Occurrence state of cobalt in Jingchong copper-cobalt deposit in Northeast Hunan Province, China
-
摘要:
湘东北矿集区井冲铜钴矿床蕴含中型规模的钴资源量,但目前对钴的赋存状态和铜钴成矿关系尚不完全清楚。在详细的坑道调查基础上,结合显微镜鉴定、微区X射线荧光扫描分析(μ-XRF)扫面、背散射电子成像(BSE)及电子探针定量分析,详细划分了成矿阶段,开展了钴的赋存状态和铜钴成矿关系研究,在此基础上提出了钴的综合利用建议。结果表明,井冲铜钴矿床钴的赋存形式包括两大类,第一大类为赋存于粗粒黄铁矿中的不可见钴,钴是以溶解−再沉淀方式进入粗粒黄铁矿内部;第二大类为独立的辉砷钴矿,又细分为4种不同的赋存形式,分别为:以镶边结构或穿插结构产于粗粒黄铁矿边缘或内部的辉砷钴矿、产于粗粒黄铁矿内部多孔状部位边缘的辉砷钴矿、产于粗粒黄铁矿旁边石英中的细粒辉砷钴矿−黄铁矿集合体、产于石英生长环带中定向展布的细粒辉砷钴矿−黄铁矿集合体。从钴资源量贡献来看,粗粒黄铁矿中的不可见钴占据主导地位。此外,在成矿顺序上,钴成矿发生在热液期的中阶段,而铜成矿发生在热液期的晚阶段,铅锌成矿与铜成矿近于同时或稍晚。由于辉砷钴矿含量较少且粒径主体小于30 μm,常规的选矿磨细度难以使其分离,因此钴综合利用的重点应该放在含钴的黄铁矿上。未来研究建议进一步圈定富钴矿体,优化选矿工艺,有望提升硫精矿中的钴品位,以实现钴的综合利用。
Abstract:Objective The Jingchong copper-cobalt deposit, located in the ore-concentration area of northeastern Hunan Province, contains medium-scale cobalt resources. However, the cobalt occurrence and the relationship between copper and cobalt mineralization remian unclear.
Methods Based on detailed underground mine investigations, combined with microscopic observation, μ-XRF scanning, backscattered electron imaging (BSE), and electron probe quantitative analysis, the mineralization stages were divided, and the cobalt occurrence and the relationship between copper and cobalt mineralization were studied. We proposed the comprehensive utilization of cobalt .
Results The results indicate that the cobalt occurrence in the Jingchong copper-cobalt deposit can be classified into two major categories. The first category consists of invisible cobalt hosted in coarse-grained pyrite, where cobalt enters the interior of coarse-grained pyrite through a dissolution-reprecipitation process. The second category is the independent cobaltite mineral, which is further subdivided into four different occurrences: cobaltite occurring as a rim or interstitial texture along the margins or within the interior of coarse-grained pyrite; cobaltite located at the edge of the porous within coarse-grained pyrite; fine-grained cobaltite-pyrite aggregates hosted in quartz adjacent to the coarse-grained pyrite; and fine-grained cobaltite-pyrite aggregates oriented and distributed in the quartz growth bands. In terms of cobalt resource contribution, invisible cobalt in coarse-grained pyrite dominates. Additionally, the mineralization sequence indicates that cobalt mineralization mainly occurs in the intermediate stage of the hydrothermal period, while copper mineralization occurs in the late stage, and lead-zinc mineralization is nearly simultaneous with or slightly later than copper mineralization.
Conclusion Due to the relatively low content of cobaltite minerals and its grain size predominantly less than 30 μm, conventional mineral processing fineness is difficult to effectively separate them. Therefore, the focus of comprehensive cobalt utilization should be on the coarse-grained cobalt-rich pyrite. The delineation of cobalt-rich ore bodies and the optimization of beneficiation process could potentially enhance the cobalt grade in sulfide concentrates and achieve comprehensive cobalt utilization.
-
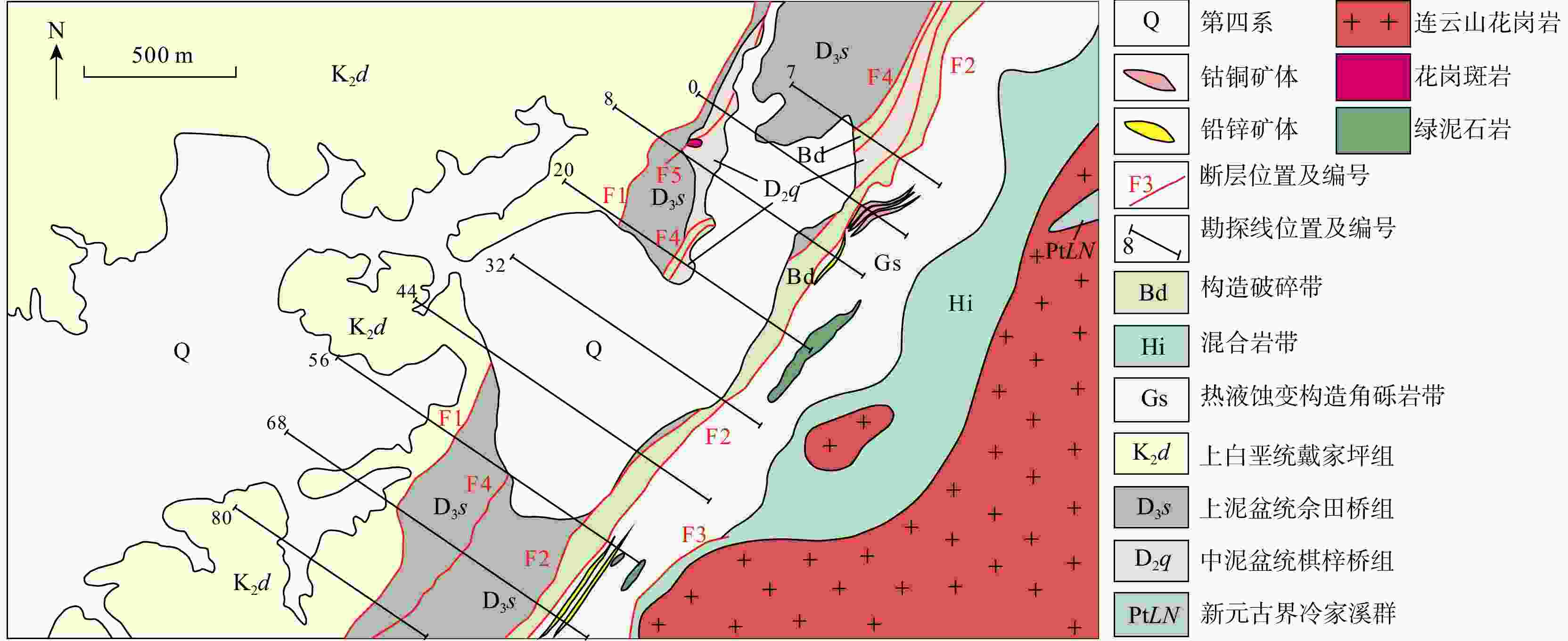
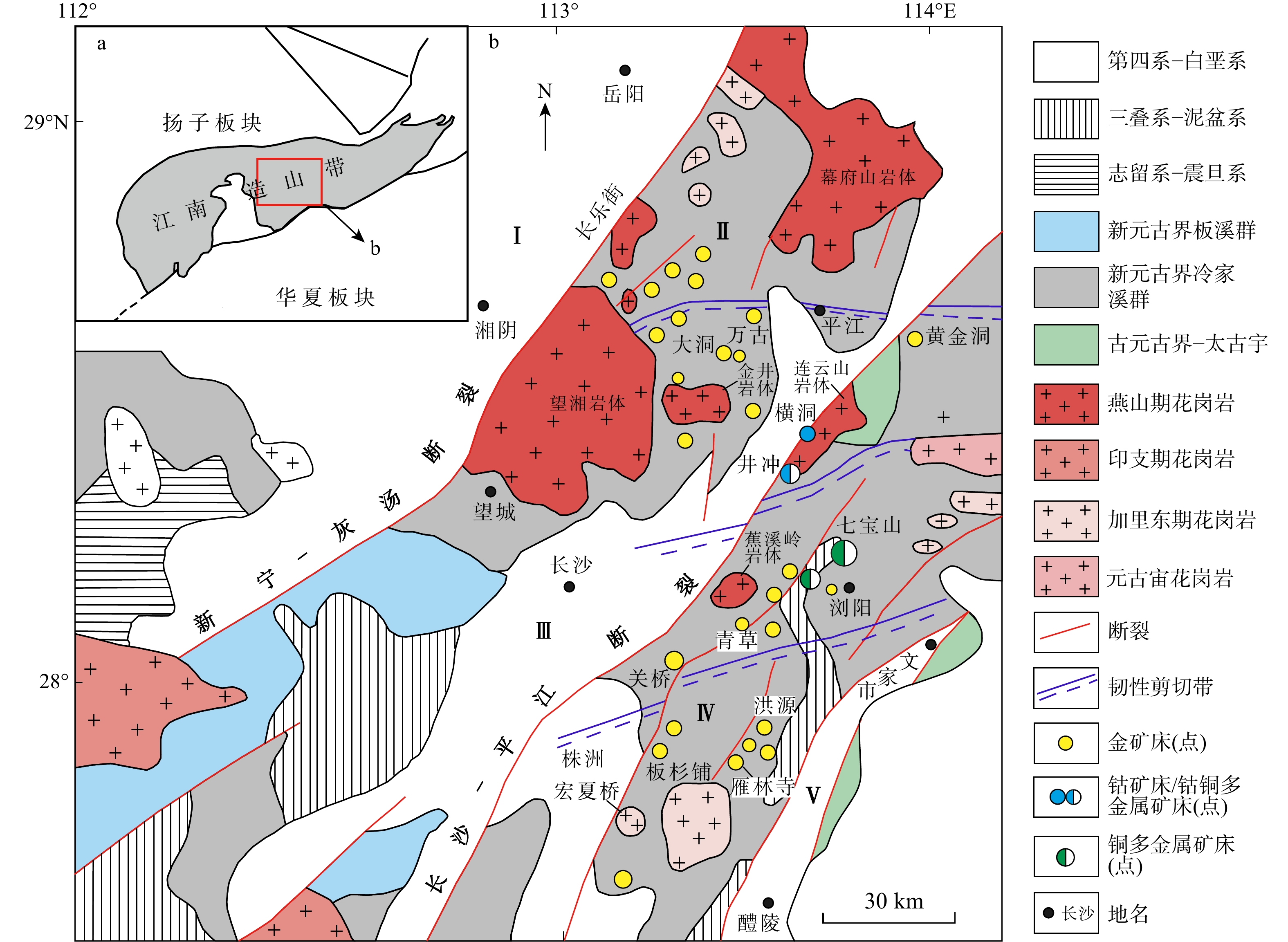
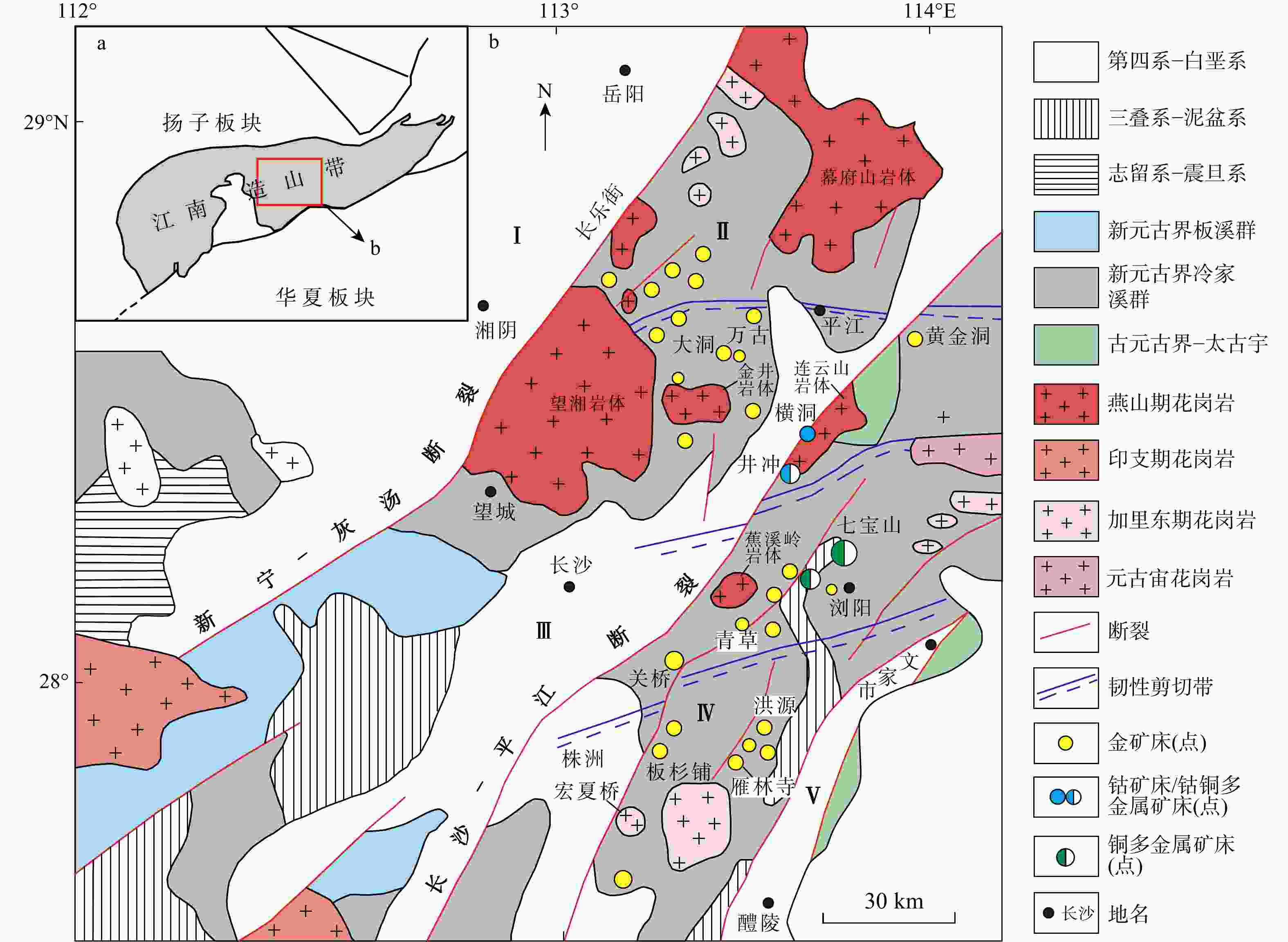
图 1 浏阳井冲铜钴矿床的大地构造位置示意图(a)及区域地质图(b)(据文献[6]修改)
Ⅰ. 汨罗断陷盆地;Ⅱ. 幕府山−望湘断隆;Ⅲ. 长沙−平江断陷盆地;Ⅳ. 浏阳−衡东断隆;Ⅴ. 醴陵−攸县断陷盆地
Figure 1. Geotectonic location (a) and regional geological map (b) of the Jingchong copper-cobalt deposit in Liuyang city
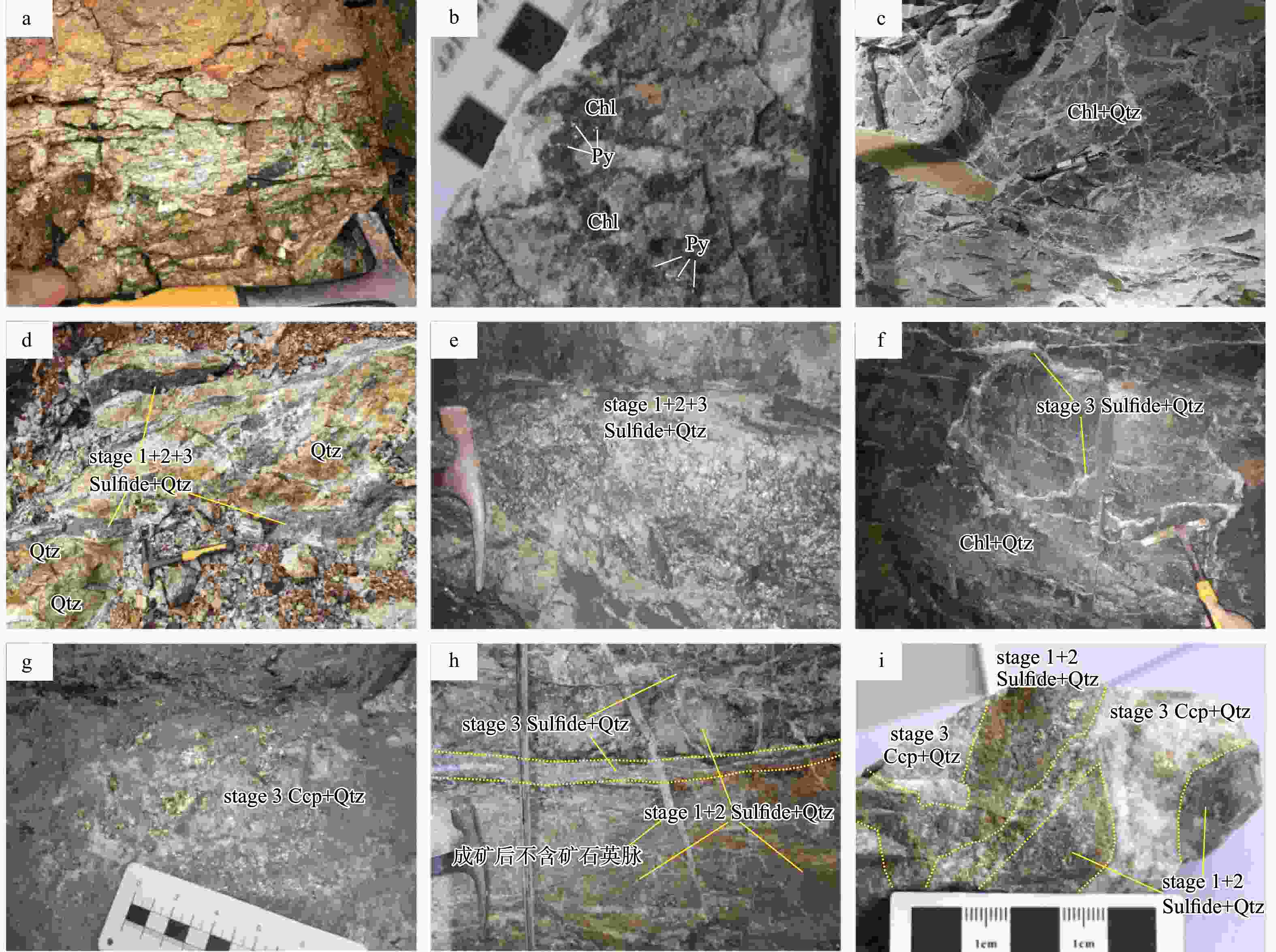
图 4 浏阳井冲铜钴矿床围岩及矿石的特征
a. 矿区内F2断裂下盘的花岗质糜棱岩;b. 沿糜棱理分布的绿泥石和黄铁矿化;c. 构造蚀变带上盘的强绿泥石化和硅化蚀变带;d. 7号和8号矿体的总体矿化特征,由石英−粗粒硫化物脉叠加在强硅化蚀变带上形成;e. 7号和8号矿体的矿石特征,由石英和黄铁矿为主的硫化物组成;f. 9号矿体的总体矿化特征,由石英−硫化物叠加在绿泥石化蚀变岩上形成;g. 9号矿体矿石特征,由石英和黄铜矿组成;h. 8号矿体内热液期第3阶段的含黄铜矿石英−硫化物脉穿插第1和2阶段形成的石英−黄铁矿;I. 8号矿体的矿石标本,指示第3阶段的石英−黄铜矿脉穿插第1和第2阶段形成的石英−黄铁矿,导致后者呈角砾产出。stage1~3. 成矿第1~3阶段;Py. 黄铁矿;Qtz. 石英;Chl. 绿泥石;Ccp. 黄铜矿;Sulfide. 硫化物;下同
Figure 4. Surrounding rock and ore characteristics of the Jingchong copper-cobalt deposit in Liuyang city
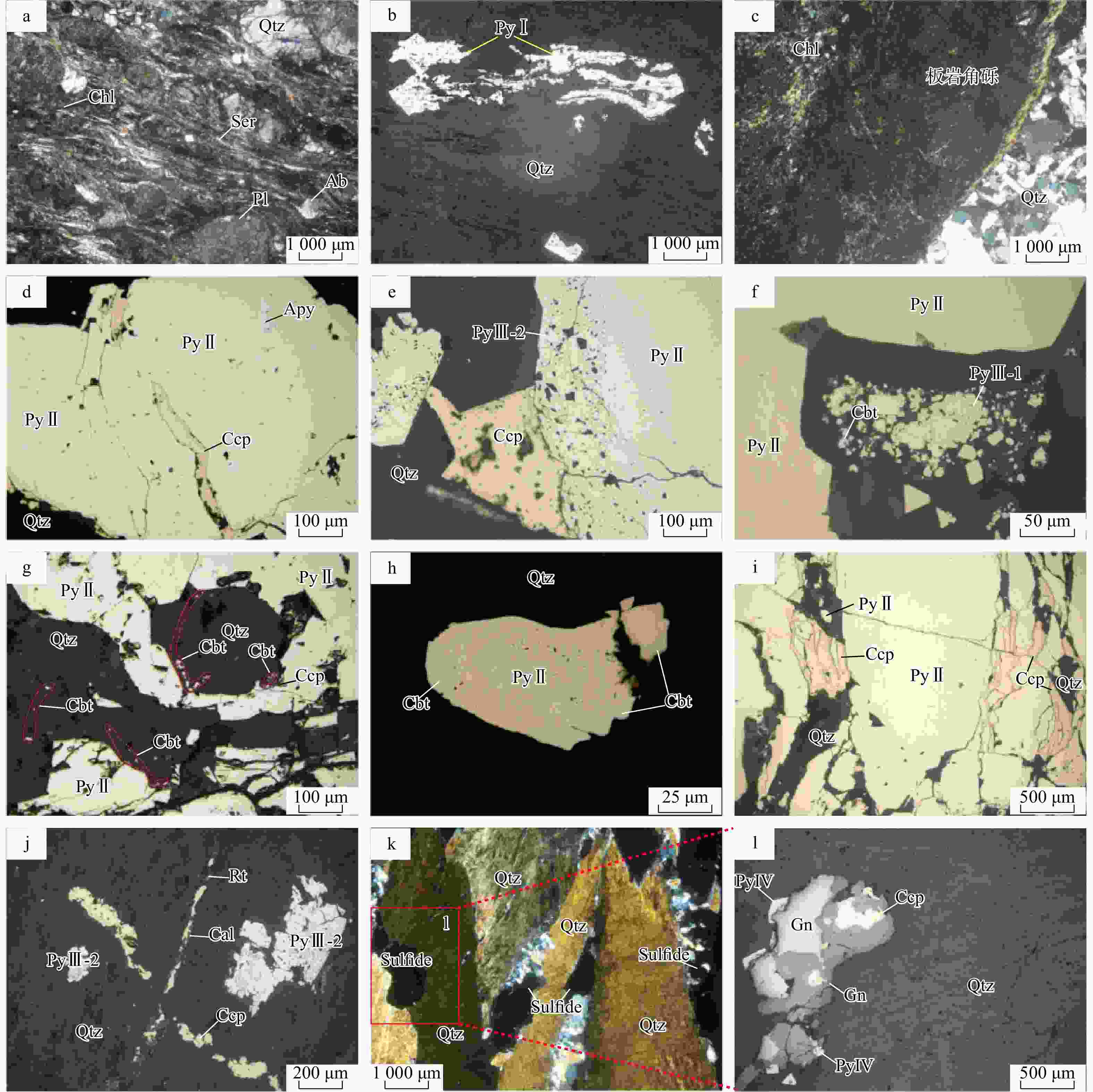
图 5 井冲铜钴矿床不同成矿阶段矿物组合特征
a. 花岗质糜棱岩;b. 动力变质作用期形成的细粒黄铁矿(PyⅠ),具有细粒集合体特征,且具有明显的定向变形特征,沿着糜棱岩的糜棱理分布;c. 热液成矿期绿泥石−石英−黄铁矿阶段的绿泥石化和硅化,包含被交代的早期板岩角砾;d. 绿泥石−石英−黄铁矿阶段的粗粒黄铁矿(PyⅡ)包含少量自形−半自形粒状毒砂颗粒,黄铁矿(PyⅡ)被石英−多金属硫化物−碳酸盐阶段的黄铜矿沿裂隙穿插交代;e. 绿泥石−石英−黄铁矿阶段的粗粒黄铁矿(PyⅡ)边缘产出多孔状黄铁矿(PyⅢ-2),其中包含大量石英等透明矿物,且颜色相对于核部(PyⅡ)偏暗,外缘被石英−多金属硫化物−碳酸盐阶段的黄铜矿交代;f. 黄铁矿-辉砷钴矿−石英阶段的自形−半自形粒状微细粒黄铁矿(PyⅢ-1)与辉砷钴矿共生,分布于粗粒黄铁矿(PyⅡ)边缘的石英中;g. 绿泥石−石英−黄铁矿阶段粗粒黄铁矿(PyⅡ)和黄铁矿−辉砷钴矿−石英阶段的辉砷钴矿与石英,可见细粒辉砷钴矿沿半自形粒柱状石英晶体生长环带呈细脉状分布,也可见细粒辉砷钴矿聚集产于粗粒黄铁矿(PyⅡ)边部,以及独立颗粒状辉砷钴矿产于石英中;h. 辉砷钴矿分布于粗粒黄铁矿(PyⅡ)边缘,呈尖角状、镶边状交代粗粒黄铁矿(PyⅡ);i. 热液期第3阶段石英−黄铜矿脉穿插交代热液期第1阶段粗粒黄铁矿(PyⅡ);j. 热液期第3阶段黄铜矿−方解石细脉呈“X”状穿插交代早阶段石英和黄铁矿;k. 热液期第3阶段碳酸盐−多金属硫化物−石英阶段金属硫化物沿对称梳状石英脉中心分布(正交偏光);l. 照片j局部放大(反射光),产于石英中的黄铁矿(PyⅣ)−黄铜矿−闪锌矿−方铅矿共生组合。Py. 黄铁矿;Apy. 毒砂;Cbt. 辉砷钴矿;Sp. 闪锌矿;Po. 磁黄铁矿;Gn. 方铅矿;Rt. 金红石;Pl. 斜长石;Ser. 绢云母;Ab. 钠长石;Cal. 方解石。PyⅢ-1. 辉砷钴矿−石英阶段中的自形细粒黄铁矿;PyⅢ-2. 绿泥石−石英−黄铁矿阶段中的粗粒黄铁矿(PyⅡ)经溶解−再沉淀作用形成的多孔状黄铁矿或富钴环带黄铁矿;Py-Ⅰ. 动力变质作用期形成的细粒黄铁矿;Py-Ⅳ. 产于石英中的黄铁矿;下同
Figure 5. Mineral association of different mineralization stages at the Jingchong copper-cobalt deposit
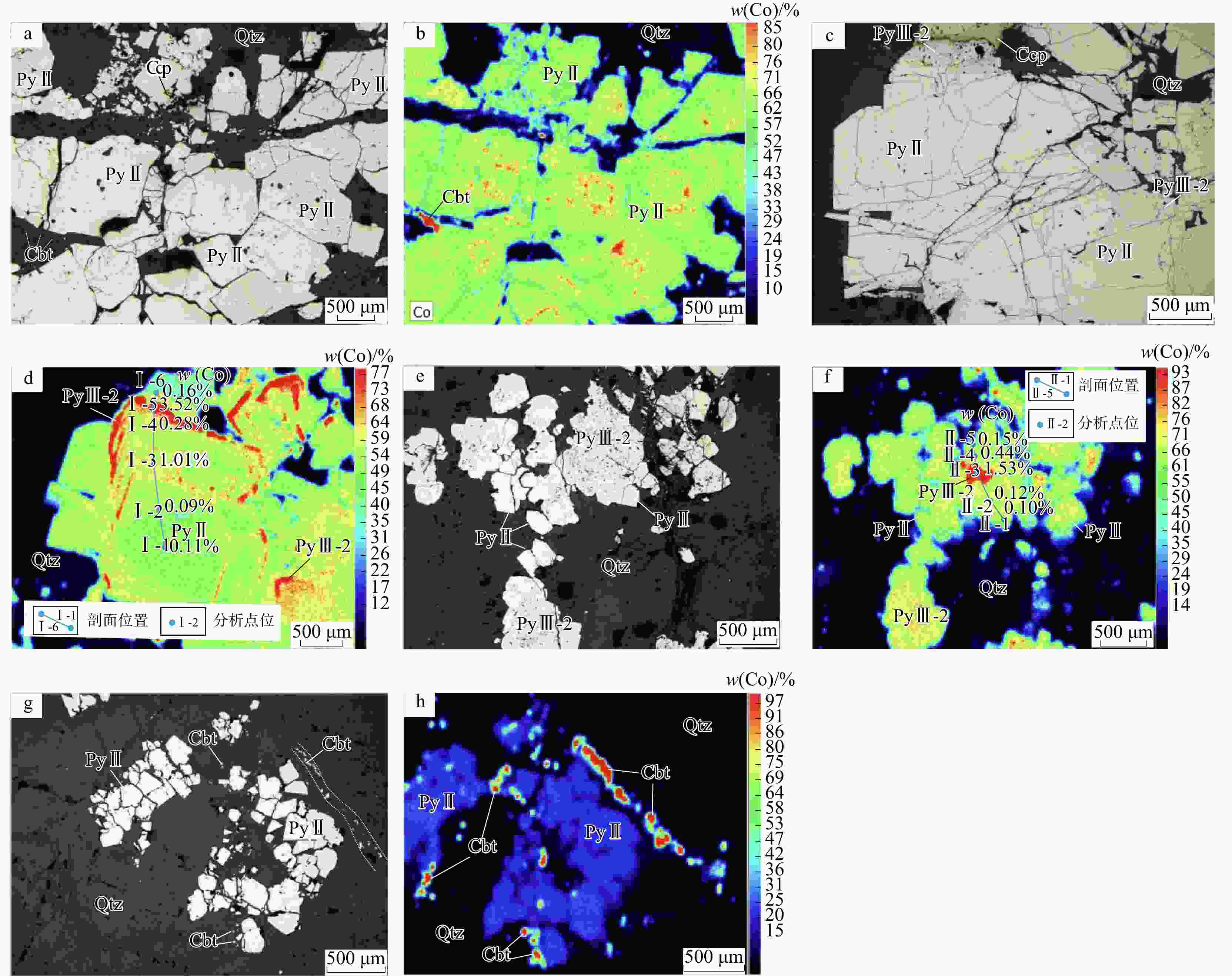
图 6 井冲铜钴矿床典型含钴黄铁矿中Co元素μ-XRF扫面结果
a. 大范围粗粒黄铁矿(PyⅡ)集合体,边部的石英中产出细粒的辉砷钴矿;b. 照片a范围的μ-XRF扫面结果,显示黄铁矿(PyⅡ)中出现不均匀分布的富钴环带和不规则状富钴部位;c. 绿泥石−石英−黄铁矿阶段的黄铁矿(PyⅡ)颗粒粗大,结晶形态好,局部受构造应力作用发生破碎呈碎裂状,沿黄铁矿颗粒边缘及破碎裂隙可见明显的多孔状结构;d. 照片c范围的μ-XRF扫面结果,显示Co元素富集于黄铁矿环带中,右下角可见不规则的钴富集部位,图中标注的蓝色线条及圆点为分析剖面I所在位置和分析点位,分析点编号和Co含量分别位于剖面线的左侧和右侧;e. 绿泥石−石英−黄铁矿阶段自形−半自形粒状黄铁矿(PyⅡ)中心为多孔状黄铁矿(PyⅢ-2),含石英等杂质,指示溶解再沉淀作用;f. 照片e范围的μ-XRF扫面结果,显示Co富集于多孔状黄铁矿(PyⅢ-2)的核心,图中标注的蓝色线条及圆点为分析剖面II所在位置和分析点位,分析点编号和Co含量分别位于剖面线的左侧和右侧;g. 绿泥石−石英−黄铁矿阶段,自形−半自形粒状黄铁矿(PyⅡ)集合体呈细小团块状或角砾状,表面干净,无溶解再沉淀作用发生,细小的辉砷钴矿分布于黄铁矿边缘的石英中,或沿石英生长环带呈细脉状分布;h. 照片g范围的μ-XRF扫面结果,黄铁矿(PyⅡ)无明显Co元素异常,细小的辉砷钴矿颗粒分布于石英中,或沿石英结晶生长环带细脉状分布。扫面结果中的富钴部位及辉砷钴矿的面积,均略大于实际面积,这是由μ-XRF扫面最小束径17 μm导致的“马赛克”效应
Figure 6. μ-XRF mapping of Co from typical cobalt-rich pyrite at the Jingchong copper-cobalt deposit
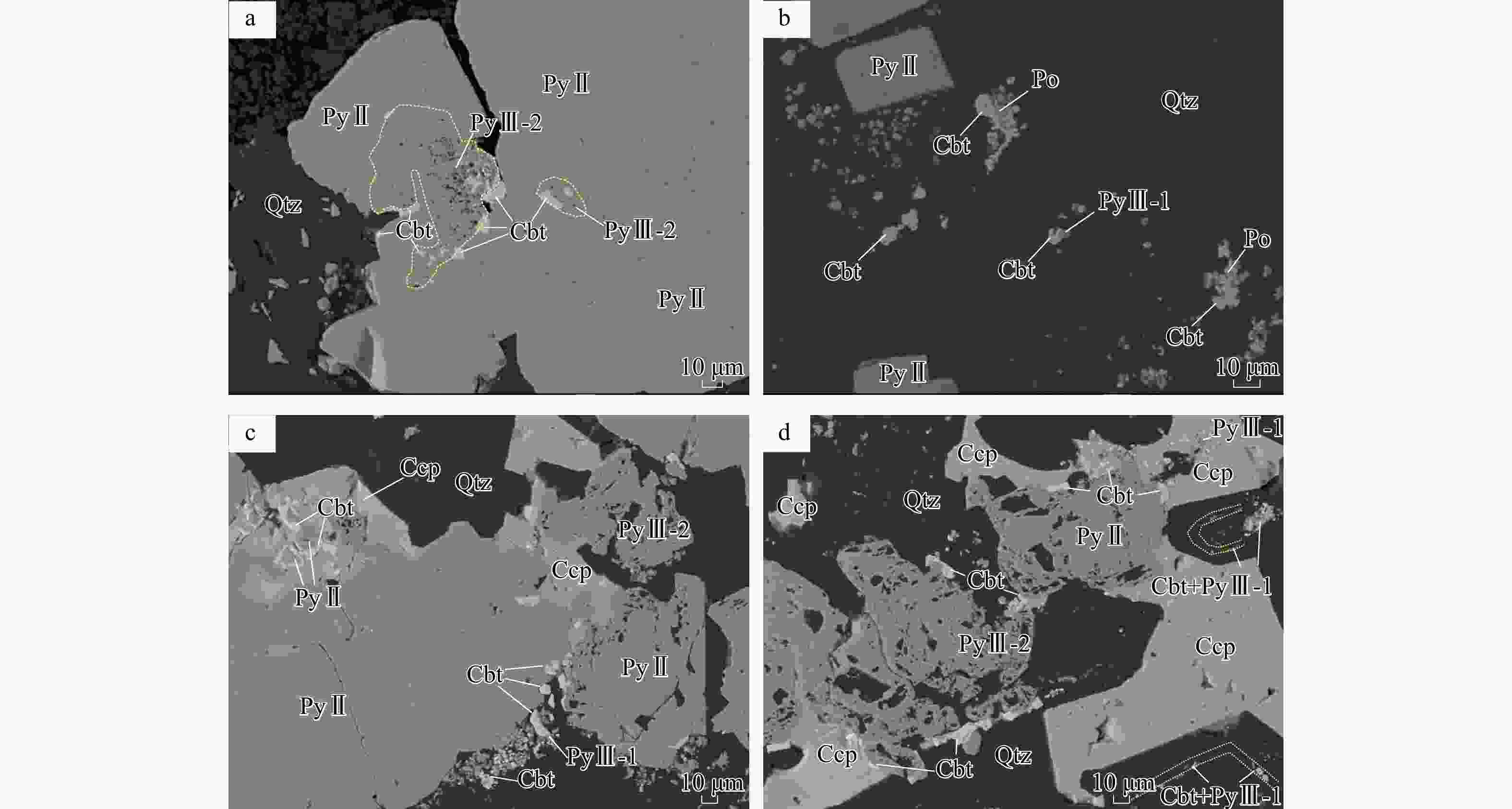
图 7 井冲铜钴矿床典型辉砷钴矿的BSE照片
a. 黄铁矿−辉砷钴矿的BSE图像,表面洁净的黄铁矿(PyⅡ)内部产出多孔状黄铁矿(PyⅢ-2),包含石英等矿物杂质,指示溶蚀重结晶作用发生,辉砷钴矿沿该多孔状黄铁矿中心的边缘分布;b. 黄铁矿−辉砷钴矿−石英阶段,自形−半自形粒状微细粒黄铁矿(PyⅢ-1)与辉砷钴矿共生,分布于石英中,局部被磁黄铁矿沿其边缘及裂隙交代;c. 微细粒黄铁矿(PyⅢ-1)−辉砷钴矿集合体分布于绿泥石−石英−黄铁矿阶段的粗粒黄铁矿(PyⅡ)边缘的石英中,辉砷钴矿沿粗粒黄铁矿颗粒(PyⅡ)边缘及裂隙呈尖角状交代或镶边状交代,最晚阶段黄铜矿交代粗粒黄铁矿(PyⅡ)及辉砷钴矿,呈包含结构;d. 黄铜矿呈填隙状分布于黄铁矿−辉砷钴矿−石英阶段的石英中,包裹交代细粒辉砷钴矿、细粒黄铁矿(PyⅢ-1)和更早阶段的粗粒黄铁矿(PyⅡ),较粗粒的辉砷钴矿沿着多孔状黄铁矿(PyⅢ-2)边缘分布,细粒辉砷钴矿−黄铁矿(PyⅢ-1)组合在石英的结晶生长环带中定向分布
Figure 7. BSE photos of the representative cobaltite in the Jingchong copper-cobalt deposit
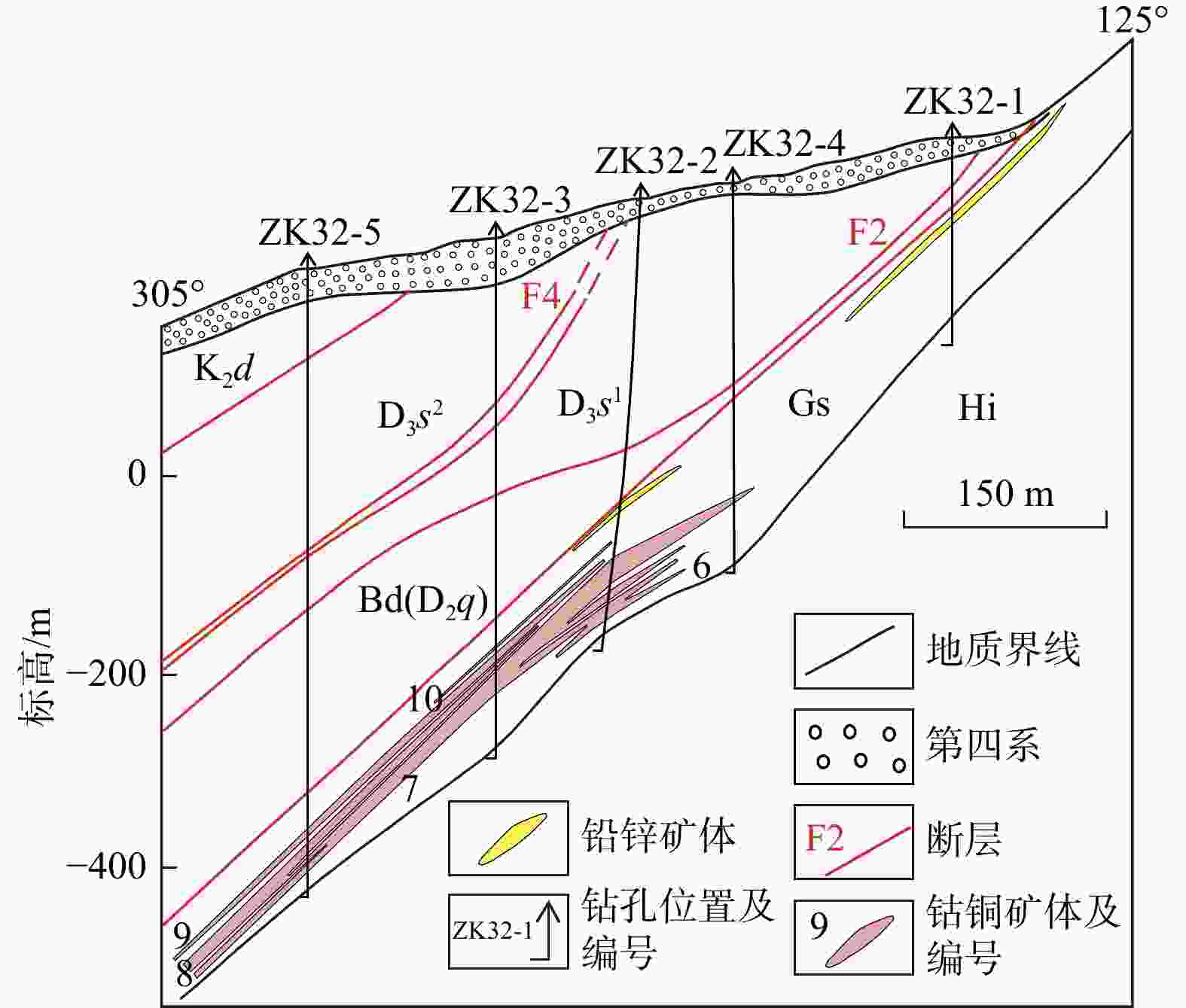
表 1 井冲铜钴矿床矿物生成顺序
Table 1. Mineral sequence of the Jingchong copper-cobalt deposit

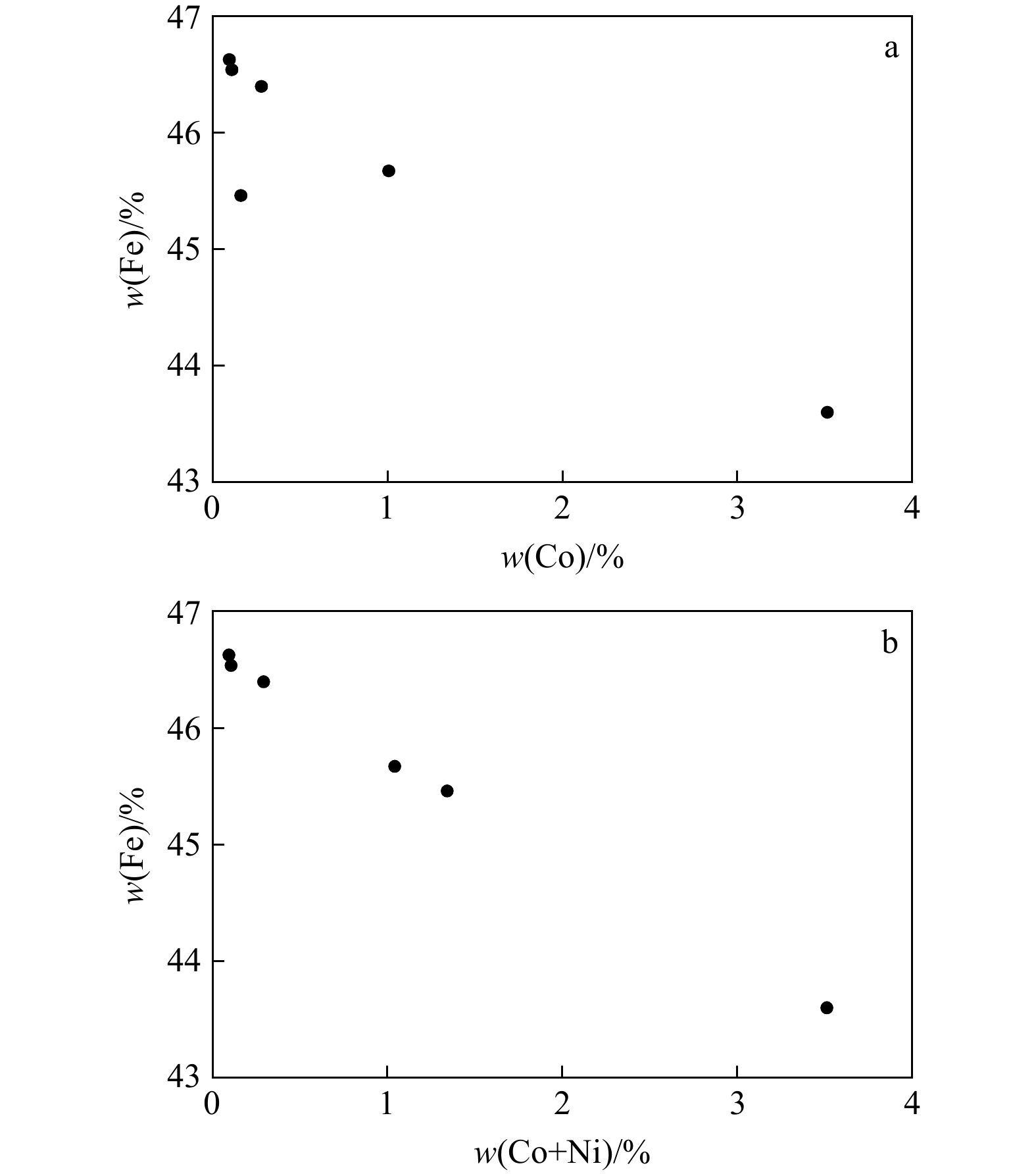
表 2 井冲铜钴矿床不同世代及特征的黄铁矿电子探针成分
Table 2. Electron probe data and characteristics of different generations pyrite at the Jingchong copper-cobalt deposit
分析点号 黄铁矿世代 黄铁矿特征 S Pb Bi Ag Co Zn Te As Se Fe Ni Cu 总计 分子式 wB/% 200-D06-2-1-Py1-3 PyⅠ 细粒黄铁矿集合体 53.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.09 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 45.93 0.01 0.94 100.00 Fe1.00S2.01 200-D06-2-1-Py1-4 PyⅠ 53.09 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.10 0.00 0.00 0.14 0.00 46.41 0.00 0.01 99.76 Fe1.00S1.99 200-D06-2-1-Py-7 PyⅠ 53.05 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.15 0.01 0.01 0.03 0.00 46.18 0.00 0.32 99.75 Fe1.00S2.00 200-D06-2-1-Py-19 PyⅠ 53.29 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.33 0.01 0.00 0.05 0.01 46.22 0.00 0.00 99.93 Fe1.00S2.01 50-D06-2-Py-2 PyⅠ 52.57 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.08 0.00 0.01 1.15 0.00 45.38 0.00 0.01 99.24 Fe1.00S2.02 50-D06-2-Py-5 PyⅠ 52.69 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.26 0.00 0.00 1.01 0.00 45.92 0.03 0.01 99.91 Fe1.00S2.00 50-D06-2-Py-10 PyⅠ 53.22 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.15 0.00 0.00 0.12 0.00 46.07 0.00 0.00 99.56 Fe1.00S2.01 0-D03-1-Py-1 PyⅡ 普通粗粒 53.53 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.17 0.00 0.06 0.08 0.00 46.50 0.00 0.00 100.34 Fe1.00S2.00 0-D03-1-Py-2 PyⅡ 53.70 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.11 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 46.38 0.00 0.00 100.20 Fe1.00S2.02 0-D03-1-Py-3 PyⅡ 53.17 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.15 0.00 0.02 0.12 0.02 46.42 0.00 0.02 99.92 Fe1.00S1.99 0-D03-1-Py-4 PyⅡ 53.56 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.60 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.03 46.07 0.00 0.00 100.28 Fe1.00S2.02 0-D03-1-Py-5 PyⅡ 53.16 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.10 0.00 0.00 0.59 0.01 46.21 0.00 0.00 100.08 Fe1.00S2.00 0-D03-1-Py-25 PyⅡ 碎裂状粗粒,无重结晶 53.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.08 0.00 0.00 0.19 0.00 46.44 0.00 0.01 99.96 Fe1.00S2.00 0-D03-1-Py-26 PyⅡ 53.13 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.16 0.00 0.01 0.75 0.00 46.10 0.02 0.00 100.16 Fe1.00S2.01 0-D03-1-Py-27 PyⅡ 52.53 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.07 0.00 0.00 1.52 0.00 46.10 0.00 0.00 100.21 Fe1.00S1.98 0-D03-1-Py-28 PyⅡ 53.73 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.08 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.01 46.59 0.00 0.02 100.44 Fe1.00S2.01 0-D03-1-Py-29 PyⅡ 53.46 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.14 0.00 0.00 0.12 0.00 46.27 0.00 0.02 100.01 Fe1.00S2.01 0-D03-1-Py-30 PyⅡ 52.11 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.08 0.00 0.00 2.46 0.00 46.08 0.00 0.00 100.73 Fe1.00S1.97 200-D06-2-1-Py-1 PyⅡ 粗粒,重结晶 53.18 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.07 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.01 46.24 0.00 0.02 99.56 Fe1.00S2.00 200-D06-2-1-Py-2 PyⅡ 53.33 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.08 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 46.49 0.01 0.03 99.98 Fe1.00S2.00 200-D06-2-1-Py-5 PyⅡ 51.44 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.08 0.00 0.03 2.78 0.00 45.82 0.00 0.00 100.14 Fe1.00S1.96 200-D06-2-1-Py-4 PyⅡ 52.72 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.11 0.00 0.00 0.07 0.01 45.56 0.00 0.90 99.37 Fe1.00S2.01 200-D06-2-1-Py-8 PyⅡ 52.38 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.07 0.00 0.00 1.36 0.00 46.05 0.00 0.00 99.86 Fe1.00S1.98 200-D06-2-1-Py-9 PyⅡ 51.11 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.07 0.00 0.00 3.22 0.00 45.41 0.03 0.01 99.87 Fe1.00S1.96 -150-D2-Py-16 PyⅡ 剖面Ⅰ-1,粗粒黄铁矿 53.53 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.11 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 46.53 0.00 0.00 100.20 Fe1.00S2.00 -150-D2-Py-15 PyⅡ 剖面Ⅰ-2,粗粒黄铁矿 53.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.09 0.00 0.00 0.43 0.03 46.62 0.00 0.00 100.18 Fe1.00S1.98 -50-D7-Py-13 PyⅡ 剖面Ⅱ-1,粗粒黄铁矿 52.89 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.10 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 45.09 0.00 0.00 98.09 Fe1.00S2.04 -50-D7-Py-14 PyⅡ 剖面Ⅱ-2,粗粒黄铁矿 52.87 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.12 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.00 45.46 0.00 0.00 98.51 Fe1.00S2.03 0-D03-1-Py-6 PyⅢ-1 辉砷钴矿共生细粒黄铁矿 52.17 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.11 0.01 0.00 1.82 0.00 45.73 0.00 0.02 99.86 Fe1.00S1.99 0-D03-1-Py-7 PyⅢ-1 53.38 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.32 0.02 0.00 0.50 0.00 46.06 0.00 0.00 100.30 Fe1.00S2.02 0-D03-1-Py-8 PyⅢ-1 52.09 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.08 0.00 0.00 2.15 0.00 45.75 0.00 0.00 100.10 Fe1.00S1.98 0-D03-1-Py-9 PyⅢ-1 53.57 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.08 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.00 46.55 0.02 0.00 100.26 Fe1.00S2.00 0-D03-1-Py-10 PyⅢ-1 53.54 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.13 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.04 46.20 0.01 0.02 99.95 Fe1.00S2.02 0-D03-1-Py-11 PyⅢ-1 53.45 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.65 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 46.00 0.00 0.00 100.11 Fe1.00S2.02 0-D03-1-Py-12 PyⅢ-1 51.40 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.09 0.00 0.01 3.37 0.00 45.79 0.00 0.00 100.65 Fe1.00S1.96 0-D03-1-Py-13 PyⅢ-1 53.26 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.19 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.02 46.44 0.00 0.01 99.94 Fe1.00S2.00 0-D03-1-Py-14 PyⅢ-1 53.69 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.16 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.02 46.00 0.00 0.00 99.89 Fe1.00S2.03 0-D03-1-Py-15 PyⅢ-1 53.56 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.13 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 46.69 0.01 0.01 100.44 Fe1.00S2.00 0-D03-1-Py-16 PyⅢ-1 52.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.16 0.00 0.04 2.30 0.00 45.95 0.01 0.00 100.48 Fe1.00S1.97 0-D03-1-Py-17 PyⅢ-1 53.76 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.12 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.00 46.59 0.00 0.00 100.54 Fe1.00S2.01 0-D03-1-Py-18 PyⅢ-1 51.08 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.37 0.02 0.01 3.67 0.00 45.19 0.01 0.02 100.35 Fe1.00S1.97 -150-D2-Py-14 PyⅢ-2 剖面Ⅰ-3,富钴环带黄铁矿 53.34 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.01 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.04 45.67 0.04 0.00 100.11 Fe1.00S2.03 -150-D2-Py-13 PyⅢ-2 剖面Ⅰ-4,富钴环带黄铁矿 53.60 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.28 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 46.39 0.02 0.00 100.30 Fe1.00S2.01 -150-D2-Py-12 PyⅢ-2 剖面Ⅰ-5,富钴环带黄铁矿 53.59 0.00 0.00 0.00 3.52 0.00 0.05 0.01 0.02 43.60 0.00 0.00 100.78 Fe1.00S2.14 -150-D2-Py-11 PyⅢ-2 剖面Ⅰ-6,富钴环带黄铁矿 53.87 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.16 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.00 45.46 1.18 0.09 100.79 Fe1.00S2.06 -50-D7-Py-15 PyⅢ-2 剖面Ⅱ-3,多孔状黄铁矿 52.98 0.00 0.00 0.01 1.53 0.00 0.00 0.35 0.00 44.82 0.00 0.38 100.08 Fe1.00S2.06 -50-D7-Py-16 PyⅢ-2 剖面Ⅱ-4,多孔状黄铁矿 52.77 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.44 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 45.26 0.02 0.00 98.48 Fe1.00S2.03 -50-D7-Py-20 PyⅢ-2 剖面Ⅱ-5,多孔状黄铁矿 52.88 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.15 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.04 45.11 0.00 0.00 98.23 Fe1.00S2.04 sph-1-1-Py-12 PyⅣ 多金属硫化阶段黄铁矿 53.15 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.07 0.03 0.02 0.79 0.00 46.22 0.00 0.02 100.29 Fe1.00S2.00 sph-1-1-Py-13 PyⅣ 53.34 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.10 0.04 0.00 0.61 0.00 46.31 0.00 0.01 100.42 Fe1.00S2.01 sph-1-1-Py-14 PyⅣ 53.45 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.21 0.27 0.00 0.50 0.00 46.07 0.10 0.00 100.61 Fe1.00S2.02 sph-1-1-Py-15 PyⅣ 52.82 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.09 0.07 0.03 1.66 0.00 46.18 0.00 0.01 100.85 Fe1.00S1.99 注:分子式计算均以Fe原子数为1进行了标准化。 表 3 井冲铜钴矿床毒砂电子探针成分
Table 3. Electron probe composition of arsenopyrite at the Jingchong copper-cobalt deposit
分析点号 S Pb Bi Ag Co Zn Te As Se Fe Ni Cu 总计 分子式 wB/% 50-D06-2-Apy-1 21.12 0.04 0.30 0.00 0.08 0.00 0.00 43.14 0.00 34.20 0.00 0.01 98.89 Fe1.00As0.94S1.08 50-D06-2-Apy-2 20.82 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.09 0.00 0.00 43.63 0.00 34.19 0.00 0.02 98.76 Fe1.00As0.95S1.06 50-D06-2-Apy-3 20.98 0.10 0.00 0.00 1.95 0.00 0.00 43.86 0.00 32.46 0.28 0.02 99.65 Fe1.00As1.01S1.13 50-D06-2-Apy-4 21.75 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.12 0.00 0.00 42.35 0.00 34.43 0.00 0.00 98.65 Fe1.00As0.92S1.10 50-D02-Apy-1 20.09 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.09 0.01 0.00 46.86 0.00 33.77 0.00 0.06 100.89 Fe1.00As1.03S1.04 50-D02-Apy-2 21.46 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.08 0.00 0.00 44.06 0.00 34.14 0.00 0.00 99.74 Fe1.00As0.96S1.09 50-D02-Apy-3 22.80 0.02 0.00 0.03 0.09 0.02 0.03 42.88 0.00 34.71 0.00 0.02 100.60 Fe1.00As0.92S1.14 50-D02-Apy-4 19.69 0.06 0.00 0.00 0.10 0.00 0.00 46.88 0.00 34.11 0.00 0.00 100.85 Fe1.00As1.02S1.01 注:分子式计算均以Fe原子数为1进行了标准化。 表 4 浏阳井冲铜钴矿床辉砷钴矿电子探针成分
Table 4. Electron probe composition of cobaltite at the Jingchong copper-cobalt deposit in Liuyang City
分析点号 S Pb Bi Ag Co Zn Te As Se Fe Ni Cu 总计 分子式 wB/% 100-D011-Co-2 20.64 0.00 0.00 0.00 36.01 0.00 0.00 40.82 0.24 0.95 0.20 0.00 98.86 Co1.00Fe0.03As0.89S1.05 100-D011-Co-3 20.17 0.00 0.00 0.00 33.79 0.00 0.04 41.08 0.24 2.84 0.15 0.00 98.32 Co1.00Fe0.09As0.96S1.10 100-D011-Co-5 19.92 0.00 0.00 0.01 34.53 0.00 0.02 41.23 0.21 2.04 0.16 0.00 98.11 Co1.00Fe0.06As0.94S1.06 0-D03-1-Co-8 18.37 0.00 0.00 0.00 31.70 0.00 0.00 43.78 0.21 1.67 2.44 0.00 98.18 Co1.00Fe0.06As1.09S1.07 50-D03-2-Co-1 19.27 0.00 0.00 0.00 33.22 0.00 0.01 43.65 0.26 2.03 0.06 0.00 98.50 Co1.00Fe0.06As1.03S1.07 200-D06-2-1-Co-4 20.64 0.00 0.41 0.02 32.66 0.02 0.05 42.61 0.16 2.55 0.64 0.00 99.74 Co1.00Fe0.08As1.03S1.16 200-D06-2-1-Co-5 20.85 0.00 0.00 0.00 30.52 0.00 0.01 41.71 0.21 4.74 0.49 0.00 98.53 Co1.00Fe0.03As0.89S1.12 200-D06-2-1-Co-6 20.46 0.00 0.00 0.00 32.58 0.00 0.00 42.32 0.24 3.19 0.32 0.00 99.11 Co1.00Fe0.03As0.89S1.13 200-D06-2-1-Co-7 20.65 0.02 0.00 0.00 31.39 0.00 0.00 42.19 0.22 5.51 0.16 0.00 100.15 Co1.00Fe0.03As0.89S1.14 注:分子式计算均以Co原子数为1进行了标准化。 表 5 浏阳井冲铜钴矿床黄铜矿电子探针成分
Table 5. Electron probe composition of chalcopyrite at the Jingchong copper-cobalt deposit in Liuyang City
分析点号 S Pb Bi Ag Co Zn Te As Se Fe Ni Cu 总计 分子式 wB/% 0-D07-1-Ccp-2 33.46 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.00 30.43 0.00 34.36 98.27 Cu1.00Fe1.01S1.93 0-D07-1-Ccp-3 33.87 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 30.35 0.00 34.47 98.71 Cu1.00Fe1.00S1.95 0-D07-1-Ccp-4 33.93 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 30.40 0.00 34.43 98.81 Cu1.00Fe1.00S1.95 0-D03-1-Ccp-1 34.23 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.00 30.35 0.00 34.70 99.30 Cu1.00Fe1.00S1.95 0-D03-1-Ccp-2 33.45 0.06 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.00 0.00 0.02 30.01 0.00 34.83 98.40 Cu1.00Fe0.98S1.90 50-D03-2-Ccp-1 34.06 0.04 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.03 0.05 0.03 0.00 30.04 0.02 34.39 98.67 Cu1.00Fe0.99S1.96 -100-D5-2-Ccp-1 33.97 0.06 0.00 0.05 0.04 0.02 0.04 0.01 0.04 30.55 0.00 34.68 99.43 Cu1.00Fe1.00S1.94 -100-D5-2-Ccp-2 34.08 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.03 0.05 30.33 0.00 34.83 99.33 Cu1.00Fe0.99S1.94 注:分子式计算均以Cu原子数为1进行了标准化。 -
[1] U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY. Mineral commodity summaries[R]. Reston:Virginia,2023. [2] 付浩,王加昇,李金龙,等. 全球钴矿资源时空分布及成因类型[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(1):1-22.FU H,WANG J S,LI J L,et al. Spatiotemporal distribution and genesis types of global cobalt resources[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(1):1-22. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 段俊,徐刚,汤中立,等. 我国钴资源产业发展现状、问题与对策[J]. 中国工程科学,2024,26(3):98-107. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2024.03.009DUAN J,XU G,TANG Z L,et al. Analysis of development of China's cobalt industry:Current status,problems and countermeasures[J]. Strategic Study of CAE,2024,26(3):98-107. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2024.03.009 [4] 海连富,张晓军,孙永亮,等. 宁夏卫宁北山地区伴生钴矿床地质特征、控矿因素及找矿方向[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(5):55-69.HAI L F,ZHANG X J,SUN Y L,et al. Geological characteristics,controlling factors and prospecting directions of a ssociated cobalt deposits in the Weiningbeishan area,Ningxia[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(5):55-69. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 许德如,王智琳,聂逢君,等. 中国钴矿资源现状与关键科学问题[J]. 中国科学基金,2019,33(2):125-132.XU D R,WANG Z L,NIE F J,et al. Cobalt resources in China:Current research status and key scientific issues[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China,2019,33(2):125-132. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 许德如,王力,李鹏春,等. 湘东北地区连云山花岗岩的成因及地球动力学暗示[J]. 岩石学报,2009,25(5):1056-1078.XU D R,WANG L,LI P C,et al. Petrogenesis of the Lianyunshan granites in northeastern Hunan Province,South China,and its geodynamic implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2009,25(5):1056-1078. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 陈剑锋,黄建中,文春华,等. 浅论湘东北地区与燕山期花岗岩有关矿床的成矿系列与找矿方向[J]. 地球学报,2023,44(5):815-833. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2023.012901CHEN J F,HUANG J Z,WEN C H,et al. A preliminary study of metallogenic series and its prospecting direction related to Yanshannian granites in northeastern of Hunan Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2023,44(5):815-833. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2023.012901 [8] 周怡湘,程巨能. 湘东北思村−砰山剥离断层特征及控矿研究[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,1999,23(4):334-344. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.1999.04.007ZHOU Y X,CHENG J N. The Sicun-Pengshan denudational fault and its control on ore mineralization,northeastern Hunan,China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,1999,23(4):334-344. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.1999.04.007 [9] 易祖水,罗小亚,周东红,等. 浏阳市井冲钴铜多金属矿床地质特征及成因浅析[J]. 华南地质与矿产,2010,26(3):12-18.YI Z S,LUO X Y,ZHOU D H,et al. Geological characteristics and genesis of Jinchong Co-Cu polymetal deposit,Liuyang,Hunan Province[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China,2010,26(3):12-18. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 周岳强,许德如,董国军,等. 湖南长沙−平江断裂带构造演化及其控矿作用[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版),2019,42(3):201-208.ZHOU Y Q,XU D R,DONG G J,et al. Structural evolution of the Changsha-Pingjiang fault zone and its controlling on mineralization[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science),2019,42(3):201-208. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 宁钧陶,黄宝亮,董国军,等. 湘东北热液型钴矿床中含钴矿物特征及其对成矿的指示意义[J]. 黄金科学技术,2023,31(4):531-545.NING J T,HUANG B L,DONG G J,et al. Characteristics of cobalt-bearing minerals in hydrothermal cobalt deposits in northeastern Hunan Province and their implication for mineralization[J]. Gold Science and Technology,2023,31(4):531-545. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 王智琳,伍杨,许德如,等. 湘东北长沙−平江断裂带关键金属钴的赋存状态与成矿规律[J]. 黄金科学技术,2020,28(6):779-785.WANG Z L,WU Y,XU D R,et al. Occurrence state and ore-forming regularity of critical metal cobalt in the Changsha-Pingjiang fault zone,northeastern Hunan Province[J]. Gold Science and Technology,2020,28(6):779-785. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] ZOU S H,ZOU F H,NING J T,et al. A stand-alone Co mineral deposit in northeastern Hunan Province,South China:Its timing,origin of ore fluids and metal Co,and geodynamic setting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2018,92:42-60. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.11.008 [14] PENG E K,KOLB J,WALTER B F,et al. New insights on the formation of the Jingchong Cu-co-Pb-Zn deposit,South China:Evidence from sphalerite mineralogy and muscovite 40Ar-39Ar dating[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2023,162:105667. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2023.105667 [15] 陕亮,王川,康博,等. 江南造山带中段井冲钴铜矿床成矿时代、流体性质与成矿模式[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2024,48(6):1299-1314.SHAN L,WANG C,KANG B,et al. Mineralization age,fluid properties,and metallogenic model of the Jingchong Co-Cu deposit in the central Jiangnan Orogen,South China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2024,48(6):1299-1314. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 陕亮,黄啸坤,王川,等. 湘东北地区井冲钴铜矿床中辉砷钴矿的发现、成因及开发利用价值[J]. 中国地质,2022,49(5):1705-1707. doi: 10.12029/gc20220525SHAN L,HUANG X K,WANG C,et al. Discovery of cobaltite in the Jingchong Co-Cu deposit,northeastern Hunan Province,South China:Implications for ore genesis and exploration[J]. Geology in China,2022,49(5):1705-1707. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12029/gc20220525 [17] WANG Z L,WANG Y F,PENG E K,et al. Micro-textural and chemical fingerprints of hydrothermal cobalt enrichment in the Jingchong Co-Cu polymetallic deposit,South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2022,142:104721. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.104721 [18] ZHAO J H,ZHOU M F,YAN D P,et al. Reappraisal of the ages of Neoproterozoic strata in South China:No connection with the grenvillian orogeny[J]. 2011,39(4):299-302. [19] 王孝磊,周金城,陈昕,等. 江南造山带的形成与演化[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2017,36(5):714-735. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2017.05.003WANG X L,ZHOU J C,CHEN X,et al. Formation and evolution of the Jiangnan Orogen[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry,2017,36(5):714-735. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2017.05.003 [20] 许德如,邓腾,董国军,等. 湘东北连云山二云母二长花岗岩的年代学和地球化学特征:对岩浆成因和成矿地球动力学背景的启示[J]. 地学前缘,2017,24(2):104-122.XU D R,DENG T,DONG G J,et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronological and geochemical characteristics of the Lianyunshan two-mica monzogranites in northeastern Hunan Province:Implications for petrogenesis and tectonic setting associated with polymetallic mineralization[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2017,24(2):104-122. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 张文山. 湘东北长沙−平江断裂动力变质带的构造及地球化学特征[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,1991,15(2):100-109.ZHANG W S. Structural and geochemical features of the Changsha-Pingjiang fracture dynamic metamorphism zone in NE Hunan Province,China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,1991,15(2):100-109. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 高林志,陈峻,丁孝忠,等. 湘东北岳阳地区冷家溪群和板溪群凝灰岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄:对武陵运动的制约[J]. 地质通报,2011,30(7):1001-1008. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.07.001GAO L Z,CHEN J,DING X Z,et al. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb dating of the tuff bed of Lengjiaxi and Banxi Groups,northeastern Hunan:Constraints on the Wuling Movement[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2011,30(7):1001-1008. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.07.001 [23] 杨雪,张玉芝,崔翔,等. 湘东北新元古代冷家溪群沉积岩的地球化学特征和碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 地球科学,2020,45(9):3461-3474.YANG X,ZHANG Y Z,CUI X,et al. Geochemistry and detrital zircon U-Pb ages of sedimentary rocks from Neoproterozoic Lengjiaxi Group in NE Hunan Province[J]. Earth Science,2020,45(9):3461-3474. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] WANG J Q,SHU L S,SANTOSH M. Petrogenesis and tectonic evolution of Lianyunshan complex,South China:Insights on Neoproterozoic and Late Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the central Jiangnan Orogen[J]. Gondwana Research,2016,39:114-130. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.06.015 [25] JI W B,LIN W,FAURE M,et al. Origin of the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous peraluminous granitoids in the northeastern Hunan Province (Middle Yangtze region),South China:Geodynamic implications for the Paleo-Pacific subduction[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2017,141:174-193. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.07.005 [26] 张鲲,徐德明,宁钧陶,等. 湘东北井冲钴铜矿区连云山花岗岩的岩石成因:锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石地球化学和Hf同位素约束[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,2019,38(1):21-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2019.01.002ZHANG K,XU D M,NING J T,et al. Petrogenisis of the Lianyunshan granites in Jingchong Co-Cu polymetallic deposit in northeastern Hunan:Constraints from zircon U-Pb chronology,petrochemistry and Hf isotope[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica,2019,38(1):21-33. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2019.01.002 [27] DENG T,XU D R,CHI G X,et al. Geology,geochronology,geochemistry and ore genesis of the Wangu gold deposit in northeastern Hunan Province,Jiangnan Orogen,South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2017,88:619-637. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.01.012 [28] DENG T,XU D R,CHI G X,et al. Caledonian (Early Paleozoic) veins overprinted by Yanshanian (Late Mesozoic) gold mineralization in the Jiangnan Orogen:A case study on gold deposits in northeastern Hunan,South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2020,124:103586. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103586 [29] XU D R,DENG T,CHI G X,et al. Gold mineralization in the Jiangnan Orogenic Belt of South China:Geological,geochemical and geochronological characteristics,ore deposit-type and geodynamic setting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2017,88:565-618. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.004 [30] XU J W,LAI J Q,LI B,et al. Tungsten mineralization during slab subduction:A case study from the Huxingshan deposit in northeastern Hunan Province,South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2020,124:103657. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103657 [31] WEN C H,SHAO Y J,XIONG Y Q,et al. Ore genesis of the Baishawo Be-Li-Nb-Ta deposit in the northeast Hunan Province,South China:Evidence from geological,geochemical,and U-Pb and Re-Os geochronologic data[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2021,129:103895. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103895 [32] YU D S,XU D R,ZHAO Z X,et al. Genesis of the Taolin Pb-Zn deposit in northeastern Hunan Province,South China:Constraints from trace elements and oxygen-sulfur-lead isotopes of the hydrothermal minerals[J]. Mineralium Deposita,2020,55(7):1467-1488. doi: 10.1007/s00126-019-00947-8 [33] YU D S,XU D R,WANG Z L,et al. Trace element geochemistry and O-S-Pb-He-Ar isotopic systematics of the Lishan Pb-Zn-Cu hydrothermal deposit,NE Hunan,South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2021,133:104091. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104091 [34] 杨紫文,李艳军,周豹,等. 幕阜山复式花岗岩体西北缘伟晶岩中石榴子石成因及对Nb-Ta成矿的制约:成矿和未成矿微斜长石伟晶岩对比[J]. 地质科技通报,2025,44(2):238-256.YANG Z W,LI Y J,ZHOU B,et al. Genesis of garnet in pegmatites from the northwestern margin of the Mufushan composite granite pluton and its constraints on Nb-Ta mineralization:Comparison from mineralized and unmineralized pegmatites[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2025,44(2):238-256. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] ZU B,ZHANG H,CHI G X,et al. Generation of Cu-Au skarn mineralization by mafic magma recharge:Insights from the Bozymchak deposit in the Chatkal-Kurama region,Kyrgyzstan,West Tianshan[J]. 2024,137(5/6):1964-1984. [36] ZHANG R X,YANG S Y. A mathematical model for determining carbon coating thickness and its application in electron probe microanalysis[J]. Microscopy and Microanalysis,2016,22(6):1374-1380. doi: 10.1017/S143192761601182X [37] YANG S Y. Electron probe microanalysis in geosciences:Analytical procedures and recent advances[J]. Atomic Spectroscopy,2022,43(2):186-200. [38] WANG Z L,XU D R,CHI G X,et al. Mineralogical and isotopic constraints on the genesis of the Jingchong Co-Cu polymetallic ore deposit in northeastern Hunan Province,South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2017,88:638-654. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.02.011 [39] PUTNIS A. Mineral replacement reactions:From macroscopic observations to microscopic mechanisms[J]. Mineralogical Magazine, 2002,66(5):689-708. [40] PUTNIS A. Mineral replacement reactions[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry,2009,70(1):87-124. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2009.70.3 [41] 胡浩,段壮,LUO Y,等. 鄂东程潮铁矿床磁铁矿的微量元素组成及其矿床成因意义[J]. 岩石学报,2014,30(5):1292-1306.HU H,DUAN Z,LUO Y,et al. Trace element systematics of magnetite from the Chengchao iron deposit in the Daye district:A laser ablation ICP-MS study and insights into ore genesis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2014,30(5):1292-1306. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] CLARK C,GRGURIC B,MUMM A S. Genetic implications of pyrite chemistry from the Palaeoproterozoic Olary Domain and overlying Neoproterozoic Adelaidean sequences,northeastern South Australia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2004,25(3/4):237-257. [43] REICH M,SIMON A C,DEDITIUS A,et al. Trace element signature of pyrite from the Los Colorados iron oxide-apatite (ioa) deposit,Chile:A missing link between Andean ioa and iron oxide copper-gold systems?[J]. Economic Geology 2016,111(3):743-761. [44] GEISLER T,PIDGEON R T,KURTZ R,et al. Experimental hydrothermal alteration of partially metamict zircon[J]. American Miner alogist,2003,88(10):1496-1513. [45] ALTREE-WILLIAMS A,PRING A,NGOTHAI Y,et al. Textural and compositional complexities resulting from coupled dissolution-reprecipitation reactions in geomaterials[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2015,150:628-651. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.08.013 [46] 刘萌,王智琳,许德如,等. 湖南井冲钴铜多金属矿床绿泥石、黄铁矿和黄铜矿的矿物学特征及其成矿指示意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学,2018,42(5):862-879.LIU M,WANG Z L,XU D R,et al. Mineralogy of chlorite,pyrite and chalcopyrite in the Jingchong Co-Cu polymetallic deposit in northeastern Hunan Province,South China:Implications for ore genesis[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia,2018,42(5):862-879. (in Chinese with English abstract [47] VASYUKOVA O V,WILLIAMS-JONES A E. Constraints on the genesis of cobalt deposits:Part Ⅱ. Applications to natural systems[J]. Economic Geology. 2022,117(3):529-544. [48] SU H M,JIANG S Y,CHI G X,et al. Formation of the giant Luiswishi Cu-Co deposit in the Central African copper belt by Neoproterozoic syn-sedimentary-diagenetic processes overprinted by Pan-African orogenic mineralization events[J]. Precambrian Research,2024,402:107299. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2024.107299 [49] 王慧宁,刘福来,朱志勇,等. 吉林省大横路铜钴矿复杂的沉积−变质变形−热液作用演化过程及其对钴的赋存状态和富集成矿的制约[J]. 岩石学报,2023,39(4):998-1018. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2023.04.04WANG H N,LIU F L,ZHU Z Y,et al. Complex evolution of the sedimentation,metamorphism-deformation and hydrothermal processes and their constraints on the occurrence,enrichment and mineralization of Co in the Dahenglu Cu-Co deposit,Jilin Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2023,39(4):998-1018. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2023.04.04 [50] 湖南省地质矿产勘查开发局四零二队. 湖南省浏阳市井冲矿区潭玲钴铜多金属矿详查报告[R]. 长沙:出版者不详,2008.HUNAN PROVINCIAL GEOLOGICAL AND MINERAL DEVELOPMENT BUREAU TEAM 402. Detailed investigation report of Tanling cobalt-copper polymetallic deposit in Jingchong mining area,Liuyang City,Hunan Province[R]. Changsha:[S. n. ],2008. (in Chinese) [51] 金吉梅. 四川某铜多金属矿石优先浮选工艺试验研究[J]. 有色冶金设计与研究,2017,38(3):11-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4345.2017.03.004JIN J M. Experimental study on selective flotation process of a certain copper polymetallic ore in Sichuan[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering & Research,2017,38(3):11-14. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4345.2017.03.004 [52] 严伟平,陈晓青,周家云,等. 提高拉拉铜矿资源综合利用率的选矿新工艺研究[J]. 矿产综合利用,2016(6):49-54.YAN W P,CHEN X Q,ZHOU J Y,et al. Research on new mineral processing technology for improving the comprehensive utilization rate of the resources of the lala copper mine[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources,2016(6):49-54. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: