Research on the I-D-M threshold model for regional rainfall-induced landslide hazard early warning at a regional scale
-
摘要:
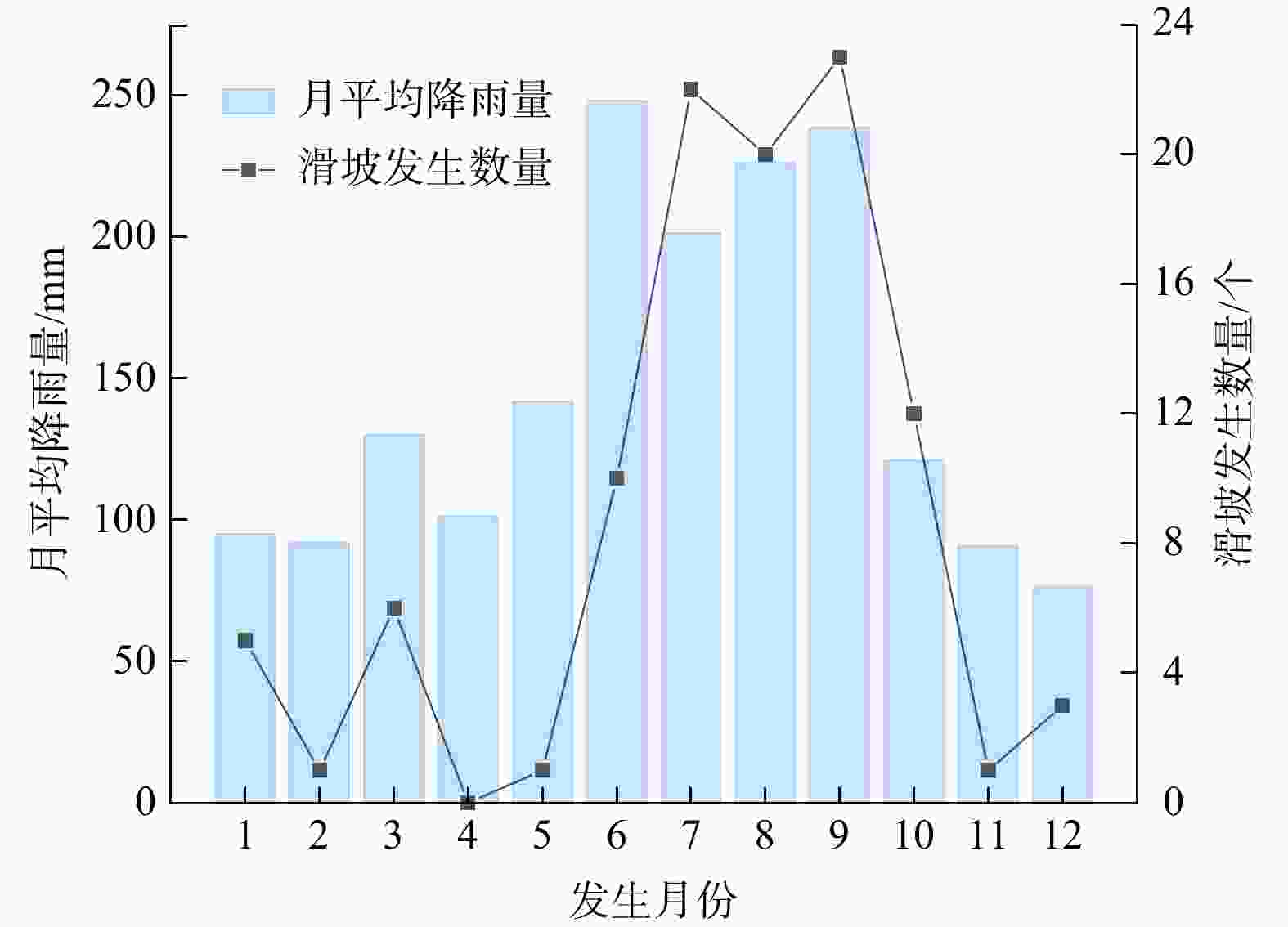
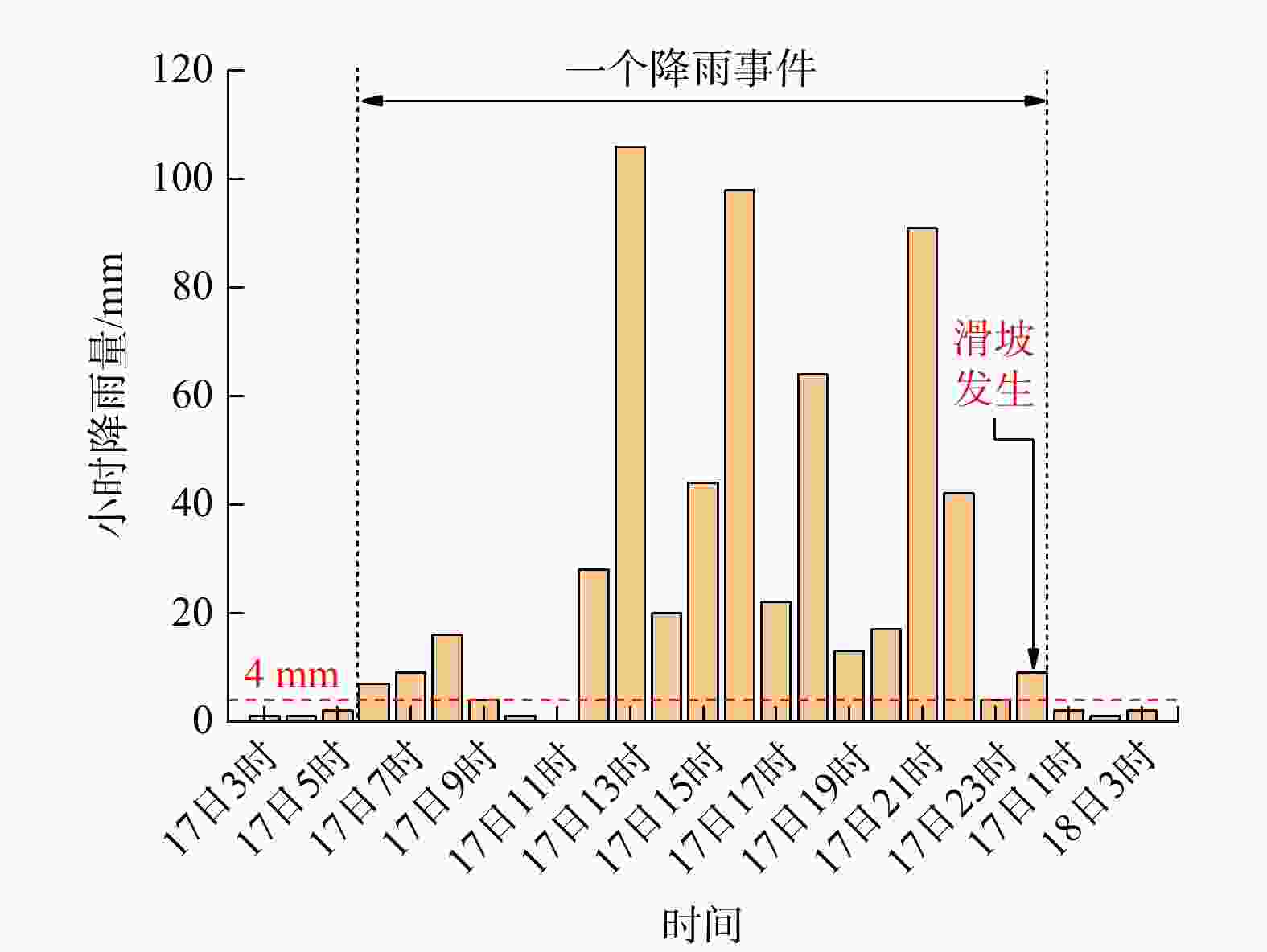
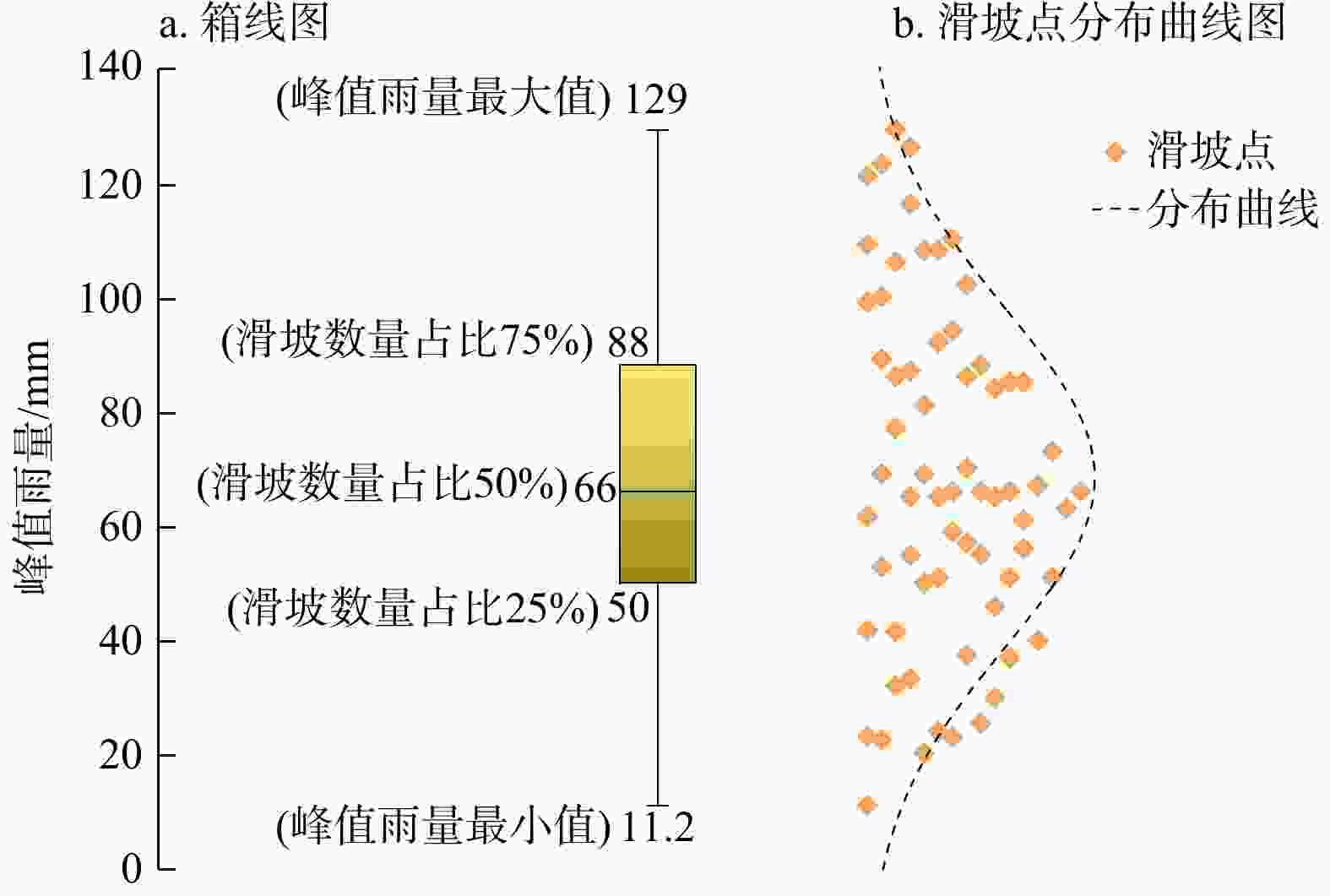
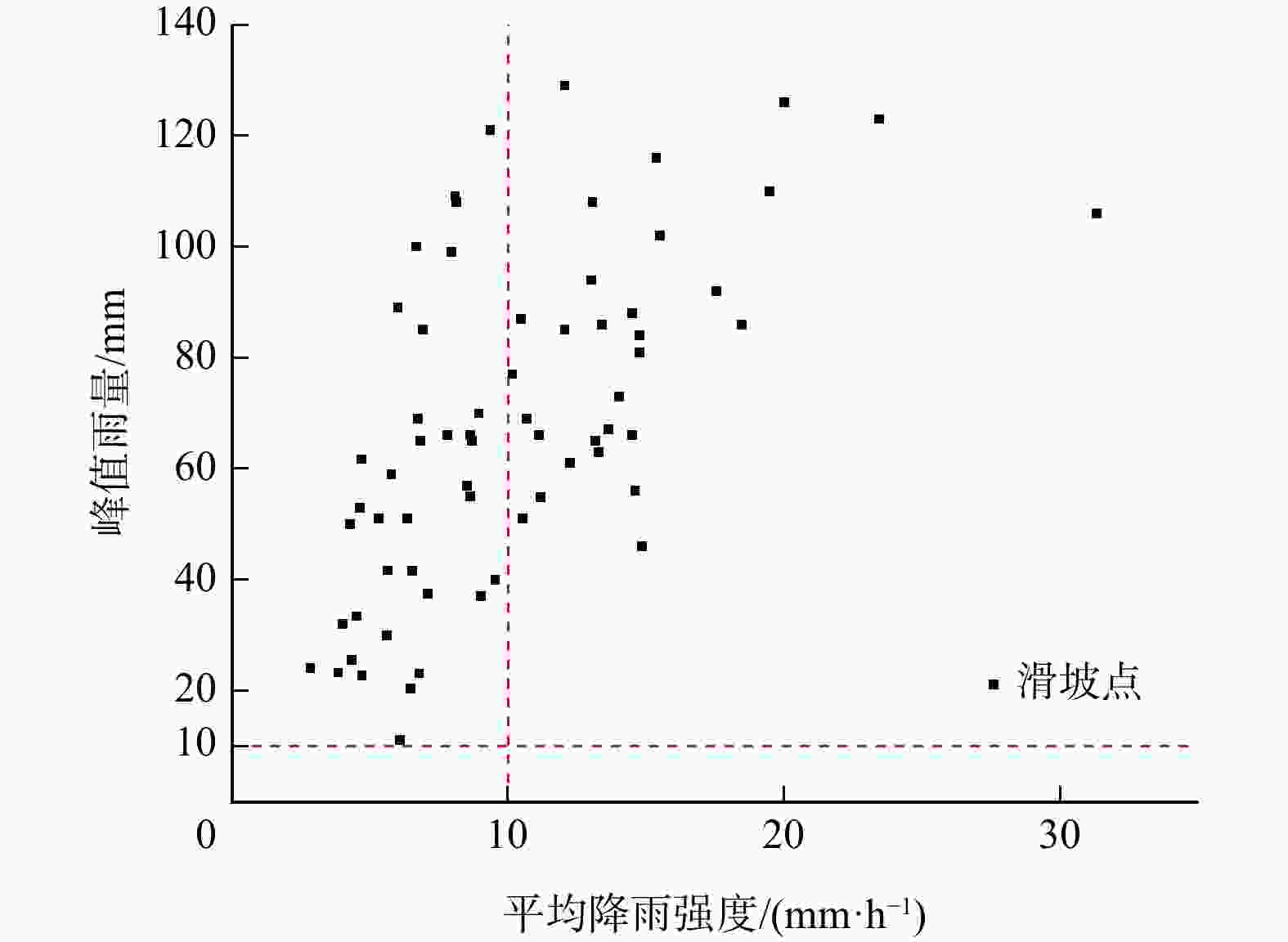
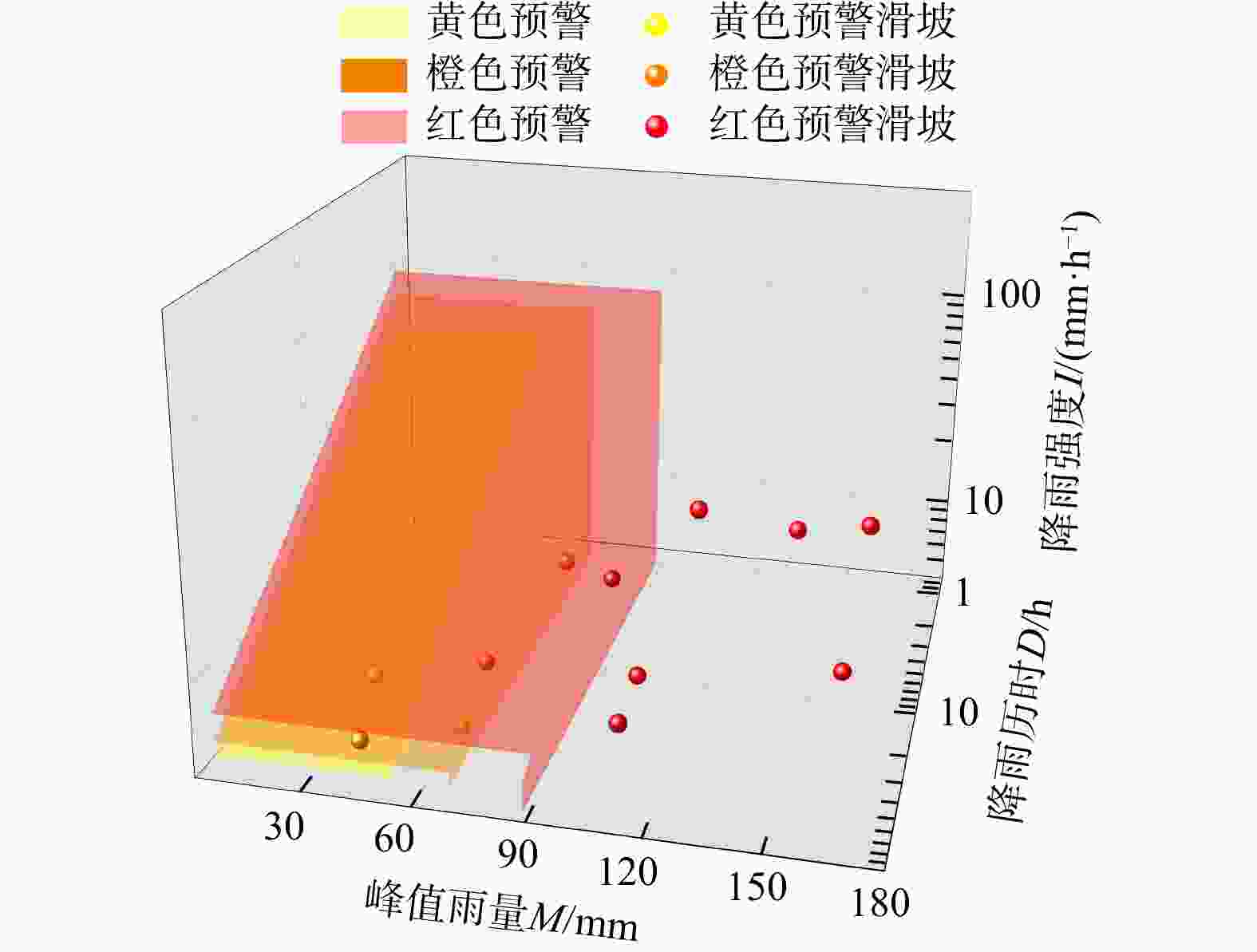
区域滑坡灾害降雨预警是近年来研究的热点问题,其难点在于拟定降雨阈值模型。基于逐时雨量数据引入峰值雨量(
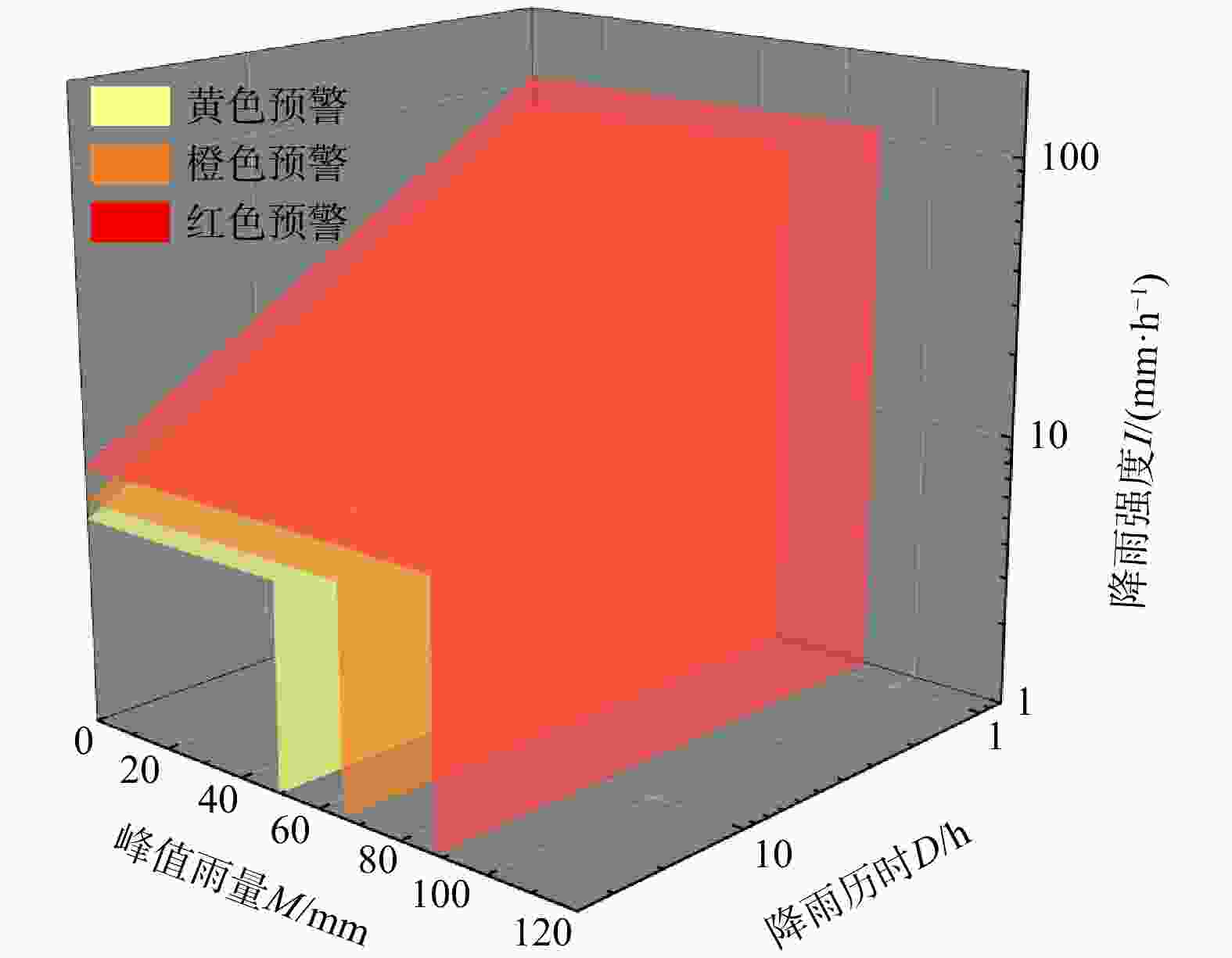
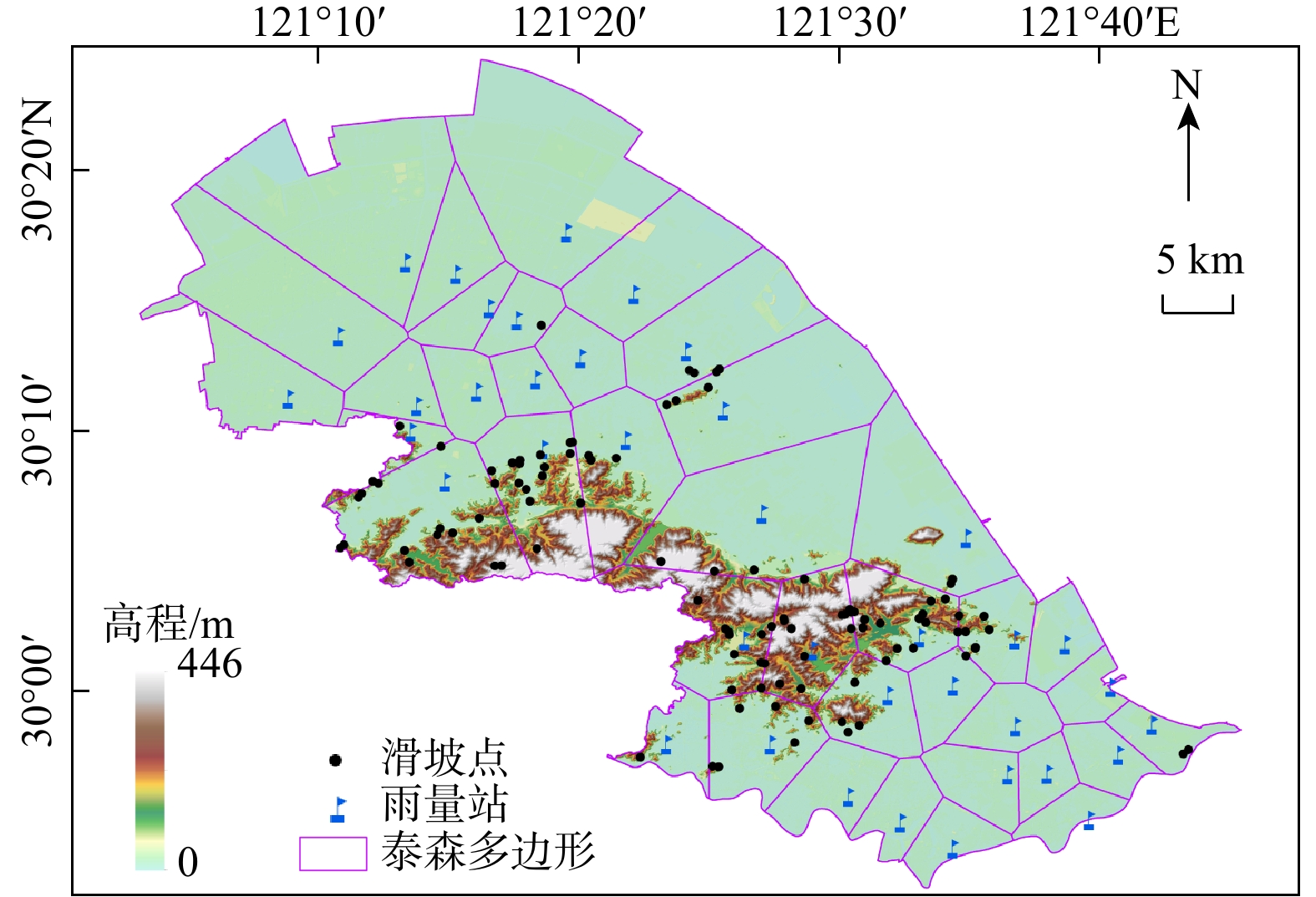
M ),构建了滑坡灾害的三维表征降雨阈值模型,可为区域滑坡灾害降雨预警提供科学依据。在浙江省宁波市慈溪市、江北区、镇海区北部3区2010−2022年期间的104处降雨型滑坡事件基础上开展了研究。首先,利用泰森多边形划分单元网格方法划定与灾害相关联的雨量站空间分布,揭示滑坡灾害的有效降雨特征信息;其次,基于滑坡事件编录构建灾害发生时的逐时降雨强度−降雨历时(I -D )阈值模型,并采用分位数回归方法划分临界阈值曲线;最后,针对I -D 阈值模型不足引入峰值雨量(M )改进提出I -D -M 模型。以受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic,简称ROC)和滑坡实例对比检验上述2种模型精度,据此确定最优阈值模型作为本地区降雨预警判据。结果表明,考虑峰值雨量(M )的I -D -M 阈值模型相比于I -D 模型具有更高的预警精度,滑坡发生概率黄色预警提高8%,橙色预警提高17%,红色预警提高16%,表明峰值雨量对滑坡的发生具有重要影响;基于分位数回归的I -D -M 阈值模型可作为本地区滑坡灾害红、橙、黄三级降雨预警的判据。研究成果提出的三维表征降雨阈值模型对区域滑坡灾害降雨预警具有理论指导意义。Abstract:Objective Regional early warning of rainfall-induced landslide has been a research hotpot in recent years, with the primary challenge being the formulation of rainfall threshold models. Based on hourly rainfall data, this study introduces peak rainfall (
M ) to construct a three-dimensional characterization model, which can provide a scientific basis for regional rainfall-induced landslide early warning.Methods The research was conducted using data from 104 rainfall-induced landslide events recorded between 2010 and 2022 in the three northern districts of Ningbo City (Cixi, Jiangbei, and Zhenhai). Firstly, the spatial distribution of rainfall stations associated with landslides was delineated using Voronoi diagram method to reveal the effective rainfall characteristic information of landslide hazards. Secondly, the rainfall intensity-rainfall duration (
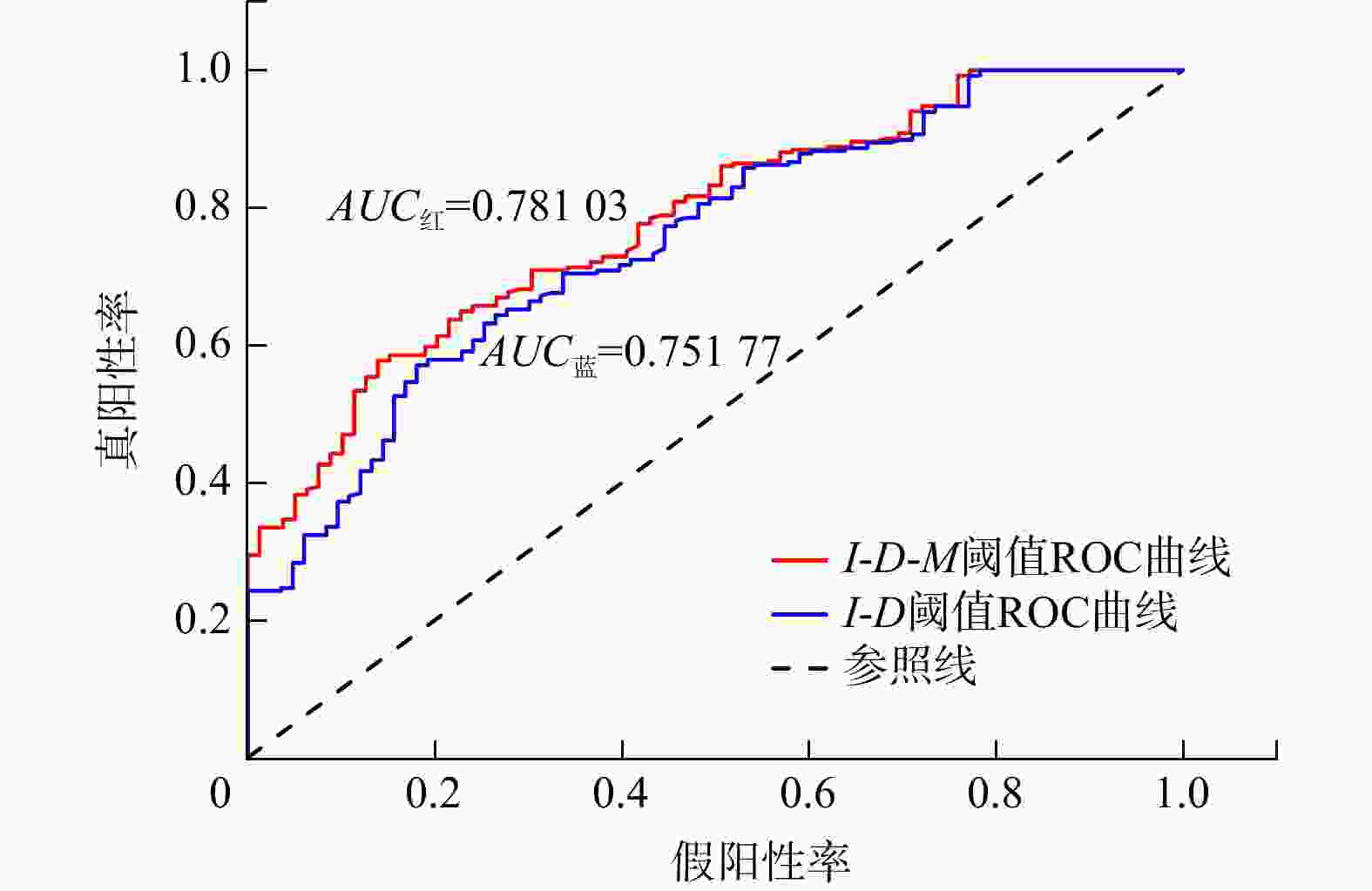
I -D ) threshold model was established based on landslide inventory, with critical threshold curves defined using quantile regression. Finally, to address the limitations of theI -D model, peak rainfall (M ) was incorporated to propose an improvedI -D -M model. The accuracy of both models was evaluated and compared using ROC curves and historical landslide cases to identify the optimal threshold model for regional early warning.Results The results demonstrate that the
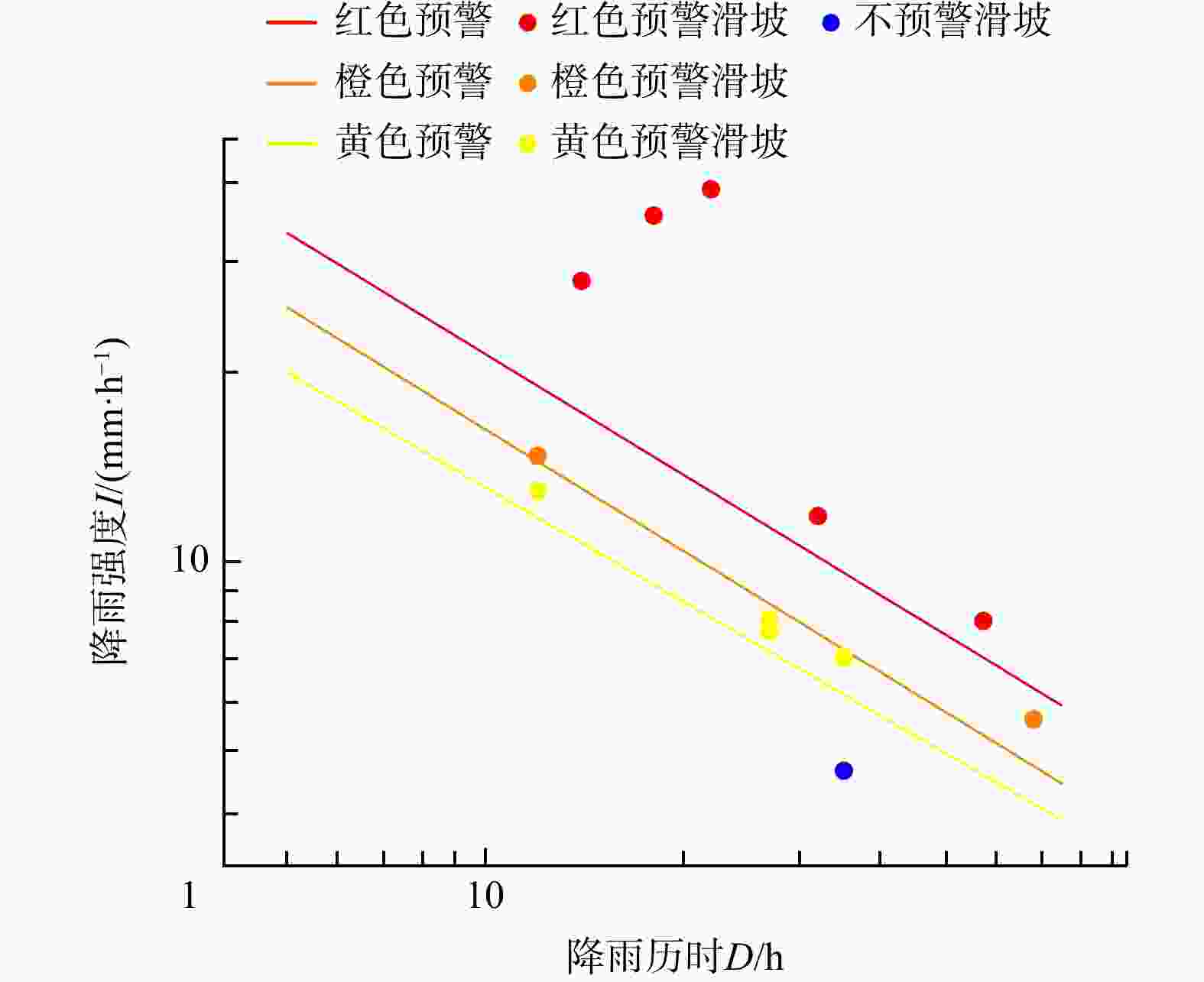
I -D -M model, incorporating peak rainfall (M ), achieves higher warning accuracy than the conventionalI -D model. Probability of landslide occurrence increased by 8% for yellow warnings, 17% for orange warnings, and 16% for red warnings, indicating the significant role of peak rainfall on landslide initiation. The quantile regression-basedI -D -M threshold model can be effectively applied as a criterion for implementing three-tiered (red, orange, yellow) rainfall landslide early warning in the study area.Conclusion The proposed three-dimensional rainfall threshold model provides theoretical and practical insights for improving regional landslide early warning systems, demonstrating enhanced predictive capability and operational applicability.
-
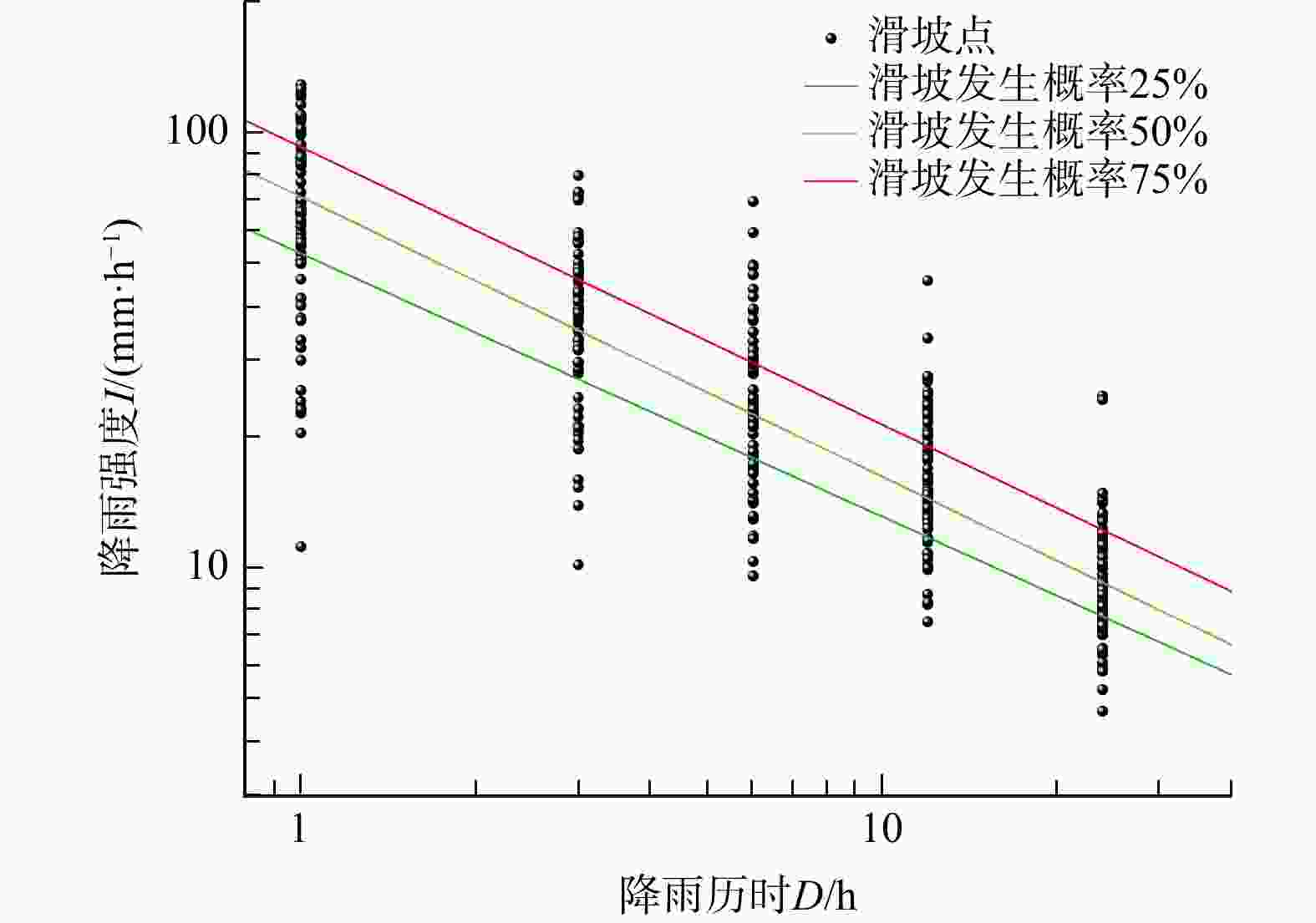
表 1 不同预警等级降雨阈值方程
Table 1. Rainfall threshold equations for different warning levels
等级划分 分位数回归方程 黄色预警(滑坡发生概率25%) $ {52.76D}^{-0.604} $ 橙色预警(滑坡发生概率50%) $ {71.23D}^{-0.642} $ 红色预警(滑坡发生概率75%) $ {92.68D}^{-0.637} $ 注:D. 降雨历时,h;下同 -
[1] THOMAS J, GUPTA M, PRUSTY G. Assessing global parameters of slope stability model using Earth data observations for forecasting rainfall–induced shallow landslides[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2023, 212: 104994. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2023.104994 [2] ZHAN Q H, WANG S M, GUO F, et al. Early warning model and model test verification of rainfall-induced shallow landslide[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2022, 81(8): 318. doi: 10.1007/s10064-022-02827-4 [3] MA S Y, SHAO X Y, XU C. Physically-based rainfall-induced landslide thresholds for the Tianshui area of Loess Plateau, China by TRIGRS model[J]. Catena, 2023, 233: 107499. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2023.107499 [4] WANG C H, FANG L, CHANG D T, et al. Back-analysis of a rainfall-induced landslide case history using deterministic and random limit equilibrium methods[J]. Engineering Geology, 2023, 317: 107055. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2023.107055 [5] SEOK K, ONDA Y, UCHIDA T, et al. Effect of seepage on shallow landslides in consideration of changes in topography: Case study including an experimental sandy slope with artificial rainfall[J]. Catena, 2018, 161: 50-62. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.10.004 [6] LUO X X, LI C J, ZHOU J W. GIS-based prediction method of shallow landslides induced by heavy rainfall in large mountainous areas[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2024, 21(5): 1534-1548. doi: 10.1007/s11629-023-8535-2 [7] 卢操, 晏鄂川, 张瑜, 等. 降雨作用下青石镇政府后山堆积层滑坡渗流与稳定性[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 139-147.LU C, YAN E C, ZHANG Y, et al. Seepage and stability of the colluvial landslide on the back hill of Qingshi Town Government under rainfall[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 139-147. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] POSNER A J, GEORGAKAKOS K P. Soil moisture and precipitation thresholds for real-time landslide prediction in El Salvador[J]. Landslides, 2015, 12(6): 1179-1196. doi: 10.1007/s10346-015-0618-x [9] BEZAK N, ŠRAJ M, MIKOŠ M. Copula-based IDF curves and empirical rainfall thresholds for flash floods and rainfall-induced landslides[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 541: 272-284. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.02.058 [10] IRAWAN A M, VIRGIANTO R H, SAFRIL A, et al. Rainfall threshold and soil moisture indexes for the initiation of landslide in Banjarmangu sub-district, central Java, Indonesia[J]. IOP Conference Series (Earth and Environmental Science), 2019, 243(1): 012028. [11] LI W Y, LIU C, SCAIONI M, et al. Spatio-temporal analysis and simulation on shallow rainfall-induced landslides in China using landslide susceptibility dynamics and rainfall I-D thresholds[J]. Science China (Earth Sciences), 2017, 60(4): 720-732. doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-9008-4 [12] YANG H J, WEI F Q, MA Z F, et al. Rainfall threshold for landslide activity in Dazhou, southwest China[J]. Landslides, 2020, 17(1): 61-77. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01270-z [13] SEGONI S, ROSI A, ROSSI G, et al. Analysing the relationship between rainfalls and landslides to define a mosaic of triggering thresholds for regional-scale warning systems[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2014, 14(9): 2637-2648. doi: 10.5194/nhess-14-2637-2014 [14] ROSI A, PETERNEL T, JEMEC-AUFLIČ M, et al. Rainfall thresholds for rainfall-induced landslides in Slovenia[J]. Landslides, 2016, 13(6): 1571-1577. doi: 10.1007/s10346-016-0733-3 [15] 李环禹, 陈朝晖, 范文亮, 等. 区域降雨型滑坡风险分析统计模型研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2018, 27(4): 103-111.LI H Y, CHEN Z H, FAN W L, et al. The statistical risk analysis model of rainfall-induced landslide in large areas[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2018, 27(4): 103-111. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] CAINE N. The rainfall intensity: Duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows[J]. Geografiska Annaler Series A, Physical Geography, 1980, 62(1/2): 23-27. doi: 10.2307/520449 [17] GUZZETTI F, PERUCCACCI S, ROSSI M, et al. The rainfall intensity-duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows: An update[J]. Landslides, 2008, 5(1): 3-17. doi: 10.1007/s10346-007-0112-1 [18] MILLÁN-ARANCIBIA C, LAVADO-CASIMIRO W. Rainfall thresholds estimation for shallow landslides in Peru from gridded daily data[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2023, 23(3): 1191-1206. doi: 10.5194/nhess-23-1191-2023 [19] 夏梦想, 李远耀, 吴吉民, 等. 基于I-D统计模型的张家界市滑坡灾害降雨预警阀值研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2021, 30(4): 203-212.XIA M X, LI Y Y, WU J M, et al. Research on rainfall early warning threshold of landslide disaster in Zhangjiajie City based on I-D statistical model[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2021, 30(4): 203-212. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 龚泉冰, 殷坤龙, 肖常贵, 等. 基于I-D阈值的滑坡气象预警双指标模型[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(1): 262-274.GONG Q B, YIN K L, XIAO C G, et al. Double-index model of landslide meteorological warning based on the I-D threshold[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(1): 262-274. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 黄发明, 曹中山, 姚池, 等. 基于决策树和有效降雨强度的滑坡危险性预警[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2021, 55(3): 472-482.HUANG F M, CAO Z S, YAO C, et al. Landslides hazard warning based on decision tree and effective rainfall intensity[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2021, 55(3): 472-482. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] ROSSI M, LUCIANI S, VALIGI D, et al. Statistical approaches for the definition of landslide rainfall thresholds and their uncertainty using rain gauge and satellite data[J]. Geomorphology, 2017, 285: 16-27. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.02.001 [23] DAS S, PANDIT K, KANUNGO D P, et al. Developing hillslope hydrology based probabilistic rainfall threshold for shallow landslides[J]. Natural Hazards, 2025, 121(5): 5363-5385. doi: 10.1007/s11069-024-07018-w [24] 李长江, 麻土华, 李炜, 等. 滑坡频度-降雨量的分形关系[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2010, 21(1): 87-93.LI C J, MA T H, LI W, et al. Fractal relation of landslide frequency and rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2010, 21(1): 87-93. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 张永双, 姚鑫, 郭长宝, 等. 龙门山地区震后泥石流灾害区域预警研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(5): 1014-1023.ZHANG Y S, YAO X, GUO C B, et al. Regional warning of debris flow hazards after Wenchuan earthquake in Longmenshan region[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(5): 1014-1023. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] NOCENTINI N, MEDICI C, BARBADORI F, et al. Optimization of rainfall thresholds for landslide early warning through false alarm reduction and a multi-source validation[J]. Landslides, 2024, 21(3): 557-571. doi: 10.1007/s10346-023-02176-7 [27] 刘谢攀, 殷坤龙, 肖常贵, 等. 基于I-D-R阈值模型的滑坡气象预警[J]. 地球科学, 2024, 49(3): 1039-1051.LIU X P, YIN K L, XIAO C G, et al. Meteorological early warning of landslide based on I-D-R threshold model[J]. Earth Science, 2024, 49(3): 1039-1051. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] WANG S W, SUN L S, RONG J, et al. Transit traffic analysis zone delineating method based on Thiessen polygon[J]. Sustainability, 2014, 6(4): 1821-1832. doi: 10.3390/su6041821 [29] ZHAO B R, DAI Q, HAN D W, et al. Probabilistic thresholds for landslides warning by integrating soil moisture conditions with rainfall thresholds[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 574: 276-287. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.04.062 [30] KOENKER R, BASSETT G. Regression quantiles[J]. Econometrica, 1978, 46(1): 33. [31] 陈建宝, 丁军军. 分位数回归技术综述[J]. 统计与信息论坛, 2008, 23(3): 89-96.CHEN J B, DING J J. A review of technologies on quantile regression[J]. Statistics & Information Forum, 2008, 23(3): 89-96. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] SEGONI S, PICIULLO L, GARIANO S L. A review of the recent literature on rainfall thresholds for landslide occurrence[J]. Landslides, 2018, 15(8): 1483-1501. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-0966-4 [33] CHIEN L K, HSU C F, YIN L C. Warning model for shallow landslides induced by extreme rainfall[J]. Water, 2015, 7(8): 4362-4384. doi: 10.3390/w7084362 [34] HUANG J, JU N P, LIAO Y J, et al. Determination of rainfall thresholds for shallow landslides by a probabilistic and empirical method[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2015, 15(12): 2715-2723. doi: 10.5194/nhess-15-2715-2015 [35] FAWCETT T. An introduction to ROC analysis[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2006, 27(8): 861-874. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010 [36] DOU H Q, WANG R, WANG H, et al. Rainfall early warning threshold and its spatial distribution of rainfall-induced landslides in China[J]. Rock Mechanics Bulletin, 2023, 2(3): 100056. doi: 10.1016/j.rockmb.2023.100056 [37] TAN J Y, YANG C, WANG Y Z, et al. A hybrid model to overcome landslide inventory incompleteness issue for landslide susceptibility prediction[J]. Geocarto International, 2024, 39(1): 2322066. doi: 10.1080/10106049.2024.2322066 [38] LÜ Q, WU J Y, LIU Z H, et al. The Fuyang shallow landslides triggered by an extreme rainstorm on 22 July 2023 in Zhejiang, China[J]. Landslides, 2024, 21(11): 2725-2740. doi: 10.1007/s10346-024-02314-9 [39] XIAO T, ZHANG L M, CHEUNG R W M, et al. Predicting spatio-temporal man-made slope failures induced by rainfall in Hong Kong using machine learning techniques[J]. Géotechnique, 2023, 73(9): 749-765. [40] 窦杰, 向子林, 许强, 等. 机器学习在滑坡智能防灾减灾中的应用与发展趋势[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(5): 1657-1674.DOU J, XIANG Z L, XU Q, et al. Application and development trend of machine learning in landslide intelligent disaster prevention and mitigation[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(5): 1657-1674. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 屈鹏鑫, 谢婉丽, 刘琦琦, 等. 基于机器学习方法改进IVM-RF耦合模型的崩滑灾害危险性评价: 以延安市志丹县为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(3): 280-295.QU P X, XIE W L, LIU Q Q, et al. Collapse and landslide risk assessment based on machine learning improved IVM-RF coupling method: A case study of Zhidan County, Yan'an City[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(3): 280-295. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: