Spectral inversion using generalized cosine broadband spectrum and its application in the Junggar Basin
-
摘要:
准噶尔盆地勘探目的层埋深大,地震波高频吸收衰减严重,地震子波主频低、频带窄,导致地震数据分辨率不足,严重影响了砂泥岩薄互层的识别精度。反褶积是提高地震数据分辨率的重要手段,提出了一种频率域反褶积方法,通过优化目标谱设计达到拓宽地震数据有效频带范围、提高地震数据垂向分辨率的目的。首先构建了广义余弦宽带目标谱,根据目标谱与地震记录频谱对角矩阵和拓频因子之间的关系建立了拓频正演模型,然后利用整形正则化反演方法进行了拓频因子反演,最终实现了对地震数据的拓频处理。模型测试结果验证了基于广义余弦宽带目标谱反演的拓频方法的有效性,准噶尔盆地实际数据应用结果表明地震频带得到了有效拓宽,薄层识别能力得到了有效提高。广义余弦目标谱设计灵活,具有较宽的频带范围,其对应子波旁瓣振幅小,旁瓣宽度窄,基于广义余弦宽带频谱反演可有效提高地震资料分辨率,为非常规油气勘探提供可靠的数据支撑。
Abstract:Objective In the Junggar Basin, the exploration targets are deeply buried beneath the earth surface, posing significant challenges for seismic exploration. Specifically, this result in severe high-frequency absorption and attenuation of seismic wave energy. The recorded seismic data are characterized by a limited bandwidth with low dominant frequency, which significantly compromises the accuracy of the sandstone-shale thin interbed identification. Thus, the poor quality of the seismic data makes the reservoir distribution and potential hydrocarbon prediction tasks extremely challenging. Deconvolution is a key technique to improve the seismic data resolution. It aims to reverse the effects of wavelet convolution in the recorded seismic data, and can be performed in either the time domain or the frequency domain. Frequency domain deconvolution usually uses the estimation of seismic spectrum to construct a spectral-broadening operator, thereby expanding the frequency band and increasing the dominant frequency of the seismic data. We develop a frequency-domain deconvolution method to enhance the vertical seismic resolution. The key to this method lies in the use of an optimized target spectrum, and the final goal is to expand the seismic bandwidth effectively.
Methods We propose a generalized cosine broadband spectrum and incorporate it into the spectral inversion. Based on the relationship between the expected spectrum and diagonal matrix of the seismic spectrum, a spectral-broadening forward model is established. Subsequently, a shaping regularization inversion method is used to invert for the spectral-broadening operator. Ultimately, by applying the obtained spectral-broadening operator to the seismic data, the vertical seismic resolution can be enhanced. This is beneficial for more accurate geological interpretation and hydrocarbon exploration.
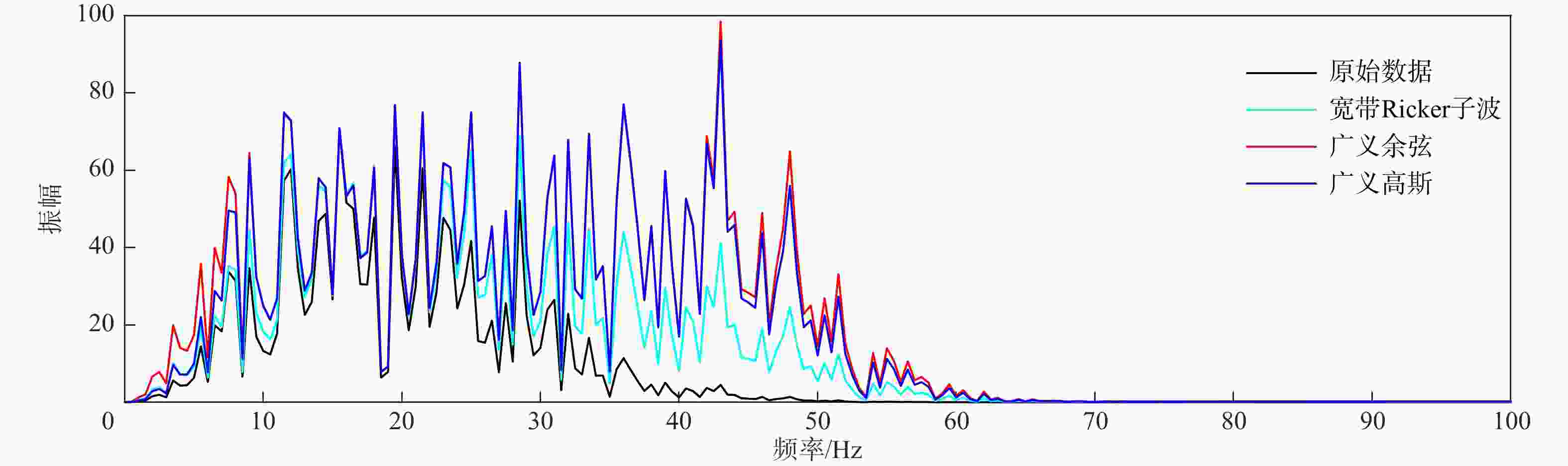
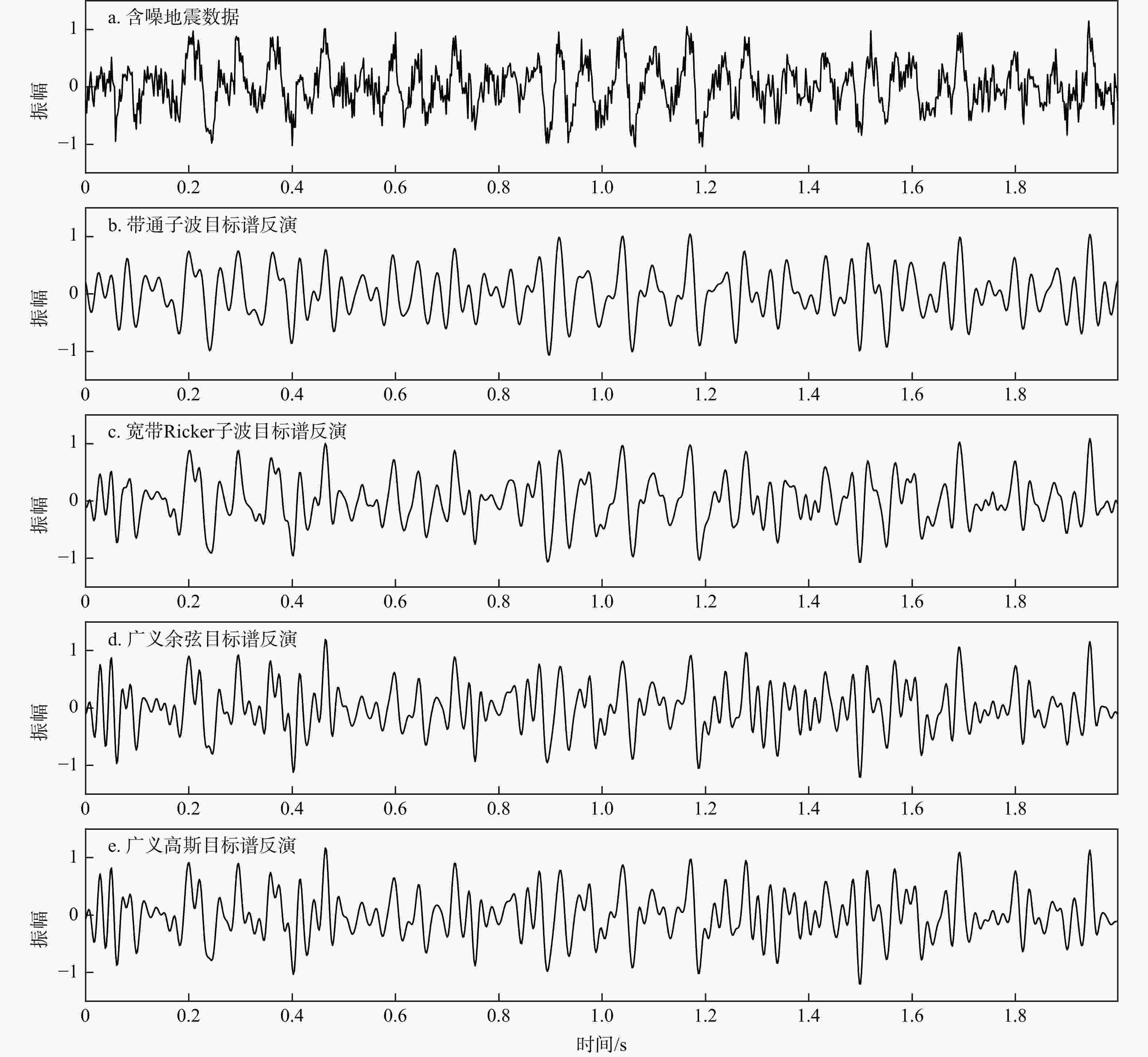
Results We use a theoretical model and field seismic data in the Junggar Basin to validate of the proposed method. The theoretical model has verified the effectiveness of the proposed method using the generalized cosine broadband spectrum. Subsequently, we apply the method to real seismic data from the Junggar Basin, where an optimized generalized cosine broadband spectrum is constructed based on the original seismic spectrum. The real seismic data processing results show that the frequency bandwidth of the seismic data has been effectively increased, leading to improved resolution of thin interbeds. The theoretical and field data results confirm the robustness and practical applicability of the proposed method.
Conclusion The generalized cosine broadband spectrum has a wide frequency band range, and can be flexibly designed. Additionally, the corresponding wavelet exhibits low side-lobe amplitude and narrow side-lobe width, which minimizes interference from reflected waves. The proposed spectral inversion using the generalized cosine broadband spectrum can be used to improve the seismic resolution and provides reliable seismic data for unconventional hydrocarbon exploration.
-
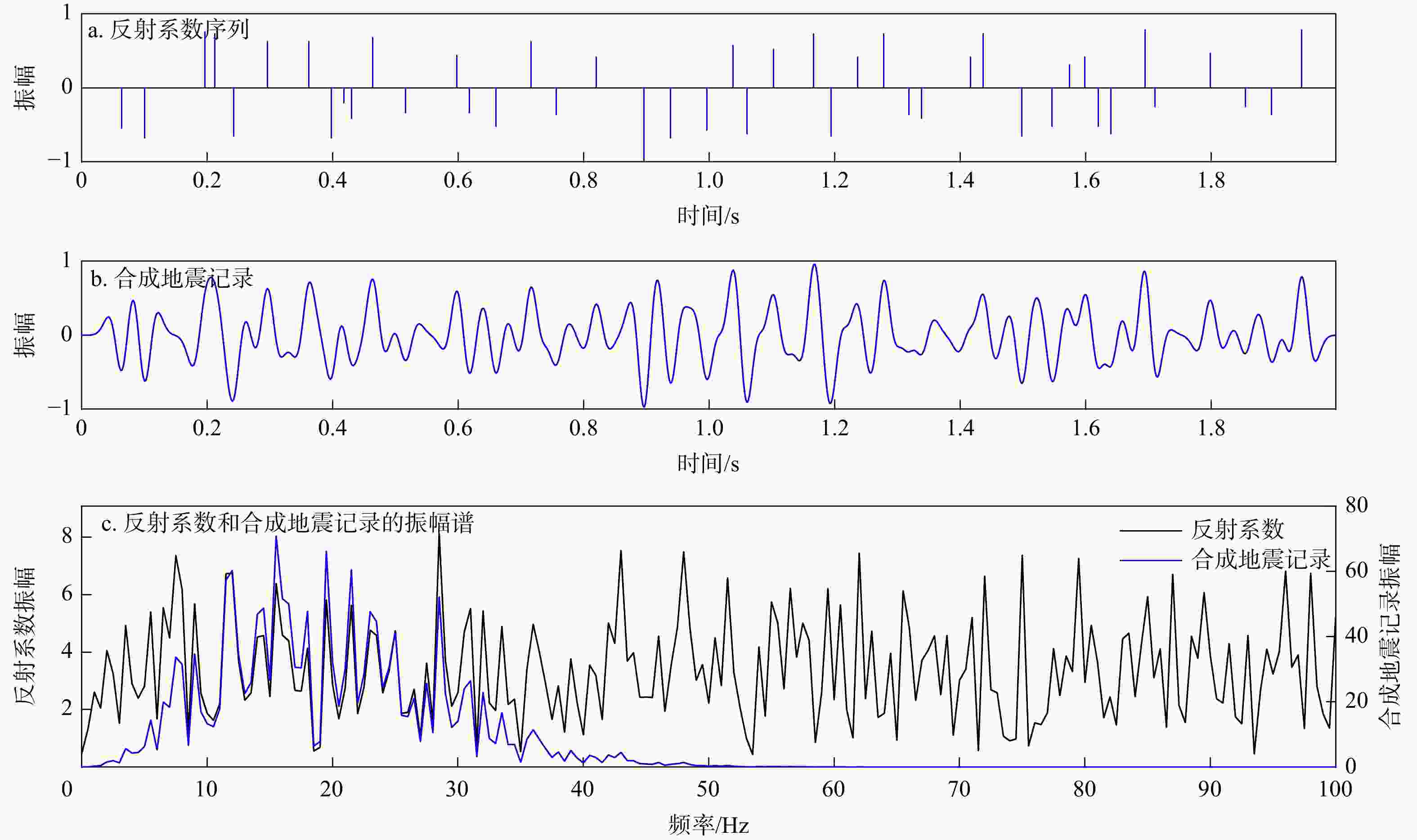
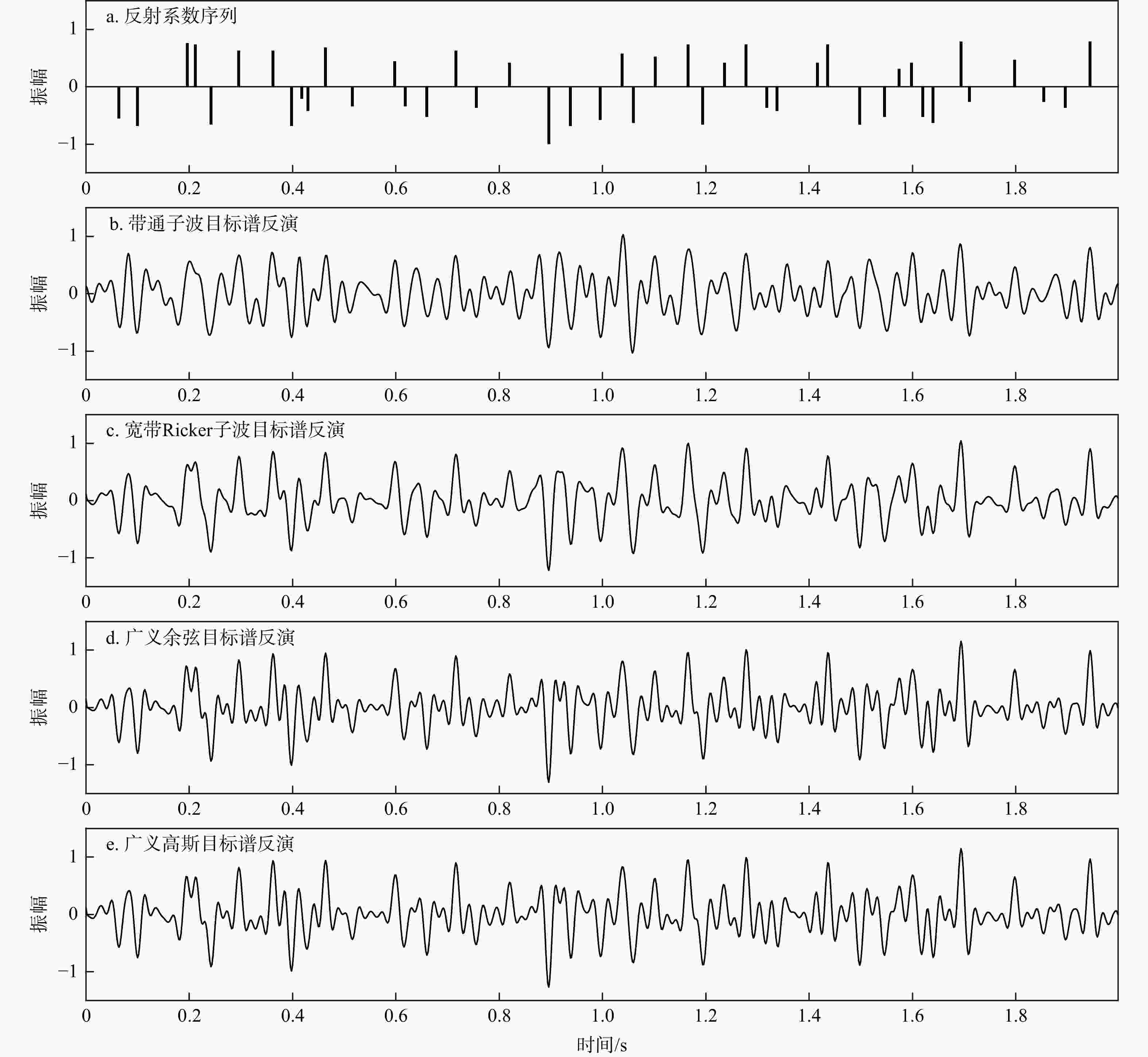
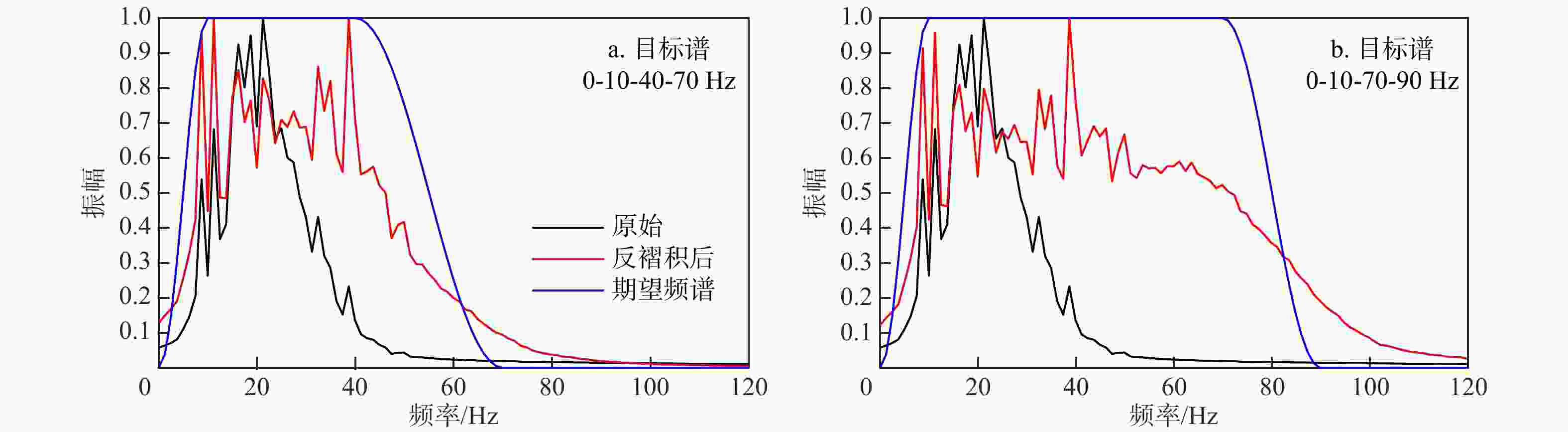
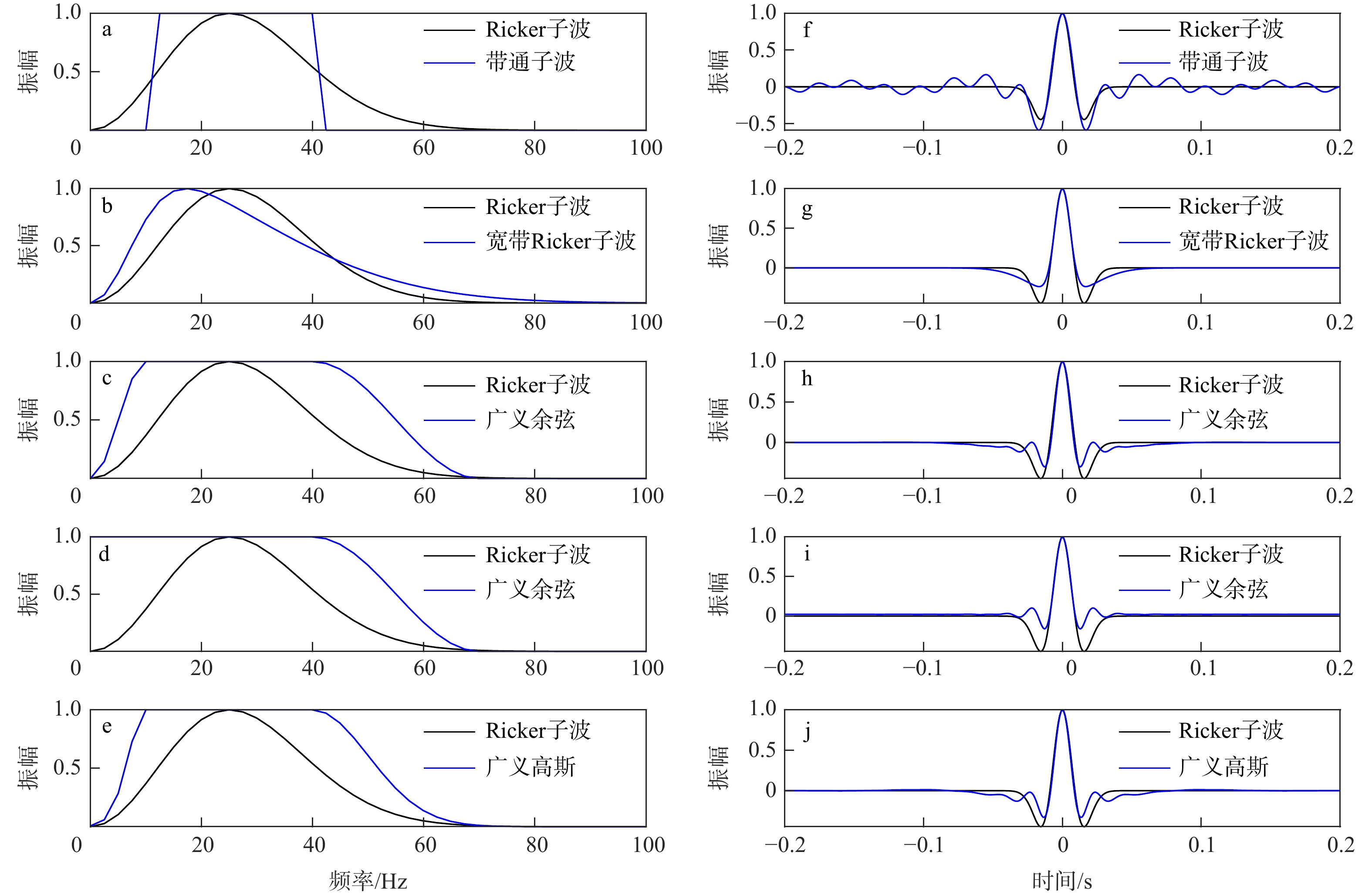
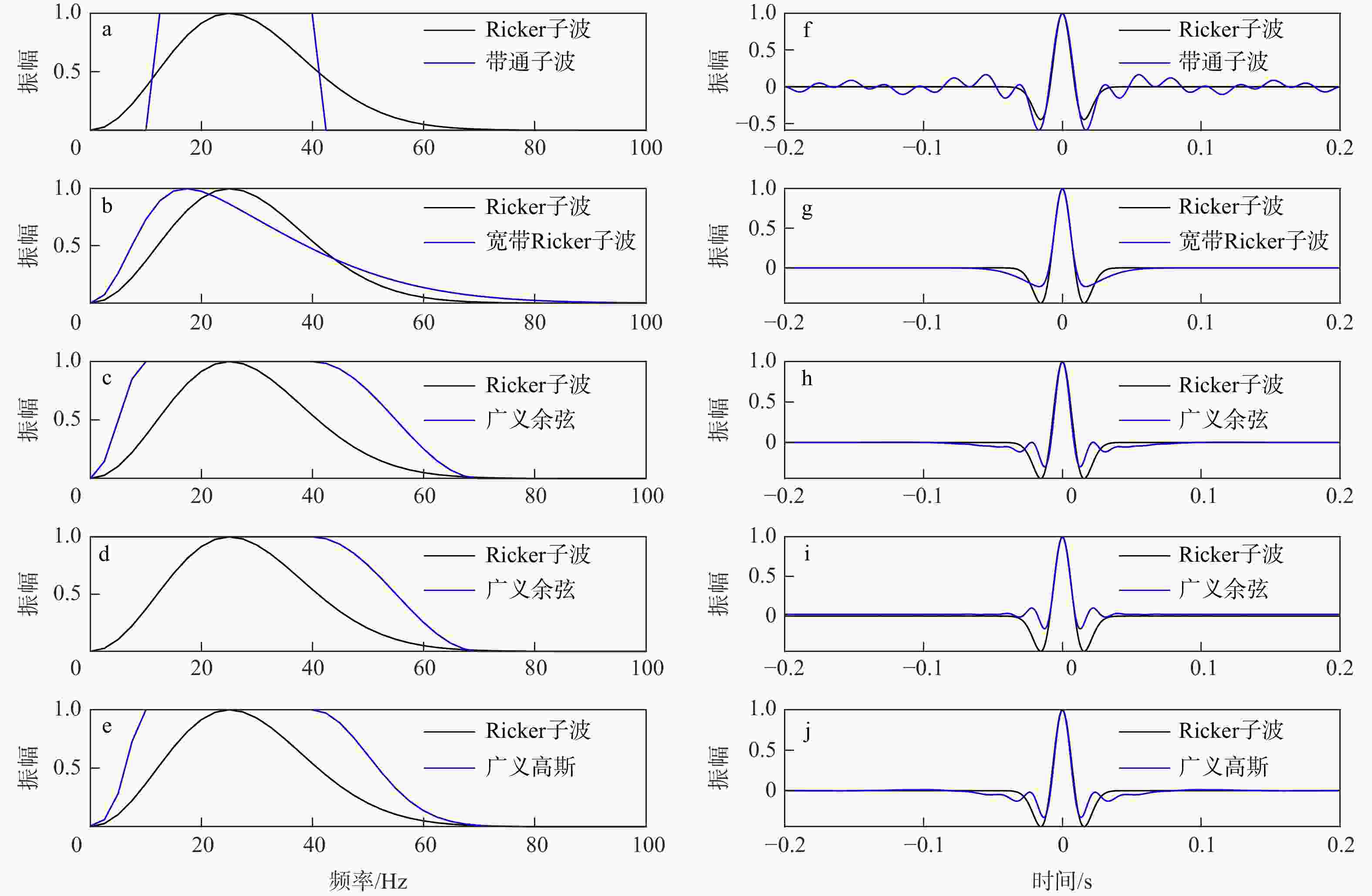
图 1 理论目标谱(a~e)及其对应子波(f~j)
a. 带通子波,低频截止频率10 Hz,高频截止频率40 Hz;b. 宽带Ricker子波,p = 10 Hz, q = 40 Hz;c. 广义余弦,lp = 10 Hz, hp = 40 Hz, hc = 70 Hz;d. 广义余弦,lp = 0 Hz, hp = 40 Hz, hc = 70 Hz;e. 广义高斯,fL = 10 Hz,fH = 40 Hz;p,q分别为Ricker子波峰值频率积分的下限和上限;lp,hp,hc分别为广义余弦目标谱的低通频率、高通频率和高截频率;fL,fH分别为广义高斯目标谱的低通频率和高通频率
Figure 1. Theoretical expected spectra (a-e) and the corresponding wavelets (f-j)
-
[1] 何登发, 张磊, 吴松涛, 等. 准噶尔盆地构造演化阶段及其特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5): 845-861. doi: 10.11743/ogg20180501HE D F, ZHANG L, WU S T, et al. Tectonic evolution stages and features of the Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5): 845-861. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11743/ogg20180501 [2] 夏世威, 马强, 黄传炎, 等. 准噶尔盆地东部吉木萨尔−吉南凹陷构造演化及原型盆地恢复[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(3): 170-179.XIA S W, MA Q, HUANG C Y, et al. Tectonic evolution and prototype basin reconstruction in the Jimsar and Jinan depressions, eastern Junggar Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(3): 170-179. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 于宝利, 贾承造, 刘可禹, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘多滑脱层控制的冲断构造特征及深层油气勘探方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2025, 52(3): 593-606. doi: 10.11698/PED.20240694YU B L, JIA C Z, LIU K Y, et al. Multi-detachment-controlled thrust structures and deep hydrocarbon exploration targets in southern margin of Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2025, 52(3): 593-606. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.20240694 [4] 龚德瑜, 刘泽阳, 何文军, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷风城组有机质多元富集机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2024, 51(2): 260-272. doi: 10.11698/PED.20230673GONG D Y, LIU Z Y, HE W J, et al. Multiple enrichment mechanisms of organic matter in the Fengcheng Formation of Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2024, 51(2): 260-272. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.20230673 [5] 何文军, 费李莹, 阿布力米提·依明, 等. 准噶尔盆地深层油气成藏条件与勘探潜力分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(1): 189-201.HE W J, FEI L Y, ABLIMITI Y M, et al. Accumulation conditions of deep hydrocarbon and exploration potential analysis in Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(1): 189-201. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 蔡忠贤, 陈发景, 贾振远. 准噶尔盆地的类型和构造演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(4): 431-440. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.04.010CAI Z X, CHEN F J, JIA Z Y. Types and tectonic evolution of Junger Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2000, 7(4): 431-440. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.04.010 [7] 党文龙, 高岗, 尤新才, 等. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷大油区不同类型原油分布及成因[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2023, 50(4): 731-741. doi: 10.11698/PED.20230078DANG W L, GAO G, YOU X C, et al. Genesis and distribution of oils in Mahu Sag province, Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2023, 50(4): 731-741. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.20230078 [8] 史乐, 李婷, 杜引鱼, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘LQ区石炭系火山岩风化壳储层分带性及勘探方向[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(3): 82-93.SHI L, LI T, DU Y Y, et al. Zonality and exploration direction of Carboniferous volcanic weathering crust reservoirs in the LQ area, northwest margin of the Junggar Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(3): 82-93. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 王大兴, 胡海燕, 邹佳群, 等. 准噶尔盆地东道海子凹陷二叠系下乌尔禾组陆相页岩气形成富集条件及主控因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(4): 98-112.WANG D X, HU H Y, ZOU J Q, et al. Enrichment conditions and main controlling factors of continental shale gas in the Permian Lower Wuerhe Formation in the Dongdaohaizi Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(4): 98-112. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] WANG Y J, GAO X Y, ZHANG G Q, et al. Seismic multichannel deconvolution via 2-D K-SVD and MSD-oCSC[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5904713. [11] SUN Y G, CAO S Y, CHEN S Y, et al. Blind spectral inversion of seismic data[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2024, 72(9): 3436-3447. doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.13594 [12] WANG Y, ZHANG G, LI H, et al. The high-resolution seismic deconvolution method based on joint sparse representation using logging-seismic data[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2022, 70(8): 1313-1326. doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.13232 [13] SACCHI M D, VELIS D R, COMÍNGUEZ A H. Minimum entropy deconvolution with frequency-domain constraints[J]. Geophysics, 1994, 59(6): 938-945. doi: 10.1190/1.1443653 [14] 卫泽, 潘树林, 程祎, 等. 自适应变分模态分解同态反褶积方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2023, 58(1): 105-113.WEI Z, PAN S L, CHENG Y, et al. Homomorphic deconvolution method based on adaptive variational mode decomposition[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2023, 58(1): 105-113. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] DE MACEDO I A S, DE FIGUEIREDO J J S, DE SOUSA M C, et al. Estimation of the seismic wavelet through homomorphic deconvolution and well log data: Application on well-to-seismic tie procedure[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2020, 68(4): 1328-1340. doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.12908 [16] ROSEC O, BOUCHER J M, NSIRI B, et al. Blind marine seismic deconvolution using statistical MCMC methods[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2003, 28(3): 502-512. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2003.816683 [17] MAMASANI M G, MANAMAN N S, KAZEMI K, et al. Resolution enhancement of seismic data using spectral modeling based on dominant Ricker components and separable nonlinear least squares[J]. The Leading Edge, 2017, 36(6): 480-486. doi: 10.1190/tle36060480.1 [18] ROSA A L R, ULRYCH T J. Processing via spectral modeling[J]. Geophysics, 1991, 56(8): 1244-1251. doi: 10.1190/1.1443144 [19] 孙成禹. 谱模拟方法及其在提高地震资料分辨率中的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2000, 35(1): 27-35. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2000.01.004SUN C Y. Spectrum modeling method and its application to seismic resolution improvement[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2000, 35(1): 27-35. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-7210.2000.01.004 [20] LIU X W, GAO F X, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Seismic resolution enhancement in shale-oil reservoirs[J]. Geophysics, 2018, 83(5): 281-287. doi: 10.1190/geo2017-0765.1 [21] OTIS R M, SMITH R B. Homomorphic deconvolution by log spectral averaging[J]. Geophysics, 1977, 42(6): 1146-1157. doi: 10.1190/1.1440780 [22] CHEN Y K, JIN Z Y. Simultaneously removing noise and increasing resolution of seismic data using waveform shaping[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2016, 13(1): 102-104. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2499166 [23] YUAN Y J, LI Y C, ZHOU S C. Multichannel statistical broadband wavelet deconvolution for improving resolution of seismic signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(2): 1772-1783. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2997977 [24] 程朝辉, 苑益军, 刘晟, 等. 宽带子波反褶积方法在致密储层地震资料处理中的应用[J]. 石油物探, 2023, 62(1): 119-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2023.01.010CHENG Z H, YUAN Y J, LIU S, et al. Application of wideband wavelet deconvolution for tight oil exploration[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2023, 62(1): 119-129. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2023.01.010 [25] ZHAO Y X, LI Y, WANG S N, et al. Physical model and super-resolution theory-guided unsupervised deep learning deconvolution for seismic resolution enhancement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2025, 63: 5905813. [26] YU H Z, CHEN W C, WANG X K, et al. Unsupervised diffusion model for seismic deconvolution[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2025, 22: 7504405. [27] 倪文军, 刘少勇, 王丽萍, 等. 基于深度学习的子波整形反褶积方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2023, 58(6): 1313-1321.NI W J, LIU S Y, WANG L P, et al. Wavelet shaping deconvolution based on deep learning[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2023, 58(6): 1313-1321. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] MIN F, TANG J Y, PAN S L, et al. CAUC: Combining channel attention U-Net and convolution for seismic data resolution improvement[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2023, 20: 3003105. [29] CHEN S Q, WANG Y H. Seismic resolution enhancement by frequency-dependent wavelet scaling[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(5): 654-658. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2018.2809564 [30] ALAEI N, ROSHANDEL KAHOO A, KAMKAR ROUHANI A, et al. Seismic resolution enhancement using scale transform in the time-frequency domain[J]. Geophysics, 2018, 83(6): 305-314. doi: 10.1190/geo2017-0248.1 [31] XUE J, CAI C G, GU H M, et al. Seismic resolution enhancement by spectral shaping using shaping-regularized inversion[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2021, 19: 7506905. [32] 杨培杰. 复数域约束最小二乘拓频[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2021, 56(6): 1244-1253.YANG P J. Constrained complex-domain least-squares spectrum blueing[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2021, 56(6): 1244-1253. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 赵宝银, 陈思远, 陶钰, 等. 应用宽带Ricker子波的期望目标频谱整形[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2020, 55(3): 541-547.ZHAO B Y, CHEN S Y, TAO Y, et al. Spectrum shaping of desired targets based on broadband Ricker wavelets[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2020, 55(3): 541-547. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 唐甜, 巴素玉, 时瑞坤, 等. 基于正交匹配追踪的深度波数谱分解及其在含油气储层预测中的应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(1): 360-370.TANG T, BA S Y, SHI R K, et al. Depth wavenumber spectral decomposition based on orthogonal matching pursuit and its application in hydrocarbon reservoir prediction[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(1): 360-370. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 俞寿朋. 宽带Ricker子波[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 1996, 31(5): 605-615.YU S P. Wide-band Ricker wavelet[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 1996, 31(5): 605-615. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 王华忠. 客户定制反射子波的可控震源地震勘探方法[J]. 石油物探, 2020, 59(5): 683-694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2020.05.002WANG H Z. Vibroseis seismic exploration with customized wavelet[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2020, 59(5): 683-694. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2020.05.002 [37] ZHANG J H, ZHANG B B, ZHANG Z J, et al. Low-frequency data analysis and expansion[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2015, 12(2): 212-220. doi: 10.1007/s11770-015-0484-2 [38] FOMEL S. Shaping regularization in geophysical-estimation problems[J]. Geophysics, 2007, 72(2): 29-36. [39] 乐友喜, 陈艺都, 吴佳伟, 等. 自适应整形正则化迭代最小二乘谱反演方法[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(3): 54-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2022.03.006YUE Y X, CHEN Y D, WU J W, et al. Iterative least squares spectrum inversion based on adaptive shaping regularization[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2022, 46(3): 54-61. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2022.03.006 [40] 薛姣, 顾汉明, 贺梅, 等. 基于自适应整形正则化的AVAz反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2024, 67(6): 2429-2438. doi: 10.6038/cjg2023R0365XUE J, GU H M, HE M, et al. AVAz inversion using adaptive shaping regularization[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(6): 2429-2438. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg2023R0365 -




 下载:
下载: