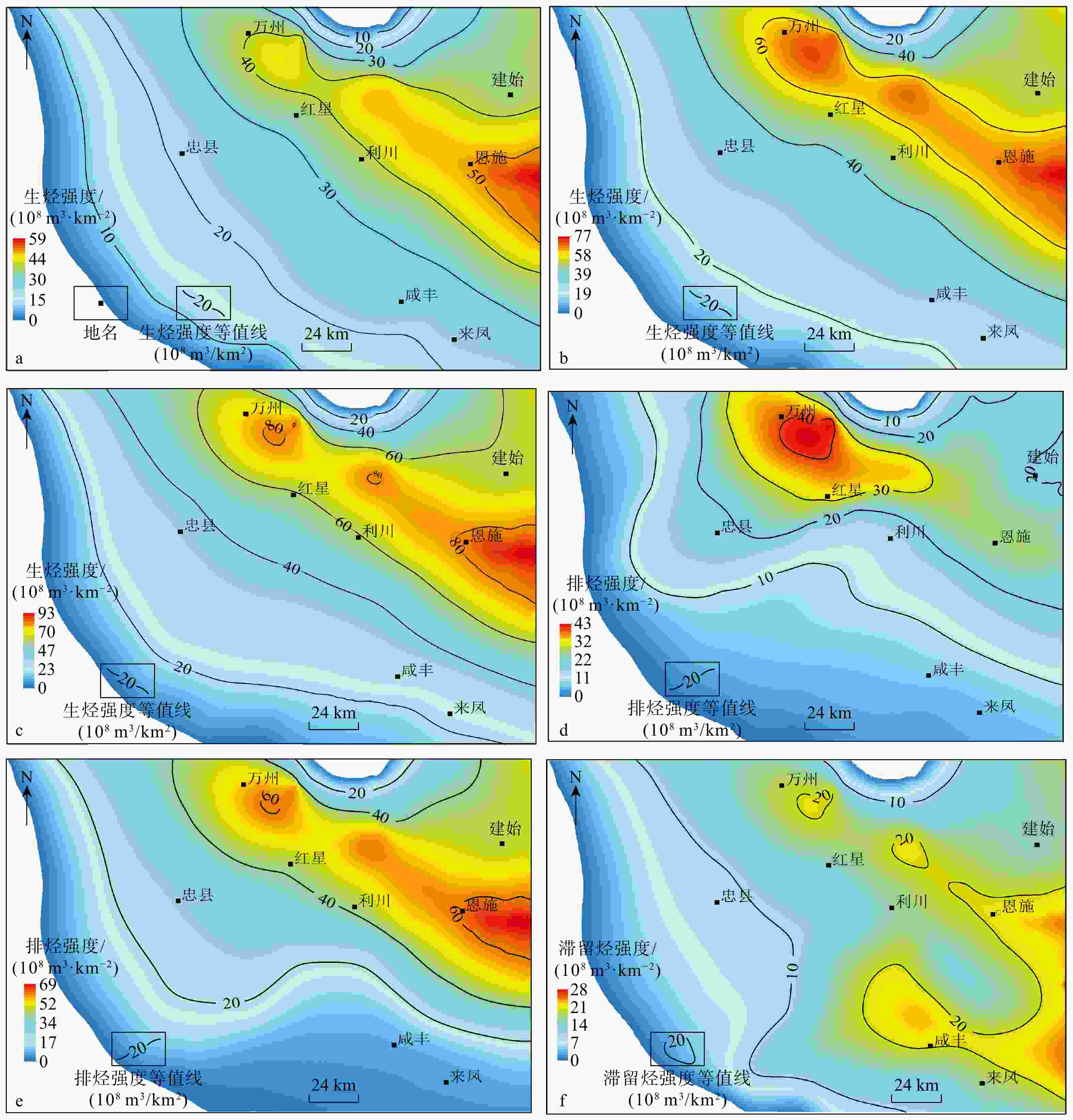
图 9 红星地区吴二段烃源岩三叠纪末期(a)、侏罗纪末期(b)和现今(c)生烃强度平面图,侏罗纪末期(d)和现今(e)排烃强度平面图以及现今滞留烃强度平面图(f)
Figure 9. Plan view of hydrocarbon generation intensity of Late Triassic(a), Late Jurassic(b) and present-day(c), plan view of hydrocarbon expulsion intensity of Late Jurassic(d) and present-day(e), plan view of hydrocarbon retention intensity of present-day(f) of the Wu Second Member source shale in the Hongxing area
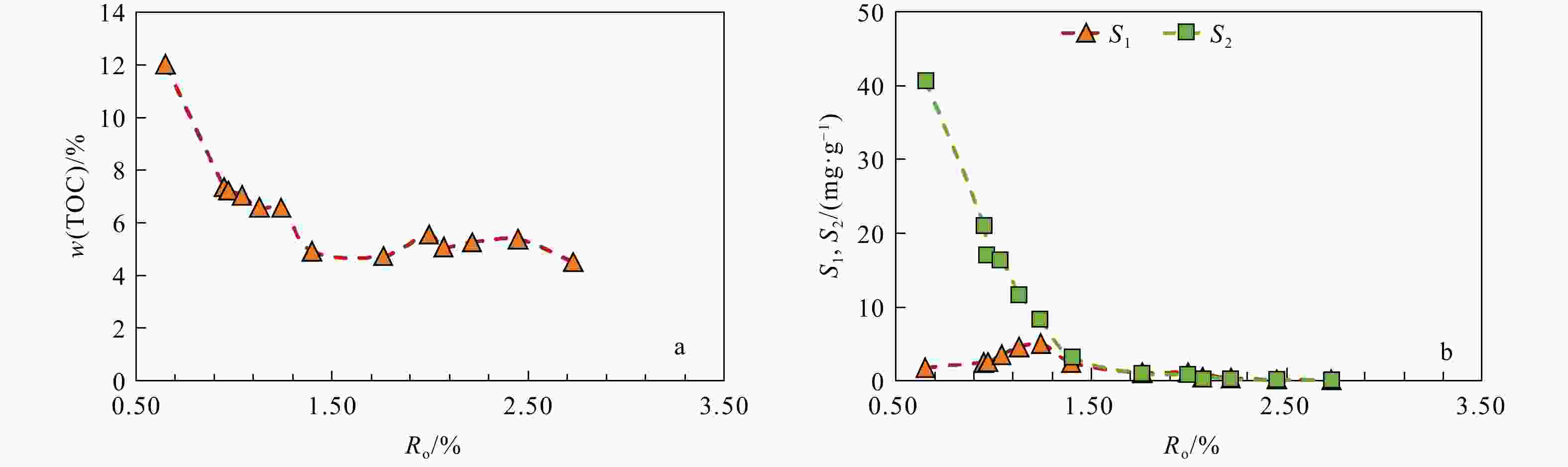
表 1 红星地区吴二段页岩有机质特征
Table 1. Organic matter characteristics of the Wu Second Member shale in the Hongxing area
样品编号 w(TOC)/% Tmax/℃ S1/(mg·g−1) S2/(mg·g−1) Ro/% 腐泥组 壳质组 镜质组 惰质组 干酪根类型 wB/% HY1-1 6.06 602 0.07 0.26 2.64 74.0 / 26.0 / Ⅱ1 HY1-2 3.65 602 0.03 0.14 2.65 71.3 / 28.7 / Ⅱ1 HY1-3 6.27 603 0.05 0.28 2.65 69.3 / 30.7 / Ⅱ1 HY2-1 5.47 602 0.04 0.21 2.61 67.7 / 32.3 / Ⅱ1 HY2-2 4.18 359 0.05 0.28 2.59 69.7 / 30.7 / Ⅱ1 HY3-1 4.04 601 0.06 0.25 2.93 72.0 / 28.0 / Ⅱ1 HY3-2 9.50 599 0.11 0.35 2.72 70.7 / 29.3 / Ⅱ1 HY3-3 9.68 599 0.10 0.35 2.74 74.3 / 25.7 / Ⅱ1 注:w(TOC)为有机碳质量分数;Tmax为最大热解峰温;S1为残留烃质量分数;S2为裂解烃质量分数;Ro为镜质体反射率;下同 -
[1] 张金川, 陶佳, 李振, 等. 中国深层页岩气资源前景和勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(1): 15-28.ZHANG J C, TAO J, LI Z, et al. Prospect of deep shale gas resources in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(1): 15-28. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 杨玉茹, 孟凡洋, 白名岗, 等. 世界最古老页岩气层储层特征与勘探前景分析[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(1): 14-28. doi: 10.12029/gc20200102YANG Y R, MENG F Y, BAI M G, et al. An analysis of reservoir characteristics, resources and exploration prospects of the oldest shale gas in the world[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(1): 14-28. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12029/gc20200102 [3] 董大忠, 邹才能, 戴金星, 等. 中国页岩气发展战略对策建议[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(3): 397-406. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.03.0397DONG D Z, ZOU C N, DAI J X, et al. Suggestions on the development strategy of shale gas in China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(3): 397-406. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.03.0397 [4] YANG R, WANG B J, BAO H Y, et al. Shale oil mobility of terrestrial shale: Dongyuemiao Member of Jurassic Ziliujing Formation in the Fuxing area, eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2025, 53(1): 55-76. [5] 彭平安, 贾承造. 深层烃源演化与原生轻质油/凝析油气资源潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(12): 1543-1555. doi: 10.7623/syxb202112001PENG P A, JIA C Z. Evolution of deep source rock and resource potential of primary light oil and condensate[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(12): 1543-1555. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7623/syxb202112001 [6] 管宏林, 蒋小琼, 王恕一, 等. 普光气田与建南气田长兴组、飞仙关组储层对比研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2010, 32(2): 130-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.02.006GUAN H L, JIANG X Q, WANG S Y, et al. A comparative study of reservoirs of the Changxing and Feixianguan Formation between Puguang gasfield and Jiannan gasfield in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2010, 32(2): 130-135. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.02.006 [7] 包汉勇, 赵帅, 梁榜, 等. 川东红星地区二叠系吴家坪组页岩气富集高产主控因素与勘探启示[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2023, 28(1): 71-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2023.01.007BAO H Y, ZHAO S, LIANG B, et al. Enrichment and high yield of shale gas in the Permian Wujiaping Formation in Hongxing area of eastern Sichuan and its exploration implications[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2023, 28(1): 71-82. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2023.01.007 [8] 包汉勇, 赵帅, 张莉, 等. 川东红星地区中上二叠统页岩气勘探成果及方向展望[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(4): 12-24. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240402BAO H Y, ZHAO S, ZHANG L, et al. Exploration achievements and prospects for shale gas of Middle-Upper Permian in Hongxing area, eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2024, 36(4): 12-24. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240402 [9] 易雨昊, 包汉勇, 朱红涛, 等. 四川盆地东部上二叠统吴家坪组放射虫组合及其烃源意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(4): 167-180.YI Y H, BAO H Y, ZHU H T, et al. Radiolarian assemblage from the Upper Permian Wujiaping Formation in the eastern Sichuan Basin and its hydrocarbon source significance[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(4): 167-180. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 聂海宽, 张金川, 金之钧, 等. 论海相页岩气富集机理: 以四川盆地五峰组−龙马溪组为例[J]. 地质学报, 2024, 98(3): 975-991.NIE H K, ZHANG J C, JIN Z J, et al. Enrichment mechanism of marine shale gas: A case study of the Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in the Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2024, 98(3): 975-991. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] WANG H J, ZHAO G P, LU S F, et al. Investigation on hydrocarbon generation and expulsion potential by deep learning and comprehensive evaluation method: A case study of Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2022, 144: 105841. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2022.105841 [12] 陈建平, 孙永革, 钟宁宁, 等. 地质条件下湖相烃源岩生排烃效率与模式[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(11): 2005-2032.CHEN J P, SUN Y G, ZHONG N N, et al. The efficiency and model of petroleum expulsion from the lacustrine source rocks within geological frame[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(11): 2005-2032. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] BURNHA J J S A A K. Evaluation of a simple model of vitrinite reflectance based on chemical kinetics (1)[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1990, 74(10): 1559-1570. [14] UNGERER B P T R P P. Thermal history of sedimentary basins, maturation indices, and kinetics of oil and gas generation[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1987, 71(12): 1445-1466. [15] 饶松, 胡圣标, 汪集旸. 有机质生烃动力学参数研究进展: 回顾和展望[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2010, 25(4): 1424-1432. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.04.034RAO S, HU S B, WANG J Y. Hydrocarbon generation kinetic parameters of organic matter: Review and outlook[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2010, 25(4): 1424-1432. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2903.2010.04.034 [16] PANG X Q, LI M W, LI S M, et al. Geochemistry of petroleum systems in the Niuzhuang South Slope of Bohai Bay Basin: Part 3. Estimating hydrocarbon expulsion from the Shahejie Formation[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2005, 36(4): 497-510. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2004.12.001 [17] LI C R, PANG X Q, HUO Z P, et al. A revised method for reconstructing the hydrocarbon generation and expulsion history and evaluating the hydrocarbon resource potential: Example from the First Member of the Qingshankou Formation in the northern Songliao Basin, Northeast China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 121: 104577. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104577 [18] 李敏, 庞雄奇, 罗冰, 等. 生烃潜力法在深层页岩气资源评价中的应用: 以四川盆地五峰−龙马溪组优质烃源岩为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2021, 50(6): 1096-1107.LI M, PANG X Q, LUO B, et al. Application of hydrocarbon generation potential method to deep shale gas resource evaluation: A case study of high-quality source rocks of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2021, 50(6): 1096-1107. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 张心罡, 庞宏, 庞雄奇, 等. 四川盆地上二叠统龙潭组烃源岩生、排烃特征及资源潜力[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(3): 621-632.ZHANG X G, PANG H, PANG X Q, et al. Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion characteristics and resource potential of source rocks in the Longtan Formation of Upper Permian, Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(3): 621-632. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 邵新荷. 页岩热演化过程中滞留油气机制及含油气性评价[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2021.SHAO X H. Hydrocarbon retention mechanism during thermal maturation of shaland evaluation of oil and gas potential[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 马新华, 杨雨, 文龙, 等. 四川盆地海相碳酸盐岩大中型气田分布规律及勘探方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(1): 1-13. doi: 10.11698/PED.2019.01.01MA X H, YANG Y, WEN L, et al. Distribution and exploration direction of medium- and large-sized marine carbonate gas fields in Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(1): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.2019.01.01 [22] 陈瑞银, 朱光有, 周文宝, 等. 川北地区大隆组烃源岩地球化学特征与生气潜力初探[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(1): 99-107.CHEN R Y, ZHU G Y, ZHOU W B, et al. Geochemical characteristics and hydrocarbon resource potential of Permian Dalong Formation , Northeast Sichuan[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(1): 99-107. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 米敬奎, 张水昌, 王晓梅. 不同类型生烃模拟实验方法对比与关键技术[J]. 石油实验地质, 2009, 31(4): 409-414. doi: 10.11781/sysydz200904409MI J K, ZHANG S C, WANG X M. Comparison of different hydrocarbon generation simulation approaches and key technique[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2009, 31(4): 409-414. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11781/sysydz200904409 [24] 邓模, 翟常博, 杨振恒, 等. 低成熟海相黑色页岩生烃特征的热模拟实验[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(1): 130-137.DENG M, ZHAI C B, YANG Z H, et al. Thermal simulation experiment on hydrocarbon generation characteristics of low-mature marine black shale[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(1): 130-137. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] TANG Y, JENDEN P D, NIGRINI A, et al. Modeling early methane generation in coal[J]. Energy & Fuels, 1996, 10(3): 659-671. [26] 谢增业, 李志生, 魏国齐, 等. 腐泥型干酪根热降解成气潜力及裂解气判识的实验研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(6): 1057-1066.XIE Z Y, LI Z S, WEI G Q, et al. Experimental research on the potential of sapropelic kerogen cracking gas and discrimination of oil cracking gas[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(6): 1057-1066. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 班东师. 柴达木盆地一里坪地区新近纪咸化湖相烃源岩生烃模式研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2018.BAN D S. Hydrocarbon generation pattern of Neogene salinized lacustrine source rocks in Yiliping area, Qaidam Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] GAI H F, TIAN H, XIAO X M. Late gas generation potential for different types of shale source rocks: Implications from pyrolysis experiments[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2018, 193: 16-29. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2018.04.009 [29] 张东东, 刘文汇, 王晓锋, 等. 深层油气藏成因类型及其特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021, 42(5): 1169-1180.ZHANG D D, LIU W H, WANG X F, et al. Genetic types and characteristics of deep oil and gas plays[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021, 42(5): 1169-1180. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] PENG J W, PANG X Q, SHI H S, et al. Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion characteristics of Eocene source rocks in the Huilu area, northern Pearl River Mouth basin, South China Sea: Implications for tight oil potential[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 72: 463-487. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.02.006 [31] ZHENG D Y, PANG X Q, MA X H, et al. Hydrocarbon generation and expulsion characteristics of the source rocks in the Third Member of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation and its effect on conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon resource potential in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 109: 175-192. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.06.014 [32] 庞雄奇, 李倩文, 陈践发, 等. 含油气盆地深部高过成熟烃源岩古TOC恢复方法及其应用[J]. 古地理学报, 2014, 16(6): 769-789. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2014.06.062PANG X Q, LI Q W, CHEN J F, et al. Recovery method of original TOC and its application in source rocks at high mature-over mature stage in deep petroliferous basins[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2014, 16(6): 769-789. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2014.06.062 [33] MA Z L, TAN J Q, ZHENG L J, et al. Evaluating gas generation and preservation of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation shale in southeastern Sichuan Basin, China: Implications from semiclosed hydrous pyrolysis[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 129: 105102. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105102 [34] 卢庆治, 马永生, 郭彤楼, 等. 鄂西−渝东地区热史恢复及烃源岩成烃史[J]. 地质科学, 2007, 42(1): 189-198. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2007.01.016LU Q Z, MA Y S, GUO T L, et al. Thermal history and hydrocarbon generation history in western Hubei-eastern Chongqing area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica), 2007, 42(1): 189-198. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2007.01.016 [35] 田辉, 吴子瑾, 盖海峰, 等. 川西北地区中泥盆统腐泥型烃源岩晚期生气特征实验研究[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(1): 46-54. doi: 10.11743/ogg20230104TIAN H, WU Z J, GAI H F, et al. Experimental study on late gas generation characteristics of the Middle Devonian sapropelic source rocks of in northwestern Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(1): 46-54. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11743/ogg20230104 [36] 李剑, 马卫, 王义凤, 等. 腐泥型烃源岩生排烃模拟实验与全过程生烃演化模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(3): 445-454. doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.03.09LI J, MA W, WANG Y F, et al. Modeling of the whole hydrocarbon-generating process of sapropelic source rock[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(3): 445-454. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.2018.03.09 [37] 腾格尔, 邱楠生, 俞凌杰, 等. 中国南方不同埋藏条件下海相页岩气差异保存机理[J]. 地质学报, 2024, 98(11): 3285-3301.BORJIGEN T, QIU N S, YU L J, et al. Differential preservation mechanisms of marine shale gas under varying burial conditions in southern China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2024, 98(11): 3285-3301. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 赵文智, 卞从胜, 李永新, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系长73亚段页岩有机质转化率、排烃效率与页岩油主富集类型[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2023, 50(1): 12-23. doi: 10.11698/PED.20220459ZHAO W Z, BIAN C S, LI Y X, et al. Organic matter transformation ratio, hydrocarbon expulsion efficiency and shale oil enrichment type in Chang 73 shale of Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(1): 12-23. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.20220459 [39] 雍锐, 杨洪志, 吴伟, 等. 四川盆地北部二叠系大隆组页岩气富集高产主控因素及勘探潜力[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2025, 52(2): 253-266. doi: 10.11698/PED.20240734YONG R, YANG H Z, WU W, et al. Controlling factors and exploration potential of shale gas enrichment and high yield in the Permian Dalong Formation, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2025, 52(2): 253-266. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.20240734 [40] 谌志远. 南方海相页岩气散失控制因素研究: 以四川盆地南缘为例[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019.CHEN Z Y. Study on controlling factors of marine shale gas dispersion in South China: A case study of southern margin of Sichuan Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 刘义生, 金吉能, 潘仁芳, 等. 渝东南盆缘转换带五峰组−龙马溪组常压页岩气保存条件评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 253-263.LIU Y S, JIN J N, PAN R F, et al. Preservation condition evaluation of normal pressure shale gas in the Wufeng and Longmaxi formations of basin margin transition zone, Southeast Chongqing[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 253-263. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: