Identification of oil sources from marine-continental faces source rooks and quantitative evaluation of mixed-source oil contributions in the southern slope of Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin: A case study of the Yaha structure zone
-
摘要:
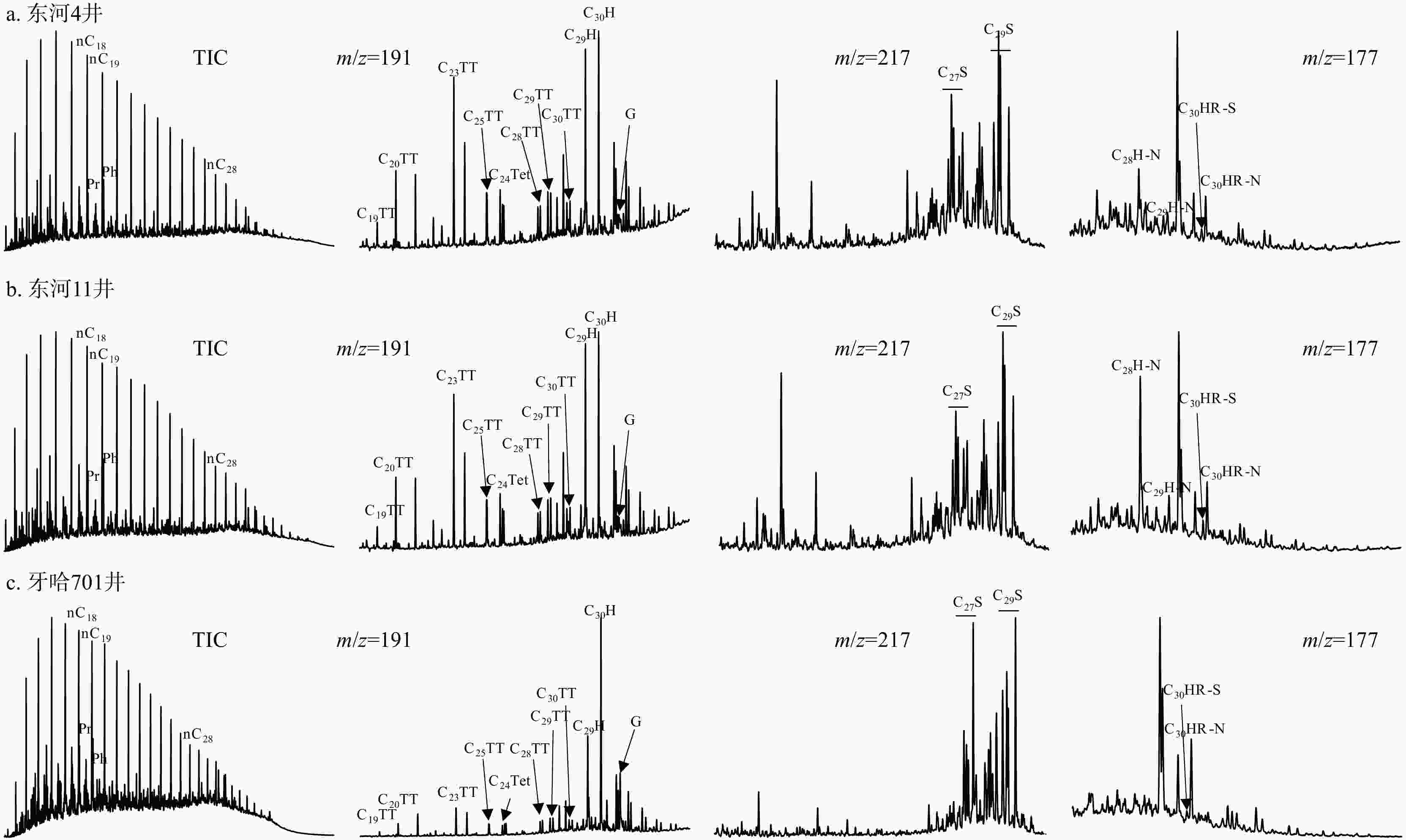
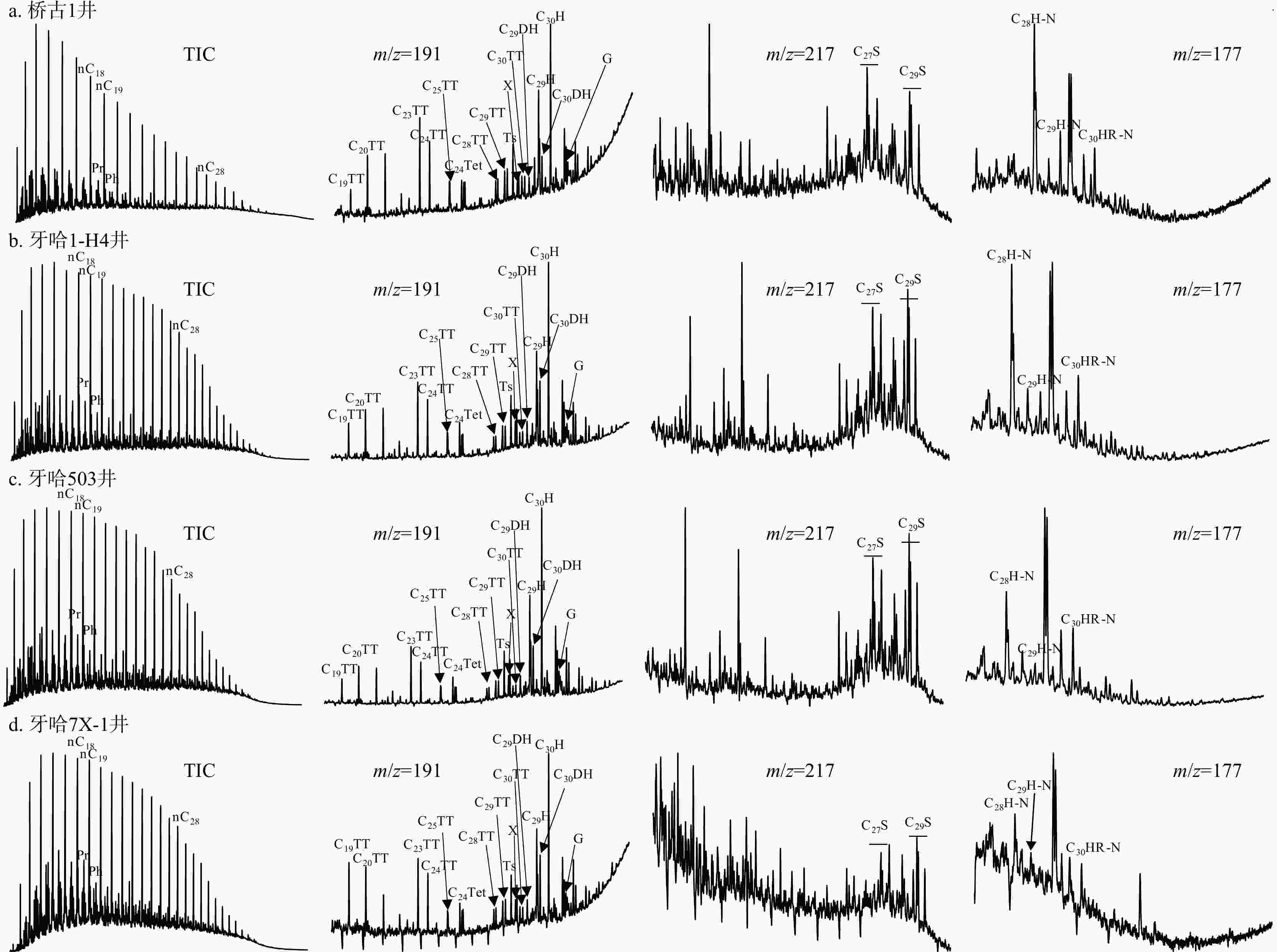
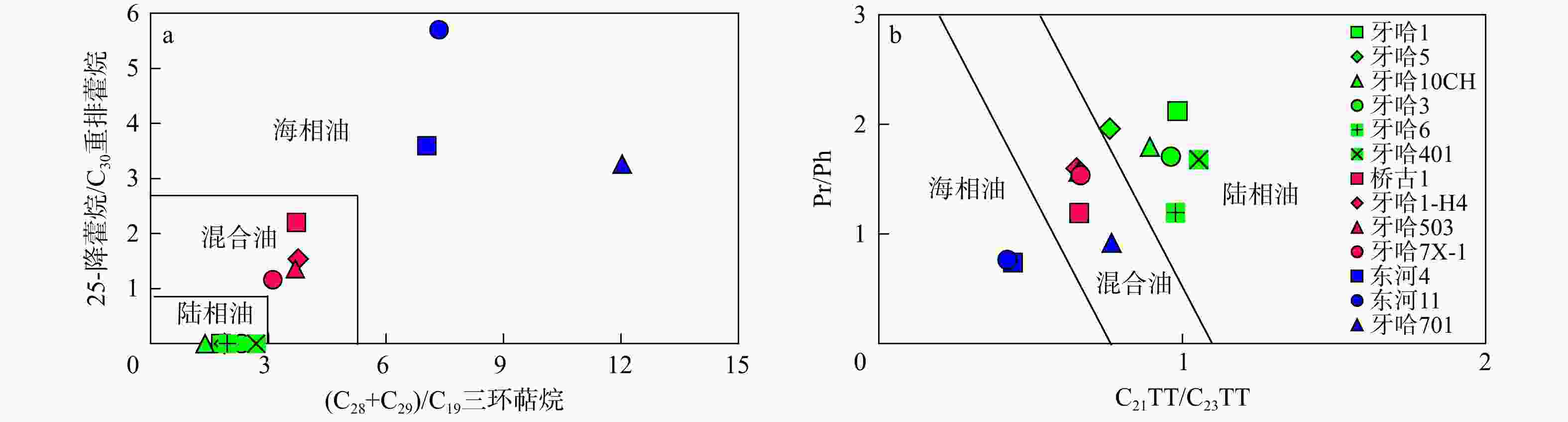
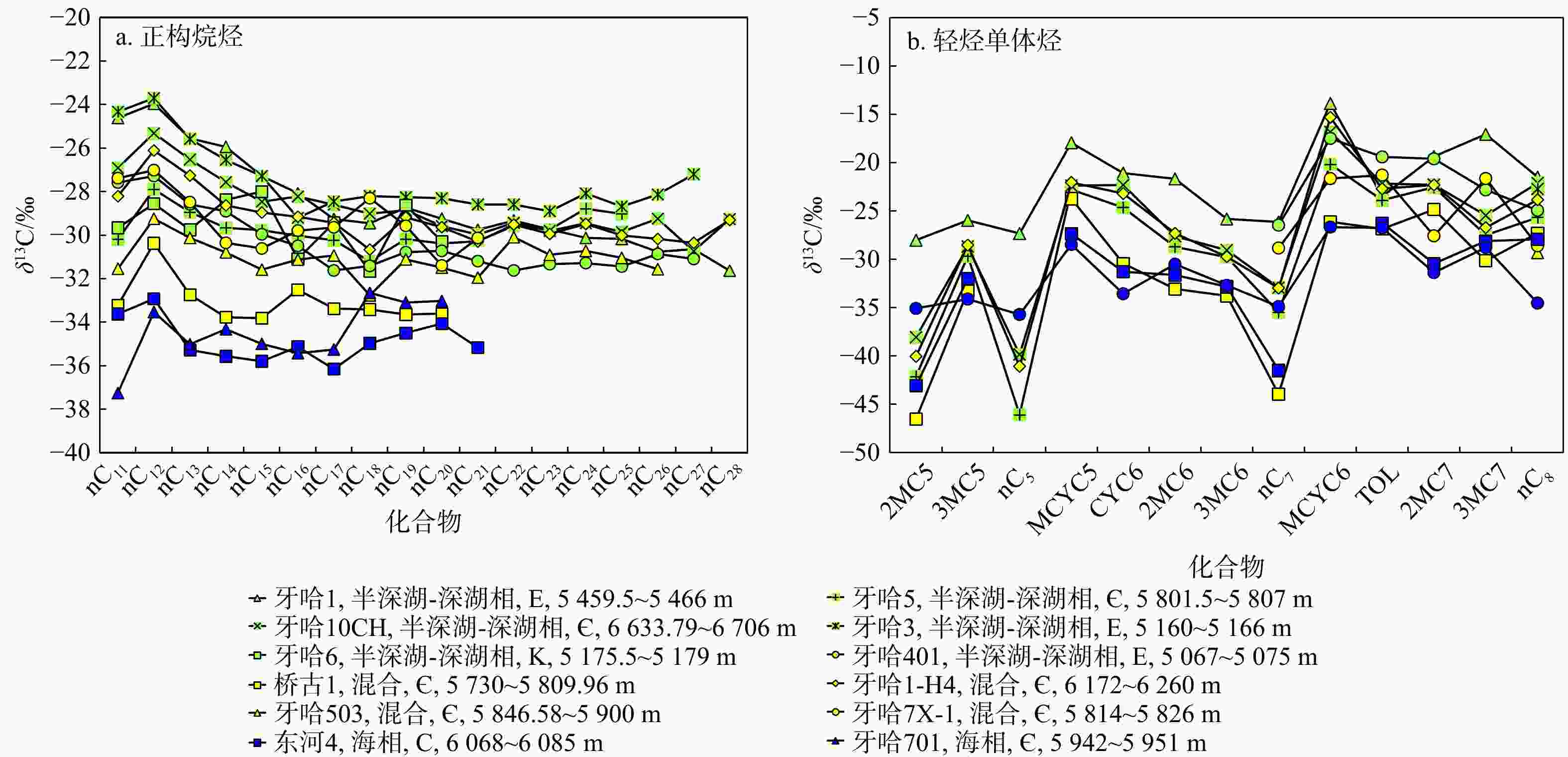
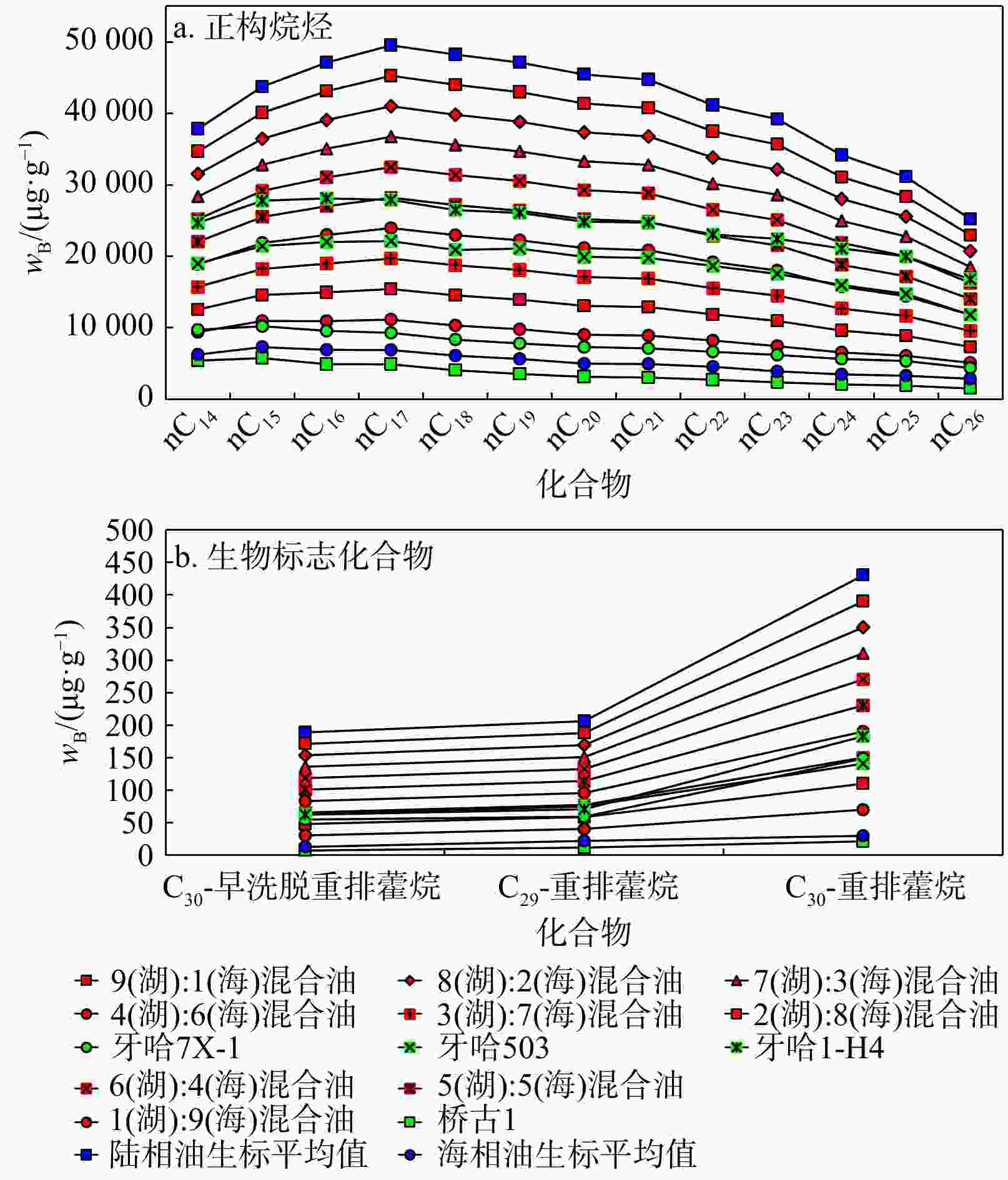
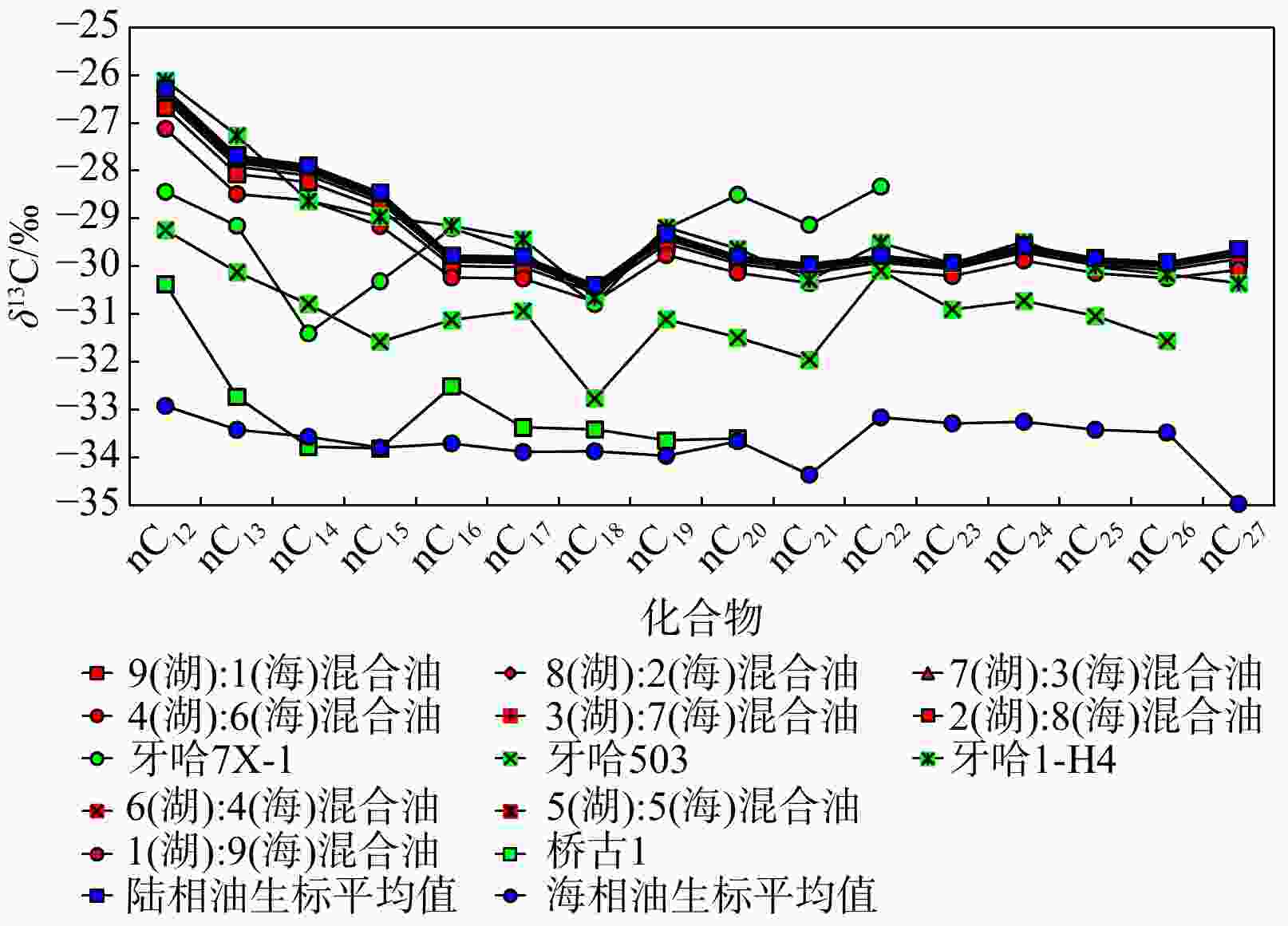
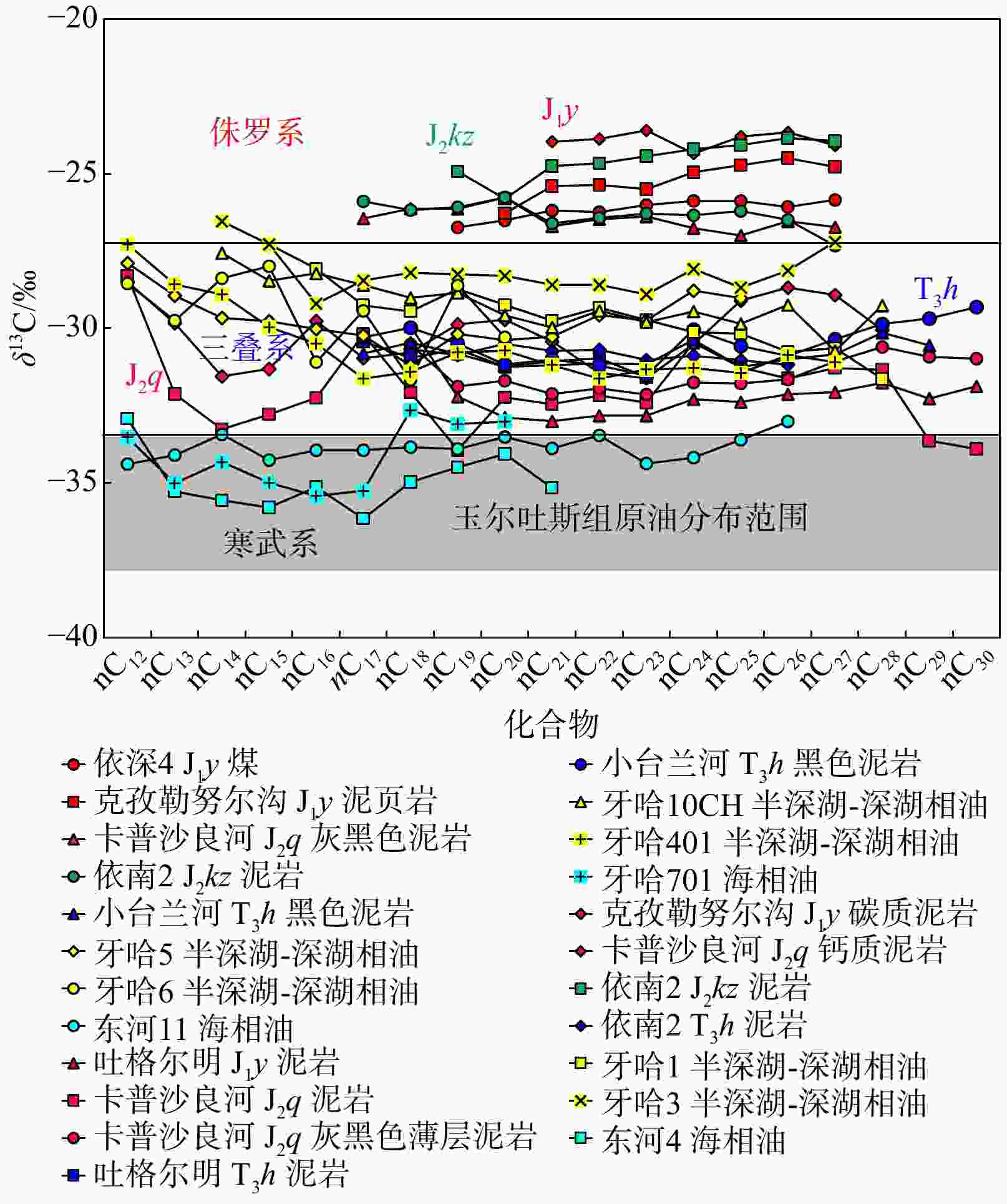
库车坳陷南斜坡牙哈地区是塔里木盆地重要的油气富集区,然而其原油来源仍不明确。选取了牙哈地区13个原油样品对其进行了有机地球化学分析,并采用端元油模拟混合的方法揭示了混源油中海陆相油混源贡献。依据原油生物标志化合物特征,牙哈地区原油可以大致分为3类:陆相油、海相油以及混合油。陆相油主要来自陆相源岩,姥鲛烷和植烷比值(Pr/Ph)介于1.20~2.35,平均值为1.74,三环萜烷(TT)以C20TT和C21TT为主峰,存在高丰度的C30早洗脱重排藿烷(X化合物)等重排类化合物,正构烷烃碳同位素值介于−28‰~−32‰。海相油是多期海相油的混合,Pr/Ph介于0.74~0.92,平均值为0.81,三环萜烷以C23TT和C24TT为主峰,存在高丰度的长链三环萜烷,正构烷烃碳同位素值均轻于−32‰。此外,海相油中均检测到25-降藿烷类化合物,指示海相原油早期遭受了强烈的生物降解。混合油兼具海相和陆相油的生物标志化合物和碳同位素特征。除牙哈401和牙哈3井计算的原油绝对成熟度值偏低外(牙哈401井镜质体反射率
R c为0.54%,牙哈3井R c为0.57%),研究区内其他原油的成熟度总体分布比较均匀,R c介于0.86%~1.11%,平均值为0.97%。二端元混合贡献计算结果表明,研究区混合油中海相油占比均超过60%,其中桥古1井海相油占比可达到90%以上。油源分析表明研究区的陆相油主要来源于三叠系黄山街组,海相油来源于寒武系玉尔吐斯组。研究成果表明库车坳陷南斜坡传统陆相油区依然存在发现海相油气的潜力,对拓展南斜坡下一步油气勘探领域具有重要指导意义。Abstract:Objective The Yaha area on the southern slope of the Kuqa sub-basin is a significant hydrocarbon-rich region in the Tarim Basin; however, the origin of its crude oil remains unclear.
Methods This study analyzed 13 crude oil samples from the Yaha area using organic geochemical techniques and employed an end-member oil mixing model to quantify the contributions of marine and terrestrial sources in the mixed oils.
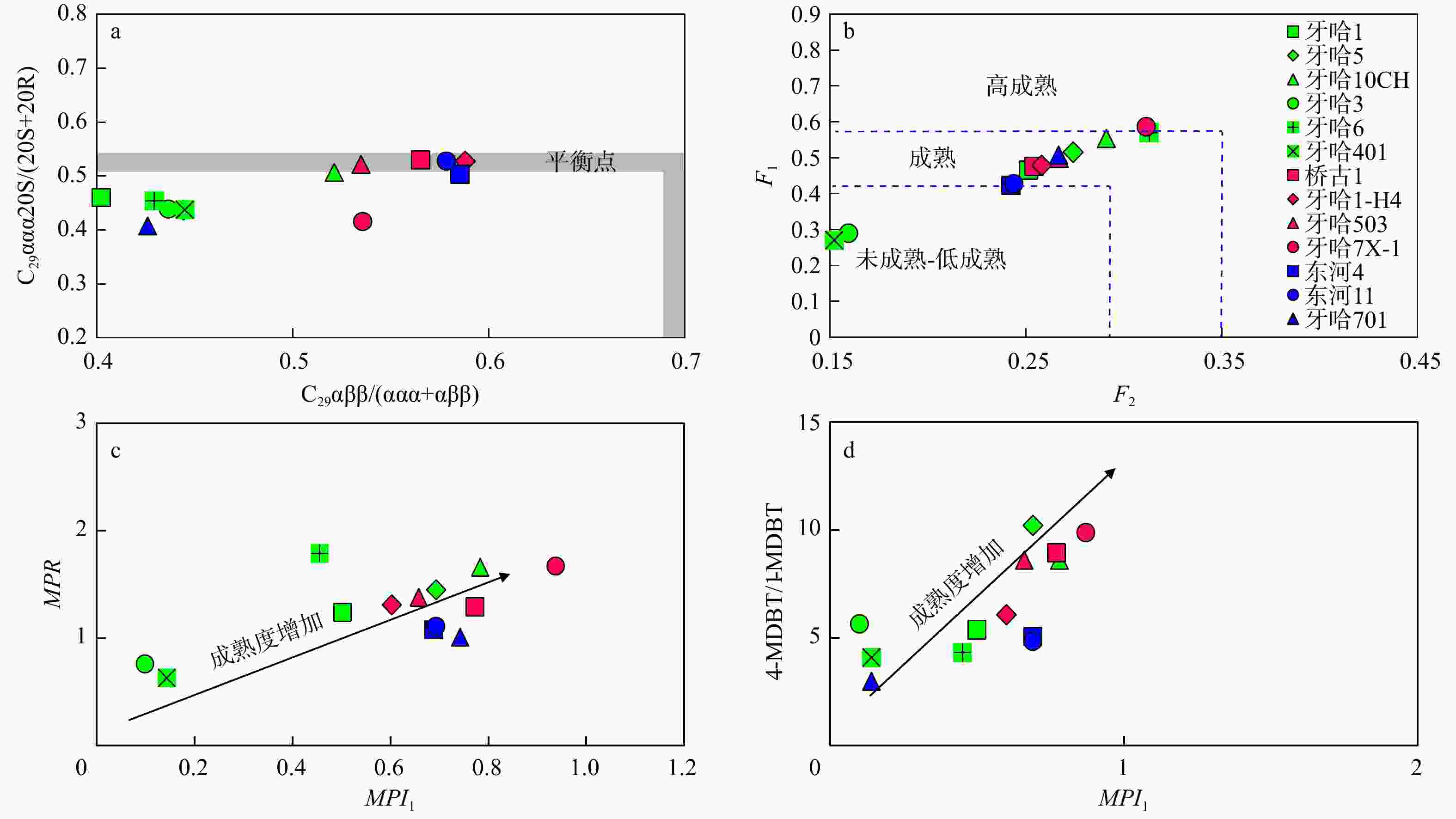
Results Biomarker characteristics indicate that the crude oils in the Yaha area can be broadly classified into three types: Terrestrial oils, marine oils, and mixed oils. Terrestrial oils primarily derive from lacustrine source rocks, with pristane/phytane (Pr/Ph) values ranging from 1.20 to 2.35 (averaging 1.74). The tricyclic terpanes (TT) are dominated by C20TT and C21TT, with a high abundance of rearranged compounds such as C30 early-eluting rearranged hopanes (compound X). The n-alkane carbon isotope values range from −28‰ to 32‰. Marine oils are a mixture of multi-stage marine source rock contributions, exhibiting Pr/Ph values between 0.74 and 0.92 (average of 0.81), with peak C23TT and C24TT compounds and a high abundance of long-chain tricyclic terpanes. Their n-alkane carbon isotope values are generally lighter than −32‰. Additionally, the presence of 25-norhopane compounds in the marine oils indicates significant early-stage biodegradation.. Mixed oils display biomarker and isotopic features characteristic of both marine and terrestrial oils. Except for the lower absolute maturity values observed in wells Yaha5, Yaha 401, and Yaha 3 (Well Yaha 3: 0.57%
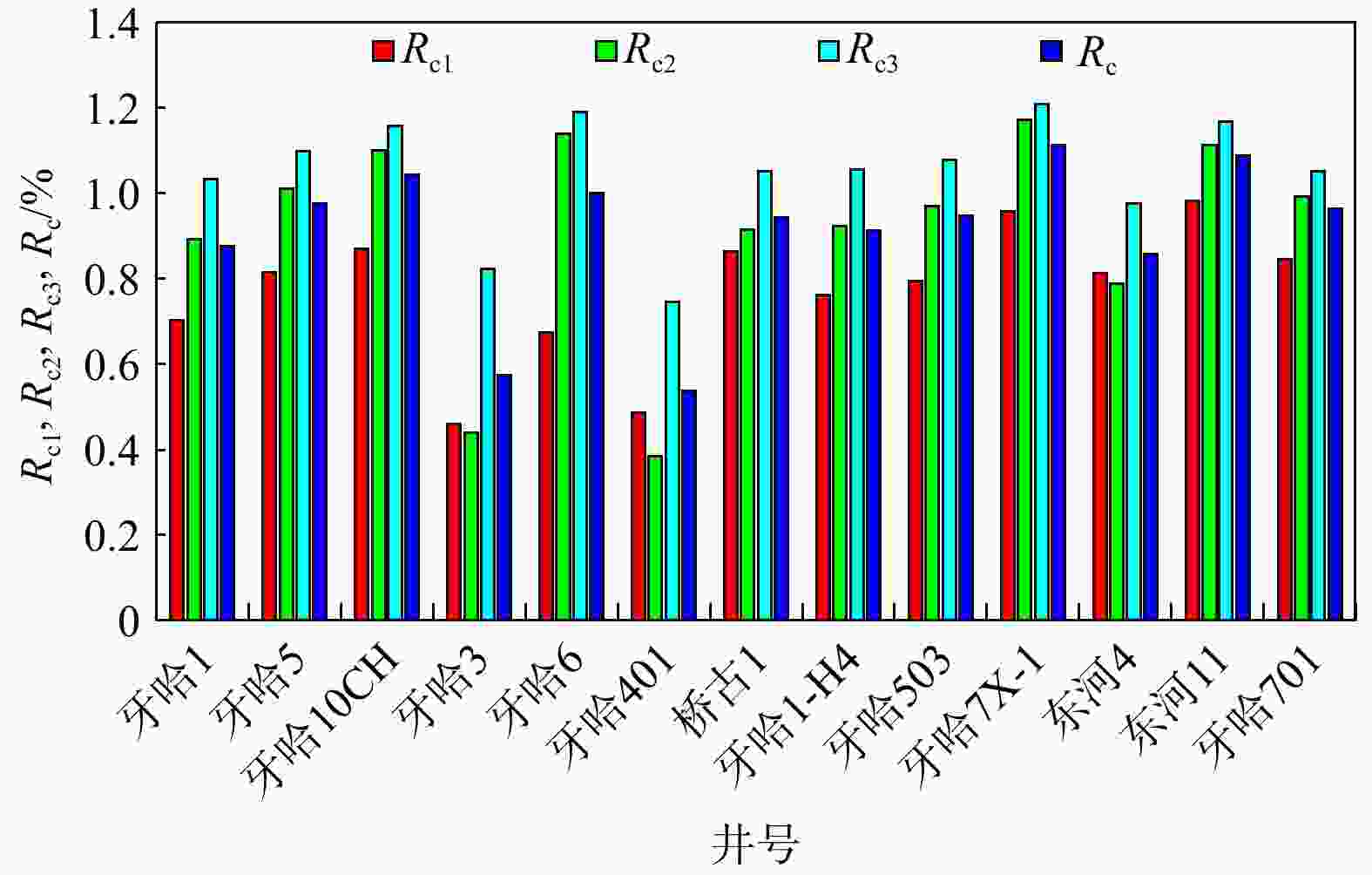
R c; Well Yaha 401: 0.54%R c), the overall maturity distribution across the study area is relatively uniform, ranging from 0.86 to 1.11%R c, with an average of 0.97%R c. Two-end-member mixing calculation suggests that marine oils account for over 60% of the mixed oils in the study area, with marine the contribution in Well Qiaogu 1 exceeding 90%. Source analysis indicates that the terrestrial oils primarily originate from the Triassic Huangshanjie Formation, while the marine oils are derived from the Cambrian Yuertusi Formation.Conclusion These findings demonstrate that the continental oil prospects on the southern slope of the Kuqa sub-basin remain promising for discovering marine oil and gas resources. This has significant implications for expanding future oil and gas exploration in the southern slope of the Kuqa Depression.
-
Key words:
- Yaha area /
- biomarker /
- carbon isotope /
- mixed source contribution /
- Yuertusi Formation /
- oil source identification /
- Kuqa Depression
-
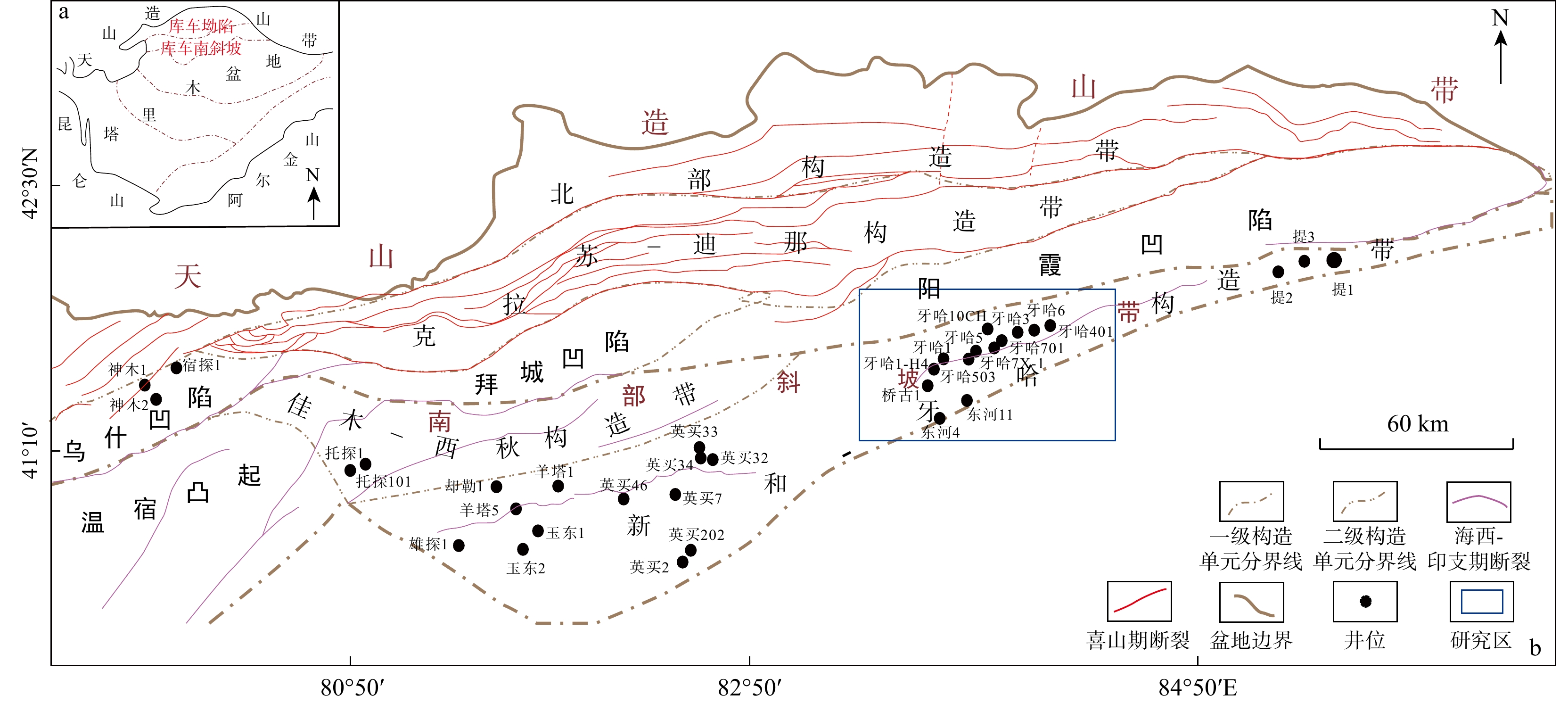
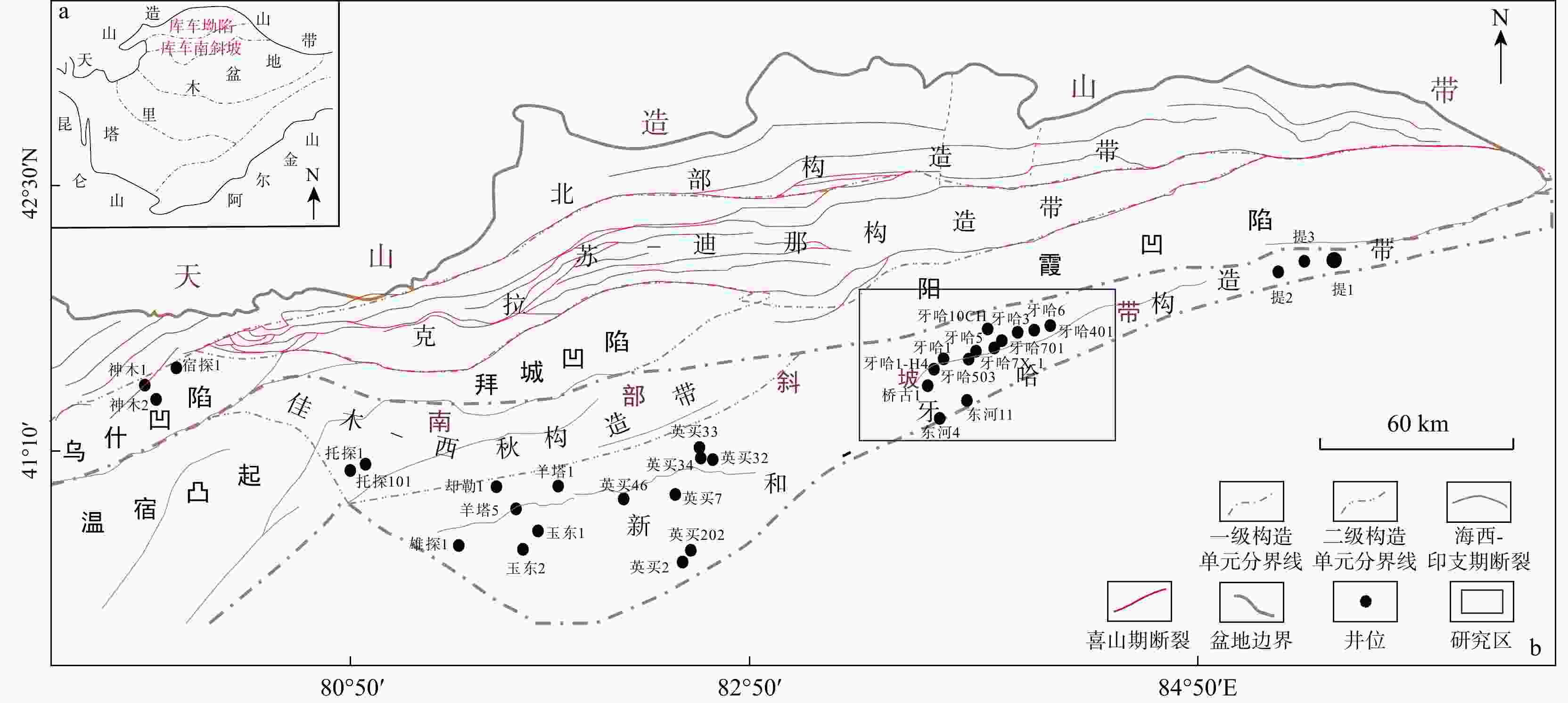
图 1 库车坳陷南斜坡位置示意图(a)和构造单元图(b)[3]
Figure 1. Location map (a) and structural unit map (b) of the south slope of Kuqa Depression
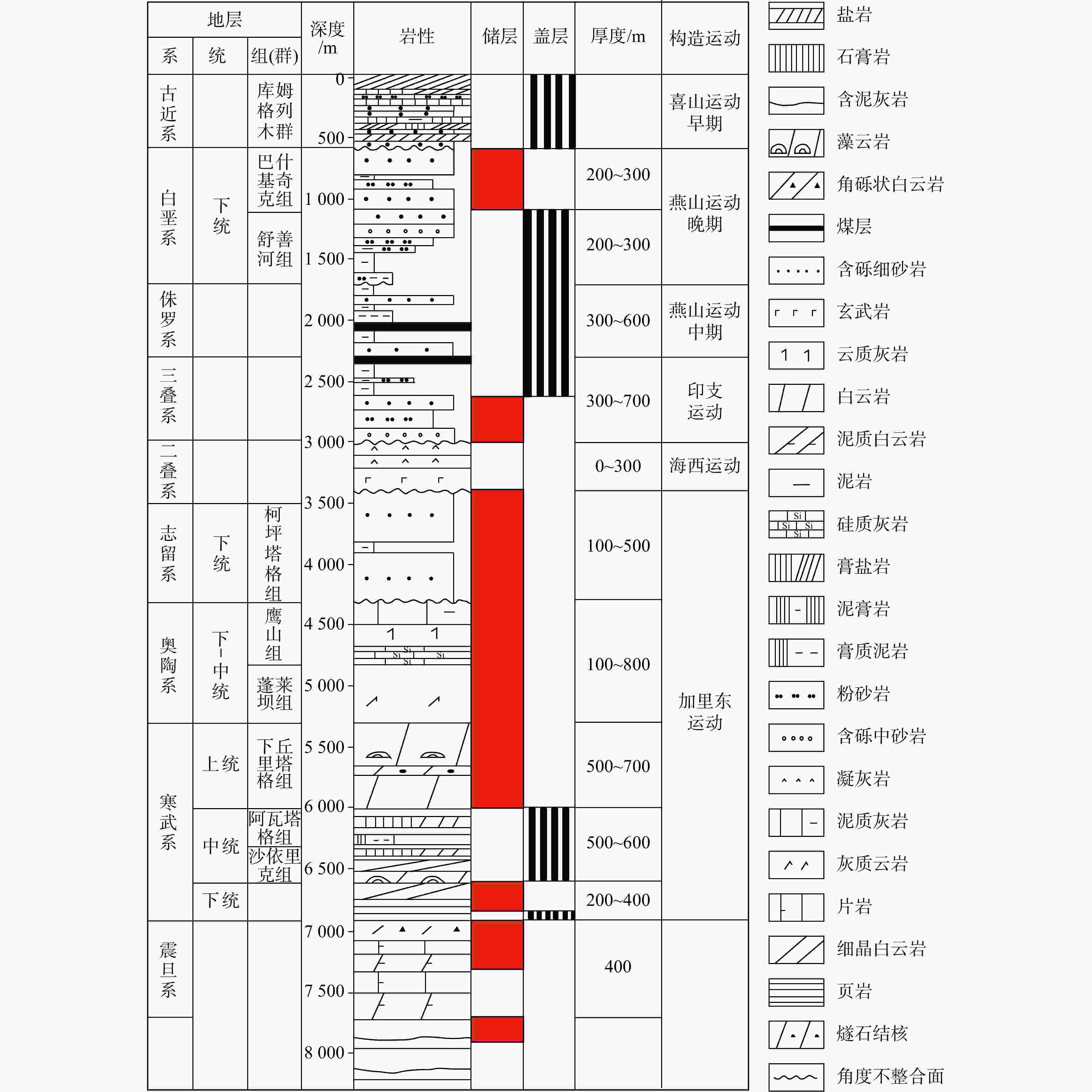
图 2 库车坳陷南斜坡地层综合柱状图[14]
Figure 2. Stratigraphic histogram of the south slope of Kuqa Depression
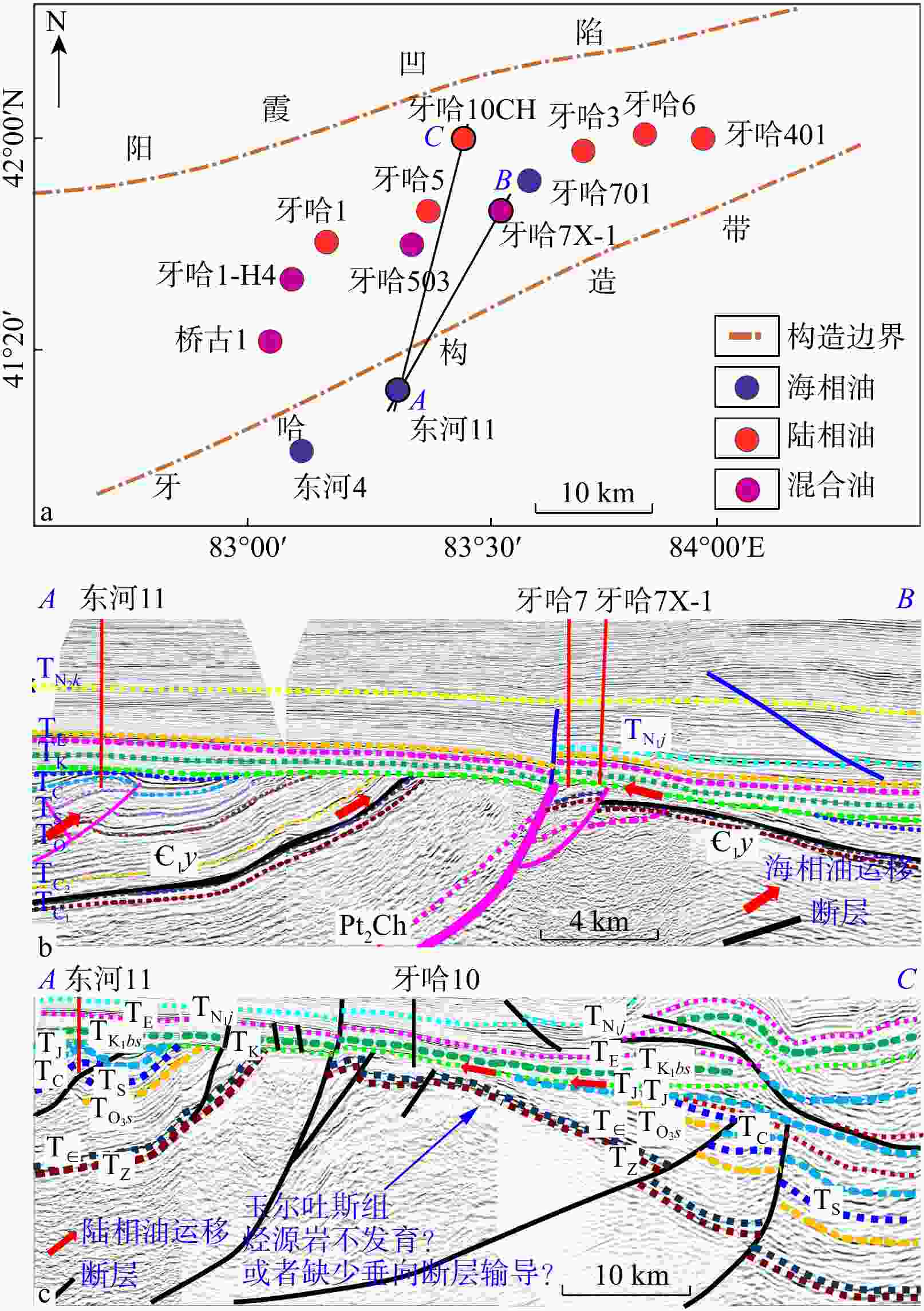
图 14 牙哈地区海陆相原油平面分布(a)和东河11-牙哈7X-1井成藏剖面图(b)及东河11-牙哈10CH井油运移剖面图(c)
T. 地层界限;N2k. 上新统库车组;N1j. 中新统吉迪克组;Є1y. 下寒武统玉尔吐斯组;K1bs. 下白垩统巴什基奇克组;O3s. 上奥陶统桑塔木组;S. 志留系;O. 奥陶系;Є1. 下寒武统;Є2. 中寒武统;Pt2Ch. 中元古界长城系;J. 侏罗系;Z. 震旦系
Figure 14. Spatial distribution(a), accumulation profile of Well Donghe11 and Well Yaha7X-1(b) and oil migration profile of Well Donghe11 and Well Yaha10(c) of marine and continental crude oil in the Yaha area
表 1 牙哈地区原油物性及族组分数据
Table 1. Physical properties and grouped composition content of crude oil in the Yaha area
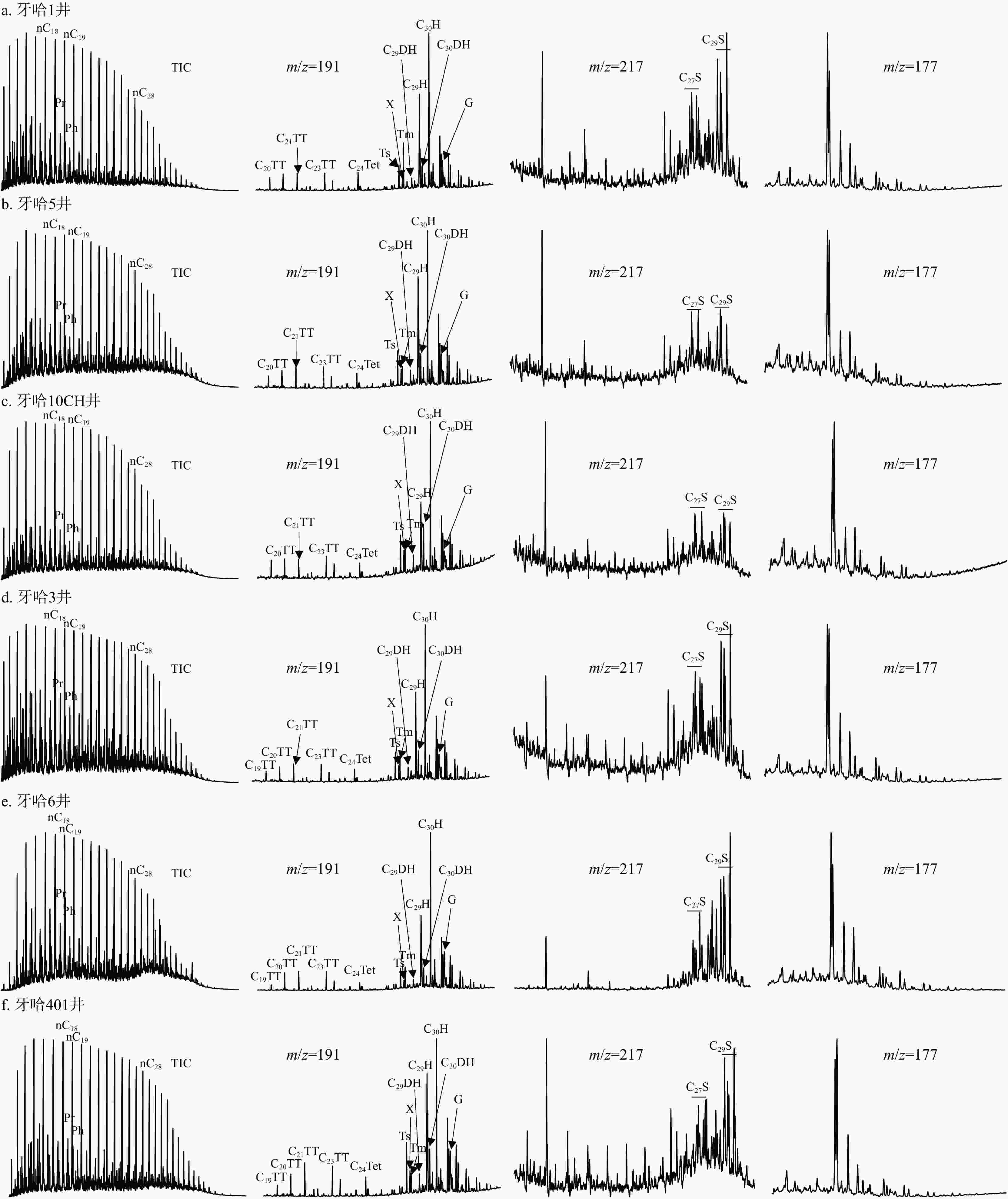
井号 深度/m 层位 密度/(g·cm−3) 饱和烃 芳烃 胶质 沥青质 闭合度/% wB/% 牙哈1 5459.5 ~5466 E / 62.93 16.51 4.67 3.43 87.54 牙哈5 5801.5 ~5807 Є 0.76 72.02 17.10 1.55 0.52 91.90 牙哈10CH 6633.79 ~6706 Є 0.83 71.92 20.00 1.54 0.77 94.23 牙哈3 5160 ~5166 E 0.82 79.32 8.46 0.75 0.19 88.72 牙哈6 5175.5 ~5179 K / 52.34 16.82 3.74 16.82 89.72 牙哈401 5067 ~5075 E / 73.52 13.94 0.70 0.35 88.50 桥古1 5730 ~5809.96 Є / 55.20 19.00 14.34 1.08 89.61 牙哈1-H4 6172 ~6260 Є / 65.12 22.48 2.84 0.52 90.96 牙哈503 5846.58 ~5900 Є 0.84 59.76 23.67 3.85 0.89 88.17 牙哈7X-1 5814 ~5826 Є 0.83 62.53 22.74 2.33 0.78 88.37 东河4 6068 ~6085 C / 46.24 13.62 1.79 31.18 92.83 东河11 5828 ~5883 C / 40.71 29.49 6.73 14.10 91.03 牙哈701 5942 ~5951 Є 0.87 40.23 32.42 7.03 6.25 85.94 注:E. 古近系;Є. 寒武系;K. 白垩系;C. 石炭系;下同 表 2 牙哈地区原油饱和烃地球化学参数
Table 2. Geochemistry parameters of saturated hydrocarbon in crude oil from the Yaha area
井号 深度/m 层位 Pr/
PhPr/
nC17Ph/
nC18C19TT/
C23TT(C28+C29) TT/
(C19+C20) TTC30DH/
C30HG/
C30Hααα20RC27/
C29SC29ααα20S/
(20S+20R)C29αββ/
(ααα+αββ)牙哈1 5459.5 ~5466 E 2.12 0.28 0.14 0.71 0.77 0.16 0.18 0.43 0.40 0.46 牙哈5 5801.5 ~5807 Є 1.83 0.20 0.11 0.62 0.79 0.22 0.19 0.32 0.44 0.44 牙哈10CH 6633.79 ~6706 Є 1.80 0.19 0.11 0.91 0.68 0.35 0.14 0.35 0.52 0.51 牙哈3 5160 ~5166 E 1.71 0.20 0.12 0.51 0.89 0.20 0.23 0.41 0.44 0.44 牙哈6 5175.5 ~5179 K 1.20 0.33 0.29 0.31 1.01 0.14 0.24 0.31 0.43 0.45 牙哈401 5067 ~5075 E 1.68 0.21 0.12 0.38 0.93 0.31 0.34 0.20 0.44 0.44 桥古1 5730 ~5809.96 Є 1.19 0.21 0.21 0.35 1.40 0.26 0.22 0.53 0.57 0.53 牙哈1-H4 6172 ~6260 Є 1.60 0.25 0.16 0.47 1.06 0.38 0.09 0.39 0.59 0.53 牙哈503 5846.58 ~5900 Є 1.57 0.27 0.18 0.35 1.25 0.29 0.16 0.35 0.53 0.52 牙哈7X-1 5814 ~5826 Є 1.57 0.16 0.11 0.84 0.65 0.34 0.08 0.41 0.54 0.42 东河4 6068 ~6085 C 0.74 0.26 0.41 0.15 1.27 0.07 0.13 0.48 0.59 0.50 东河11 5828 ~5883 C 0.74 0.34 0.51 0.16 1.95 0.08 0.16 0.40 0.58 0.53 牙哈701 5942 ~5951 Є 0.92 0.32 0.39 0.16 3.15 0.07 0.28 0.71 0.43 0.41 注:Pr. 姥鲛烷;Ph. 植烷;TT. 三环萜烷;DH. 重排藿烷;H. 藿烷;G. 伽马蜡烷;R. C31H的构型;S. 甾烷;下同 表 3 牙哈地区原油芳烃热成熟度参数
Table 3. Thermal maturity parameters of aromatics in crude oil from the Yaha area
井号 深度/m 层位 MPI1 MPR MPR1 4-MDBT/1-MDBT F1 F2 Rc1 Rc2 Rc3 Rc 牙哈1 5459.5 ~5466 E 0.50 1.24 0.87 5.36 0.47 0.25 0.70 1.03 0.89 0.87 牙哈5 5801.5 ~5807 Є 0.69 1.45 0.36 10.20 0.52 0.27 0.82 1.10 1.01 0.98 牙哈10CH 6633.79 ~6706 Є 0.78 1.66 1.24 8.59 0.55 0.29 0.87 1.16 1.10 1.04 牙哈3 5160 ~5166 E 0.10 0.76 0.41 5.64 0.29 0.16 0.46 0.82 0.44 0.57 牙哈6 5175.5 ~5179 K 0.45 1.79 1.32 4.31 0.57 0.31 0.67 1.19 1.14 1.00 牙哈401 5067 ~5075 E 0.14 0.63 0.37 4.08 0.27 0.15 0.49 0.74 0.38 0.54 桥古1 5730 ~5809.96 Є 0.77 1.29 0.91 8.93 0.48 0.25 0.86 1.05 0.91 0.94 牙哈1-H4 6172 ~6260 Є 0.60 1.31 0.92 6.07 0.48 0.26 0.76 1.06 0.92 0.91 牙哈503 5846.58 ~5900 Є 0.66 1.38 0.99 8.60 0.50 0.27 0.79 1.08 0.97 0.95 牙哈7X-1 5814 ~5826 Є 0.87 1.67 1.25 9.87 0.56 0.29 0.96 1.21 1.17 1.11 东河4 6068 ~6085 C 0.69 1.08 0.73 5.06 0.42 0.24 0.81 0.97 0.79 0.86 东河11 5828 ~5883 C 0.69 1.11 1.27 4.84 0.43 0.24 0.98 1.17 1.11 1.09 牙哈701 5942 ~5951 Є 0.14 1.01 1.03 2.98 0.39 0.22 0.85 1.05 0.99 0.96 注:MPI1=1.5(2-MP+3-MP)/(P+1-MP+9-MP);MPR=(2-MP/1-MP);MPR1=(2-MP+3-MP)/(1-MP+9-MP);F1=(2-MP+3-MP)/(2-MP+3-MP+1-MP+9-MP)[18];F2=2-MP/(2-MP+3-MP+1-MP+9-MP)[18];Rc1=0.6MPI1+0.4[19];Rc2=0.99lgMPR+0.94[20];Rc3= 0.5946 lnMPR1+0.9728 [21];MPI1. 甲基菲指数;P. 菲;MP. 甲基菲;1-MP. 1-甲基菲;2-MP. 2-甲基菲;3-MP. 3-甲基菲;9-MP. 9-甲基菲;MPR,MPR1. 甲基菲比值;F1,F2. 甲基菲分布系数;Rc. 原油绝对成熟度换算的原油等效镜质体反射率的平均值;Rc1,Rc2,Rc3. 不同成熟度参数换算的原油等效镜质体反射率;4-MDBT/1-MDBT. 甲基二苯并噻吩参数比值;下同 -
[1] 智凤琴,张荣虎,余朝丰. 库车坳陷东部阳霞凹陷侏罗系石油地质条件与勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质,2023,28(2):186-195. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2023.02.008ZHI F Q,ZHANG R H,YU C F. Jurassic petroleum geological conditions and exploration direction in Yangxia Sag,eastern Kuqa Depression[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology,2023,28(2):186-195. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2023.02.008 [2] 周兴熙,贾进华,周东延,等. 库车坳陷乌什凹陷东部成藏作用初步研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2006,33(2):184-188. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.02.012ZHOU X X,JIA J H,ZHOU D Y,et al. Gas pool forming process in Wushi Sag of Kuqa Depression,Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2006,33(2):184-188. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.02.012 [3] 王清华,杨海军,蔡振忠,等. 塔里木盆地库车南斜坡托探1井油气勘探重大突破及意义[J]. 中国石油勘探,2023,28(5):28-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2023.05.003WANG Q H,YANG H J,CAI Z Z,et al. Major breakthrough and significance of petroleum exploration in Well Tuotan 1 on the south slope of Kuqa Depression,Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration,2023,28(5):28-42. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2023.05.003 [4] 王飞宇,杜治利,张水昌,等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷烃源灶特征和天然气成藏过程[J]. 新疆石油地质,2009,30(4):431-439.WANG F Y,DU Z L,ZHANG S C,et al. Source kitchen and natural gas accumulation in Kuqa Depression,Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,2009,30(4):431-439. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 赵孟军,张宝民. 库车前陆坳陷形成大气区的烃源岩条件[J]. 地质科学,2002,37(增刊1):35-44.ZHAO M J,ZHANG B M. Source rocks for a giant gas-accumulating area in the Kuqa Foreland Depression[J]. Scientia Geologica Sinica,2002,37(S1):35-44. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 朱光有,刘星旺,朱永峰,等. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘地区复杂油气藏特征及其成藏机制[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2013,32(2):231-242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.02.009ZHU G Y,LIU X W,ZHU Y F,et al. The characteristics and the accumulation mechanism of complex reservoirs in the Hanilcatam area,Tarim Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry,2013,32(2):231-242. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.02.009 [7] 张慧芳,王祥,张科,等. 塔里木盆地乌什−温宿地区油源对比与成藏演化[J]. 天然气地球科学,2022,33(1):24-35.ZHANG H F,WANG X,ZHANG K,et al. Oil-source correlation and accumulation evolution in Wushi-Wensu area of Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2022,33(1):24-35. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 赵海涛,孙琦,李文浩,等. 塔北隆起英买力地区白垩系油气成藏规律:以英买46井区为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2022,51(1):137-147. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1964.2022.1.zgkydxxb202201013ZHAO H T,SUN Q,LI W H,et al. Cretaceous hydrocarbon accumulation rules of the Yingmaili area in the Tabei uplift:A case study of the Yingmai 46 well block[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2022,51(1):137-147. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1964.2022.1.zgkydxxb202201013 [9] 刘春,陈世加,赵继龙,等. 库车南斜坡中−新生界油气运移地球化学示踪[J]. 地质学报,2020,94(11):3488-3502. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.11.021LIU C,CHEN S J,ZHAO J L,et al. Geochemical tracer of hydrocarbon migration path of Middle-Cenozoic in the south slope of the Kuqa Foreland Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2020,94(11):3488-3502. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.11.021 [10] 李素梅,庞雄奇,杨海军,等. 塔里木盆地海相油气源与混源成藏模式[J]. 地球科学,2010,35(4):663-673.LI S M,PANG X Q,YANG H J,et al. Generation,migration and accumulation model for the marine oils in the Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science,2010,35(4):663-673. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 刘军,王鹏程,陈军,等. 地震沉积学技术在库车坳陷南斜坡白垩系砂体尖灭线识别中的应用[J]. 石油物探,2018,57(5):788-794. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2018.05.018LIU J,WANG P C,CHEN J,et al. Identification of the Cretaceous sandbody pinchout line in the south slope of Kuqa Depression,China,via seismic sedimentology[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum,2018,57(5):788-794. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2018.05.018 [12] 郑民,彭更新,雷刚林,等. 库车坳陷乌什凹陷构造样式及对油气的控制[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2008,35(4):444-451. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2008.04.008ZHENG M,PENG G X,LEI G L,et al. Structural pattern and its control on hydrocarbon accumulations in Wushi Sag,Kuche Depression,Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2008,35(4):444-451. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2008.04.008 [13] 宋金鹏,郇志鹏,田盼盼,等. 超深致密砂岩储层特征及影响因素:以库车坳陷阳霞凹陷侏罗系为例[J]. 断块油气田,2021,28(5):592-597.SONG J P,HUAN Z P,TIAN P P,et al. Features and influence factors of ultra-deep tight sandstone reservoirs:A case study of Jurassic in Yangxia Sag,Kuqa Depression[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field,2021,28(5):592-597. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 赫英福,周成刚,李强,等. 库车地区阳霞凹陷侏罗系层序地层特征[C]//中国石油学会石油物探专业委员会. 第二届中国石油物探学术年会论文集(下册). 新疆库尔勒:中国石油集团东方地球物理勘探有限责任公司塔里木物探研究院,2024:293-296.HE Y F,ZHOU C G,LI Q,et al. Sequence stratigraphic characteristics of Jurassic in Yangxia Sag,Kuqa area[C]//Society of Petroleum Geophysicists. Proceedings of the Second Annual Conference on Petroleum Geophysical Exploration in China. Korla Xinjiang:Tarim Geophysical Research Institute,CNPC Bureau of Geophysical Prospecting INC,2024:293-296. (in Chinese) [15] 于志超,刘可禹,赵孟军,等. 库车凹陷克拉2气田储层成岩作用和油气充注特征[J]. 地球科学,2016,41(3):533-545.YU Z C,LIU K Y,ZHAO M J,et al. Characterization of diagenesis and the petroleum charge in Kela 2 gas field,Kuqa Depression,Tarim Basin[J]. Earth Science,2016,41(3):533-545. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 包建平,朱翠山,张秋茶,等. 库车坳陷前缘隆起带上原油地球化学特征[J]. 石油天然气学报,2007,29(4):40-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2007.04.007BAO J P,ZHU C S,ZHANG Q C,et al. Geochemical characteristics of crude oil from frontal uplift in Kuqa Depression[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology,2007,29(4):40-44. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2007.04.007 [17] 刘建良,刘可禹,姜振学,等. 库车前陆盆地玉东地区白垩系油气成藏过程[J]. 石油学报,2018,39(6):620-630. doi: 10.7623/syxb201806002LIU J L,LIU K Y,JIANG Z X,et al. Cretaceous hydrocarbon accumulation process in Yudong area,Kuqa foreland basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2018,39(6):620-630. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7623/syxb201806002 [18] KVALHEIM O M,CHRISTY A A,TELNÆS N,et al. Maturity determination of organic matter in coals using the methylphenanthrene distribution[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1987,51(7):1883-1888. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90179-7 [19] RADKE M,LEYTHAEUSER D,TEICHMÜLLER M. Relationship between rank and composition of aromatic hydrocarbons for coals of different origins[J]. Organic Geochemistry,1984,6:423-430. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(84)90065-2 [20] RADKE M. Application of aromatic compounds as maturity indicators in source rocks and crude oils[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,1988,5(3):224-236. doi: 10.1016/0264-8172(88)90003-7 [21] 陈琰,包建平,刘昭茜,等. 甲基菲指数及甲基菲比值与有机质热演化关系:以柴达木盆地北缘地区为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2010,37(4):508-512.CHEN Y,BAO J P,LIU Z Q,et al. Relationship between methylphenanthrene index,methylphenanthrene ratio and organic thermal evolution:Take the northern margin of Qaidam Basin as an example[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2010,37(4):508-512. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] LU Z D,CHEN Z L,PING H W,et al. A small-scale silica gel column chromatography method for separating carbazole compounds from highly mature crude oil[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2024,1713:464536. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2023.464536 [23] SPIKER E C,HATCHER P G. The effects of early diagenesis on the chemical and stable carbon isotopic composition of wood[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1987,51(6):1385-1391. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(87)90323-1 [24] CRAIG H. Isotopic standards for carbon and oxygen and correction factors for mass-spectrometric analysis of carbon dioxide[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1957,12(1/2):133-149. [25] LU Z D,PING H W,CHEN H H,et al. Geochemical characteristics of Ordovician crude oils in the FI17 strike-slip fault zone of the Fuman oilfield,Tarim Basin:Implications for ultra-deep hydrocarbon accumulation in the Tarim Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2024,163:106800. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2024.106800 [26] BEIN A,SOFFER Z. Origin of oils in Helez region,Israel:Implications for exploration in the eastern Mediterranean[J]. AAPG Bulletin,1987,71(1):65-75. [27] 倪春华,包建平,梁世友. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷原油成熟度的多参数综合评价[J]. 石油实验地质,2009,31(4):399-402. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.04.016NI C H,BAO J P,LIANG S Y. Overall evaluation by multi-parameters on maturity of crude oil from the Bozhong Sag,the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment,2009,31(4):399-402. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2009.04.016 [28] 张小琴,李威,王飞龙,等. 辽东湾地区古近系烃源岩生物标志物特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩性油气藏,2022,34(1):73-85. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20220108ZHANG X Q,LI W,WANG F L,et al. Biomarker characteristics and geological significance of Paleogene source rocks in Liaodong Bay[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs,2022,34(1):73-85. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20220108 [29] RADKE M,WELTE D H,WILLSCH H. Maturity parameters based on aromatic hydrocarbons:Influence of the organic matter type[J]. Organic Geochemistry,1986,10(1/2/3):51-63. [30] SIVAN P,DATTA G C,SINGH R R. Aromatic biomarkers as indicators of source,depositional environment,maturity and secondary migration in the oils of Cambay Basin,India[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2008,39(11):1620-1630. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2008.06.009 [31] PETERS K E,WALTERS C C,MOLDOWAN J M. Biomarkers:Assessment of petroleum source-rock age and depositional environment[M]. Cham:Springer International Publishing,2017:1-11. [32] MOLDOWAN J M,FAGO F J,CARLSON R M K,et al. Rearranged hopanes in sediments and petroleum[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1991,55(11):3333-3353. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(91)90492-N [33] PETERS K E,MOLDOWAN J M. Effects of source,thermal maturity,and biodegradation on the distribution and isomerization of homohopanes in petroleum[J]. Organic Geochemistry,1991,17(1):47-61. doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(91)90039-M [34] MA A L,JIN Z J,ZHU C S,et al. Cracking and thermal maturity of Ordovician oils from Tahe oilfield,Tarim Basin,NW China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Geoscience,2017,2(4):239-252. doi: 10.1016/j.jnggs.2017.12.001 [35] FARRIMOND P,TAYLOR A,TELNÆS N. Biomarker maturity parameters:The role of generation and thermal degradation[J]. Organic Geochemistry,1998,29(5/6/7):1181-1197. [36] 黄第藩,张大江,李晋超. 论4-甲基甾烷和孕甾烷的成因[J]. 石油勘探与开发,1989,16(3):8-15. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1989.03.002HUANG D F,ZHANG D J,LI J C. On origin of 4-methyl steranes and pregnanes[J]. Petroleum Expoloration and Development,1989,16(3):8-15. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1989.03.002 [37] CONNAN J. Biodegradation of crude oils in reservoirs[M]. Amsterdam:Elsevier,1984:299-335. [38] LI N X,HUANG H P,JIANG W L,et al. Biodegradation of 25-norhopanes in a Liaohe Basin (NE China) oil reservoir[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2015,78:33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2014.10.007 [39] PING H W,LI C Q,CHEN H H,et al. Overpressure release:Fluid inclusion evidence for a new mechanism for the formation of heavy oil[J]. Geology,2020,48(8):803-807. doi: 10.1130/G47227.1 [40] ZHANG Y D,SUN Y G,CHEN J P. Stable carbon isotope evidence for the origin of C28 steranes in lacustrine source rocks from the Qikou Sag,Bohai Bay Basin,eastern China[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2020,145:104028. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2020.104028 [41] WANG L,SONG Z G,CAO X X,et al. Compound-specific carbon isotope study on the hydrocarbon biomarkers in lacustrine source rocks from Songliao Basin[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2015,87:68-77. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2015.07.011 [42] CLAYTON J L,BOSTICK N H. Temperature effects on kerogen and on molecular and isotopic composition of organic matter in Pierre shale near an igneous dike[J]. Organic Geochemistry,1986,10(1/2/3):135-143. [43] ANDRUSEVICH V E,ENGEL M H,ZUMBERGE J E,et al. Secular,episodic changes in stable carbon isotope composition of crude oils[J]. Chemical Geology,1998,152(1/2):59-72. [44] ZIMMERMANN J,WANNER P,HUNKELER D. Compound-specific carbon isotope analysis of volatile organic compounds in complex soil extracts using purge and trap concentration coupled to heart-cutting two-dimensional gas chromatography-isotope ratio mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2021,1655:462480. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462480 [45] WANG Z M,XIAO Z Y. A comprehensive review concerning the problem of marine crudes sources in Tarim Basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2004,49(1):1-9. [46] ZHANG S C,HUANG H P. Geochemistry of Palaeozoic marine petroleum from the Tarim Basin,NW China:Part 1. oil family classification[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2005,36(8):1204-1214. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2005.01.013 [47] ZHAN Z W,ZOU Y R,PAN C C,et al. Origin,charging,and mixing of crude oils in the Tahe oilfield,Tarim Basin,China[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2017,108:18-29. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2017.03.007 [48] ZHAN Z W,TIAN Y K,ZOU Y R,et al. De-convoluting crude oil mixtures from Palaeozoic reservoirs in the Tabei uplift,Tarim Basin,China[J]. Organic Geochemistry,2016,97:78-94. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2016.04.004 [49] ZHOU C X,YU S,HUANG W Y,et al. Oil maturities,mixing and charging episodes in the cratonic regions of the Tarim Basin,NW China:Insight from biomarker and diamondoid concentrations and oil bulk properties[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2021,126:104903. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.104903 [50] 陈中红,柴智. 原油混合后成熟度参数的差异性及其地质意义:以塔北隆起托甫台地区奥陶系为例[J]. 岩性油气藏,2022,34(5):38-49. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20220503CHEN Z H,CHAI Z. Difference of maturity parameters of mixed crude oil and its geological significance:A case study of Ordovician in Tuofutai area,Tabei uplift[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs,2022,34(5):38-49. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20220503 [51] 陈致林,李素娟,王忠. 低-中成熟演化阶段芳烃成熟度指标的研究[J]. 沉积学报,1997,15(2):192-197.CHEN Z L,LI S J,WANG Z. Study on maturity index of aromatic hydrocarbons in low-medium maturity evolution stage[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,1997,15(2):192-197. (in Chinese with English abstract [52] 马安来,金之钧,朱翠山. 塔里木盆地塔河油田奥陶系原油成熟度及裂解程度研究[J]. 天然气地球科学,2017,28(2):313-323. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2017.01.003MA A L,JIN Z J,ZHU C S. Maturity and oil-cracking of the Ordovician oils from Tahe oilfield,Tarim Basin,NW China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2017,28(2):313-323. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2017.01.003 [53] ZHU G Y,CHEN F R,WANG M,et al. Discovery of the Lower Cambrian high-quality source rocks and deep oil and gas exploration potential in the Tarim Basin,China[J]. 2018,102(10):2123-2151. -




 下载:
下载: