Intelligent early warning method for subsidence deformation in goaf based on the frequency of microseismic events
-
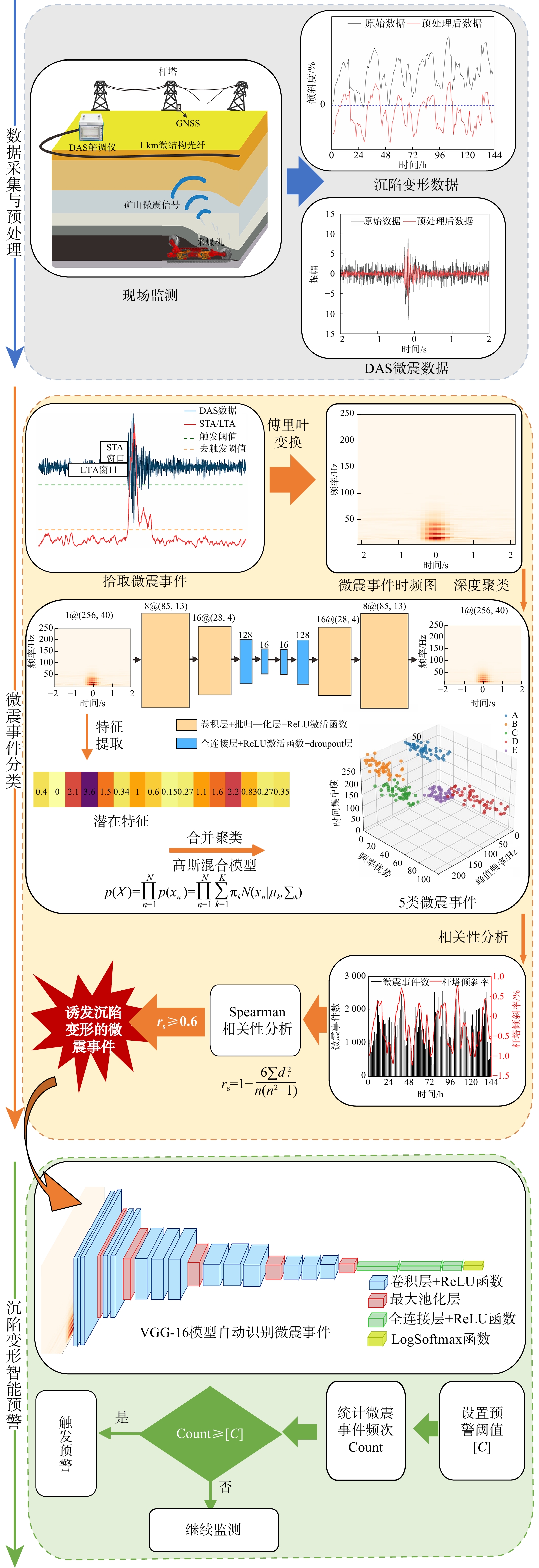
摘要:
“三下”开采引发的沉陷变形对输电线路等地表建(构)筑物的安全构成威胁,亟需一种采空区沉陷变形早期感知与智能预警方法。为此,提出了一种基于微震事件频次的采空区沉陷变形智能预警框架。该框架利用分布式声波传感(distributed acoustic sensing,简称DAS)系统采集微震数据,通过STA/LTA算法提取微震事件,借助结合自编码器(autoEncoder,简称AE)与高斯混合模型(Gaussian mixture models,简称GMM)的深度聚类方法对其分类,基于微震事件频次与沉陷变形数据之间的相关系数筛选诱发沉陷变形的微震事件,进而采用VGG-16深度学习模型实现对这类微震事件的智能识别,通过设定预警阈值开展实时预警。以我国西部某典型煤矿采空区为例,将该框架应用于实地监测。结果表明,该框架将采集到的采空区微震事件分为五大类,从中提取出诱发沉陷变形的一类微震事件,结合微震事件智能识别模型,成功对沉陷变形引发的杆塔倾斜度激增事件作出预警。实例证明该框架能够有效捕捉微震事件与沉陷变形的关联,实现对采空区沉陷变形的预警,具有实践可行性和工程应用价值。
Abstract:Objective The subsidence deformation caused by the "three underground" mining pose a threat to the safety of surface buildings such as transmission lines, and there is an urgent need for an early perception and intelligent warning method for subsidence and deformation in goaf areas.
Methods This paper proposed an intelligent early warning framework for subsidence and deformation in goaf areas based on the frequency of microseismic events. This framework utilized a Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) system to collect microseismic data, extracted microseismic events using the STA/LTA algorithm, and classified the microseismic events using a deep clustering method that combined AutoEncoder (AE) and Gaussian Mixture Models (GMM). Based on the correlation coefficient between microseismic event frequency and subsidence deformation data, microseismic events that induced subsidence deformation were selected. The VGG-16 deep learning model was then used to achieve intelligent recognition of such microseismic events, and real-time warning was carried out by setting warning thresholds.
Results This paper took a typical coal mine goaf in western China as the research area and applied the framework to field monitoring. The results show that the framework classifies the collected microseismic events in goaf into five categories, extracts one type of microseismic event that induces subsidence deformation, and combines with an intelligent microseismic event recognition model to successfully issue a warning for the sudden increase in tower inclination caused by subsidence deformation.
Conclusion Therefore, this framework can effectively capture the correlation between microseismic events and subsidence and deformation, to achieve early warning of subsidence and deformation in goaf areas, and has practical feasibility and engineering application value.
-
表 1 5类微震事件相关性分析结果
Table 1. Correlation analysis results of 5 types of microseismic events
微震事件类型 Spearman秩相关系数 p值 A 0.614 2.65×10−16 B −0.258 1.83×10−3 C 0.058 4.87×10−1 D −0.588 9.46×10−15 E −0.237 4.16×10−3 表 2 VGG-16模型性能测试集分类结果
Table 2. Classification results of VGG-16 model performance test set
标签 准确率 召回率 “1”:A类事件 0.92 0.95 “0”:其他事件 0.87 0.80 表 3 时序信号−时频图字典库
Table 3. Dictionary library of temporal signal-time and frequency diagrams
事件编码 标签 005753 “1”:A类事件 005754 “0”:其他事件 005755 “1”:A类事件 005756 “1”:A类事件 005757 “1”:A类事件 005758 “1”:A类事件 005759 “1”:A类事件 005760 “1”:A类事件 005761 “0”:其他事件 005762 “0”:其他事件 005763 “1”:A类事件 005764 “0”:其他事件 005765 “0”:其他事件 005766 “1”:A类事件 005767 “1”:A类事件 -
[1] BAI E H,GUO W B,TAN Y. Negative externalities of high-intensity mining and disaster prevention technology in China[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2019,78(7):5219-5235. doi: 10.1007/s10064-019-01468-4 [2] 王亚军. 750 kV渭延输电线路150号塔采空区塌陷分析[J]. 电力勘测设计,2011(4):11-14.WANG Y J. Analysis on pick empty area to cave in No. 150 tower of 750 kV overhead transmission line[J]. Electric Power Survey & Design,2011(4):11-14. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 梁双,王涉,徐辉. 中国西电东送40年发展成效与政策建议[J]. 中国电力,2024,57(11):88-93.LIANG S,WANG S,XU H. Development achievements and policy suggestions of China's west to east power transmission for 40 years[J]. Electric Power,2024,57(11):88-93. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 郭文兵,马志宝,白二虎. 我国煤矿“三下一上” 采煤技术现状与展望[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2020,48(9):16-26.GUO W B,MA Z B,BAI E H. Current status and prospect of coal mining technology under buildings,water bodies and railways,and above confined water in China[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2020,48(9):16-26. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 孙庆先,张勇,陈清通,等. 我国开采沉陷学70年研究综述及技术展望[J]. 中国矿业,2024,33(3):86-99.SUN Q X,ZHANG Y,CHEN Q T,et al. 70 year review and technical outlook on mining subsidence research in China[J]. China Mining Magazine,2024,33(3):86-99. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 杨永杰,陈绍杰,张兴民,等. 煤矿采场覆岩破坏的微地震监测预报研究[J]. 岩土力学,2007,28(7):1407-1410.YANG Y J,CHEN S J,ZHANG X M,et al. Forecasting study on fracturing of overburden strata of coal face by microseism monitoring technology[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2007,28(7):1407-1410. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] LI Z L,HE X Q,DOU L M,et al. Rockburst occurrences and microseismicity in a longwall panel experiencing frequent rockbursts[J]. Geosciences Journal,2018,22(4):623-639. doi: 10.1007/s12303-017-0076-7 [8] GHOSH G K,SIVAKUMAR C. Application of underground microseismic monitoring for ground failure and secure longwall coal mining operation:A case study in an Indian mine[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics,2018,150:21-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2018.01.004 [9] SALVONI M,DIGHT P M. Rock damage assessment in a large unstable slope from microseismic monitoring-MMG Century mine (Queensland,Australia) case study[J]. Engineering Geology,2016,210:45-56. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.06.002 [10] 董陇军,闫先航,裴重伟,等. 岩体多源声学设备在地压与顶板灾害监测防控中的应用[J]. 金属矿山,2023(5):185-194.DONG L J,YAN X H,PEI Z W,et al. Case study of rock mass multi-source acoustic equipment in monitoring and prevention of ground pressure and roof disaster[J]. Metal Mine,2023(5):185-194. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 刘威,朱鸿鹄,王涛,等. 基于分布式声波传感的大地探测技术研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):29-41.LIU W,ZHU H H,WANG T,et al. Research progress of earth exploration technologies based on distributed acoustic sensing[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):29-41. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] LIOR I,SLADEN A,RIVET D,et al. On the detection capabilities of underwater distributed acoustic sensing[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth),2021,126(3):e2020JB020925. doi: 10.1029/2020JB020925 [13] TAWEESINTANANON K,LANDRø M,POTTER J R,et al. Distributed acoustic sensing of ocean-bottom seismo-acoustics and distant storms:A case study from Svalbard,Norway[J]. Geophysics,2023,88(3):B135-B150. [14] LINDSEY N J,DAWE T C,AJO-FRANKLIN J B. Illuminating seafloor faults and ocean dynamics with dark fiber distributed acoustic sensing[J]. Science,2019,366:1103-1107. doi: 10.1126/science.aay5881 [15] BOOTH A D,CHRISTOFFERSEN P,SCHOONMAN C,et al. Distributed acoustic sensing of seismic properties in a borehole drilled on a fast-flowing Greenlandic outlet glacier[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2020,47(13):e2020GL088148. doi: 10.1029/2020GL088148 [16] WALTER F,GRÄFF D,LINDNER F,et al. Distributed acoustic sensing of microseismic sources and wave propagation in glaciated terrain[J]. Nature Communications,2020,11:2436. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15824-6 [17] HUDSON T S,BAIRD A F,KENDALL J M,et al. Distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) for natural microseismicity studies:A case study from Antarctica[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth),2021,126(7):e2020JB021493. doi: 10.1029/2020JB021493 [18] WANG B S,ZENG X F,SONG Z H,et al. Seismic observation and subsurface imaging using an urban telecommunication optic-fiber cable[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2021,66(20):2590-2595. doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-1427 [19] YANG Y,ATTERHOLT J W,SHEN Z C,et al. Sub-kilometer correlation between near-surface structure and ground motion measured with distributed acoustic sensing[J]. Geophysical Research Letters,2022,49(1):e2021GL096503. doi: 10.1029/2021GL096503 [20] SHAO J,WANG Y B,CHEN L. Near-surface characterization using high-speed train seismic data recorded by a distributed acoustic sensing array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2022,60:5912911. [21] 施斌,王宝善,张诚成,等. 川西甲基卡锂矿 3211 m科学深钻多物理量分布式光纤观测[J]. 科学通报,2022,67(23):2719-2726. doi: 10.1360/TB-2021-1380SHI B,WANG B S,ZHANG C C,et al. Multi-physical distributed fiber optic observation in a3211 -m-deep scientific borehole at Jiajika lithium mine,western Sichuan[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2022,67(23):2719-2726. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/TB-2021-1380[22] 朱鸿鹄. 工程地质界面:从多元表征到演化机理[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):1-19.ZHU H H. Engineering geological interface:From multivariate characterization to evolution mechanism[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):1-19. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 蔡海文,叶青,王照勇,等. 分布式光纤声波传感技术研究进展[J]. 应用科学学报,2018,36(1):41-58.CAI H W,YE Q,WANG Z Y,et al. Progress in research of distributed fiber acoustic sensing techniques[J]. Journal of Applied Sciences,2018,36(1):41-58. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] KARRENBACH M,COLE S,RIDGE A,et al. Fiber-optic distributed acoustic sensing of microseismicity,strain and temperature during hydraulic fracturing[J]. Geophysics,2018,84(1):D11-D23. [25] DALEY T M,MILLER D E,DODDS K,et al. Field testing of modular borehole monitoring with simultaneous distributed acoustic sensing and geophone vertical seismic profiles at Citronelle,Alabama[J]. Geophysical Prospecting,2016,64(5):1318-1334. doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.12324 [26] WANG J,ZHU H H,MEI G X,et al. Field monitoring of bearing capacity efficiency of permeable pipe pile in clayey soil:A comparative study[J]. Measurement,2021,186:110151. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110151 [27] ANIKIEV D,BIRNIE C,BIN WAHEED U,et al. Machine learning in microseismic monitoring[J]. Earth-Science Reviews,2023,239:104371. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2023.104371 [28] ALLEN R V. Automatic earthquake recognition and timing from single traces[J]. The Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America,1978,68(5):1521-1532. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0680051521 [29] COOLEY J W,TUKEY J W. An algorithm for the machine calculation of complex Fourier series[J]. Mathematics of Computation,1965,19:297-301. doi: 10.1090/S0025-5718-1965-0178586-1 [30] KRAMER M A. Nonlinear principal component analysis using autoassociative neural networks[J]. AIChE Journal,1991,37(2):233-243. doi: 10.1002/aic.690370209 [31] OUILLON G,SORNETTE D. Segmentation of fault networks determined from spatial clustering of earthquakes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth),2011,116(B2):B02306. [32] REYNOLDS D. Gaussian mixture models[M]//Anon. Encyclopedia of biometrics. Boston,MA:Springer US,2015:827-832. [33] SCHOBER P,BOER C,SCHWARTE L A. Correlation coefficients:Appropriate use and interpretation[J]. Anesthesia and Analgesia,2018,126(5):1763-1768. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002864 [34] ROSS Z E,MEIER M A,HAUKSSON E. P wave arrival picking and first-motion polarity determination with deep learning[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth),2018,123(6):5120-5129. doi: 10.1029/2017JB015251 [35] WILKINS A H,STRANGE A,DUAN Y,et al. Identifying microseismic events in a mining scenario using a convolutional neural network[J]. Computers & Geosciences,2020,137:104418. [36] 赵洪宝,刘瑞,刘一洪,等. 基于深度学习方法的矿山微震信号分类识别研究[J]. 矿业科学学报,2022,7(2):166-174.ZHAO H B,LIU R,LIU Y H,et al. Research on classification and identification of mine microseismic signals based on deep learning method[J]. Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2022,7(2):166-174. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 朱鸿鹄,施斌,严珺凡,等. 基于分布式光纤应变感测的边坡模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2013,32(4):821-828.ZHU H H,SHI B,YAN J F,et al. Physical model testing of slope stability based on distributed fiber-optic strain sensing technology[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2013,32(4):821-828. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 程刚,施斌,朱鸿鹄,等. 光纤和砂土界面耦合性能的分布式感测试验研究[J]. 高校地质学报,2019,25(4):487-494.CHENG G,SHI B,ZHU H H,et al. Experimental study on coupling performance of fiber and sand interface based on distributed sensing[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2019,25(4):487-494. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 窦林名,曹晋荣,曹安业,等. 煤矿矿震类型及震动波传播规律研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术,2021,49(6):23-31.DOU L M,CAO J R,CAO A Y,et al. Research on types of coal mine tremor and propagation law of shock waves[J]. Coal Science and Technology,2021,49(6):23-31. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 曹安业,窦林名,秦玉红,等. 高应力区微震监测信号特征分析[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2007,24(2):146-149.CAO A Y,DOU L M,QIN Y H,et al. Characteristic of microseismic monitoring signal in high stressed zone[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2007,24(2):146-149. (in Chinese with English abstract -





 下载:
下载: