Pressure distribution characteristics and overpressure genesis of the Oligocene Linhe Formation in the Xinglong structural belt, Linhe Depression of the Hetao Basin
-
摘要:
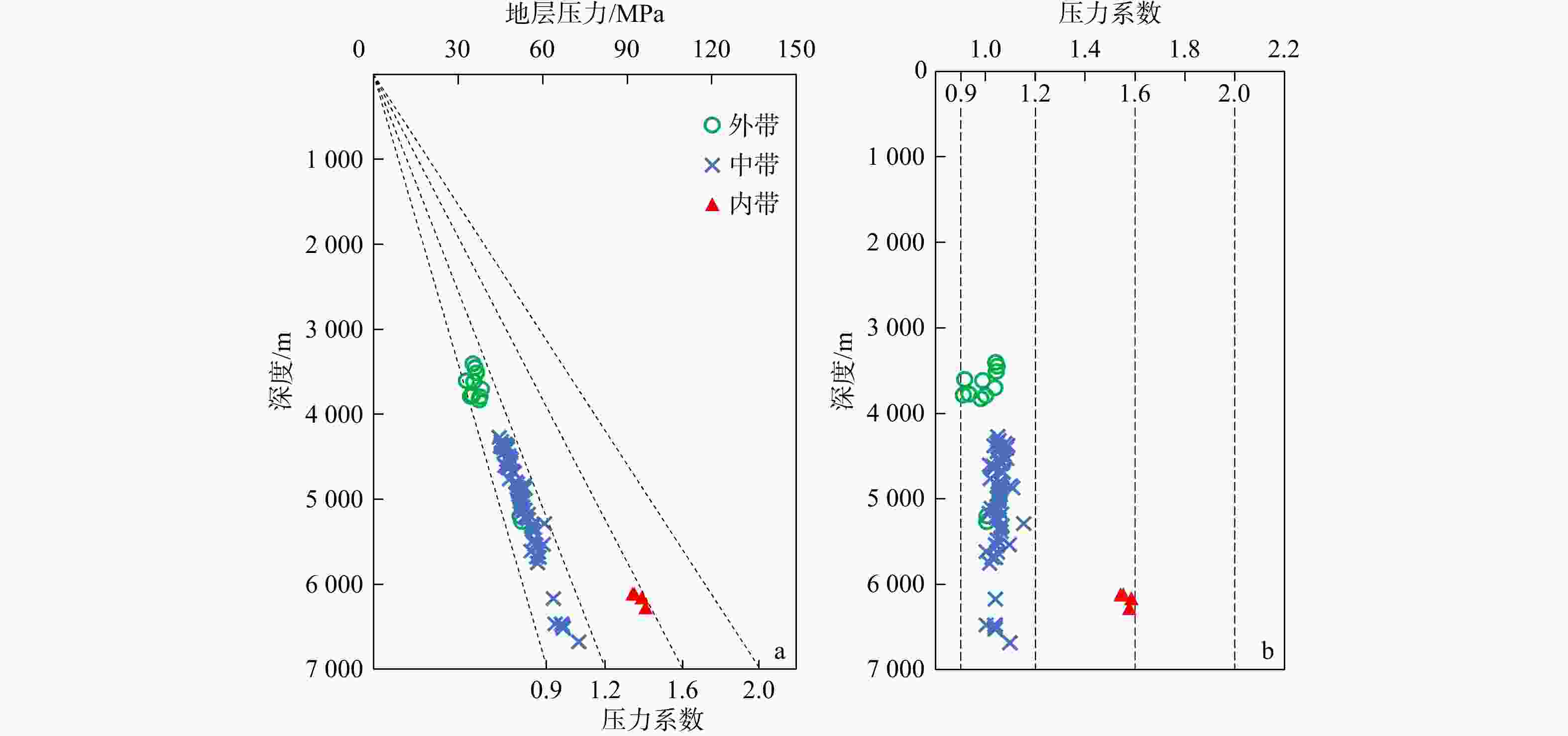
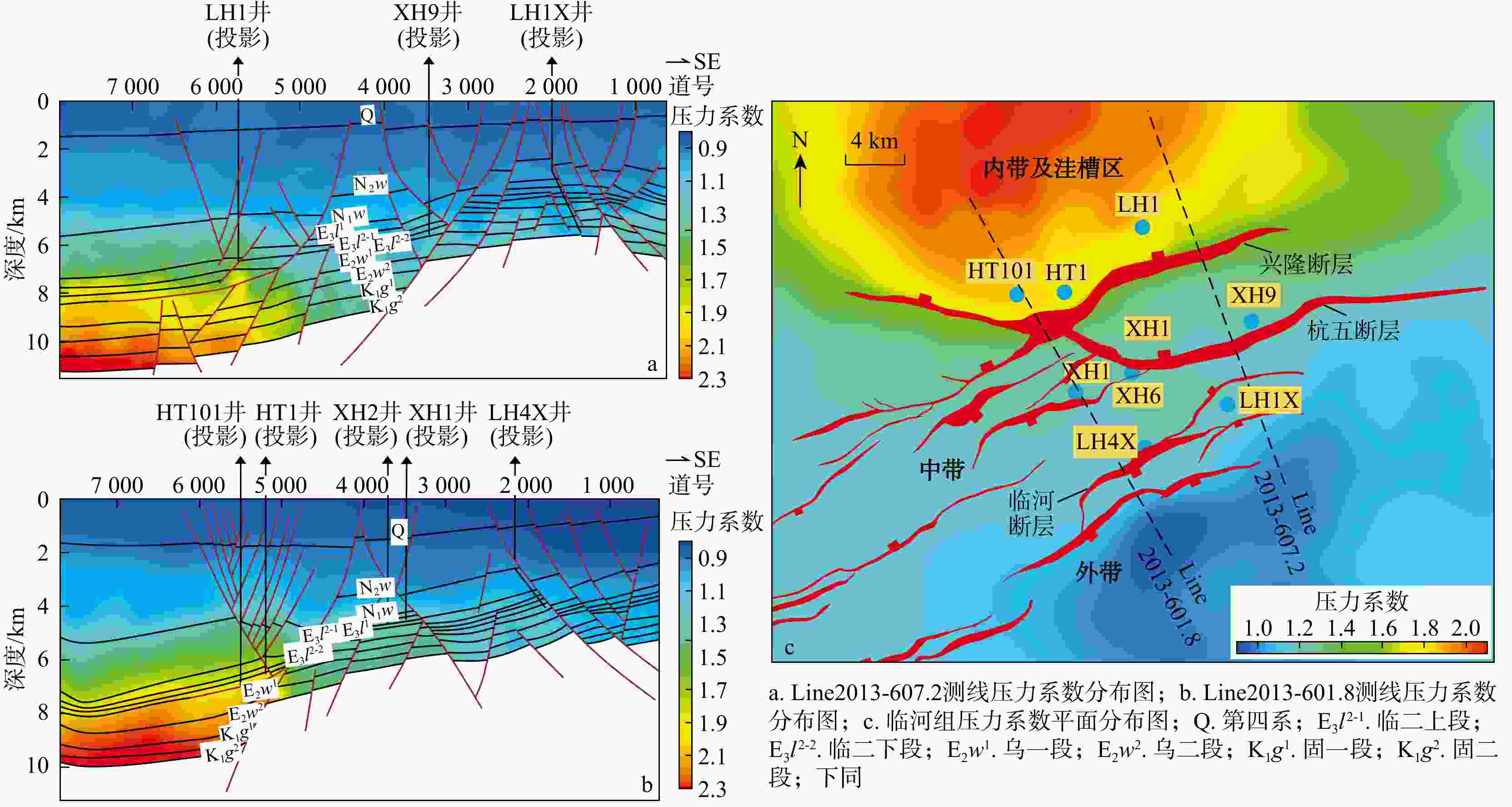
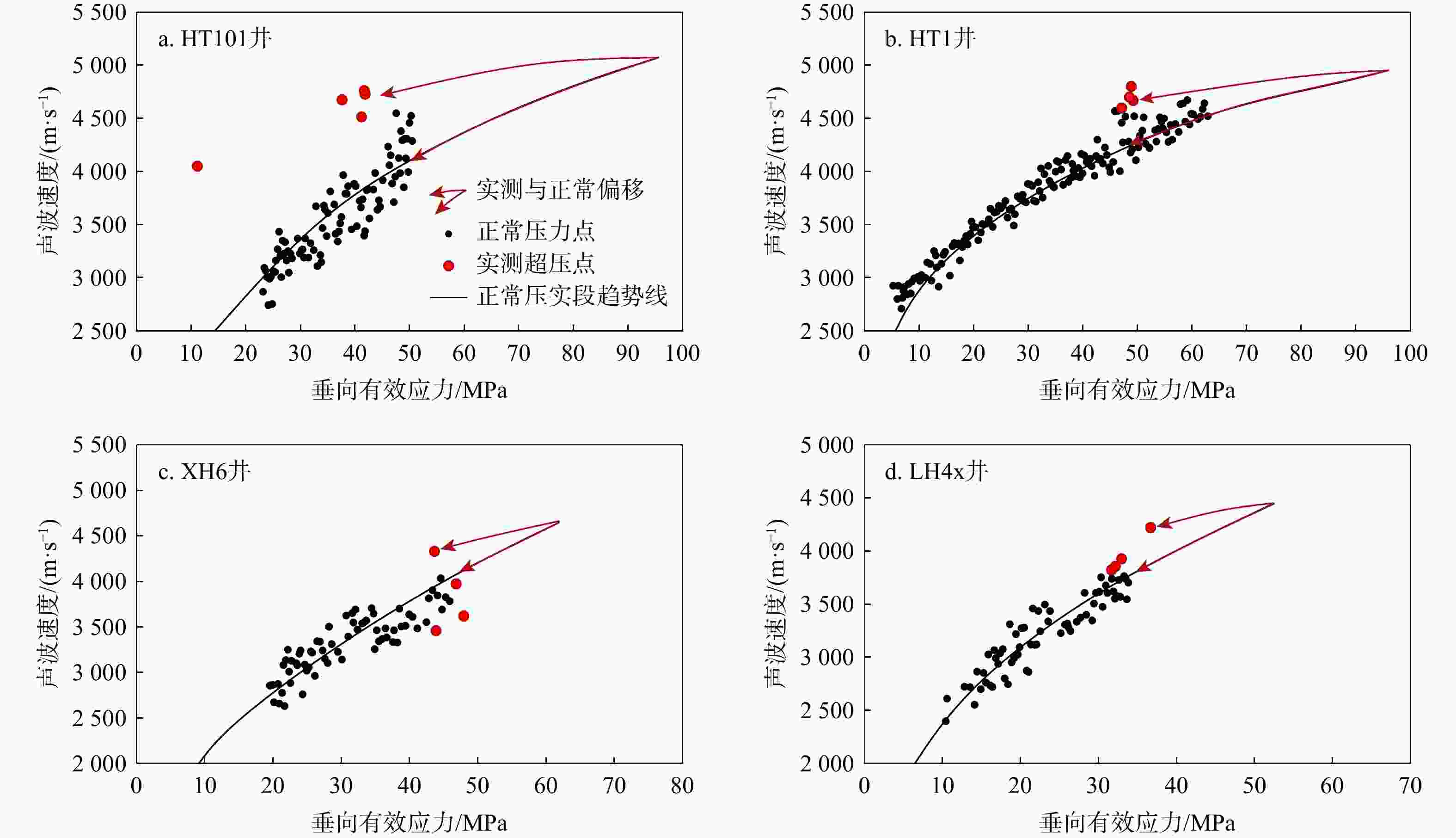
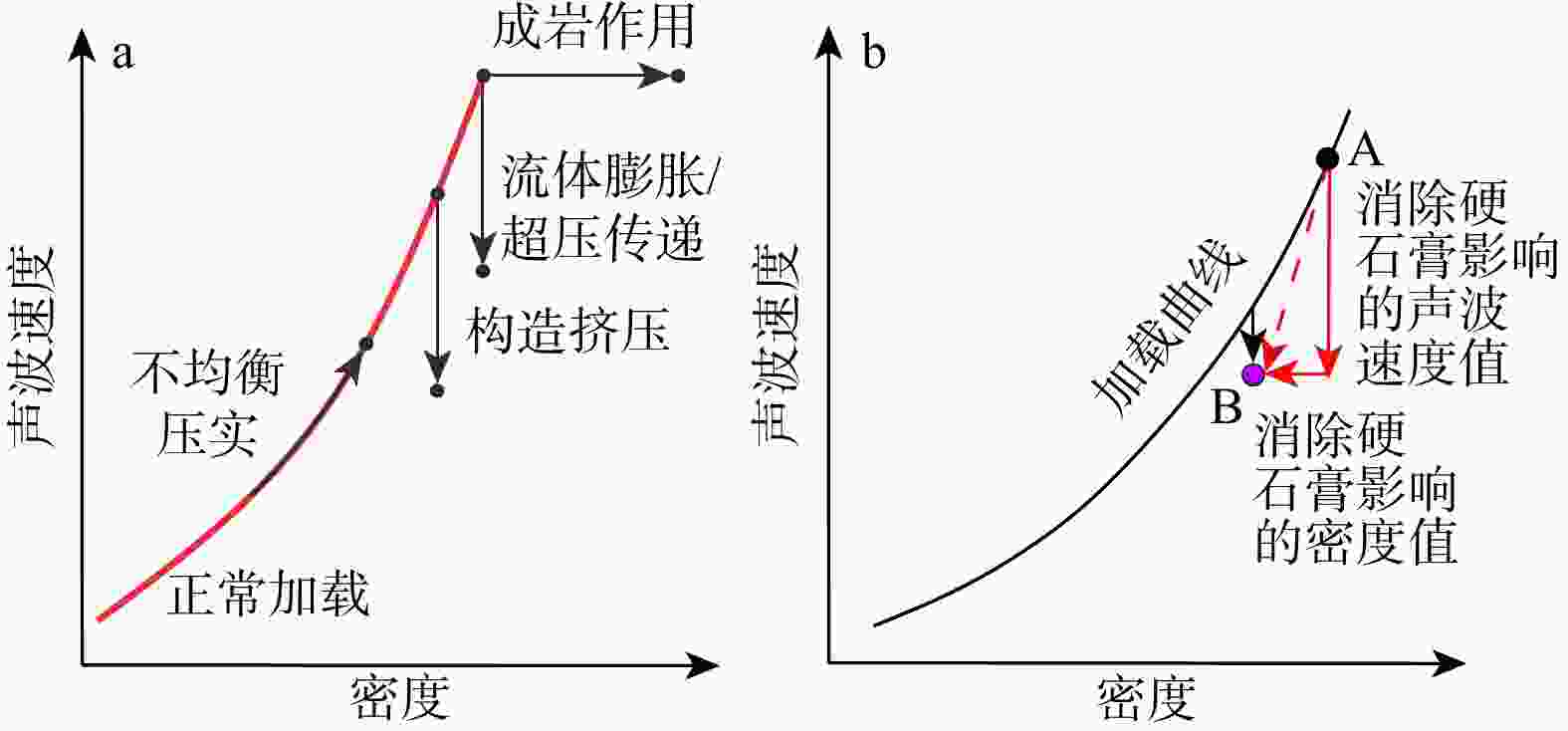
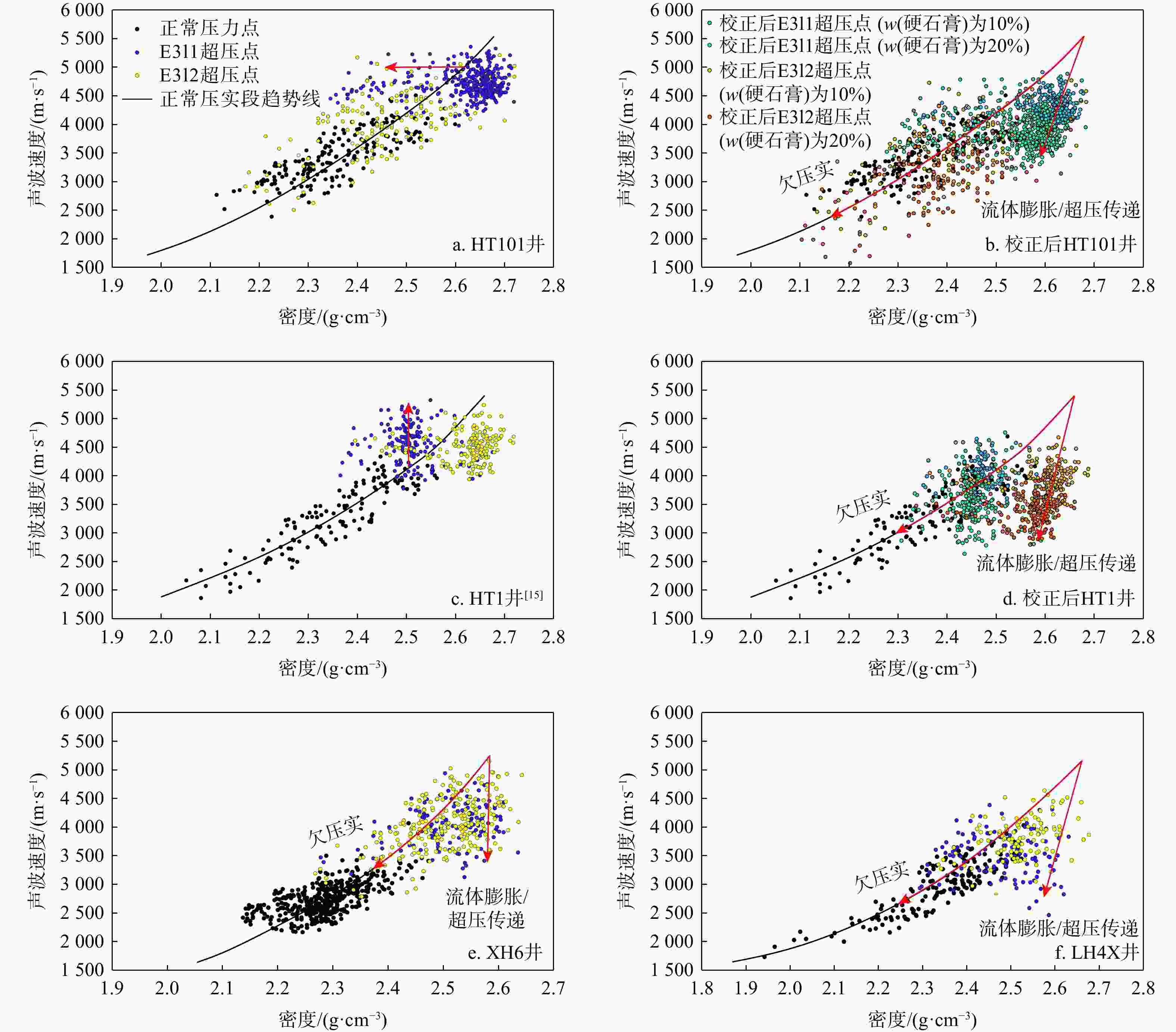
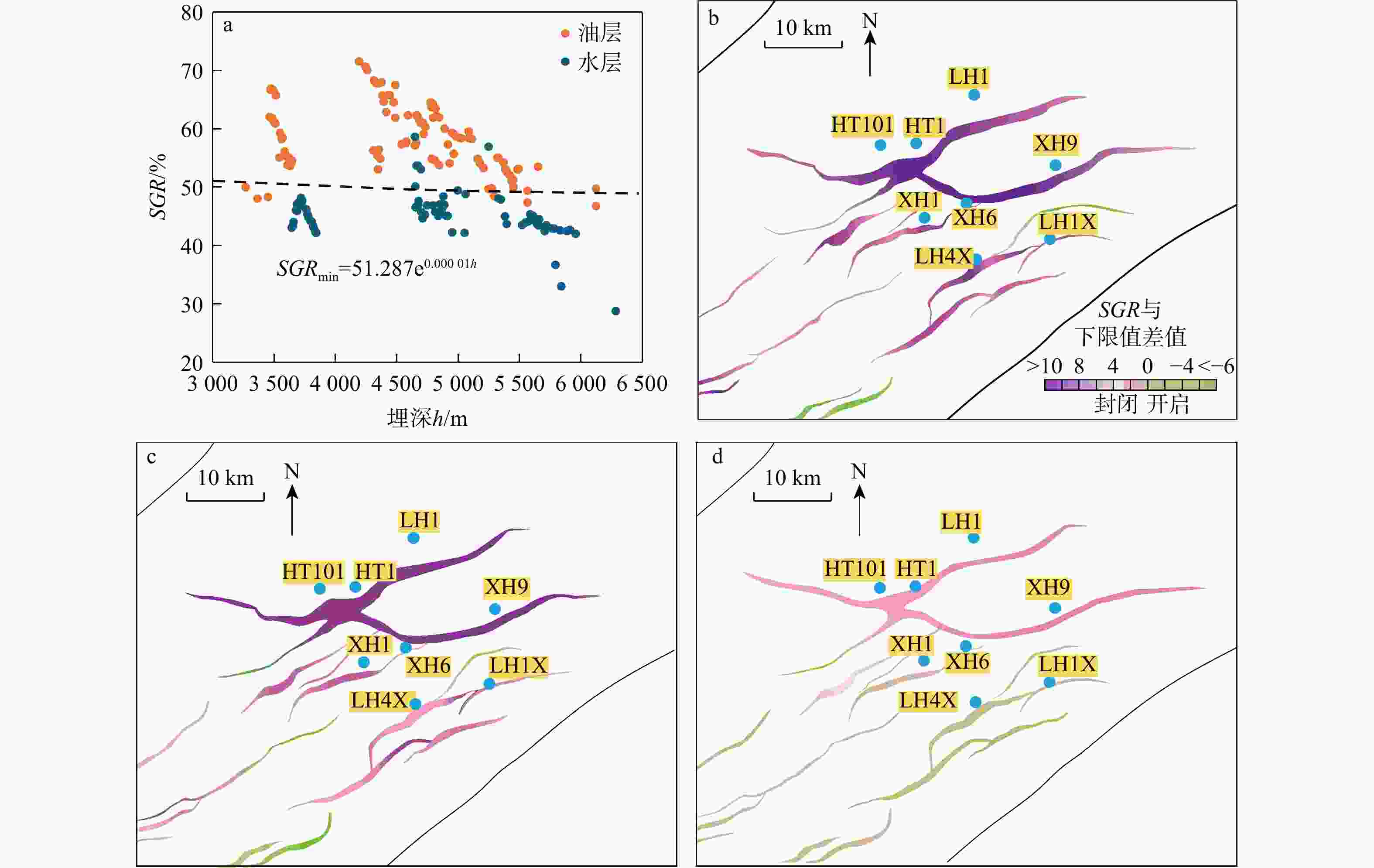
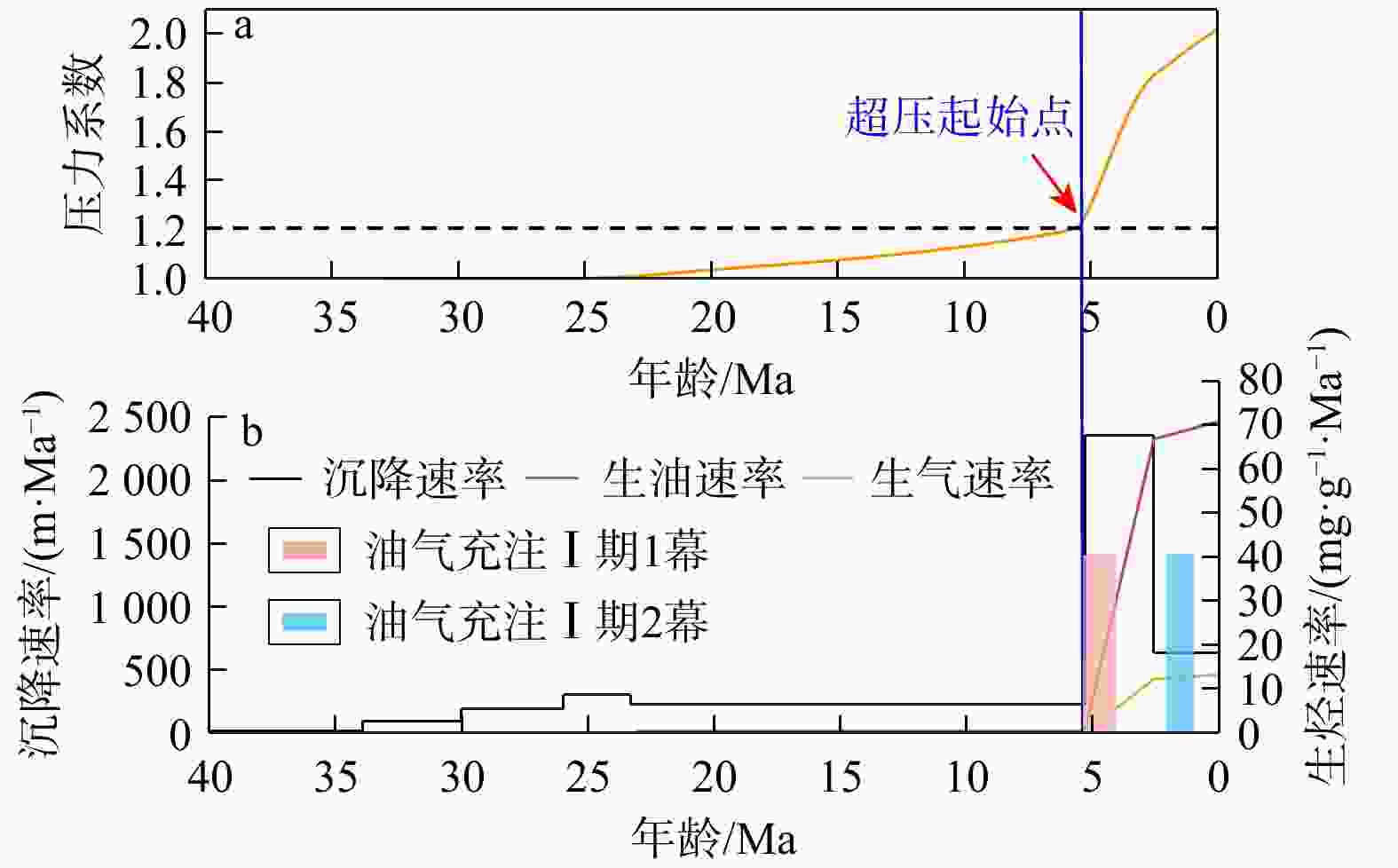
河套盆地临河坳陷兴隆构造带洼槽区钻井资料匮乏,压力系统展布规律及演化机制尚不明确。基于钻井、测井、地震及相关测试等资料,联合地球物理方法与地质背景,运用盆地数值模拟与流体包裹体分析测试技术,综合分析了河套盆地临河坳陷兴隆构造带临河组压力分布、成因机制、保存条件与演化历史。结果表明:研究区临河组压力分布总体具有“北高南低,西高东低”的特征。其中临河组烃源岩层横向分带性显著,内带及洼槽区−中带−外带呈极强超压/强超压−弱超压−常压特征分布;纵向上,超压顶界面普遍位于五原组,自上而下,发育厚层泥岩的五原组超压成因以欠压实为主,生烃增压主导了临河组烃源岩层超压的形成,内带临河组储层超压的主要成因为超压传递;临河组兴隆断层和杭五断层的泥岩百分比(
SGR )与下限值差值普遍在4以上,具有强侧向封堵性,优异的保存条件使得内带成为一个独立的超高压系统;临河组超压形成于五原组快速埋藏期(5.3 Ma),受烃源岩热演化与欠压实−生烃增压双控机制驱动,形成弱超压,第四纪(2.6 Ma)生烃持续强化,内带储层经压力传递超压跃升为强超压,其他位置因走滑构造调整超压未保存,呈常压特征。研究成果有利于厘清临河坳陷成藏动力学条件,为后续油气勘探与开发有一定的指导作用。Abstract:Objective Drilling data are sparse in the trough area of the Xinglong structural belt within the Linhe Depression of the Hetao Basin, and the distribution pattern and evolution mechanism of the pressure system remain unclear.
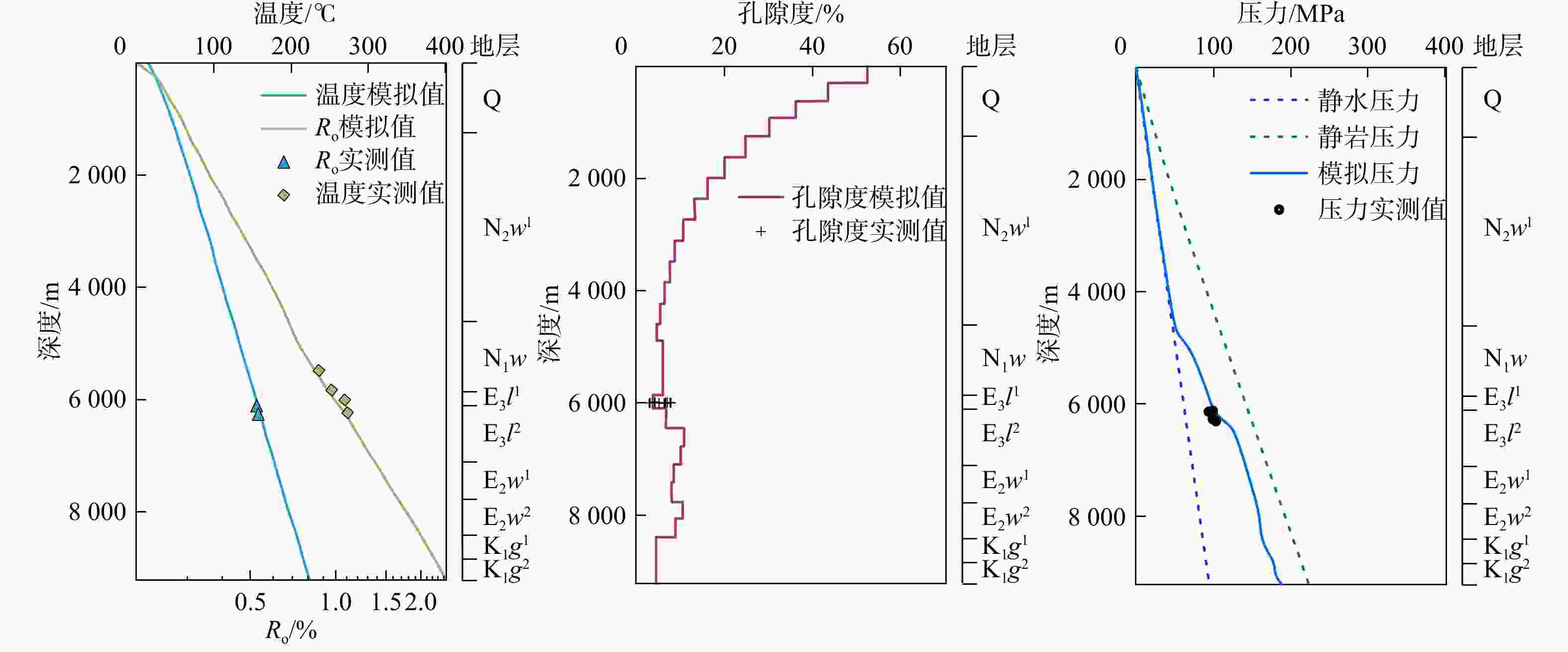
Methods Integrating data from drilling, logging, seismic, and related tests with geophysical methods and geological context, this study conducts a comprehensive analysis of the pressure distribution, genetic, mechanism, preservation conditions, and evolution history of the Linhe Formation in the Xinglong Tectonic Belt of the Linhe Depression in the Hetao Basin. The analysis employs basin-scale numerical simulation, fluid inclusion analysis, and testing techniques.
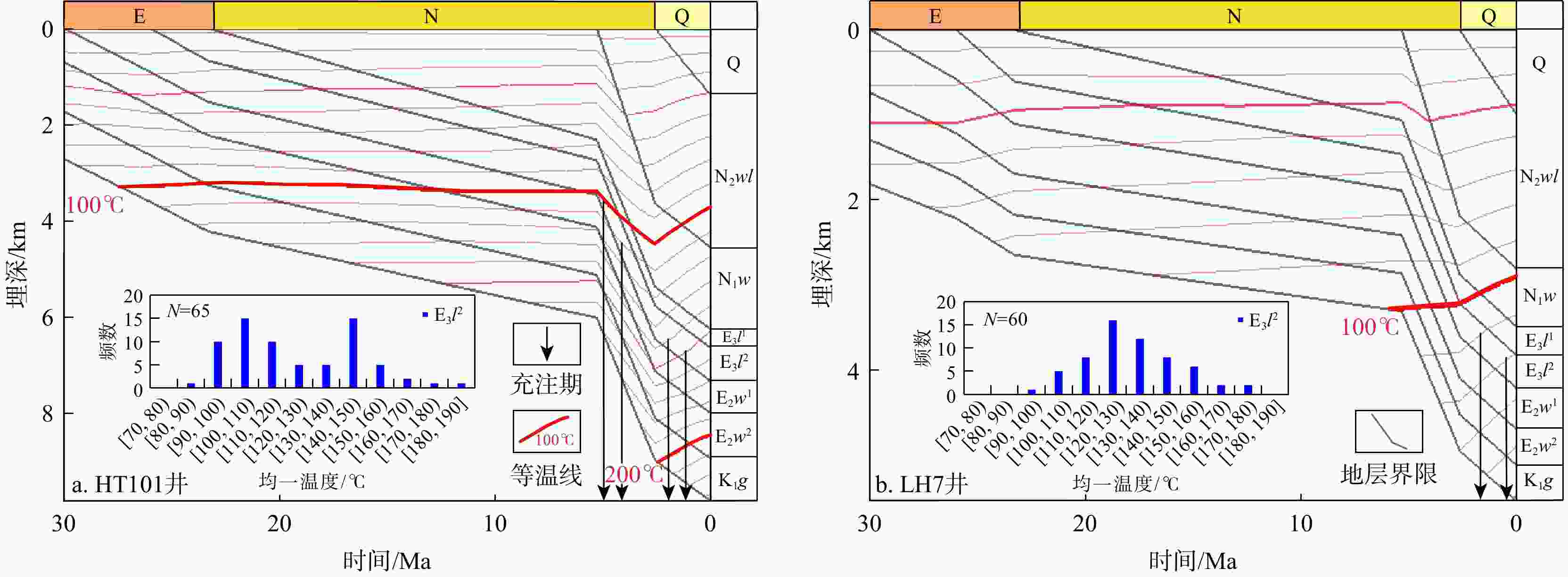
Results The results indicate that the Linhe Formation's pressure distribution in the study area follows a "high in the north and low in the south, high in the west and low in the east" pattern. Among them, the source rock strata of the Linhe Formation exhibit pronounced lateral zonation: The inner zone and trough area-middle zone-outer zone presenting extremely strong overpressure/strong overpressure-weak overpressure-normal pressure. The reservoirs of the Linhe Formation develop overpressure only in the inner zone and trough area, while most other areas exhibit normal pressure. Longitudinally, the overpressure top interface generally lies within the Wuyuan Formation. From top to bottom, overpressure in the Wuyuan Formation (with thick-bedded mudstone) is mainly caused by undercompacted. Hydrocarbon generation pressurization dominates overpressure formation in the Linhe Formation's source rocks, and the principal cause of overpressure in the Linhe Formation reservoirs is pressure transmission. The overpressure of the Linhe Formation formed during the rapid burial of the Wuyuan Formation (5.3 Ma), driven by the dual control mechanism of source rock thermal evolution and undercompaction-hydrocarbon generation pressurization, resulting in weak overpressure. Overpressure intensification occurred during the Quaternary (approximately 2.6 Ma), with inner-belt reservoir pressures increasing to strong overpressure through pressure transfer. However, overpressure was not preserved in other areas due to strike-slip tectonic adjustment, resulting in normal pressure.
Conclusions This study clarifies the hydrocarba accumulation dynamics conditions of the Linhe Depression and guides subsequent oil and gas exploration and development.
-
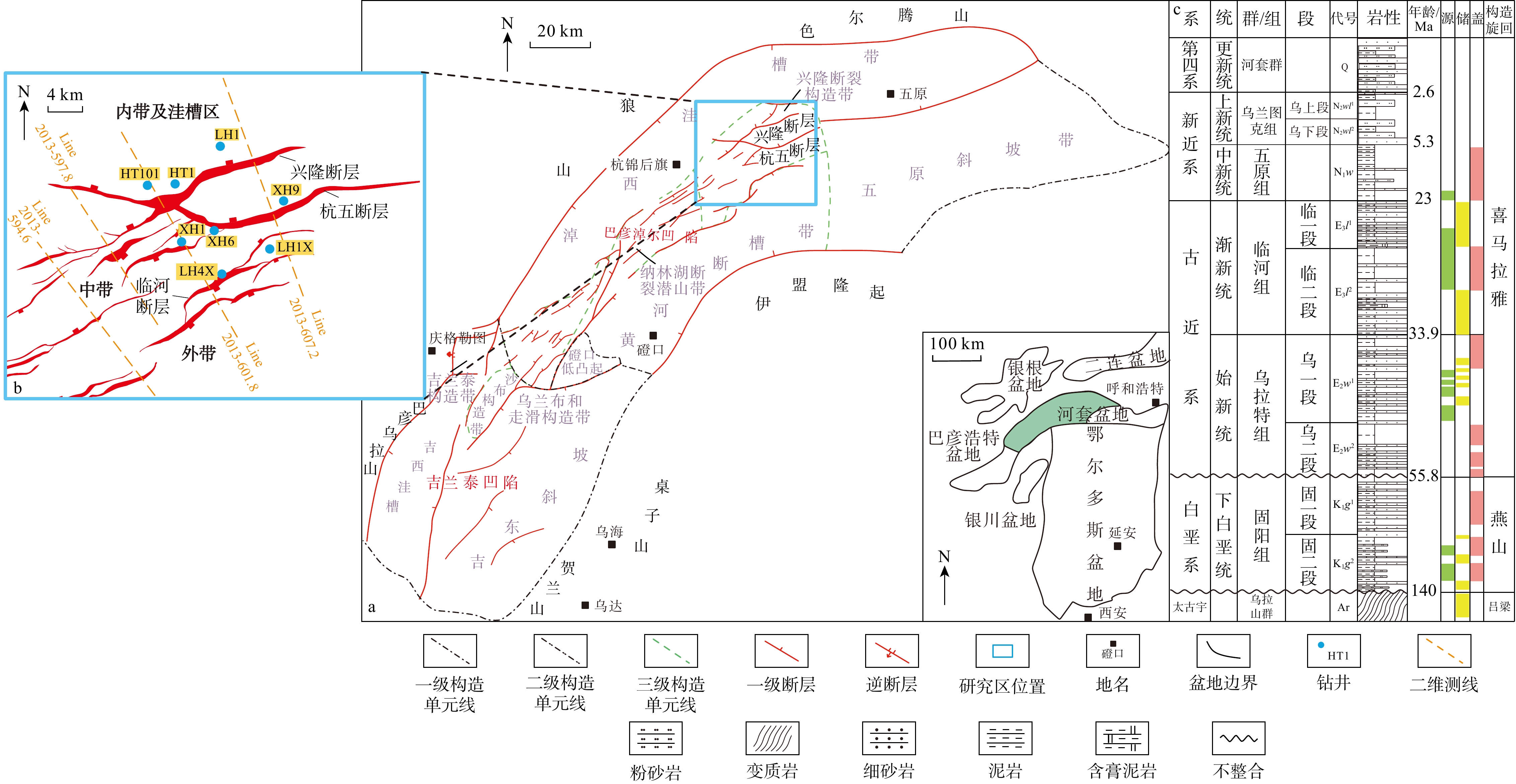
图 1 河套盆地临河坳陷兴隆构造带综合地质图(据文献[5]修改)
a. 构造地质图;b. 断层及井位分布图;c. 岩性柱状图
Figure 1. Comprehensive geological map of Xinglong tectonic belt in Linhe Depression, Hetao Basin
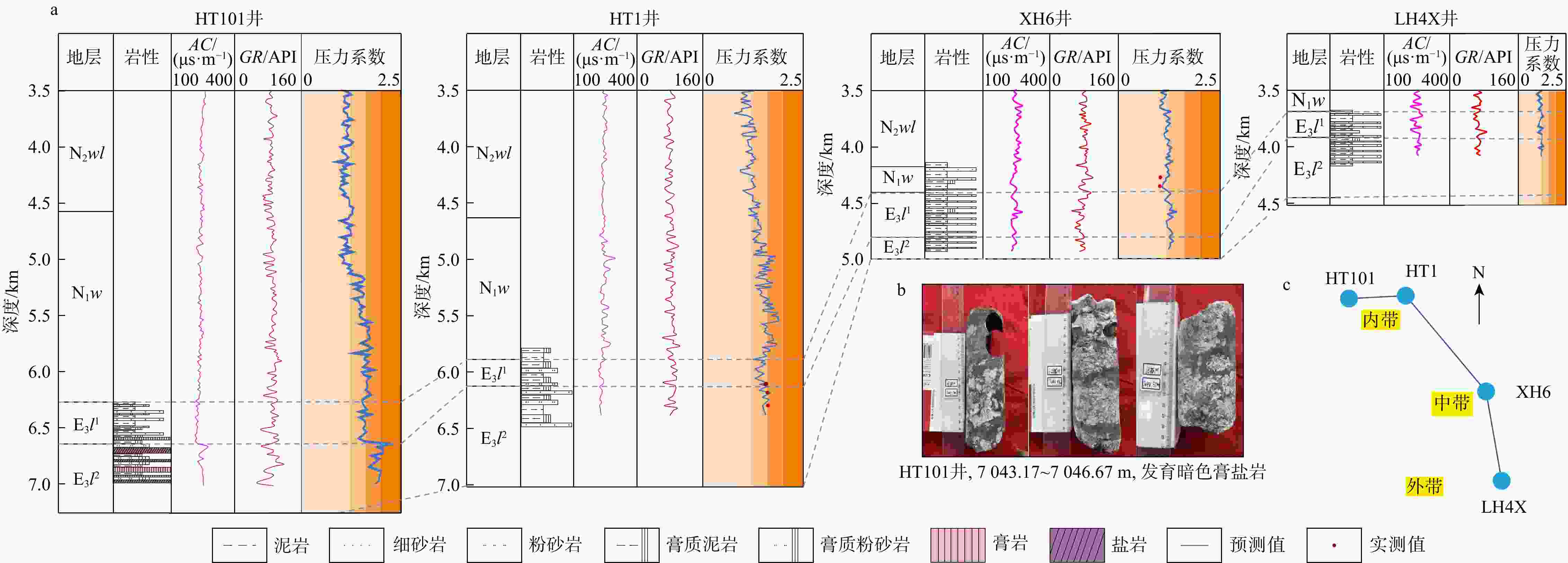
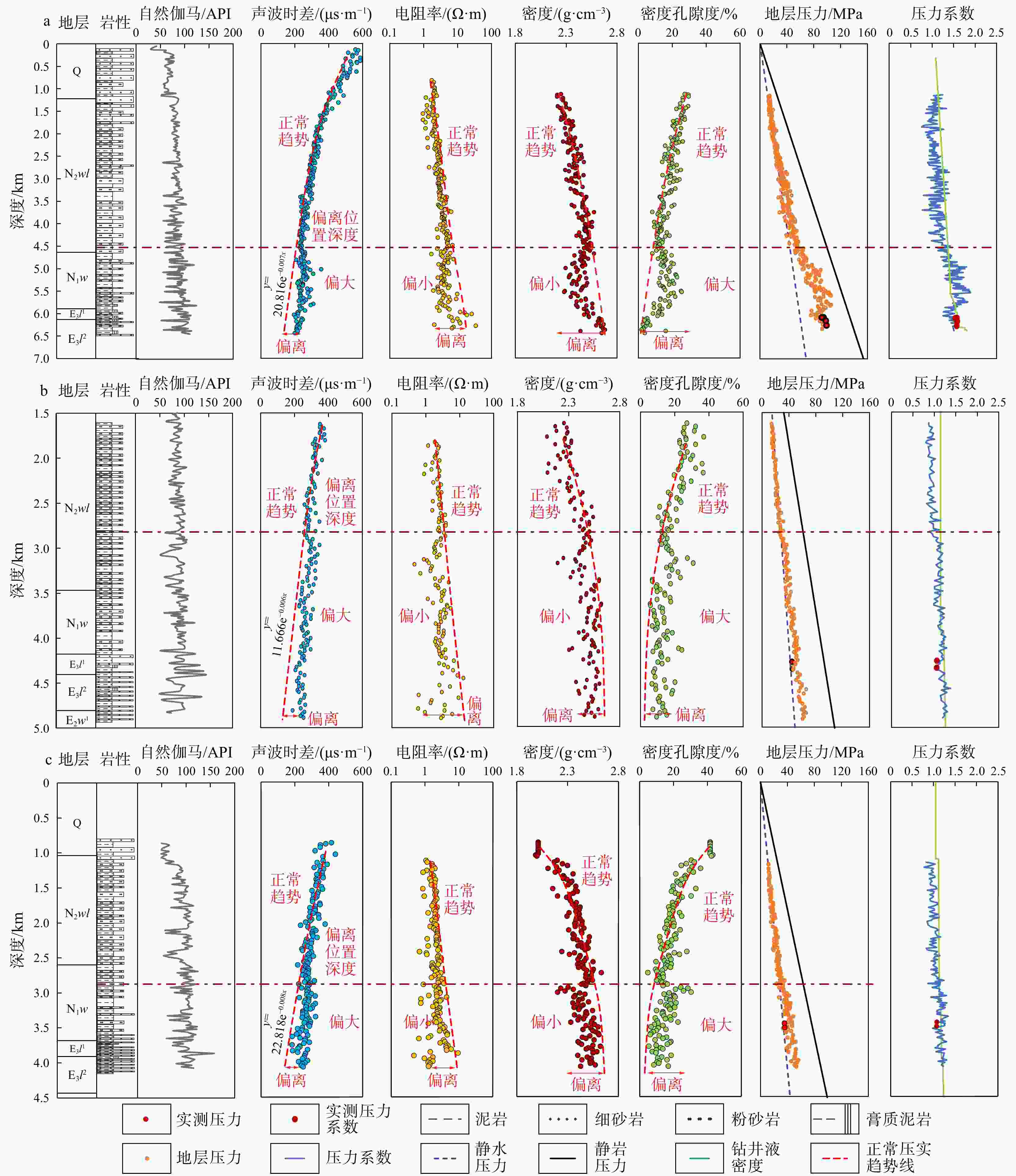
图 3 临河坳陷兴隆构造带临河组测井压力预测与岩性连井特征(a)、HT101井临河组岩心观察照片(b)和联井剖面井位分布平面示意图(c)
N2wl. 乌兰图克组;N1w. 五原组;E3l1. 临一段;E3l2. 临二段;AC. 声波时差;GR. 自然伽马;下同
Figure 3. Well logging pressure prediction and lithology connection characteristics of Linhe Formation (a), core observation photos of Linhe Formation in Well HT101 (b) and schematic plan of well position distribution of the joint well section (c) in Xinglong tectonic belt of Linhe Depression
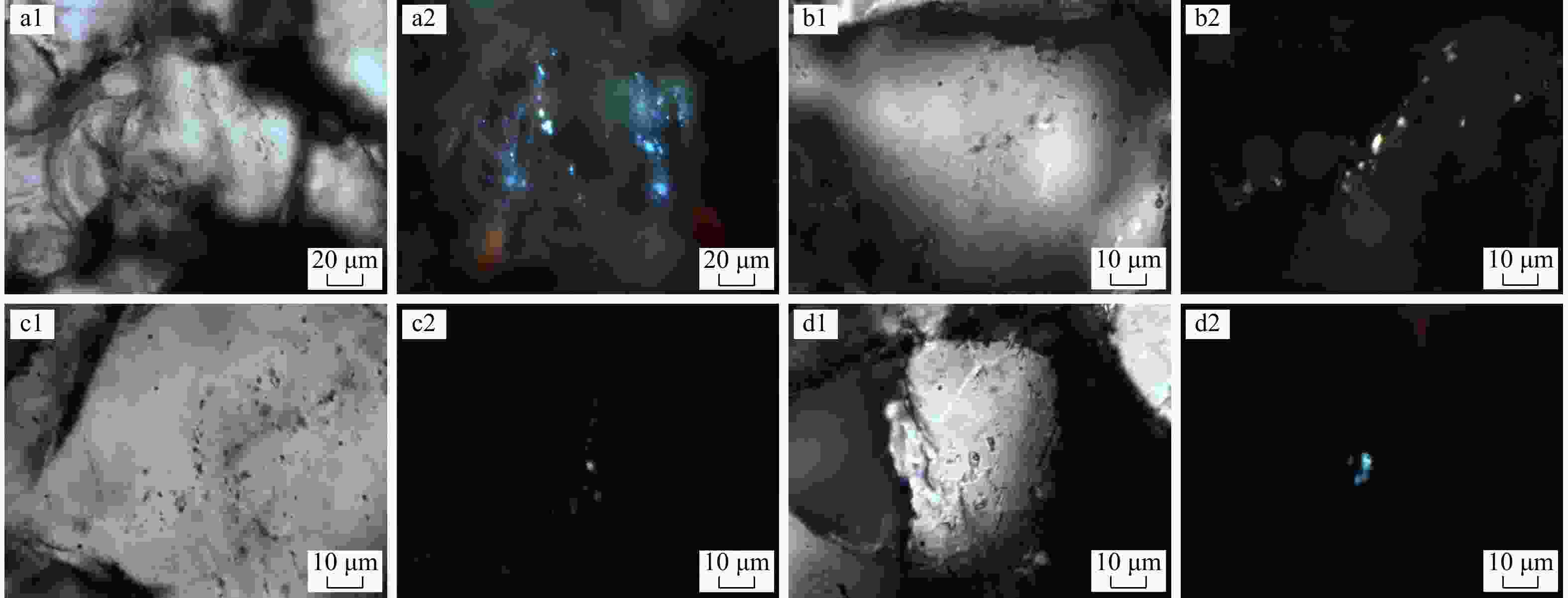
图 12 临河坳陷兴隆构造带临河组流体包裹体显微岩相学及荧光特征
a1,a2. XH5井,
4515.35 m,砂岩,石英裂纹中可见蓝白色荧光包裹体及伴生盐水包裹体;b1,b2. LH7井,3850.8 m,浅灰色细砂岩,石英裂纹中可见线状黄色荧光包裹体及伴生盐水包裹体;c1,c2. LH1X井,3365.8 m,灰色细砂岩,石英裂纹中可见线状蓝绿色荧光包裹体及伴生盐水包裹体;d1,d2. HT101井,7039.6 m,灰色中砂岩,石英颗粒内可见蓝白色荧光包裹体Figure 12. Microscopic petrography and fluorescence characteristics of fluid inclusions of Linhe Formation in Xinglong tectonic belt of Linhe Depression
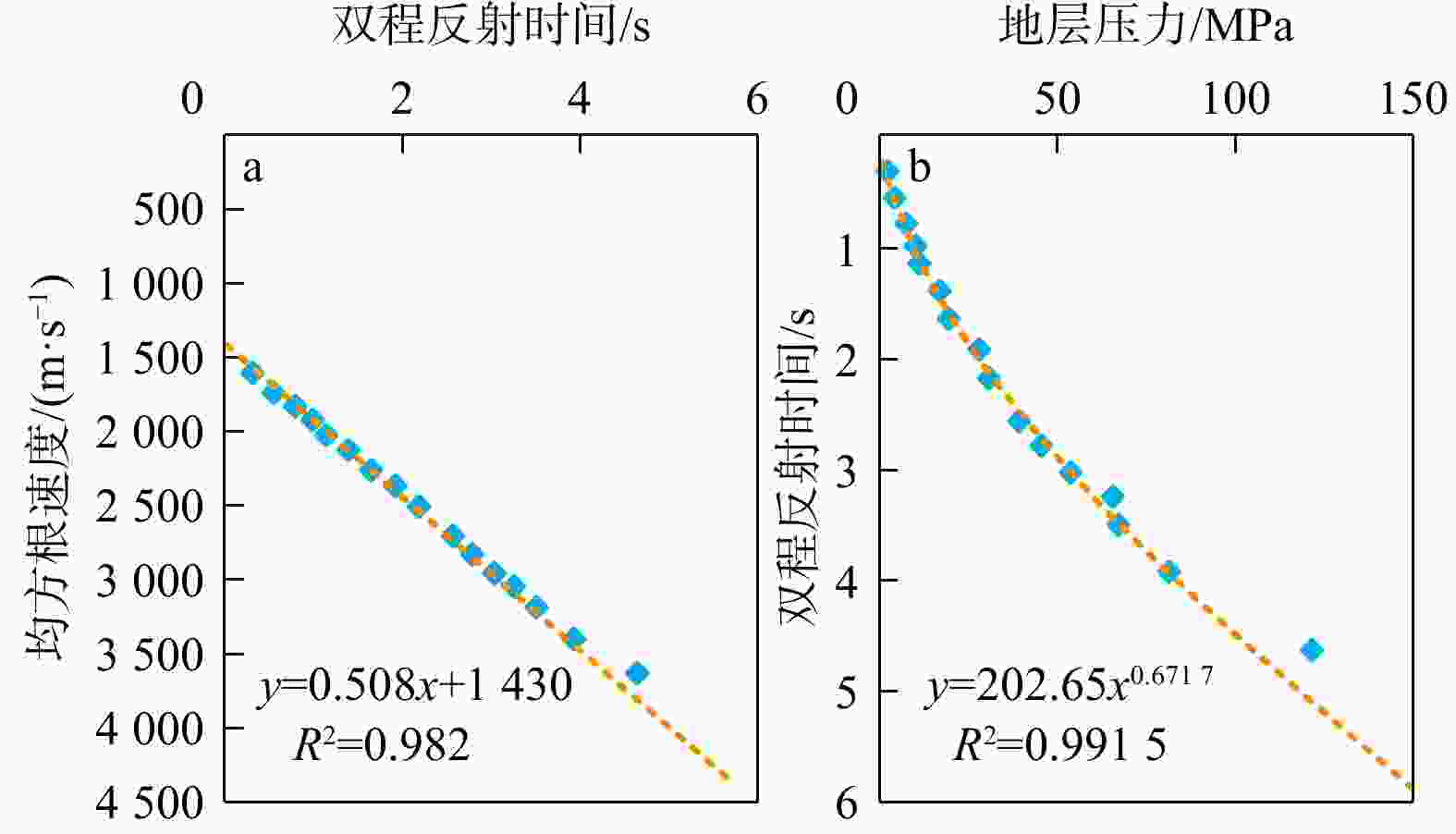
表 1 单井压力系数实测值与预测值对比
Table 1. Comparison of measured and predicted pressure coefficients in a single well
构造单元 井号 深度/m 压力系数 相对误差/% 实测 预测 兴
隆
构
造
带内带 LH1* 5700 1.87 1.62 −13.37 LH1* 6318 1.63 1.65 1.23 LH1* 6382 1.72 1.68 −2.33 LH1* 6443 1.96 1.72 −12.24 LH1* 6601 2.01 1.75 −12.94 HT101* 5590 1.63 1.65 1.23 HT101* 6403 1.5 1.7 13.33 HT101* 6410 1.6 1.78 11.25 HT101* 6566 1.68 1.82 8.33 HT101* 6827 2.13 2.05 −3.76 HT1 5200 1.54 1.58 2.60 HT1 6000 1.58 1.72 8.86 HT1 6114 1.51 1.73 14.57 HT1 6276.62 1.54 1.77 14.94 HT1* 6460 2.10 1.92 −8.57 中带 XH9 4868.8 1.05 1.18 12.38 XH9 4871.18 1.10 1.21 10.00 XH2 4406.5 1.10 1.25 13.64 XH2 4918 1.07 1.32 14.78 外带 LH1X 5199.43 1.02 1.08 5.88 LH1X 5266.92 1.05 1.15 9.52 LH4X 3448.93 1.04 1.12 7.69 LH4X 3510.08 1.05 1.16 10.48 注:*部分实测数据来自于单井盆模模拟值或Eaton法预测的地层压力 表 2 临河坳陷数值模拟阶段划分及地质时间
Table 2. Numerical simulation stage division and geological time of Linhe Depression
地层单元 起始年代/
Ma结束年代/
Ma系 群(组) 段 代号 第四系 河套群 Q1-4 2.6 0 新近系 乌兰图克组 上段 N2wl1 5.3 2.6 下段 N2wl2 五原组 N1w 23 5.3 古近系 临河组 一段 E3l1 33.9 23 二段 E3l2 乌拉特组 一段 E2w1 55.8 33.9 二段 E2w2 白垩系 * 83 55.8 固阳组 一段 K1g1 140 83 二段 K1g2 注:*. 上白垩统被剥蚀,为剥蚀事件 -
[1] 张以明, 张锐锋, 王少春, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷油气勘探重要发现的实践与认识[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2018, 23(5): 1-11.ZHANG Y M, ZHANG R F, WANG S C, et al. Practice and understanding of great discovery in oil and gas exploration in Linhe Depression of Hetao Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2018, 23(5): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 付锁堂, 付金华, 喻建, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷石油地质特征及勘探前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(5): 749-762.FU S T, FU J H, YU J, et al. Petroleum geological features and exploration prospect of Linhe Depression in Hetao Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(5): 749-762. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 赵政璋, 何海清. 中国石油近几年新区油气勘探成果及下步工作面临的挑战和措施[J]. 沉积学报, 2004, 22(增刊1): 1-7.ZHAO Z Z, HE H Q. Recent oil & gas exploration harvests in the new area of Petrochina and future challenges and measures[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2004, 22(S1): 1-7. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 赵孟为. 河套盆地断裂活动的特征及其与油气的关系[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 1988, 18(2): 85-94.ZHAO M W. Characteristics of the fault activity in Hetao Basin and its relation with oil and gas[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 1988, 18(2): 85-94. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 武玺, 史原鹏, 陈树光, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷超深层碎屑岩油气勘探突破及富集高产因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2024, 51(5): 962-971.WU X, SHI Y P, CHEN S G, et al. Exploration breakthrough and factors for enrichment and high-yield of hydrocarbons in ultra-deep clastic rocks in Linhe Depression, Hetao Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2024, 51(5): 962-971. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 沈华, 何海清, 张锐锋, 等. 河套盆地洼槽区河探1井风险勘探突破及意义[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(9): 1213-1222.SHEN H, HE H Q, ZHANG R F, et al. Breakthrough and significance of risk exploration of Well Hetan 1 in the trough area of Hetao Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(9): 1213-1222. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 张锐锋, 陈树光, 冯广业, 等. 临河坳陷北部古近系临河组超深层油气藏形成条件与勘探前景[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2024, 29(1): 119-129.ZHANG R F, CHEN S G, FENG G Y, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and exploration prospects of ultra-deep oil and gas reservoirs in the Paleogene Linhe Formation in the northern Linhe Depression, Hetao Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2024, 29(1): 119-129. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 张锐锋, 王浩宇, 冯广业, 等. 河套盆地河探101井超深层油气重大发现及勘探潜力[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2024, 29(5): 77-90.ZHANG R F, WANG H Y, FENG G Y, et al. Major oil and gas discovery and exploration potential in ultra-deep formation in Well Hetan 101, Hetao Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2024, 29(5): 77-90. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] HUNT J M. Generation and migration of petroleum from abnormally pressured fluid compartments (1)[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1990, 74(1): 1-12. [10] 陆鹿, 陈树光, 李壮福, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷白垩纪−古近纪沉积环境演化及油气地质意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2022, 24(2): 308-331.LU L, CHEN S G, LI Z F, et al. Sedimentary evolution and petroleum potential of the Cretaceous to Paleogene in Linhe Depression, Hetao Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2022, 24(2): 308-331. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 张锐锋, 何海清, 朱庆忠, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷石油地质特征与油气富集规律[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2023, 50(4): 695-705.ZHANG R F, HE H Q, ZHU Q Z, et al. Petroleum geological features and hydrocarbon enrichment of Linhe Depression in Hetao Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(4): 695-705. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 沈华, 刘震, 史原鹏, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷油气成藏过程解剖及勘探潜力分析[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(3): 871-882.SHEN H, LIU Z, SHI Y P, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation process and exploration potential in Linhe Depression, Hetao Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(3): 871-882. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 伍劲, 刘占国, 王少春, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷古近系临河组深层−超深层碎屑岩储层物性差异成因[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2024, 35(11): 1961-1972.WU J, LIU Z G, WANG S C, et al. Origin of differences in physical properties of deep and ultra deep clastic reservoirs in the Paleogene Linhe Formation of the Linhe Depression, Hetao Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2024, 35(11): 1961-1972. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 张锐锋, 于福生, 刘喜恒, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷及其周边地区中-新生代成盆演化特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(6): 1139-1150.ZHANG R F, YU F S, LIU X H, et al. Evolutionary characteristics of Linhe Depression and its surrounding areas in Hetao Basin from the Mesozoic to Cenozoic[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(6): 1139-1150. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 孙越, 谢佩宇, 张凤奇, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷兴隆构造带临河组超压成因及演化特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2024, 35(4): 661-675.SUN Y, XIE P Y, ZHANG F Q, et al. Mechanism and evolution of overpressure in the Linhe Formation of the Xinglong structural belt in the Linhe Depression of the Hetao Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2024, 35(4): 661-675. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 淡伟宁, 陈树光, 李志军, 等. 河套盆地油气勘探新领域及有利方向[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(12): 2217-2230.DAN W N, CHEN S G, LI Z J, et al. New fields and favorable directions for oil-gas exploration in Hetao Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(12): 2217-2230. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 康东雅, 向芳, 邹佐元, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上古生界砂岩岩石学特征及岩性差异[J]. 断块油气田, 2019, 26(3): 299-303.KANG D Y, XIANG F, ZOU Z Y, et al. Petrological characteristics and lithological differences of Upper Paleozoic sandstone of Ordos Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2019, 26(3): 299-303. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] 徐泽阳. 临河坳陷中-新生代盆地差异叠合及油气富集机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2023.XU Z Y. Characteristics of differential superposition between Meso-Cenozoic basins and mechanism of hydrocarbon enrichment in the Linhe Depression, Hetao Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 常德双, 万照飞, 刘冬民, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷构造脊成因模式及其与油气成藏的关系[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2024, 43(6): 11-19.CHANG D S, WAN Z F, LIU D M, et al. Genetic patterns of structural ridges in Linhe Depression of Hetao Basin and their relationship with oil and gas accumulation[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2024, 43(6): 11-19. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 王盛亮, 杨雪松, 罗胜, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷北部临河组元素地球化学特征及古环境恢复[J]. 矿物岩石, 2023, 43(3): 73-82.WANG S L, YANG X S, LUO S, et al. Element geochemical characteristics and paleoenvironment restoration of Linhe Formation in the northern Linhe Depression, Hetao Basin[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2023, 43(3): 73-82. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 付晓燕, 路俊刚, 师玉雷, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷咸湖烃源岩生烃机理[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2024, 35(4): 704-717.FU X Y, LU J G, SHI Y L, et al. Hydrocarbon generation mechanism of saline lake source rocks in Linhe Depression, Hetao Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2024, 35(4): 704-717. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 胡凯, 王奇, 王中兴, 等. 河套盆地临河坳陷固阳组-临河组烃源岩评价及展布预测[C]//佚名. 2021年中国地球科学联合学术年会论文集(二十九): 专题八十五: 东北亚块体聚合裂解过程与机制、专题八十六: 基础沉积学研究进展、专题八十七: 沉积盆地矿产资源综合勘察. [出版地不详]: [出版者不详], 2021: 50.HU K, WANG Q, WANG Z X, et al. Evaluation and distribution prediction of source rocks in the Guyang Formation-Linhe Formation of the Linhe Depression in the Hetao Basin[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 2021 Chinese Joint Academic Annual Meeting of Geosciences (Volume 29) : Topic 85: The process and mechanism of aggregation and rifting of the Northeast Asian Block. Topic 86: Research progress in basic sedimentology. Topic 87: Comprehensive exploration of mineral resources in sedimentary basins. [S. l. ]: [s. n. ], 2021: 50. (in Chinese) [23] 刘芯羽. 河套盆地临河坳陷中新生界岩性、沉积相及烃源岩、储集层特征研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2020.LIU X Y. Study on the characteristics of lithology, sedimentary facies, hydrocarbon source rock and reservoirs of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic of Linhe Depression in Hetao Basin[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 李伟, 陈竹新, 黄平辉, 等. 中国中西部典型前陆盆地超压体系形成机制与大气田关系[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(3): 536-548.LI W, CHEN Z X, HUANG P H, et al. Formation of overpressure system and its relationship with the distribution of large gas fields in typical foreland basins in central and western China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(3): 536-548. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] EATON B A. The equation for geopressure prediction from well logs[C]//Anon. Fall Meeting of the Society of Petroleum Engineers of AIME. Dallas, Texas. Richardson: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 1975: SPE-5544-MS. [26] 李敏, 练章华, 林铁军, 等. 基于VSP资料的地层压力预测[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2010, 32(3): 220-223.LI M, LIAN Z H, LIN T J, et al. Formation pressure prediction based on VSP data[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2010, 32(3): 220-223. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] CHOPRA S, HUFFMAN A R. Velocity determination for pore-pressure prediction[J]. The Leading Edge, 2006, 25(12): 1502-1515. doi: 10.1190/1.2405336 [28] 孙武亮, 孙开峰. 地震地层压力预测综述[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 2007(6): 428-432.SUN W L, SUN K F. Review of pore-pressure prediction from seismic data[J]. Progress in Exploration Geophysics, 2007(6): 428-432. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] FILLIPPONE W R. Estimation of formation parameters and the prediction of overpressures from seismic data[C]//Anon. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 1982. Dallas, Texas, USA: Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 1982: 502-503. [30] HOTTMANN C E, JOHNSON R K. Estimation of formation pressures from log-derived shale properties[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1965, 17(6): 717-722. doi: 10.2118/1110-PA [31] WARREN J K. Evaporites: Sediments, resources and hydrocarbons[M]. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2006: 44-329. [32] LIU C L, LI H H, ZHANG X, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the Paleogene and Neogene saline lacustrine source rocks in the western Qaidam Basin, northwestern China[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2016, 30(6): 4537-4549. [33] LUO X R, VASSEUR G. Contributions of compaction and aquathermal pressuring to geopressure and the influence of environmental conditions: REPLY[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1992, 76(10): 1550-1559. [34] BOWERS G L. Detecting high overpressure[J]. The Leading Edge, 2002, 21(2): 174-177. doi: 10.1190/1.1452608 [35] XU F H, LIANG J J, XU G S, et al. Genetic mechanisms and distribution characteristics of overpressures in the Paleogene reservoirs of the Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Energy Exploration & Exploitation, 2018, 36(3): 388-413. [36] TINGAY M R P, HILLIS R R, SWARBRICK R E, et al. Origin of overpressure and pore-pressure prediction in the Baram Province, Brunei[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(1): 51-74. doi: 10.1306/08080808016 [37] TINGAY M R P, MORLEY C K, LAIRD A, et al. Evidence for overpressure generation by kerogen-to-gas maturation in the northern Malay Basin[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(4): 639-672. doi: 10.1306/09041212032 [38] BOWERS G L. Pore pressure estimation from velocity data: Accounting for overpressure mechanisms besides undercompaction[J]. SPE Drilling & Completion, 1995, 10(2): 89-95. [39] 张凤奇, 鲁雪松, 卓勤功, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘下组合储层异常高压成因机制及演化特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(5): 1004-1016.ZHANG F Q, LU X S, ZHUO Q G, et al. Genetic mechanism and evolution characteristics of overpressure in the lower play at the southern margin of the Junggar Basin, northwestern China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(5): 1004-1016. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] JAYANTHI J L, NANDAKUMAR V. Fluid inclusion studies to determine the paleotemperature and hydrocarbon quality in petroliferous basins[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 197: 108082. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.108082 [41] 卫孝锋. 含盐盆地地震勘探技术浅析[J]. 海相油气地质, 2002, 7(2): 54-58.WEI X F. Overview of seismic prospecting technology in salt basins[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2002, 7(2): 54-58. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] 孙思敏, 梁德富, 黄述旺. 东濮凹陷文留油田盐岩地震反射特征及相关油藏类型[J]. 地质力学学报, 2007, 13(4): 348-354.SUN S M, LIANG D F, HUANG S W. Seismic reflection characteristics of halite and related hydrocarbon accumulation types of the Wenliu Oilfield in the Dongpu subbasin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2007, 13(4): 348-354. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] YIELDING G, FREEMAN B, NEEDHAM D T. Quantitative fault seal prediction[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1997, 81(6): 897-917. [44] 王震亮, 罗晓容, 陈荷立. 沉积盆地地下古水动力场恢复: 原理与方法[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 1997, 27(2): 155-159.WANG Z L, LUO X R, CHEN H L. Rebuilding of Palaeohydrodynamic field in sedimentary basin: Principle and means[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 1997, 27(2): 155-159. [45] 唐令, 宋岩, 赵志刚, 等. 四川盆地上奥陶统五峰组-下志留统龙马溪组页岩气藏超压成因及演化规律[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(10): 37-53.TANG L, SONG Y, ZHAO Z G, et al. Origin and evolution of overpressure in shale gas reservoirs of the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(10): 37-53. (in Chinese with English abstract [46] CHEN X L, ZHOU Z Z, XIA H Y, et al. A new view of trapping pressure estimation using PVT simulation of hydrocarbon inclusions in petroliferous basins[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 204: 108715. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108715 [47] WANG Y P, LIAO L L, GENG A S, et al. Trapping pressure estimation of single gaseous inclusion using PVT simulation and its preliminary application in NE Sichuan, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 89: 225-231. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.02.028 -




 下载:
下载: