Research and application of artificial intelligence algorithms in landslide monitoring and prediction technology
-
摘要:
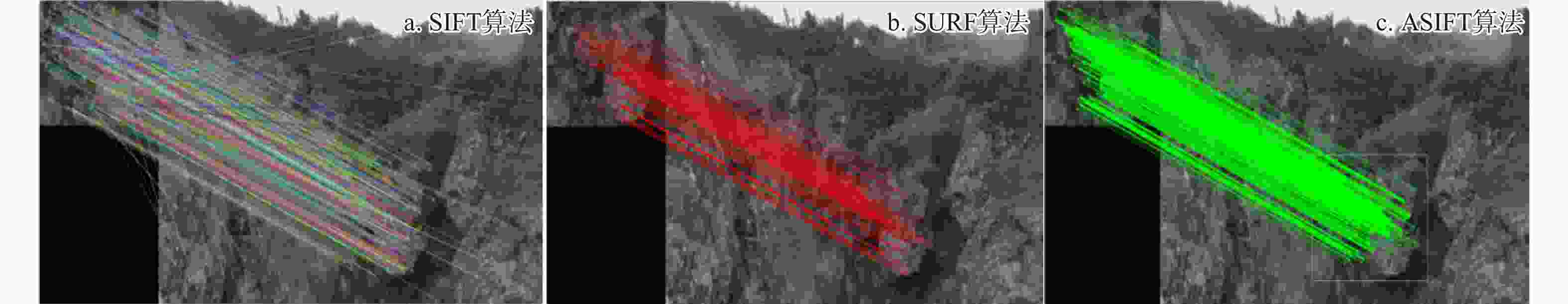
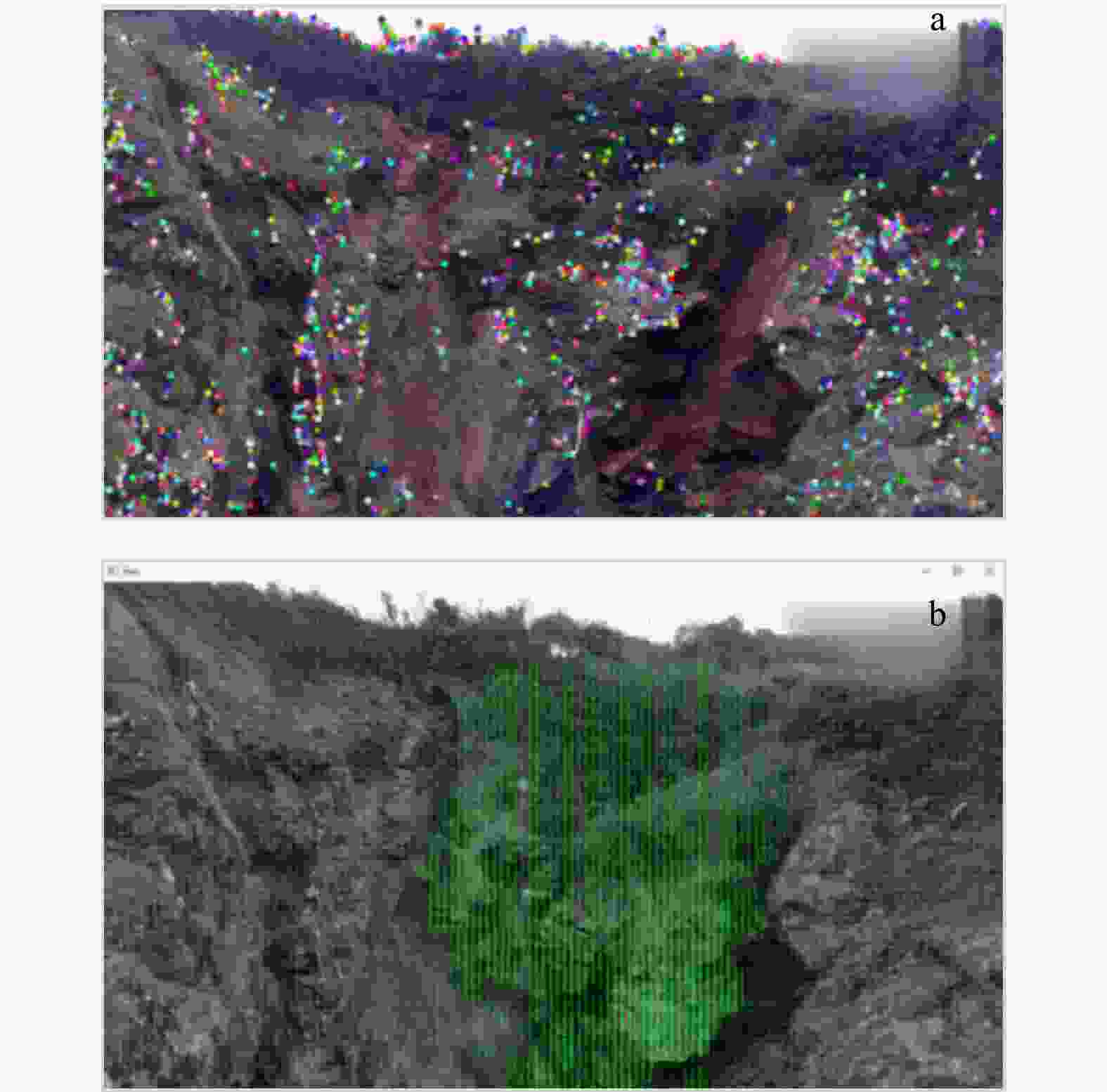
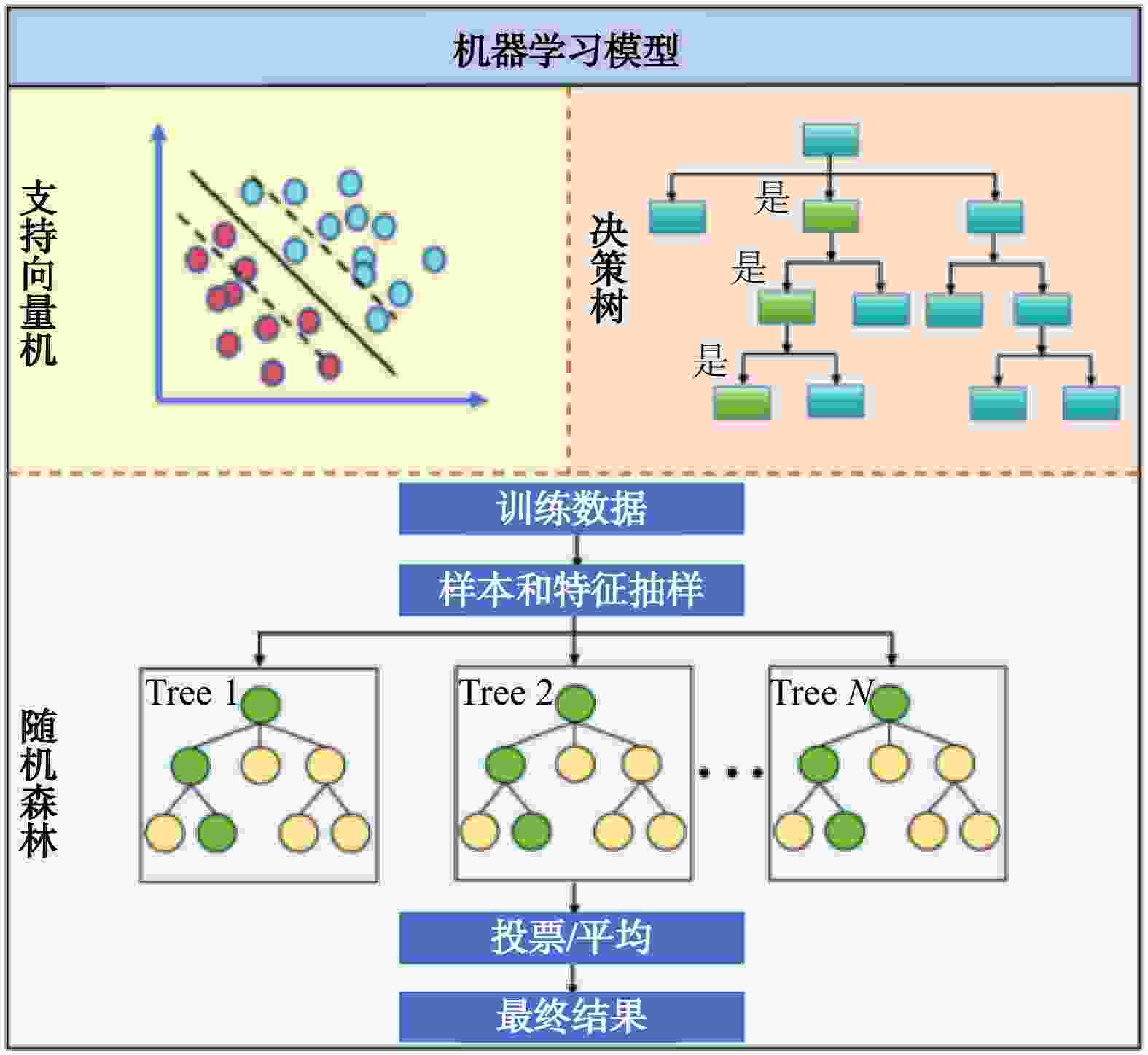
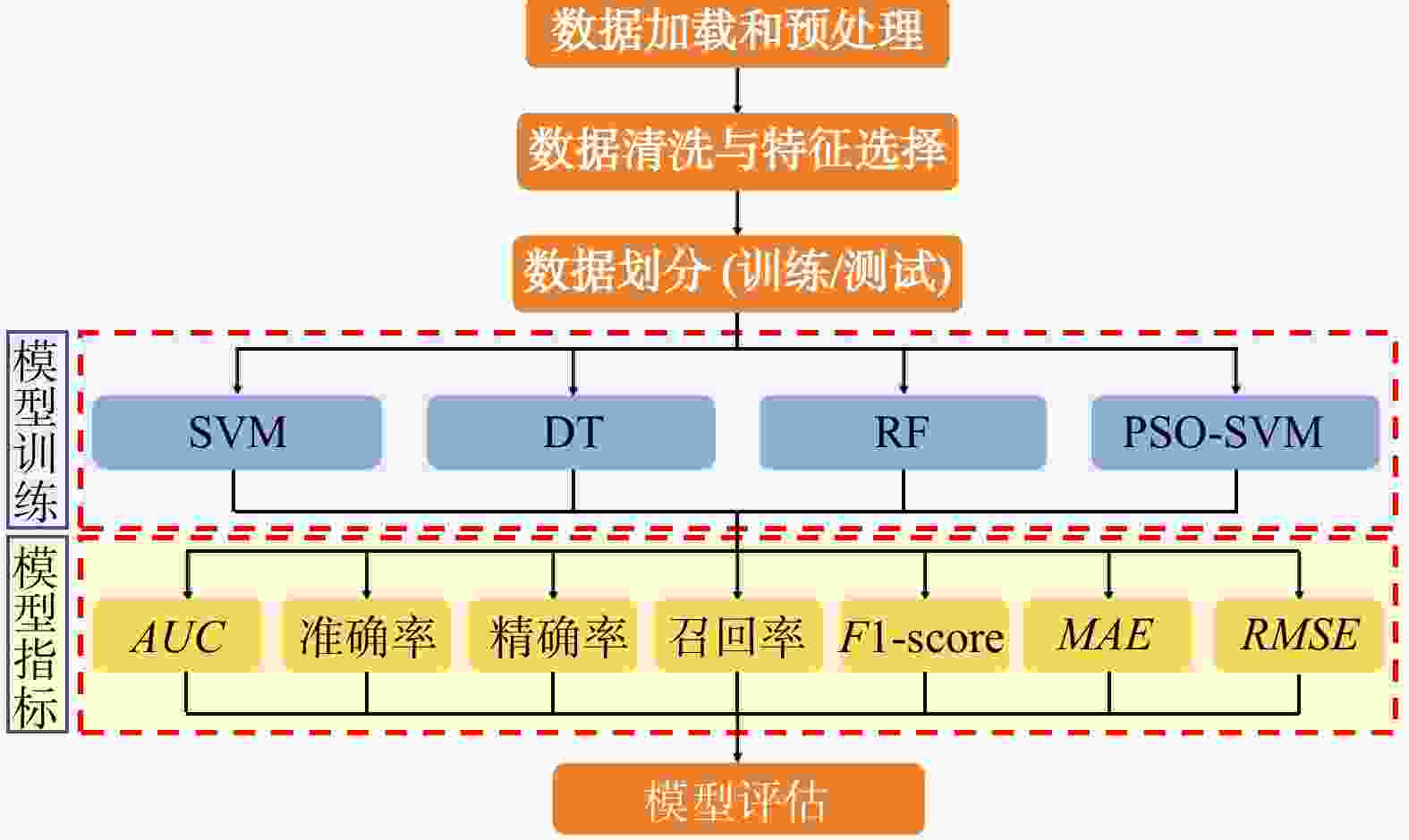
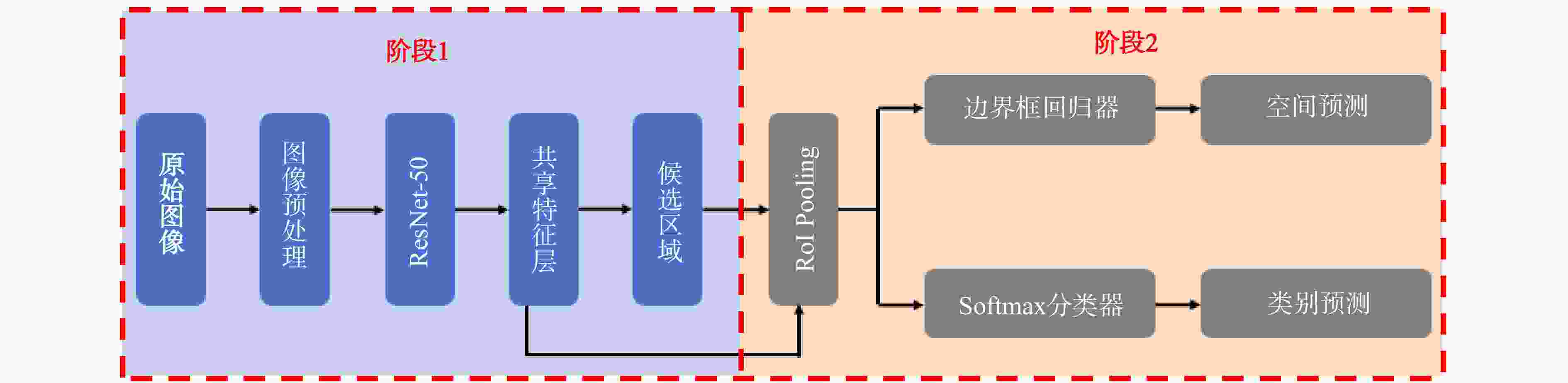
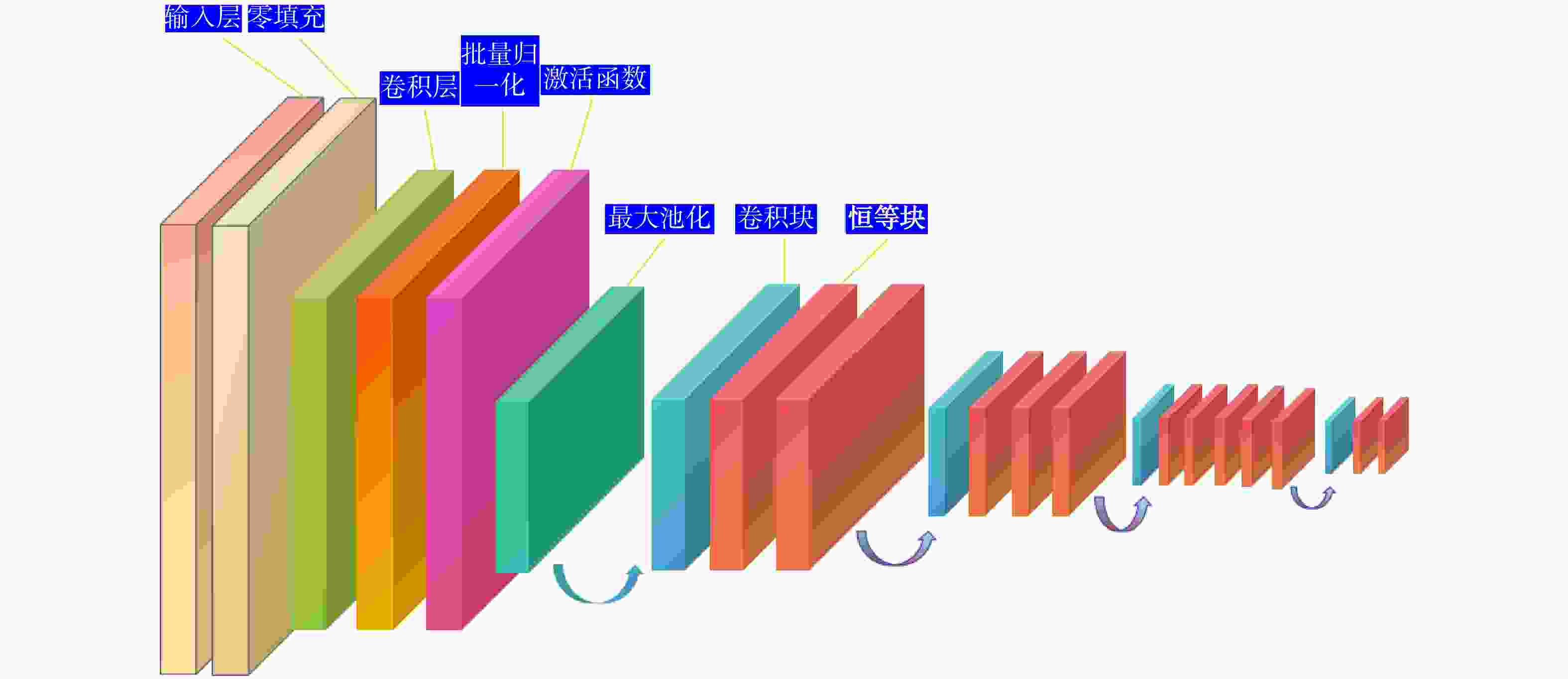
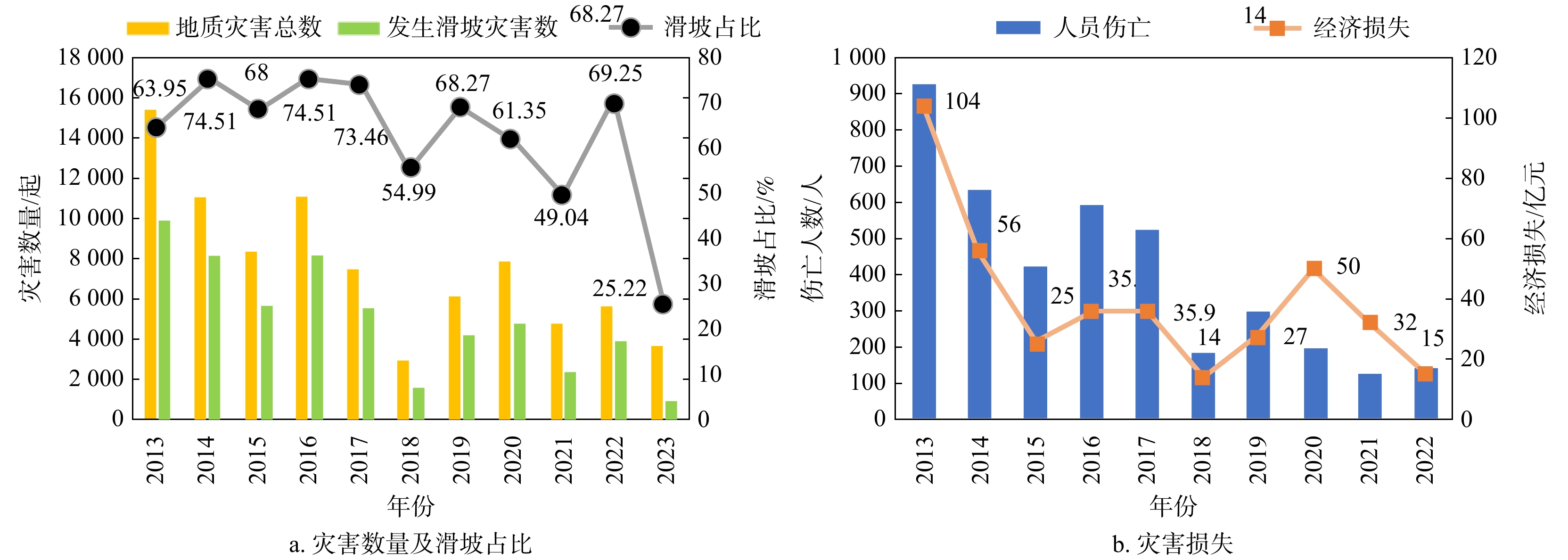
为减轻滑坡灾害风险,进一步保障区域可持续发展,开展有效的滑坡监测与预测研究具有重要的现实意义。通过研究滑坡监测与预测中的关键技术与方法,分析各类算法在滑坡监测与预测场景中的效率和精度,不断提升滑坡灾害防治水平。在特征提取技术方面,对比分析了尺度不变特征变换(SIFT)、加速鲁棒特征(SURF)和自适应尺度不变特征变换(ASIFT)3种基于图像特征匹配算法的性能,其中ASIFT在匹配数量、精确率和召回率方面具有显著优势,尤其适用于准确性要求较高的复杂环境场景;在光流分析技术方面,探讨了基于Lucas-Kanade稀疏光流法和Horn-Schunck稠密光流法的应用效果,其中Lucas-Kanade稀疏光流法计算效率高,适合实时应用场景,但存在遗漏重要运动信息风险,Horn-Schunck稠密光流法能够提供全面的光流场信息,适用于环境复杂场景,但存在计算复杂度较高的不足,因而难以用于实时处理;在滑坡易发性预测方面,详细介绍了支持向量机(SVM)、决策树(DT)和随机森林(RF)等经典机器学习方法在滑坡预测中的应用优缺点,并重点研究了基于粒子群优化支持向量机(PSO-SVM)的模型性能,该模型通过优化超参数,显著提高了模型的分类准确度、泛化能力和预测精度。此外,通过引入Faster R-CNN模型,利用其先进的卷积神经网络架构,实现了复杂场景下滑坡事件的自动识别与分类,进一步提升了滑坡监测预警的效率和准确率。研究表明,ASIFT局部特征提取的精确率为0.84,Lucas-Kanade稀疏光流法的跟踪误差为0.12,PSO-SVM模型的均方根误差为0.52,Faster R-CNN模型在滑坡图像自动识别与分类方面的置信度可达0.98,综合性能较其他算法显著提升。综上所述,通过引入人工智能算法,结合多学科技术手段,全方面提升了滑坡监测与预测技术的效率和精度,研究成果为滑坡地质灾害防治提供了更有力的技术保障。
-
关键词:
- 人工智能算法 /
- 滑坡监测与预测 /
- 特征匹配 /
- 光流法 /
- 粒子群优化支持向量机(PSO-SVM)
Abstract:Objective To reduce the risk of landslide disasters and further ensure regional sustainable development, conducting research effectively on landslide monitoring and prediction is of great practical significance. This paper aims to continuously improve the prevention and control level of landslide disasters by studying the key technologies and methods in landslide monitoring and prediction, and will analyze the efficiency and accuracy of various algorithms in scenarios of landslide monitoring and prediction.
Methods In terms of feature extraction technology, the performance of three image feature matching algorithms, namely scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT), speeded up robust features (SURF) and assessment of scale-invariant features transform (ASIFT), were compared and analyzed. Comparative results demonstrate that ASIFT has significant advantages in the number of matches, precision rate and recall rate, and is especially suitable for complex environmental scenarios with high-accuracy requirements. In terms of optical flow analysis technology, the application effects based on the Lucas-Kanade sparse optical flow method and the Horn-Schunck dense optical flow method were discussed. Among them, the Lucas-Kanade sparse optical flow method has high computational efficiency and is suitable for real-time application scenarios, but there is a risk of missing important motion information. The Horn-Schunck dense optical flow method can provide comprehensive optical flow field information and is suitable for complex environmental scenarios. However, it has the drawback of high computational complexity and thus is difficult to be used in real-time processing. In terms of landslide susceptibility prediction, the advantages and disadvantages of the application of classic machine learning methods such as support vector machine (SVM), decision tree (DT), and random forest (RF) in landslide prediction are introduced in detail. The model performance based on particle swarm optimization-support vector machine (PSO-SVM) is mainly studied. This model optimizes hyperparameters, the classification accuracy, generalization ability and prediction accuracy of the model have been significantly improved. Furthermore, by introducing the Faster R-CNN model and leveraging its advanced convolutional neural network architecture, this paper realizes the automatic identification and classification of landslide events in complex scenarios, further enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of landslide monitoring and early warning.
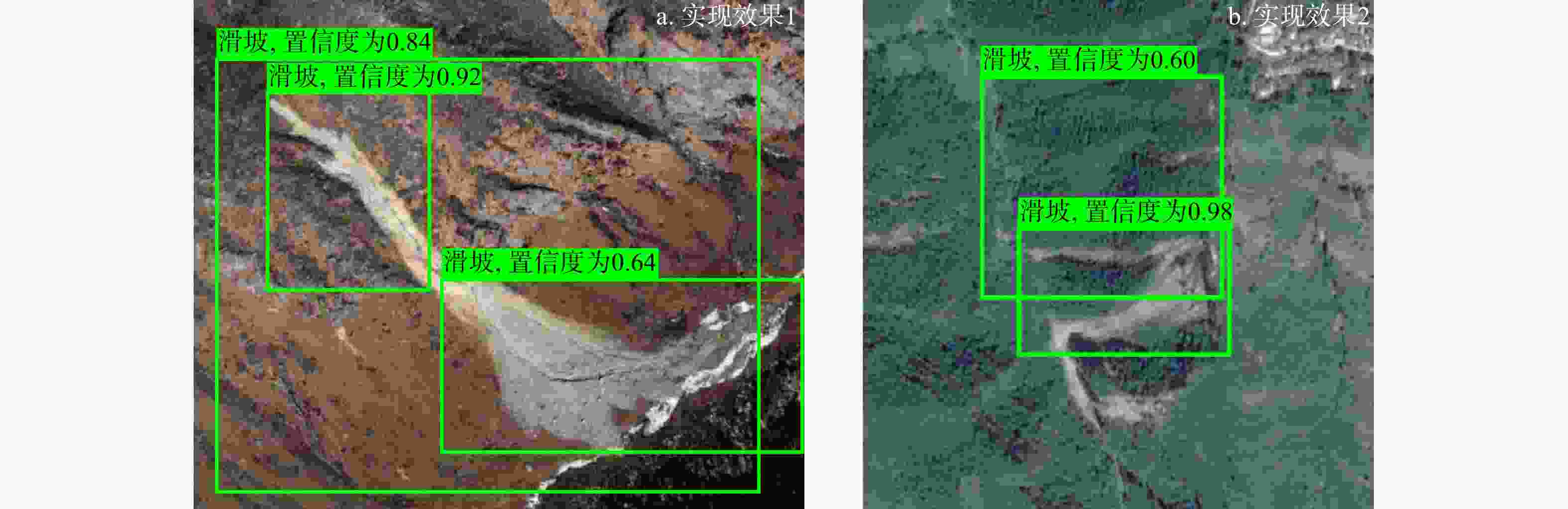
Results The research shows that the accuracy rate of local feature extraction by ASIFT is 0.84, the tracking error of the Lucas-Kanade sparse optical flow method is 0.12, the root mean square error of the PSO-SVM model is 0.52, and the confidence level of the Faster R-CNN model in the automatic recognition and classification of landslide images can reach 0.98. The comprehensive performance is significantly improved compared with other algorithms in this paper.
Conclusion In summary, by introducing artificial intelligence algorithms and integrating multi-disciplinary technical means, this paper has comprehensively enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of landslide monitoring and prediction technology. The research results provide more powerful technical support for the prevention and control of landslide geological disasters.
-
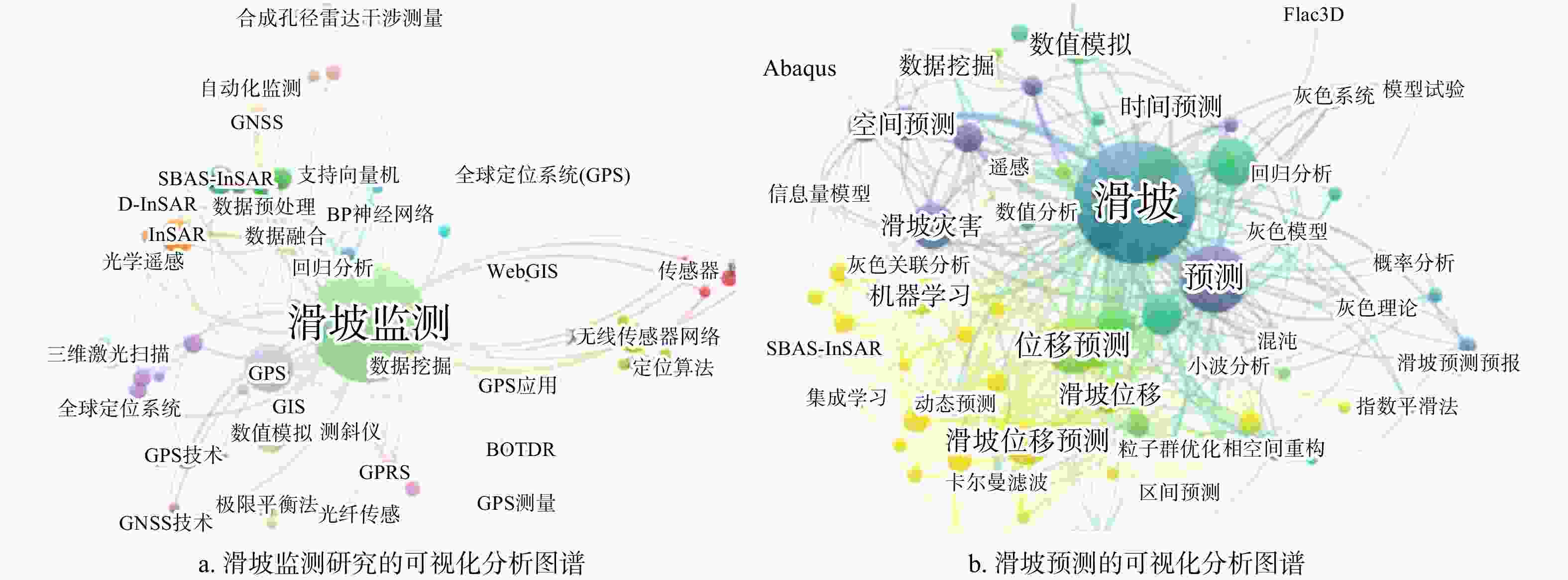
图 2 基于VOSviewer滑坡监测与预测可视化关联分析
GNSS. 全球卫星导航系统;SBAS-InSAR. 小基线集干涉测量技术;D-InSAR. 差分干涉合成孔径雷达技术;InSAR. 合成孔径雷达干涉技术;BP神经网络. 反向传播神经网络;WebGIS. 网络地理信息系统;GIS. 地理信息系统;GPRS. 通用分组无线服务技术;BOTDR. 布里渊光时域反射;Abaqus. 通用非线性有限元分析软件;Flac3D. 三维数值模拟软件
Figure 2. Visual correlation analysis of landslide monitoring and prediction based on VOSviewer
表 1 SIFT及其改进算法性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of SIFT and its improved algorithm
算法名称 匹配数量/个 耗时/s 精确率 召回率 SIFT 556 0.2786 0.55 0.56 SURF 130 0.0059 0.58 0.75 ASIFT 1404 0.2427 0.84 1.00 表 2 Horn-Schunck和Lucas-Kanade算法的对比
Table 2. Comparison of Horn-Schunck and Lucas-Kanade
算法名称 执行时间
(min:s)在HyperSparc10α
执行时间(min:s)期望帧率
时间/aHorn-Schunck 8:00 2:00 12 Lucas-Kanade 0:23 0:06 7 表 3 Lucas-Kanade和Horn-Schunck算法的性能对比
Table 3. Performance comparison between Lucas-Kanade and Horn-Schunck
算法名称 处理总帧数/个 初始跟踪点数/个 总丢失点数/个 平均跟踪误差 Lucas-Kanade 799 1197 83 0.13 Horn-Schunck 799 1472714906 1894 0.12 表 4 机器学习算法的分析与比较
Table 4. Analysis and comparison of machine learning algorithms
算法名称 AUC 准确率 精确率 召回率 F1-score MAE RMSE SVM 0.71 0.58 0.72 0.44 0.55 0.41 0.64 DT 0.57 0.54 0.57 0.55 0.55 0.43 0.65 RF 0.68 0.65 0.64 0.65 0.64 0.35 0.59 PSO-SVM 0.71 0.73 0.72 0.72 0.72 0.27 0.52 -
[1] 朱鸿鹄. 工程地质界面: 从多元表征到演化机理[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 1-19.ZHU H H. Engineering geological interface: From multivariate characterization to evolution mechanism[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 1-19. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 唐辉明. 重大滑坡预测预报研究进展与展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(6): 1-13.TANG H M. Advance and prospects of major landslides prediction and forecasting[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] HE R J, ZHANG W G, DOU J, et al. Application of artificial intelligence in three aspects of landslide risk assessment: A comprehensive review[J]. Rock Mechanics Bulletin, 2024, 3(4): 100144. doi: 10.1016/j.rockmb.2024.100144 [4] 张抒, 唐辉明, 龚文平, 等. 基于物理力学机制的滑坡数值预报模式: 综述、挑战与机遇[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(6): 14-27.ZHANG S, TANG H M, GONG W P, et al. Landslide numerical forecasting mode based on physical-mechanical mechanism: Overviews, challenges and opportunities[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 14-27. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 曹兰柱, 王珍, 王东, 等. 露天矿滑坡预警理论与方法研究[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2017, 27(3): 163-168.CAO L Z, WANG Z, WANG D, et al. Research on theory and method of landslide early warning in open-pit mine[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2017, 27(3): 163-168. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 程刚, 王振雪, 李刚强, 等. 我国滑坡监测文献计量研究的可视化分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(7): 172-179.CHENG G, WANG Z X, LI G Q, et al. Visual analysis of bibliometric research on landslide monitoring in China[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(7): 172-179. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 马宁, 李韶凯, 田峰, 等. 滑坡光纤神经感测系统: 技术与应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(6): 26-38.MA N, LI S K, TIAN F, et al. Fiber optic nerve sensing system for landslide monitoring: Technology and application[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(6): 26-38. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 吴迪, 梁泰铭, 吴静, 等. 基于MEMS传感器的滑坡监测算法设计与试验[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(6): 39-50.WU D, LIANG T M, WU J, et al. Design and experiment of landslide monitoring algorithm based on MEMS sensor[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(6): 39-50. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 陈斌, 王利, 舒宝, 等. 基于复合分界指标和CEEMD-WT的GNSS滑坡监测坐标时间序列降噪方法[J/OL]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版): 1-15[2025-9-17]. https://doi.org/10.13203/j.whugis20240123.CHEN B, WANG L, SHU B, et al. GNSS landslide monitoring coordinate time series noise reduction methods based on composite divisional indicator index and CEEMD-WT[J/OL]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University: 1-15[2025-9-17]. https://doi.org/10.13203/j.whugis20240123. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 蒲磊, 杨启贵, 程翔, 等. 基于SBAS-InSAR技术的HD库区CYP滑坡形变监测分析[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2024(11): 240-246.PU L, YANG Q G, CHENG X, et al. Analysis of deformation monitoring of CYP landslide in HD reservoir area based on SBAS-InSAR technology[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2024(11): 240-246. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] YANG B B, YIN K L, LACASSE S, et al. Time series analysis and long short-term memory neural network to predict landslide displacement[J]. Landslides, 2019, 16(4): 677-694. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-01127-x [12] 张俊, 殷坤龙, 王佳佳, 等. 基于时间序列与PSO-SVR耦合模型的白水河滑坡位移预测研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(2): 382-391.ZHANG J, YIN K L, WANG J J, et al. Displacement prediction of Baishuihe landslide based on time series and PSO-SVR model[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(2): 382-391. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] GE Q, LI J, LACASSE S, et al. Data-augmented landslide displacement prediction using generative adversarial network[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2024, 16(10): 4017-4033. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2024.01.003 [14] 石化波, 王刚, 曾怀恩. 一种ICEEMDAN-CNN-SVR滑坡位移组合预测模型[J]. 三峡大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 47(1): 37-43.SHI H B, WANG G, ZENG H E. A combined ICEEMDAN-CNN-SVR landslide displacement prediction model[J]. Journal of China Three Gorges University (Natural Sciences), 2025, 47(1): 37-43. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] VAN NATIJNE A L, LINDENBERGH R C, BOGAARD T A. Machine learning: New potential for local and regional deep-seated landslide nowcasting[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(5): 1425. doi: 10.3390/s20051425 [16] XU Z Y, CHE A L, ZHOU H X. Seismic landslide susceptibility assessment using principal component analysis and support vector machine[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14: 3734. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48196-0 [17] DOU J, YUNUS A P, TIEN B D, et al. Assessment of advanced random forest and decision tree algorithms for modeling rainfall-induced landslide susceptibility in the Izu-Oshima Volcanic Island, Japan[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 662: 332-346. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.221 [18] 黄玲. 基于Django的山体滑坡监测系统设计与实现[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2022.HUANG L. Design and implementation of a landslide monitoring system based on Django[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] YIN C, LI H R, CHE F, et al. Susceptibility mapping and zoning of highway landslide disasters in China[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(9): e0235780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235780 [20] WANG Y, FANG Z C, HONG H Y. Comparison of convolutional neural networks for landslide susceptibility mapping in Yanshan County, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 666: 975-993. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.263 [21] 唐烽顺, 郝利娜, 宋雨洋, 等. 目标检测算法在滑坡识别中的应用[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 60(2): 229-234.TANG F S, HAO L N, SONG Y Y, et al. Application of the object detection algorithm in landslide identification[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 2024, 60(2): 229-234. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] HAKIM W L, REZAIE F, NUR A S, et al. Convolutional neural network (CNN) with metaheuristic optimization algorithms for landslide susceptibility mapping in Icheon, South Korea[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 305: 114367. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114367 [23] 简小婷, 赵康, 左小清, 等. 基于Faster R-CNN目标检测的滑坡隐患识别: 以福贡县城区为例[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2022, 51(12): 19-24.JIAN X T, ZHAO K, ZUO X Q, et al. Landslides risk identification based on faster R-CNN: A case study in Fugong County[J]. Industrial Minerals & Processing, 2022, 51(12): 19-24. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 贾丰蔓, 康志忠, 于鹏. 影像同名点匹配的SIFT算法与贝叶斯抽样一致性检验[J]. 测绘学报, 2013, 42(6): 877-883.JIA F M, KANG Z Z, YU P. A SIFT and Bayes sampling consensus method for image matching[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2013, 42(6): 877-883. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 赵玉兰, 王兴伟, 黄敏, 等. 基于区域统计直方图与自适应规则的图像匹配算法[J]. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 36(6): 117-124.ZHAO Y L, WANG X W, HUANG M, et al. Research on image matching algorithm based on region statistical histogram coupling adaptive rule[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science), 2017, 36(6): 117-124. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 尚硕, 曹建荣, 汪明, 等. 机器视觉中角点检测算法研究[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2024, 32(1): 217-225.SHANG S, CAO J R, WANG M, et al. Research on corner detection algorithms in machine vision[J]. Computer Measurement & Control, 2024, 32(1): 217-225. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 张慧慧. 抚顺西露天矿大变形滑坡的多源协同监测方法研究[D]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2019.ZHANG H H. Research on the multi-source collaborative monitoring method for the large deformation landslide in Fushun west open-pit mine[D]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] LOWE D G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the Seventh IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Kerkyra, Greece: IEEE, 1999: 1150-1157. [29] BAY H, TUYTELAARS T, VAN GOOL L. SURF: Speeded up robust features[C]//LEONARDIS A, BISCHOF H, PINZ A, et al. Computer vision-ECCV 2006. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2006: 404-417. [30] MOREL J M, YU G S. ASIFT: A new framework for fully affine invariant image comparison[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2009, 2(2): 438-469. doi: 10.1137/080732730 [31] LIU H C, HONG T H, HERMAN M, et al. Accuracy vs efficiency trade-offs in optical flow algorithms[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 1998, 72(3): 271-286. doi: 10.1006/cviu.1998.0675 [32] LUCAS B D, KANADE T. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 7th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence: Volume 2 (IJCAI'81). San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc, 1981: 674-679. [33] HORN B K P, SCHUNCK B G. Determining optical flow[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 1981, 17(1/3): 181-203. [34] 窦杰, 向子林, 许强, 等. 机器学习在滑坡智能防灾减灾中的应用与发展趋势[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(5): 1657-1674.DOU J, XIANG Z L, XU Q, et al. Application and development trend of machine learning in landslide intelligent disaster prevention and mitigation[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(5): 1657-1674. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] CORTES C, VAPNIK V. Support-vector networks[J]. Machine Learning, 1995, 20(3): 273-297. doi: 10.1023/A:1022627411411 [36] SMOLA A J, SCHÖLKOPF B. A tutorial on support vector regression[J]. Statistics and Computing, 2004, 14(3): 199-222. doi: 10.1023/B:STCO.0000035301.49549.88 [37] ZHOU C, YIN K L, CAO Y, et al. Application of time series analysis and PSO-SVM model in predicting the Bazimen landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 204: 108-120. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.02.009 [38] MIAO F S, WU Y P, XIE Y H, et al. Prediction of landslide displacement with step-like behavior based on multialgorithm optimization and a support vector regression model[J]. Landslides, 2018, 15(3): 475-488. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0883-y [39] ZHAO J J, LI D Y, ZHOU J, et al. Performance evaluation of rock fragmentation prediction based on RF-BOA, AdaBoost-BOA, GBoost-BOA, and ERT-BOA hybrid models[J]. Deep Underground Science and Engineering, 2025, 4(1): 3-17. doi: 10.1002/dug2.12089 [40] VAN DEN BERGH F, ENGELBRECHT A P. A study of particle swarm optimization particle trajectories[J]. Information Sciences, 2006, 176(8): 937-971. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2005.02.003 [41] SUN C M, XU R J, WANG C, et al. Coal rock image recognition method based on improved CLBP and receptive field theory[J]. Deep Underground Science and Engineering, 2022, 1(2): 165-173. doi: 10.1002/dug2.12023 -




 下载:
下载: