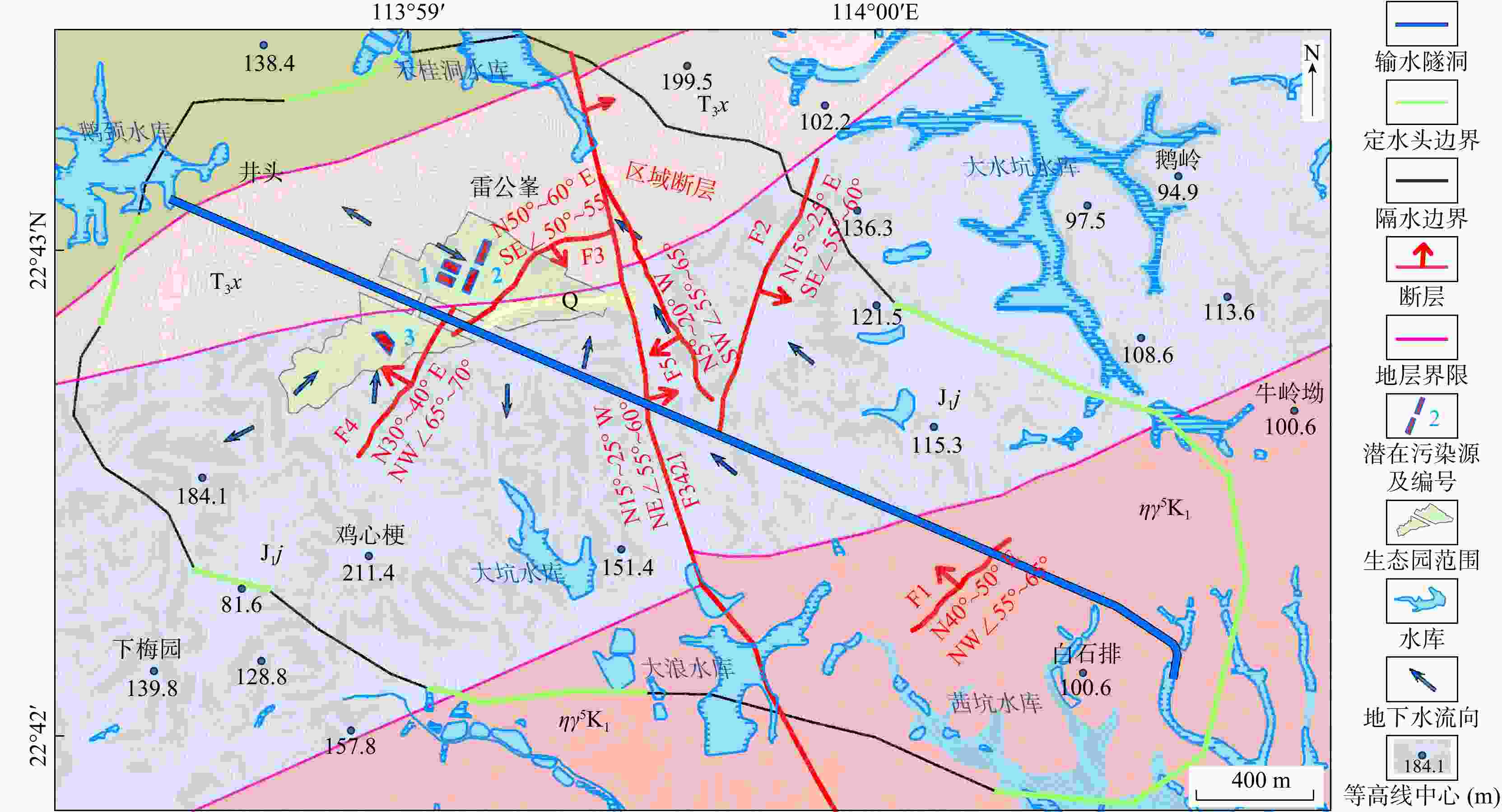
Simulation on fault effects on CODMn distribution in groundwater at landfill site:A case study of Longhua Energy Ecological Park in Shenzhen City
-
摘要:
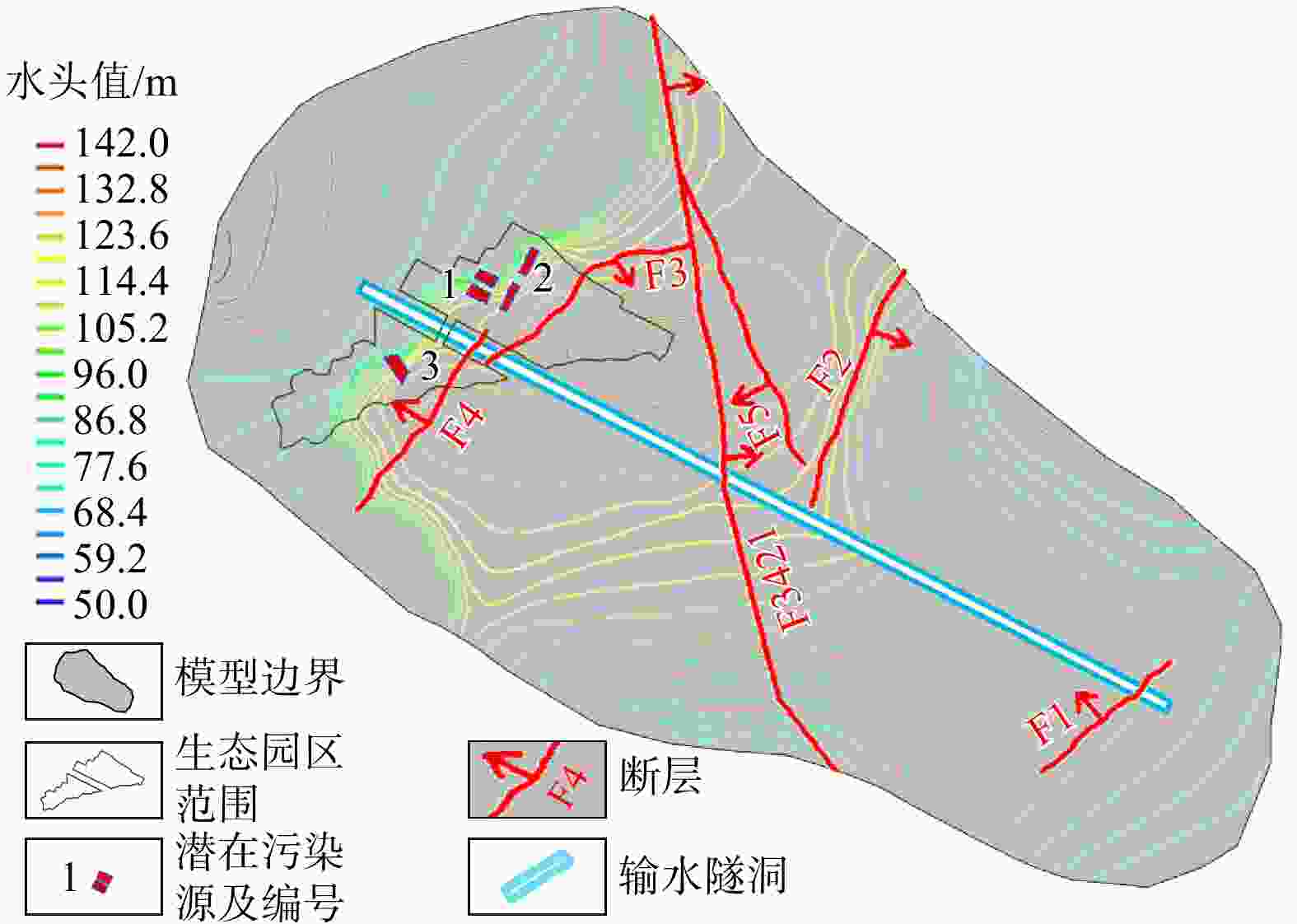
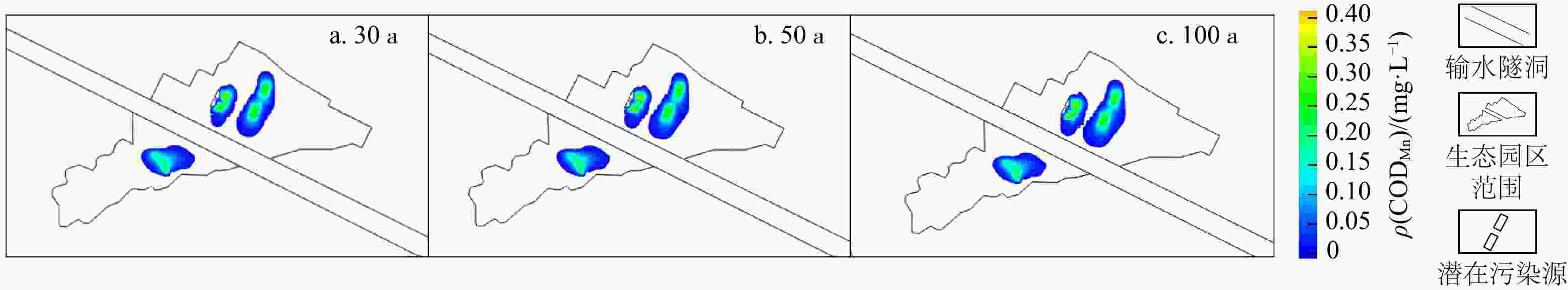
断层作为地质构造的重要组成部分,通过改变地下水流动路径、渗透性分布和溶质运移机制,显著影响污染物在地下水系统中的扩散范围和速度,然而国内外针对断层对垃圾填埋场地下水污染迁移模拟的研究尚不多见。基于GMS软件构建了包含断层渗透性的地下水流和溶质运移模型,开展了不同工况及断层渗透性增强下垃圾填埋场特征污染物渗漏对地下水环境和输水隧洞的影响模拟。模拟结果表明:在正常工况下,由于厂区底部防渗措施,污染物扩散范围基本限于厂区内部,且污染物中心最高质量浓度小于0.5 mg/L;在非正常工况下,1号、2号和3号污染源渗漏情景下污染物分别在第800,
4015 ,1095 d扩散运移至输水隧洞所在位置,3种渗漏情景下污染物垂向扩散范围逐渐增大,但在平面上扩散范围存在较小差异。在1号和3号污染源情景下断层F4渗透性增强对污染物运移存在较大环境风险,在2号污染源情景下断层F3渗透性增强对输水隧洞区域未产生更大的环境风险。研究结果可为研究区地下水污染防治和风险评价提供科学支撑。Abstract:As an important component of geological structure, faults significantly affect the diffusion range and tansport rate of pollutants within the groundwater systems by changing the groundwater flow paths, permeability distribution and solute transport mechanism. However, few studies have simulated the effect of faults on groundwater pollution migration in landfill sites, either domestically or internationally.
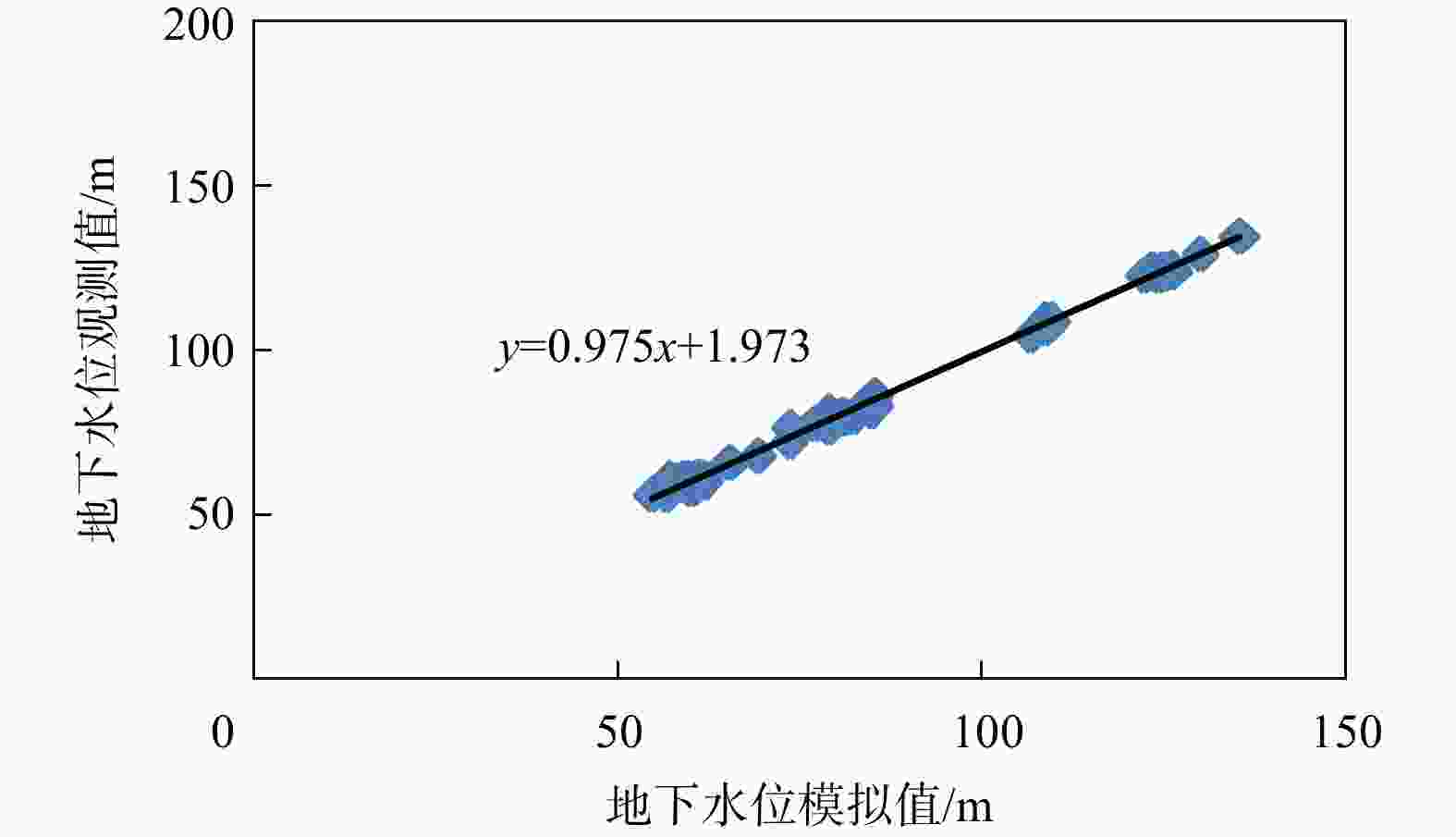
Methods A groundwater flow and solute transport model incorporating fault permeability was developed using GMS software.
Objective The model simulated the impact of characteristic landfill pollutant seepage on the groundwater environment and a water delivery tunnel under various conditions, considering enhanced fault permeability.
Result The simulation results show that: Under normal conditions, due to the anti-seepage measures at the bottom of the plant, the polluant diffusion range is largely confiend within the plant site, and the maximum pollutants concentration at the center iremains below 0.5 mg/L. Under abnormal conditions (leakage scenarios), pollutants from leakage source No.1, No.2 and No.3 reached the water delivery tunnel location on the 800th day,
4015th day and1095th day, respectively. The vertical diffusion range of pollutants progressively increased across the three leakage scenarios, whereas difference in the horizontal(area) diffusion range were minimal. Enhanced permeability of the F4 fault poses a greater environmental risk to pollutant migration in leakage source scenarios No.1 and No.3. In leakage source scenario No.2, however, the enhanced permeability of the F3 fault does not significantly increase environmental risk levels in the tunnel area. To safeguard the local soil and water environment, anti-seepage reinforcement of potentially affected tunnel areas is necessary.Conclusion The findings of this research provide scientific support for groundwater pollution prevention and risk assessment in the study area.
-
Key words:
- groundwater pollution migration /
- numerical simulation /
- risk prediction /
- fault /
- Shenzhen City /
- landfill site
-
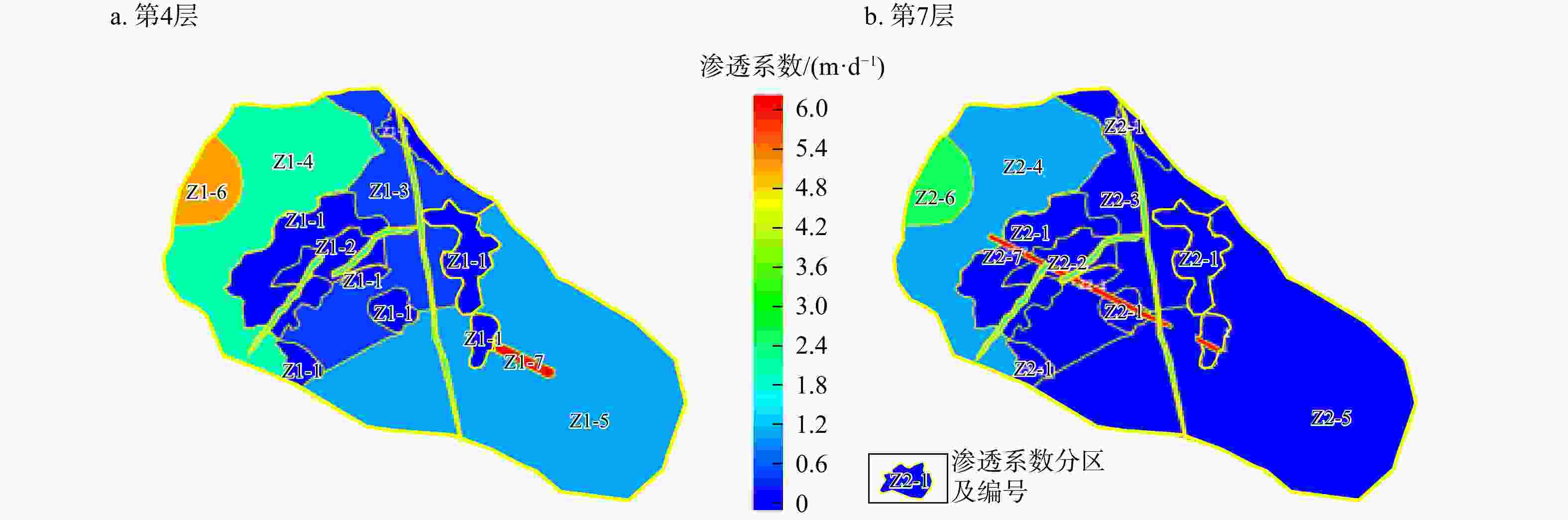
表 1 模型参数及分区值
Table 1. Model parameters and partition values
分层 岩性 渗透系数/(m·d−1) 给水度
Sy储水率
Ss/m−1纵向弥
散度/mKx Ky Kz 松散
沉积层填土 3.024 3.024 3.024 0.20 0.005 10 砂质黏土 0.389 0.389 0.389 0.05 0.001 5 强风
化层花岗岩 0.299 0.173 0.146 0.08 0.0005 10 片麻岩 1.495 0.864 0.731 0.05 0.0002 10 粉砂岩 3.741 2.160 1.832 0.06 0.0005 10 石英砂岩 0.209 0.121 0.102 0.05 0.0005 10 中风
化层花岗岩 0.081 0.029 0.022 0.05 0.0002 10 片麻岩 0.162 0.059 0.045 0.02 0.0001 10 粉砂岩 0.406 0.147 0.112 0.03 0.0001 10 石英砂岩 0.054 0.020 0.015 0.03 0.0002 10 微风
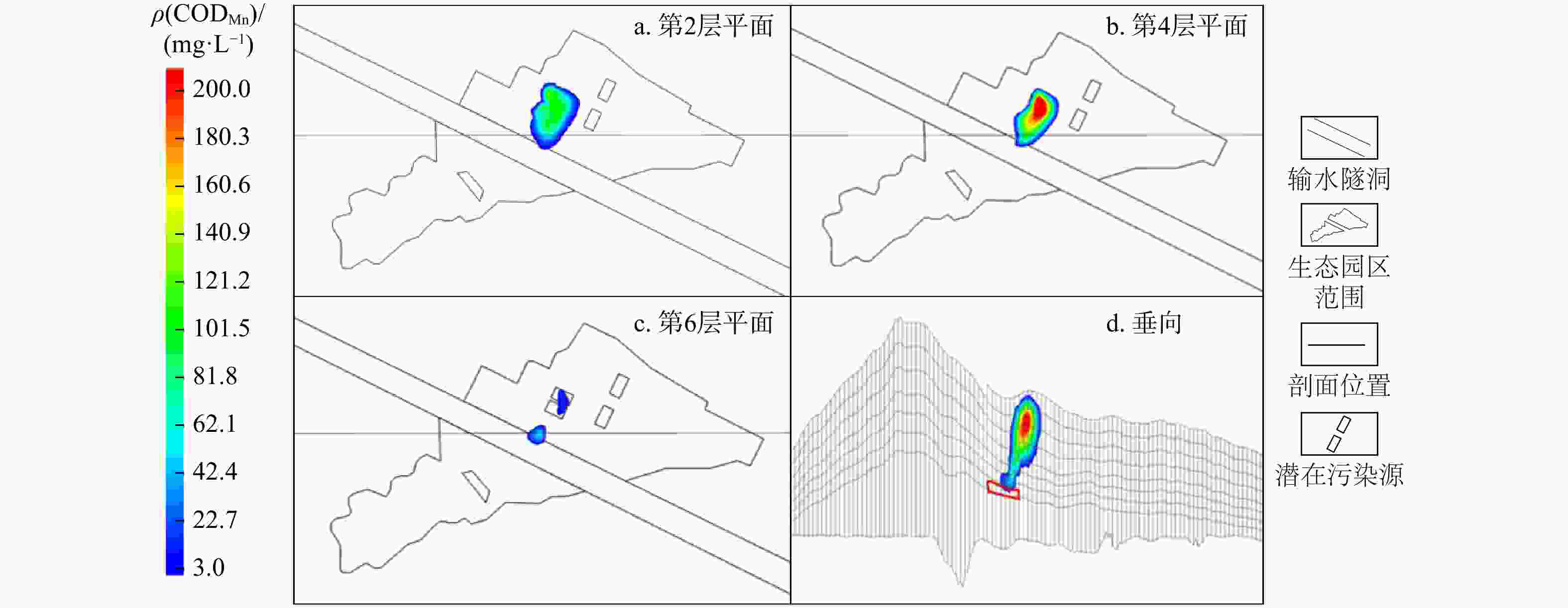
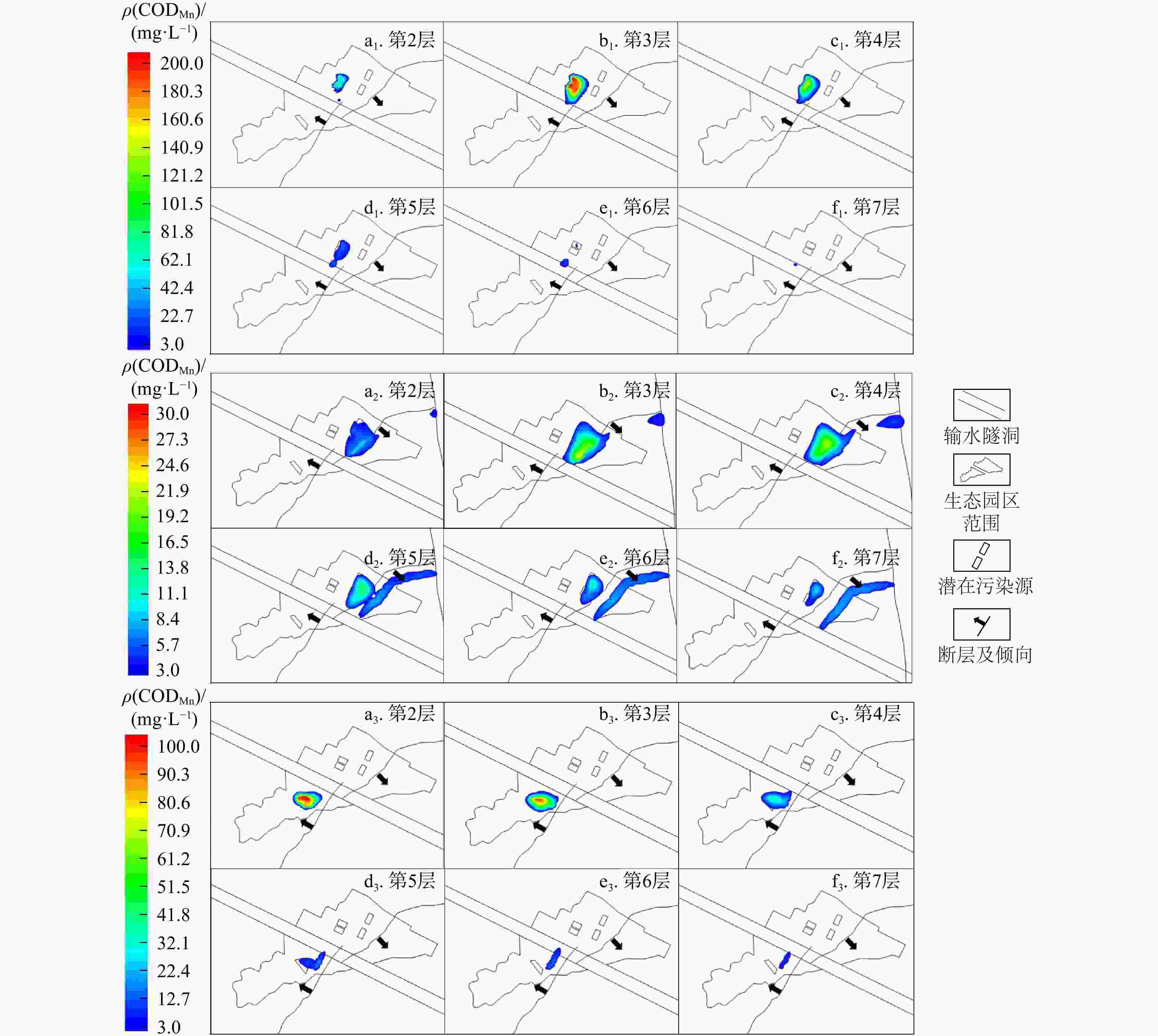
化层花岗岩 0.010 0.016 0.003 0.005 0.0001 1 片麻岩 0.009 0.015 0.003 0.002 0.0001 1 粉砂岩 0.020 0.034 0.007 0.003 0.0001 1 石英砂岩 0.009 0.015 0.003 0.003 0.0001 1 注:Kx,Ky,Kz分别为渗透系数张量主方向x,y,z的渗透系数 表 2 1号污染源情景下第2,4,6层平面污染羽及垂向污染羽CODMn特征参数
Table 2. CODMn characteristic parameters in the plane pollution plume at 2nd, 4th, and 6th layers and in the vertical pollution plume of leakage source scenario No.1
时间/d 平面污染羽 垂向污染羽 最大质量浓度/(mg·L−1) 最大质量
浓度/(mg·L−1)最大扩散
距离/m第2层 第4层 第6层 200 347.69 21.80 0 19.00 31.80 400 263.44 46.20 0 40.00 59.60 600 163.88 59.30 7.90 52.04 71.40 800 109.44 63.60 14.70 54.15 77.30 表 3 2号污染源情景下第2,4,6层平面污染羽及垂向污染羽CODMn特征参数
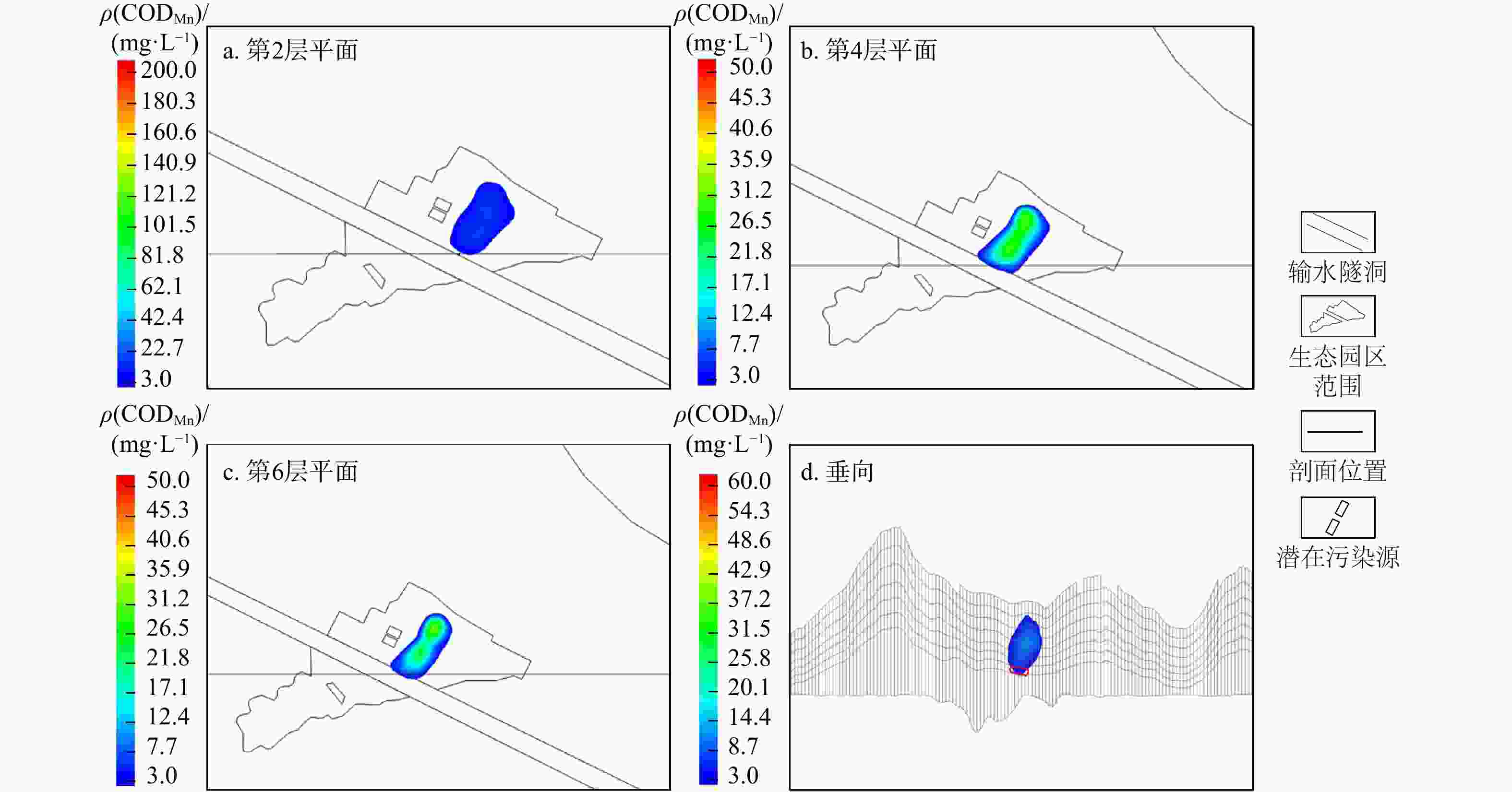
Table 3. CODMn characteristic parameters in the plane pollution plume at 2nd, 4th, and 6th layers and in the vertical pollution plume of leakage source scenario No.2
时间/d 平面污染羽 垂向污染羽 平面污染羽最大质量浓度/(mg·L−1) 最大质量
浓度/(mg·L−1)最大扩散
距离/m第2层 第4层 第6层 20 417.30 14.80 0 0 0 40 271.96 36.30 0 0 0 60 183.71 51.20 0 0 0 80 129.35 59.30 5.20 0 0 1050 88.16 63.00 10.80 0 0 1250 67.45 62.90 14.70 0 0 1825 40.72 57.90 24.00 3.63 18.10 2920 21.23 41.60 32.00 7.28 50.50 4015 12.87 29.70 31.20 10.08 64.20 表 4 3号污染源情景下第2,4,6层平面污染羽及垂向污染羽CODMn特征参数
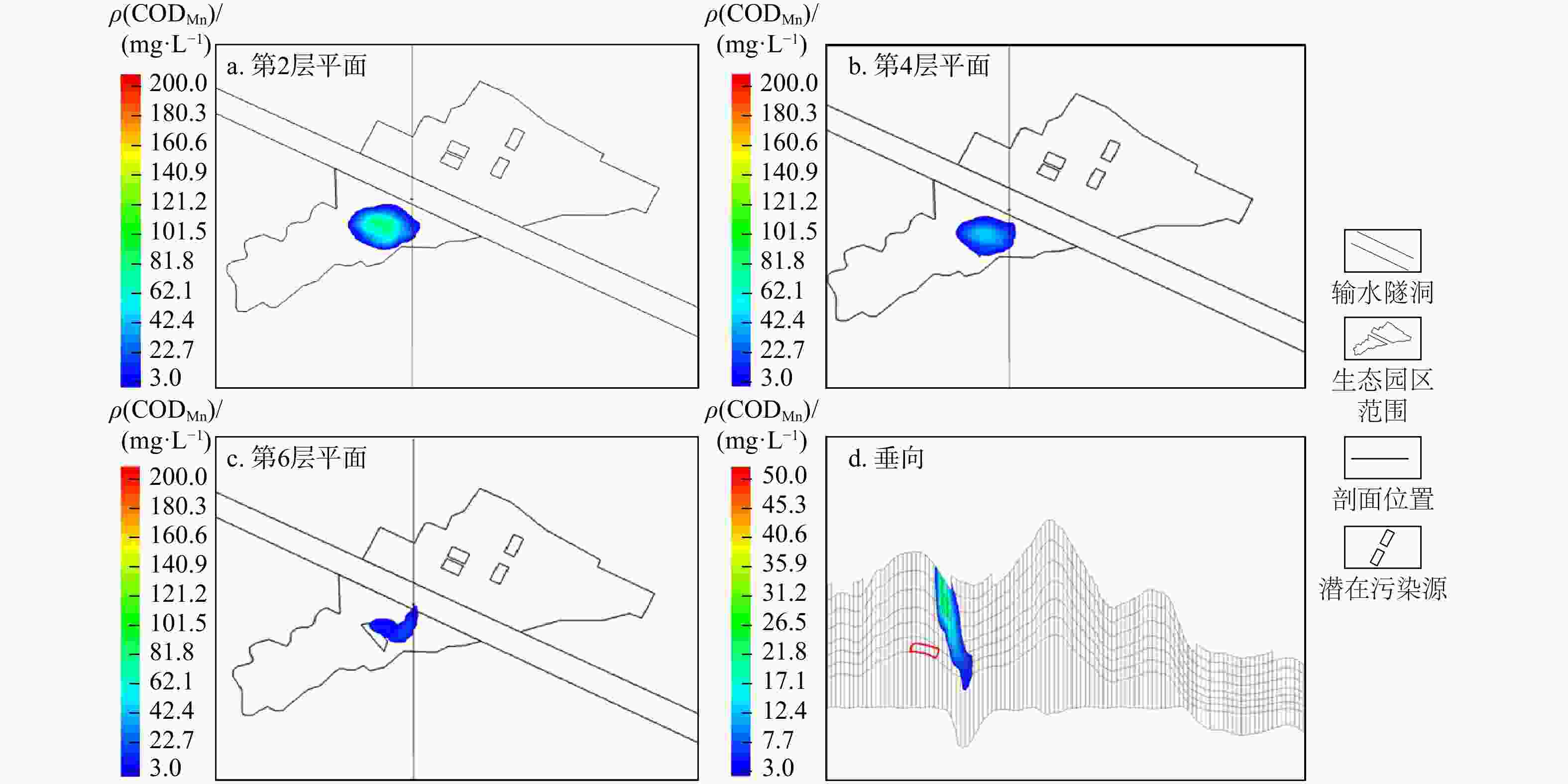
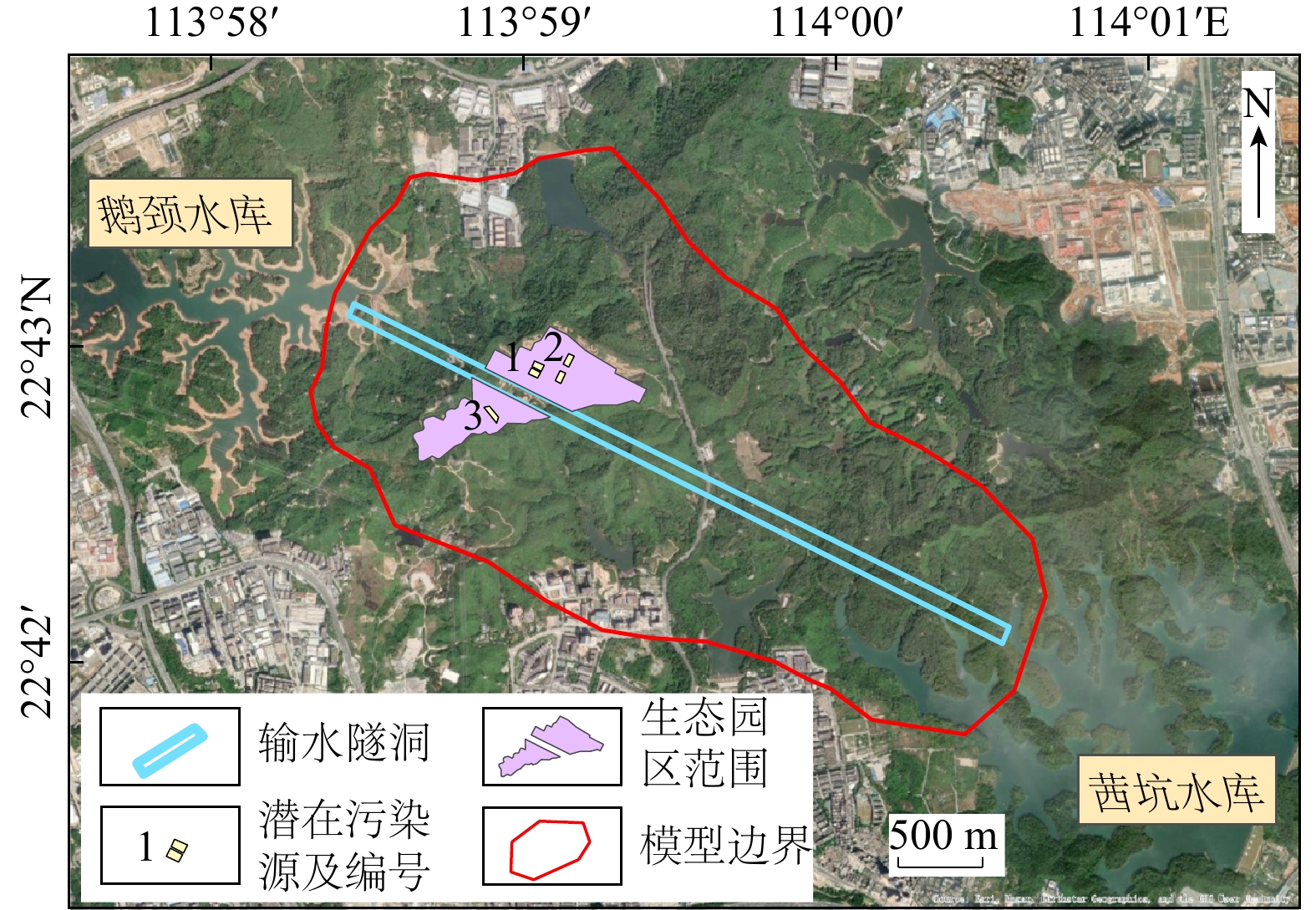
Table 4. CODMn characteristic parameters in the plane pollution plume at 2nd, 4th, and 6th layers and in the vertical pollution plume of leakage source scenario No.3
时间/d 平面污染羽 垂向污染羽 最大质量浓度/(mg·L−1) 最大质量
浓度/(mg·L−1)最大扩散
距离/m第2层 第4层 第6层 200 373.21 9.80 0 0 0 400 220.03 23.90 0 0 0 600 152.24 33.40 5.60 8.41 52.83 800 114.38 39.90 10.10 14.70 80.06 1015 81.48 43.20 13.90 21.12 110.48 -
[1] WIJESEKARA S S R M D H R, MAYAKADUWA S S, SIRIWARDANA A R, et al. Fate and transport of pollutants through a municipal solid waste landfill leachate in Sri Lanka[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 72(5): 1707-1719. [2] 周巧丽, 宋玉梅, 周漪波, 等. 广州市某生活垃圾填埋场空气及地下水污染状况分析[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(4): 760-769. doi: 10.1002/etc.4365ZHOU Q L, SONG Y M, ZHOU Y B, et al. Analysis of air and groundwater pollution in a municipal solid waste landfill site in Guangzhou[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(4): 760-769. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1002/etc.4365 [3] 王松涛, 杨霄, 王丛, 等. 城市生活垃圾填埋场污染物运移研究[J]. 中国农村水利水电, 2021(7): 81-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2021.07.013WANG S T, YANG X, WANG C, et al. Research on the transport of pollutants in municipal solid waste landfill[J]. China Rural Water and Hydropower, 2021(7): 81-86. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2284.2021.07.013 [4] SAMADDER S R, PRABHAKAR R, KHAN D, et al. Analysis of the contaminants released from municipal solid waste landfill site: A case study[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 580: 593-601. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.003 [5] 龚莉, 史浙明, 张宗文, 等. 基于多元分析的某地区垃圾填埋场地下水生态环境风险定量评价[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(3): 734-743.GONG L, SHI Z M, ZHANG Z W, et al. Quantitative ecological risk assessment on the groundwater in landfills at regional scale based on multivariate analysis methods[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(3): 734-743. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 马添翼, 李硕, 苏杰, 等. 吉林省某垃圾填埋场地下水有机污染风险评价[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2019, 41(3): 348-350.MA T Y, LI S, SU J, et al. Risk assessment of organic pollution in groundwater for a landfill in Jilin[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2019, 41(3): 348-350. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 侯少林, 李婧, 陈梦舫, 等. 垃圾填埋场地下水环境定量风险评估方法与案例分析[J]. 环境工程学报, 2024, 18(6): 1681-1693.HOU S L, LI J, CHEN M F, et al. Methodology of quantitative groundwater environmental risk assessment and a case analysis of a landfill site[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2024, 18(6): 1681-1693. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] QIAN H, CHEN J, HOWARD K W F. Assessing groundwater pollution and potential remediation processes in a multi-layer aquifer system[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2020, 263: 114669. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114669 [9] 左涛, 熊小锋, 戴柳珍. 数值模拟在地下水环境影响评价中的应用: 以福泉市某尾矿库建设为例[J]. 地下水, 2023, 45(3): 1-3.ZUO T, XIONG X F, DAI L Z. Application of quantitative tracer test in prevention and control of groundwater pollution: A case study of Longjingwan in Fuquan City[J]. Ground Water, 2023, 45(3): 1-3. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 赵珍. 基于Visual MODFLOW的某焦化项目地下水污染物运移规律研究[J]. 地下水, 2024, 46(2): 66-70.ZHAO Z. Research on groundwater pollutant transport law of a coking project based on Visual MODFLOW[J]. Ground Water, 2024, 46(2): 66-70. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 马宇琪, 徐世光. 基于GMS的某矿区地下水污染的数值模拟研究[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2024, 35(1): 123-128.MA Y Q, XU S G. Numerical simulation of groundwater pollution in a mining area based on GMS[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2024, 35(1): 123-128. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 郭飞, 朱学愚, 刘建立, 等. 山东淄博裂隙岩溶水中污染物运移的数值模拟及治污措施[J]. 水利学报, 2004, 35(7): 57-63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2004.07.010GUO F, ZHU X Y, LIU J L, et al. Numerical modeling of contaminant transport in fracture-karst aquifer and measures for pollution remediation[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2004, 35(7): 57-63. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.2004.07.010 [13] ZHOU Y, JIANG Y H, AN D, et al. Simulation on forecast and control for groundwater contamination of hazardous waste landfill[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 72(10): 4097-4104. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3302-x [14] KLINT K E S, GRAVESEN P, ROSENBOM A, et al. Multi-scale characterization of fractured rocks used as a means for the realistic simulation of pollutant migration pathways in contaminated sites: A case study[J]. Water, Air and Soil Pollution(Focus), 2004, 4(4): 201-214. [15] CHEN C S, TU C H, CHEN S J, et al. Simulation of groundwater contaminant transport at a decommissioned landfill site: A case study, Tainan City, Taiwan[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2016, 13(5): 467. doi: 10.3390/ijerph13050467 [16] 杨延梅, 夏铜, 张赟, 等. 基于Visual Modflow的重庆某垃圾填埋场封场后地下水污染物运移模拟研究[J]. 环境工程, 2024, 42(4): 40-47.YANG Y M, XIA T, ZHANG Y, et al. Simulation on transport of groundwater pollutants after closure of a landfill in Chongqing based on Visual Modflow[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2024, 42(4): 40-47. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 廖镭, 张涵, 郭珊珊. 简易垃圾填埋场渗滤液地下水溶质运移数值模拟[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2019, 26(2): 76-83.LIAO L, ZHANG H, GUO S S. Numerical simulation of mass transport of simple landfill leachate in groundwater[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2019, 26(2): 76-83. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] 王喆, 卢丽, 夏日元. 基于GMS的北京西郊垃圾场地下水溶质运移模拟[J]. 人民黄河, 2012, 34(11): 85-87.WANG Z, LU L, XIA R Y. Numerical simulation of solute transport in groundwater in the trash dump of the west suburb in Beijing based on GMS[J]. Yellow River, 2012, 34(11): 85-87. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 张汝壮. 基于GMS的某非正规垃圾填埋场地下水污染的模拟研究[J]. 环境卫生工程, 2020, 28(3): 75-79.ZHANG R Z. Simulation study of groundwater pollution in an informal landfill based on GMS[J]. Environmental Sanitation Engineering, 2020, 28(3): 75-79. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 赵春兰, 凌成鹏, 吴勇, 等. 垃圾渗滤液对地下水水质影响的数值模拟预测: 以冕宁县漫水湾生活垃圾填埋场为例[J]. 环境工程, 2017, 35(2): 163-167.ZHAO C L, LING C P, WU Y, et al. Application of numerical simulation to evaluate the impact of leachate on the groundwater quality: A case study of Manshuiwan landfill in Mianning County[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2017, 35(2): 163-167. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] FA-YOU A, WANG R, DAI X G, et al. Study on migration characteristics of pollutants in groundwater at a proposed hazardous waste landfill[J]. Recent Patents on Engineering, 2024, 18(3): e270423216281. doi: 10.2174/1872212118666230427143535 [22] KANMANI S, GANDHIMATHI R, SHANMUHARAJAN M B, et al. Leachate transport phenomenon on groundwater quality: Modeling using modflow and MT3DMS tools[J]. Global Nest Journal, 2023, 25(3): 44-55. [23] 史浙明, 叶海龙, 吕少杰, 等. 断裂带水力特性研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(4): 47-54.SHI Z M, YE H L, LÜ S J, et al. Advances in fault zone hydraulic properties[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(4): 47-54. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] ANTONELLINI M, AYDIN A. Effect of faulting on fluid flow in porous sandstones: Geometric properties[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 1995, 79: 642-671. [25] MAL'KOVSKII V I, PEK A. Evaluation of the influence of a highly permeable fault on transport of pollutants by the local groundwater flow[J]. Geology of Ore Deposits, 2001, 43(3): 216-223. [26] VERMEULEN P D, USHER B H. The effect of graben structures on the migration of groundwater contaminants at an industrial site[J]. Environmental Geology, 2009, 58(4): 739-749. doi: 10.1007/s00254-008-1548-x [27] BALSAMO F, BEZERRA F H R, VIEIRA M M, et al. Structural control on the formation of iron-oxide concretions and Liesegang bands in faulted, poorly lithified Cenozoic sandstones of the Paraiba Basin, Brazil[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2013, 125(5/6): 913-931. [28] FISHER Q J, KNIPE R J. The permeability of faults within siliciclastic petroleum reservoirs of the North Sea and Norwegian Continental Shelf[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2001, 18(10): 1063-1081. doi: 10.1016/S0264-8172(01)00042-3 [29] GARVEN G, APPOLD M S, TOPTYGINA V I, et al. Hydrogeologic modeling of the genesis of carbonate-hosted lead-zinc ores[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 1999, 7(1): 108-126. doi: 10.1007/s100400050183 [30] HANEBERG W C. Steady state groundwater flow across idealized faults[J]. Water Resources Research, 1995, 31(7): 1815-1820. doi: 10.1029/95WR01178 [31] ROBERTS S J, NUNN J A, CATHLES L, et al. Expulsion of abnormally pressured fluids along faults[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth), 1996, 101(B12): 28231-28252. doi: 10.1029/96JB02653 [32] BENSE V F, GLEESON T, LOVELESS S E, et al. Fault zone hydrogeology[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 127: 171-192. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.09.008 [33] CHU J L, LIU N N, MIAO Y, et al. Numerical simulation and pollution prediction of karst groundwater in water-conducting faults distribution area[J]. IOP Conference Series(Earth and Environmental Science), 2020, 585(1): 012097. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/585/1/012097 [34] 牛毅, 李炜, 李攻科, 等. 滨海平原区某生活垃圾填埋场地下水污染修复模拟[J]. 环境工程, 2023, 41(3): 12-20.NIU Y, LI W, LI G K, et al. Simulation of restoration of groundwater pollution in a landfill in coastal plain area[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2023, 41(3): 12-20. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] ZHAO X N, WANG D Q, XU H L, et al. Simulation and prediction of groundwater pollution based on GMS: A case study in Beijing, China[J]. IOP Conference Series(Earth and Environmental Science), 2021, 826(1): 012014. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/826/1/012014 [36] 李昀东. 龙华能源生态园环境报告书[R]. 广东深圳: 深圳市汉宇环境科技有限公司, 2019.Li Y D. Longhua Energy Ecological Park environmental report[R]. Shenzhen Guangdong: Hanyu Environmental Technology Co., Ltd., 2019. (in Chinese) [37] MATTHÄI S K. Fluid flow and (reactive) transport in fractured and faulted rock[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2003, 78: 179-182. [38] FAULKNER D R, JACKSON C A L, LUNN R J, et al. A review of recent developments concerning the structure, mechanics and fluid flow properties of fault zones[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2010, 32(11): 1557-1575. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2010.06.009 [39] SCIBEK J, GLEESON T, MCKENZIE J M. The biases and trends in fault zone hydrogeology conceptual models: Global compilation and categorical data analysis[J]. Geofluids, 2016, 16(4): 782-798. doi: 10.1111/gfl.12188 [40] SHAO S, YANG X, JIA C. Combining multi-source data to evaluate the leakage pollution and remediation effects of landfill[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, 610: 127889. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127889 [41] 袁昊辰, 张幼宽, 梁修雨. 广州某地下水污染场地监控自然衰减修复模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(4): 268-278.YUAN H C, ZHANG Y K, LIANG X Y. Modelling of groundwater remediation using monitored natural attenuation at a contamination site in Guangzhou[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(4): 268-278. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] JHAMNANI B, SINGH S K. Groundwater contamination due to Bhalaswa landfill site in New Delhi[J]. International Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering, 2009, 1(3): 181-185. [43] LI Q, CUI H L, LI Y H, et al. Challenges and engineering application of landfill leachate concentrate treatment[J]. Environmental Research, 2023, 231: 116028. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.116028 [44] 刘国, 李妍颖, 范全忠, 等. 基于Visual MODFLOW的垃圾填埋场阻隔墙设计及效果评估[J]. 环境工程, 2020, 38(6): 137-142.LIU G, LI Y Y, FAN Q Z, et al. Design and effect evaluation of the blocking wall in landfill based on Visual MODFLOW[J]. Environmental Engineering, 2020, 38(6): 137-142. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: