An improved algorithm for intelligent landslide identification based on historical sample enhancement
-
摘要:
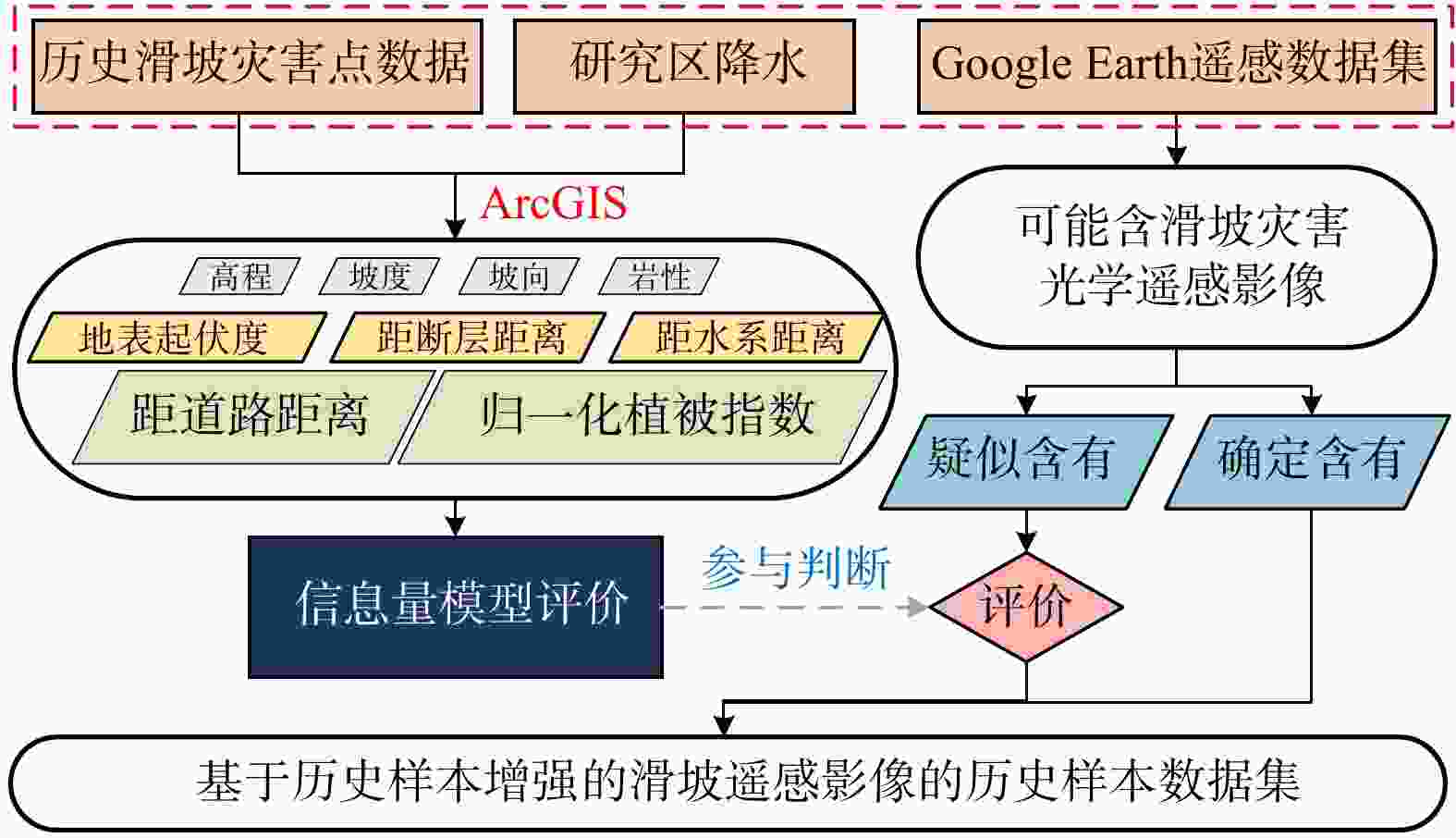
四川地形复杂,山区纵横交错处滑坡具有频发、突发、易发的特点,对人民财产和环境资源造成极大的危害,因此开展滑坡的识别检测,提取相关信息,对滑坡灾害预防监测及灾后预备有着重要的意义。针对传统目视解译方法经济成本高、耗时耗力、历史样本收集困难的问题,引入了高程、坡度、坡向、岩性、地表起伏程度、距断层距离、距水系距离、距道路距离、归一化植被指数9个滑坡影响因子,对历史滑坡的判识中引入影响因子的信息量值进行定量分析,增强了历史滑坡样本数据准确性;其次针对滑坡自动识别结果可能存在的定位不准确、分割边界模糊等问题,采用递归特征金字塔网络和
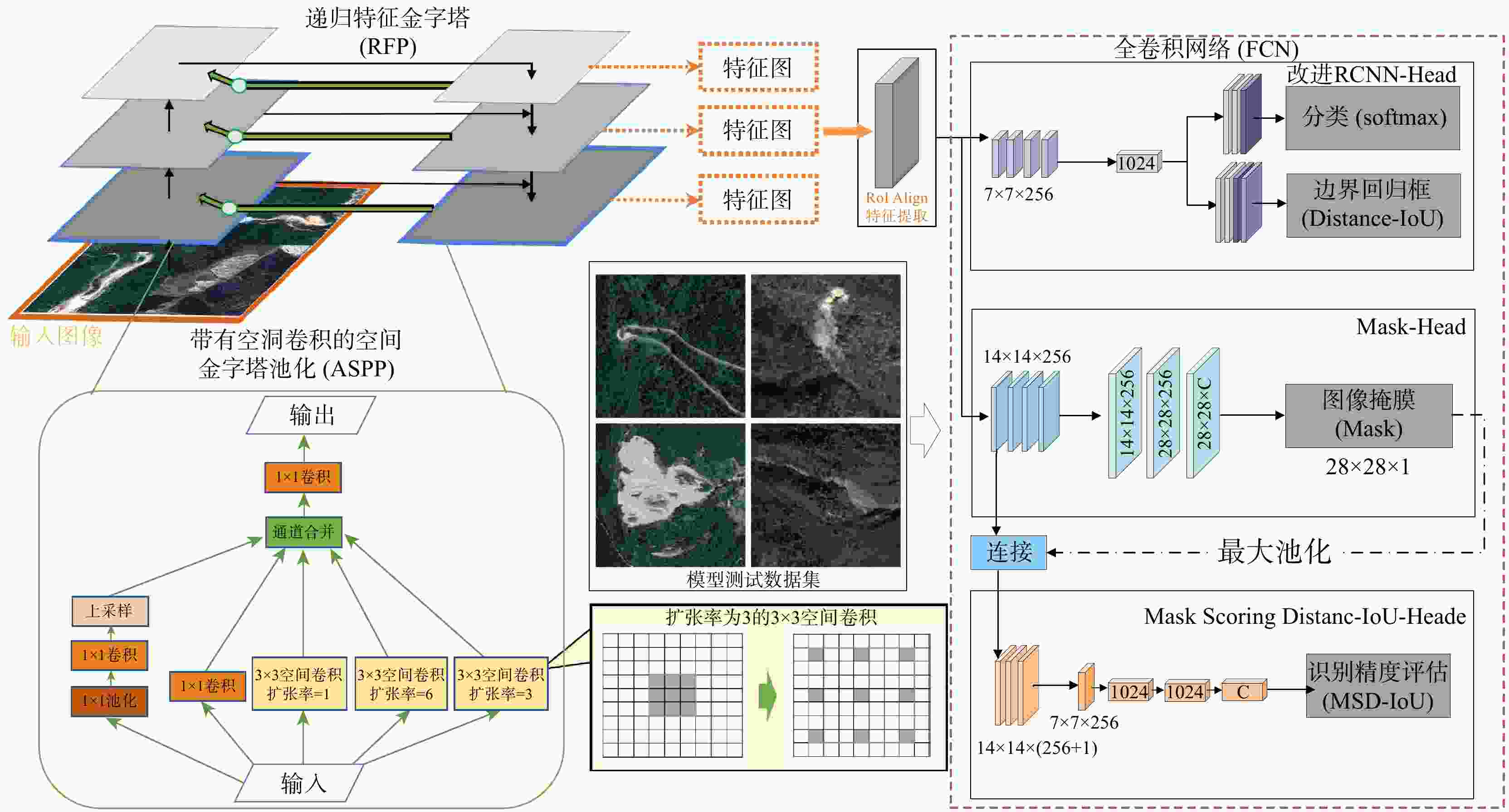
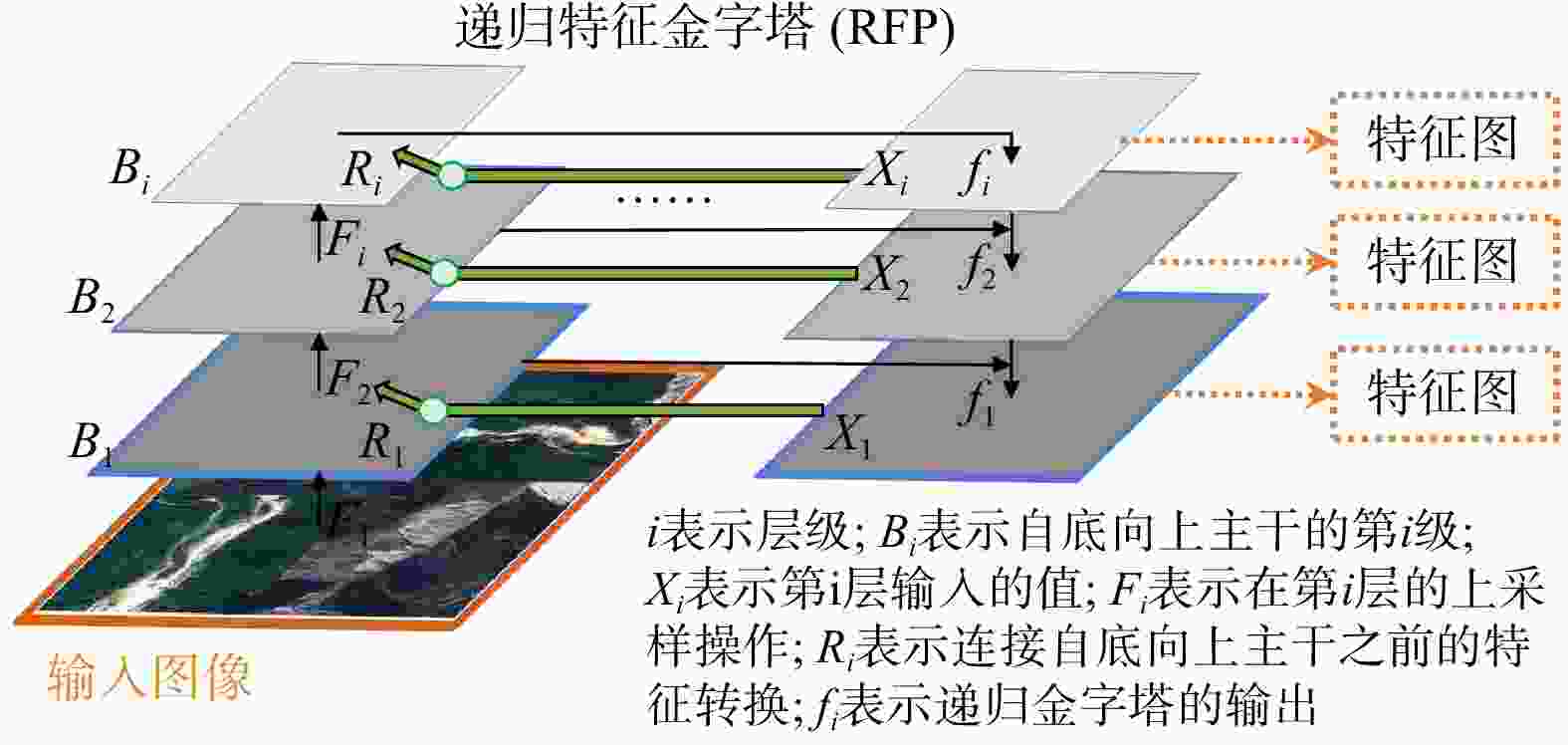
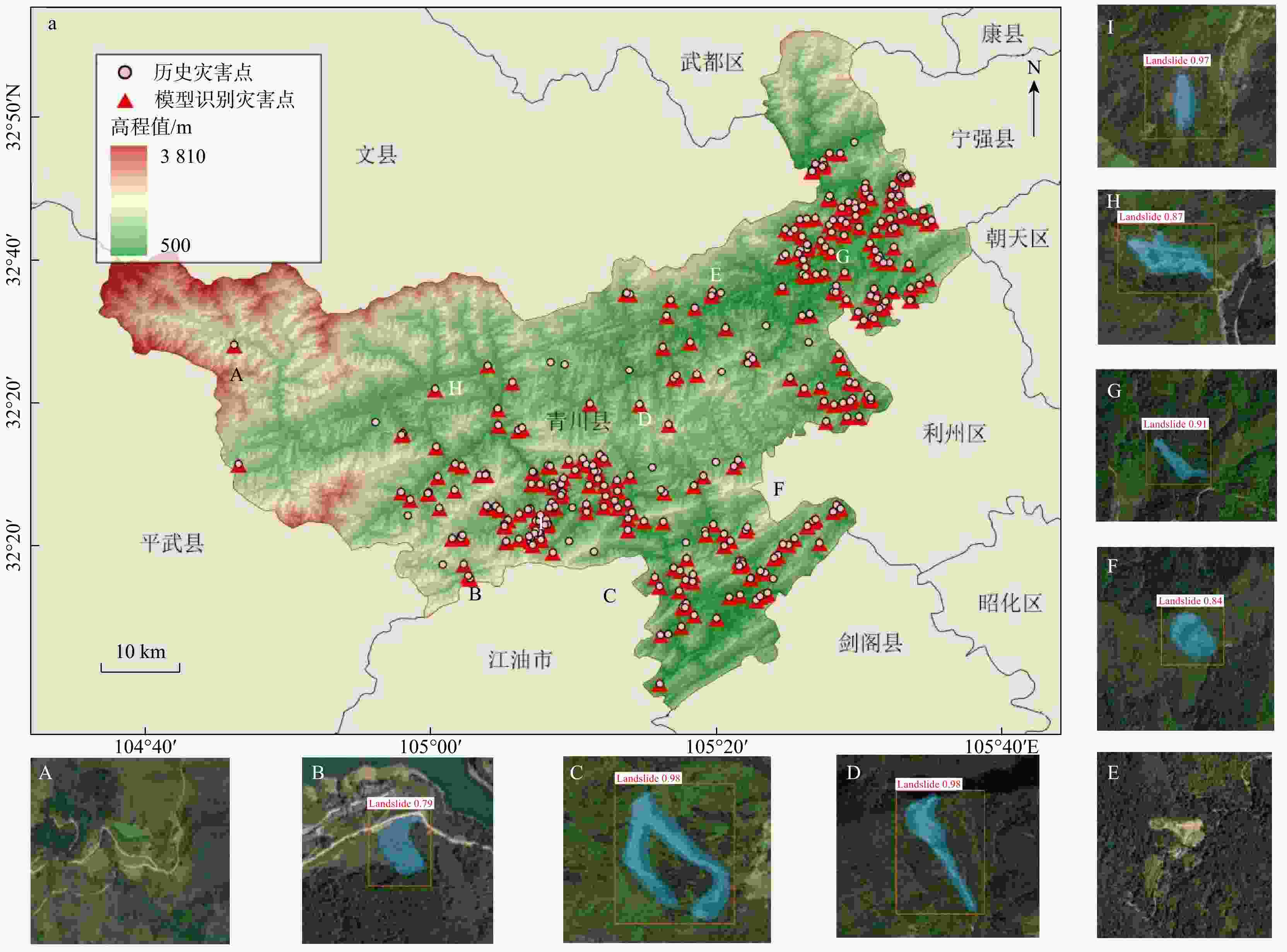
DIoU 损失对Mask R-CNN模型进行改进,提出滑坡智能识别改进算法。评价结果表明:改进算法相比原始模型,精确率提高了3.6%,召回率提高5.2%,对四川省青川县历史滑坡进行准确识别与边界分割,识别准确率达74.4%。随着卫星遥感手段与深度学习技术的发展,该改进算法对滑坡智能识别、构建地质灾害风险评价体系提供信息基础与理论参考具有重要意义。Abstract:Objective The complex topography of Sichuan Province, characterized by intersecting mountainous terrain, leads to frequent, sudden, and highly susceptible landslides. These events pose significant threats to both people's property and environmental resources. Therefore, conducting landslide identification and charaterization are crucial for effective hazard prevention, monitoring, and post-disaster preparedness.
Methods To overcome the limitations of conventional visual interpretation methods-including high economic costs, time-intensive procedures, labor demands, and challenges in acquiring historical samples, this study incorporates multiple landslide-influencing factors such as elevation, slope gradient, and aspect into the analysis framework. A quantitative information value analysis was conducted to evaluate the predictive capacity of these influencing factors for historical landslide identification, thereby improving the reliability of historical landslide inventories. To solve issues such as inaccurate localization and ambiguous segmentation boundaries in automatic landslide identification results, this paper improves the Mask R-CNN model using a recursive pyramid network and
DIoU loss, proposing an improved algorithm for intelligent landslide identification.Results Evaluation results demonstrate that the enhanced algorithm significant improvements over the baseline Mask R-CNN, with 3.6% increase in precision and 5.2% increase in recall. The model attains 74.4% identification accuracy in Qingchuan County, Sichuan, showing particular effectiveness in delineating historical landslide boundaries with clear geomorphological fidelity.
Conclusion Combining satellite remote sensing with deep learning advancements, this improved algorithm enables intelligent landslide identification and supports data-driven risk assessment, offering critical insights for geohazard mitigation.
-
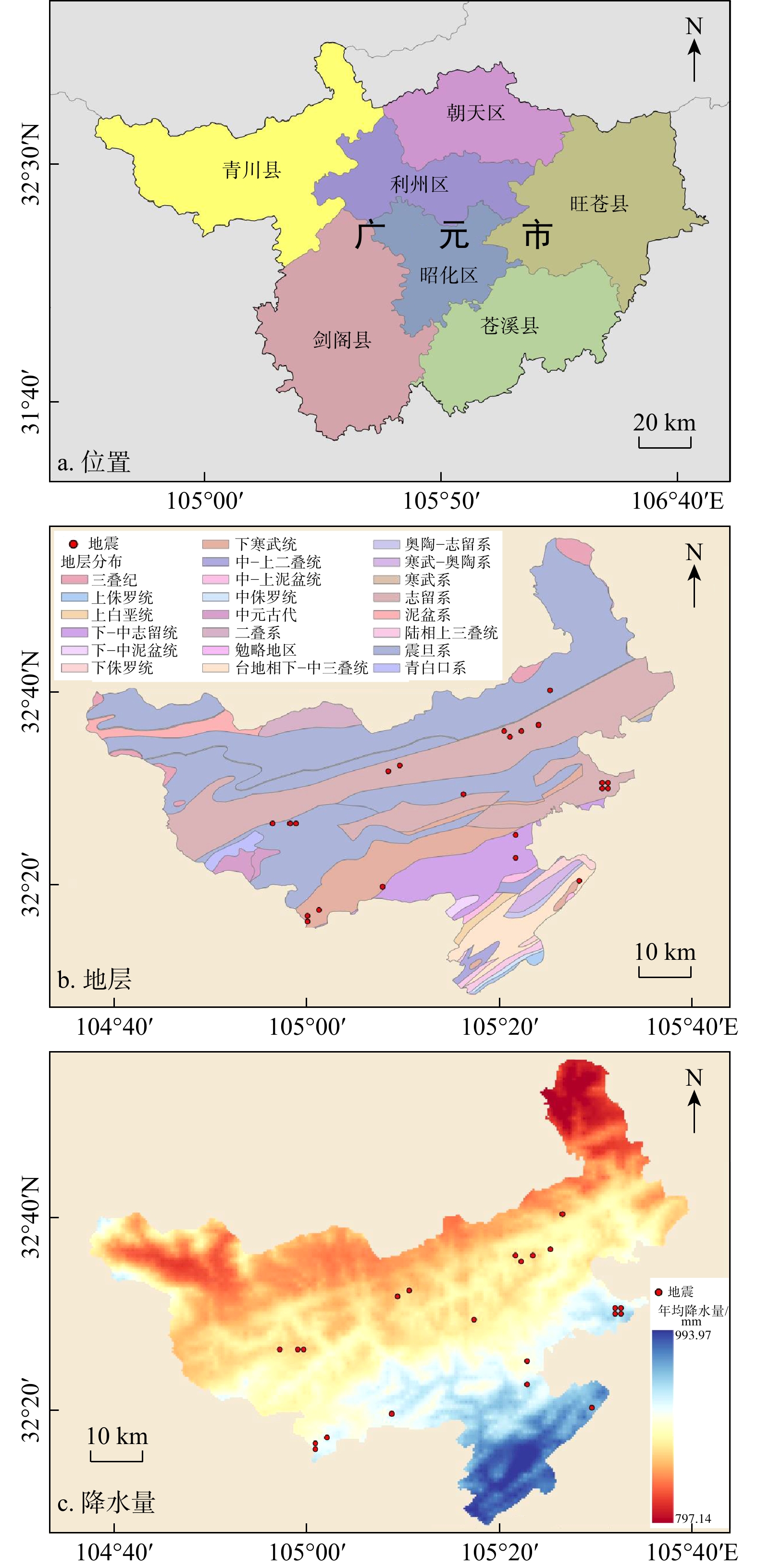
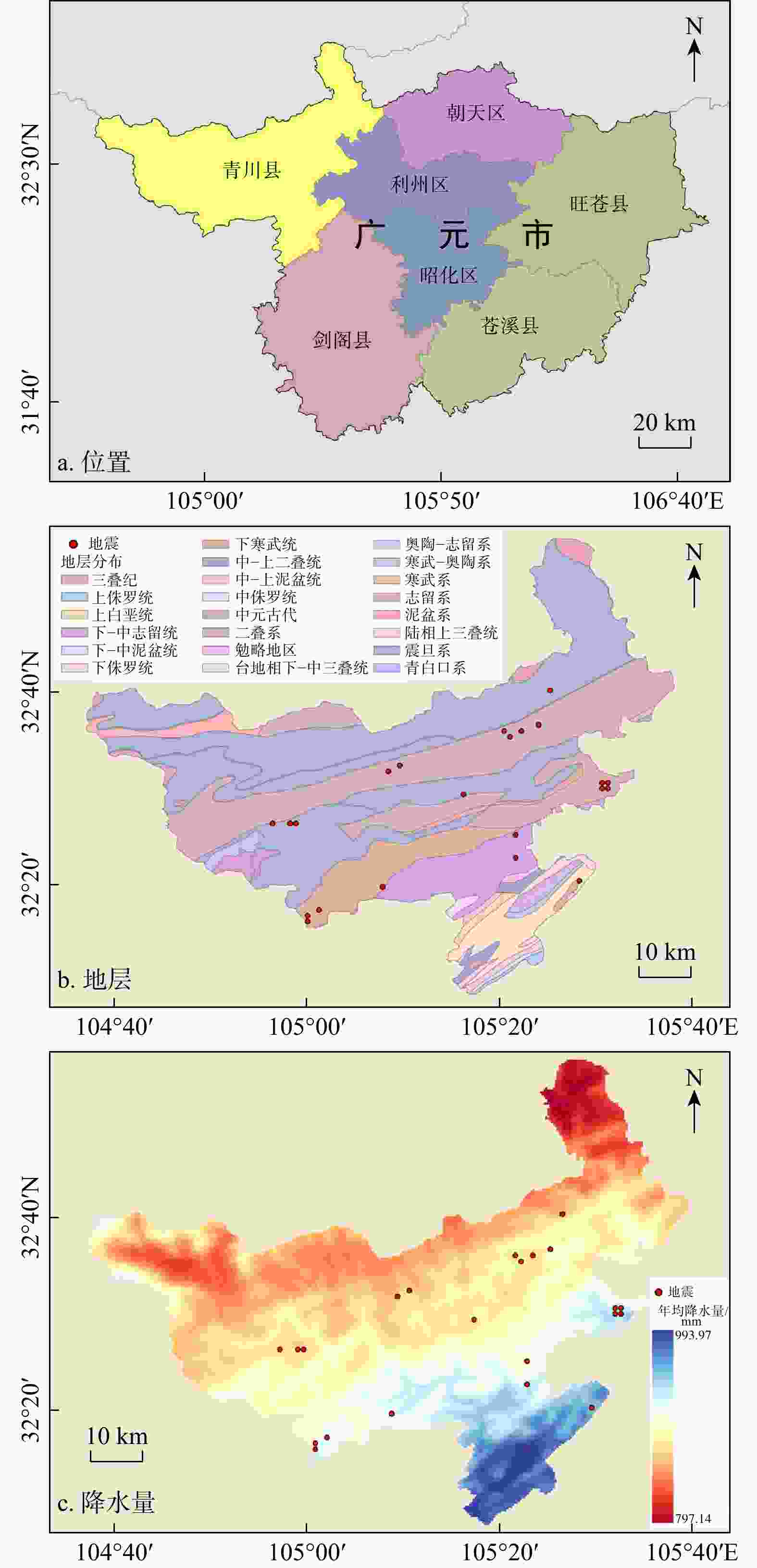
表 1 研究区原始数据获取途径及用途
Table 1. Summary of raw data acquisition and their applications in the study area
数据名称 数据来源 数据用途 行政区划 国家1∶100万基础地理信息数据 研究区概况图和底图制作 历史灾害点 中国科学院资源环境科学数据中心全国地质灾害点空间分布数据 历史灾害点 降雨量 地理遥感生态网气象监测站数据 年均雨量 地震灾害点 2015—2020年全国地震数据 地震数据 DEM数据 ASTGTM2 30 m分辨率 滑坡影响因子 地层岩性 1∶100万岩性土壤地貌矢量数据 水系、道路 1∶25万全国基础地理数据库 断层 1∶20万地质图 归一化植被指数 中国年度250 m NDVI空间分布数据集 光学遥感影像 Google Earth、公开滑坡数据集 样本数据集 表 2 研究区滑坡影响因子信息量值分布表
Table 2. Distribution table of informative values of landslide-influencing factors in the study area
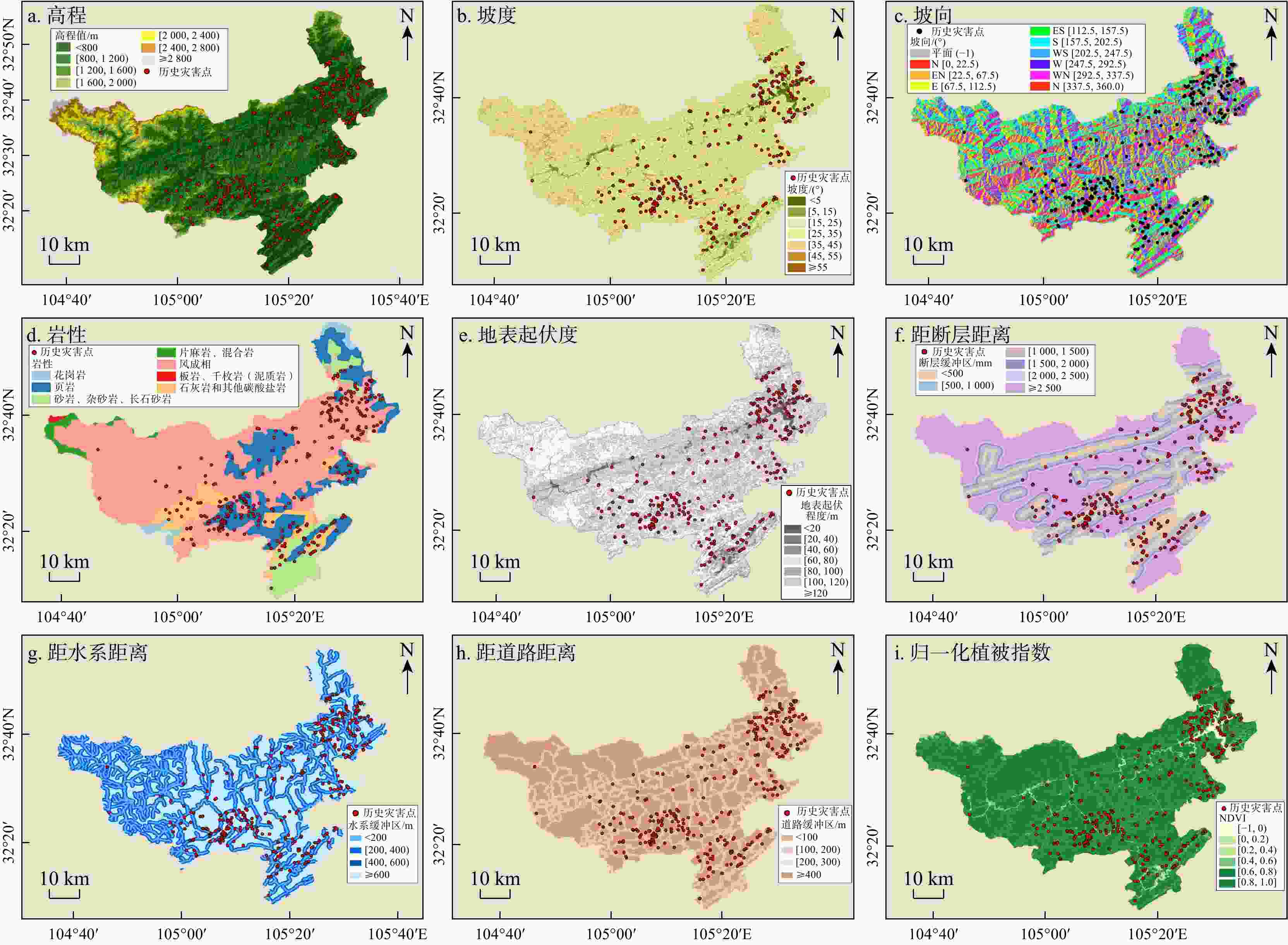
评价因子 因子分级 信息量值 评价因子 因子分级 信息量值 高程/m < 800 0.794 岩性 花岗岩 −1.873 [800, 1200 )0.324 页岩 0.568 [ 1200 ,1600 )−1.179 砂岩等 0.094 [ 1600 ,2000 )−3.490 片麻岩等 − [ 2000 ,2400 )− 风成相 −0.384 [ 2400 ,2800 )− 板岩等 − ≥ 2800 − 石灰岩等 0.516 坡度/(°) <5 0.121 地表起伏
程度/m[0,20) 0.261 [5,15) 0.289 [20,40) 0.061 [15,25) 0.175 [40,60) −0.188 [25,35) −0.102 [60,80) −0.315 [35,45) −0.208 [80,100) 0.477 [45,55) −0.236 [100,120) 0.025 ≥55 −0.612 ≥120 − 道路距
离/m[0,100) 0.562 距水系
距离/m[0,200) 0.094 [100,200) 0.256 [200,400) 0.058 [200,300) 0.422 [400,600) 0.065 ≥300 −0.298 ≥600 −0.104 距断层
距离/mm[0,500) 0.582 归一化植
被指数[−1,0) −0.948 [500, 1000 )0.451 [0,0.2) 0.801 [ 1000 ,1500 )0.128 [0.2,0.4) 0.539 [ 1500 ,2000 )−0.015 [0.4,0.6) 0.884 [ 2000 ,2500 )−0.467 [0.6,0.8) −0.140 ≥ 2500 −0.591 [0.8,1] −0.531 坡向 N −0.098 S −0.054 EN −0.149 WS −0.013 E −0.049 W 0.148 ES −0.014 WN 0.233 表 3 滑坡样本数据库统计
Table 3. Statistics table of landslide sample database
光学遥感影像分类 初始影像数量 信息量分析后影像数量 最终数量 确定含有滑坡数据集 1873 1873 2552 疑似含有滑坡数据集 845 679 表 4 软硬件配置表
Table 4. Hardware and software configuration
软硬件配置 参数 CPU AMD Ryzen 5 5600X 6-Core Processor 3.70 GHz GPU NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090 操作系统 Ubuntu 16.04 显存 24 GB 内存 32 GB CUDA 9.0 cuDNN 7.0 编程语言 Python 3.6 深度学习框架 TensorFlow1.9 +Keras2.2 表 5 不同模型实验结果对比
Table 5. Comparison of experimental results among different algorithms
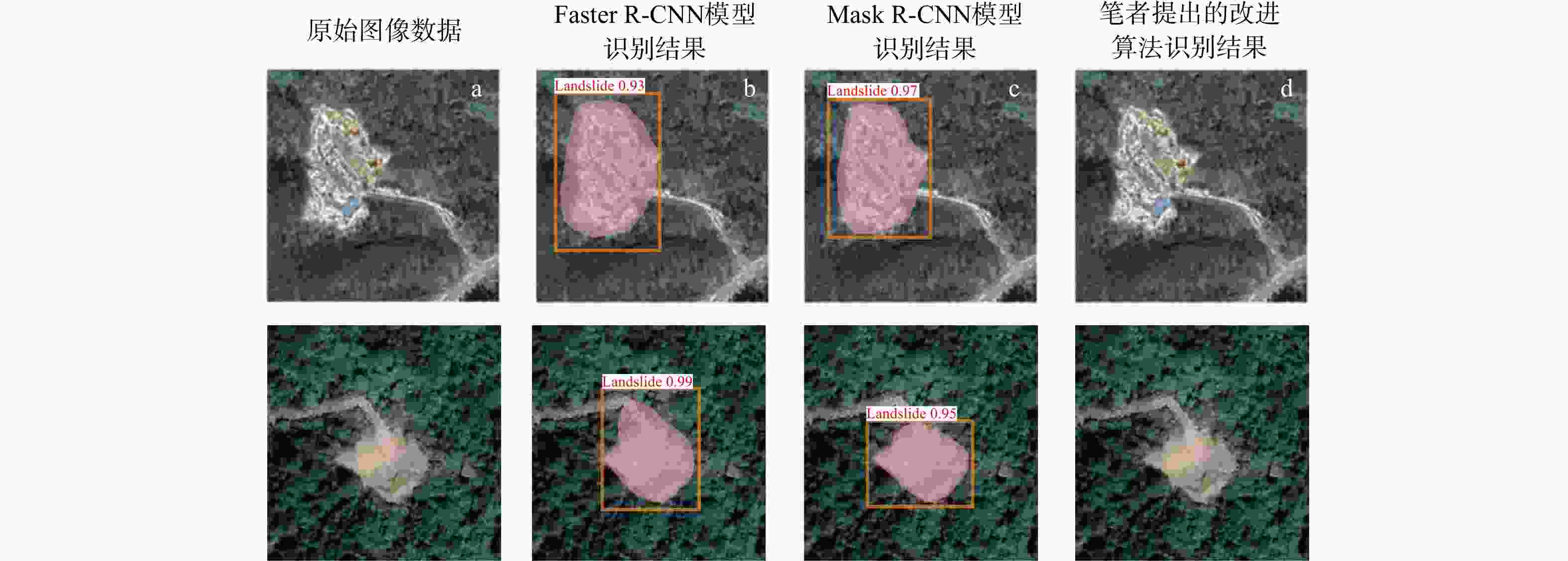
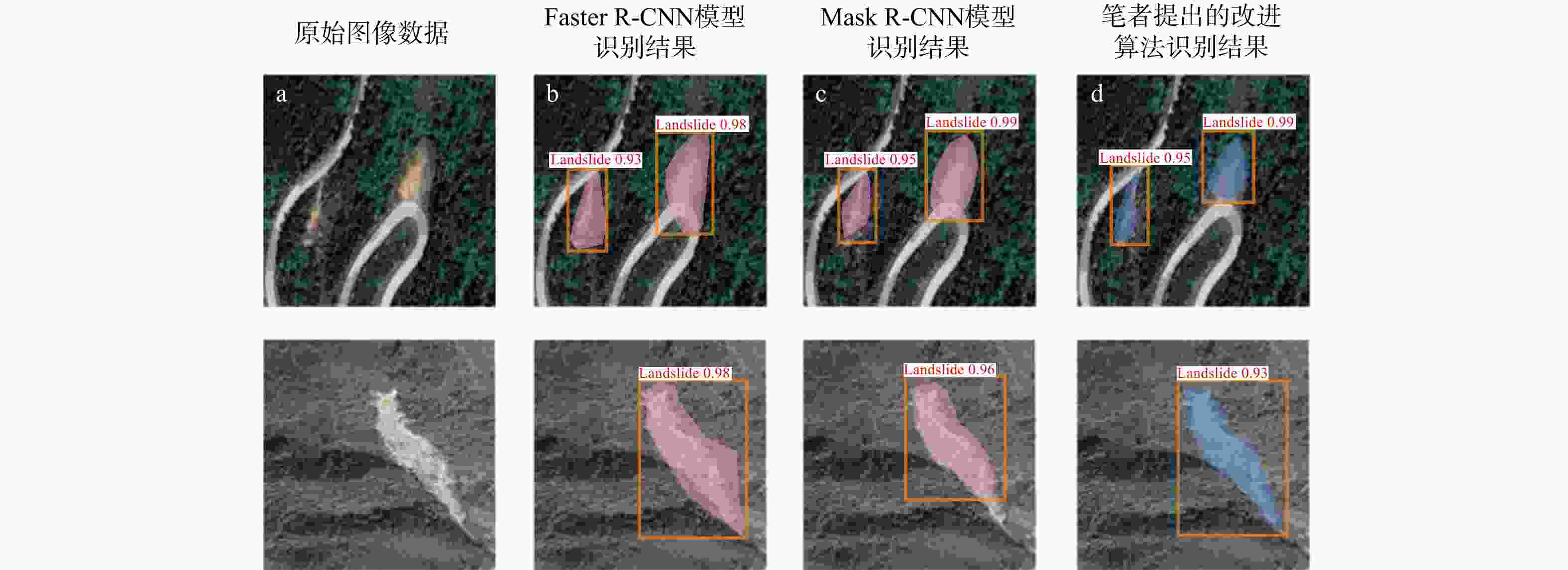
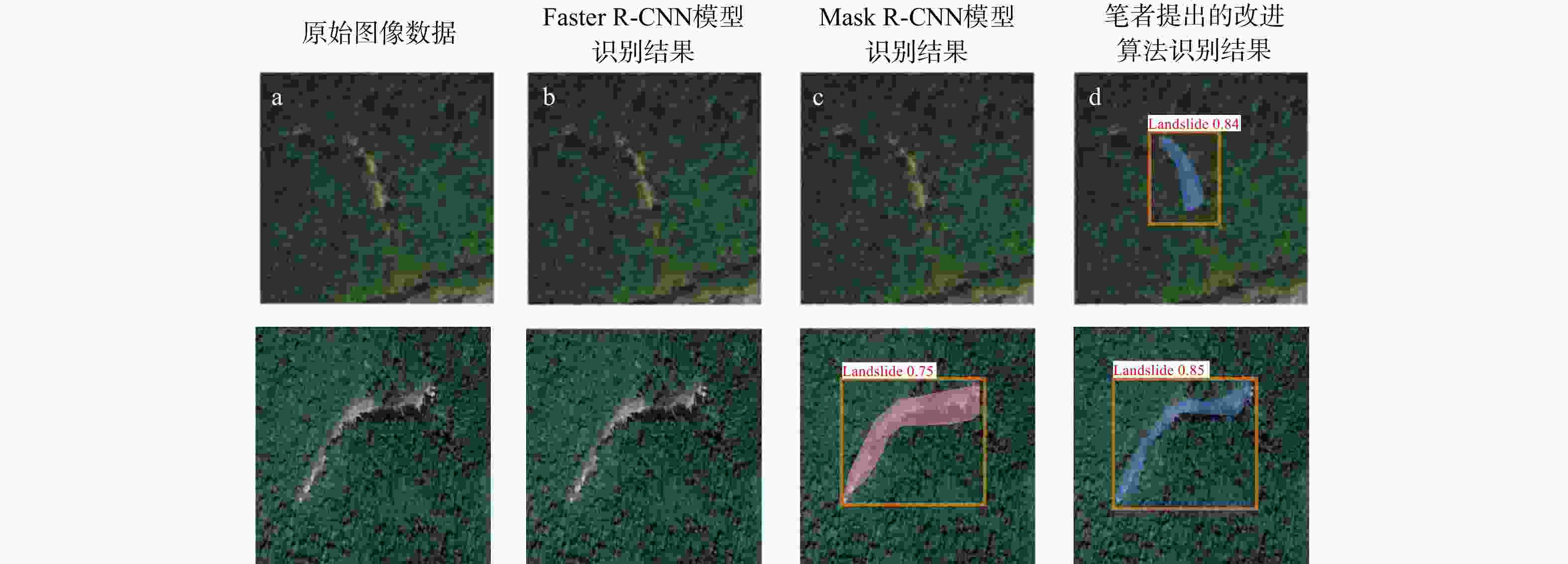
模型 精确率P/% 召回率R/% F1分数 Faster R-CNN 72.2 70.5 71.3 Mask R-CNN 77.6 74.4 76.1 本研究改进算法 81.2 79.6 80.4 -
[1] 许强,汤明高,黄润秋,等. 大型滑坡监测预警与应急处置:第2版[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2020.XU Q,TANG M G,HUANG R Q. Monitoring,early warning and emergency disposal of large landslide[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing:Science Press,2020. (in Chinese) [2] 朱颖,甘建军,鹿淇瑞,等. 降雨型花岗岩残积土滑坡碎屑流运动过程分析: 以湖北黄梅县袁山村为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2025,44(3):268-279.ZHU Y,GAN J J,LU Q R,et al. Analysis of rainfall induced-movement of landslide debris flows in granite residual soil:A case study of Yuanshan Village, Huangmei County, Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2025,44(3):268-279. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 自然资源部. 自然资源部关于印发《2022年全国地质灾害防治工作要点》的通知[J]. 自然资源通,2022(6):29-31.Ministry of Natural Resources. "Notice on Issuing the Key Points of National Geological Disaster Prevention and Control Work in 2022" [J]. Natural Resources Communication,2022(6):29-31. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 许强,董秀军,李为乐. 基于天-空-地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):957-966.XU Q,DONG X J,LI W L. Integrated space-air-ground early detection,monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):957-966. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 豆红强,黄思懿,简文彬,等. 基于遥感数据的闽东南山区公路滑坡快速识别技术研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2023,32(1):217-227.DOU H Q,HUANG S Y,JIAN W B,et al. Research on rapid identification technology of highway landslide in mountainous areas of Southeast Fujian based on remote sensing data[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2023,32(1):217-227. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 许伟,杨德芳,陈李昊,等. 多源遥感影像融合处理提取格拉丹东雪山区域特征信息[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(2):370-385. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220545.XU W,YANG D F,CHEN L H,et al. Fusion processing of multisource remote sensing images for extracting characteristic information from the Geladandong Snow Mountain area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(2):370-385. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220545. [7] LENCZNER G,LE SAUX B,LUMINARI N,et al. DISIR:Deep image segmentation with interactive refinement[EB/OL]. 2020:2003.14200. https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.14200v2. [8] SATO H P,HASEGAWA H,FUJIWARA S,et al. Interpretation of landslide distribution triggered by the 2005 northern Pakistan earthquake using SPOT5 imagery[J]. Landslides,2007,4(2):113-122. doi: 10.1007/s10346-006-0069-5 [9] 苏凤环,刘洪江,韩用顺. 汶川地震山地灾害遥感快速提取及其分布特点分析[J]. 遥感学报,2008,12(6):956-963.SU F H,LIU H J,HAN Y S. The extraction of mountain hazard induced by Wenchuan earthquake and analysis of its distributing characteristic[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing,2008,12(6):956-963. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 陆会燕,李为乐,许强,等. 光学遥感与InSAR结合的金沙江白格滑坡上下游滑坡隐患早期识别[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(9):1342-1354.LU H Y,LI W L,XU Q,et al. Early detection of landslides in the upstream and downstream areas of the baige landslide,the Jinsha River based on optical remote sensing and InSAR technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(9):1342-1354. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 张钰洁,刘佳佳,孙龙,等. 顾及无人机影像多特征信息的滑坡识别[J]. 自然灾害学报,2024,33(5):109-118.ZHANG Y J,LIU J J,SUN L,et al. Landslide identification considering multi-feature information of UAV images[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2024,33(5):109-118. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 黄发明,陈彬,毛达雄,等. 基于自筛选深度学习的滑坡易发性预测建模及其可解释性[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(5):1696-1710.HUANG F M,CHEN B,MAO D X,et al. Landslide susceptibility prediction modeling and interpretability based on self-screening deep learning model[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(5):1696-1710. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] YE C M,LI Y,CUI P,et al. Landslide detection of hyperspectral remote sensing data based on deep learning with constrains[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing,2019,12(12):5047-5060. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2019.2951725 [14] GHORBANZADEH O,BLASCHKE T,GHOLAMNIA K,et al. Evaluation of different machine learning methods and deep-learning convolutional neural networks for landslide detection[J]. Remote Sensing,2019,11(2):196. doi: 10.3390/rs11020196 [15] WANG H J,ZHANG L M,YIN K S,et al. Landslide identification using machine learning[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2021,12(1):351-364. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.02.012 [16] YU H,MA Y,WANG L F,et al. A landslide intelligent detection method based on CNN and RSG_R[C]//Anon. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA). Takamatsu,Japan:IEEE,2017:40-44. [17] GHORBANZADEH O,BLASCHKE T. Optimizing sample patches selection of CNN to improve the mIOU on landslide detection[C]//Anon. GISTAM. [S. n. ]:[S. l. ],2019:33-40. [18] SAMEEN M I,PRADHAN B. Landslide detection using residual networks and the fusion of spectral and topographic information[J]. IEEE Access,2019,7:114363-114373. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2935761 [19] HOCHREITER S,SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation,1997,9(8):1735-1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [20] 王世宝,庄建琦,郑佳,等. 基于深度学习的CZ铁路康定−理塘段滑坡易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(3):908-919.WANG S B,ZHUANG J Q,ZHENG J,et al. Landslide susceptibility evaluation based on deep learning along Kangding-Litang section of cz railway[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(3):908-919. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 赵通,张双成,何晓宁,等. 改进的DeepLabV3+模型用于震后高分遥感影像滑坡识别[J]. 遥感学报,2024,28(9):2293-2305.ZHAO T,ZHANG S C,HE X N,et al. Improved DeepLabV3+ model for landslide identification in high-resolution remote sensing images after earthquakes[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin,2024,28(9):2293-2305. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 黄发明,欧阳慰平,蒋水华,等. 考虑机器学习建模中训练/测试集时空划分原则的滑坡易发性预测建模[J]. 地球科学,2024,49(5):1607-1618.HUANG F M,OUYANG W P,JIANG S H,et al. Landslide susceptibility prediction considering spatio-temporal division principle of training/testing datasets in machine learning models[J]. Earth Science,2024,49(5):1607-1618. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 文广超,苏林雪,谢洪波,等. “5·12” 汶川地震前后四川省主要地质灾害时空发育规律[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(4):143-152.WEN G C,SU L X,XIE H B,et al. Spatio-temporal development characteristics of major geohazards in Sichuan Province around “5·12” Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(4):143-152. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 广元市统计局 广元市第七次全国人口普查领导小组办公室. 广元市第七次全国人口普查公报([1])(第一号)[N]. 广元日报,2021-06-19(004).Guangyuan City Statistics Bureau,Guangyuan City Seventh National Census Leading Group Office. Guangyuan City Seventh National Census Bulletin ([1])[N]. Guangyuan Daily,2021-06-19(004). (in Chinese) [25] 李沧海. 柒树湾不稳定斜坡变形机制分析及稳定性评价[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2010.LI C H. Deformation mechanism analysis and stability estimation of Qishuwan unstable slope[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2010. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 陈祖杰. 基于GIS的青川县滑坡灾害易发性评价与区划[D]. 四川 绵阳:西南科技大学,2017.CHEN Z J. The evaluation and zoning of susceptibility of landslide hazards based on GIS in Qingchuan County[D]. Mianyang Sichuan:Southwest University of Science and Technology,2017. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] JI S P,YU D W,SHEN C Y,et al. Landslide detection from an open satellite imagery and digital elevation model dataset using attention boosted convolutional neural networks[J]. Landslides,2020,17(6):1337-1352. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01353-2 [28] 戴悦. 基于信息量模型的三峡库区滑坡区域危险性评价方法研究[D]. 北京:清华大学,2013.DAI Y. Study on the method of regional early warning of landslide in three gorges area based on information model[D]. Beijing:Tsinghua University,2013. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 王雷,吴君平,赵冰雪,等. 基于GIS和信息量模型的安徽池州地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):96-103.WANG L,WU J P,ZHAO B X,et al. Susceptibility assessment of geohazards in Chizhou City of Anhui Province based on GIS and informative model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):96-103. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 朱庆,曾浩炜,丁雨淋,等. 重大滑坡隐患分析方法综述[J]. 测绘学报,2019,48(12):1551-1561.ZHU Q,ZENG H W,DING Y L,et al. A review of major potential landslide hazards analysis[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2019,48(12):1551-1561. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 邹富宝,付卓,樊风雷,等. 基于频率比与AHP模型的西藏东部地区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 自然灾害学报,2023,32(2):235-242. ZOU F B,FU Z,FAN F L,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility in eastern Tibet based on frequency ratio and AHP model[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2023,32(2):235-242. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] BORDONI M,GALANTI Y,BARTELLETTI C,et al. The influence of the inventory on the determination of the rainfall-induced shallow landslides susceptibility using generalized additive models[J]. Catena,2020,193:104630. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104630 [33] 兰恒星,伍法权,周成虎,等. 基于GIS的滑坡空间数据库研究:以云南小江流域为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2002,13(4):10-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2002.04.002LAN H X,WU F Q,ZHOU C H,et al. GIS based spatial database for landslide assessment:A case study in Yunnan Xiaojiang River valley[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2002,13(4):10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2002.04.002 [34] 李国营,刘平,张凯,等. 量纲统一在滑坡易发性评价中的影响分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2024,51(3):118-129.LI G Y,LIU P,ZHANG K,et al. Analysis of the influence of dimensional unity in landslide susceptibility assessment[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2024,51(3):118-129. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 喻军华. 岩质高边坡开挖与支护过程分析[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2003.YU J H. Analysis of excavation and support of high rock slope[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2003. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 黄润秋,李为乐. 汶川大地震触发地质灾害的断层效应分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2009,17(1):19-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.01.003HUANG R Q,LI W L. Fault effect analysis of geo-hazard triggered by Wenchaun earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2009,17(1):19-28. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.01.003 [37] METEN M,PRAKASHBHANDARY N,YATABE R. Effect of landslide factor combinations on the prediction accuracy of landslide susceptibility maps in the blue Nile gorge of central Ethiopia[J]. Geoenvironmental Disasters,2015,2(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s40677-015-0016-7 [38] 姜琳,冯文兰,刘志红,等. FY-3A/MERSI与MODIS的温度植被干旱指数反演及对比分析[J]. 水土保持研究,2014,21(3):231-234.JIANG L,FENG W L,LIU Z H,et al. Tempeture vegetation drought index(TVDI)retrieve and comparison between FY-3A/MERSI and MODIS[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation,2014,21(3):231-234. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] SHANNON C E. A mathematical theory of communication[J]. Bell System Technical Journal,1948,27(3):379-423. doi: 10.1002/j.1538-7305.1948.tb01338.x [40] 刘亚静,刘红健. 基于信息量-随机森林模型的地震带地质灾害易发性评价:以松潘-较场地震带为例[J]. 科学技术与工程,2024,24(1):143-154. doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2301636LIU Y J,LIU H J. Evaluation of geological hazard susceptibility in seismic zone based on information data-RF model:A case study of Songpan-Jiaochang seismic zone[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2024,24(1):143-154. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12404/j.issn.1671-1815.2301636 [41] HE K M,GKIOXARI G,DOLLÁR P,et al. Mask R-CNN[C]//Anon. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice,Italy:IEEE,2017:2980-2988. [42] QIAO S Y,CHEN L C,YUILLE A. DetectoRS:Detecting objects with recursive feature pyramid and switchable atrous convolution[C]//Anon. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville,TN,USA:IEEE,2021:10208-10219. [43] CHEN L C,PAPANDREOU G,SCHROFF F,et al. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[EB/OL]. 2017:1706.05587. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.05587v3. [44] ZHENG Z H,WANG P,LIU W,et al. Distance-IoU loss:Faster and better learning for bounding box regression[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence,2020,34(7):12993-13000. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6999 -




 下载:
下载: