Genesis of uranium reservoirs in the Upper Cretaceous Saihan Formation in the central Ulanqab Depression of the Erlian Basin and their constraints on uranium mineralization
-
摘要:
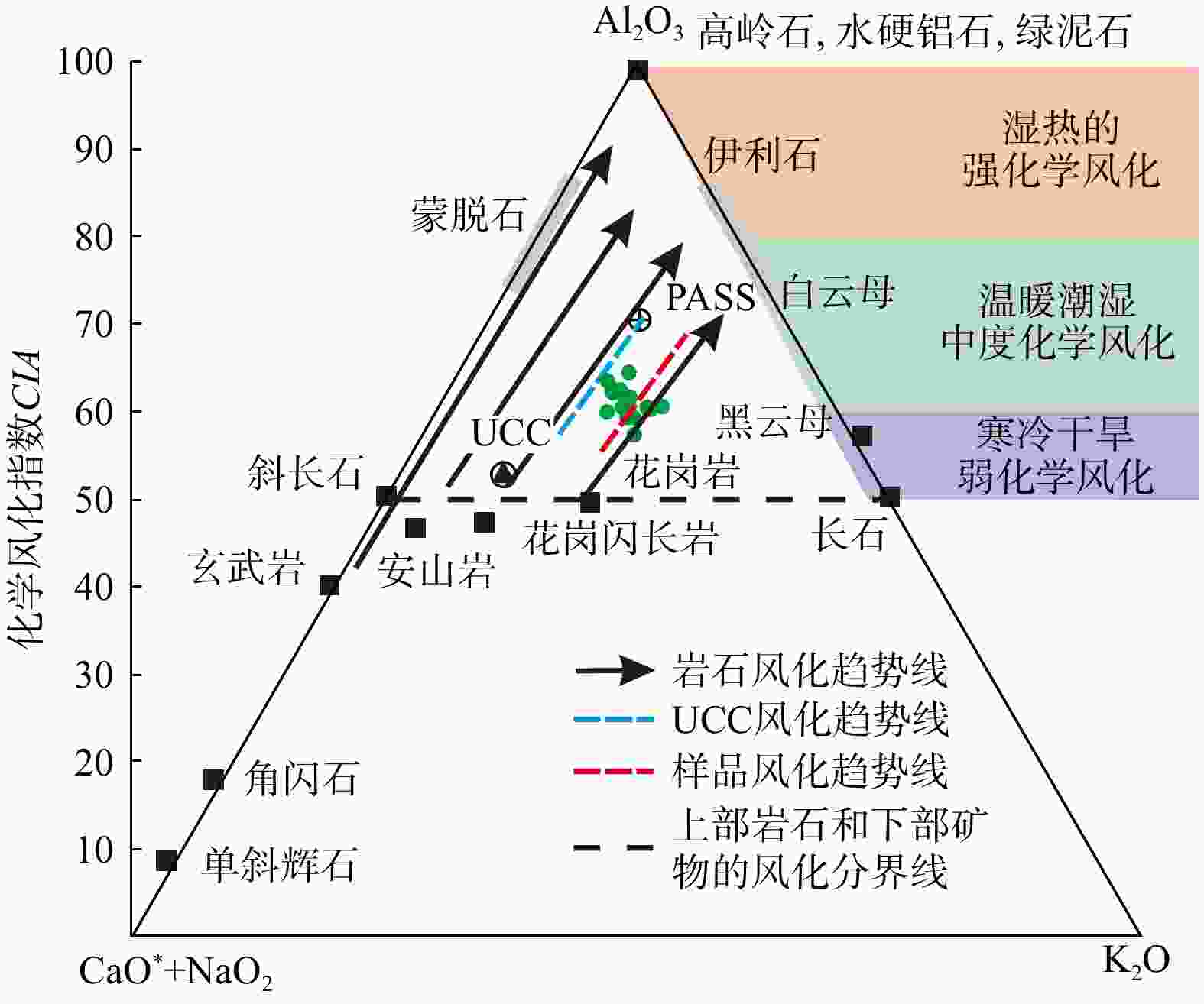
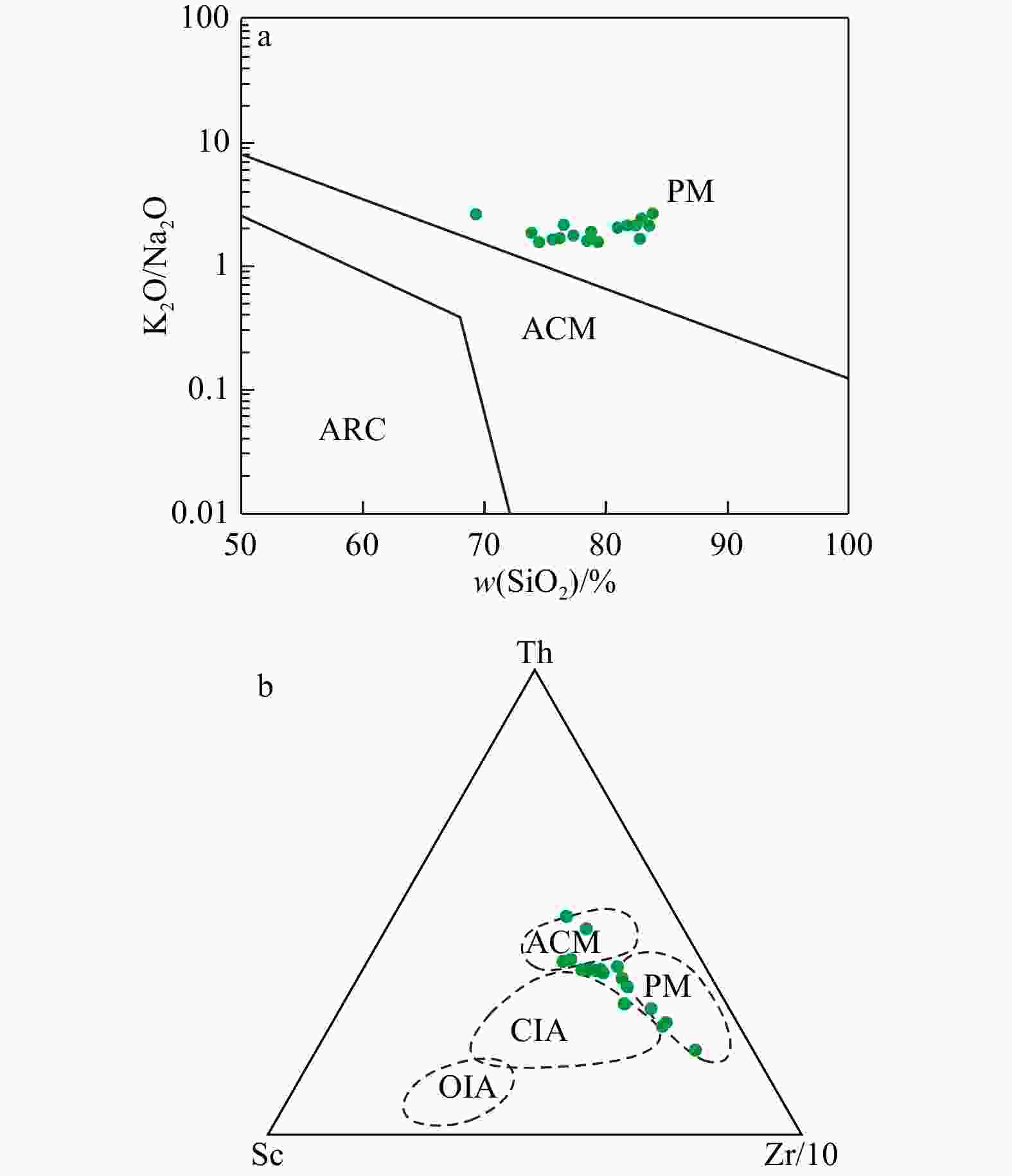
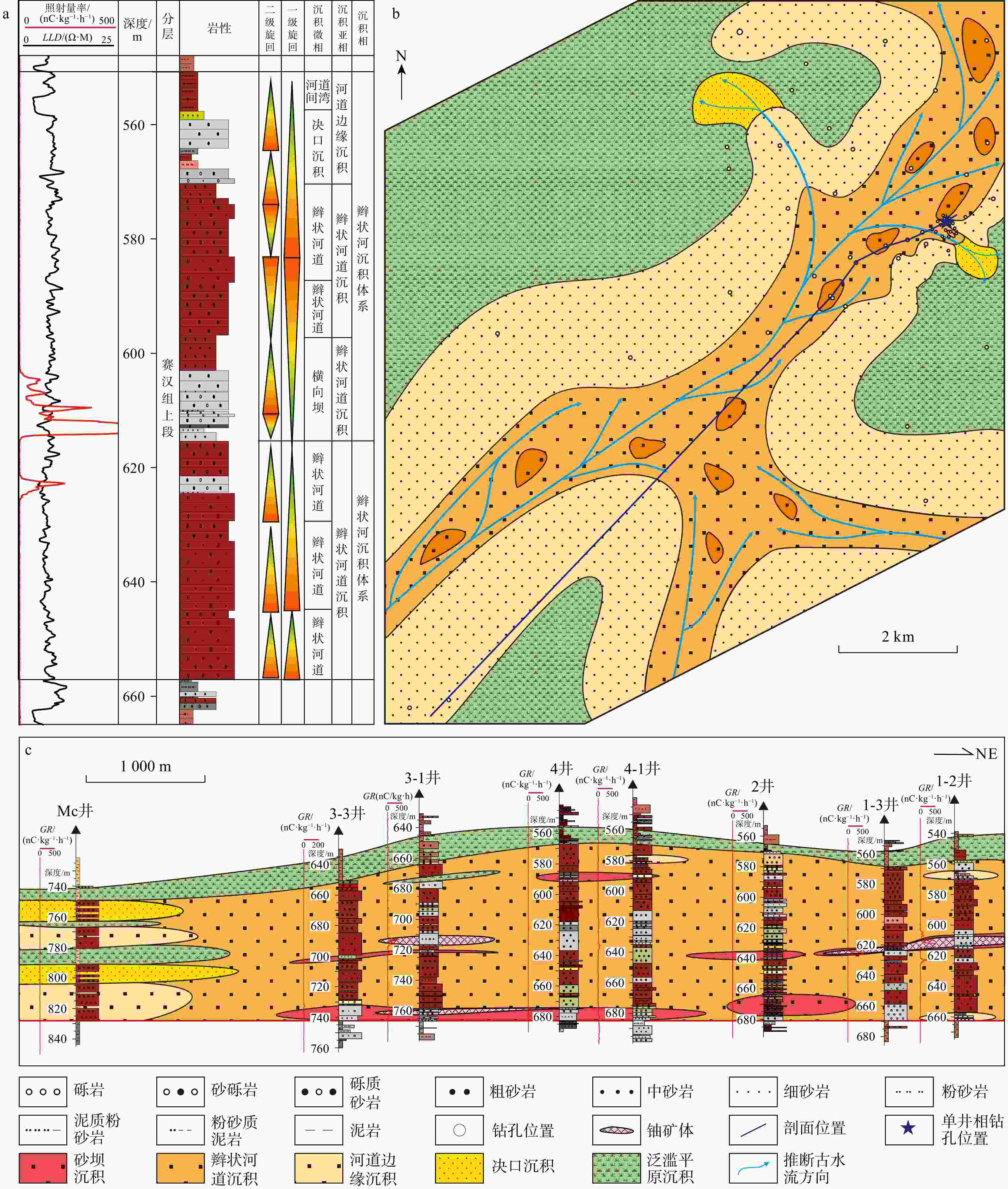
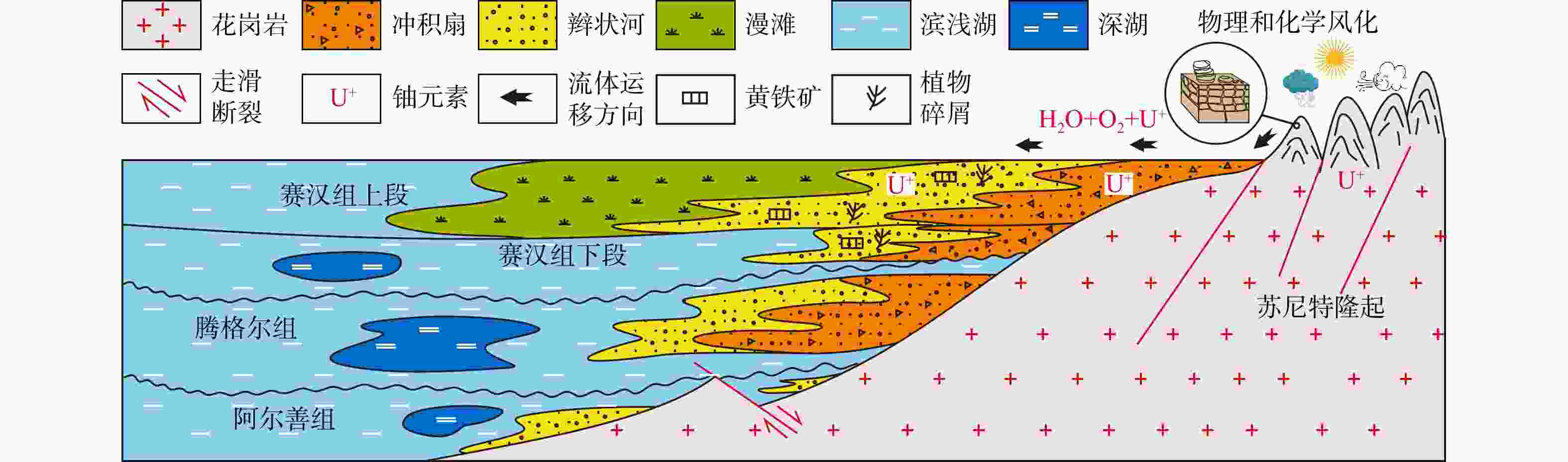
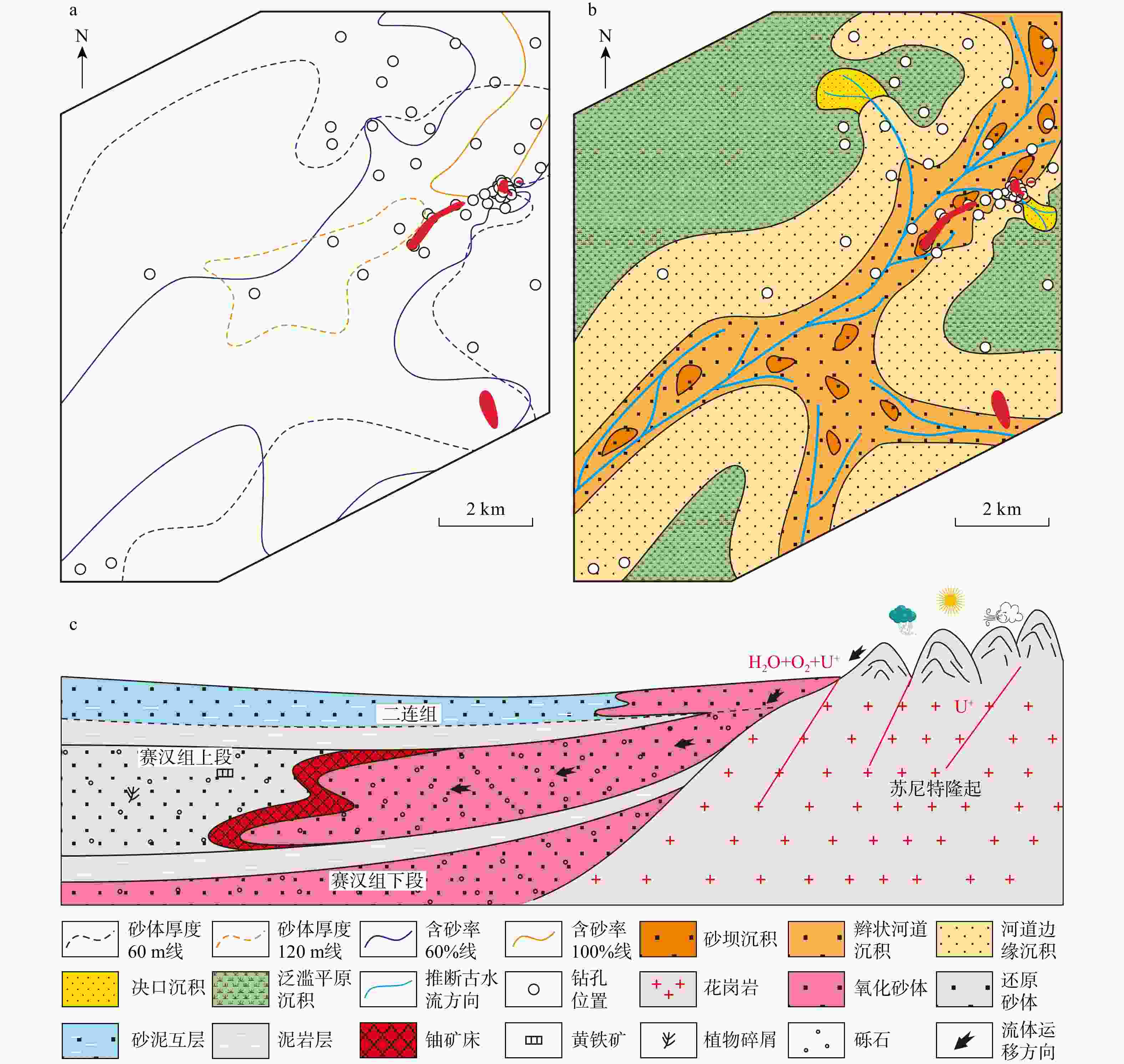
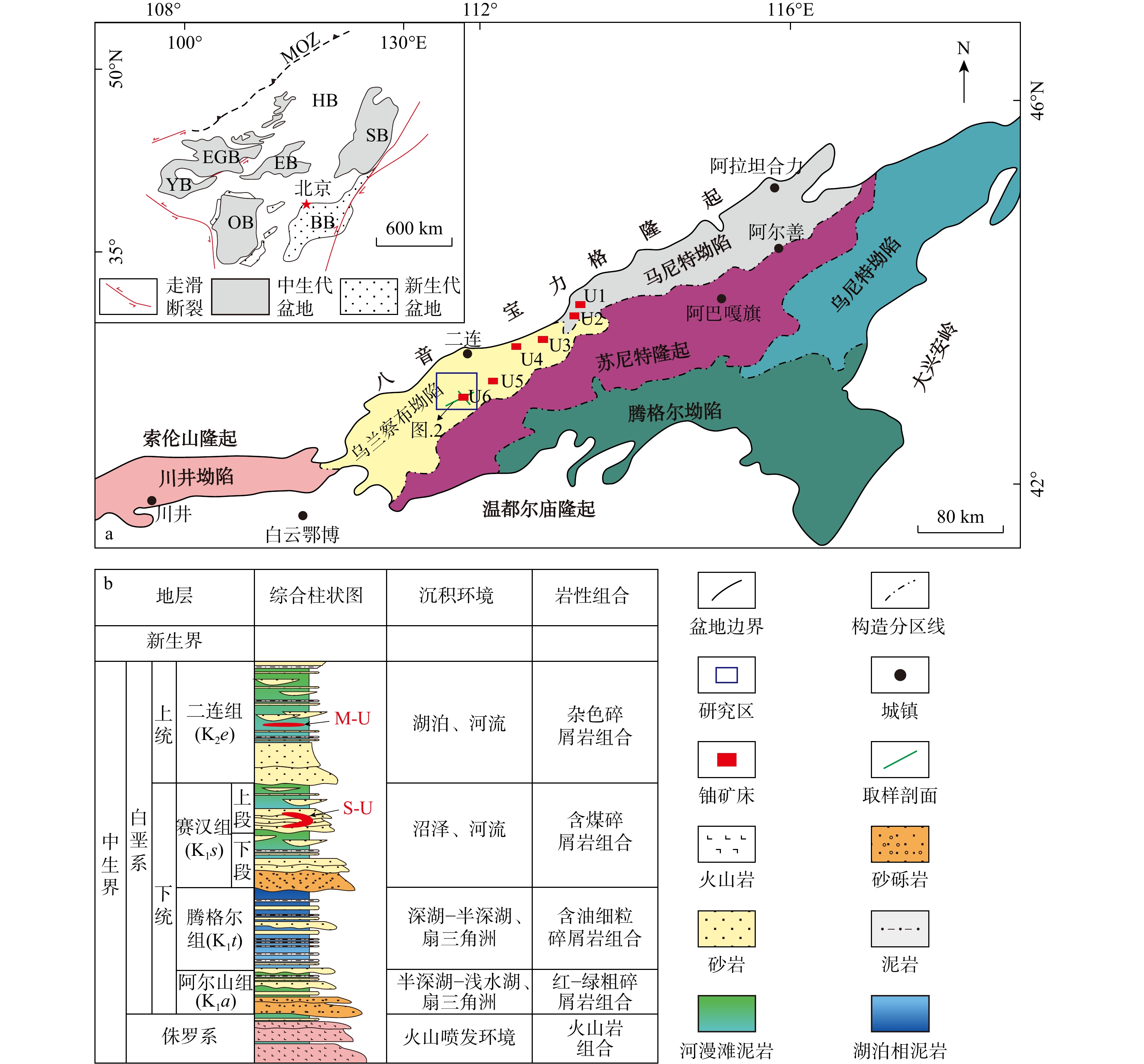
铀储层是砂岩型铀成矿基础,因此,研究铀储层的成因对于铀成矿作用及铀成矿潜力评价具有重要的意义。通过砂分散体系、沉积物碎屑组分、重矿物组合及元素组成等分析,对二连盆地乌兰察布坳陷中部赛汉组铀储层进行了成因分析。研究表明:砂岩中石英、长石、岩屑平均质量分数分别为51%,27%和12%;Fe2O3T/K2O和SiO2/Al2O3平均值分别为0.12和8.61;
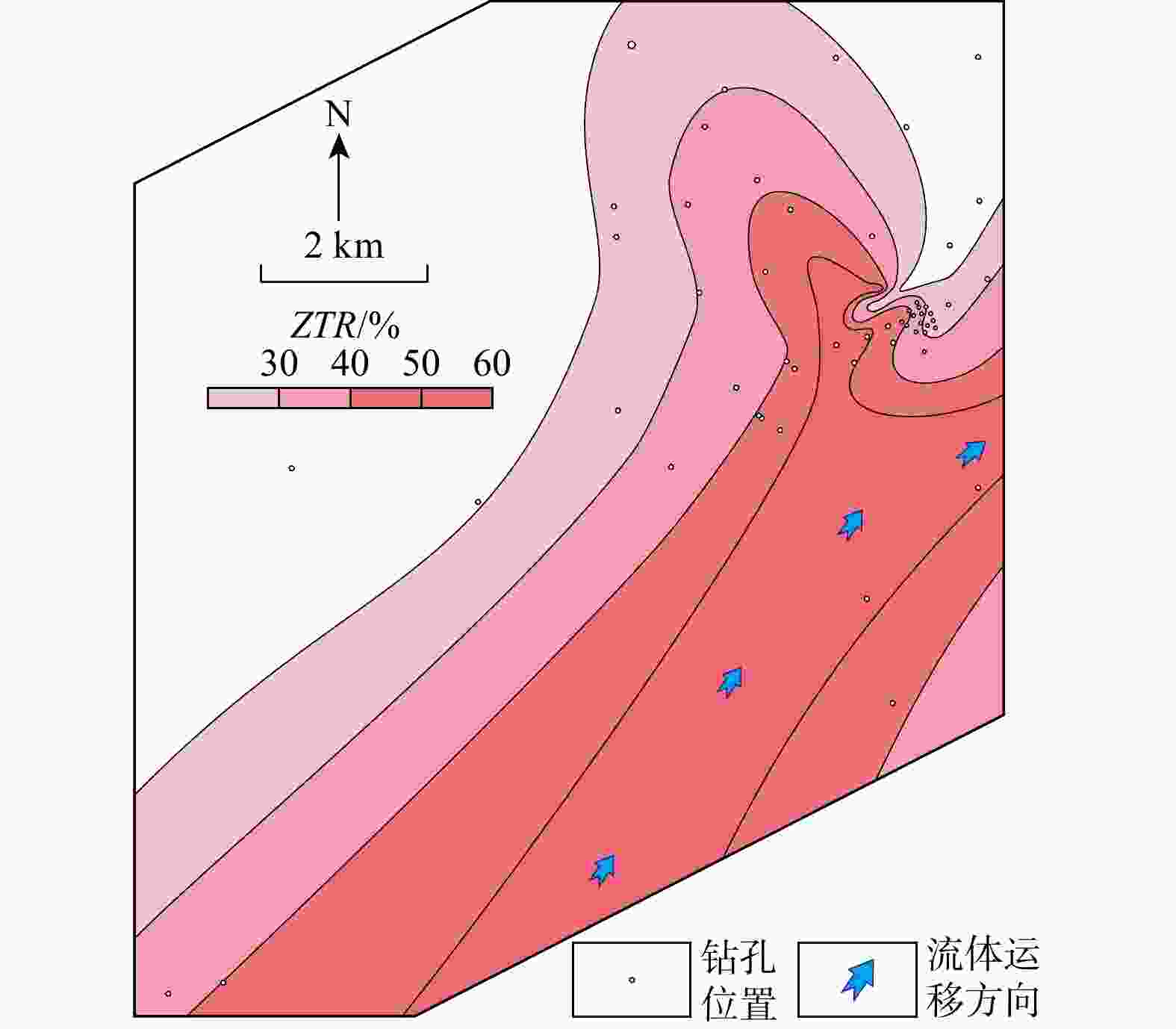
CIA 平均值为61.83;Eu/Eu*平均值为0.75;砂岩中主要重矿物23种,AT i平均值为35.2,ZG i平均值为48.8,ZTR 值在24.2%~71.6%之间。以上特征表明,赛汉组砂岩类型为长石砂岩和岩屑砂岩,母岩主要为中酸性岩浆岩。物源区母岩化学风化强度中等,反映了温暖潮湿下较强的化学风化作用。物源区母岩构造背景主要为大陆边缘,物源主要来自苏尼特隆起。综合以上研究,认为二叠纪−三叠纪和白垩纪−侏罗纪时期在大陆边缘构造背景下,在苏尼特隆起区形成的中酸性花岗岩在温暖潮湿的气候背景下,经过较强的风化作用,形成的碎屑由流体携带向盆地内搬运,形成了赛汉组上段砂岩,砂岩本身有铀元素存在。经过后期铀成矿作用,铀元素富集形成砂岩型铀矿床。Abstract:Objective The uranium reservoir is the foundation of sandstone-type uranium mineralization. Therefore, studying the genesis of uranium reservoirs is essential for understanding uranium mineralization processes and evaluating uranium mineralization potential.
Methods This paper conducts a genetic analysis of the uranium reservoir in the Saihan Formation in the central part of the Ulanqab Depression in the Erlian Basin based on analyses of the sand dispersal system, detrital components of sediments, heavy mineral assemblages, and elemental composition.
Results The study found that the average contents of quartz, feldspar, and rock fragments in the sandstone are 51%, 27%, and 12%, respectively. The average values of Fe2O3T/K2O and SiO2/Al2O3 are 0.12 and 8.61, respectively, with an average
CIA value of 61.83. The average Eu/Eu* value is 0.75. A total of 23 major heavy minerals were identified in the sandstone, with averageAT i andZG i values of 35.2 and 48.8, respectively, andZTR values ranging between 24.2% and 71.6%.Conclusions These characteristics indicate that the sandstone types in the Saihan Formation are feldspathic sandstone and lithic sandstone, with the parent rocks primarily composed of intermediate-acidic magmatic rocks. The chemical weathering intensity of the parent rocks in the source area is moderate, reflecting strong chemical weathering under warm and humid conditions. The tectonic setting of the parent rocks in the source area is mainly continental margin, with the provenance primarily derived from the Sonid Uplift. Based on comprehensive analysis, it is concluded that during the Permian-Triassic and Jurassic-Cretaceous periods, intermediate-acidic granites formed in the Sonid uplift under a continental margin tectonic setting. Under warm and humid climatic conditions, these rocks underwent intense weathering, and the resulting detrital materials were transported by fluids into the basin, forming the uranium-bearing sandstone of the Upper Saihan Formation. Through subsequent uranium mineralization processes, the uranium was enriched and formed sandstone-type uranium deposits.
-
Key words:
- Erlian Basin /
- Saihan Formation /
- uranium reservoir /
- uranium mineralization
-
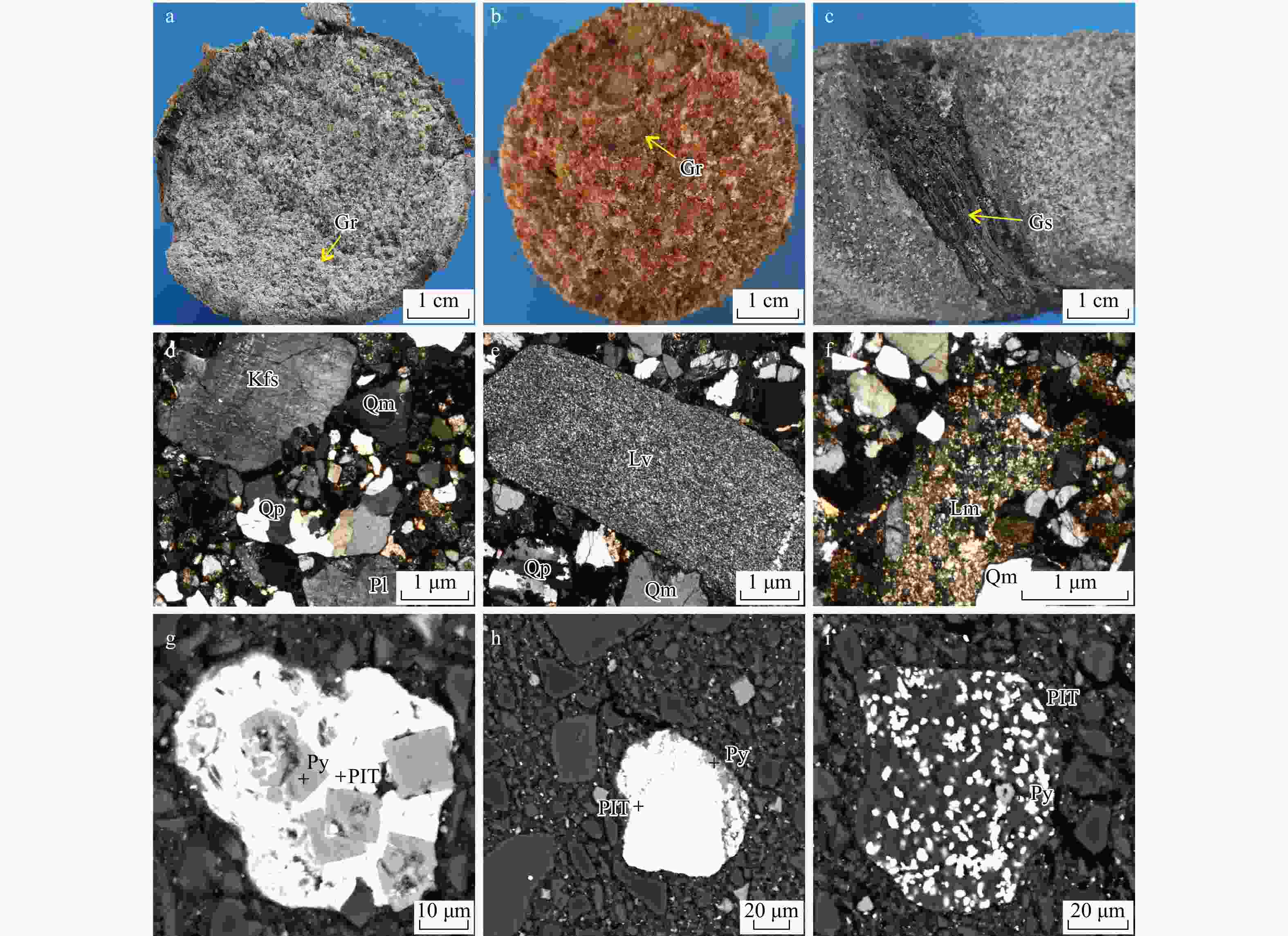
图 3 赛汉组砂岩镜下碎屑组分图版
a. 灰色砂岩,1-2井613.9 m;b. 红色砂岩,1-4井592.1 m;c. 含矿砂岩,1-15井652 m;d. 钾长石、多晶石英、单晶石英,1-1B1样品;e. 火山岩岩屑、多晶石英、单晶石英,1-4B3样品;f. 变质岩岩屑、单晶石英,1-20B5样品;g. 胶状黄铁矿与沥青铀矿,1-4TZ1样品;h. 黄铁矿与沥青铀矿,1-2TZ1样品;i. 草莓装黄铁矿与沥青铀矿,1-4TZ1样品。Gr. 砾石;Cs. 碳质条带;Qm. 单晶石英;Qp. 多晶石英;Kfs. 钾长石;Pl. 斜长石;Lv. 火山岩岩屑;Lm. 变质岩岩屑;Py. 黄铁矿;Or. 正长石;PIT. 沥青铀矿
Figure 3. Micro-photos for sandstones from the Sihan Formation, showing the detrital component
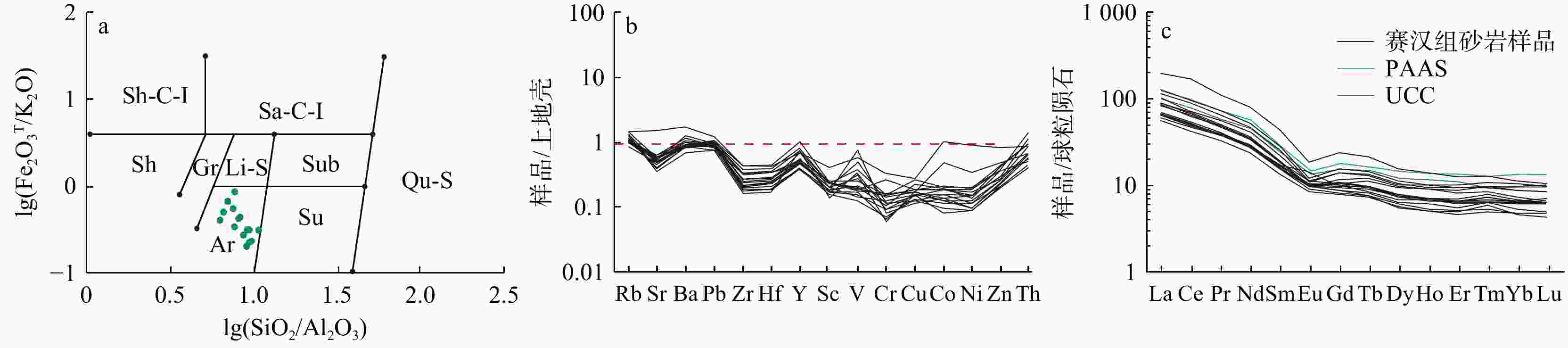
图 4 赛汉组砂岩lg(Fe2O3T/K2O)−lg(SiO2/Al2O3)(a),微量元素(b)和稀土元素(c)标准化配分曲线
Sh-C-I. 含铁页岩;Sa-C-I. 含铁砂岩;Sh. 页岩;Ar. 长石砂岩;Su. 长石石英砂岩;Li-S. 岩屑砂岩;Gr. 杂砂岩;Sub. 岩屑石英砂岩;Qu-S. 石英砂岩;a底图据文献[35];上地壳微量元素标准化值据文献[32];球粒陨石稀土元素标准化值据文献[30]
Figure 4. Diagram of Fe2O3T/K2O-SiO2/Al2O3 (a), trace element (b) and REE patterns (c) of sandstones from the Saihan Formation
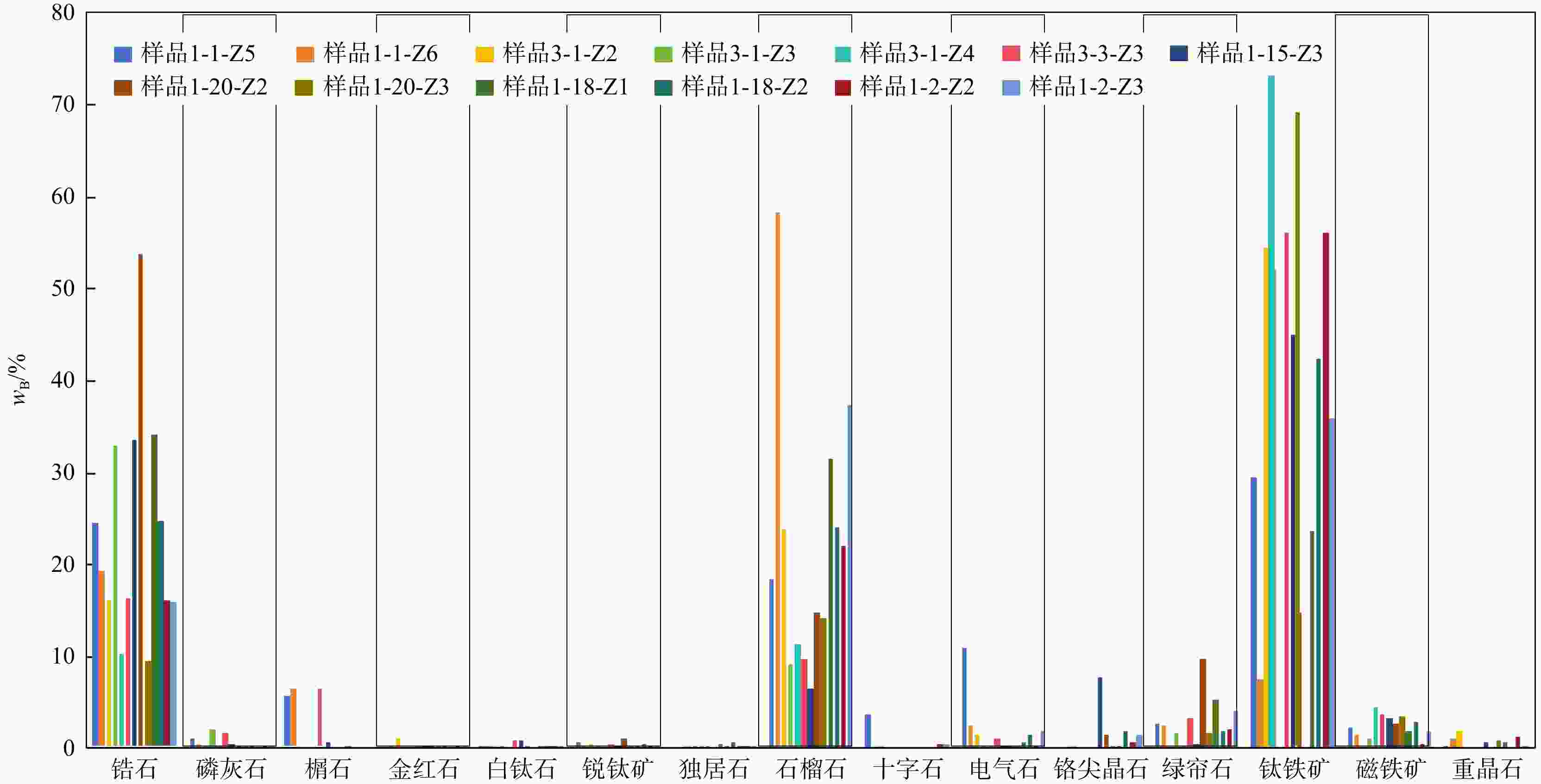
表 1 赛汉组铀储层砂岩重矿物质量分数
Table 1. Heavy mineral contents of uranium reservoir sandstone in the Saihan Formation
样品
编号岩性 锆石 磷灰石 榍石 金红石 白钛石 锐钛矿 独居石 石榴石 十字石 电气石 铬尖晶石 绿帘石 钛铁矿 磁铁矿 重晶石 总计 ZTR ATi ZGi wB/% 1-1-Z5 灰色粗砂岩 24.56 1.06 5.59 0.00 0.12 0.71 0.00 18.38 3.68 11.03 0.00 2.76 29.41 2.36 0.35 100.00 52.80 8.77 42.81 1-1-Z6 灰色粗砂岩 19.24 0.51 6.33 0.10 0.15 0.25 0.00 58.23 0.00 2.53 0.00 2.53 7.59 1.52 1.01 100.00 24.17 16.67 75.16 3-1-Z2 灰色含砾
粗砂岩16.04 0.11 0.00 1.03 0.23 0.46 0.15 23.80 0.31 1.53 0.04 0.00 54.47 0.00 1.83 100.00 41.48 6.98 59.73 3-1-Z3 灰色粗砂岩 32.94 2.04 0.00 0.00 0.08 0.08 0.39 9.10 0.00 0.39 0.00 1.73 52.08 1.18 0.00 100.00 71.55 83.87 21.64 3-1-Z4 浅灰色
中砂岩10.16 0.30 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.17 11.30 0.00 0.07 0.00 0.07 73.44 4.48 0.00 100.00 46.34 80.00 52.67 3-3-Z3 灰色中砂岩 16.29 1.61 6.36 0.24 0.87 0.20 0.31 9.85 0.00 1.10 0.00 3.35 56.15 3.67 0.00 100.00 45.08 59.35 37.68 1-15-Z3 灰色中砂岩 33.63 0.55 0.72 0.06 0.89 0.28 0.00 6.60 0.00 0.12 7.65 0.48 44.99 3.31 0.74 100.00 66.90 81.97 16.40 1-20-Z2 灰色细砂岩 53.95 0.11 0.00 0.27 0.27 1.07 0.54 14.71 0.00 0.38 1.45 9.77 14.81 2.68 0.00 100.00 67.26 22.22 21.42 1-20-Z3 灰色粗砂岩 9.31 0.09 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.09 0.15 14.18 0.00 0.30 0.30 1.78 69.40 3.56 0.80 100.00 35.83 23.08 60.35 1-18-Z1 灰色粗砂岩 34.22 0.15 0.10 0.34 0.10 0.34 0.68 31.51 0.00 0.68 0.15 5.42 23.72 1.94 0.68 100.00 47.68 17.65 47.94 1-18-Z2 灰色粗砂岩 24.63 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.12 0.48 0.24 24.03 0.00 1.43 1.85 1.91 42.32 2.99 0.00 100.00 48.18 0.00 49.39 1-2-Z2 灰色粗砂岩 16.08 0.02 0.00 0.26 0.09 0.17 0.09 22.07 0.44 0.15 0.74 2.07 56.00 0.51 1.31 100.00 38.15 10.53 57.85 1-2-Z3 灰色粗砂岩 15.77 0.06 0.00 0.12 0.12 0.09 0.31 37.41 0.53 1.86 1.58 4.21 35.87 1.98 0.09 100.00 28.66 3.23 70.35 注:ZTR=100×(w(锆石)+w(电气石)+w(金红石))/ w(总重矿物);ATi=100×w(磷灰石)/(w(磷灰石)+w(电气石));ZGi=100×w(石榴石)/(w(石榴石)+w(锆石)) 表 2 研究区赛汉组沉积物主量元素、微量稀土元素分析结果及相关元素比值
Table 2. Results of major, trace and rare earth elements analyses and related elemental ratios of sediment from the Saihan Formation in the study area
样品编号 3-1-H1 3-1-H3 3-1-H6 3-2-W1 3-3-H2 3-3-H4 1-2-H2 1-4-H7 1-13-H1 1-20-H6 1-18-H3 1-15-H3 1-3-H2 1-10-H2 1-9-H3 1-11-H2 1-12-H2 PAAS UCC SiO2 wB/% 73.90 74.54 75.67 76.17 82.79 78.80 79.27 78.50 69.29 77.35 81.08 83.52 76.56 82.52 82.97 81.68 83.84 62.80 66.60 TiO2 0.26 0.19 0.18 0.14 0.11 0.12 0.21 0.12 0.07 0.20 0.11 0.09 0.11 0.19 0.11 0.10 0.13 1.00 0.60 Al2O3 10.43 11.67 9.68 9.08 8.76 9.52 10.37 10.14 6.23 11.57 9.22 8.65 8.15 8.89 8.42 8.85 8.81 18.90 15.40 Fe2O3T 2.11 1.31 2.75 1.47 0.61 1.34 1.59 1.02 0.71 1.44 0.87 0.62 0.67 0.97 0.67 0.62 0.91 7.20 5.00 MnO 0.02 0.08 0.06 0.08 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.04 0.09 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.01 0.10 0.10 MgO 0.55 0.66 0.52 0.49 0.24 0.61 0.06 0.38 0.14 0.40 0.20 0.19 0.29 0.35 0.22 0.25 0.21 2.20 2.50 CaO 1.80 1.20 0.93 1.25 0.65 0.79 0.79 1.58 9.16 0.67 1.44 0.75 4.89 0.42 1.27 1.42 0.34 1.30 3.60 Na2O 1.73 2.09 1.90 1.98 1.71 1.76 1.87 1.93 0.90 1.64 1.57 1.31 1.28 1.53 1.28 1.46 1.13 1.20 3.30 K2O 3.13 3.22 3.08 3.28 2.79 3.13 2.89 3.00 2.29 2.85 3.14 2.80 2.73 3.10 2.86 3.11 2.89 3.70 2.80 P2O5 0.04 0.02 0.03 0.05 0.04 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.04 0.06 0.04 0.06 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.20 0.20 SO3 0.08 0.08 0.08 3.40 0.43 0.38 0.19 0.13 0.04 0.15 0.15 0.12 0.11 0.13 0.14 0.07 0.13 − − FeO 0.10 0.24 0.14 0.15 0.08 0.14 0.68 0.21 0.12 0.24 0.60 0.10 0.12 0.17 0.10 0.14 0.17 − − Fe2O3 2.00 1.04 2.59 1.30 0.52 1.18 0.83 0.79 0.58 1.17 0.20 0.51 0.54 0.78 0.56 0.46 0.72 − − 烧失量 5.54 4.57 4.56 2.45 2.07 3.45 2.86 3.56 10.60 3.83 2.61 2.08 5.56 2.26 2.50 2.75 2.11 − − 总和 101.69 100.91 102.17 101.29 100.81 101.31 101.69 101.45 100.26 101.59 101.25 100.82 101.09 101.37 101.18 100.98 101.44 Al2O3/TiO2 40.12 61.42 53.78 64.86 79.64 79.33 49.38 84.50 89.00 57.85 83.82 96.11 74.09 46.79 76.55 88.50 67.77 − − Fe2O3T/K2O 0.20 0.11 0.28 0.16 0.07 0.14 0.15 0.10 0.11 0.12 0.09 0.07 0.08 0.11 0.08 0.07 0.10 − − SiO2/Al2O3 7.09 6.39 7.82 8.39 9.45 8.28 7.64 7.74 11.12 6.69 8.79 9.66 9.39 9.28 9.85 9.23 9.52 − − CIA 61.51 64.43 62.49 55.64 63.59 58.87 65.97 59.65 60.37 69.99 60.51 64.99 60.64 59.07 60.84 59.48 63.11 − − DF1 −4.28 −4.48 −4.45 −5.68 −6.01 −5.87 −4.15 −4.66 −1.81 −4.17 −5.48 −6.11 −3.94 −6.58 −6.06 −5.99 −6.35 − − DF2 0.81 1.34 0.40 1.24 0.34 0.41 0.90 1.21 2.05 0.18 0.99 −0.15 1.36 0.24 0.06 0.75 −0.54 − − Rb wB/
10−688.50 97.10 93.20 116.00 85.00 87.50 83.90 93.10 72.80 123.00 111.00 91.60 94.00 107.00 81.30 103.00 106.00 160.00 84.00 Sr 138.20 126.30 190.20 487.60 207.00 177.50 174.20 186.30 159.10 176.40 159.60 157.60 166.00 111.70 167.30 149.80 128.20 200.00 320.00 Ba 564.20 549.90 645.20 1066.25 724.70 658.00 541.70 520.30 541.90 568.80 559.40 557.40 786.10 441.80 630.40 537.80 531.70 650.00 624.00 Pb 17.00 16.10 16.70 21.10 14.70 16.50 18.20 15.80 12.90 17.70 15.00 15.10 16.40 13.70 14.20 14.90 17.50 20.00 17.00 Zr 47.10 60.60 41.00 82.40 36.00 50.40 82.30 39.30 30.10 62.60 50.60 41.40 36.90 64.40 32.40 44.80 72.60 210.00 193.00 Hf 1.46 1.86 1.23 2.34 1.01 1.46 2.17 1.19 0.90 1.82 1.52 1.29 1.08 1.90 0.97 1.37 2.12 5.00 5.30 Y 14.51 9.78 10.50 22.30 8.08 11.40 14.40 9.63 16.00 11.80 11.50 11.40 8.14 16.10 8.79 11.20 17.50 27.00 21.00 Sc 2.72 3.23 2.84 3.47 2.36 3.39 5.64 2.85 1.95 3.60 2.38 2.34 2.45 3.24 2.24 2.42 3.29 16.00 14.00 V 48.80 19.10 14.00 17.40 15.20 17.90 56.60 26.30 33.20 25.40 74.00 30.50 20.50 38.20 12.40 17.00 19.60 150.00 97.00 Cr 9.65 13.70 11.70 15.10 8.00 24.30 30.00 10.50 8.60 14.10 7.05 5.20 13.10 14.00 6.30 5.70 9.90 110.00 92.00 Cu 4.26 5.14 4.32 4.53 4.41 5.25 7.78 3.56 3.57 5.18 3.20 4.96 4.76 7.40 3.90 4.37 6.63 50.00 28.00 Co 3.18 3.17 2.16 8.46 1.43 3.30 17.40 2.74 1.68 3.75 2.38 2.20 2.35 3.52 1.97 2.80 3.36 23.00 17.30 Ni 7.06 7.90 5.94 16.40 4.22 9.20 42.70 7.00 4.11 8.60 4.60 4.65 7.20 9.80 5.55 5.24 6.41 55.00 47.00 Zn 20.00 18.50 17.60 32.10 14.20 24.90 56.00 29.40 13.60 29.40 16.40 15.70 20.20 25.50 14.40 18.10 24.80 85.00 67.00 Th 6.30 10.00 4.20 7.10 14.50 6.00 8.50 7.50 8.20 7.90 6.80 9.10 4.50 9.70 6.20 11.60 5.10 7.84 14.6 La wB/
10−624.51 16.17 15.60 47.00 13.60 15.80 14.60 16.40 16.30 21.00 20.60 20.00 16.60 27.70 16.30 21.90 31.10 38.20 31.00 Ce 43.68 30.78 30.00 107.00 25.80 28.80 29.00 30.40 32.60 38.90 41.20 40.60 33.30 55.00 32.50 43.10 59.20 79.60 63.00 Pr 5.47 3.78 3.64 10.80 3.20 3.58 3.58 3.74 3.79 4.71 4.70 4.56 3.89 6.32 3.64 4.91 6.95 8.80 7.10 Nd 18.93 13.96 13.21 38.40 11.20 12.90 13.30 13.20 13.60 16.50 16.40 16.10 13.70 22.40 13.10 17.40 24.60 33.90 27.00 Sm 3.43 2.49 2.47 6.82 2.05 2.50 2.63 2.40 2.68 2.89 2.90 2.87 2.44 3.94 2.37 3.00 4.35 5.60 4.70 Eu 0.61 0.61 0.85 1.09 0.49 0.57 0.59 0.57 0.56 0.65 0.56 0.57 0.58 0.65 0.54 0.57 0.69 1.10 1.00 Gd 2.88 2.05 2.04 5.02 1.60 1.90 2.20 1.79 2.39 2.14 2.08 2.08 1.80 2.93 1.69 2.27 3.17 4.70 4.00 Tb 0.48 0.32 0.35 0.82 0.28 0.34 0.42 0.31 0.45 0.37 0.36 0.37 0.29 0.50 0.29 0.37 0.55 0.80 0.70 Dy 2.64 1.72 1.84 4.04 1.45 1.93 2.38 1.63 2.48 1.98 1.88 1.93 1.40 2.67 1.54 2.01 2.83 4.70 3.90 Ho 0.58 0.38 0.42 0.79 0.30 0.40 0.51 0.34 0.52 0.41 0.38 0.39 0.28 0.54 0.30 0.40 0.58 1.00 0.80 Er 1.55 1.01 1.07 2.09 0.81 1.10 1.45 0.93 1.37 1.12 1.08 1.05 0.78 1.55 0.84 1.10 1.72 2.90 2.30 Tm 0.25 0.16 0.19 0.33 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.16 0.22 0.20 0.17 0.17 0.13 0.24 0.14 0.18 0.27 0.40 0.30 Yb 1.64 1.08 1.15 1.95 0.78 1.12 1.51 0.90 1.23 1.16 1.10 1.05 0.82 1.52 0.81 1.13 1.76 2.80 2.00 Lu 0.26 0.16 0.18 0.27 0.11 0.15 0.21 0.12 0.17 0.16 0.17 0.16 0.12 0.22 0.12 0.16 0.25 0.40 0.30 ΣREE 106.92 74.69 73.00 226.42 61.80 71.28 72.63 72.89 78.36 92.19 93.58 91.90 76.11 126.17 74.17 98.50 138.02 − − LREE/
HREE13.43 14.42 13.05 21.00 14.99 12.62 9.79 15.59 11.17 16.07 17.22 16.96 18.99 16.44 17.40 17.41 16.34 − − Eu/Eu* 0.60 0.82 1.15 0.57 0.82 0.80 0.75 0.84 0.68 0.80 0.70 0.72 0.84 0.58 0.82 0.66 0.57 − − 注:CIA=[Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO*+Na2O+K2O)]×100,式中为每种氧化物的摩尔质量,其中CaO*为校正含量;DF1=−1.773TiO2+0.607Al2O3+0.76Fe2O3T−1.5MgO+0.616CaO+0.509Na2O−1.224K2O−9.09; DF2=0.445TiO2+0.07Al2O3−0.25Fe2O3T−1.142MgO+0.438CaO+1.475Na2O+1.426K2O−6.681;球粒陨石标准化依据文献[30];Eu/Eu*=EuN/(SmN×GdN)1/2;PAAS. 太古宙平均页岩,依据文献[31];UCC. 上地壳,依据文献[32];REE. 稀土元素;LREE. 轻稀土元素;HREE. 重稀土元素;下同 表 3 赛汉组砂岩和不同构造背景砂岩的主要元素和稀土元素
Table 3. Major and rare earth elements of sandstones from the Saihan Formation and different tectonic settings
构造背景 来源类型 主量元素指标 稀土元素指标 Fe2O3T+MgO TiO2 Al2O3/
SiO2K2O/
Na2OAl2O3/
(CaO+Na2O)La Ce ∑REE La/Yb LaN/YbN ∑LREE/
∑HREEEu/Eu* wB/% wB/10−6 大洋岛弧(OIA) 未切割岩浆弧 11.73 1.06 0.29 0.39 1.72 8±1.7 19±3.7 58±10 4.2±1.3 2.8±0.9 3.8±0.9 1.04±0.11 大陆岛弧(CIA) 切割岩浆弧 6.79 0.64 0.20 0.61 2.42 27±4.5 59±8.2 146±20 11.0±3.6 7.5±2.5 7.7±1.7 0.79±0.13 主动大陆边缘(ACM) 隆升基底 4.63 0.46 0.18 0.99 2.56 37 78 186 12.5 8.5 9.1 0.6 被动大陆边缘(PM) 克拉通内部
构造高地2.89 0.49 0.10 1.60 4.15 39 85 210 15.9 10.8 8.5 0.56 赛汉组铀储层砂岩(样品数N=17) 1.50 0.14 0.12 1.92 3.42 20.89 41.29 91.32 17.16 12.31 15.46 0.75 注:不同构造背景砂岩中主要元素的参数引自文献[42-43],LaN/YbN 和 Eu/Eu*参数引自文献[30, 37];REE参数引自文献[44] -
[1] LEEDER M R. Sedimentary basins: Tectonic recorders of sediment discharge from drainage catchments[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 1997, 22(3): 229-237. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9837(199703)22:3<229::AID-ESP750>3.0.CO;2-F [2] MEADE R H. Sources, sinks, and storage of river sediment in the Atlantic drainage of the United States[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1982, 90(3): 235-252. doi: 10.1086/628677 [3] SØMME T O, JACKSON C A, VAKSDAL M. Source-to-sink analysis of ancient sedimentary systems using a subsurface case study from the Møre-Trøndelag area of southern Norway: Part 1–Depositional setting and fan evolution[J]. Basin Research, 2013, 25(5): 489-511. doi: 10.1111/bre.12013 [4] 张龙, 吴柏林, 刘池洋, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部砂岩型铀矿直罗组物源分析及其铀成矿意义[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(12): 3441-3453.ZHANG L, WU B L, LIU C Y, et al. Provenance analysis of the Zhiluo Formation in the sandstone-hosted uranium deposits of the northern Ordos Basin and implications for uranium mineralization[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(12): 3441-3453. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] BERRYMAN K, MARDEN M, PALMER A, et al. The post-glacial downcutting history in the Waihuka tributary of Waipaoa River, Gisborne district: Implications for tectonics and landscape evolution in the Hikurangi subduction margin, New Zealand[J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 270(1/2/3/4): 55-71. [6] CARTER L, ORPIN A R, KUEHL S A. From mountain source to ocean sink–the passage of sediment across an active margin, Waipaoa Sedimentary System, New Zealand[J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 270(1/2/3/4): 1-10. [7] LOWE D G, SYLVESTER P J, ENACHESCU M E. Provenance and paleodrainage patterns of Upper Jurassic and Lower Cretaceous synrift sandstones in the Flemish Pass Basin, offshore Newfoundland, east coast of Canada[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2011, 95(8): 1295-1320. doi: 10.1306/12081010005 [8] 朱华汇, 陈家旭, 张佼杨, 等. 歧口凹陷滨海斜坡沙一中亚段烃源岩地球化学特征及沉积环境[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(3): 43-56.ZHU H H, CHEN J X, ZHANG J Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and sedimentary environment of source rock in the Middle Section of Es1 in the Binhai slope, Qikou Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(3): 43-56. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 师淑娟, 代永刚, 陈军威, 等. 冀北地区火山岩型隐伏铀矿地球化学勘查方法试验研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(2): 103-108.SHI S J, DAI Y G, CHEN J W, et al. Experimental study of geochemical exploration methods for volcanic-type concealed uranium deposit in northern Hebei[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(2): 103-108. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 涂颖, 蒋孝君, 任志勇, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地苏台庙地区砂岩地球化学环境和常量元素特征及对铀成矿的指示意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2022, 58(1): 61-72.TU Y, JIANG X J, REN Z Y, et al. Geochemical environment and major elements characteristics of sandstones in the Sutaimiao area, Ordos Basin and their implications for uranium mineralization[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2022, 58(1): 61-72. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 刘华健, 徐增连, 汤超, 等. 二连盆地马尼特坳陷赛汉组上段赋铀沉积物源特征及其对砂岩型铀成矿的启示[J]. 地球科学, 2024, 49(10): 3589-3609.LIU H J, XU Z L, TANG C, et al. Provenance characteristics of uranium-bearing sediments of Upper Saihan Formation and its implications for sandstone-type uranium mineralization in Manite Depression, Erlian Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2024, 49(10): 3589-3609. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 李盛富, 陈洪德, 周剑, 等. 沉积盆地源−汇过程及其演化对砂岩型铀矿成矿的制约: 以新疆伊犁盆地南缘蒙其古尔铀矿床为例[J]. 铀矿地质, 2016, 32(3): 137-145.LI S F, CHEN H D, ZHOU J, et al. Source convergence process and its restriction on sandstone type uranium metallization: A case study of Mengqiguer uranium deposit in the southern margin of Yili Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Uranium Geology, 2016, 32(3): 137-145. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 贺锋, 刘鑫扬, 刘卫红, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘砂岩型铀矿“源−汇”系统研究[J]. 铀矿地质, 2022, 38(4): 671-682.HE F, LIU X Y, LIU W H, et al. Analysis on source to convergence systems of sandstone type uranium deposit in the southwestern margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Uranium Geology, 2022, 38(4): 671-682. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 彭虎. 松辽盆地东南缘砂岩型铀矿关键控矿要素时空耦合配置与“源−汇”系统重建[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2023.PENG H. Spatio-temporal coupling configuration for key elements of ore-controlling and "source-sink"system reconstruction of sandstone-type uranium deposit in southeastern margin of Songliao Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 刘波, 彭云彪, 康世虎, 等. 二连盆地巴赛齐赛汉组含铀古河谷沉积特征及铀成矿流体动力学[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2018, 37(2): 316-325.LIU B, PENG Y B, KANG S H, et al. Depositional characteristics and uranium metallogenic fluid dynamics of uranium bearing paleo-valley of the Saihan Formation in Basaiqi, Erlian Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2018, 37(2): 316-325. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 谢惠丽, 李西得, 刘武生, 等. 二连盆地乔尔古−齐哈地区赛汉组上段砂体成因分析及找矿意义[J]. 铀矿地质, 2020, 36(5): 354-361.XIE H L, LI X D, LIU W S, et al. Genesis analysis of sandstone of the Upper Member of Saihan Formation and its prospecting significance in the Qiaoergu-Qiha area of Erlian Basin[J]. Uranium Geology, 2020, 36(5): 354-361. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] NIE F J, YAN Z B, FENG Z B, et al. Genetic models and exploration implication of the paleochannel sandstone-type uranium deposits in the Erlian Basin, North China: A review and comparative study[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 127: 1-16. [18] 秦彦伟. 二连盆地巴赛齐地区下白垩统赛汉组古河谷氧化带特征与铀成矿[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2022.QIN Y W. Characteristics of paleo-valley oxidation zone and uranium mineralization of Lower Cretaceous Saihan Formation in Basaiqi area, Erlian Basin[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] CHENG Y H, WANG S Y, JIN R S, et al. Global Miocene tectonics and regional sandstone-style uranium mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 106: 238-250. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.02.003 [20] 梁宏斌, 吴冲龙, 李林波, 等. 二连盆地层序地层单元统一划分及格架层序地层学[J]. 地球科学, 2010, 35(1): 97-106.LIANG H B, WU C L, LI L B, et al. Unifying division of sequence stratigraphy unit and framework sequence stratigraphy of Erlian Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2010, 35(1): 97-106. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] BONNETTI C, MALARTRE F, HUAULT V, et al. Sedimentology, stratigraphy and palynological occurrences of the Late Cretaceous Erlian Formation, Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia, People's Republic of China[J]. Cretaceous Research, 2014, 48: 177-192. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2013.09.013 [22] 漆家福, 赵贤正, 李先平, 等. 二连盆地早白垩世断陷分布及其与基底构造的关系[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(3): 118-128.QI J F, ZHAO X Z, LI X P, et al. The distribution of Early Cretaceous faulted-sags and their relationship with basement structure within Erlian Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(3): 118-128. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] BONNETTI C, CUNEY M, MALARTRE F, et al. The Nuheting deposit, Erlian Basin, NE China: Synsedimentary to diagenetic uranium mineralization[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 69: 118-139. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.02.010 [24] 程银行, 金若时, Michel CUNEY, 等. 中国北方盆地大规模铀成矿作用: 地层篇[J]. 地质学报, 2024, 98(7): 1953-1976.CHENG Y H, JIN R S, CUNEY M, et al. The strata constraint on large scale sandstone-type uranium mineralization in Meso-Cenozoic basins, northern China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2024, 98(7): 1953-1976. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 聂逢君, 李满根, 严兆彬, 等. 内蒙古二连盆地砂岩型铀矿目的层赛汉组分段与铀矿化[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(10): 1952-1963.NIE F J, LI M G, YAN Z B, et al. Segmentation of the target layer Saihan Formation and sandstone-type uranium mineralization in Erlian Basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(10): 1952-1963. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 鲁超, 焦养泉, 彭云彪, 等. 二连盆地马尼特坳陷西部幕式裂陷作用对铀成矿的影响[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(12): 3483-3491.LU C, JIAO Y Q, PENG Y B, et al. Effect of the episodic rifting in the western Manite Depression in Erlian Basin on sandstone-type uranium mineralization[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(12): 3483-3491. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] WANG X M, JIAO Y Q, DU Y S, et al. REE mobility and Ce anomaly in bauxite deposit of WZD area, northern Guizhou, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 133: 103-117. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.08.009 [28] ZHU Z J, GUO F S, et al. Heavy mineral distribution regularity of Paleogene detrital rocks in Lanping Basin, Yunnan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2017, 36(2/3): 199-208. [29] ZHANG Y L, JIA X T, WANG Z Q, et al. New insights into provenance of Early Cambrian Xiannüdong Formation in the Micangshan area: Evidence from sedimentology, heavy mineral and detrital zircon chronology[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018(9): 1918-1935. [30] TAYLOR S R, MCLENNAN S M. The continental crust: Its composition and evolution[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1985, 94(4): 57-72. [31] MCLENNAN S M, TAYLOR S R. Sedimentary rocks and crustal evolution: Tectonic setting and secular trends[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1991, 99(1): 1-21. doi: 10.1086/629470 [32] RUDNICK R L, Gao S. Composition of the continental crust[M]. Oxford, United Kingdom: Pergamon, 2003: 1-64. [33] BLATT H, MIDDLETON G, MURRAY R. Origin of sedimentary rocks[M]. 2nd edition. New Jersey, America: Prentice-Hall, 1980: 18-266. [34] NESBITT H W, YOUNG G M. Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(7): 1523-1534. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90408-3 [35] PETTIJOHN F J, POTTER P E, SIEVER R. Sand and sandstone[M]. New York, NY: Springer, 1987. [36] HERRON M M. Geochemical classification of terrigenous sands and shales from core or log data[J]. SEPM Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1988, 58(5): 820-829. [37] ROLLINSON H R. Using geochemical data: Evaluation, presentation, interpretation[M]. Harlow, Essex, England: Longman Scientific & Technical, 1993. [38] 裴先治, 胡楠, 刘成军, 等. 东昆仑南缘哥日卓托地区马尔争组砂岩碎屑组成、地球化学特征与物源构造环境分析[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(2): 307-323.PEI X Z, HU N, LIU C J, et al. Detrital composition, geochemical characteristics and provenance analysis for the Maerzheng Formation sandstone in Gerizhuotuo area, southern margin of East Kunlun region[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(2): 307-323. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] ROSER B P, KORSCH R J. Provenance signatures of sandstone-mudstone suites determined using discriminant function analysis of major-element data[J]. Chemical Geology, 1988, 67(1/2): 119-139. [40] RIDGE G H G D L. Provenance and depositional setting of Paleozoic chert and argillite, sierra Nevada, California[J]. SEPM Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1996, 66(1): 107-118. [41] 杨海军, 蔡振忠, 李勇, 等. 塔里木盆地富满地区吐木休克组烃源岩有机地球化学特征及其油气勘探意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(3): 81-93.YANG H J, CAI Z Z, LI Y, et al. Organic geochemical characters of source rock and significance for exploration of the Tumuxiuke Formation in Fuman area, Tarim Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(3): 81-93. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] ROSER B P, KORSCH R J. Plate tectonics and geochemical composition of sandstones: A discussion[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1985, 93(1): 81-84. doi: 10.1086/628921 [43] BHATIA M R. Rare earth element geochemistry of Australian Paleozoic graywackes and mudrocks: Provenance and tectonic control[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1985, 45(1/2): 97-113. [44] TANG C, XU Z L, DUAN M, et al. Genetic model of the Luhai sandstone-type uranium deposit in the Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Minerals, 2025, 15(3): 294. doi: 10.3390/min15030294 [45] FLOYD P A, WINCHESTER J A, PARK R G. Geochemistry and tectonic setting of Lewisian clastic metasediments from the Early Proterozoic Loch Maree Group of Gairloch, NW Scotland[J]. Precambrian Research, 1989, 45(1/2/3): 203-214. [46] MCLENNAN S M, HEMMING S, MCDANIEL D K, et al. Geochemical approaches to sedimentation, provenance, and tectonics[M]. Geological Society of America, 1993: 21-40. [47] 王国茹, 陈洪德, 朱志军, 等. 川东南−湘西地区志留系小河坝组砂岩中重矿物特征及地质意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 38(1): 7-14.WANG G R, CHEN H D, ZHU Z J, et al. Characteristics and geological implications of heavy minerals in Lower Silurian Xiaoheba Formation sandstones in Southeast Sichuan-West Hunan[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2011, 38(1): 7-14. (in Chinese with English abstract [48] 林洪, 李凤杰, 李磊, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘古近系重矿物特征及物源分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2014, 25(4): 532-541.LIN H, LI F J, LI L, et al. Characteristics of Paleogene heavy mineral and its source in northern margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25(4): 532-541. (in Chinese with English abstract [49] FEDO C M, WAYNE NESBITT H, YOUNG G M. Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance[J]. Geology, 1995, 23(10): 921. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0921:UTEOPM>2.3.CO;2 [50] JIAN P, LIU D Y, KRÖNER A, et al. Evolution of a Permian intraoceanic arc–trench system in the Solonker suture zone, Central Asian Orogenic Belt, China and Mongolia[J]. Lithos, 2010, 118(1/2): 169-190. [51] SONG S G, WANG M M, XU X, et al. Ophiolites in the Xing'an-Inner Mongolia accretionary belt of the CAOB: Implications for two cycles of seafloor spreading and accretionary orogenic events[J]. Tectonics, 2015, 34(10): 2221-2248. doi: 10.1002/2015TC003948 [52] 刘建峰, 李锦轶, 赵硕, 等. 中亚造山带东南部晚古生代−早中生代地壳增生和古亚洲洋演化: 来自内蒙古东南部林西−东乌旗地区岩浆岩的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2022, 38(8): 2181-2215. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.08.02LIU J F, LI J Y, ZHAO S, et al. Crustal accretion and Paleo-Asian Ocean evolution during Late Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic in southeastern Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Evidence from magmatism in Linxi-Dongwuqi area, southeastern Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2022, 38(8): 2181-2215. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.08.02 [53] WU Z J, HAN X Z, LIN Z X, et al. Tectonic, sedimentary, and climate evolution of Meso-Cenozoic basins in North China and its significance of coal accumulation and uranium mineralization[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2020, 44(4): 710-724. [54] 徐强. 二连盆地脑木根凹陷早白垩世构造变形及演化过程[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2022, 34(3): 31-37.XU Q. Early Cretaceous structural deformation and evolutionary process in Nomgen Sag, Erenhot Basin[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2022, 34(3): 31-37. (in Chinese with English abstract [55] 唐军. 苏左旗南部瑙木浑尼地区中三叠世二长花岗岩年代学与地球化学研究及其地质意义[D]. 石家庄: 河北地质大学, 2019.TANG J. The geochronological, geochemical researches and tectonic implications of Middle Triassic monzonitic granites in the Naomuhunni area, southern Sonid Zuoqi[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei GEO University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [56] 张晓飞, 滕超, 周毅, 等. 内蒙古西乌旗地区晚二叠世−早中三叠世花岗岩年代学和地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(8): 1903-1927.ZHANG X F, TENG C, ZHOU Y, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Late Permian to Early-Middle Triassic granites in Xiwu Banner, Inner Mongolia and its tectonic significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(8): 1903-1927. (in Chinese with English abstract [57] 王帅, 李英杰, 孔星蕊, 等. 古亚洲洋东段洋盆闭合与后造山伸展: 来自内蒙古苏尼特右旗中三叠世A型花岗岩的证据[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2022, 41(3): 555-568.WANG S, LI Y J, KONG X R, et al. Ocean basin closure and post orogenic extension in the eastern Paleo-Asian Ocean: Evidence from Middle Triassic A-type granite in Sonid Youqi, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2022, 41(3): 555-568. (in Chinese with English abstract [58] 张金带. 我国砂岩型铀矿成矿理论的创新和发展[J]. 铀矿地质, 2016, 32(6): 321-332.ZHANG J D. Innovation and development of metallogenic theory for sandstone type uranium deposit in China[J]. Uranium Geology, 2016, 32(6): 321-332. (in Chinese with English abstract [59] 聂逢君, 夏菲, 严兆彬, 等. 二连盆地西部隆起区卫境岩体铀丢失与盆内铀矿成矿关系探讨[J]. 地球学报, 2022, 43(5): 616-632.NIE F J, XIA F, YAN Z B, et al. Study on uranium loss of Weijing granite and sandstone-type uranium mineralization in Erlian Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2022, 43(5): 616-632. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: