Characteristics and enlightenment of deep coal rocks in the Jurassic Kizilnur Formation of Kuqa Depression
-
摘要:
目前库车坳陷侏罗系克孜勒努尔组煤层的研究主要集中在浅部,有关深部煤层的研究较少。针对库车坳陷侏罗系克孜勒努尔组煤层煤岩特征、储层物性和含气性不明等问题,依托钻井资料,采用地震资料处理、连井分析、取样观察及气测孔渗、等温吸附实验等方法,对该区块煤层的几何分布特征、煤岩煤质特征、储层物性、吸附性和含气量等方面进行了研究。研究表明:①研究区克孜勒努尔组深部煤层以原生结构为主,有机显微组分以镜质组为主,平均占比达62.20%,有机质类型均为Ⅲ型,中煤阶;整体属于中高挥发分、特低硫分、特低−低灰分的煤层;②深部煤层的气测孔隙度平均值为7.10%,平均渗透率为0.685×10−3 μm2,其甲烷的吸附能力受镜质体反射率、水分含量和灰分产率的影响大;③库车坳陷侏罗系克孜勒努尔组埋深2 000~5 000 m的煤层主要分布在北部构造带内,面积达2 800 km2,单层厚度最高可达22 m,实测深部煤层平均含气量11.77 m3/t,资源潜力巨大。对比浅部煤层,研究区克孜勒努尔组深部煤层受埋深影响明显,成熟度高并已规模产气,具备勘探潜力;含水饱和度是影响克孜勒努尔组煤层含气性的关键因素;含水饱和度低且有利于游离气富集的迪北缓坡平台将是库车坳陷煤岩气的有利目标区。
Abstract:Objective Current research on the Jurassic Kizilnur Formation coal seams in the Kuqa Depression mainly focuses on shallow sections, with limited study of deep coal seams.
Methods To address unknown coal-rock characteristics, reservoir properties, and gas content in the Jurassic Kizilnur Formation coal seams, the geometric distribution characteristics, the characteristics of coal rock and coal quality, reservoir properties, adsorption properties, and gas content of the coal seam in this block were studied based on the following methods, such as drilling data, seismic data processing, wellbore analysis, sampling observation, gas measurement, pore permeability, and isothermal adsorption experiments.
Results The deep coal seams in the research area are predominantly composed of primary structures, with vitrinite as the major organic component (average 62.2%), indicating type Ⅲ organic matter. The coal is of medium rank, generally characterized by medium-to-high volatile matter, ultra-low sulfur, and low to very low ash content. The average gas porosity is 7.10%, and the average permeability is 0.685×10−3 μm2. Furthermore, methane adsorption capacity is strongly influenced by macrinite reflectance, water content, and ash yield. In the Kuqa Depression, deep coal seams occur at burial depths of 2 000 –5 000 m, are mainly distributed in the Northern Structural Zone, cover about 2 800 km2, with a maximum single-layer thickness of 22 m. The average gas content of the deep coal seam measured is 11.77 m3/t, indicating substantial resource potential.
Conclusion Compared with shallow coal seams, the deep coal seams of the Kezilnur Formation in the study area are more strongly affected by burial depth, exhibit high maturation, and have achieved large-scale gas production, underscoring their exploration potential. Water saturation emerges as a critical factor controlling gas content in these seams. Notably, the Dibei gentle-slope platform in the Kuqa Depression offers particular advantages for CBM extraction due to favorable hydrological and geological attributes.
-
Key words:
- Kuqa Depression /
- Kizilnur Formation /
- coal seam /
- coal reservoir characteristic
-
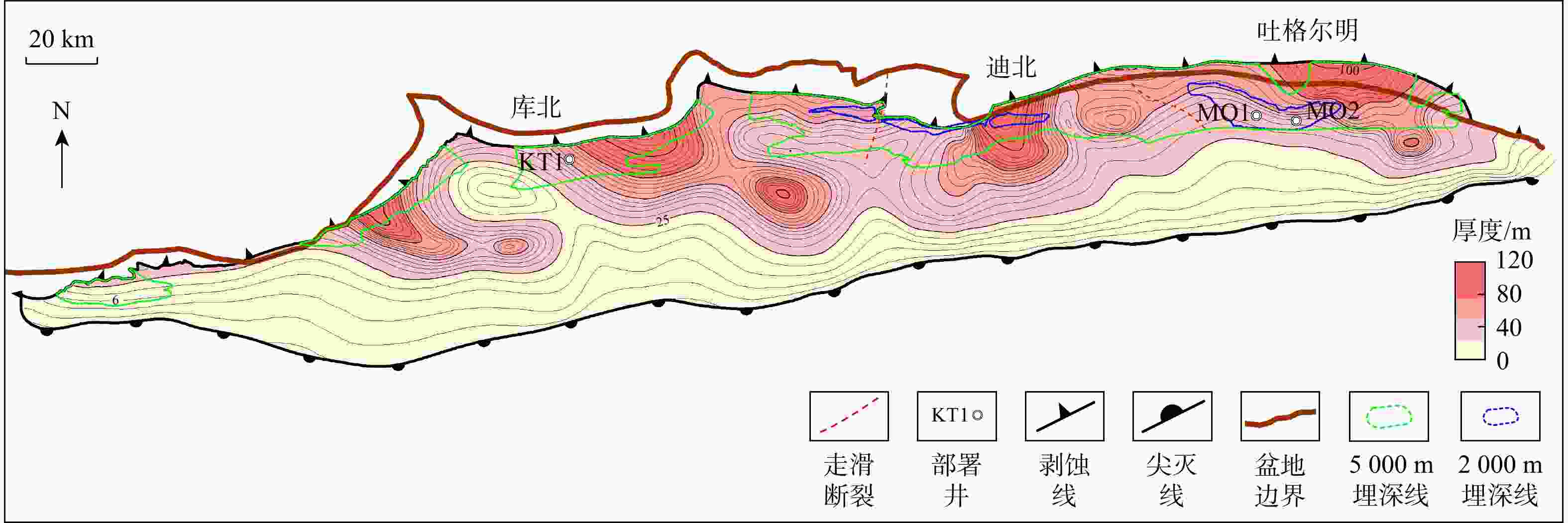
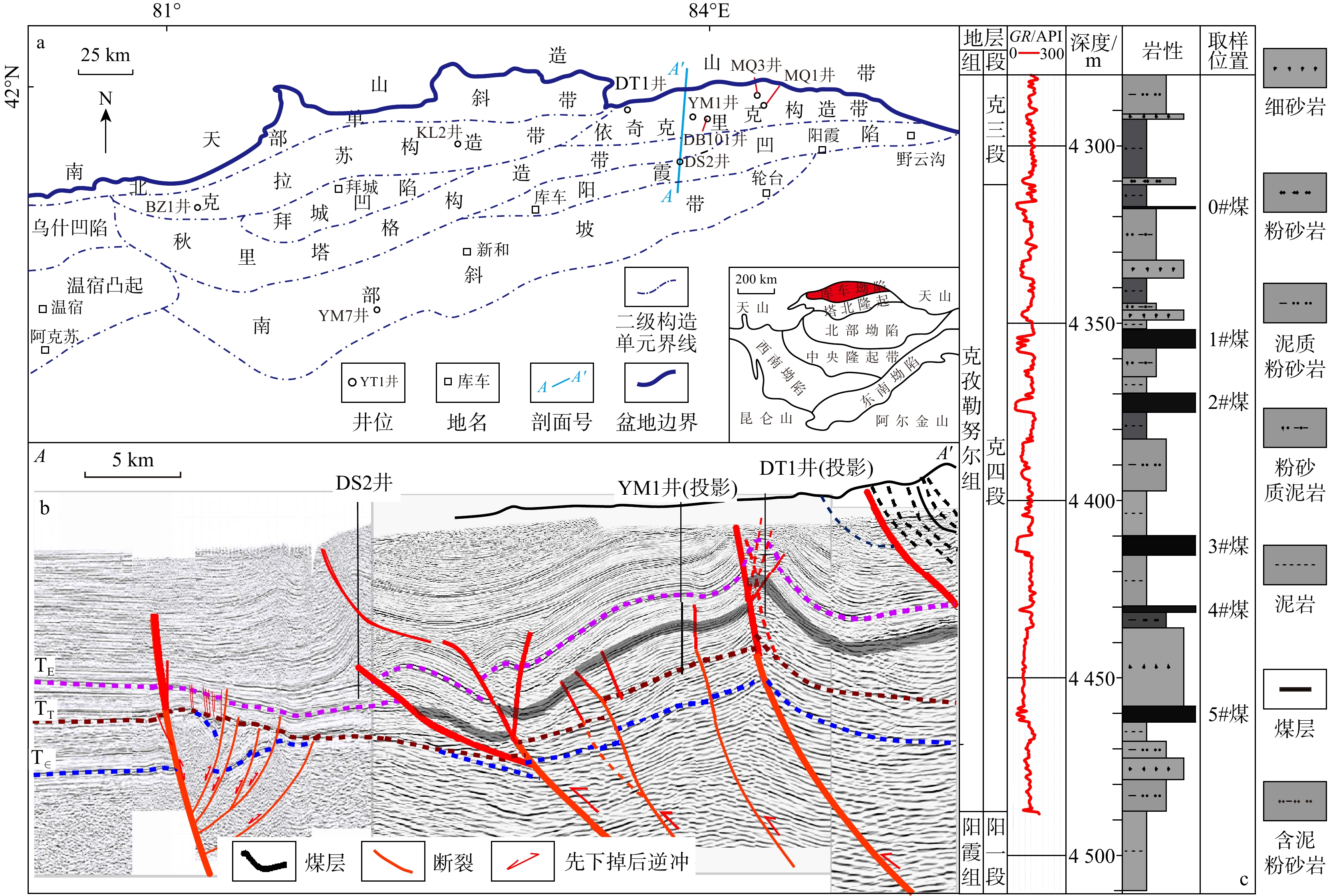
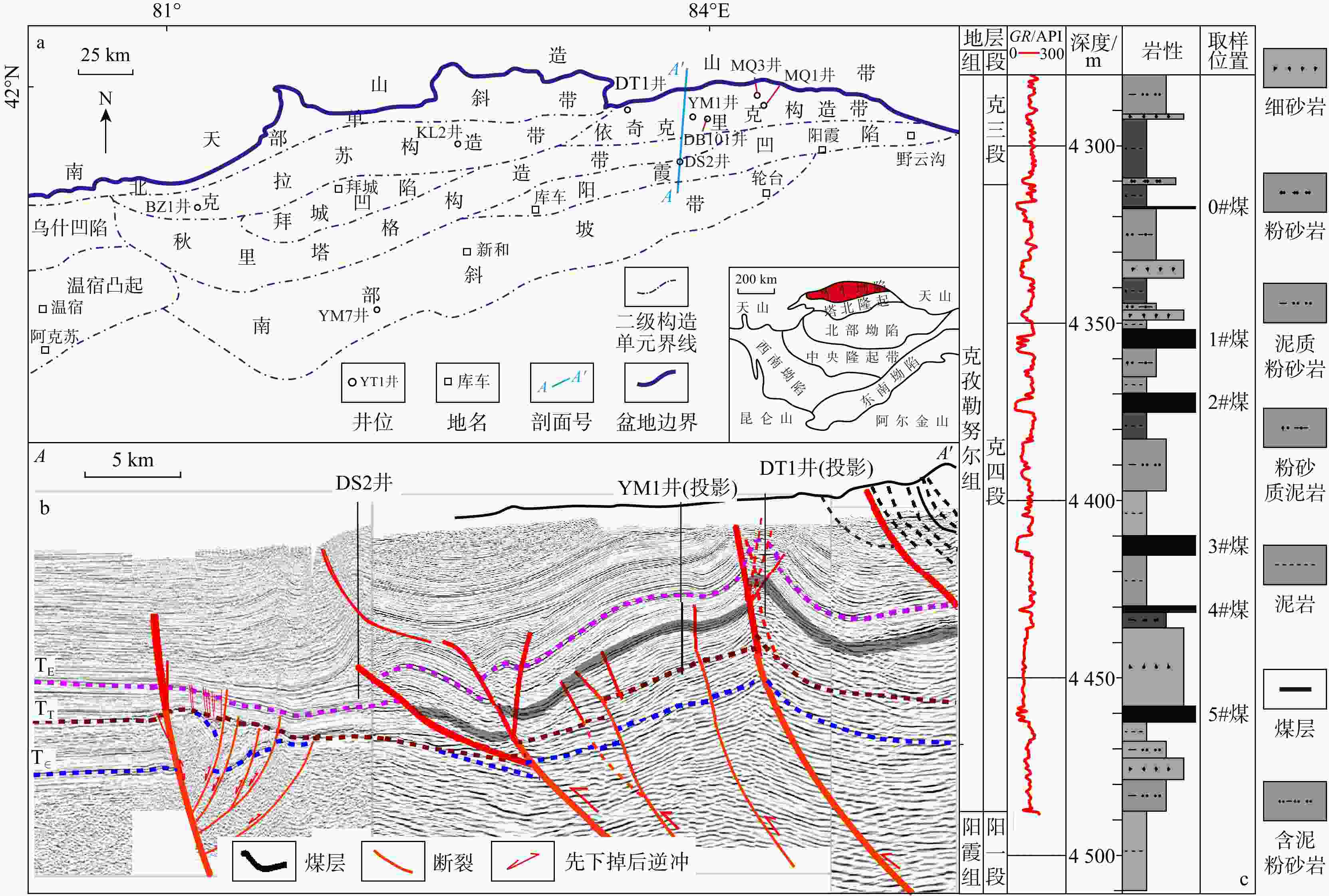
图 1 库车坳陷构造单元分布图(a)(修改自王珂等[26])、过DS2井南北向地震叠前深度偏移剖面(b)(剖面位置见图a)和克孜勒努尔组克三、四段(YM1井)(c)(TK. 白垩系地震界限,其他类推)
Figure 1. Structural units in the Kuqa Depression (a), north-south seismic profiles passing through Well DS2 (b) and stratigraphic system of sections 3-4 in the Kizilnur Formation (c)
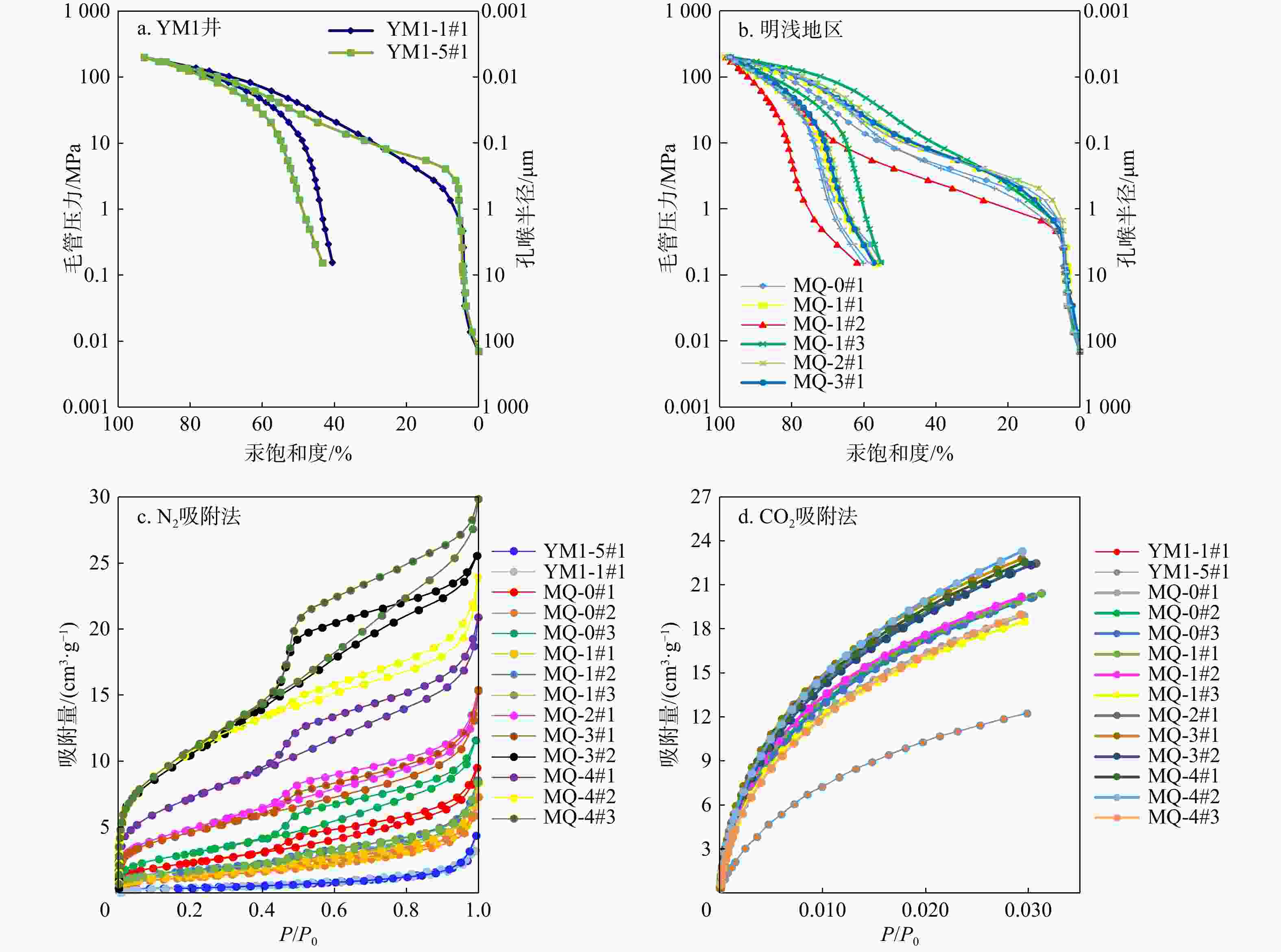
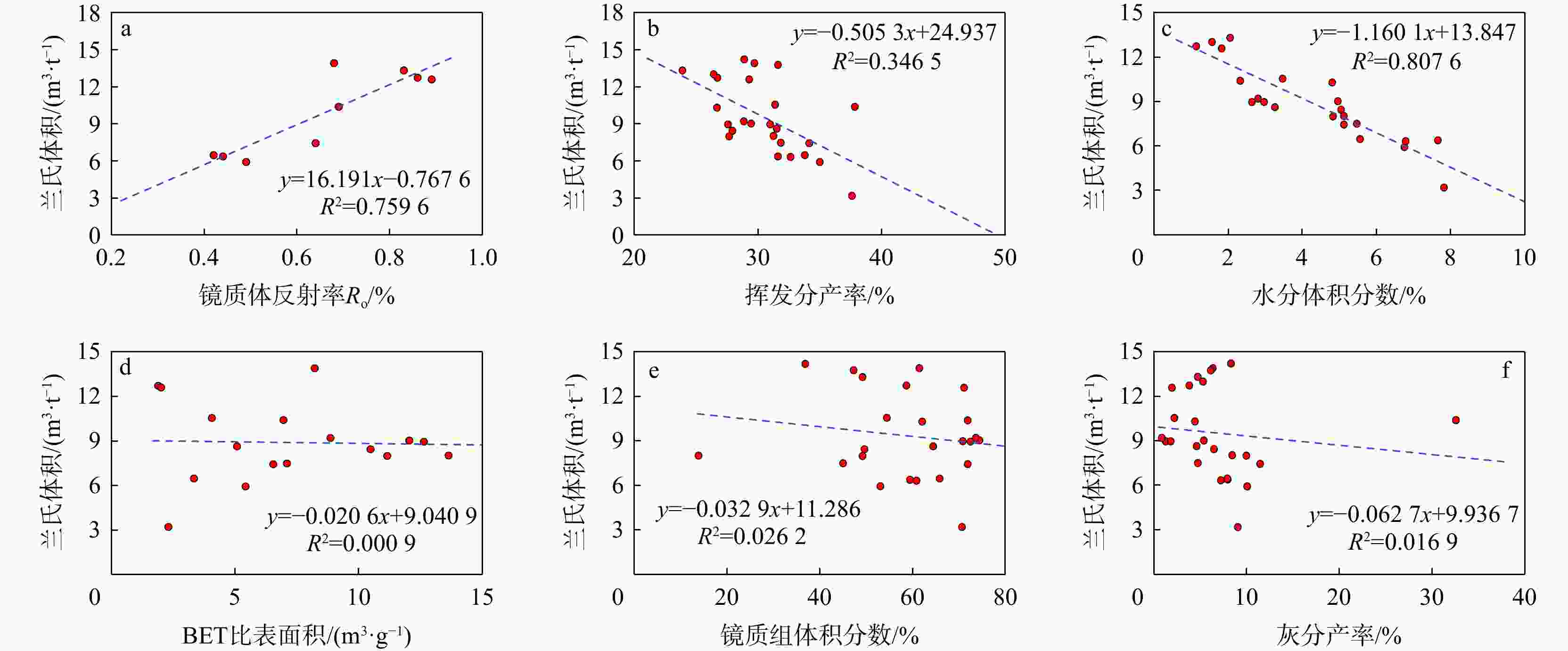
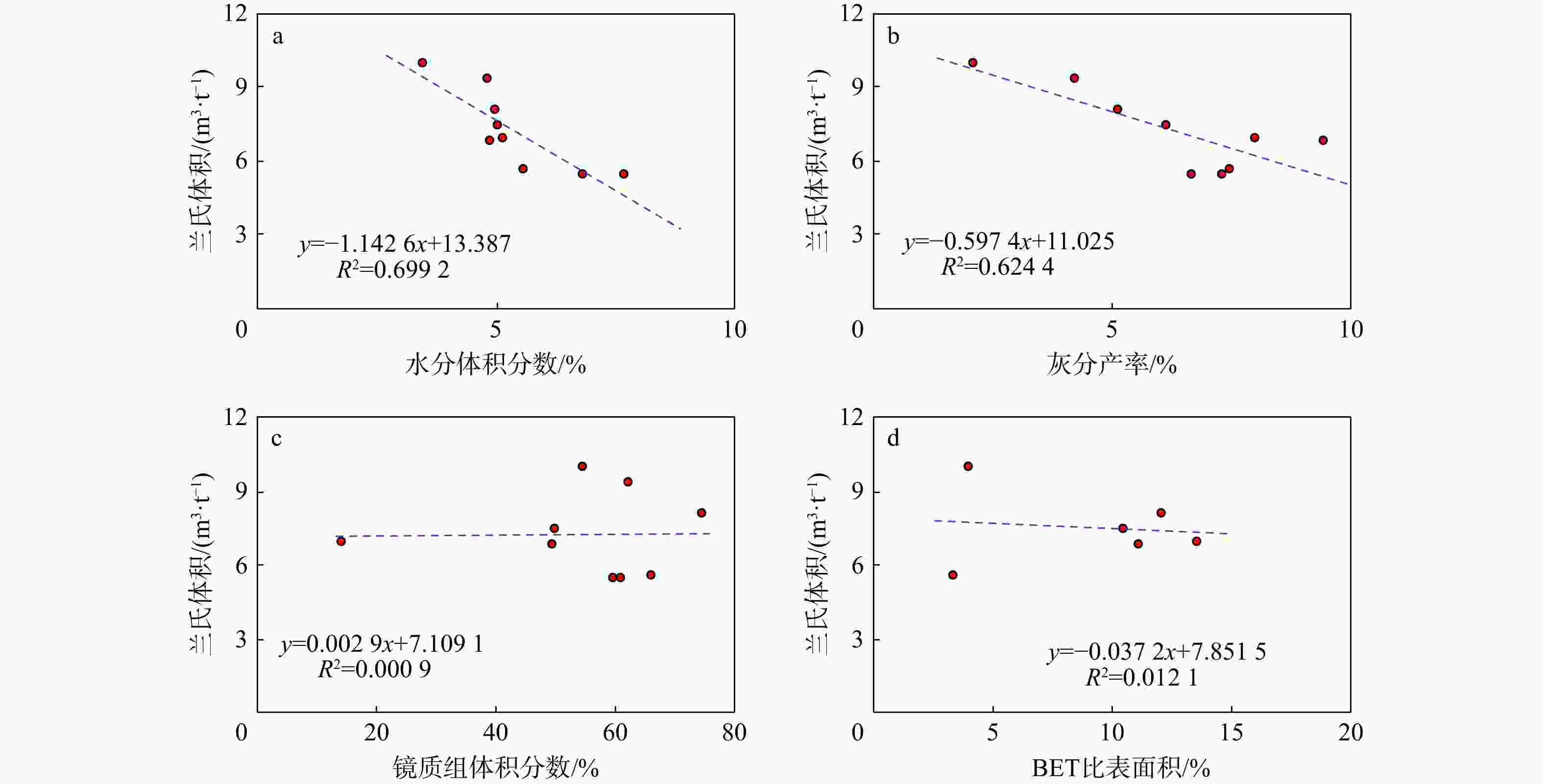
图 8 YM1井和明浅地区克孜勒努尔组煤层兰氏体积和镜质体反射率(a)、挥发分产率(b)、水分体积分数(c)、BET比表面积(d)、镜质组体积分数(e)、灰分产率(f)的关系图
Figure 8. Relationships among Lange volume of coal seams and reflectance (a), volatile yield (b), water content (c), BET specific surface area (d), macrinite-group content (e), ash content (f) in the Kizilnur Formation, Well YM1 and MQ area
表 1 YM1井和明浅地区克孜勒努尔组煤层的煤质实验结果
Table 1. Quality experimental results of coal seams of the Kizilnur Formation, Well YM1 and MQ area
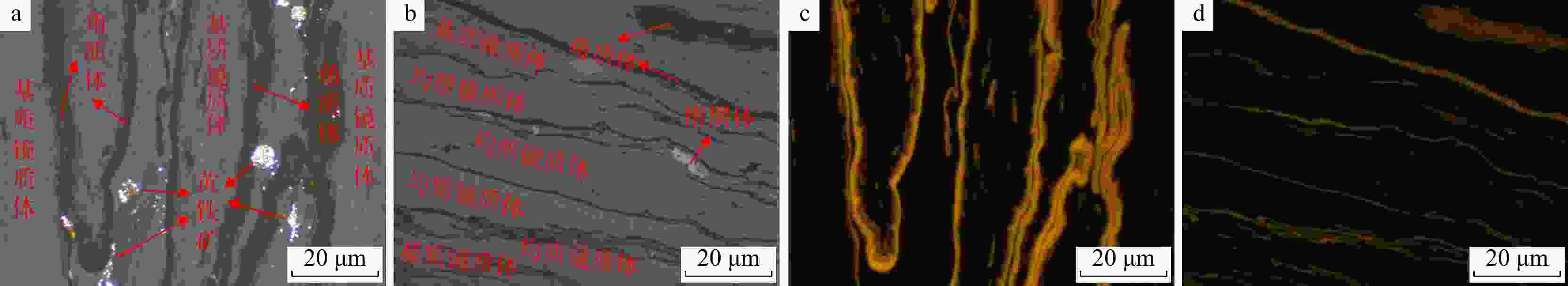
区块 煤号 深度/m 镜质组 惰质组 壳质组 Mad Ad Vdaf St,d Ro/% 占比/% YM1井 1 4352.00 ~4354.97 49.20~48.80
61.0516.60~46.20
30.152.70~17.30
6.701.14~2.05
1.420.76~10.01
4.8323.87~41.64
30.960.21~0.42
0.290.82~0.86
0.842 4369.70 ~4375.10 61.80~75.20
69.8318.80~33.80
25.331.40~3.90
2.381.32~1.69
1.5213.32~24.41
17.5327.02~35.82
29.83/ 0.80~0.86
0.843 4409.90 ~4415.40 / / / 4.39 17.30 31.79 / / 5 4458.00 ~4462.50 42.20 52.80 3.50 1.07~1.82
1.451.96~26.42
14.1929.25~34.40
31.830.48 0.89 平均值 62.20 30.00 5.50 1.53 15.70 31.19 0.33 0.85 明浅地区 0 84.00~
648.2553.00~77.20
61.3016.80~42.60
33.002.00~4.60
3.302.44~6.75
3.951.38~11.01
7.4836.02~40.12
37.040.15~1.51
0.750.49 1 153.85~
710.0041.40~77.80
59.5013.60~54.20
34.801.40~6.40
3.302.79~7.82
4.922.26~14.83
7.1727.64~41.04
33.090.13~0.62
0.330.47~0.64
0.562 227.00~
796.0013.80~78.40
55.8017.60~81.60
39.101.60~5.20
2.803.10~7.65
4.711.55~16.16
6.8426.65~34.61
30.060.06~0.55
0.170.42~0.52
0.463 268.40~
841.0536.80~85.80
63.108.20~57.63
31.801.60~3.80
2.402.32~5.91
4.522.42~32.57
7.6124.63~37.78
30.810.11~1.47
0.320.48~0.69
0.624 341.30~
898.5056.20~77.80
64.7017.20~39.20
30.301.40~4.60
2.601.76~7.55
3.751.66~11.50
6.1322.98~35.97
32.000.08~0.39
0.200.59~0.60
0.60平均值 60.43 34.54 2.64 4.13 6.57 31.56 0.28 0.55 注:$ \dfrac{49.20\sim48.80}{61.05} $. $\dfrac{最小值\sim 最大值}{平均值} $;Mad. 水分(空气干燥基);Ad. 灰分(干燥基);Vdaf. 挥发分(干燥无灰基);St,d. 全硫分(干燥基);Ro. 镜质体反射率 表 2 ${\mathrm{YM}}1 $和明浅地区煤层${\mathrm{N}}_2 $吸附法和${\mathrm{CO}}_2 $吸附法联测的孔隙结构数据
Table 2. Porosity-structure data from combined N2 and CO2 adsorption experiments for coal seams in Well YM1 and MQ area
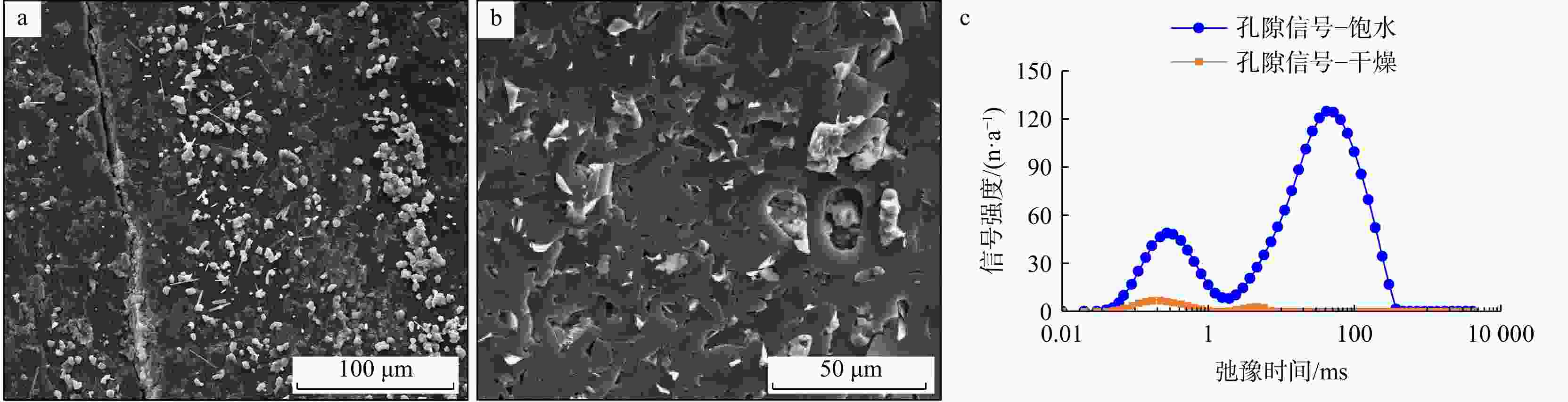
井号或地区 平均深度/m 氮气吸附 低压CO2吸附 吸附量/(cm3·g−1) 比表面积/(m2·g−1) 孔体积/(cm3·g−1) 吸附量/(cm3·g−1) 比表面积/(m2·g−1) 孔体积/(cm3·g−1) YM1井 4353 范围 3.223~4.353 1.869~2.000 0.005~0.007 10.614~12.247 108.010~126.460 0.034~0.039 平均 3.788 1.935 0.006 11.430 117.235 0.036 明浅地区 490 范围 5.596~29.860 2.283~39.156 0.009~0.044 9.116~23.288 94.151~240.660 0.029~0.071 平均 11.577 11.404 0.018 18.995 195.453 0.057 表 3 ${\mathrm{YM}}1 $井克孜勒努尔组煤岩现场含气量测试结果
Table 3. Gas content test results for coal seams in the Kizilnur Formation, Well YM1
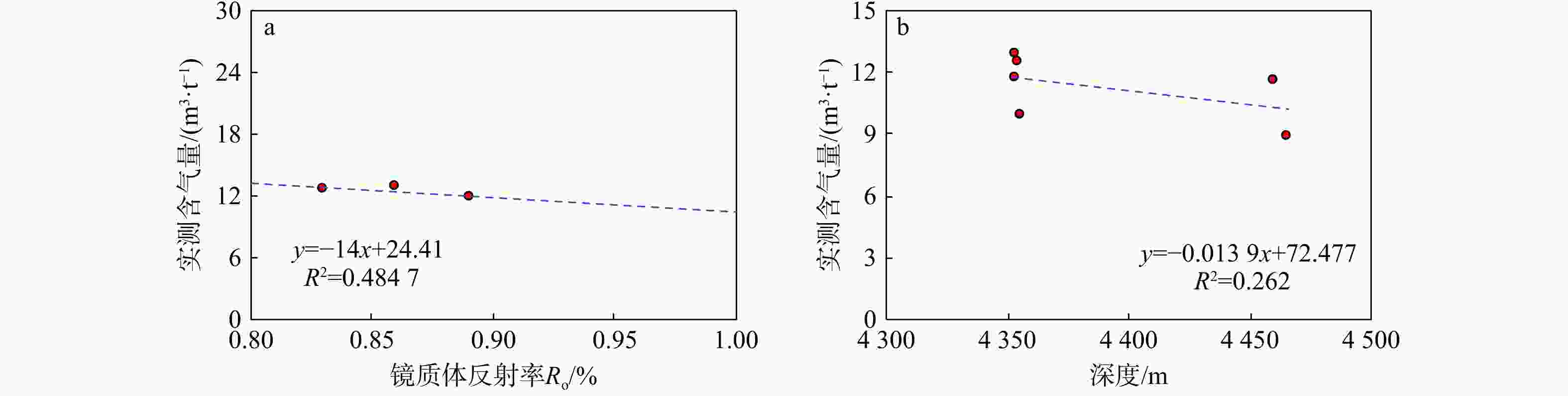
序号 测试编号 取样深度/m 损失气/(m3·t−1) 解吸气/(m3·t−1) 残余气/(m3·t−1) 干燥无灰基总气量/(m3·t−1) 1 YM1-1 4352.34 3.93 7.99 0.18 12.87 2 YM1-2 4353.06 2.81 7.93 0.16 11.80 3 YM1-3 4353.75 2.65 8.78 0.16 12.54 4 YM1-4 4354.69 2.77 5.18 0.22 9.92 5 YM5-1 4459.76 2.70 8.34 0.11 11.70 6 YM5-2 4465.06 1.11 5.24 0.12 8.97 表 4 库车侏罗系克孜勒努尔组和准噶尔白家海凸起、鄂尔多斯大吉区块煤层地质特征对比
Table 4. Comparison of geological characteristics of coal seams in the Jurassic Kizilnur Formation of Kuqa, the Baijiahai Uplift of Junggar Basin, and the Daji Block of the Ordos Basin
地区地层 库车北部构造带深部侏罗系
克孜勒努尔组(J2kz)煤层准噶尔盆地白家海凸起西山窑组(J2x)煤层 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘大宁−吉县区块石炭系
本溪组(C1b)煤层埋深/m 2000 ~5000 2200 ~3200 1865 ~2520 厚度/m 1.8~17,平均6.6 5~20,平均8.3 4~12,平均7.8 煤体结构 以原生结构为主,割理、裂隙较发育 以原生结构为主,煤体结构完整、
力学强度好以原生结构为主,割理、裂隙发育 盖层条件 顶板以泥岩、粉砂质泥岩为主,厚10~20 m;底板泥岩分布稳定,厚30~65 m 顶板泥岩厚30~70 m,
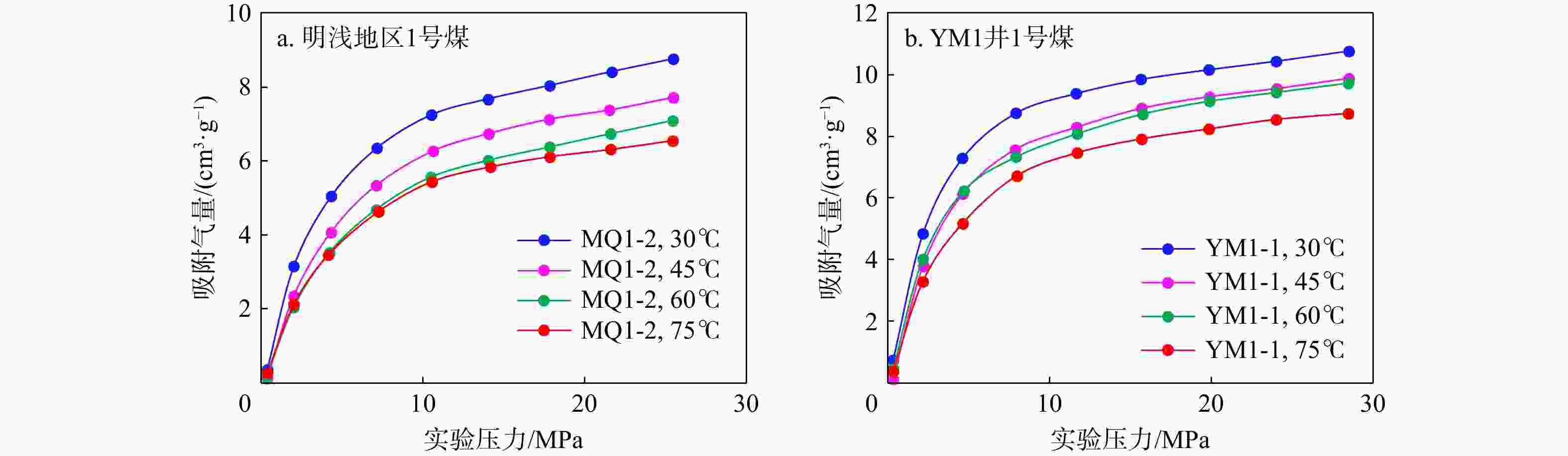
底板泥岩厚5~30 m,较稳定顶板灰岩厚度4~8 m,底板发育泥岩 成熟度/% 0.70~1.4,平均0.88 0.60~0.85,平均0.71 平均2.6,热演化程度相对较高 压力系数 1.15(邻井试油井口压力反推) 0.91~1.00 0.90~0.94 储层温度/℃ 65~145(邻井预测温度) 66~78 61. 3~73. 4 等温吸附特征 兰氏体积(VL)平均12.28 m3/t,
兰氏压力(PL)平均3.24 MPa兰氏体积(VL)平均7.98 m3/t,
兰氏压力(PL)平均5.80 MPa兰氏体积(VL)平均28.29 m3/t,
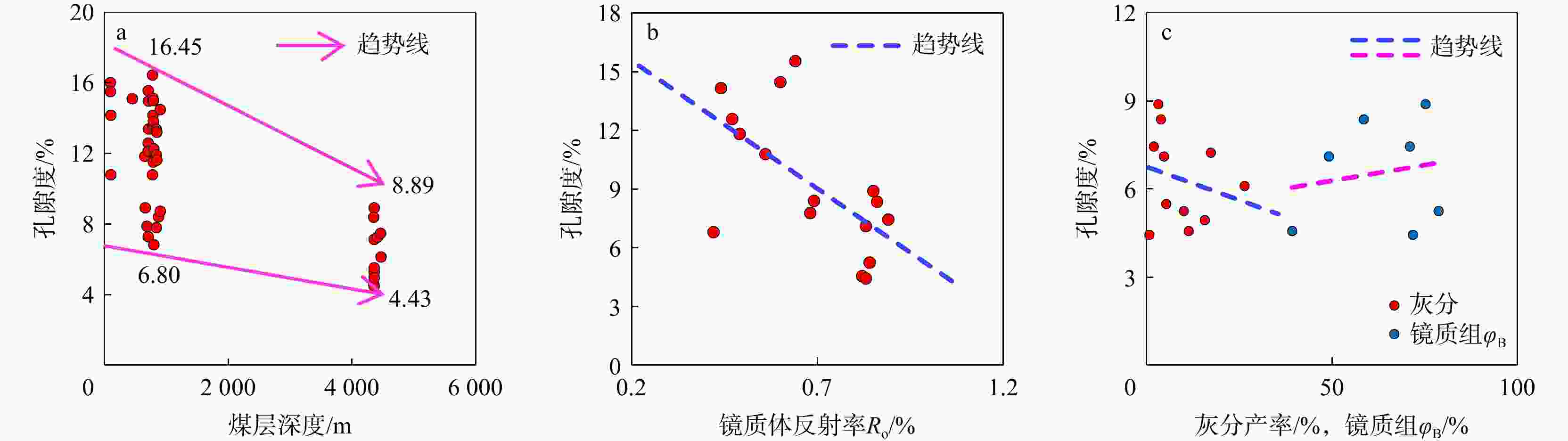
兰氏压力(PL)平均3.06 MPa含气量/(m3·t−1) 11.77 14.77 15.00~26.00 孔隙度/% 5.49~8.36,平均6.96 5.00~13.33,平均8.76 0.49~6.11,平均 2.92 渗透率/10−3 μm2 0.685 1.360 0.03~0.05 -
[1] JOHNSON R C, FLORES R M. Developmental geology of coalbed methane from shallow to deep in Rocky Mountain Basins and in Cook Inlet-Matanuska Basin, Alaska, U. S. A. and Canada[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 1998, 35(1/2/3/4): 241-282. [2] TONNSEN R R, MISKIMINS J. Simulation of deep-coalbed-methane permeability and production assuming variable pore-volume compressibility[J]. Journal of Canadian Petroleum Technology, 2011, 50(5): 23-31. doi: 10.2118/138160-PA [3] NELSON C R. Deep coalbed gas plays in the U. S. Rocky Mountain region[C]// Anon. Proceedings of the AAPG Annual Meeting. Salt Lake City, Utah, USA: [s. n.], 2003: 5-8. [4] KUUSKRAA V A, WYMAN R E. Deep coal seams: An overlooked source for long-term natural gas supplies[C]// Anon. SPE Gas Technology Symposium. Calgary, Alberta, Canada: SPE, 1993: SPE-26196-MS. [5] 陈刚. 深部低阶含煤层气系统及其成藏机制: 以准噶尔盆地彩南地区为例[D]. 江苏徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2014.CHEN G. Deep low-rank coalbed methane system and reservoiring mechanism in the case of the cainan block in Junggar Basin[D]. Xuzhou Jiangsu: China University of Mining and Technology, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 秦勇. 中国深部煤层气地质研究进展[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(11): 1791-1811. doi: 10.7623/syxb202311004QIN Y. Progress on geological research of deep coalbed methane in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(11): 1791-1811. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7623/syxb202311004 [7] LI H Y, LAU H C, HUANG S. Coalbed methane development in China: Engineering challenges and opportunities[C]// Anon. SPE/IATMI Asia Pacific Oil & Gas Conference and Exhibition. Jakarta, Indonesia: SPE, 2017: D012S036R098. [8] 李曙光, 王红娜, 徐博瑞, 等. 大宁−吉县区块深层煤层气井酸化压裂产气效果影响因素分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2022, 50(3): 165-172. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.12.0800LI S G, WANG H N, XU B R, et al. Influencing factors on gas production effect of acid fractured CBM wells in deep coal seam of Daning-Jixian Block[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2022, 50(3): 165-172. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.21.12.0800 [9] 郭绪杰, 支东明, 毛新军, 等. 准噶尔盆地煤岩气的勘探发现及意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(6): 38-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.06.003GUO X J, ZHI D M, MAO X J, et al. Discovery and significance of coal measure gas in Junggar Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(6): 38-49. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2021.06.003 [10] FU H J, TANG D Z, XU T, et al. Characteristics of pore structure and fractal dimension of low-rank coal: A case study of Lower Jurassic Xishanyao coal in the southern Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Fuel, 2017, 193: 254-264. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.11.069 [11] AYERS W B Jr. Coalbed gas systems, resources, and production and a review of contrasting cases from the San Juan and Powder River Basins[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11): 1853-1890. [12] PASHIN J C, GROSHONG R H. Structural control of coalbed methane production in Alabama[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 1998, 38(1/2): 89-113. [13] PILLALAMARRY M, HARPALANI S, LIU S M. Gas diffusion behavior of coal and its impact on production from coalbed methane reservoirs[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2011, 86(4): 342-348. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2011.03.007 [14] CHEN S D, TANG D Z, TAO S, et al. Characteristics of in situ stress distribution and its significance on the coalbed methane (CBM) development in Fanzhuang-Zhengzhuang Block, southern Qinshui Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 161: 108-120. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.11.042 [15] FU H J, TANG D Z, XU T, et al. Preliminary research on CBM enrichment models of low-rank coal and its geological controls: A case study in the middle of the southern Junggar Basin, NW China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 83: 97-110. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.03.007 [16] 李登华, 高煖, 刘卓亚, 等. 中美煤层气资源分布特征和开发现状对比及启示[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(1): 252-261.LI D H, GAO X, LIU Z Y, et al. Comparison and revelation of coalbed methane resources distribution characteristics and development status between China and America[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46(1): 252-261. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] FU H J, YAN D T, SU X B, et al. Biodegradation of early thermogenic gas and generation of secondary microbial gas in the Tieliekedong region of the northern Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2022, 261: 104075. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2022.104075 [18] XU H, TANG D Z, TANG S H, et al. Geologic and hydrological controls on coal reservoir water production in marine coal-bearing strata: A case study of the Carboniferous Taiyuan Formation in the Liulin area, eastern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 59: 517-526. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.10.005 [19] BURRA A, ESTERLE J S, GOLDING S D. Horizontal stress anisotropy and effective stress as regulator of coal seam gas zonation in the Sydney Basin, Australia[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2014, 132: 103-116. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2014.08.008 [20] PAPENDICK S L, DOWNS K R, VO K D, et al. Biogenic methane potential for Surat Basin, Queensland coal seams[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2011, 88(2/3): 123-134. [21] YAO Y B, LIU D M, YAN T T. Geological and hydrogeological controls on the accumulation of coalbed methane in the Weibei field, southeastern Ordos Basin[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2014, 121: 148-159. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2013.11.006 [22] TAO S, TANG D Z, XU H, et al. Factors controlling high-yield coalbed methane vertical wells in the Fanzhuang Block, southern Qinshui Basin[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2014, 134: 38-45. [23] MENG Y J, TANG D Z, XU H, et al. Geological controls and coalbed methane production potential evaluation: A case study in Liulin area, eastern Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2014, 21: 95-111. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2014.07.034 [24] 田军, 杨海军, 吴超, 等. 博孜9井的发现与塔里木盆地超深层天然气勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(1): 11-19.TIAN J, YANG H J, WU C, et al. Discovery of Well Bozi 9 and ultra-deep natural gas exploration potential in the Kelasu tectonic zone of the Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(1): 11-19. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 王珂, 杨海军, 李勇, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷北部构造带地质特征与勘探潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(7): 885-905.WANG K, YANG H J, LI Y, et al. Geological characteristics and exploration potential of the northern tectonic belt of Kuqa Depression in Tarim Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(7): 885-905. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 吴斌, 安庆, 杜世涛. 新疆库拜煤田煤层气多层合采特征煤层探索[J]. 中国煤层气, 2019, 16(4): 9-13.WU B, AN Q, DU S T. Exploration on coal seams with characteristics of CBM multi-layer drainage in Kubay coalfield in Xinjiang[J]. China Coalbed Methane, 2019, 16(4): 9-13. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 马君慧, 李鑫, 田继军. 库拜煤田西部煤层气资源评价[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2023, 35(5): 162-164.MA J H, LI X, TIAN J J. Evaluation of coalbed methane resources in western Kubai coalfield[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2023, 35(5): 162-164. (in Chinese) [28] 李玲, 唐淑玲, 王斌, 等. 库车坳陷北部构造带克孜勒努尔组煤层煤岩学特征及煤相约束作用[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2025, 53(3): 124-138.LI L, TANG S L, WANG B, et al. Coal petrography characteristics and coal facies constraints of Kezilenur Formation coal seams in the northern tectonic belt of Kuqa Depression[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2025, 53(3): 124-138. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 郭泽清, 王斌, 董才源, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷北部构造带侏罗系煤岩气地质特征及有利区带评价[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2025, 36(5): 953-972.GUO Z Q, WANG B, DONG C Y, et al. Geological characteristics of Jurassic coal rock gas and evaluation of favorable zones in the northern structural belt of the Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2025, 36(5): 953-972. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 赵孟军, 鲁雪松, 卓勤功, 等. 库车前陆盆地油气成藏特征与分布规律[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(4): 395-404.ZHAO M J, LU X S, ZHUO Q G, et al. Characteristics and distribution law of hydrocarbon accumulation in Kuqa Foreland Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(4): 395-404. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 付晓飞, 杨勉, 吕延防, 等. 库车坳陷典型构造天然气运移过程物理模拟[J]. 石油学报, 2004, 25(5): 38-43.FU X F, YANG M, LU Y F, et al. Physical simulation on gas migration process of typical structure in Kuqa Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2004, 25(5): 38-43. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 魏国齐, 贾承造, 姚慧君. 塔里木盆地晚海西期逆冲−走滑构造与含油气性[J]. 新疆石油地质, 1995, 6(2): 96-102.WEI G Q, JIA C Z, YAO H J. Late Hercynian overthrust and strike-slip structure and oil & gas potential of the Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 1995, 6(2): 96-102. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 姜潇俊, 史玲玲, 莫涛, 等. 深层−超深层致密砂岩储层特征及物性差异成因: 以库车坳陷博孜地区巴什基奇克组为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(3): 151-164.JIANG X J, SHI L L, MO T, et al. Characteristics and causes of physical property differences of deep and ultradeep tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of the Bashijiqike Formation in the Bozi area of the Kuqa Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(3): 151-164. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 刘宏坤, 艾勇, 王贵文, 等. 深层、超深层致密砂岩储层成岩相测井定量评价: 以库车坳陷博孜−大北地区为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 299-310.LIU H K, AI Y, WANG G W, et al. Quantitative well logging evaluation of diagenetic facies of deep and ultra deep tight sandstone reservoirs: A case study of Bozi-Dabei area in Kuqa Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 299-310. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 张冠杰, 张滨鑫, 徐珂, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷博孜区块超深层致密砂岩储层裂缝特征及其对油气产能的影响[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 75-86.ZHANG G J, ZHANG B X, XU K, et al. Fracture characteristics of ultra-deep tight sandstone reservoirs in the Bozi Block, Kuqa Depression of Tarim Basin, and effects on oil-gas production[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 75-86. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] LIU J L, YANG X Z, LIU K Y, et al. Differential hydrocarbon generation and evolution of typical terrestrial gas-prone source rocks: An example from the Kuqa Foreland Basin, NW China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2023, 152: 106225. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2023.106225 [37] 王高成, 田文广, 章超, 等. 四川盆地大安区块深层煤岩气储层特征及勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 2025, 45(3): 68-81.WANG G C, TIAN W G, ZHANG C, et al. Reservoir characteristics and exploration potential of deep CBM in the Da'an Block, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2025, 45(3): 68-81. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 兰浩, 杨兆彪, 仇鹏, 等. 新疆准噶尔盆地白家海凸起深部煤层气勘探开发进展及启示[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2024, 52(2): 13-22.LAN H, YANG Z B, QIU P , et al. Exploration and exploitation of deep coalbed methane in the Baijiahai Uplift, Junggar Basin: Progress and its implications[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2024, 52(2): 13-22. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 邢丽茹, 张洲, 任峻杉, 等. 准噶尔盆地深部与浅部煤层气储层物性特征对比分析[J]. 中国煤炭, 2024, 50(9): 9-17.XING L R, ZHANG Z, REN J S, et al. Comparative analysis of physical properties of deep and shallow CBM reservoirs in Junggar Basin[J]. China Coal, 2024, 50(9): 9-17. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 闫霞, 徐凤银, 聂志宏, 等. 深部微构造特征及其对煤层气高产“甜点区” 的控制: 以鄂尔多斯盆地东缘大吉地区为例[J]. 煤炭学报, 2021, 46(8): 2426-2439.YAN X, XU F Y, NIE Z H, et al. Microstructure characteristics of Daji area in east Ordos Basin and its control over the high yield dessert of CBM[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(8): 2426-2439. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 孙斌, 杨敏芳, 杨青, 等. 准噶尔盆地深部煤层气赋存状态分析[J]. 煤炭学报, 2017, 42(增刊1): 195-202.SUN B, YANG M F, YANG Q, et al. Analysis on occurrence state of deep coalbed methane in Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2017, 42(S1): 195-202. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] 陈河青, 杨兆彪, 李道清, 等. 新疆准噶尔盆地白家海凸起深部煤层气孔渗系统特征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2024, 52(6): 33-43. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.24.02.0141CHEN H Q, YANG Z B, LI D Q, et al. Characteristics of the pore and seepage system of deep coalbed methane in the Baijiahai Uplift, Junggar Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2024, 52(6): 33-43. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.24.02.0141 -




 下载:
下载: