Evaluation of coal structure based on machine learning logging inversion: A case from No.8 coal of Benxi Formation in Yulin area of Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
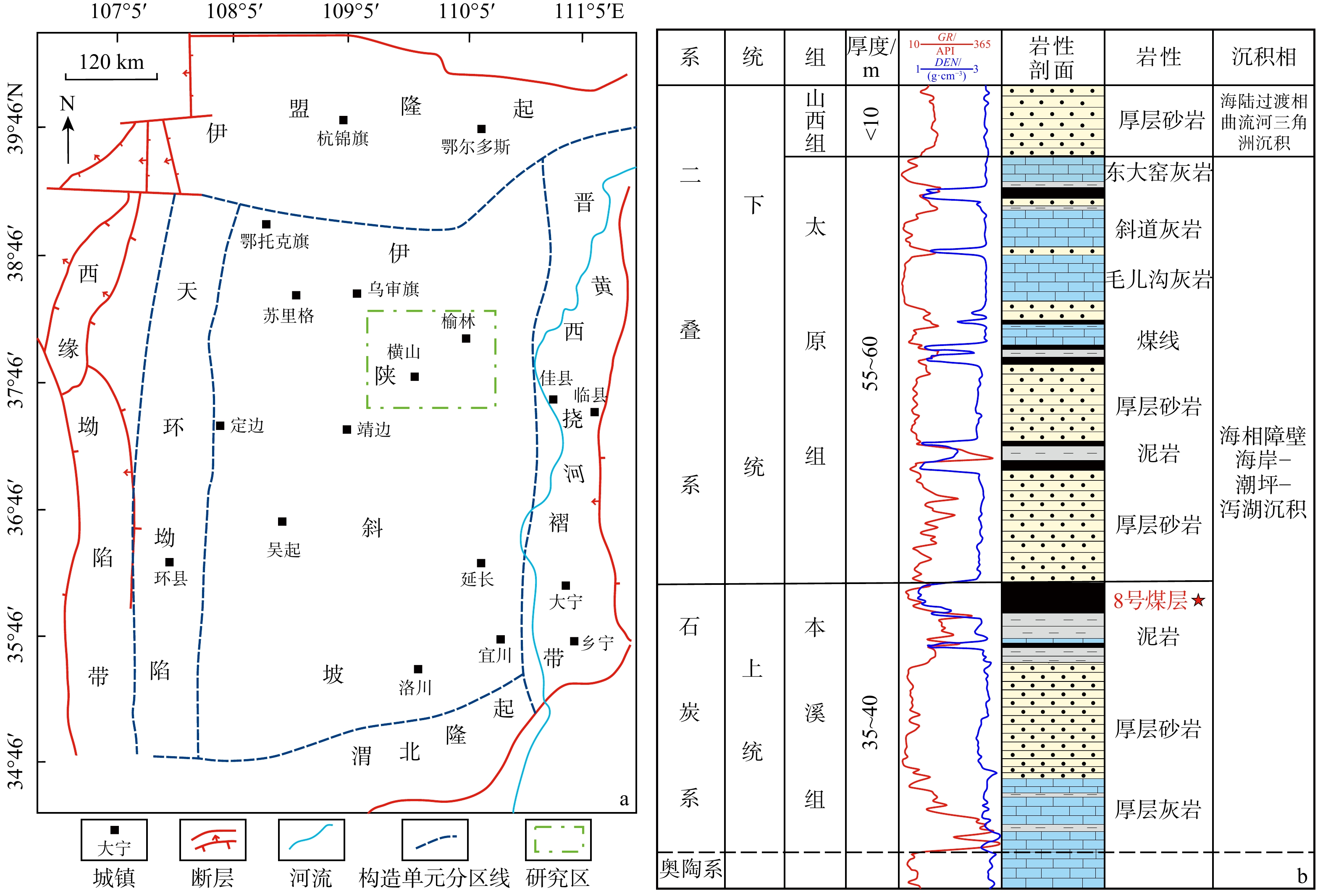
煤体结构直接影响煤储层孔裂隙发育,其准确判识对煤层压裂及煤层气开采具有重要指导价值。以鄂尔多斯盆地榆林地区本溪组8号煤为例,其煤体结构复杂,引入机器学习方法可解决煤层气储层测井中的非线性问题。采用区内已完成预处理的取心井数据,采用BP神经网络、随机森林以及XGBoost算法进行训练和全区煤体结构反演,并结合区内煤层顶底板及煤厚,剖析构造控制下的煤体结构发育特征。结果表明:①随机森林以及XGBoost算法相较于BP神经网络,对目标煤层煤体结构的反演结果更接近于岩心观测的真实情况,准确度更高;②榆林地区8号煤从NW向SE,煤体破碎程度逐渐加剧;③区内由中部至东南部发育构造带,在构造带影响下煤厚减小且原生结构煤逐渐转变为糜棱结构煤。本研究可为研究区实际煤层气生产中的煤体结构识别以及构造带分析提供参考。
Abstract:Objective Coal structure directly affects the pore and fracture system of coal reservoir. Therefore, the accurate identification of coal structure is crucial for guiding the coal seam fracturing and coalbed methane extraction. Taking the No. 8 coal seam of the Benxi Formation in the Yulin area of the Ordos Basin as an example, the complex coal structure necessitates the introduction of machine learning methods to address the nonlinear challenges in logging data interpretation.
Methods In this study, Back Propagation (BP) neural network, Random Forest, and XGBoost algorithms were used to train on preprocessed core well data from the study area to invert the coal structure across this region. By integrating the top and bottom plates of the coal seam and the coal seam thickness, we explored the development of coal structure under tectonic control.
Results The results indicated that: (1) Compared to the BP neural network, the Random Forest and XGBoost algorithms provided more accurate inversion results, aligning more closely with actual core observations. (2) The degree of coal structure fragmentation in No. 8 coal in the Yulin area increased progressively from northwest to southeast. (3) Tectonic zones, developed from the central to the southeastern part of the study area, caused a decrease in coal thickness and led to the transition of coal structure from primary coal to mylonitic coal.
Conclusion The three machine learning algorithms employed in this study successfully inverted the complex coal structure, with Random Forest and XGBoost achieving higher inversion accuracy. Additionally, the relationship between coal structural variations and the development of tectonic zones was analyzed, providing valuable insights for identifying coal structures and evaluating tectonic zones in coalbed methane production.
-
Key words:
- coal structure /
- machine learning /
- Back Propagation neural network /
- Random Forest /
- XGBoost /
- structural control /
- Ordos Basin /
- logging
-
表 1 随机森林算法主要参数设置
Table 1. Main parameter settings of Random Forest algorithm
环节 参数名 含义 设定值 样本数据划分 random_state 算法随机种子 1 test_size 验证集样本比例 0.3 决策树建立 max_depth 决策树树深 5 random_state 算法随机种子 42 随机森林建立 n_estimators 决策树数量 40 表 2 XGBoost算法主要参数设置
Table 2. Main parameter settings of XGBoost algorithm
参数类型 参数名 参数含义 设定值 通用参数 booster 弱学习器类型 gbtree silent 缄默运行判定 1 nthread 线程数 4 Tree Booster参数 eta 学习率 0.1 gamma 损失函数下降阈值 0.1 max_depth 树深 6 min_child_weight 最小建模样本数 3 subsample 决策树采样样本比例 0.7 colsample_bytree 决策树特征采样比例 0.7 Linear Booster参数 lambda L2正则化的惩罚系数 2 alpha L1正则化的惩罚系数 1 学习任务参数 objective 算法目标 multi:softmax num_class 目标类型数 3 seed 算法随机种子 1000 表 3 3种算法基于不同样本容量的适用情况
Table 3. Applicability of the three algorithms based on different sample sizes
算法类型 样本容量 小容量 中容量 大容量 BP神经网络 表现不佳,易导致过拟合或欠拟合 性能有所提升,但仍存在过拟合的风险 充分识别数据特征,反演准确度较高 随机森林 集成算法优势明显,反演准确度较高 性能稳定,准确度略微下降 性能稳定程度变差,泛化能力提高 XGBoost 正则化能力强大,反演准确度较高 充分发挥迭代优势,反演准确度较高 并行处理数据,保持反演高效性及准确性 -
[1] LI Y, WANG Y G, CHEN B Q, et al. Oxygen/nitrogen Co-doped flexible ultramicroporous carbon monolith with a high CH4 adsorption capacity for CH4/N2 separation from low-concentration coalbed methane[J]. Separation and Purification Technology, 2025, 359: 130582. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2024.130582 [2] 李倩, 李童, 蔡益栋, 等. 煤层气储层水力裂缝扩展特征与控因研究进展[J]. 煤炭学报, 2023, 48(12): 4443-4460.LI Q, LI T, CAI Y D, et al. Research progress on hydraulic fracture characteristics and controlling factors of coalbed methane reservoirs[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2023, 48(12): 4443-4460. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 蔡益栋, 高国森, 刘大锰, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘临兴中区煤系气富集地质条件及成藏模式[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(11): 25-36.CAI Y D, GAO G S, LIU D M, et al. Geological conditions for coal measure gas enrichment and accumulation models in Linxingzhong Block along the eastern margin of the Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(11): 25-36. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 刘羽欣, 邓志宇. 沁水盆地南部煤层气井产能影响地质分析[J]. 石化技术, 2020, 27(1): 101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2020.01.054LIU Y X, DENG Z Y. The geology influence factors analysis of CBM production in the southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 2020, 27(1): 101. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2020.01.054 [5] 刘大锰, 刘正帅, 蔡益栋. 煤层气成藏机理及形成地质条件研究进展[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(10): 1-16.LIU D M, LIU Z S, CAI Y D. Research progress on accumulation mechanism and formation geological conditions of coalbed methane[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(10): 1-16. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 房祥龙, 蔡益栋, 刘大锰. 基于低场核磁共振法的甲烷扩散特征研究[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2021, 33(10): 31-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2021.10.05FANG X L, CAI Y D, LIU D M. Study on methane diffusion features based on low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (LF-NMR) method[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2021, 33(10): 31-38. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2021.10.05 [7] 张瑶, 赵军龙. 基于地球物理测井的煤体结构识别及对煤层气开采的影响[J]. 矿产勘查, 2020, 11(10): 2194-2200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2020.10.018ZHANG Y, ZHAO J L. Coal structure identification based on geophysical logging and influence of coal-bed gas exploitation[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2020, 11(10): 2194-2200. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2020.10.018 [8] 中煤科工集团西安研究院. 煤体结构分类: GB/T30050-2013[S]. 北京: 中国煤炭工业协会, 2013: 1.CCTEG XI'AN Research Institute. Classification of coal-body structure: GB/T30050-2013[S]. Beijing: China National Coal Association, 2013: 1. (in Chinese) [9] 罗沙, 汪凌霞. 关于煤体结构判识方法的探讨[J]. 石油化工应用, 2017, 36(4): 98-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5285.2017.04.025LUO S, WANG L X. Discussion on methods of coal body structure identification[J]. Petrochemical Industry Application, 2017, 36(4): 98-101. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5285.2017.04.025 [10] 雷崇利. 用钻孔煤心鉴别煤层煤体结构及其应用[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2001, 29(2): 11-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2001.02.004LEI C L. Identification of coal block tcxture with core and application[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2001, 29(2): 11-13. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2001.02.004 [11] SHI J X, ZENG L B, DONG S Q, et al. Identification of coal structures using geophysical logging data in Qinshui Basin, China: Investigation by kernel Fisher discriminant analysis[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2020, 217: 103314. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2019.103314 [12] WANG Z H, CAI Y D, LIU D M, et al. Intelligent classification of coal structure using multinomial logistic regression, random forest and fully connected neural network with multisource geophysical logging data[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2023, 268: 104208. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2023.104208 [13] 李存磊, 杨兆彪, 孙晗森, 等. 多煤层区煤体结构测井解释模型构建[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(2): 721-730.LI C L, YANG Z B, SUN H S, et al. Construction of a logging interpretation model for coal structure from multi-coal seams area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(2): 721-730. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 徐光波, 赵金环, 崔周旗, 等. 沁水盆地南部安泽区块煤体结构测井识别研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(5): 179-184.XU G B, ZHAO J H, CUI Z Q, et al. Study on well logging identification of coal structure in Anze Block of southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46(5): 179-184. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 冯小英, 杨延辉, 左银卿, 等. 敏感属性与参数反演融合定量预测煤体结构[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2019, 54(5): 1115-1122.FENG X Y, YANG Y H, ZUO Y Q, et al. Coal structure quantitative prediction with sensitive-attribute and parameter-inversion fusion[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2019, 54(5): 1115-1122. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 邱峰, 刘晋华, 蔡益栋, 等. 基于测井的煤层力学特性评价及煤层气开发有利区预测: 以沁南郑庄区块3号煤层为例[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2023, 51(4): 46-56. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.10.0808QIU F, LIU J H, CAI Y D, et al. Mechanical property evaluation of coal bed and favorable area prediction of coalbed methane(CBM) development based on well logging: A case study of No. 3 coal bed in Zhengzhuang Block, southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2023, 51(4): 46-56. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.22.10.0808 [17] CHENG C, LI P, CHEN Y, et al. Research progress of reservoir logging evaluation based on machine learning [J]. Progress in Geophysiscs, 2022, 37(1), 164-177. [18] 郭建宏, 杜婷, 张占松, 等. 基于支持向量机与地球物理测井资料的煤体结构识别方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(3): 768-777.GUO J H, DU T, ZHANG Z S, et al. The coal structure identification method based on support vector machine and geophysical logging data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3): 768-777. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] ULLAH J, LI H, ASHRAF U, et al. A multidisciplinary approach to facies evaluation at regional level using well log analysis, machine learning, and statistical methods[J]. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources, 2023, 9(1): 152. doi: 10.1007/s40948-023-00689-y [20] 邓秀芹, 楚美娟, 王龙, 等. 中晚三叠世鄂尔多斯盆地两期沉降及其形成机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2024, 51(3): 501-512. doi: 10.11698/PED.20230410DENG X Q, CHU M J, WANG L, et al. Two stages of subsidence and its formation mechanisms in Mid-Late Triassic Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2024, 51(3): 501-512. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.20230410 [21] 席胜利, 闫伟, 刘新社, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地天然气勘探新领域、新类型及资源潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2024, 45(1): 33-51.XI S L, YAN W, LIU X S, et al. New fields, new types and resource potentials of natural gas exploration in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2024, 45(1): 33-51. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 赵伟波, 刘洪林, 王怀厂, 等. 煤相对孔隙结构控制作用: 以鄂尔多斯盆地榆林8#煤为例[J/OL]. 煤炭科学技术, 2023: 1-17. (2023-11-20). https: //kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=MTKJ20231025005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ.ZHAO W B, LIU H L, WANG H C, et al. Research on the controlling effect of coal facies on pore structure: Deeply buried coal seam 8 # in Yulin area, Ordos Basin for example[J/OL]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023: 1-17. (2023-11-20). https: //kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=MTKJ20231025005&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ.(in Chinese with English abstract [23] 闫建平, 蔡进功, 郑德顺, 等. 成像测井数据处理中分辨率匹配及深度校正方法[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2009, 37(1): 62-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2009.01.013YAN J P, CAI J G, ZHENG D S, et al. The method of resolution matching and depth correction in image logging data processing[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2009, 37(1): 62-65. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2009.01.013 [24] FU X H, QIN Y, WANG G G X, et al. Evaluation of gas content of coalbed methane reservoirs with the aid of geophysical logging technology[J]. Fuel, 2009, 88(11): 2269-2277. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.06.003 [25] WANG Z H, CAI Y D, LIU D M, et al. A review of machine learning applications to geophysical logging inversion of unconventional gas reservoir parameters[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2024, 258: 104969. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2024.104969 [26] 王健, 徐加放, 赵密福, 等. 基于神经网络的钻井液漏失裂缝宽度预测研究[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2023, 51(9): 81-88. doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.05.0240WANG J, XU J F, ZHAO M F, et al. Prediction of crack width of drilling fluid leakage based on neural network[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2023, 51(9): 81-88. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12363/issn.1001-1986.23.05.0240 [27] 徐海文, 史家财, 汪腾. 基于深度全连接神经网络的离港航班延误预测模型[J]. 计算机应用, 2022, 42(10): 3283-3291.XU H W, SHI J C, WANG T. Departure flight delay prediction model based on deep fully connected neural network[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2022, 42(10): 3283-3291. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] ZHANG L, WANG F L, SUN T, et al. A constrained optimization method based on BP neural network[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2018, 29(2): 413-421. doi: 10.1007/s00521-016-2455-9 [29] WANG H J, JIN T. Comparative study of BP neural network and RBF neural network in surface reconstruction[C]// Anon. 2019 4th International Conference on Mechanical, Control and Computer Engineering (ICMCCE). Hohhot, China: IEEE. 2019: 405-4054. [30] 杨阳, 雷友波, 王倩楠, 等. 基于二维散射变换的湖相碳酸盐岩储层厚度预测方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2024, 67(4): 1601-1612. doi: 10.6038/cjg2023Q0974YANG Y, LEI Y B, WANG Q N, et al. Reservoir thickness prediction method of lacustrine carbonate based on two-dimension scattering transformation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(4): 1601-1612. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg2023Q0974 [31] FENG R H, GRANA D, BALLING N. Imputation of missing well log data by random forest and its uncertainty analysis[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2021, 152: 104763. [32] 刘粤蛟, 赖富强, 徐浩, 等. 基于测井曲线深程度耦合的页岩岩相智能识别方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(1): 308-320.LIU Y J, LAI F Q, XU H, et al. Intelligent identification methods for shale lithology based on the coupling deeply of logging curves[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(1): 308-320. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 林秋婷, 刘建军, 逄辉, 等. 应用MIPSO-XGBoost算法预测汽油产率[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2023, 39(3): 659-667. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2023.03.019LIN Q T, LIU J J, PANG H, et al. Application of MIPSO-XGBoost algorithm in prediction of gasoline yield[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 2023, 39(3): 659-667. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2023.03.019 [34] MADAAN A, PANDEY J. Development of machine learning based model for low-temperature PEM fuel cells[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2024, 188: 108754. [35] CHEN T Q, GUESTRIN C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. San Francisco: ACM, 2016: 785-794. [36] REN Y G, LV Z Q, XU Z Q, et al. Slurry-ability mathematical modeling of microwave-modified lignite: A comparative analysis of multivariate non-linear regression model and XGBoost algorithm model[J]. Energy, 2023, 281: 128143. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2023.128143 [37] 赵军, 汪峻宇, 赖强, 等. 基于XGBoost算法的走滑断裂内部特征带的精细识别[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(2): 182-192.ZHAO J, WANG J Y, LAI Q, et al. Fine-grained identification of internal characteristic zones within strike-slip faults via the XGBoost algorithm[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(2): 182-192. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 黎子豪, 蒋恕. 基于机器学习和SHAP算法的声波测井曲线重构及可解释性分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(1): 321-331.LI Z H, JIANG S. Reconstructing and interpreting analysis of sonic logging curves based on machine learning and SHAP algorithm[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(1): 321-331. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 刘大锰, 周三栋, 蔡益栋, 等. 地应力对煤储层渗透性影响及其控制机理研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2017, 45(6): 1-8.LIU D M, ZHOU S D, CAI Y D, et al. Study on effect of geo-stress on coal permeability and its controlling mechanism[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2017, 45(6): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 刘大锰, 王颖晋, 蔡益栋. 低阶煤层气富集主控地质因素与成藏模式分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(6): 1-8.LIU D M, WANG Y J, CAI Y D. Analysis of main geological controls on coalbed methane enrichment and accumulation patterns in low rank coals[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46(6): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 李可心, 张聪, 李俊, 等. 沁水盆地南部煤层气水平井射孔优化[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2024, 45(5): 581-589.LI K X, ZHANG C, LI J, et al. Optimization of perforation in CBM horizontal wells in southern Qinshui Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2024, 45(5): 581-589. (in Chinese with English abstract -





 下载:
下载: