A self-attention enhanced generative adversarial network approach for three-dimensional reservoir modeling
-
摘要:
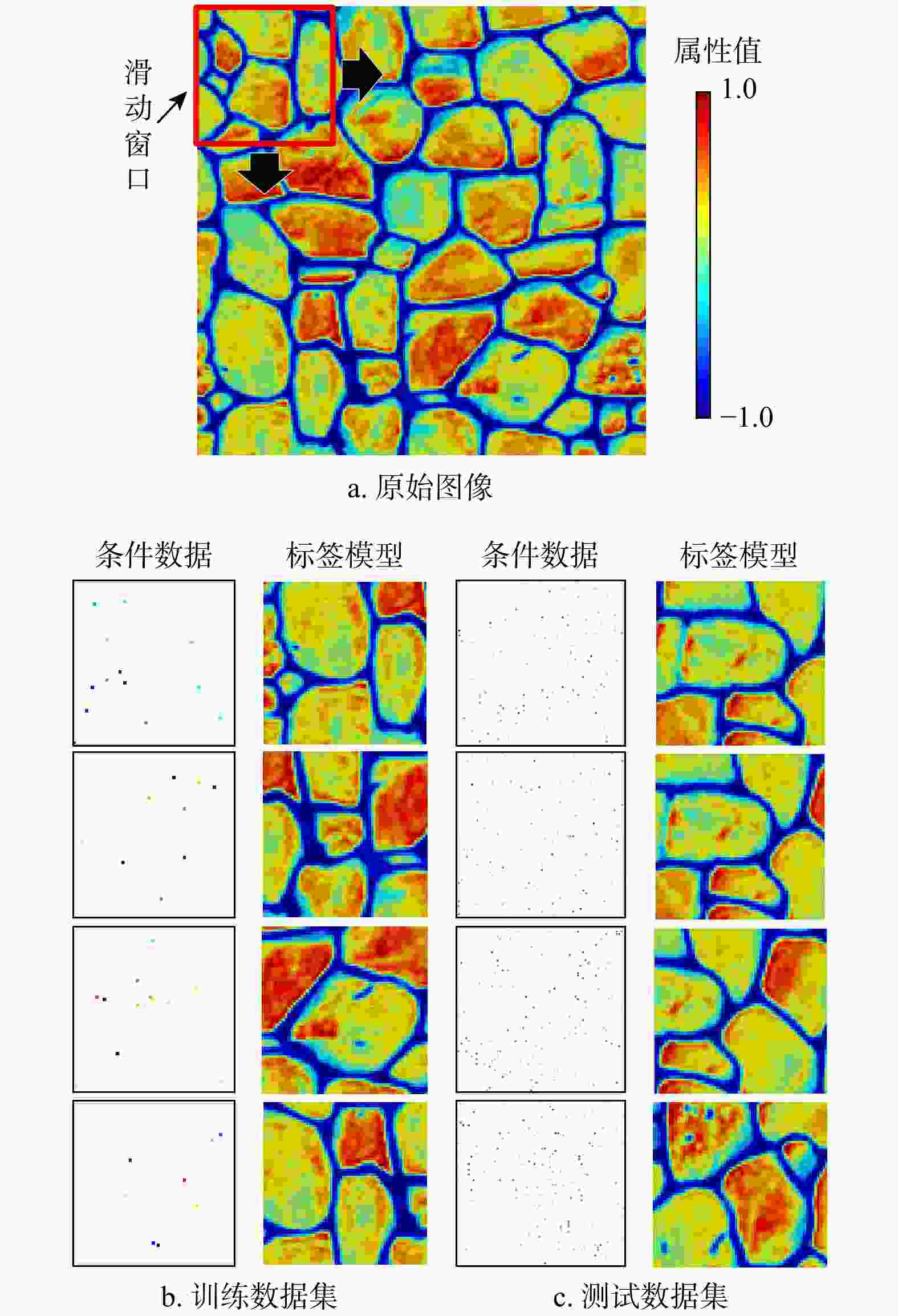
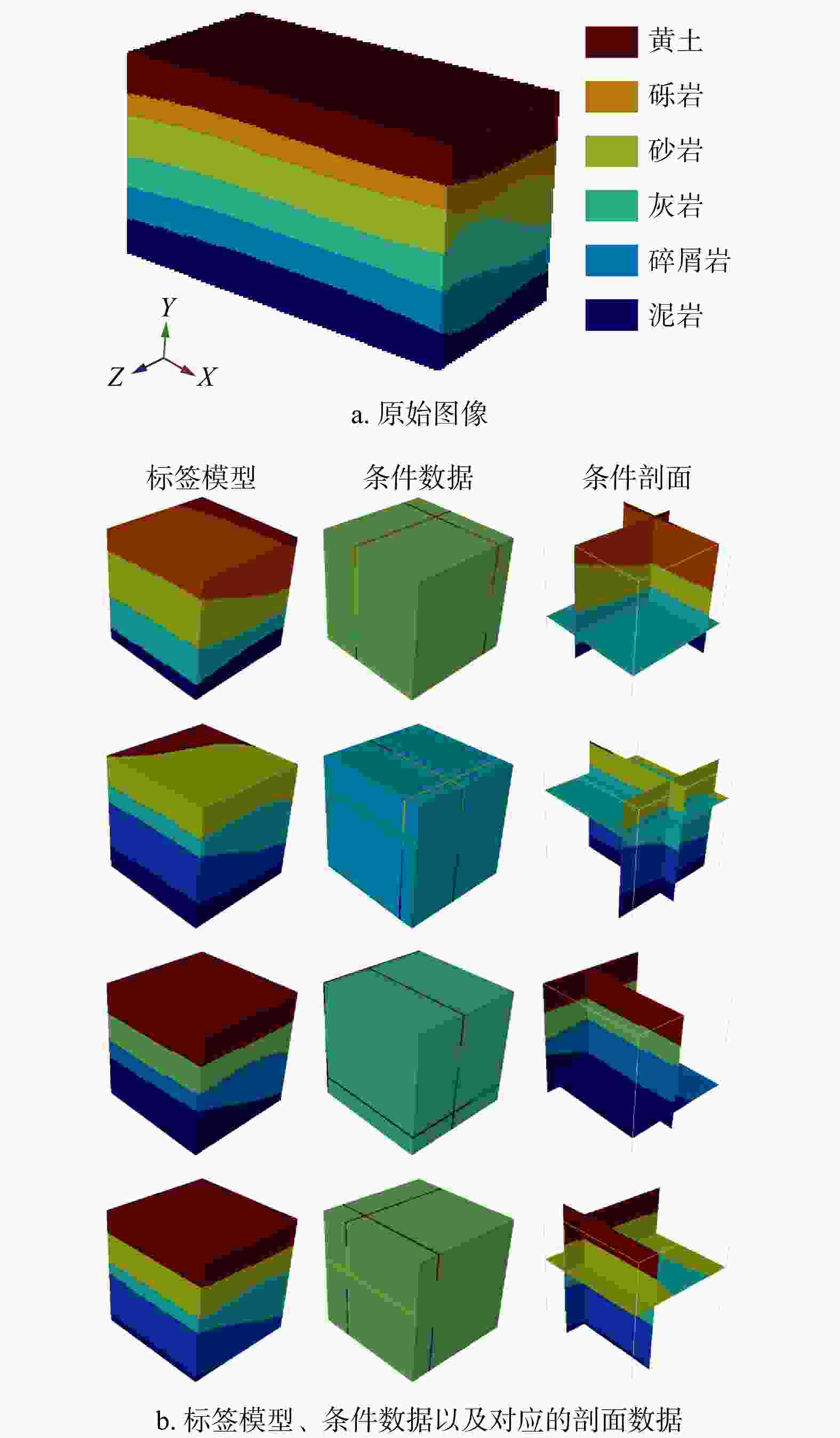
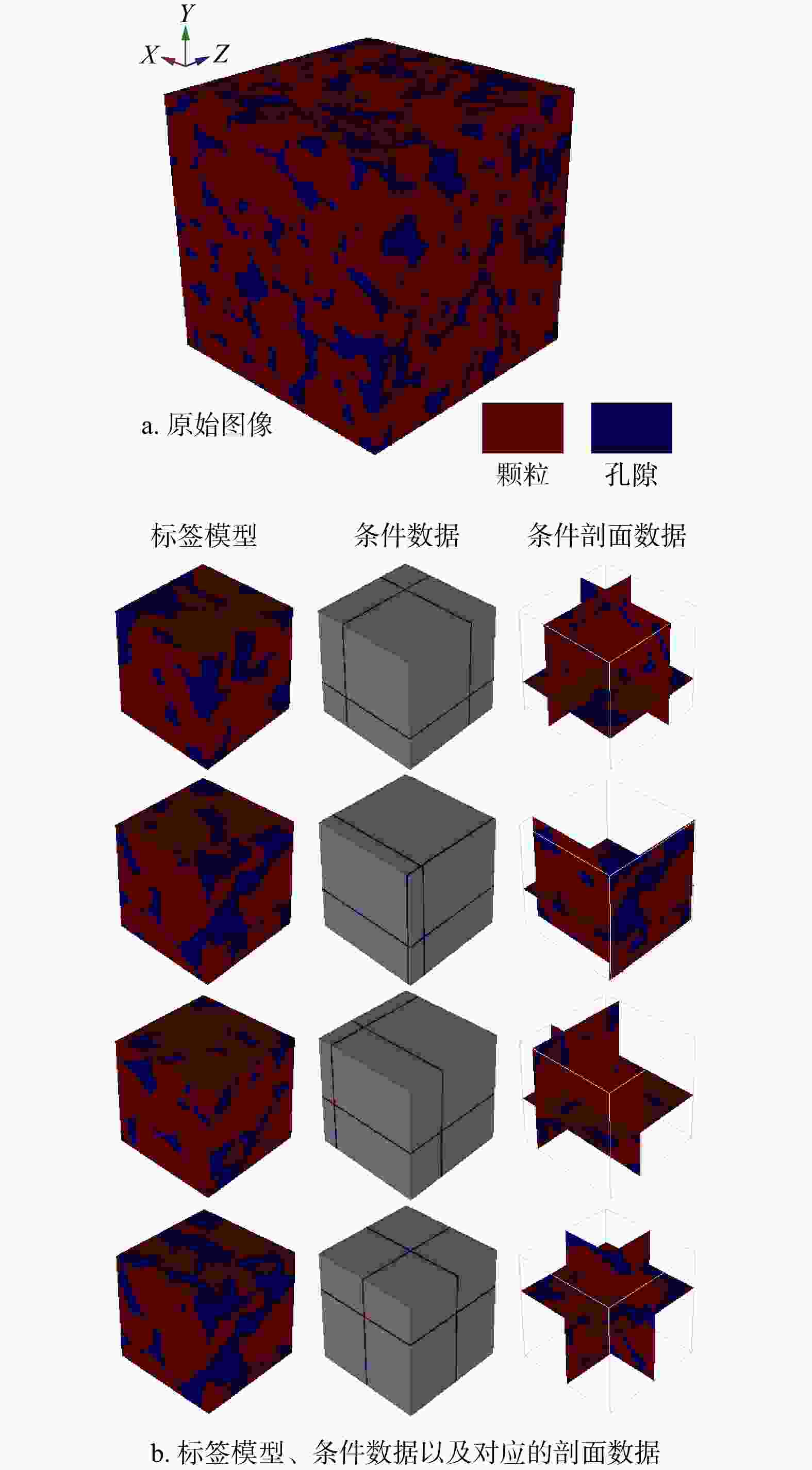
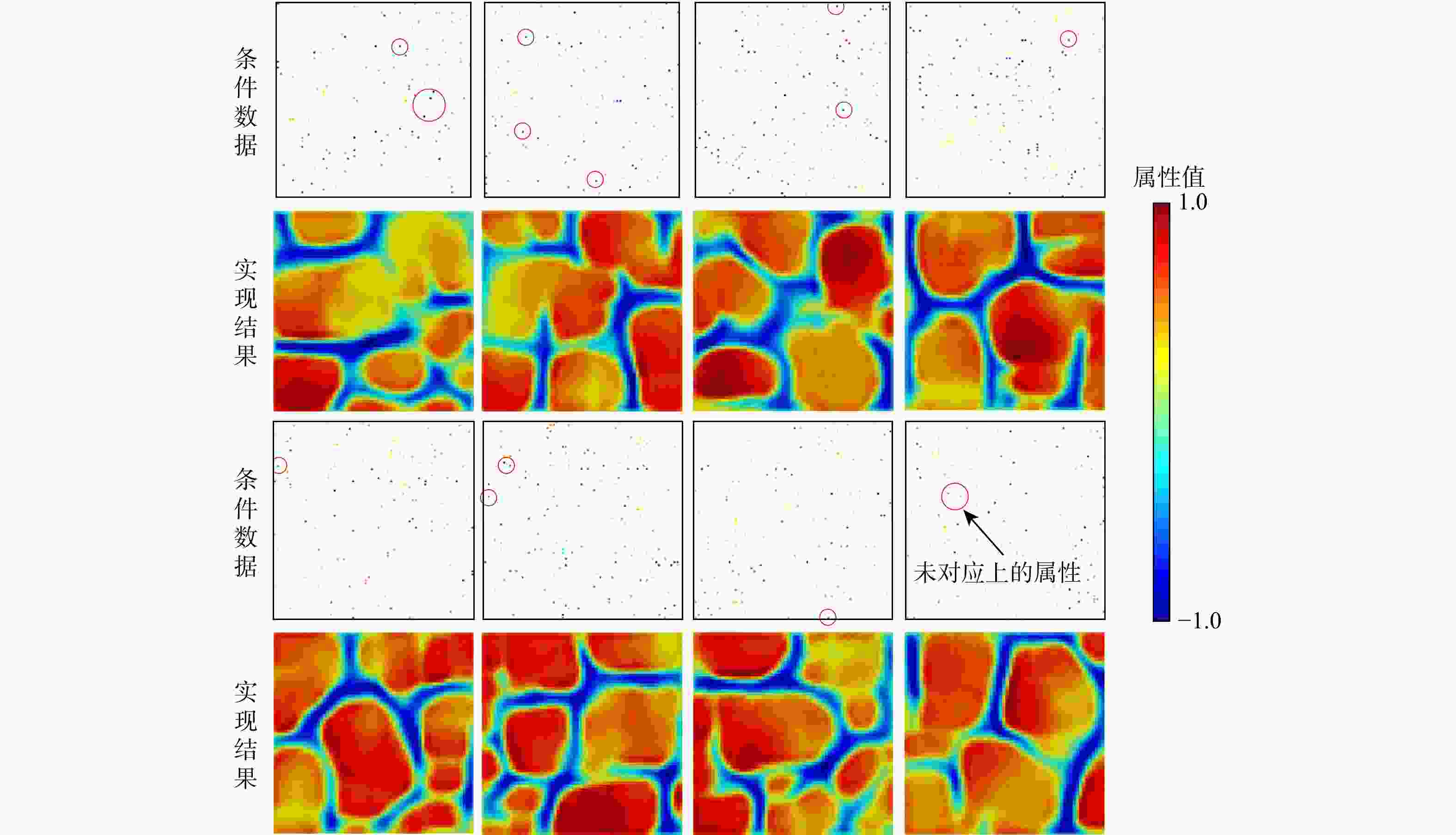
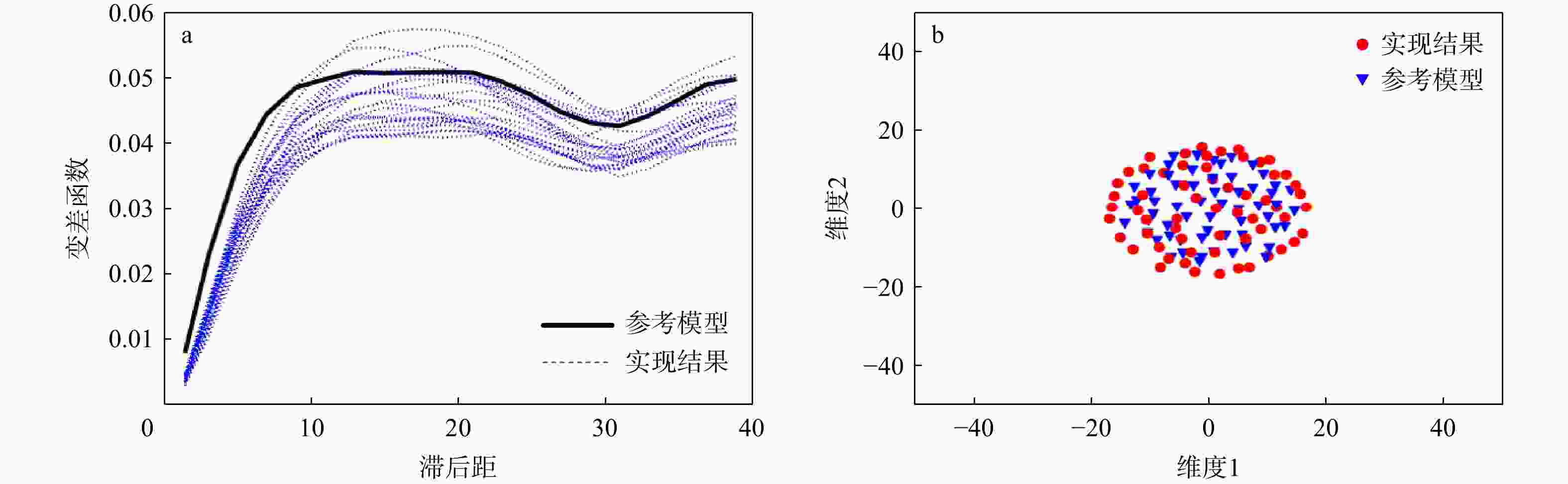
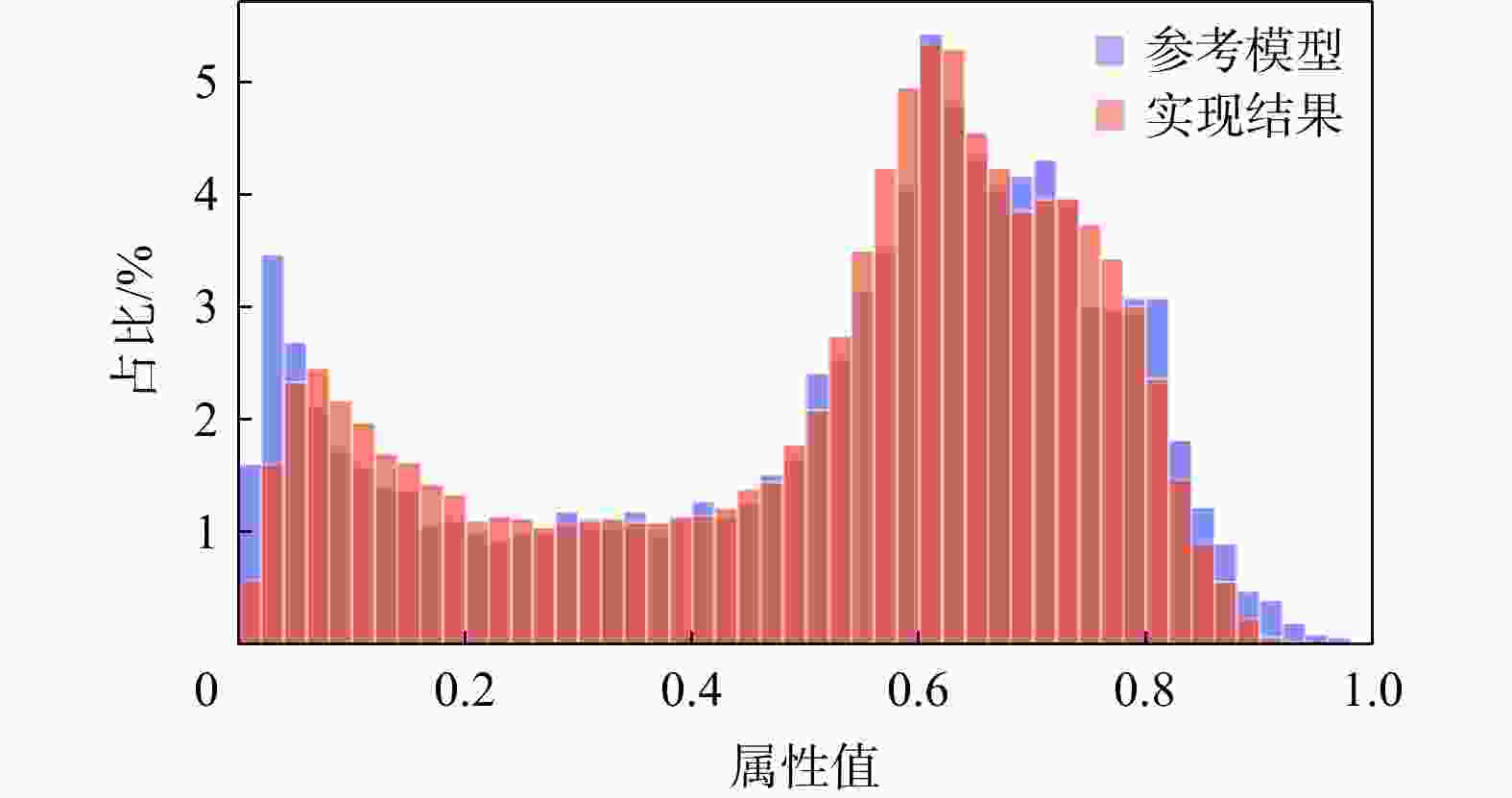
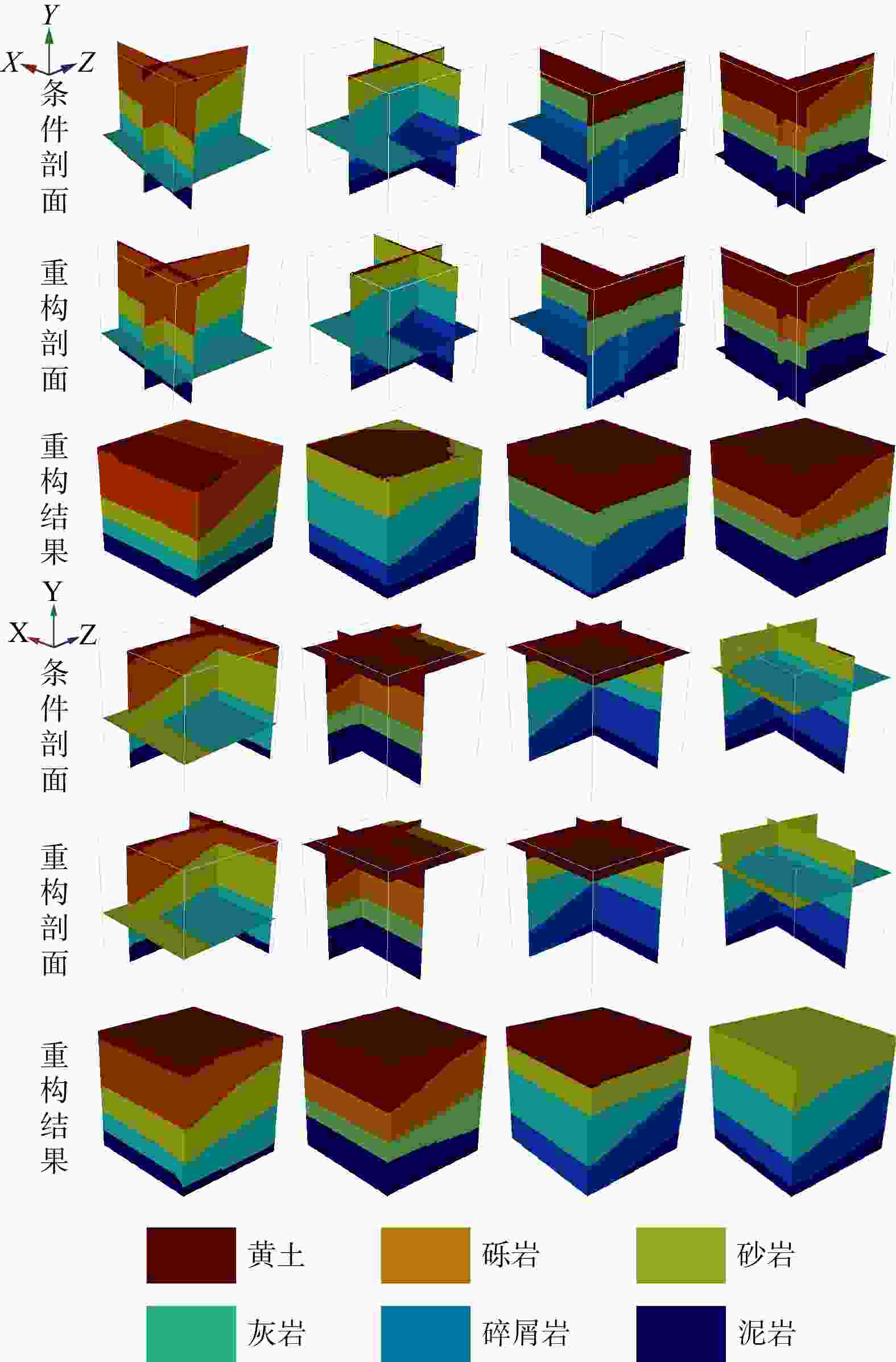
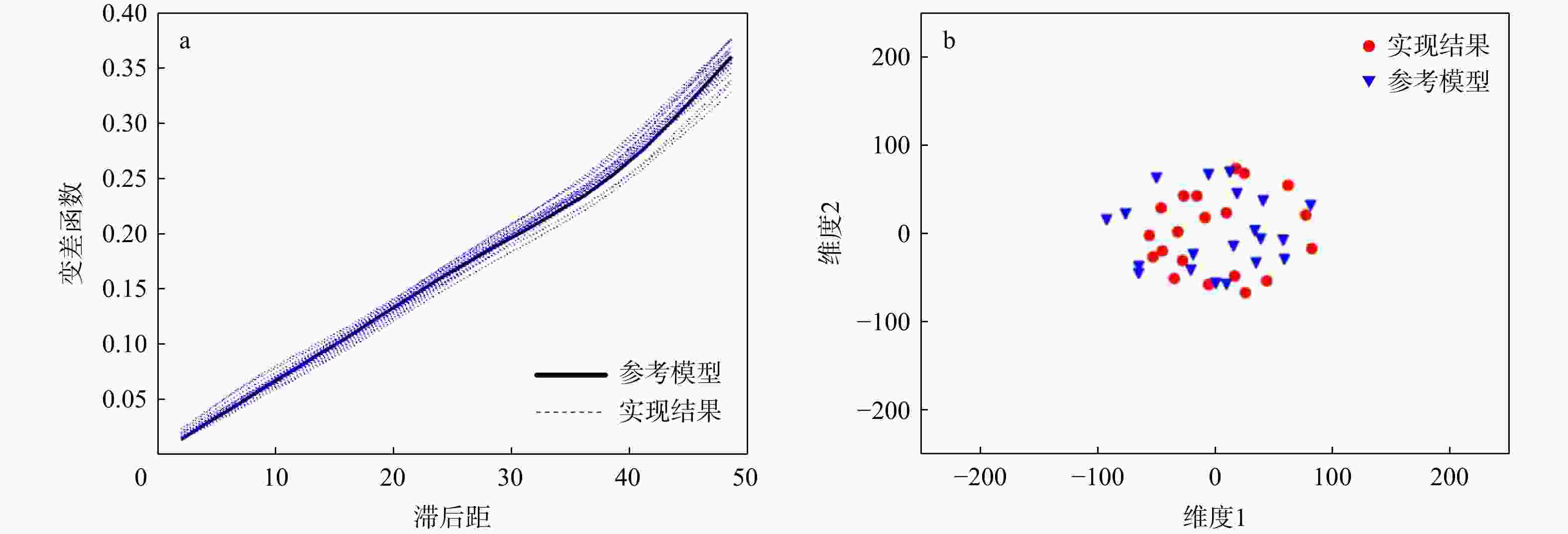
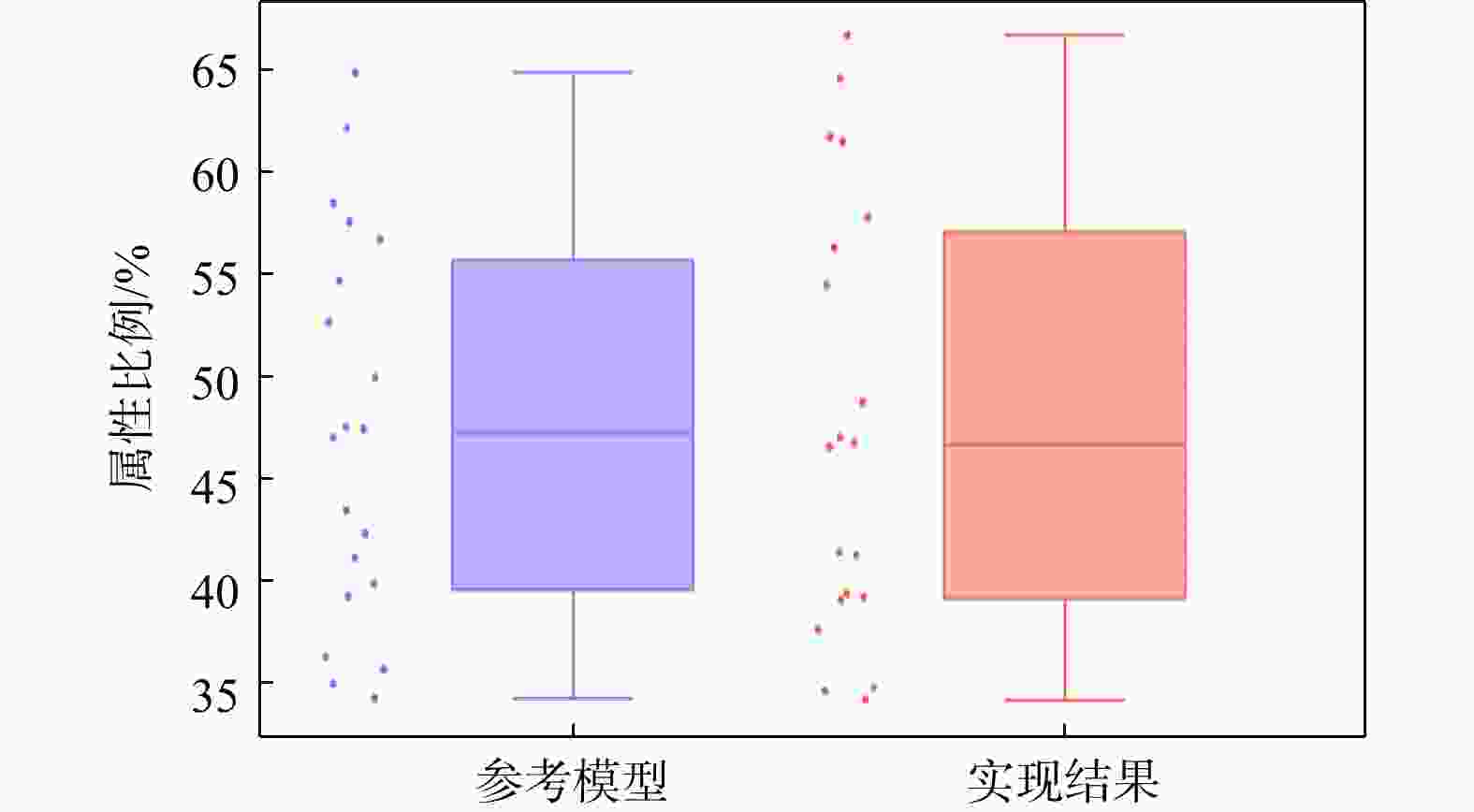
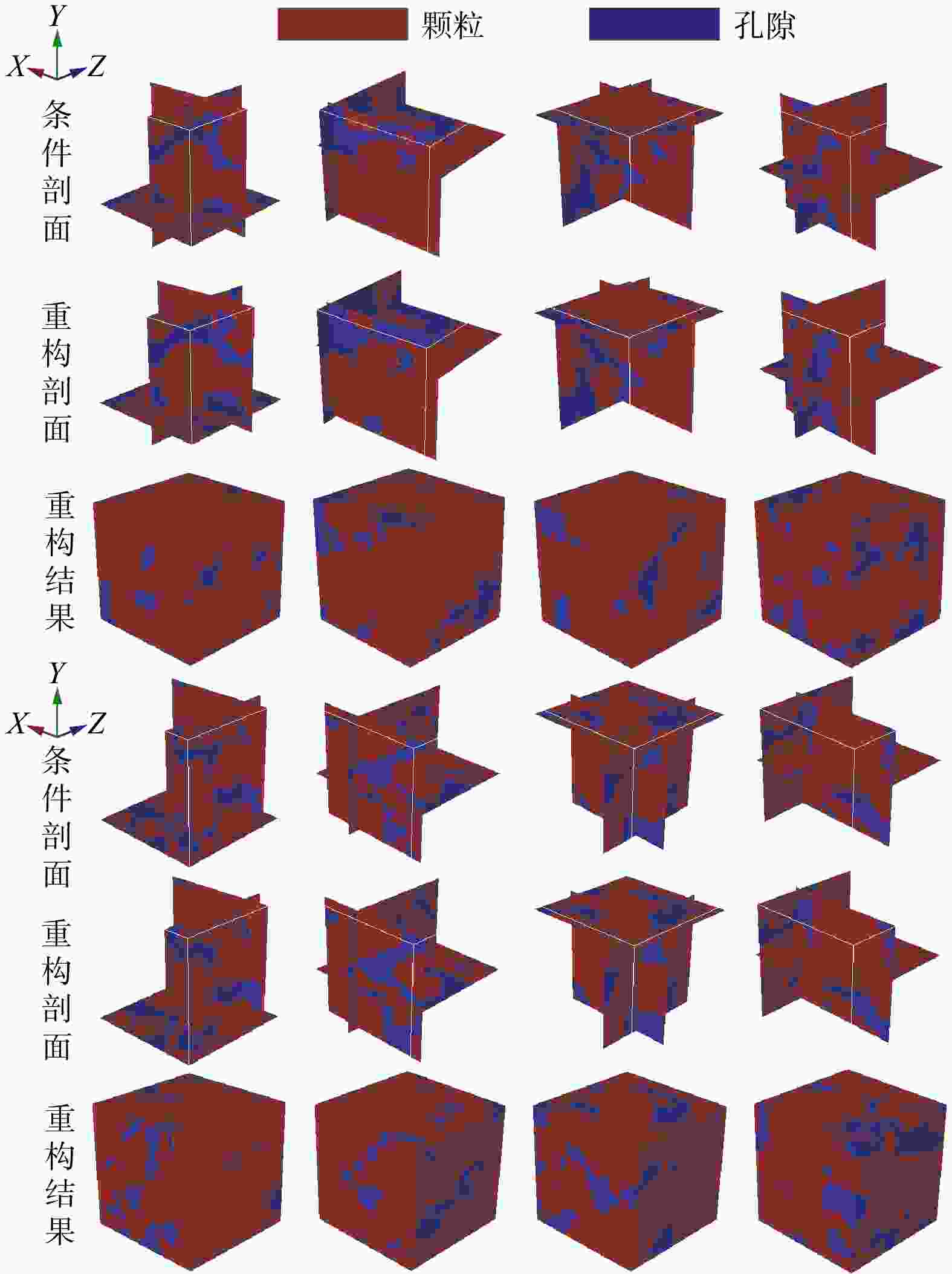
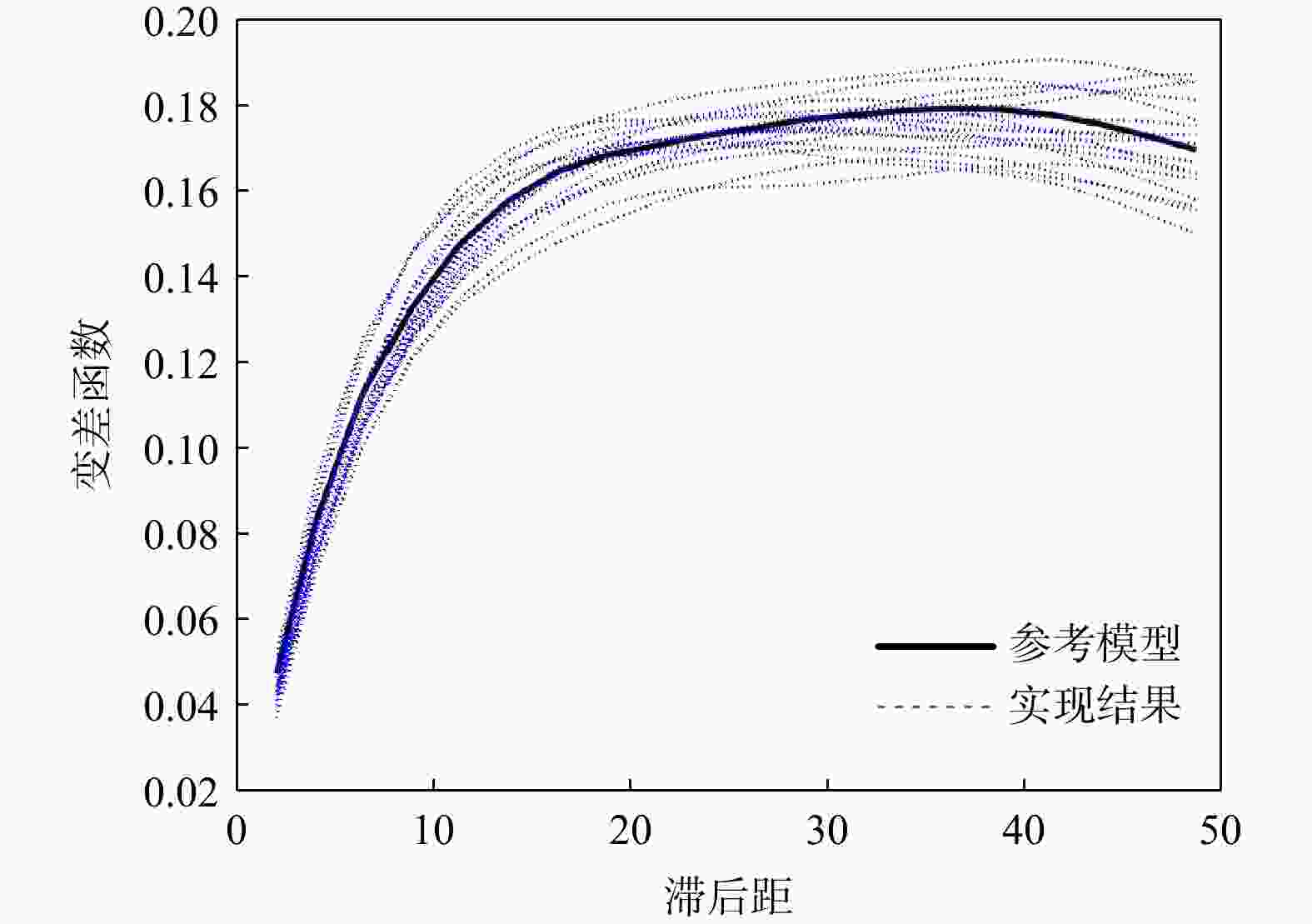
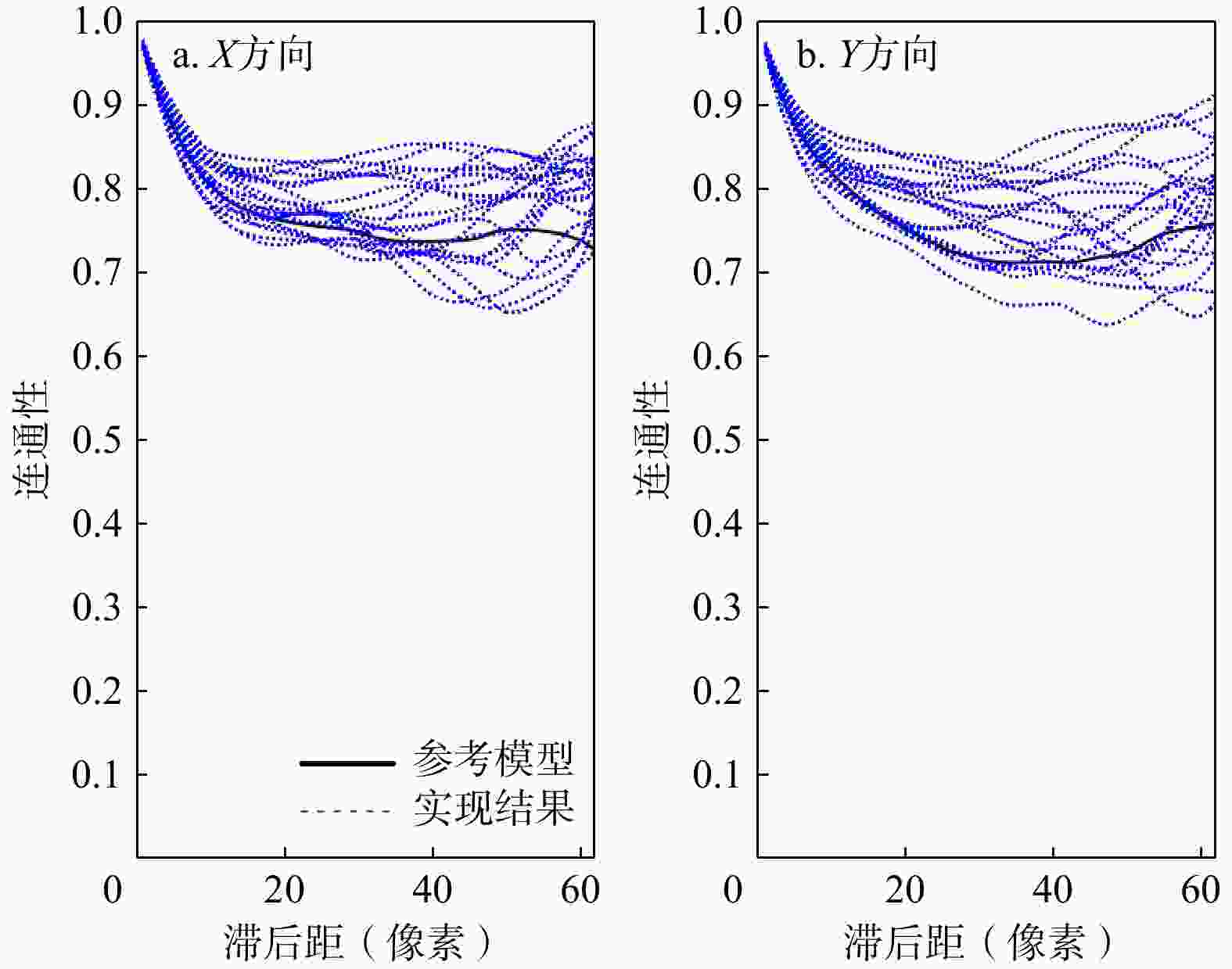
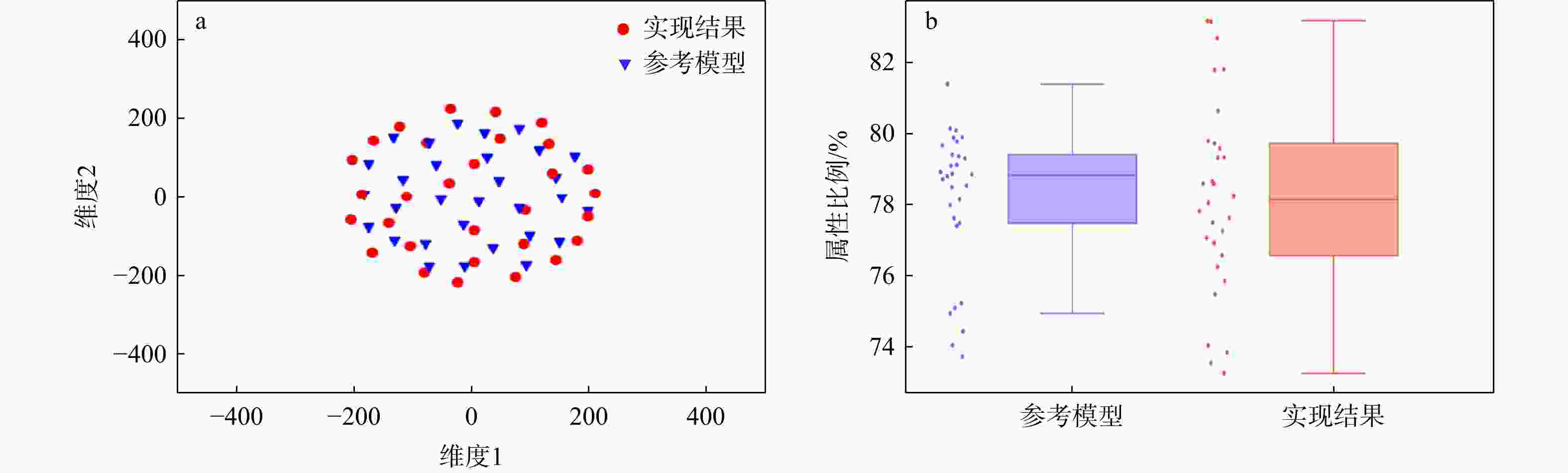
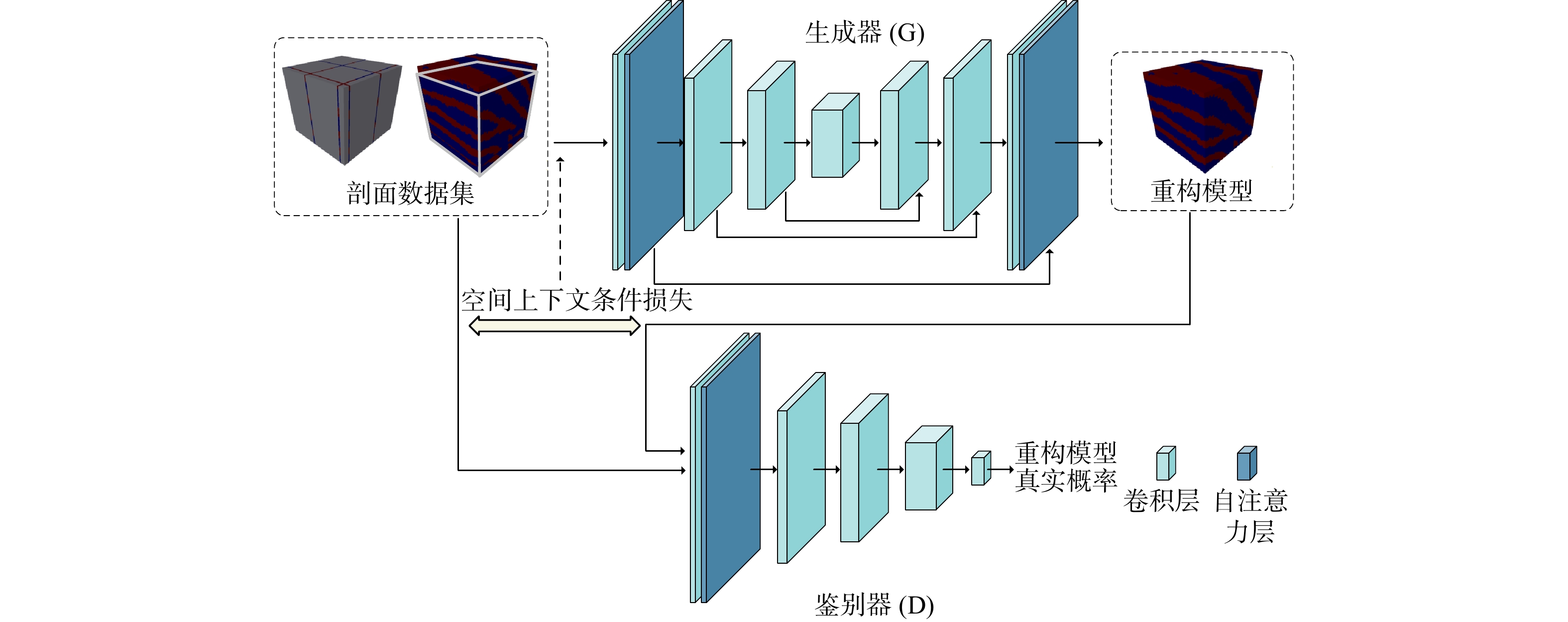
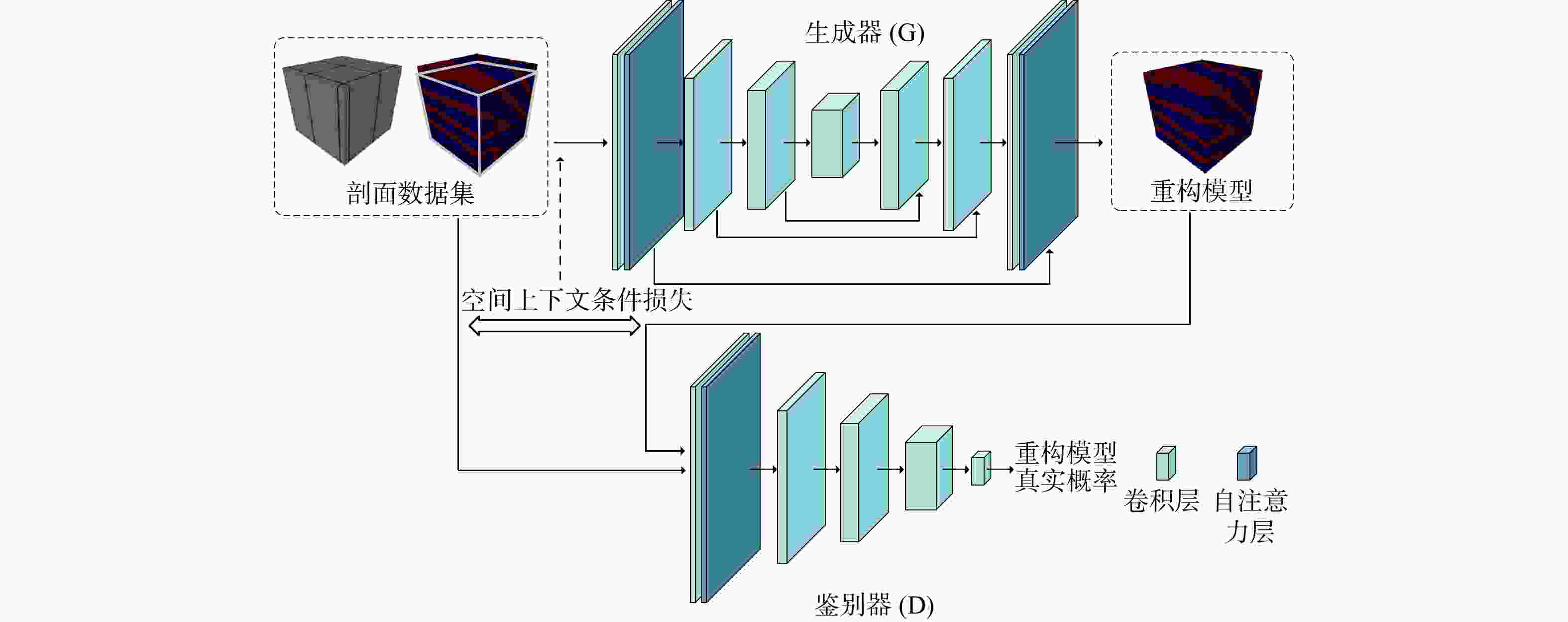
三维储层建模技术可实现储层空间异质结构的自动表征,然而部分油田开采难度大、开发成本高致使油田井距大、钻井资料少,如何根据稀疏有限的可用资料指导油气储层三维建模,一直是油气开发工作的难点。本研究提出了一种基于自注意力机制生成对抗网络的三维储层建模方法,引入具有丰富空间结构信息的地质剖面或钻孔作为条件约束数据,使用U-Net网络结构结合自注意力机制提取关键结构特征,设计空间上下文条件损失函数,以进一步约束重建过程,使得重构结果的条件分布更接近于真实数据的条件分布。多组三维地层结构及复杂砂岩孔隙建模实验结果表明,本研究提出的三维储层建模方法能够再现地质空间结构特征,且符合参考模型的条件数据分布,重构准确率达90%。本研究所提出的方法,成功捕捉了那些对于传统卷积层来说难以识别的远距离依赖特征,克服了由条件数据稀疏性引起的潜在问题,模拟结果可反映地质随机性,能够应用于多种储层地质结构的高效准确重建工作中。
Abstract:Objective Three-dimensional reservoir modeling technology can automatically characterize the spatial heterogeneous structure of the reservoir. However, in some oilfields, the high exploitation difficulty and development cost result in large well spacing and limited drilling data.The three-dimensional modeling of oil and gas reservoirs based on sparse and limited available data has always been a challenge in oil and gas development.
Methods Therefore, this study proposed a three-dimensional reservoir modeling method based on the self-attention mechanism and generative adversarial network. Geological profiles or boreholes with rich spatial structure information were introduced as conditional constraint data. The U-Net network structure combined with the self-attention mechanism was used to extract key structural features. A spatial context conditional loss function was designed to further constrain the reconstruction process, so that the conditional distribution of the reconstructed result was closer to that of the real data.
Results The results of multiple sets of three-dimensional reservoir structure and complex sandstone pore modeling experiments showed that the three-dimensional reservoir modeling method proposed in this study can reproduce the geological spatial structure features and is consistent with the conditional data distribution of the reference model, with a reconstruction accuracy of 90%.
Conclusions The method proposed in this study successfully captures those long-distance dependent features that are difficult to identify by traditional convolutional layers. It overcomes the potential problems caused by the sparse conditional data and the simulation results can reflect geological randomness. It can be applied to the efficient and accurate reconstruction of various reservoir geological structures.
-
表 1 SAGAN网络超参数设置
Table 1. Hyper-parameter configuration of SAGAN
训练数据 石墙结构模型 地层结构模型 砂岩结构模型 总训练次数 200 200 200 批训练数量 16 8 8 生成器:卷积层数、
卷积核大小、步长6, 4×4, 2 7, 4×4×4, 2 7, 4×4×4, 2 鉴别器:卷积层数、
卷积核大小、步长5, 4×4, 2 5, 4×4×4, 2 5, 4×4×4, 2 学习率(生成器、鉴别器) 4×10−4, 1×10−4 4×10−4, 1×10−4 4×10−4, 1×10−4 空间上下文条件损失权重系数 500 100 100 优化器类型(生成器、鉴别器) RMSprop -
[1] 曹砚锋, 李汉兴, 黄辉, 等. 海上油田高效开发钻完井关键技术研究新进展[J]. 中国海上油气, 2022, 34(6): 124-134.CAO Y F, LI H X, HUANG H, et al. Research progress on drilling and completion technology for efficient development of offshore oilfields[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2022, 34(6): 124-134. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 孙福街. 中国海上油田高效开发与提高采收率技术现状及展望[J]. 中国海上油气, 2023, 35(5): 91-99.SUN F J. Status and prospects of efficient development and EOR technologies in China offshore oilfields[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2023, 35(5): 91-99. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 唐骥, 蒋潇, 姜雪莲, 等. 矿体三维可视化建模技术在成矿模式分析中的应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(5): 273-284.TANG J, JIANG X, JIANG X L, et al. Application of three-dimensional visualization modeling technology of ore bodies in metallogenic mode analysis[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(5): 273-284. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] CHEN X P, LI S G, ZHANG J, et al. 3D geomechanical modeling for an extra deep fractured carbonate reservoir, Northwest China[C]//Anon. SPE Asia Pacific Oil & Gas Conference and Exhibition. [S. 1. ]: [S. n. ], 2020: SPE-202334-MS. [5] SOLEIMANI M, JODEIRI SHOKRI B. 3D static reservoir modeling by geostatistical techniques used for reservoir characterization and data integration[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 74(2): 1403-1414. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4130-3 [6] 林良俊, 李亚民, 葛伟亚, 等. 中国城市地质调查总体构想与关键理论技术[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(6): 1086-1101. doi: 10.12029/gc20170604LIN L J, LI Y M, GE W Y, et al. General ideas for urban geological survey in China and key theory and techniques[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(6): 1086-1101. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12029/gc20170604 [7] 李德仁, 龚健雅, 邵振峰. 从数字地球到智慧地球[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2010, 35(2): 127-132.LI D R, GONG J Y, SHAO Z F. From digital Earth to smart Earth[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2010, 35(2): 127-132. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] CUI Z S, CHEN Q Y, LIU G, et al. Hybrid parallel framework for multiple-point geostatistics on Tianhe-2: A robust solution for large-scale simulation[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2021, 157: 104923. [9] 吴冲龙, 何珍文, 翁正平, 等. 地质数据三维可视化的属性、分类和关键技术[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(5): 642-649. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.05.003WU C L, HE Z W, WENG Z P, et al. Property, classification and key technologies of three-dimensional geological data visualization[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(5): 642-649. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.05.003 [10] CHEN Q Y, LIU G, MA X G, et al. 3D stochastic modeling framework for Quaternary sediments using multiple-point statistics: A case study in Minjiang Estuary area, Southeast China[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2020, 136: 104404. [11] GUARDIANO F B, SRIVASTAVA R M. Multivariate geostatistics: Beyond bivariate moments[M]. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, 1993: 133-144. [12] COMUNIAN A, GIUDICI M, LANDONI L, et al. Improving Bowen-ratio estimates of evaporation using a rejection criterion and multiple-point statistics[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 563: 43-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.05.050 [13] FENG W J, WU S H, YIN Y S, et al. A training image evaluation and selection method based on minimum data event distance for multiple-point geostatistics[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2017, 104: 35-53. [14] ARPAT G B, CAERS J. Conditional simulation with patterns[J]. Mathematical Geology, 2007, 39(2): 177-203. doi: 10.1007/s11004-006-9075-3 [15] BAI T, TAHMASEBI P. Hybrid geological modeling: Combining machine learning and multiple-point statistics[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2020, 142: 104519. [16] 高小洋, 何文祥, 胡勇. 基于深度生成模型的河道砂建模方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 94-104.GAO X Y, HE W X, HU Y. A modeling method of channel sand based on deep generation models[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 94-104. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] SONG S H, MUKERJI T, HOU J G. Bridging the gap between geophysics and geology with generative adversarial networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60: 5902411. [18] LOPEZ-ALVIS J, LALOY E, NGUYEN F, et al. Deep generative models in inversion: The impact of the generator's nonlinearity and development of a new approach based on a variational autoencoder[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2021, 152: 104762. [19] CUI Z S, CHEN Q Y, LIU G. Characterization of subsurface hydrogeological structures with convolutional conditional neural processes on limited training data[J]. Water Resources Research, 2022, 58(12): e2022WR033161. doi: 10.1029/2022WR033161 [20] ZUO R G, XIONG Y H, WANG J, et al. Deep learning and its application in geochemical mapping[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2019, 192: 1-14. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.02.023 [21] JESSELL M, GUO J T, LI Y Q, et al. Into the Noddyverse: A massive data store of 3D geological models for machine learning and inversion applications[J]. Earth System Science Data, 2022, 14(1): 381-392. doi: 10.5194/essd-14-381-2022 [22] TAHMASEBI P, KAMRAVA S, BAI T, et al. Machine learning in geo- and environmental sciences: From small to large scale[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2020, 142: 103619. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2020.103619 [23] GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2020, 63(11): 139-144. doi: 10.1145/3422622 [24] DRAMSCH J S. 70 years of machine learning in geoscience in review[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2020: 1-55. [25] GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO Y, COURVILLE A. Deep learning[M]. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2016. [26] CHEN Q Y, CUI Z S, LIU G, et al. Deep convolutional generative adversarial networks for modeling complex hydrological structures in Monte-Carlo simulation[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, 610: 127970. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127970 [27] CUI Z S, CHEN Q Y, LIU G. A two-stage downscaling hydrological modeling approach via convolutional conditional neural process and geostatistical bias correction[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2023, 620: 129498. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129498 [28] NESVOLD E, MUKERJI T. Simulation of fluvial patterns with GANs trained on a data set of satellite imagery[J]. Water Resources Research, 2021, 57(5): e2019WR025787. doi: 10.1029/2019WR025787 [29] CAO D P, HOU Z Y, LIU Q, et al. Reconstruction of three-dimension digital rock guided by prior information with a combination of InfoGAN and style-based GAN[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 208: 109590. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109590 [30] YANG Z X, CHEN Q Y, CUI Z S, et al. Automatic reconstruction method of 3D geological models based on deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[J]. Computational Geosciences, 2022, 26(5): 1135-1150. doi: 10.1007/s10596-022-10152-8 [31] ZHANG T F, TILKE P, DUPONT E, et al. Generating geologically realistic 3D reservoir facies models using deep learning of sedimentary architecture with generative adversarial networks[J]. Petroleum Science, 2019, 16(3): 541-549. doi: 10.1007/s12182-019-0328-4 [32] LIU Q B, LIU W L, YAO J P, et al. An improved method of reservoir facies modeling based on generative adversarial networks[J]. Energies, 2021, 14(13): 3873. doi: 10.3390/en14133873 [33] FAN W Y, LIU G, CHEN Q Y, et al. Geological model automatic reconstruction based on conditioning Wasserstein generative adversarial network with gradient penalty[J]. Earth Science Informatics, 2023, 16(3): 2825-2843. doi: 10.1007/s12145-023-01012-9 [34] CHEN D J, CHEN Q Y, CUI Z S, et al. SA-VAE: A novel approach for reservoir characterization based on variational auto-encoder and selective attention mechanism[J]. Earth Science Informatics, 2023, 16(4): 3283-3301. doi: 10.1007/s12145-023-01095-4 [35] DU G T, CAO X, LIANG J M, et al. Medical image segmentation based on U-Net: A review[J]. Journal of Imaging Science and Technology, 2020, 64(2): 20508-1-020508-12. [36] ZHANG H, GOODFELLOW I, METAXAS D, et al. Self-attention generative adversarial networks[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. Long Beach: PMLR, 2019: 7354-7363. [37] AZEVEDO L, PANEIRO G, SANTOS A, et al. Generative adversarial network as a stochastic subsurface model reconstruction[J]. Computational Geosciences, 2020, 24(4): 1673-1692. doi: 10.1007/s10596-020-09978-x [38] 周飞燕, 金林鹏, 董军. 卷积神经网络研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2017, 40(6): 1229-1251. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.01229ZHOU F Y, JIN L P, DONG J. Review of convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2017, 40(6): 1229-1251. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2017.01229 [39] GARNELO M D, ROSENBAUM C, MADDISON T, et al. Conditional neural processes[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. [S. 1. ]: [s. n. ], 2018: 1704-1713. [40] WILLIAMS C, FALCK F, DELIGIANNIDIS G, et al. A unified framework for U-Net design and analysis[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2023, 36: 27745-27782. -




 下载:
下载: