Spatial-temporal distribution characteristics and driving factors of nitrogen in groundwater of river-lake-groundwater interaction zone along middle reaches of the Yangtze River
-
摘要:
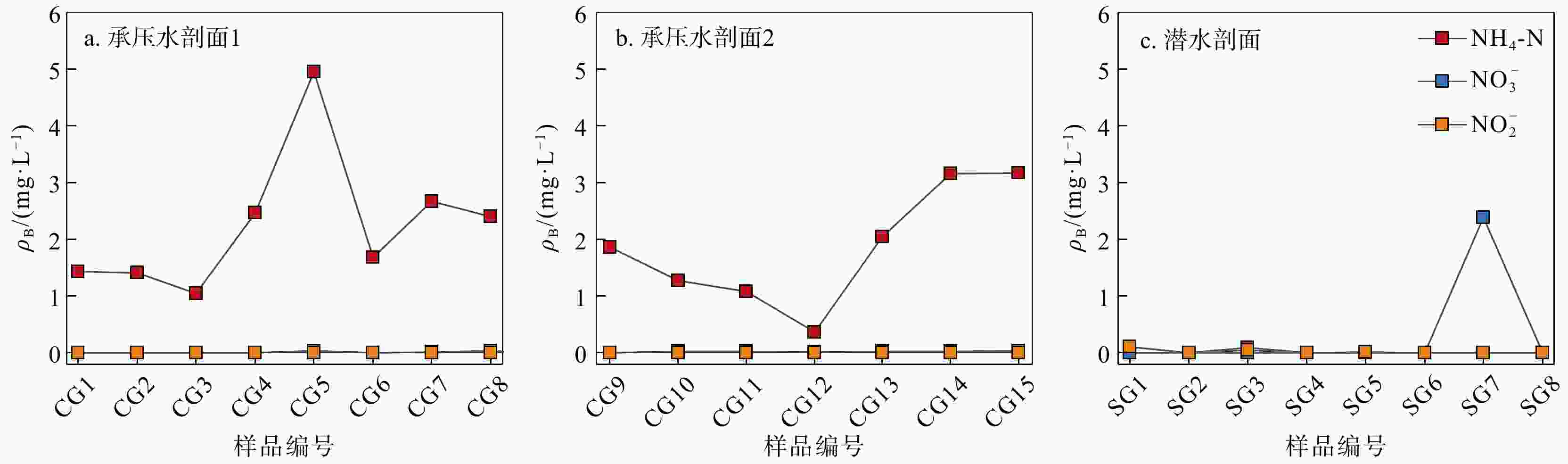
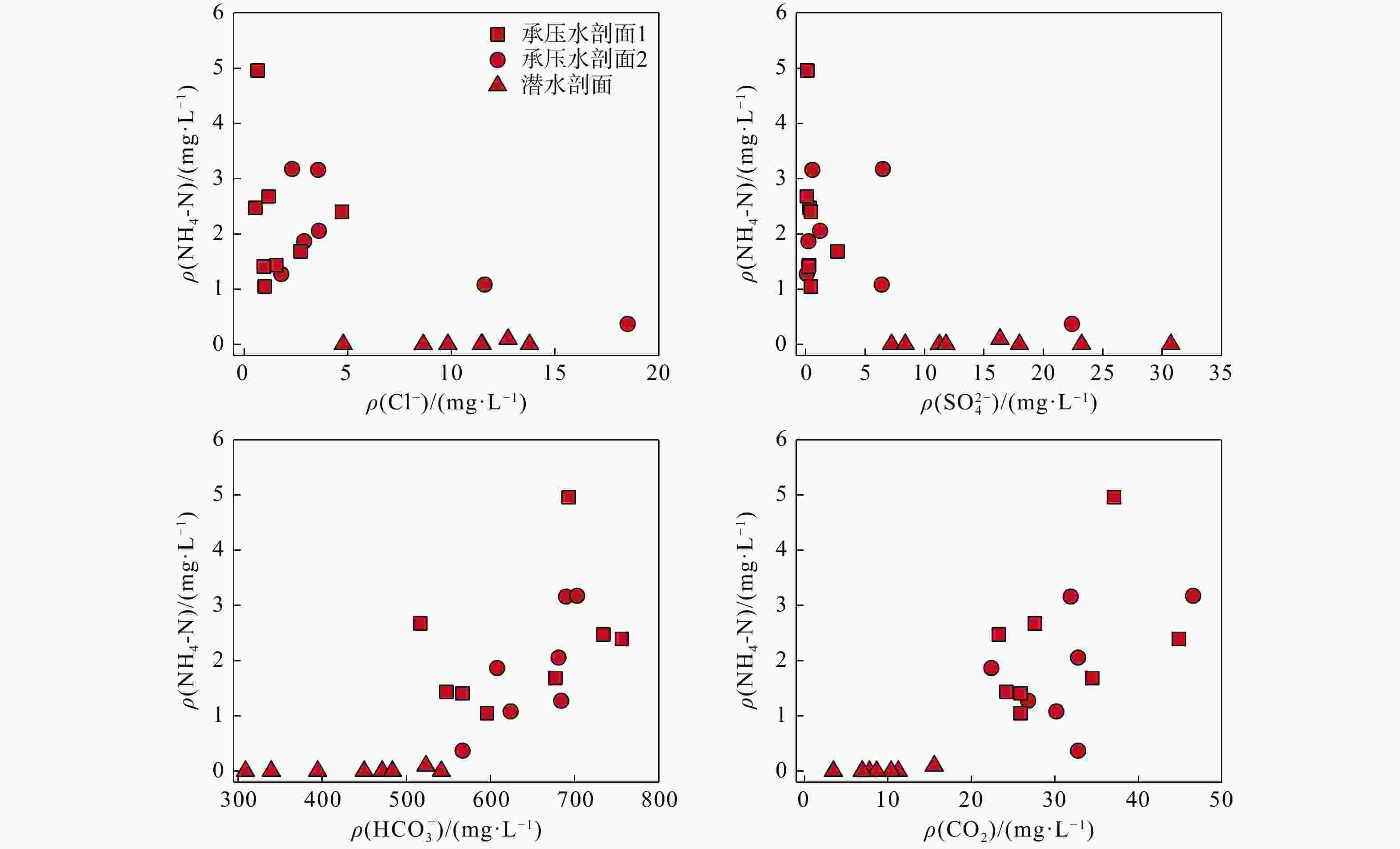
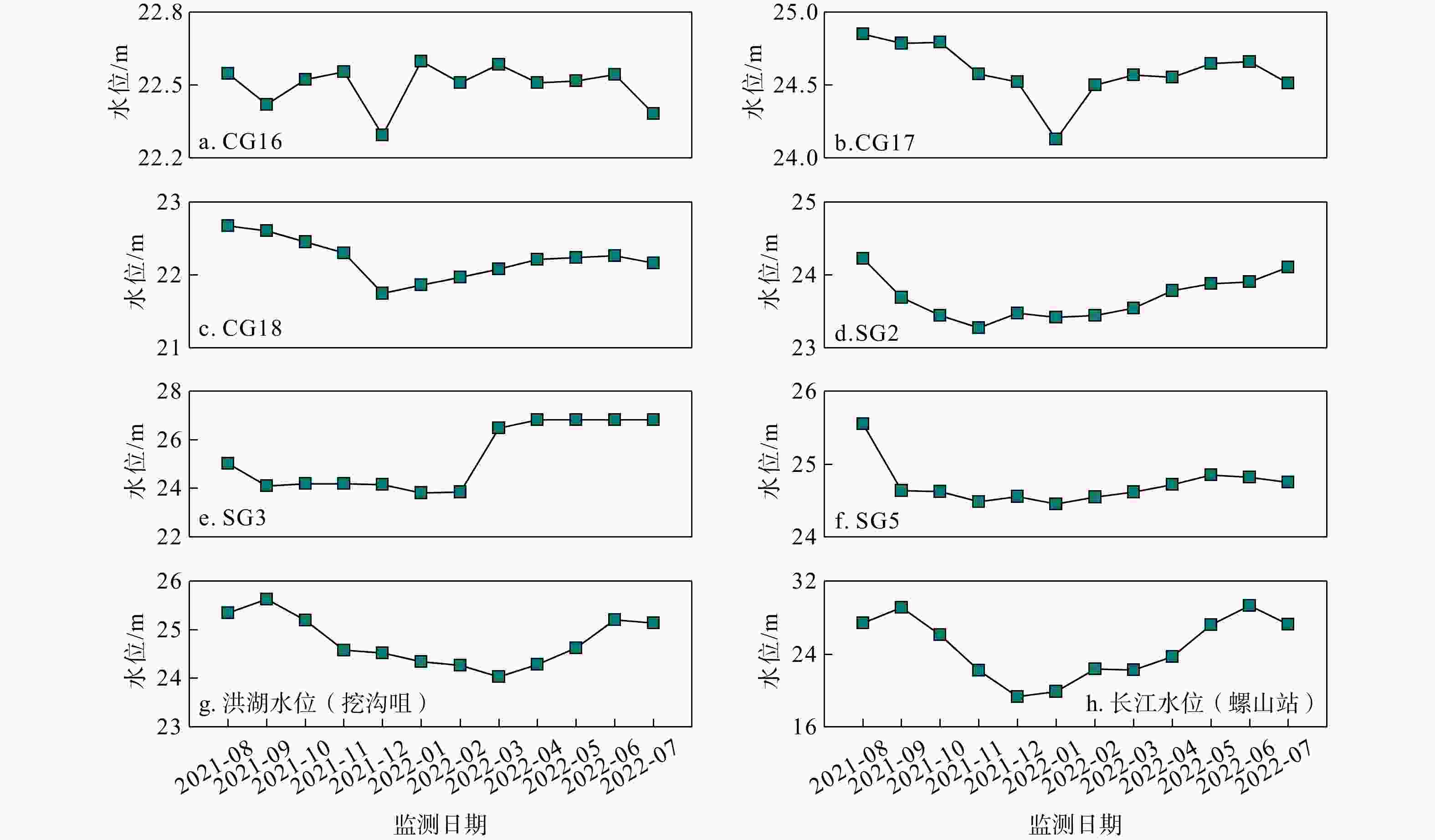
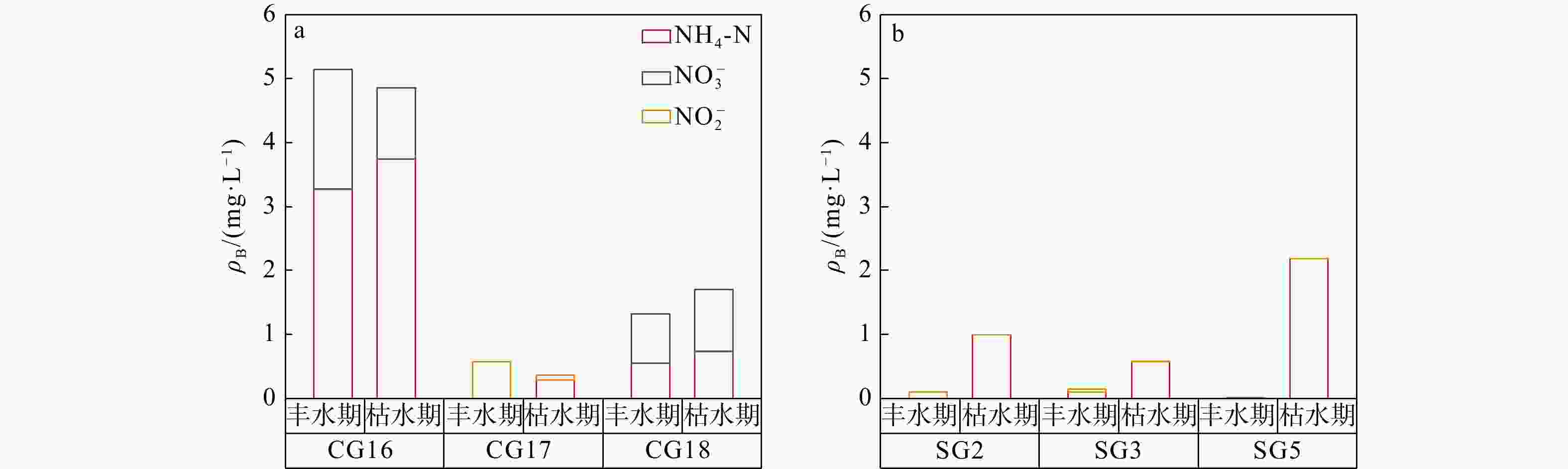
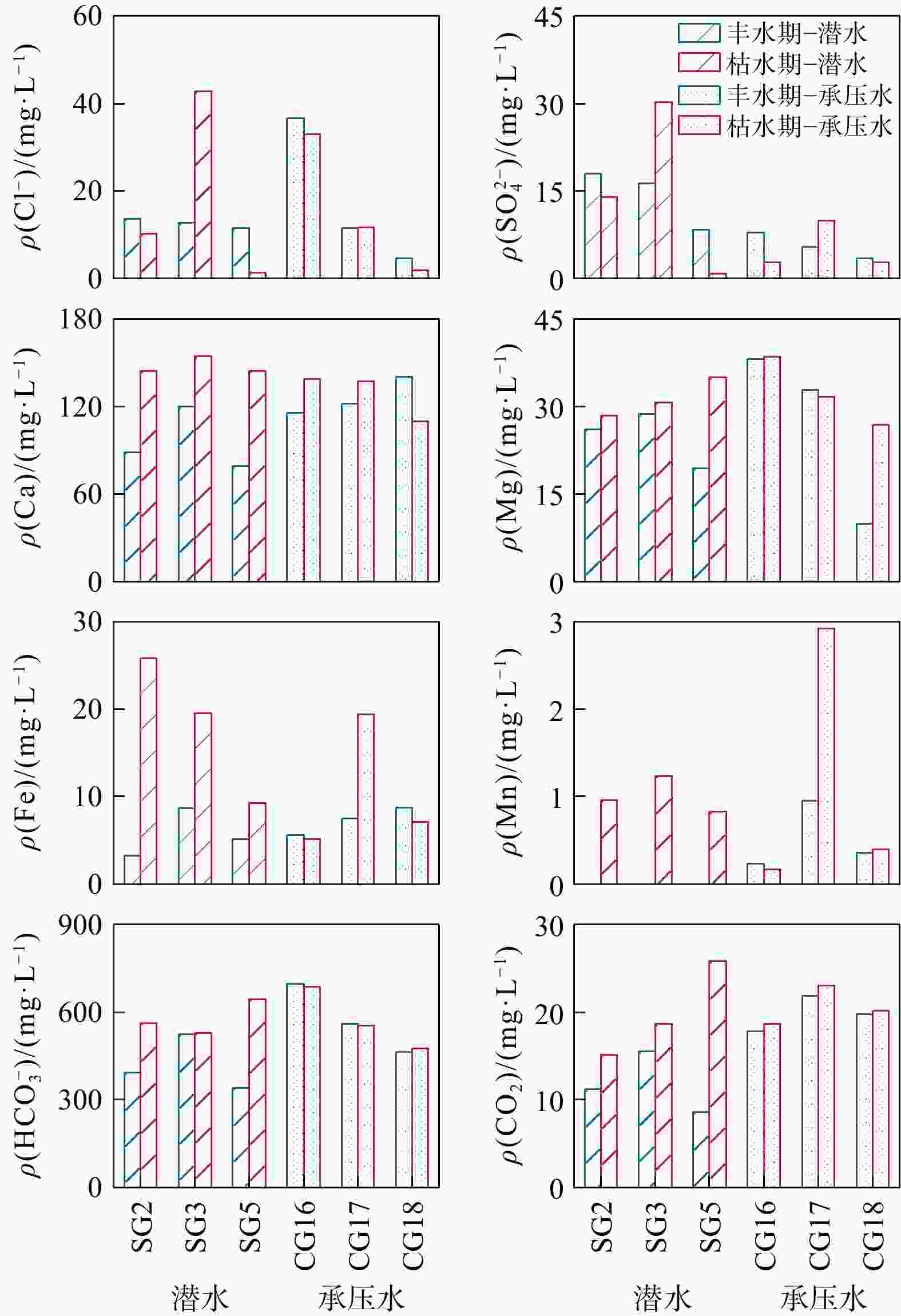
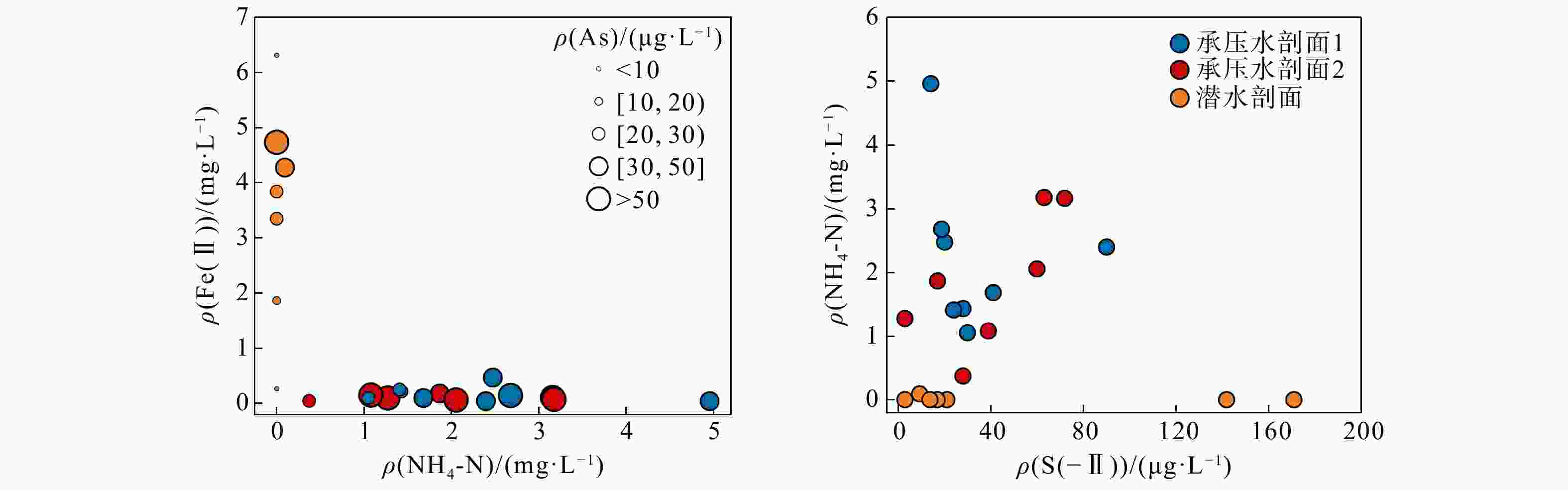
河湖−地下水交互带的复杂结构驱动着营养盐的迁移转化与归宿,探究氮素在地下水中的时空分布特征及其控制因素对于水质和生态系统的保护具有重要指导意义。以长江中游河湖−地下水交互带为研究对象,分别于丰水期和枯水期采集2个承压水剖面以及1个潜水剖面的地下水样品,进行水文地球化学分析,并运用随机森林模型探讨了氮素富集的控制因素。结果表明:地下水中氮素的主要存在形态为铵氮(NH4-N),丰水期承压水NH4-N质量浓度(0.37~4.96 mg/L, 均值2.07 mg/L)显著高于潜水(0~0.096 mg/L, 均值0.012 mg/L)。其低浓度Cl−/SO42−以及高浓度CO2/HCO3−指示NH4-N的富集与天然成因条件下含氮有机质矿化过程密切相关。相比承压水,潜水枯水期NH4-N质量浓度(均值1.25 mg/L)显著高于丰水期(均值0.032 mg/L),呈显著的季节性变化,且其Fe/Mn比值也相对较高。结合水位波动情况,潜水受人为活动影响较大,该含水层中NH4-N富集后可进一步发生厌氧铁铵氧化过程。研究成果丰富了河湖−地下水交互带氮素赋存规律的认识,并可为氮循环相关的生物地球化学过程提供理论基础。
Abstract:Objective The complex structure of river-lake-groundwater interaction zone governs the migration and transformation and the fate of nutrients. Investigating the spatial-temporal distribution characteristic and controlling factors of nitrogen in groundwater holds significant implications for water quality and ecosystem protection.
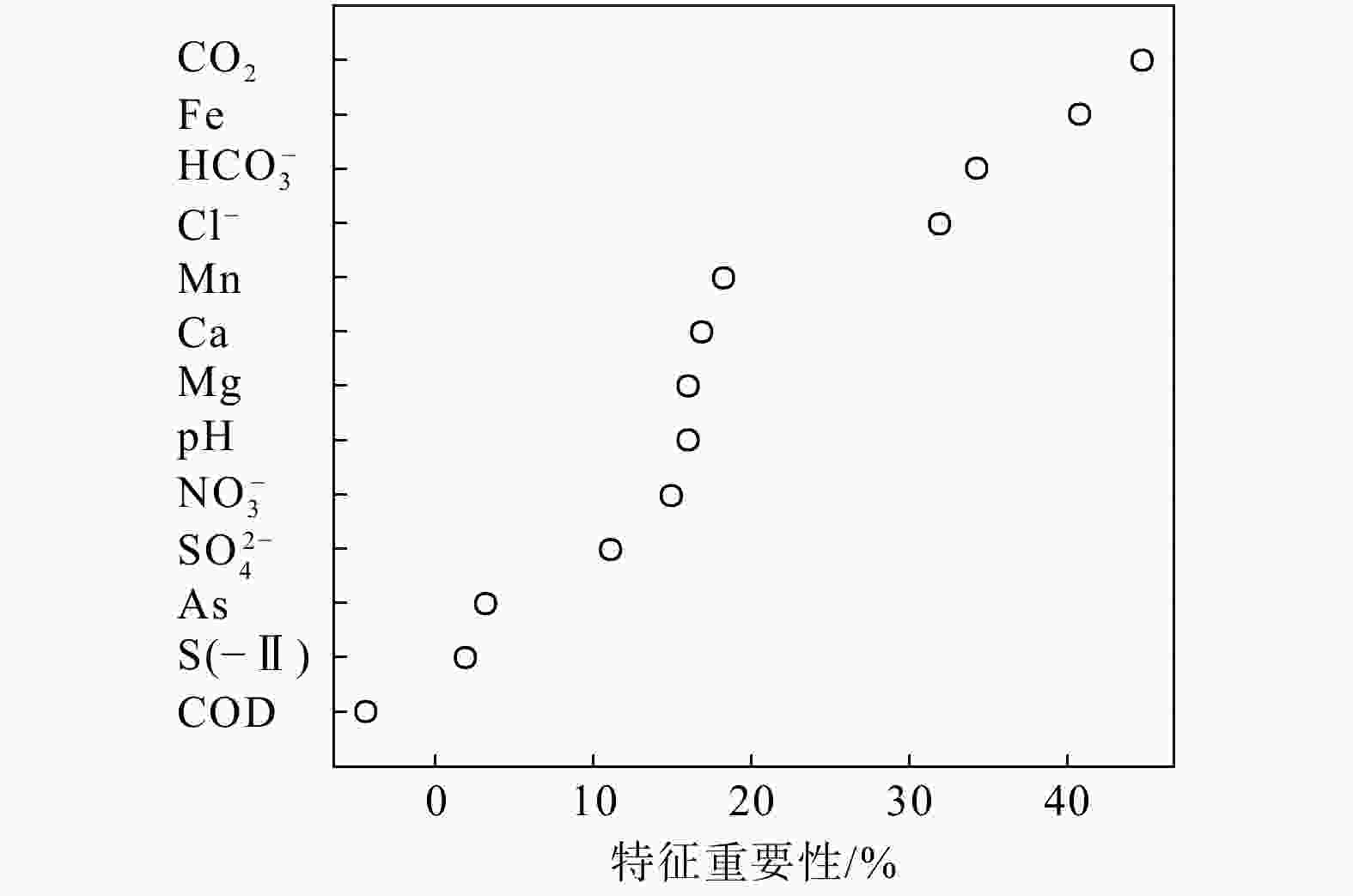
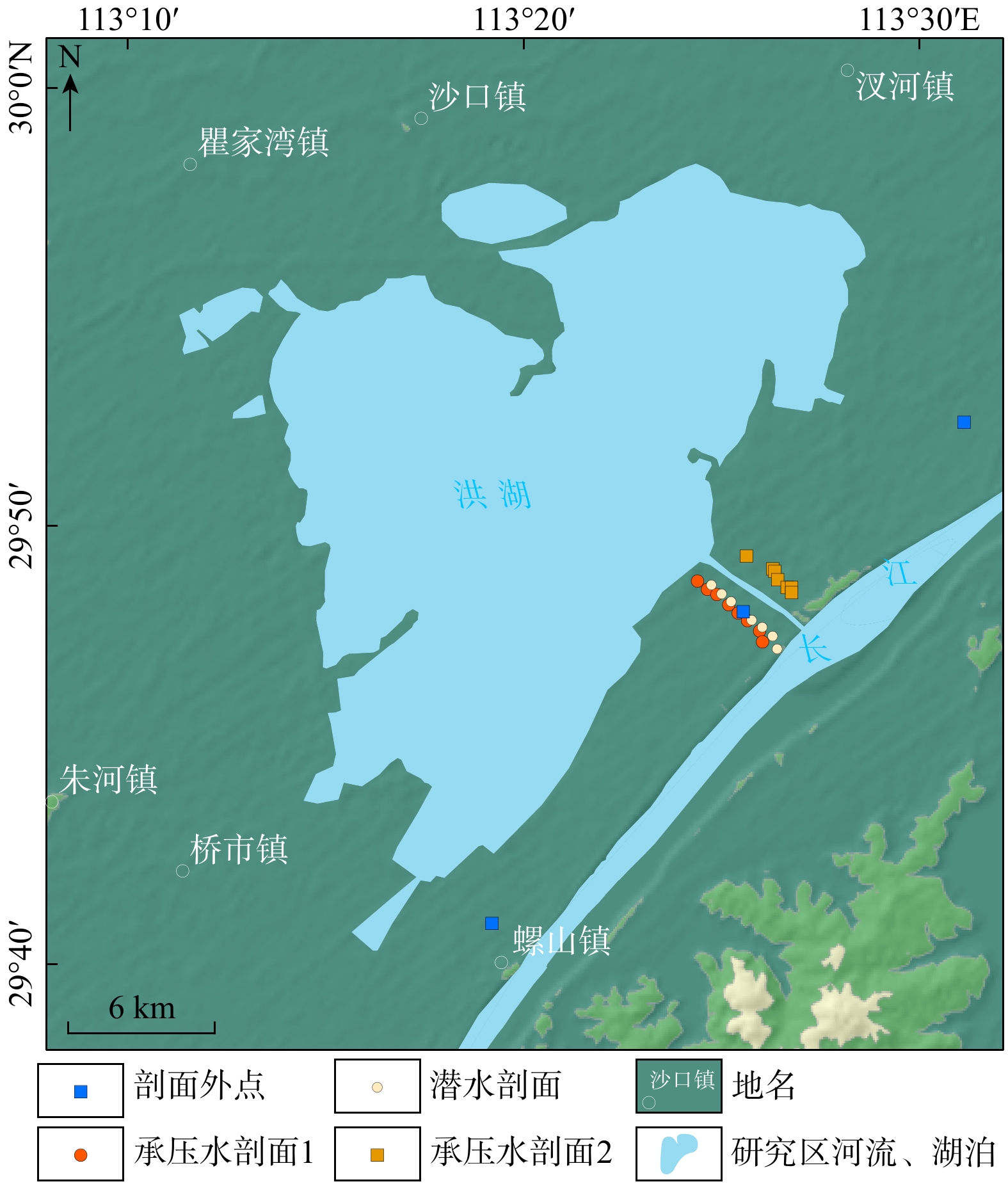
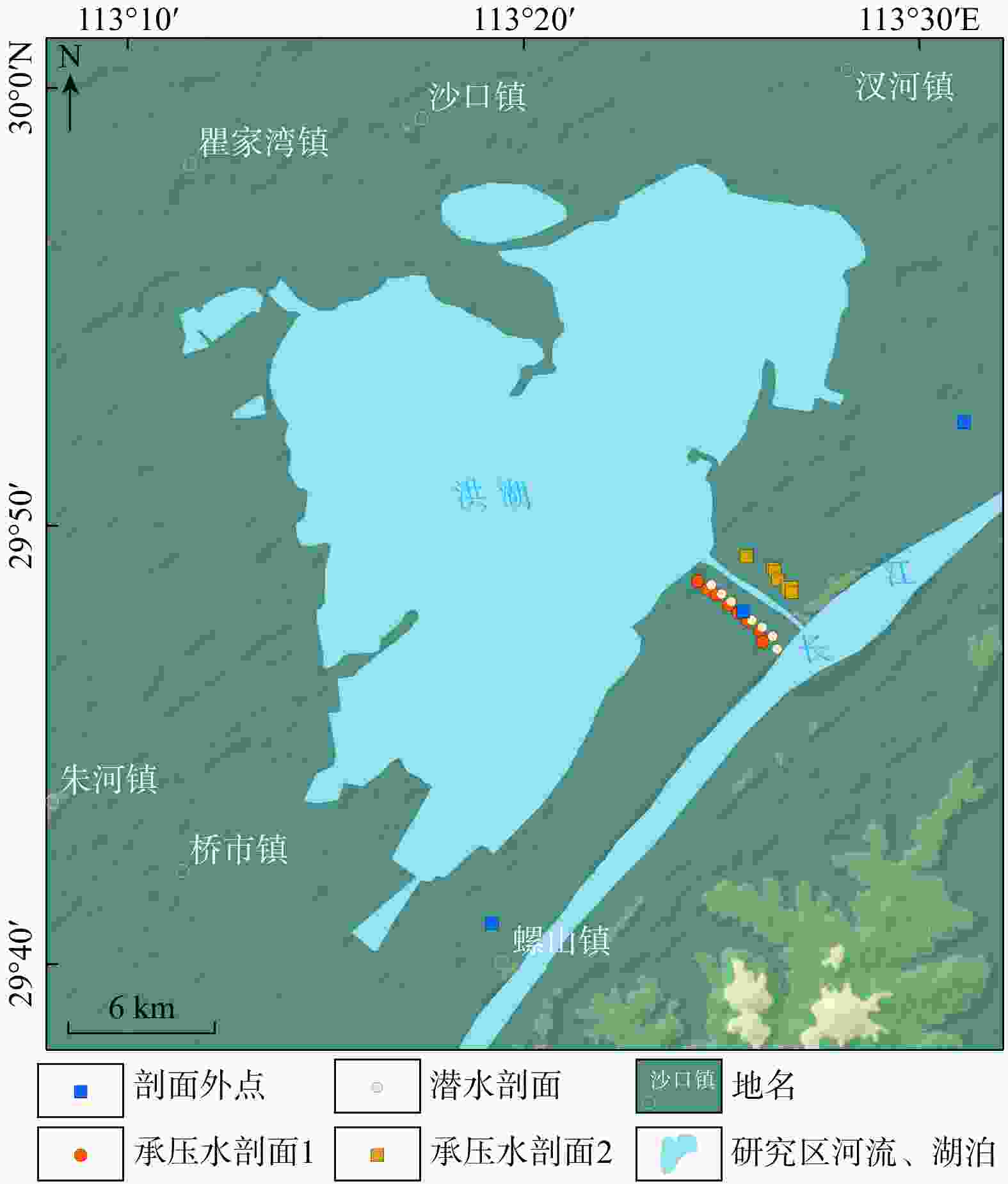
Methods This study focus on the river-lake-groundwater interaction zone along the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Groundwater samples were collected from two confined aquifer profile and one phreatic aquifer profile during both monsoon season and non-monsoon season. Hydrogeochemical analysis was conducted, and the controlling factors of nitrogen enrichment were identified using random forest regression.
Results The results indicate that the main form of nitrogen in groundwater is ammonium (NH4-N). The content of NH4-N in confined groundwater during monsoon season (0.37−4.96 mg/L, average 2.07 mg/L) was significantly higher than that in the pore phreatic water (0−0.096 mg/L, average 0.012 mg/L).Low concentration of Cl− / SO42− and high concentration of CO2 / HCO3− indicate that NH4-N enrichment is closely related to the mineralization of nitrogen-bearing organic matter under natural condition. In contrast, in pore phreatic groundwater during the non-monsoon season, the NH4-N concentration (average 1.25 mg/L) was significantly higher than during monsoon season(average 0.032 mg/L), displaying prominent seasonal variation. The concentration of Fe / Mn was also relatively high in this aquifer during the non-monsoon season. Combined with water-level fluctuation data, the pore phreatic water is significantly influenced by human activities. Following NH4-N enrichment within the aquifer, feammox can occur.
Conclusion This study enhances understanding of the occurrence patterns of nitrogen within river-lake-groundwater interaction zone and provides a theoretical basis for studying biogeochemical processes associated with the nitrogen cycle.
-
表 1 丰水期和枯水期承压水以及潜水中COD质量浓度
Table 1. Change of the concentration of COD in confined groundwater and phreatic water during monsoon season and non-monsoon season
ρB/(mg·L−1) 采样期 承压水 潜水 CG16 CG17 CG18 SG2 SG3 SG5 枯水期 2.22 3.04 0.98 5.18 5.92 3.29 丰水期 2.35 2.80 1.13 3.76 3.13 1.76 -
[1] HAVRIL T, TÓTH Á, MOLSON J W, et al. Impacts of predicted climate change on groundwater flow systems: Can wetlands disappear due to recharge reduction?[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 563: 1169-1180. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.09.020 [2] REZANEZHAD F, COUTURE R M, KOVAC R, et al. Water table fluctuations and soil biogeochemistry: An experimental approach using an automated soil column system[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 509: 245-256. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.11.036 [3] 张安广, 梁莹, 马瑞. 地表水−地下水相互作用下NH4-N的吸附/解吸行为及其对N迁移转化的影响[J]. 地球科学, 2024, 49(10): 3761-3772.ZHANG A G, LIANG Y, MA R. Adsorption/desorption behavior of NH4-N under surface water-groundwater interaction and its impact on N migration and transformation[J]. Earth Science, 2024, 49(10): 3761-3772. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] YANG W H, WEBER K A, SILVER W L. Nitrogen loss from soil through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron reduction[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5(8): 538-541. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1530 [5] XIONG Y J, DU Y, DENG Y M, et al. Feammox in alluvial-lacustrine aquifer system: Nitrogen/iron isotopic and biogeochemical evidences[J]. Water Research, 2022, 222: 118867. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118867 [6] RAKHIMBEKOVA S, O'CARROLL D M, OLDFIELD L E, et al. Spatiotemporal controls on septic system derived nutrients in a nearshore aquifer and their discharge to a large lake[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 752: 141262. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141262 [7] 冷智超, 杜尧, 陶艳秋, 等. 长江中游沿岸地下水中铵氮与磷的共存规律及其控制因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 300-308.LENG Z C, DU Y, TAO Y Q, et al. Coexistence and controlling factors of ammonium and phosphorus in groundwater along the middle reaches of the Yangtze River[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 300-308. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] YU L, ROZEMEIJER J C, BROERS H P, et al. Drivers of nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in a groundwater-fed urban catchment revealed by high-frequency monitoring[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2021, 25(1): 69-87. doi: 10.5194/hess-25-69-2021 [9] DU Y, DENG Y M, LIU Z H, et al. Novel insights into dissolved organic matter processing pathways in a coastal confined aquifer system with the highest known concentration of geogenic ammonium[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 55(21): 14676-14688. [10] JELLALI S, DIAMANTOPOULOS E, KALLALI H, et al. Dynamic sorption of ammonium by sandy soil in fixed bed columns: Evaluation of equilibrium and non-equilibrium transport processes[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2010, 91(4): 897-905. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2009.11.006 [11] JIANG Q H, JIN G Q, TANG H W, et al. Ammonium (NH4+) transport processes in the riverbank under varying hydrologic conditions[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 826: 154097. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154097 [12] YAN A L, GUO X Y, HU D H, et al. Reactive transport of NH4+ in the hyporheic zone from the ground water to the surface water[J]. Water, 2022, 14(8): 1237. doi: 10.3390/w14081237 [13] RÜTTING T, BOECKX P, MÜLLER C, et al. Assessment of the importance of dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium for the terrestrial nitrogen cycle[J]. Biogeosciences, 2011, 8(7): 1779-1791. doi: 10.5194/bg-8-1779-2011 [14] KRAFT B, TEGETMEYER H E, SHARMA R, et al. The environmental controls that govern the end product of bacterial nitrate respiration[J]. Science, 2014, 345: 676-679. doi: 10.1126/science.1254070 [15] 杜尧. 江汉平原地表水−地下水相互作用及其对铵氮迁移转化的影响[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2017.DU Y. Surface water-groundwater interaction and its effect on ammonium transport and fate in Jianghan Plain, central China[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] LUTZ S R, TRAUTH N, MUSOLFF A, et al. How important is denitrification in riparian zones? combining end-member mixing and isotope modeling to quantify nitrate removal from riparian groundwater[J]. Water Resources Research, 2020, 56(1): e2019WR025528. doi: 10.1029/2019WR025528 [17] ZHU G B, WANG S Y, WANG W D, et al. Hotspots of anaerobic ammonium oxidation at land-freshwater interfaces[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2013, 6(2): 103-107. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1683 [18] ZHAO Y Q, XIA Y Q, KANA T M, et al. Seasonal variation and controlling factors of anaerobic ammonium oxidation in freshwater river sediments in the Taihu Lake region of China[J]. Chemosphere, 2013, 93(9): 2124-2131. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.063 [19] 郭华明, 高志鹏, 修伟. 地下水氮循环与砷迁移转化耦合的研究现状和趋势[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2022, 49(3): 153-163.GUO H M, GAO Z P, XIU W. Research status and trend of coupling between nitrogen cycle and arsenic migration and transformation in groundwater systems[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(3): 153-163. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] BUSS S R, HERBERT A W, MORGAN P, et al. A review of ammonium attenuation in soil and groundwater[J]. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology, 2004, 37(4): 347-359. doi: 10.1144/1470-9236/04-005 [21] GUAN Q S, CAO W Z, WANG M, et al. Nitrogen loss through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled with iron reduction in a mangrove wetland[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2018, 69(4): 732-741. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12552 [22] MOSLEY O E, GIOS E, CLOSE M, et al. Nitrogen cycling and microbial cooperation in the terrestrial subsurface[J]. The ISME Journal, 2022, 16(11): 2561-2573. doi: 10.1038/s41396-022-01300-0 [23] 朱鹏光, 甘义群, 赖咏毅, 等. 海南东寨港红树林湿地沉积物氮形态空间分布特征及影响因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 369-377.ZHU P G, GAN Y Q, LAI Y Y, et al. Spatial distribution and controlling factors of sediment nitrogen forms in the mangrove wetland at Dongzhai Port, Hainan Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 369-377. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] DU Y, DENG Y M, LI Y P, et al. Paleo-geomorphology determines spatial variability of geogenic ammonium concentration in quaternary aquifers[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2023, 57(14): 5726-5738. [25] SHEN S, LUO K W, MA T, et al. Nitrogen burial characteristics of Quaternary sediments and its controls on high ammonium groundwater in the Central Yangtze River Basin[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 842: 156659. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.156659 [26] SHEN S, MA T, DU Y, et al. Contrastive mechanisms of groundwater ammonium enrichment in different hydrogeologic settings[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 875: 162542. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.162542 [27] 罗可文. 天鹅洲湿地区地下水中铵氮源−汇的动态变化机制[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2023.LUO K W. Dynamic change mechanism of NH4+ source-sink in the groundwater of Tianezhou wetland area[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 熊耀劲. 典型冲湖积平原地下水系统中厌氧铁铵氧化过程的识别与控制因素研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2023.XIONG Y J. Identification and controlling factors of feammox in groundwater system of typical alluvial-lacustrine plain [D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 中华人民共和国自然资源部. 地下水质分析方法第47部分: 游离二氧化碳的测定滴定法: DZ/T0064.47-2021[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021.Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. Part 47 of the analytical methods for groundwater quality-titration method for determination of free carbon dioxide: DZ/T0064.47-2021[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2021. (in Chinese) [30] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 地下水质量标准: GB/T14848-2017[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2017.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, National Standardization Administration. Standard for groundwater quality: GB/T14848-2017[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2017. (in Chinese) [31] MCARTHUR J M, SIKDAR P K, HOQUE M A, et al. Waste-water impacts on groundwater: Cl/Br ratios and implications for arsenic pollution of groundwater in the Bengal Basin and Red River Basin, Vietnam[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 437: 390-402. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.07.068 [32] 吴海燕, 傅世锋, 蔡晓琼, 等. 东山岛地下水“三氮” 空间分布特征[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(9): 3203-3211.WU H Y, FU S F, CAI X Q, et al. Spatial variation of ammonia-N, nitrate-N and nitrite-N in groundwater of Dongshan Island[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36(9): 3203-3211. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 黄艳雯, 杜尧, 徐宇, 等. 洞庭湖平原西部地区浅层承压水中铵氮的来源与富集机理[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 165-174.HUANG Y W, DU Y, XU Y, et al. Source and enrichment mechanism of ammonium in shallow confined aquifer in the west of Dongting Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 165-174. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 沈帅, 马腾, 杜尧, 等. 江汉平原东部浅层地下水氮的空间分布特征[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(2): 47-56.SHEN S, MA T, DU Y, et al. The spatial distribution characteristic and genesis of nitrogen of shallow groundwater in the east of Jianghan Plain[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(2): 47-56. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] DU Y, MA T, DENG Y M, et al. Sources and fate of high levels of ammonium in surface water and shallow groundwater of the Jianghan Plain, central China[J]. Environmental Science (Processes & Impacts), 2017, 19(2): 161-172. [36] MENG L, ZUO R, BRUSSEAU M L, et al. Groundwater pollution containing ammonium, iron and manganese in a riverbank filtration system: Effects of dynamic geochemical conditions and microbial responses[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2020, 34(22): 4175-4189. doi: 10.1002/hyp.13856 [37] CLINE L C, HUGGINS J A, HOBBIE S E, et al. Organic nitrogen addition suppresses fungal richness and alters community composition in temperate forest soils[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2018, 125: 222-230. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.07.008 [38] HUANG Y W, DU Y, MA T, et al. Dissolved organic matter characterization in high and low ammonium groundwater of Dongting Plain, central China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2021, 208: 111779. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111779 [39] DU Y, DENG Y M, MA T, et al. Enrichment of geogenic ammonium in Quaternary alluvial-lacustrine aquifer systems: Evidence from carbon isotopes and DOM characteristics[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2020, 54(10): 6104-6114. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c00131 [40] WANG H L, LI P, LIU X H, et al. An overlooked influence of reactive oxygen species on ammonia-oxidizing microbial communities in redox-fluctuating aquifers[J]. Water Research, 2023, 233: 119734. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2023.119734 [41] HAN L L, WANG H L, GE L H, et al. Transition of source/sink processes and fate of ammonium in groundwater along with redox gradients[J]. Water Research, 2023, 231: 119600. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2023.119600 [42] LIANG Y, MA R, WANG Y X, et al. Hydrogeological controls on ammonium enrichment in shallow groundwater in the central Yangtze River Basin[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 741: 140350. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140350 [43] 刘波, 李红梅, 石长柏, 等. 基于洪湖湿地生态水位控制的地下水位响应关系研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2021, 35(6): 827-833.LIU B, LI H M, SHI C B, et al. Study on response relationship of groundwater level based on ecological water level control of Honghu wetland[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2021, 35(6): 827-833. (in Chinese with English abstract [44] LIANG Y, MA R, NGHIEM A, et al. Sources of ammonium enriched in groundwater in the central Yangtze River Basin: Anthropogenic or geogenic?[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022, 306: 119463. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.119463 [45] ZHAI Y Z, HAN Y F, LU H, et al. Interactions between anthropogenic pollutants (biodegradable organic nitrogen and ammonia) and the primary hydrogeochemical component Mn in groundwater: Evidence from three polluted sites[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 808: 152162. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.152162 [46] 徐雨潇, 郑天亮, 高杰, 等. 江汉平原浅层含水层中土著硫酸盐还原菌对砷迁移释放的影响[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(2): 652-660.XU Y X, ZHENG T L, GAO J, et al. Effect of indigenous sulfate reducing bacteria on arsenic migration in shallow aquifer of Jianghan Plain[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(2): 652-660. (in Chinese with English abstract [47] ZHENG T L, DENG Y M, WANG Y X, et al. Microbial sulfate reduction facilitates seasonal variation of arsenic concentration in groundwater of Jianghan Plain, central China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 735: 139327. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139327 [48] 曹益, 李逸凡, 周传富, 等. 武汉蔡甸区浅层地下水氮污染来源识别及其迁移转化过程解析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(1): 262-273.CAO Y, LI Y F, ZHOU C F, et al. Sources, transport and transformation of nitrogen pollution in shalllow groundwater in Caidian District, Wuhan, China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(1): 262-273. (in Chinese with English abstract [49] 韩鹏, 甘义群, 杜尧, 等. 洪湖地下水排泄及其携带营养盐通量量化的方法学研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(1): 285-297.HAN P, GAN Y Q, DU Y, et al. A methodological study on the quantification of lacustrine groundwater discharge and nutrient fluxes to Honghu Lake[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(1): 285-297. (in Chinese with English abstract [50] DING B J, CHEN Z H, LI Z K, et al. Nitrogen loss through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to iron reduction from ecosystem habitats in the Taihu estuary region[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 662: 600-606. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.231 [51] HUANG F G, JIA S Y, LIU Y, et al. Reductive dissolution of ferrihydrite with the release of As(V) in the presence of dissolved S (-II)[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 286: 291-297. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.12.035 -




 下载:
下载: