Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis of high-fluoride groundwater in the Wanshan Archipelago, Zhuhai, Guangdong Province
-
摘要:
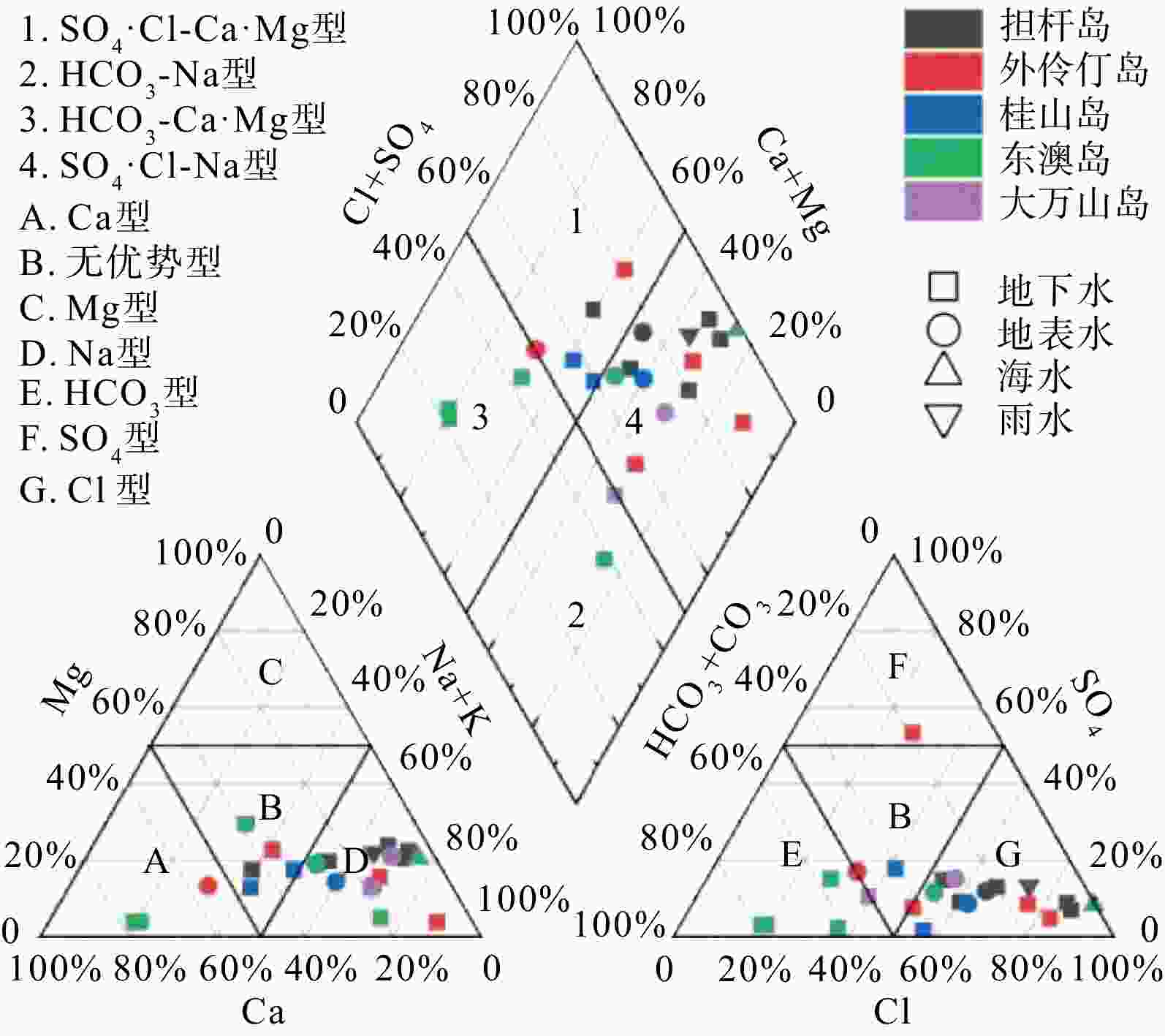
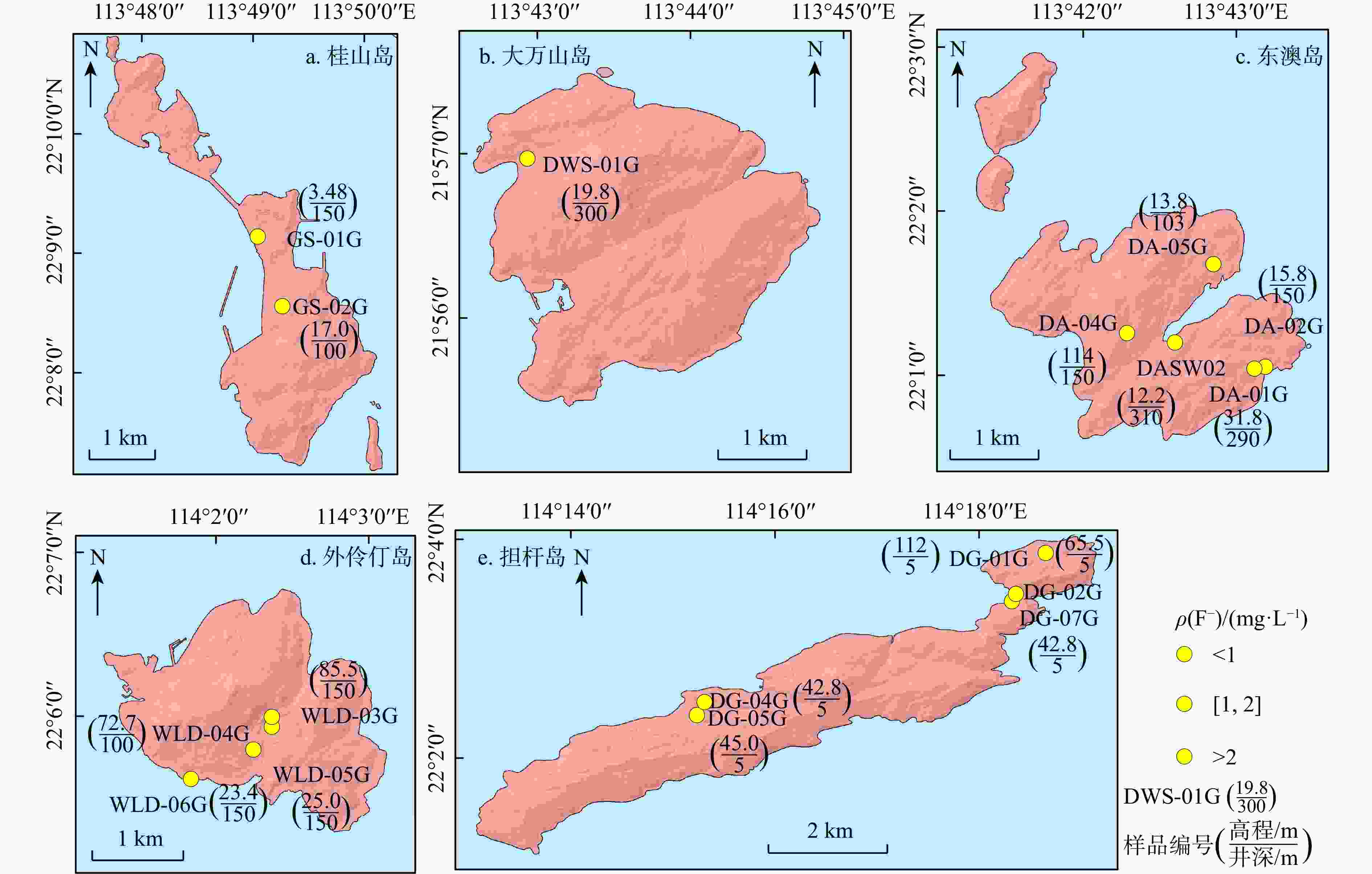
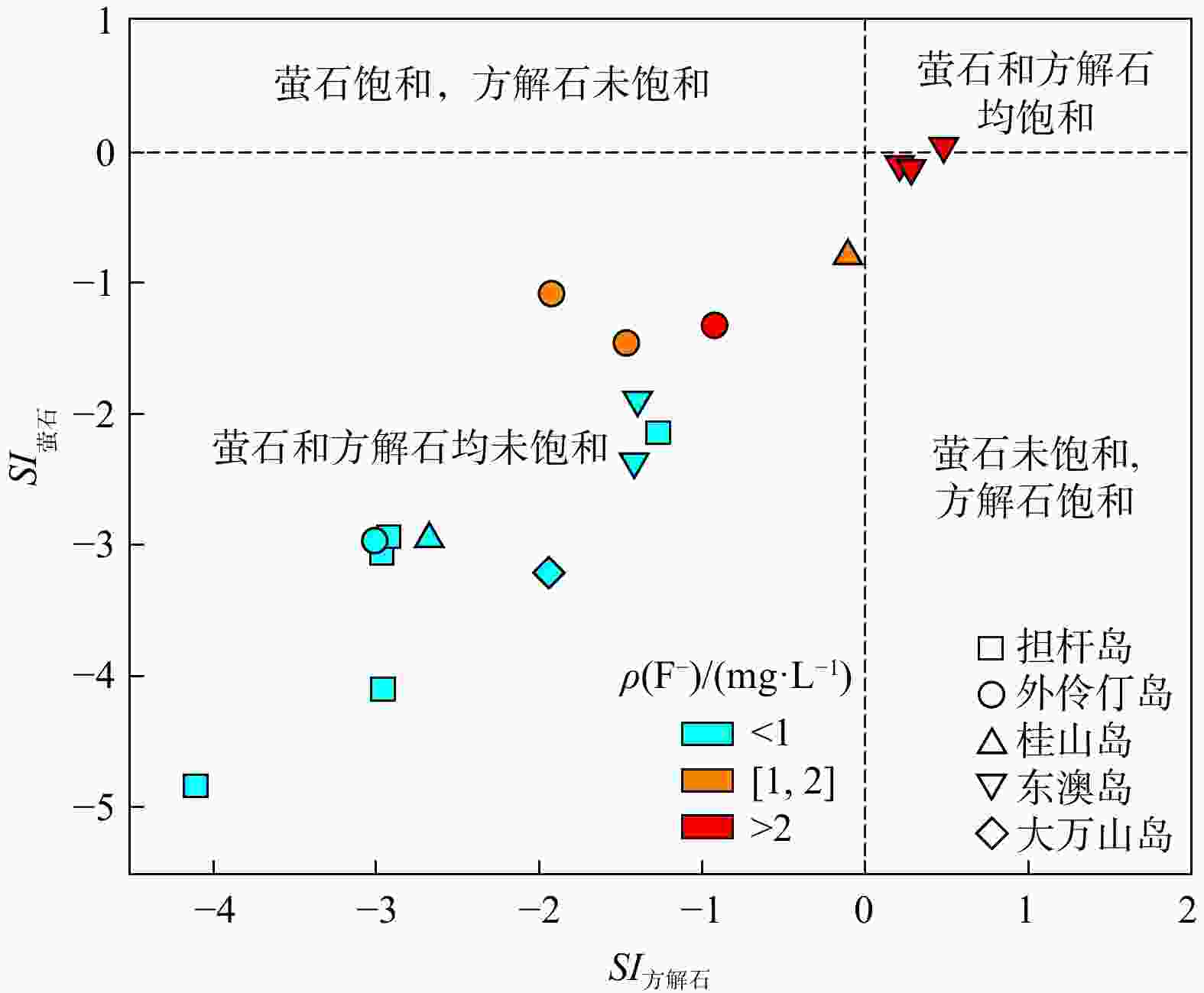
随着全球气候变化和人类活动的影响,地下水资源的质量受到严重威胁,特别是高氟地下水的污染问题,已成为沿海地区亟待解决的环境挑战之一。以广东珠海万山群岛为研究区域,深入探讨了该地区地下水中氟的分布特征及其成因,并分析了地质与水文地质条件对水质的影响。结果表明,万山群岛地区地下水的氟质量浓度范围为0.17~3.22 mg/L,53%的样品含氟量超标,不同岛屿的地下水水化学类型差异显著,氟超标的水样主要集中在东澳岛、外伶仃岛等地,且多出现在深度100~150 m的地下水中。通过矿物溶解、沉淀作用以及水−岩相互作用的分析,发现氟的富集与含水层中的萤石溶解、阳离子交换作用及高pH值环境密切相关。此外,部分地区的海水入侵可能对氟的富集产生了影响。研究成果为进一步理解海岛地区高氟地下水的形成机理提供了重要数据和理论支持,有助于为该地区的地下水资源保护和水质改善提供科学依据。
Abstract:Objective Under the combined impacts of global climate change and human activities, groundwater quality is facing severe threats. The problem of high-fluoride groundwater has emerged as a pressing environmental challenge in coastal regions.
Methods Focusing on the Wanshan Archipelago, Zhuhai, Guangdong Province, this study investigates the distribution characteristics and enrichment mechanisms of fluoride in groundwater, and analyzes the impacts of geological and hydrochemical conditions on water quality.
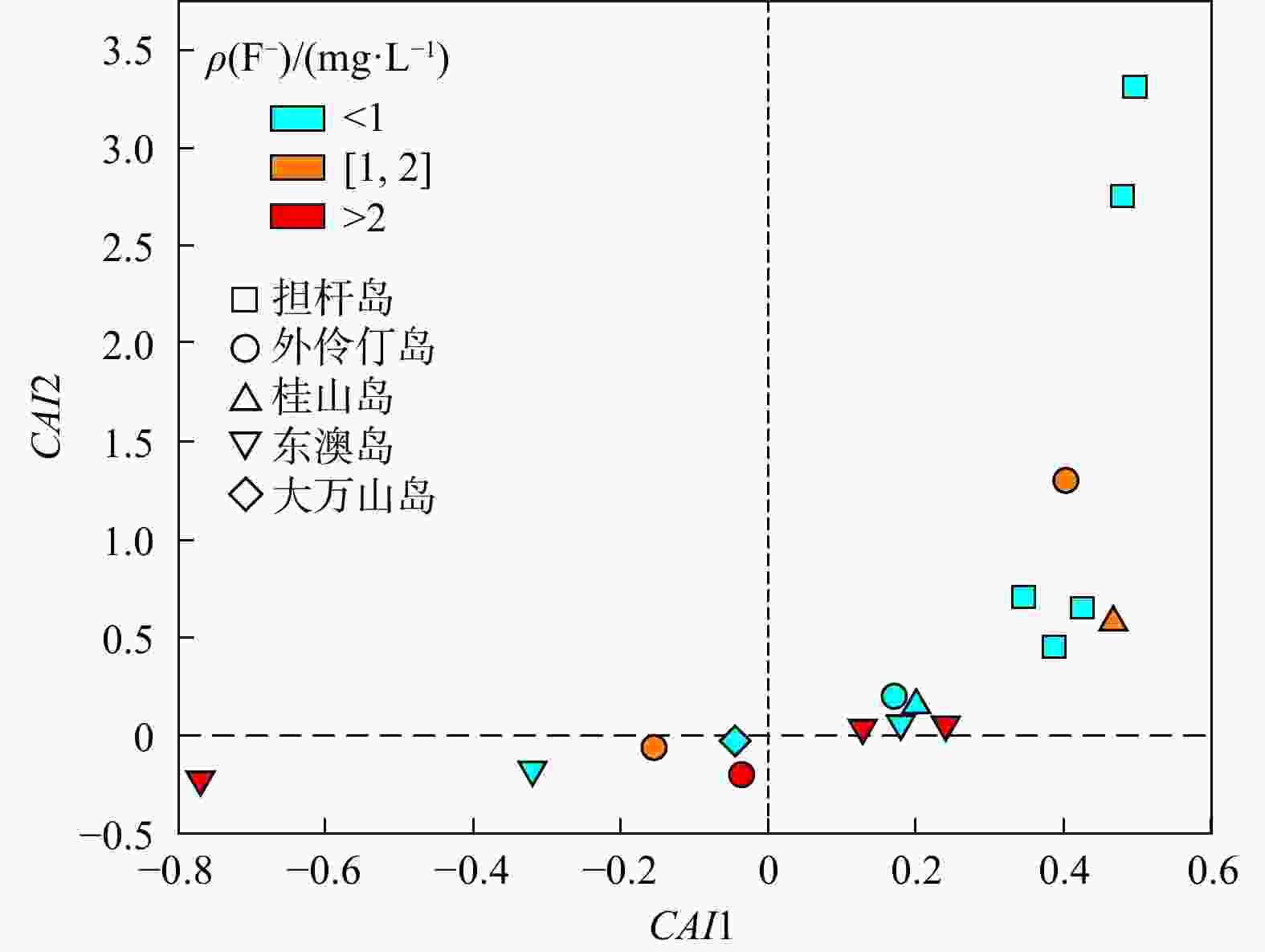
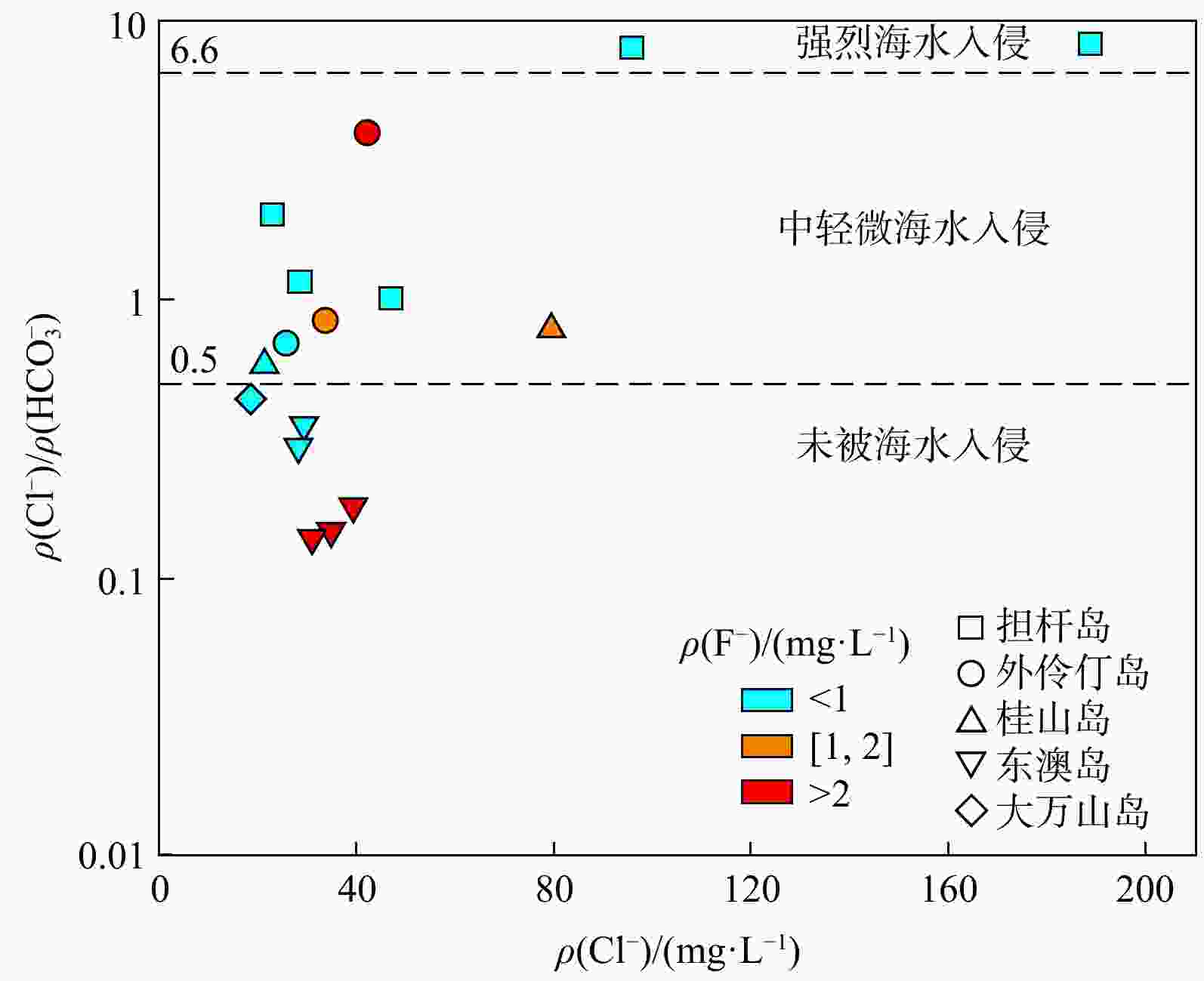
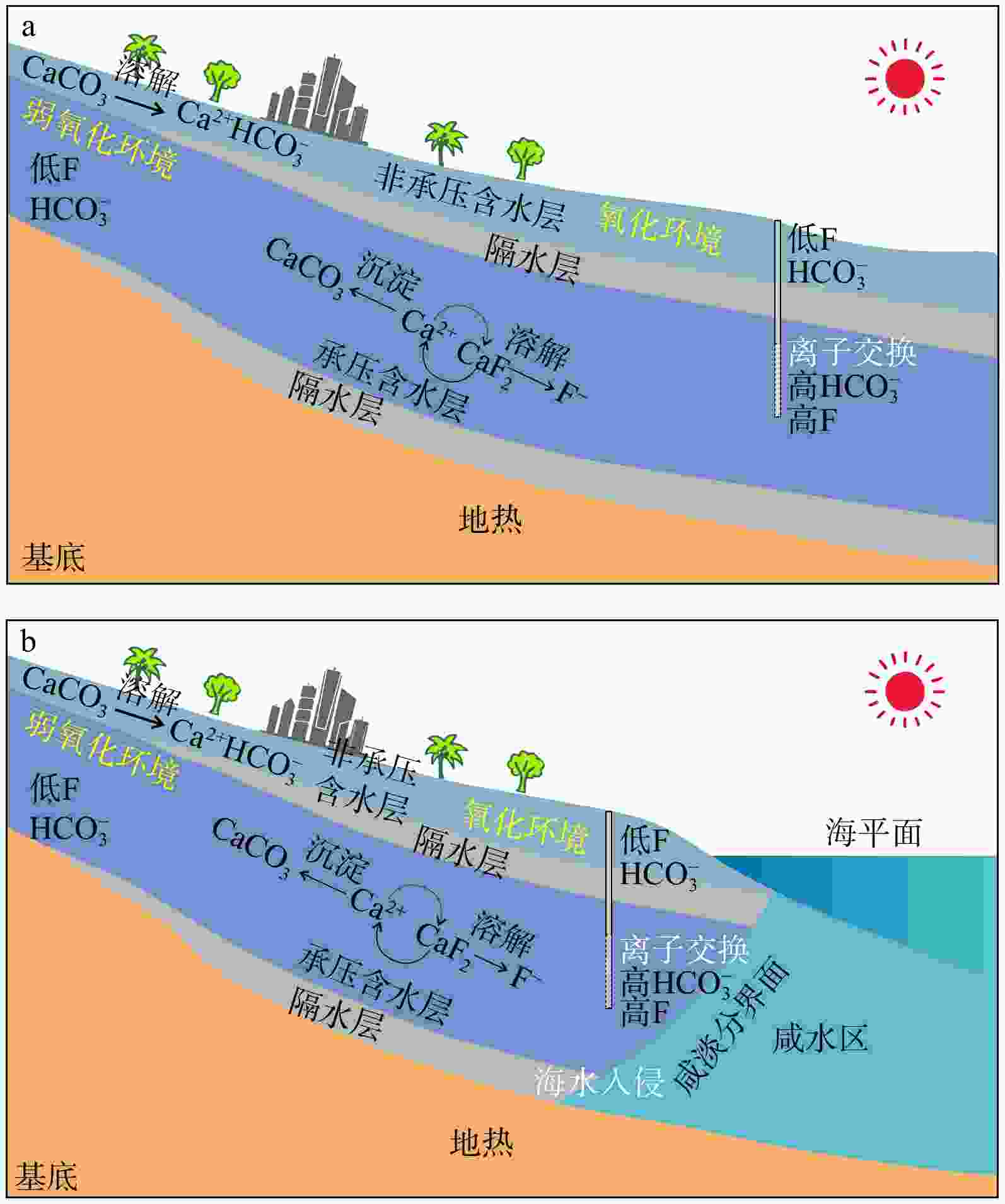
Results The results show that fluoride concentrations in the groundwater of the Wanshan Archipelago range from 0.17 to 3.22 mg/L, with 53% of the samples exceeding the fluoride standard. Significant variations in hydrochemical types exist among different islands. Excessive fluoride concentrations are mainly distributed on islands such as Dong'ao Island and Wailingding Island, predominantly detected in groundwater at depths of 100–150 m. Analysis of mineral dissolution, precipitation, and water-rock interactions indicates that fluoride enrichment is closely associated with fluorite dissolution in aquifers, cation exchange reactions, and alkaline conditions (high pH). Furthermore, seawater intrusion in some regions may also contribute to fluoride enrichment.
Conclusion This study provides crucial data and a theoretical basis for understanding the formation mechanisms of high-fluoride groundwater in island settings, and offers scientific support for the protection and improvement of local groundwater resources.
-
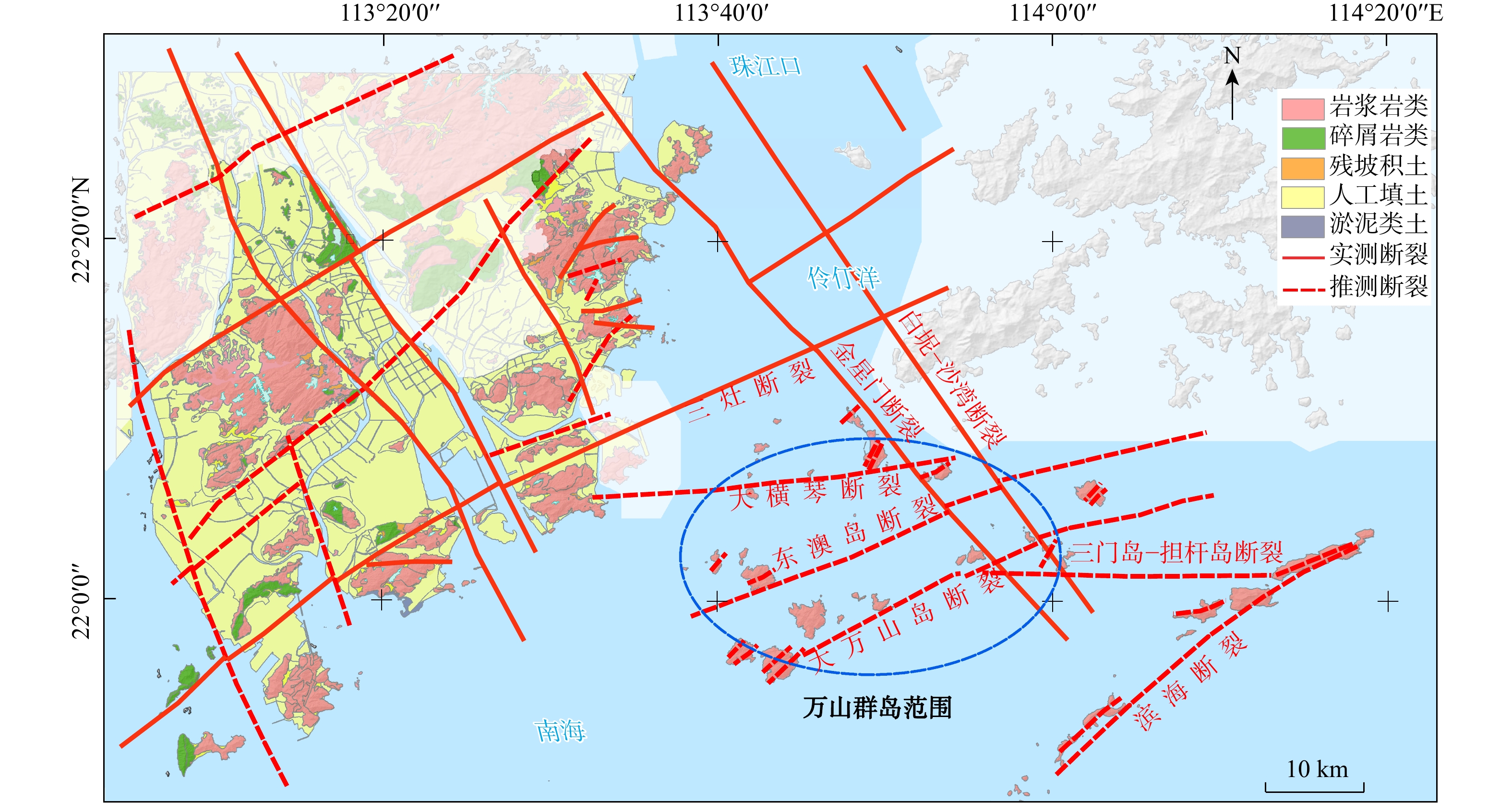
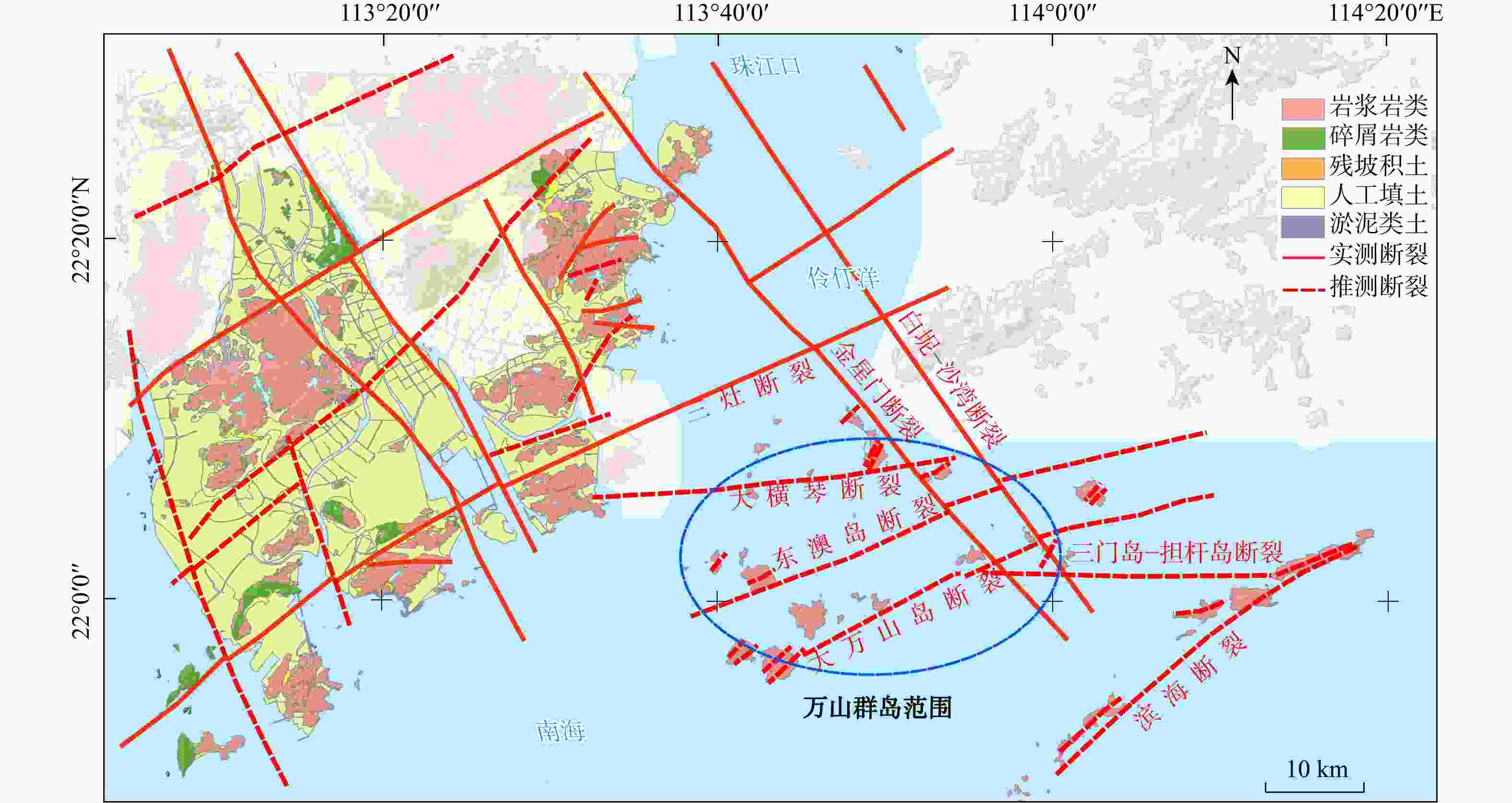
图 1 万山群岛构造纲要图(据1∶5万《珠海区域地质综合调查报告》[42]修编)
Figure 1. Structural outline map of the Wanshan Archipelago
表 1 万山群岛海岛侵入岩单元划分
Table 1. Classification of intrusive rock units in the Wanshan Archipelago
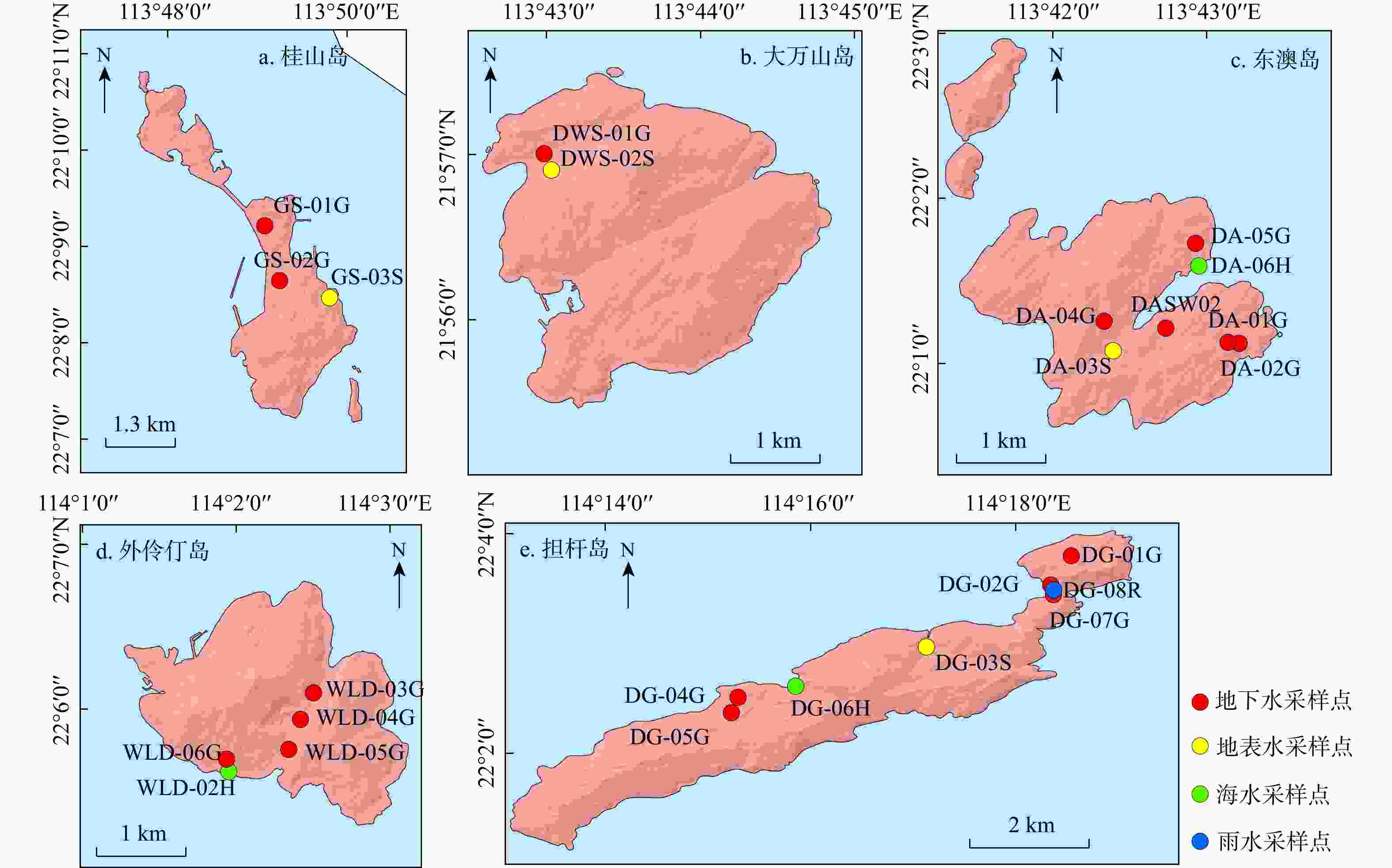
纪 世 阶段期次 代号 岩性 岛屿 白垩纪 晚白垩世 不明 γπK2 花岗斑岩 东澳岛、大万山岛 早白垩世 第二阶段第一次侵入 γK12a 细粒(含斑)黑云母花岗岩 桂山岛 侏罗纪 晚侏罗世 第一阶段第三次侵入 ηγJ31c 中细−中粗粒黑云母二长花岗岩 桂山岛、外伶仃岛、东澳岛、大万山岛、担杆岛 表 2 研究区采样点分布、样品编号、水样类型、经纬度及井深
Table 2. Sampling points distribution, sample numbers, water types, coordinates (latitude/longitude), and well depth in the study area
岛屿 样品编号 水样类型 经度 纬度 井深/m 担杆岛 DG-01G 地下水 114°18' 29.7342 "22°03' 42.5085 "5 DG-02G 地下水(泉) 114°18' 20.4065 "22°03' 27.0176 "5 DG-03S 地表水(水库) 114°17'08.4697" 22°03'00.0888" − DG-04G 地下水(泉水) 114°15' 13.9114 "22°02' 23.8950 "5 DG-05G 地下水 114°15' 18.7394 "22°02' 30.5898 "5 DG-06H 海水 114°15' 52.0525 "22°02' 37.2308 "− DG-07G 地下水 114°18' 20.4644 "22°03' 29.9798 "5 DG-08R 雨水 114°18' 21.0535 "22°03' 28.4943 "− 外伶仃岛 WLD-02H 海水 114°01' 50.1017 "22°05' 39.6276 "− WLD-03G 地下水 114°02' 30.3187 "22°06'05.2956" 150 WLD-04G 地下水 114°02' 22.6905 "22°05' 57.6910 "100 WLD-05G 地下水 114°02' 18.2391 "22°05' 46.6330 "150 WLD-06G 地下水 114°02' 19.2144 "22°05' 51.6610 "150 桂山岛 GS-01G 地下水 113°49'05.9199" 22°09'06.8039" 150 GS-02G 地下水 113°49' 13.7799 "22°08' 38.3458 "100 GS-03S 地表水(水库) 113°49' 42.5353 "22°08' 32.7470 "− 东澳岛 DA-01G 地下水 113°43' 10.7354 "22°01'08.1517" 290 DA-02G 地下水 113°43' 15.0613 "22°01'07.4580" 150 DA-03S 地表水(水库) 113°42' 21.9921 "22°01'04.5532" − DA-04G 地下水 113°42' 19.0857 "22°01' 21.2389 "150 DA-05G 地下水 113°42' 54.7355 "22°01' 40.6720 "103 DA-06H 海水 113°42' 54.8031 "22°01' 38.4253 "− DASW02 地下水 113°42′45.89″ 22°1′14.28″ 310 大万山岛 DWS-01G 地下水 113°42' 58.3178 "21°56' 59.1636 "300 DWS-02S 地表水(河流) 113°43' 24.7751 "21°55' 54.4524 "− -
[1] JHA S K, SINGH R K, DAMODARAN T, et al. Fluoride in groundwater: Toxicological exposure and remedies[J]. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health Part B, Critical Reviews, 2013, 16(1): 52-66. doi: 10.1080/10937404.2013.769420 [2] 许乃政, 刘林, 王赫生, 等. 淮河流域平原区高氟地下水的环境健康风险及其成因[J/OL]. 中国地质: 1-13[2025-09-29]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1167.P.20231107.1307.008.XU N Z, LIU L, WANG H S, et al. Exposure risk and genesis of groundwater fluoride contamination in the Huaihe River Plain, China[J/OL]. Geology in China: 1-13[2025-09-29]. https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.1167.P.20231107.1307.008. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 邢世平, 吴萍, 胡学达, 等. 化隆-循化盆地含水层沉积物地球化学特征及其对地下水氟富集的影响[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(2): 526-538.XING S P, WU P, HU X D, et al. Geochemical characteristics of aquifer sediments and their influence on fluoride enrichment in groundwater in the Hualong-Xunhua Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(2): 526-538. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] FENG F, JIA Y F, YANG Y, et al. Hydrogeochemical and statistical analysis of high fluoride groundwater in northern China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(28): 34840-34861. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-09784-z [5] FUGE R. Fluorine in the environment, a review of its sources and geochemistry[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2019, 100: 393-406. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.12.016 [6] MORALES-ARREDONDO I, RODRÍGUEZ R, ARMIENTA M A, et al. The origin of groundwater arsenic and fluorine in a volcanic sedimentary basin in central Mexico: A hydrochemistry hypothesis[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2016, 24(4): 1029-1044. doi: 10.1007/s10040-015-1357-8 [7] SINGARAJA C, CHIDAMBARAM S, JACOB N, et al. Origin of high fluoride in groundwater of the Tuticorin District, Tamil Nadu, India[J]. Applied Water Science, 2018, 8(2): 54. doi: 10.1007/s13201-018-0694-x [8] 李祥志, 曹文庚, 李英, 等. 含氟地下水的危害、治理技术现状与进展[J]. 中国地质, 2024, 51(2): 457-482.LI X Z, CAO W G, LI Y, et al. Harmfulness of fluorine-bearing groundwater and its current situation and progress of treatment technology[J]. Geology in China, 2024, 51(2): 457-482. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] BERGER T, MATHURIN F A, DRAKE H, et al. Fluoride abundance and controls in fresh groundwater in Quaternary deposits and bedrock fractures in an area with fluorine-rich granitoid rocks[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2016, 569/570: 948-960. [10] CHAE G T, YUN S T, MAYER B, et al. Fluorine geochemistry in bedrock groundwater of South Korea[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2007, 385(1/2/3): 272-283. [11] CHEN Q, DONG F Y, JIA Z W, et al. The experimental study of fluorine-leaching ability of granite with different solutions: A new insight into the dynamic of groundwater fluorine levels along coastal zones[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2020, 235: 103703. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2020.103703 [12] CHEN Q, HAO D C, GAO Z J, et al. The enrichment process of groundwater fluorine in sea water intrusion area of Gaomi City, China[J]. Groundwater, 2020, 58(6): 882-891. doi: 10.1111/gwat.12990 [13] 金喆, 孙晨, 孔令昊, 等. 松嫩平原典型高氟区水库周边浅层地下水化学特征及高氟成因[J]. 环境科学学报, 2023, 43(12): 250-258.JIN Z, SUN C, KONG L H, et al. Chemical characteristics and high-fluoride origins of shallow groundwater around typical high fluorine reservoir in Songnen Plain[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2023, 43(12): 250-258. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] JIANMIN B, YU W, JUAN Z. Arsenic and fluorine in groundwater in western Jilin Province, China: Occurrence and health risk assessment[J]. Natural Hazards, 2015, 77(3): 1903-1914. doi: 10.1007/s11069-015-1682-1 [15] SU H, KANG W D, LI Y R, et al. Fluoride and nitrate contamination of groundwater in the Loess Plateau, China: Sources and related human health risks[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 286: 117287. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117287 [16] TANG J X, ZHU Y L, XIANG B, et al. Multiple pollutants in groundwater near an abandoned Chinese fluorine chemical park: Concentrations, correlations and health risk assessments[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022, 12: 3370. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07201-8 [17] WANG J W, ZHENG N Z, LIU H, et al. Distribution, formation and human health risk of fluorine in groundwater in Songnen Plain, NE China[J]. Water, 2021, 13(22): 3236. doi: 10.3390/w13223236 [18] WANG T T, ZHAO W, WANG Z H, et al. Occurrence, main source and health risks of fluorine in mine water[J]. Exposure and Health, 2025, 17(1): 279-292. doi: 10.1007/s12403-024-00660-6 [19] 赵增锋, 付永亮, 邱小琮, 等. 黄河流域宁夏段地表水氟污染特征与风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2023, 43(11): 5800-5811.ZHAO Z F, FU Y L, QIU X C, et al. Characteristics and risk assessment of surface water fluorine pollution in Ningxia Section of Yellow River basin[J]. China Environmental Science, 2023, 43(11): 5800-5811. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 韩萱, 黄磊, 刘廷玺, 等. 西北煤电集聚区不同水体水化学特征及氟成因[J]. 中国环境科学, 2024, 44(7): 3810-3822.HAN X, HUANG L, LIU T X, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and fluorine genesis of different water bodies in coal-fired power agglomeration area of Northwest China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2024, 44(7): 3810-3822. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 米屹东, 周凌峰, 冯承莲, 等. 氟化物毒性效应与水质基准标准研究进展与展望[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2024, 19(2): 148-164.MI Y D, ZHOU L F, FENG C L, et al. Toxicity effect, water quality criteria and standards of fluoride: Progress and prospects[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2024, 19(2): 148-164. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 张宇琦, 徐惠风, 文波龙, 等. 环境中的氟及其环境效应与污染治理[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2024, 41(1): 164-174.ZHANG Y Q, XU H F, WEN B L, et al. Environmental fluorine: Effects and pollution management[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2024, 41(1): 164-174. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 陈婷, 李巧, 宿彦鹏, 等. 奎屯河流域高氟地下水对微生物多样性的影响[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2023, 46(11): 144-152.CHEN T, LI Q, SU Y P, et al. Effects of high fluoride groundwater on microbial diversity in Kuitun River basin[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2023, 46(11): 144-152. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 李曼, 张薇, 廖煜钟, 等. 鲁中南典型地热区地热水氟分布特征及其驱动机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(3): 36-47.LI M, ZHANG W, LIAO Y Z, et al. Characteristics and mechanisms of fluorine enrichment in the geothermal water of south central Shandong Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(3): 36-47. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 孙丹阳, 李和学, 刘强, 等. 地下水停采后地面沉降区地下水氟的演化规律: 以沧州市为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(4): 218-227.SUN D Y, LI H X, LIU Q, et al. Evolution of groundwater fluoride in land subsidence areas after groundwater cessation: A case study at Cangzhou[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(4): 218-227. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 王新峰, 龚磊, 刘元晴, 等. 水土质量调查评价与人群健康关系的融合路径研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 305-314.WANG X F, GONG L, LIU Y Q, et al. Integration path research of water and soil quality investigation and evaluation and human health relationship[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 305-314. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 李堃正, 白雪山, 杜垚, 等. 廊坊平原区高氟地下水分布及形成机理[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2025, 41(4): 496-505.LI K Z, BAI X S, DU Y, et al. Distribution and formation mechanism of high fluoride groundwater in Langfang Plain area[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2025, 41(4): 496-505. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 张寿川, 刘凯, 王路瑶, 等. 江西洪江−钱山断裂带中低温高氟地热水水文地球化学特征与成因机制[J]. 岩矿测试, 2024, 43(4): 568-581.ZHANG S C, LIU K, WANG L Y, et al. Identifying the hydrochemical characteristics and genetic mechanism of medium-low temperature fluoride-enriched geothermal groundwater in the Hongjiang-Qianshan fault of Jiangxi Province[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2024, 43(4): 568-581. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 张玉贤, 甘义群, 周肖瑜, 等. 微生物参与下高氟区沉积物中氟的迁移行为[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 228-235.ZHANG Y X, GAN Y Q, ZHOU X Y, et al. Mobilization of fluoride in sediments at high fluoride area enhanced by microorganisms[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3): 228-235. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] LI C C, GAO X B, WANG Y X. Hydrogeochemistry of high-fluoride groundwater at Yuncheng Basin, northern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 508: 155-165. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.11.045 [31] SHI M J, GAO Z J, FENG J G, et al. Characteristics and effects of fluorine release from shallow high-fluoride soils[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2019, 78(20): 604. doi: 10.1007/s12665-019-8618-0 [32] SU H, WANG J D, LIU J T. Geochemical factors controlling the occurrence of high-fluoride groundwater in the western region of the Ordos Basin, northwestern China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2019, 252: 1154-1162. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.06.046 [33] WANG Z, GUO H M, XING S P, et al. Hydrogeochemical and geothermal controls on the formation of high fluoride groundwater[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 598: 126372. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126372 [34] 赵增锋, 王楚尤, 邱小琮, 等. 宁夏清水河流域地表水水化学特征及高氟水成因机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(6): 462-473.ZHAO Z F, WANG C Y, QIU X C, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of surface water and genetic mechanism of high fluorine water in Qingshui River basin in Ningxia[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(6): 462-473. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 孟甲, 郑慧铭, 宋帅良, 等. 鲁西南黄河下游地下水氟富集规律及其影响因素[J]. 地质通报, 2024, 43(9): 1663-1672.MENG J, ZHENG H M, SONG S L, et al. Fluorine enrichment pattern of groundwater in the lower reaches of the Yellow River in southwestern Shandong Province and influencing factors[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2024, 43(9): 1663-1672. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 王晓燕, 张梦南, 尹德超, 等. 黑河干流中游地区地下水中氟分布特征及成因分析[J]. 环境科学, 2025, 46(5): 2757-2766.WANG X Y, ZHANG M N, YIN D C, et al. Distribution characteristics and genetic analysis of fluorine in groundwater in middle reaches of Heihe River[J]. Environmental Science, 2025, 46(5): 2757-2766. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 王振, 郭华明, 刘海燕, 等. 贵德盆地高氟地下水稀土元素特征及其指示意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(3): 505-514.WANG Z, GUO H M, LIU H Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of rare earth elements in high-fluoride groundwater in the Guide Basin and its implications[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(3): 505-514. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 袁天君, 金戈, 李逸凡, 等. 大同盆地地下水系统中氟的来源与富集机制解析[J/OL]. 安全与环境工程: 1-16[2025-09-29]. https://doi.org/10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.20240139.YUAN T J, JIN G, LI Y F, et al. Analysis on the source and enrichment mechanisms of the fluoride in the groundwater system of Datong Basin[J/OL]. Safety and Environmental Engineering: 1-16[2025-09-29]. https://doi.org/10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.20240139. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 郑钰, 孙英, 周金龙, 等. 新疆额尔齐斯河流域平原区地下水水化学特征及高氟水成因机制[J]. 干旱区研究, 2024, 41(12): 2056-2070.ZHENG Y, SUN Y, ZHOU J L, et al. Hydrochemical properties and genetic mechanisms of high-fluoride groundwater in the Irtysh River basin plain, Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2024, 41(12): 2056-2070. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 周娇, 陈菁, 王收, 等. 丰县浅层高氟地下水化学特征及富集机理[J]. 地球与环境, 2024, 52(1): 122-132.ZHOU J, CHEN J, WANG S, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and enrichment mechanism of shallow high fluorine groundwater in Feng County[J]. Earth and Environment, 2024, 52(1): 122-132. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 颜彬, 谢敬谦, 黄博, 等. 广东近岸海域矿物特征指数分布及指示意义[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(11): 1-8.YAN B, XIE J Q, HUANG B, et al. Detrital mineral indexes of the bottom sediments of Guangdong coastal water: Distribution and implications[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(11): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] 广东省地质矿产局. 珠海区域地质综合调查报告[R]. 广州: 广东省地质矿产局, 1989.Geological and Mineral Bureau of Guangdong Province. Comprehensive regional geological survey report of Zhuhai [R]. Guangzhou: Geological and Mineral Bureau of Guangdong Province, 1989. (in Chinese) [43] 全国自然资源与国土空间规划标准化技术委员会. 地下水质分析方法第82部分: 钠量的测定火焰原子吸收分光光度法: DZ/T0064.82−2021[S]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2021.National Technical Committee for Standardization of Natural Resources and Territorial Spatial Planning. Methods for the analysis of groundwater: Part 82: Determination of sodium amount by flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry: DZ/T0064.82−2021[S]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2021. (in Chinese) [44] 全国自然资源与国土空间规划标准化技术委员会. 地下水质分析方法第12部分: 钙和镁量的测定火焰原子吸收分光光度法: DZ/T0064.12−2021[S]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2021.National Technical Committee for Standardization of Natural Resources and Territorial Spatial Planning. Methods for the analysis of groundwater: Part 12: Determination of calcium and magnesium content by flame atomic absorption spectrophotometry: DZ/T0064.12−2021[S]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2021. (in Chinese) [45] 全国自然资源与国土空间规划标准化技术委员会. 地下水质分析方法第8部分: 悬浮物的测定重量法: DZ/T0064.8−2021[S]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2021.National Technical Committee for Standardization of Natural Resources and Territorial Spatial Planning. Methods for the analysis of groundwater quality: Part 8: Determination of suspended matter gravimetric method: DZ/T0064.8−2021[S]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2021. (in Chinese) [46] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. 生活饮用水卫生标准: GB5749-2022[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2022.National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China. Hygienic standard for drinking water: GB5749-2022[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2022. (in Chinese) [47] 全国国土资源标准化技术委员会. 地下水质量标准: GB/T14848-2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.National Technical Committee for Standardization of Land and Resources. Groundwater quality standard: GB/T14848-2017[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2017. (in Chinese) [48] PARKHURST D L, APPELO C A J. Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3: A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations[R]. Reston, VA: U. S. Geological Survey, 2013. [49] PARKHURST D L, WISSMEIER L. PhreeqcRM: A reaction module for transport simulators based on the geochemical model PHREEQC[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2015, 83: 176-189. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2015.06.001 [50] LU M Y, LIU Y, LIU G J, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and prediction of fluorine concentration in groundwater based on driving factors analysis[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 857: 159415. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159415 [51] GUO H M, ZHANG Y, XING L N, et al. Spatial variation in arsenic and fluoride concentrations of shallow groundwater from the town of Shahai in the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2012, 27(11): 2187-2196. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.01.016 [52] KAU P M H, SMITH D W, BINNING P. Fluoride retention by kaolin clay[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 1997, 28(3): 267-288. doi: 10.1016/S0169-7722(96)00081-2 [53] HAN L, WANG Y W, LU H, et al. Structural engineering of natural clay for superior adsorption efficiency of fluoride[J]. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 2025, 70: 107055. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2025.107055 -




 下载:
下载: