Analysis of rainfall induced-movement of landslide debris flows in granite residual soil: A case study of Yuanshan Village, Huangmei County, Hubei Province
-
摘要:
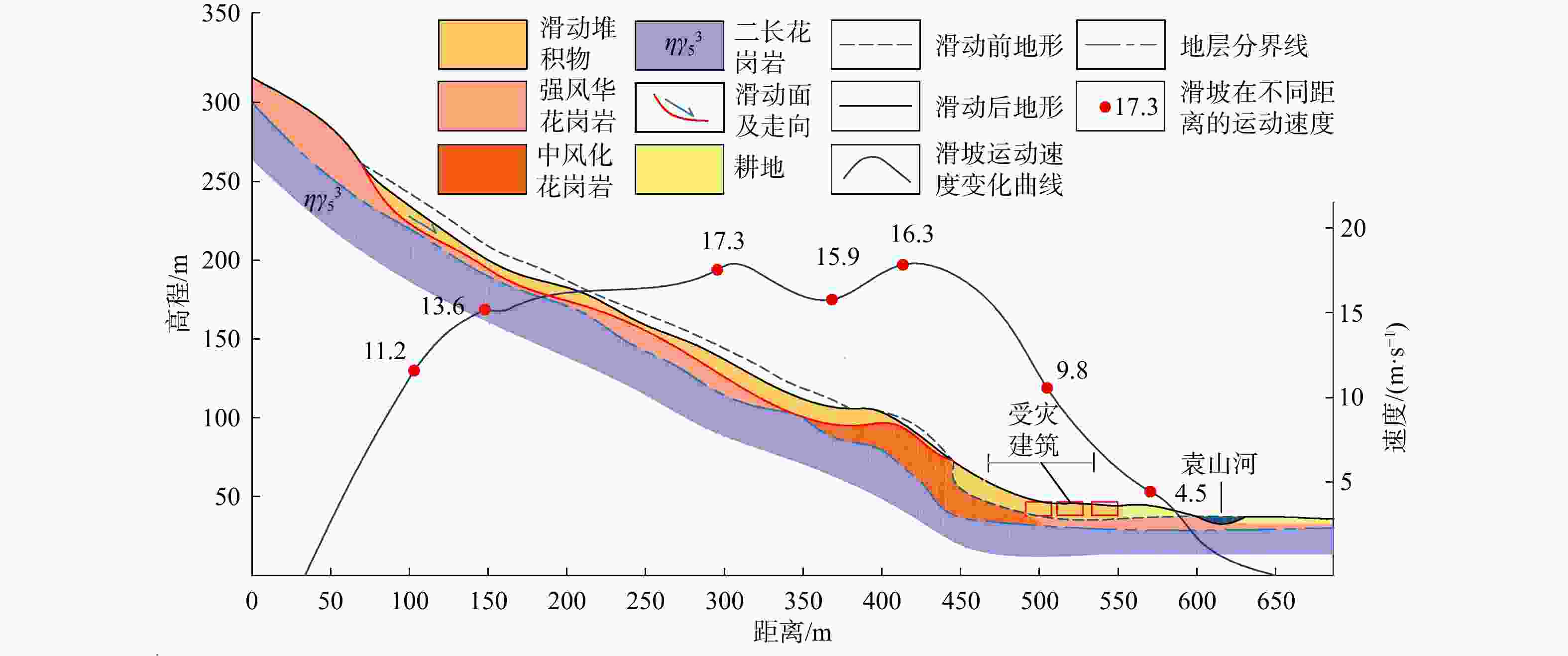
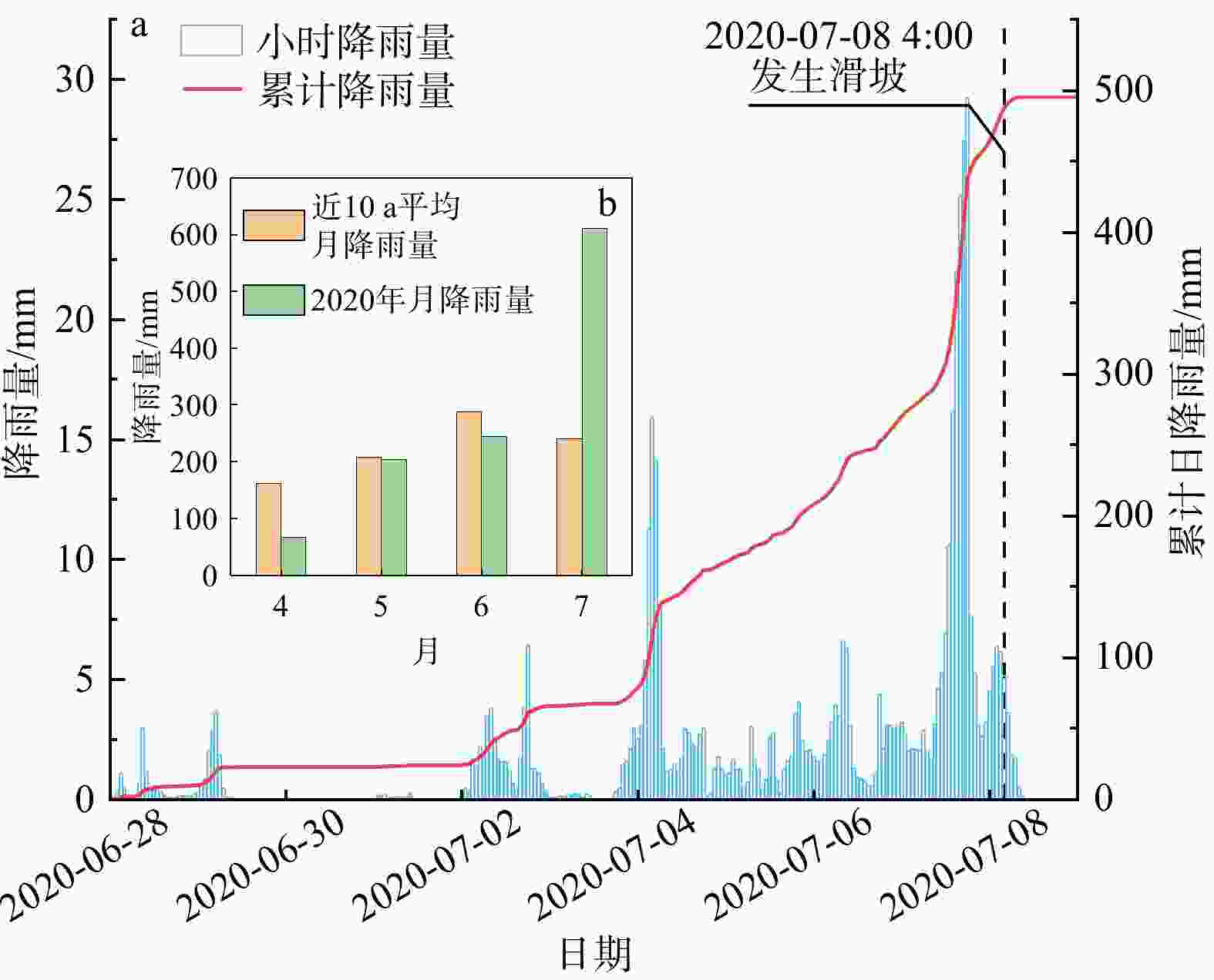
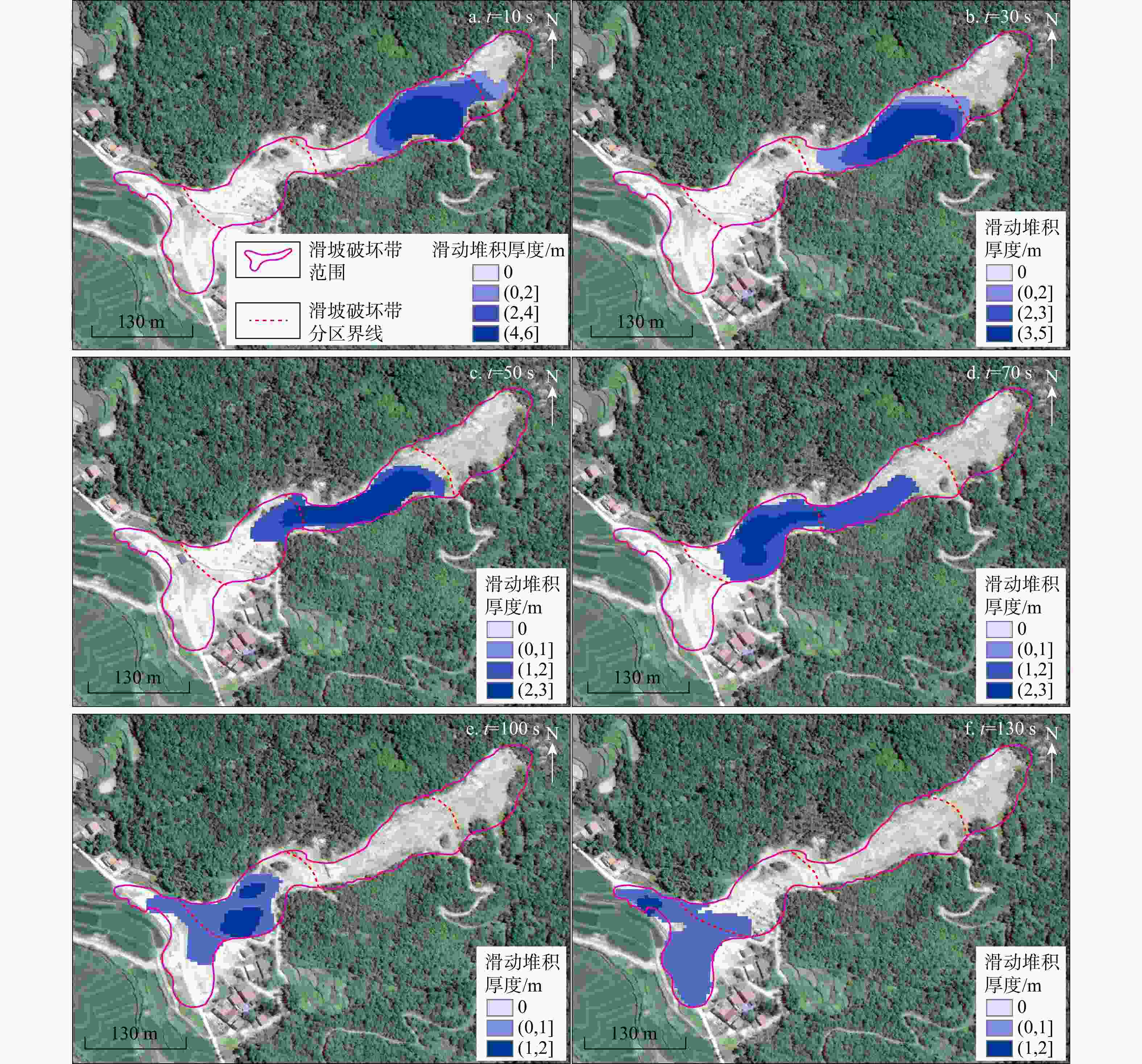
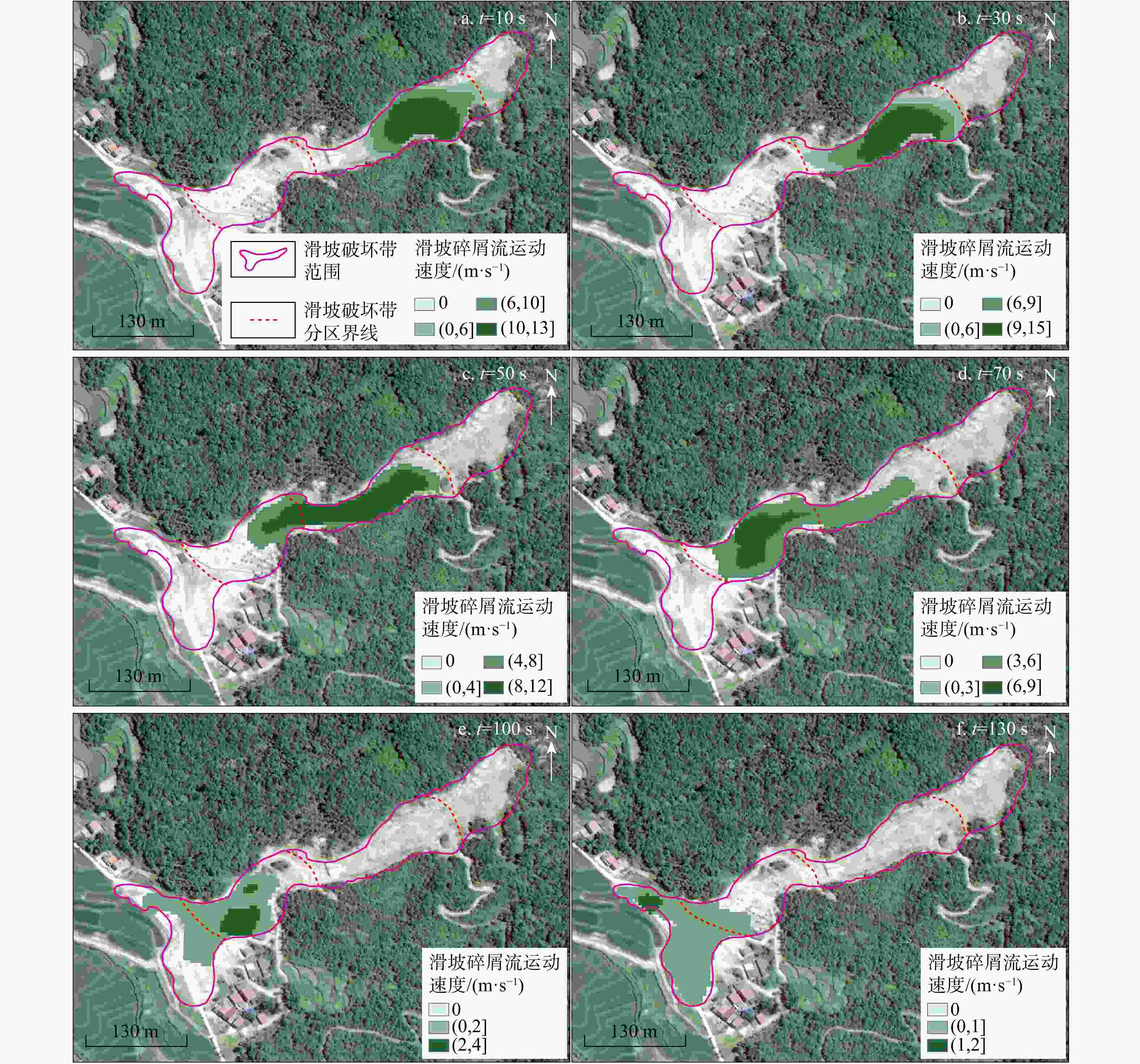
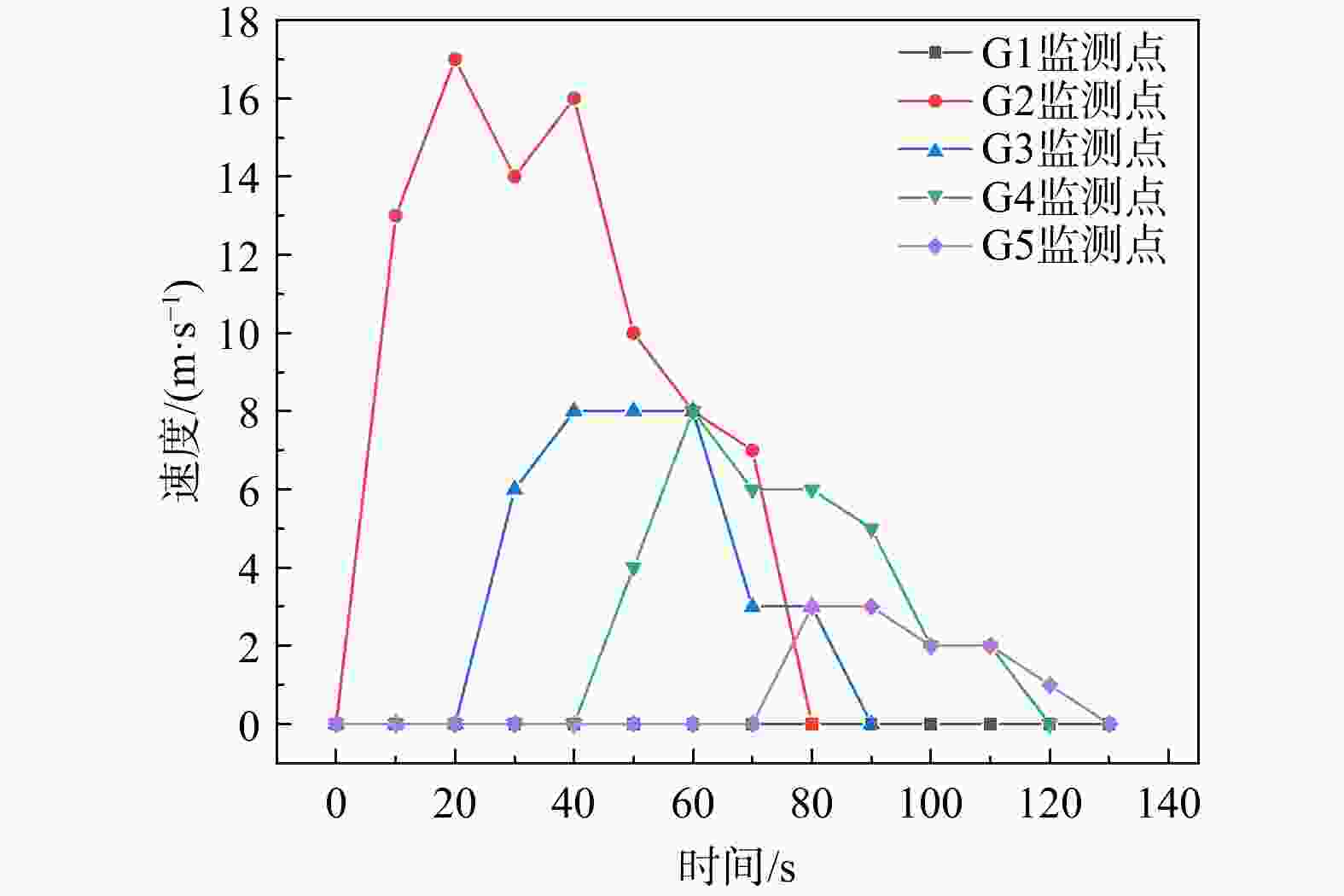
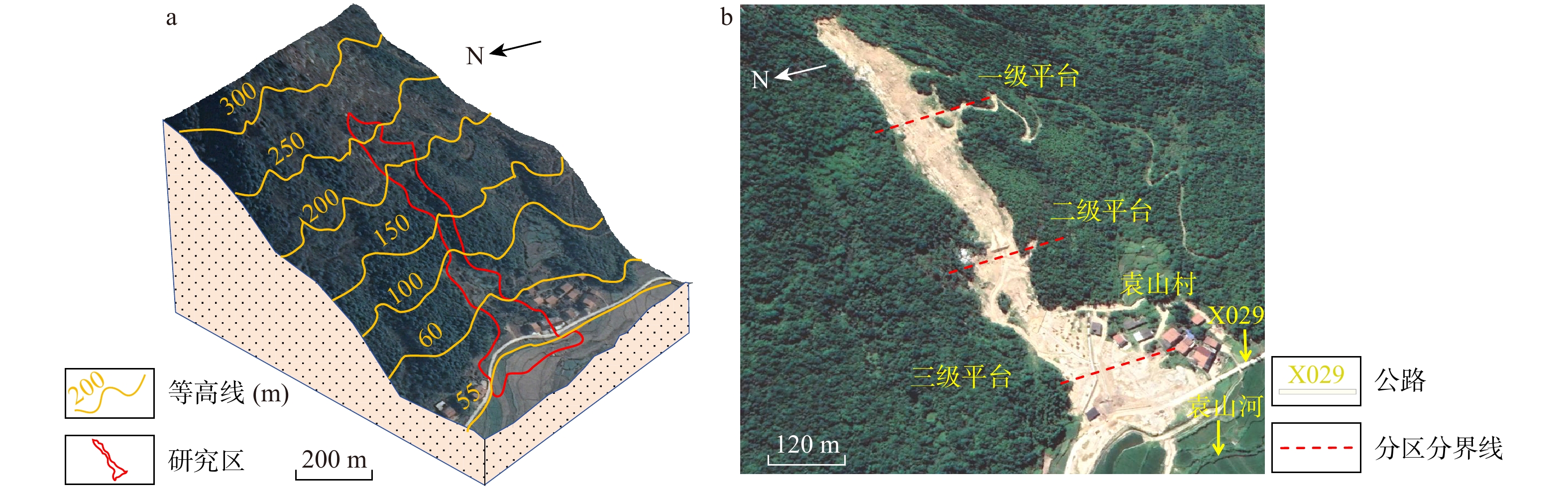
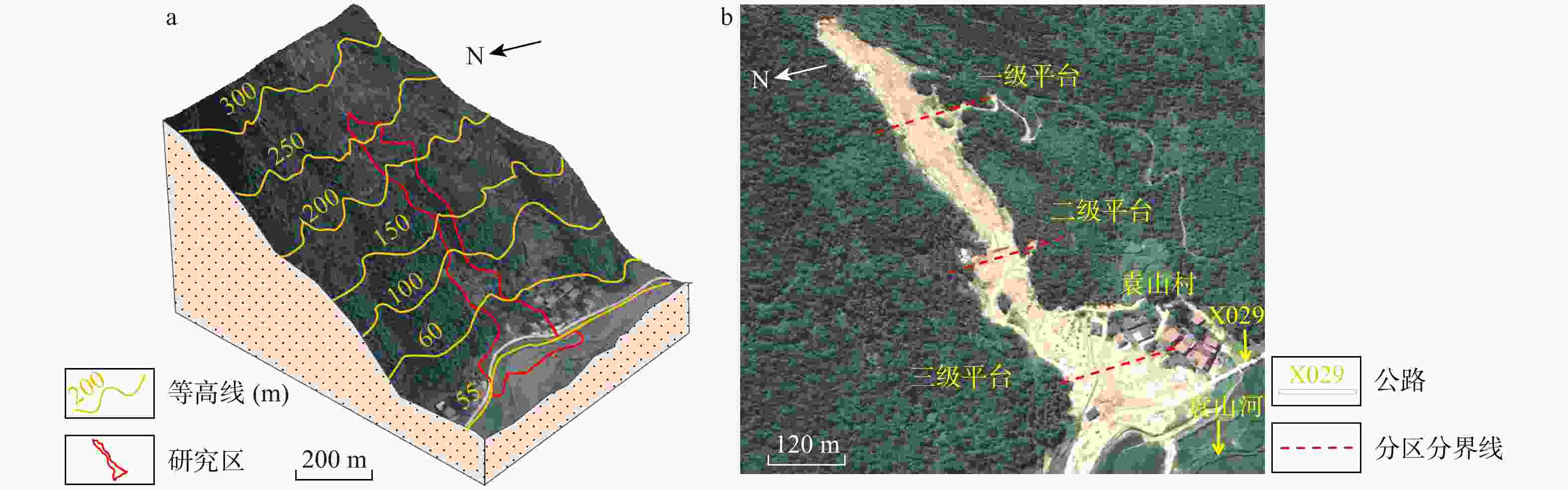
湖北黄梅县袁山村滑坡碎屑流是花岗岩残积土滑坡碎屑流,受地质条件影响,其运动过程较为复杂,突发性强。为研究中低山区花岗岩残积土滑坡碎屑流动力机制,分析降雨型花岗岩残积土滑坡碎屑流的运动过程,通过野外地质调查,利用无人机航拍(unmanned aerial vehicle,简称UAV)、遥感影像形成的数字地表模型(digital elevation model,简称DEM)、现场勘查及地质资料分析、数值模拟等方法对滑坡碎屑流进行运动过程分析。结果表明,滑坡碎屑流的运动过程中最大堆积厚度为6 m,在
t =20 s时达到运动峰值17 m/s,而实际运动峰值应当更大,出现在滑源区开始失稳的阶段,整个运动过程分为3个阶段:0~30 s为滑坡碎屑流失稳启动阶段,在一级平台加速;30~70 s受地形影响,滑动体进行二次加速并发生部分偏转运动,冲毁袁山村的建筑物;70~130 s为减速堆积阶段,掩埋和堆积了建筑物。本研究可为类似滑坡碎屑流的防治提供参考。Abstract:Objective The landslide in Yuanshan Village, Huangmei County, Hubei Province, represents a granite residual soil avalanche debris flow with complex and abrupt movement dynamics influenced by geological conditions. This study investigates the kinematic mechanisms of such landslide-debris flows in mid-low mountainous areas by analyzing the motion process of this specific event.
Methods Through the field geological survey, the movement process of the landslide debris flow was analyzed based on UAV aerial photography, digital elevation model (DEM), on-site investigation, geological data analysis, and numerical simulations.
Results The results show that the maximum accumulation thickness of the avalanche is 6 m during the movement process. The peak velocity reaches 17 m/s at
t =10 s. The actual peak velocity should be larger and appears when the slip source area begins to be unstable. The whole movement process could be divided into three stages: during the first 30 s, the granite residual soil lost its stability, which resulted in the initiation and acceleration of the debris flow at the first-level platform; in 30-70 s, affected by the terrain, the debris flow was accelerated for the second time. A part of the debris flow changed its flow direction and destroyed the buildings in Yuanshan Village. From 70 s to 130 s, the debris flow decelerated and accumulated, during this stage the buildings were buried and accumulated by the debris flow.Conclusion This study can provide a reference for the prevention and control of similar disasters.
-
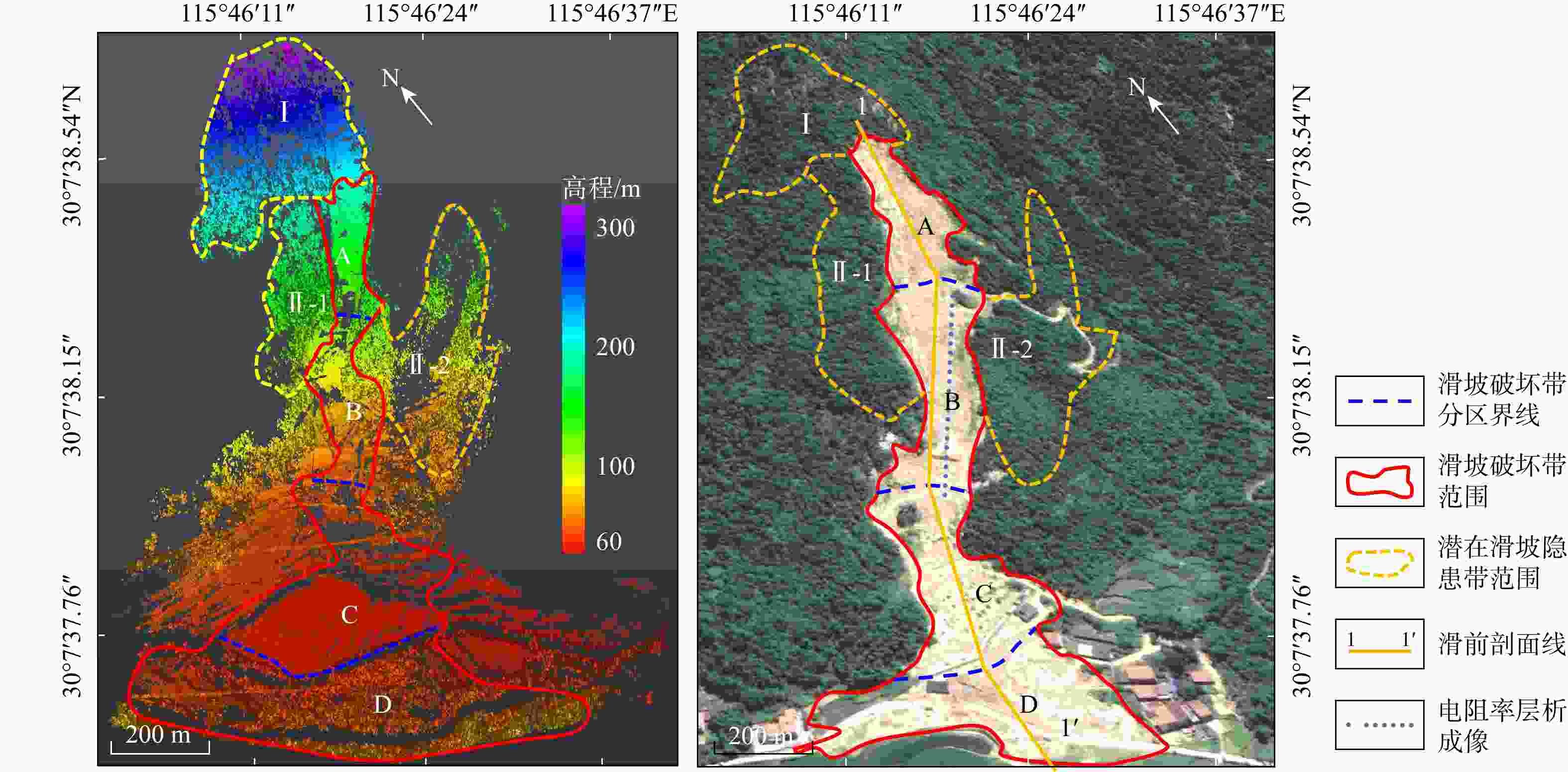
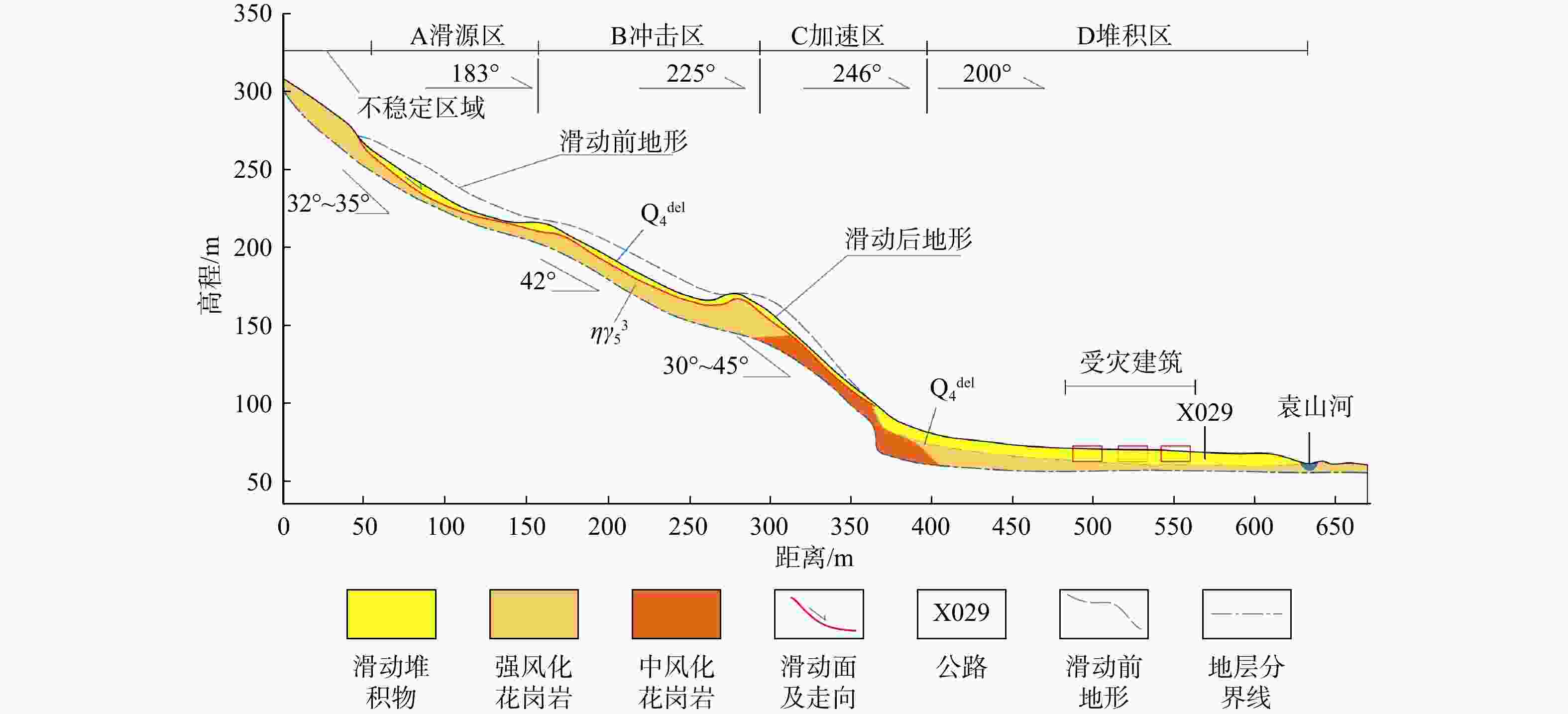
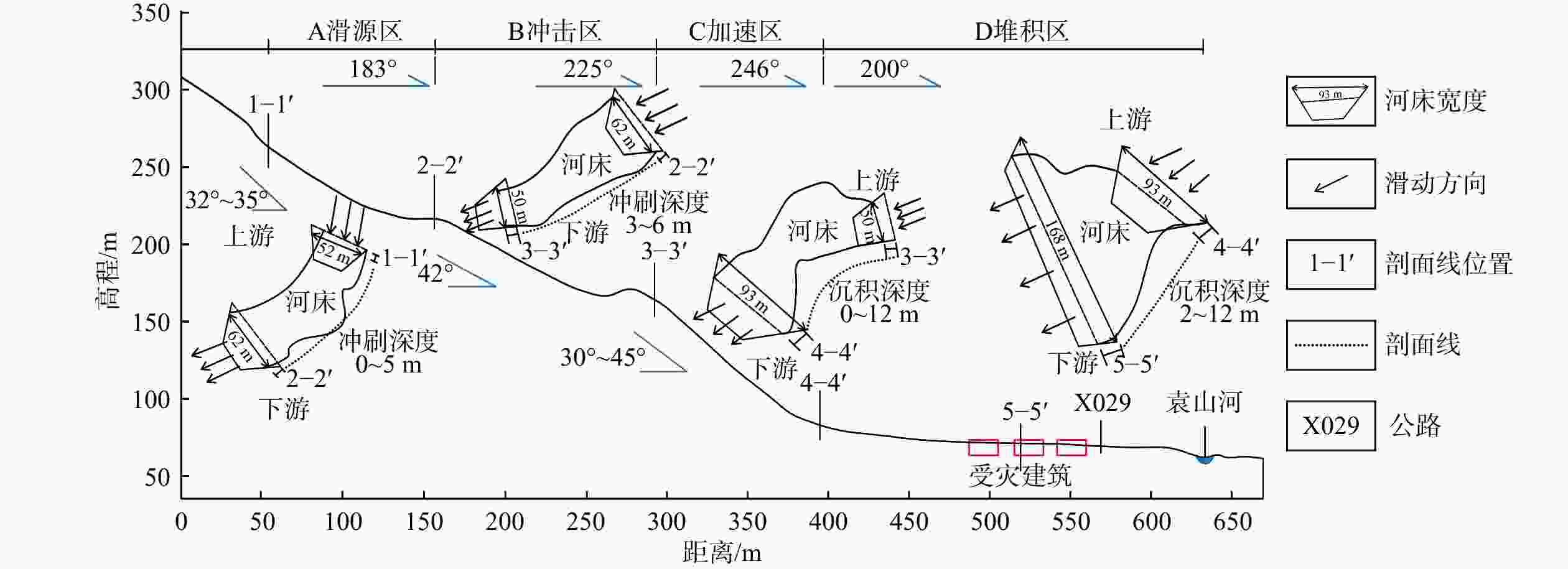
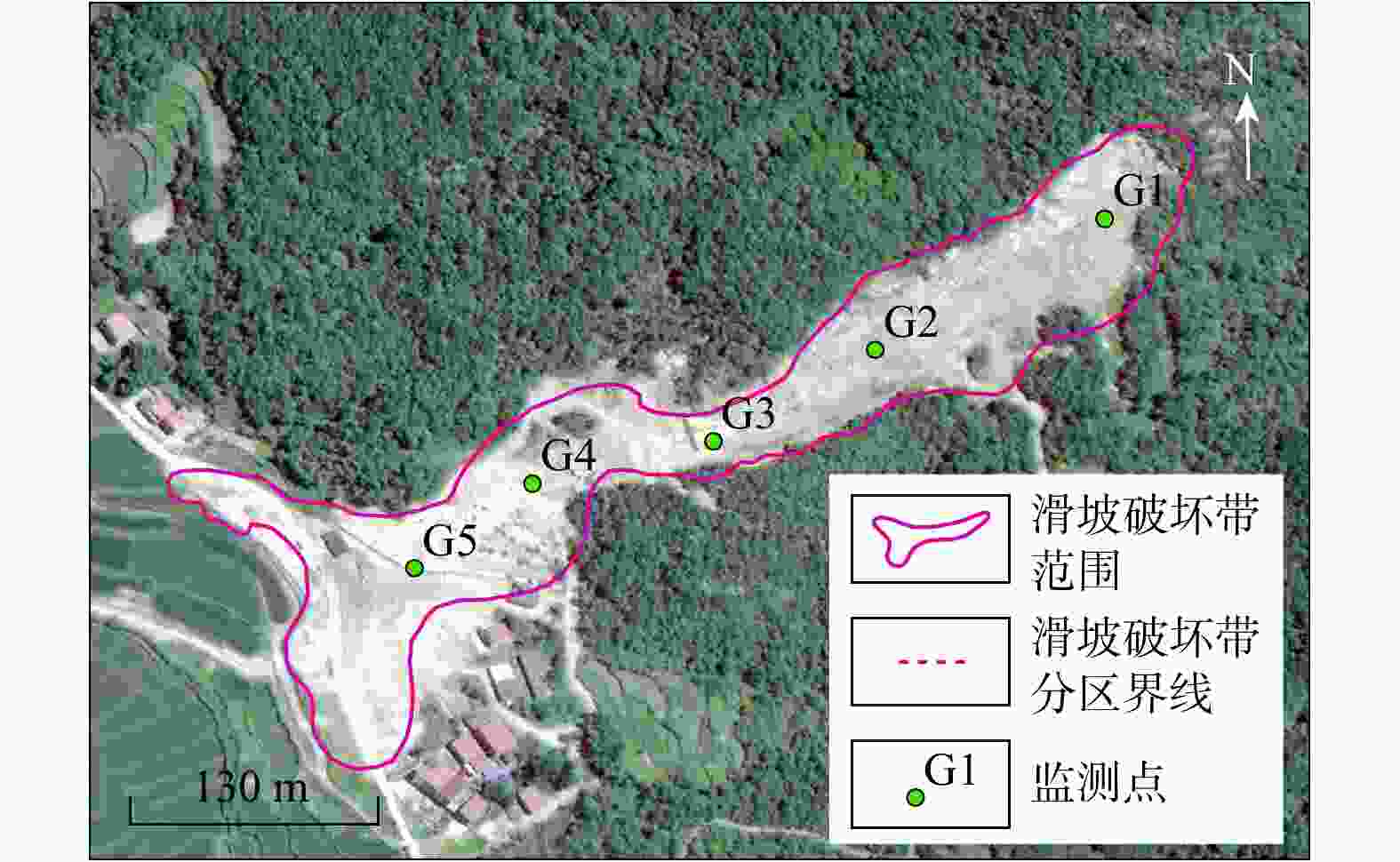
表 1 袁山村滑坡碎屑流7个分区的主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters of the seven zones in Yuanshan Village landslide debris flow
分区 长度/m 宽度/m 深度/m 厚度/m 坡度/(°) 面积/m2 体积/m3 A(滑源区) 130 200~265 52~62 0~4.0 32~35 0.65×104 2.4×104 B(冲击区) 160 120~200 50~62 4~6.0 42 0.88×104 4.4×104 C(加速区) 80 85~200 50~93 1~5.0 35~45 0.89×104 2.2×104 D(堆积区) 238 65~85 93~168 1~6.0 2~3 1.80×104 5.4×104 Ⅰ(上方不稳定区) 265 120~220 55~185 0~3.0 33~42 3.50×104 7.0×104 Ⅱ-1(右岸不稳定区) 170 200~265 65~136 2~6.0 22~72 1.79×104 5.4×104 Ⅱ-2(左岸不稳定区) 163 115~200 20~136 1~8.0 5~40 1.82×104 6.0×104 表 2 研究区花岗岩残积土试样物理力学参数试验结果
Table 2. Experimental Results of Physical and Mechanical Parameters of Granite Residual Soil of the study area
试样
序号含水率/
%湿密度/
%液限/
%塑限/
%饱和度/
%内黏聚
力/kPa内摩擦
角/(°)S1 34.2 1.96 33.5 20.8 93.4 13.6 14.5 S2 36.8 1.84 35.3 25.8 84.8 14.3 16.2 S3 34.2 1.87 34.8 21.5 70.8 17.8 24.3 S4 32.6 2.00 32.7 20.5 94.8 22.2 25.4 S5 35.3 1.92 29.3 19.8 91.4 23.5 17.3 S6 40.6 1.93 41.2 25.5 99.5 23.3 18.2 表 3 Voellmy模型选取参数
Table 3. Parameters of the Voellmy Model
平均密度/(kg·m−3) 摩擦系数 黏聚力/kPa 运行总时长/s 2000 0.43 15 130 -
[1] 王维早,许强,郑光,等. 强降雨诱发缓倾堆积层边坡失稳离心模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2016,37(1):87-95.WANG W Z,XU Q,ZHENG G,et al. Centrifugal model tests on sliding failure of gentle debris slope under rainfall[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2016,37(1):87-95. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 吴李泉,张锋,凌贤长,等. 强降雨条件下浙江武义平头村山体高边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2009,28(6):1193-1199.WU L Q,ZHANG F,LING X Z ,et al. Stability analysis of high slope subjected to heavy rainfall in Pingtou Village of Wuyi County,Zhejiang Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2009,28(6):1193-1199. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] YAN Y J,TU N,CEN L P,et al. Characteristics and dynamic mechanism of rill erosion driven by extreme rainfall on karst plateau slopes,SW China[J]. Catena,2024,238:107890. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2024.107890 [4] ERING P,SIVAKUMAR BABU G L. Probabilistic back analysis of rainfall induced landslide:A case study of Malin landslide,India[J]. Engineering Geology,2016,208:154-164. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.05.002 [5] YUNUS A P,FAN X M,SUBRAMANIAN S S,et al. Unraveling the drivers of intensified landslide regimes in western Ghats,India[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2021,770:145357. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145357 [6] GELORMINI M,GRIPENBERG M,MARKE D,et al. Coverage survey and lessons learned from a pre-emptive cholera vaccination campaign in urban and rural communities affected by landslides and floods in Freetown Sierra Leone[J]. Vaccine,2023,41(14):2397-2403. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2023.01.026 [7] KUO Y S,TSAI Y J,CHEN Y S,et al. Movement of deep-seated rainfall-induced landslide at Hsiaolin Village during typhoon morakot[J]. Landslides,2013,10(2):191-202. doi: 10.1007/s10346-012-0315-y [8] ZHAN Q H,WANG S M,WANG L,et al. Analysis of failure models and deformation evolution process of geological hazards in Ganzhou City,China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2021,9:731447. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.731447 [9] QI X,LI Q H,JIAO Y Y,et al. Experimental study on response law and failure process of slopes in fully weathered granites under precipitation infiltration[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2021,80(20):685. doi: 10.1007/s12665-021-09995-8 [10] 刘红军,武闻禹,耿林,等. 全风化花岗岩滑坡稳定性与降雨关系分析[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2024,44(2):322-332.LIU H J,WU W Y,GENG L,et al. Analysis of the relationship between stability of fully weathered granite landslides and rainfall[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2024,44(2):322-332. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 李钰,陈明亮,黄会宝,等. 新华滑坡变形演化规律与预警判据[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):227-239.LI Y,CHEN M L,HUANG H B,et al. Deformation evolution law and early warning criterion of Xinhua landslide[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):227-239. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 张学臣. 基于渗流应力耦合的降雨型堆积层滑坡稳定性评价[J]. 工业建筑,2023,53(增刊1):508-512.ZHANG X C. Stability evaluation of rainfall-type accumulation landslide based on seepage stress coupling[J]. Industrial Construction,2023,53(S1):508-512. (in Chinese). [13] 张磊,刘岁海,顾彩玉,等. 基于FLAC3D软件的降雨型滑坡稳定性分析[J]. 中国水土保持,2023(5):53-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2023.05.020ZHANG L,LIU S H,GU C Y,et al. Stability analysis of rainfall induced landslides based on FLAC3D software[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China,2023(5):53-57. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0941.2023.05.020 [14] 兰腾达. 基于FLAC 3D数值分析的福安白莲寺降雨型滑坡稳定性评价[J]. 福建地质,2025,44(1):61-68.LAN T D. Stability evaluation of Bailian temple landslide in Fu'an City based on FLAC 3D[J]. Geology of Fujian,2025,44(1):61-68. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] CHEN Z,SONG D Q. Numerical investigation of the recent Chenhecun landslide (Gansu,China) using the discrete element method[J]. Natural Hazards,2021,105(1):717-733. doi: 10.1007/s11069-020-04333-w [16] 田仁珺. 基于PFC3D的庞家湾滑坡运动过程模拟研究[J]. 江西建材,2024(6):205-209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2890.2024.06.086TIAN R J. Simulation of motion process of pangjiawan landslide based on PFC3D[J]. Jiangxi Building Materials,2024(6):205-209. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2890.2024.06.086 [17] GUO J,CUI Y F,XU W J,et al. Numerical investigation of the landslide-debris flow transformation process considering topographic and entrainment effects:A case study[J]. Landslides,2022,19(4):773-788. doi: 10.1007/s10346-021-01791-6 [18] 庞海松,谢骏锦,张小明,等. 基于RAMMS数值模拟的短时强降雨型泥石流危险性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(2):215-225.PANG H S,XIE J J,ZHANG X M,et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow induced by short-time heavy rainfall based on RAMMS numerical simulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(2):215-225. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] FAN X M,YANG F,SIVA SUBRAMANIAN S,et al. Prediction of a multi-hazard chain by an integrated numerical simulation approach:The Baige landslide,Jinsha River,China[J]. Landslides,2020,17(1):147-164. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01313-5 [20] JABOYEDOFF M,CARREA D,DERRON M H,et al. A review of methods used to estimate initial landslide failure surface depths and volumes[J]. Engineering Geology,2020,267:105478. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105478 [21] LUCAS A ,MANGENEY A ,MÈGE D,et al. Influence of the scar geometry on landslide dynamics and deposits:Application to Martian landslides[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Planets,2011,116(E10). [22] SCHEIDEGGER A E. On the prediction of the reach and velocity of catastrophic landslides 2F,1T,14R[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts,1974,11(3):65. [23] SANDEEP C S,HE H,SENETAKIS K. Experimental and analytical studies on the influence of weathering degree and ground-environment analog conditions on the tribological behavior of granite[J]. Engineering Geology,2022,304:106644. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106644 [24] PRADHAN A M S,KIM Y T. Relative effect method of landslide susceptibility zonation in weathered granite soil:A case study in Deokjeok-ri Creek,South Korea[J]. Natural Hazards,2014,72(2):1189-1217. doi: 10.1007/s11069-014-1065-z [25] 唐辉明. 重大滑坡预测预报研究进展与展望[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):1-13.TANG H M. Advance and prospects of major landslides prediction and forecasting[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 吴善百. 广西东南部花岗岩残积土降雨型滑坡的起动机理研究[D]. 南宁:广西大学,2020.WU S B. Study on the initiation mechanism of rainfall-induced landslide of granite residual soil in southeast Guangxi[D]. Nanning:Guangxi University,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] BOGAARDI T,GUGLIELMI Y,MARC V,et al. Hydrogeochemistry in landslide research:A review[J]. Bulletin de la Societe Geologique de France,2007,178(2):113-126. doi: 10.2113/gssgfbull.178.2.113 [28] LIU H H,YU P,LU H T,et al. Experimental study on disaster mechanism of completely weathered granite landslide induced by extreme rainfall[J]. Geoenvironmental Disasters,2023,10(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40677-023-00234-9 [29] 陈慧娟,邹浩,訚遥,等. 持续强降雨影响下黄梅县袁山村三组滑坡破坏特征与成因分析[J]. 华南地质,2023,39(3):482-491. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-0013.2023.03.007CHEN H J,ZOU H,YIN Y,et al. Analysis of characteristics and causes of landslide damage in group 3 of Yuanshan Village,Huangmei County under the influence of continuous heavy rainfall[J]. South China Geology,2023,39(3):482-491. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-0013.2023.03.007 [30] SUN Y L,LIU Q X,XU H S,et al. Influences of different modifiers on the disintegration of improved granite residual soil under wet and dry cycles[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology,2022,32(4):831-845. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmst.2022.05.003 [31] YE P,YU B,CHEN W H,et al. Rainfall-induced landslide susceptibility mapping using machine learning algorithms and comparison of their performance in Hilly area of Fujian Province,China[J]. Natural Hazards,2022,113(2):965-995. doi: 10.1007/s11069-022-05332-9 [32] ZHANG J J,QIU H J,TANG B Z,et al. Accelerating effect of vegetation on the instability of rainfall-induced shallow landslides[J]. Remote Sensing,2022,14(22):5743. doi: 10.3390/rs14225743 [33] 王钟文. 基于动力过程的山区小流域泥石流灾害风险评估研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2020.WANG Z W. Hazard and risk assessment for debris flows in small watershed in mountainous area based on dynamic process[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 宋德光,吴瑞安,马德芹,等. 四川泸定昔格达组滑坡灾害运动过程模拟分析[J]. 地质通报,2023,42(12):2185-2197. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2023.12.014SONG D G,WU R A,MA D Q,et al. Simulation analysis of landslide disaster movement process in Xigeda Formation,Luding County,Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2023,42(12):2185-2197. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2023.12.014 [35] 熊朝正,吉锋,石豫川. 基于Massflow模型的青龙沟台风暴雨型泥石流运动特征研究[J]. 人民珠江,2023,44(3):17-22.XIONG C Z,JI F,SHI Y C. Movement characteristics of typhoon rainstorm-triggered debris flow in Qinglong Gully based on massflow model[J]. Pearl River,2023,44(3):17-22. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 冉林,马鹏辉,彭建兵,等. 甘肃黑方台“10·5” 黄土滑坡启动及运动特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):1-9.RAN L,MA P H,PENG J B,et al. The initiation and motion characteristics of the “10·5” loess landslide in the Heifangtai platform,Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 殷邦民. 尼续村高速远程滑坡流态化堆积与运动学特征研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2020.YIN B M. The research on rheological properties of landform and kinematics of nyixoi chongco rock avalanche[D]. Chengdu:Southwest Jiaotong University,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 石子健,陈稳,盛逸凡,等. 碎屑流滑坡变形及运动特征研究:以恩施市沙子坝滑坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2025,52(1):149-158.SHI Z J,CHEN W,SHENG Y F,et al. Deformation and movement characteristics of debris flow landslide:A case study of the Shaziba landslide in Enshi,China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2025,52(1):149-158. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 袁锦涛,韩培锋,欧小红,等. 基于DEM的滑坡碎屑流运动堆积特性研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2023,32(3):230-238.YUAN J T,HAN P F,OU X H,et al. Study of the accumulation characteristics of landslide debris flow movement based on DEM[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2023,32(3):230-238. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 丁邦政. 基于GIS和Massflow仿真的尾矿库溃坝危害下的桥梁风险评估[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学,2019.DING B Z. Bridge risk assessment under tailings dam failure hazard with GIS and massflow simulation[D]. Wuhan:Huazhong University of Science and Technology,2019. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: