Genesis of the Naneng gold deposit in southeastern Yunnan: Evidence from in-situ trace elements and isotopes of sulfides
-
摘要:
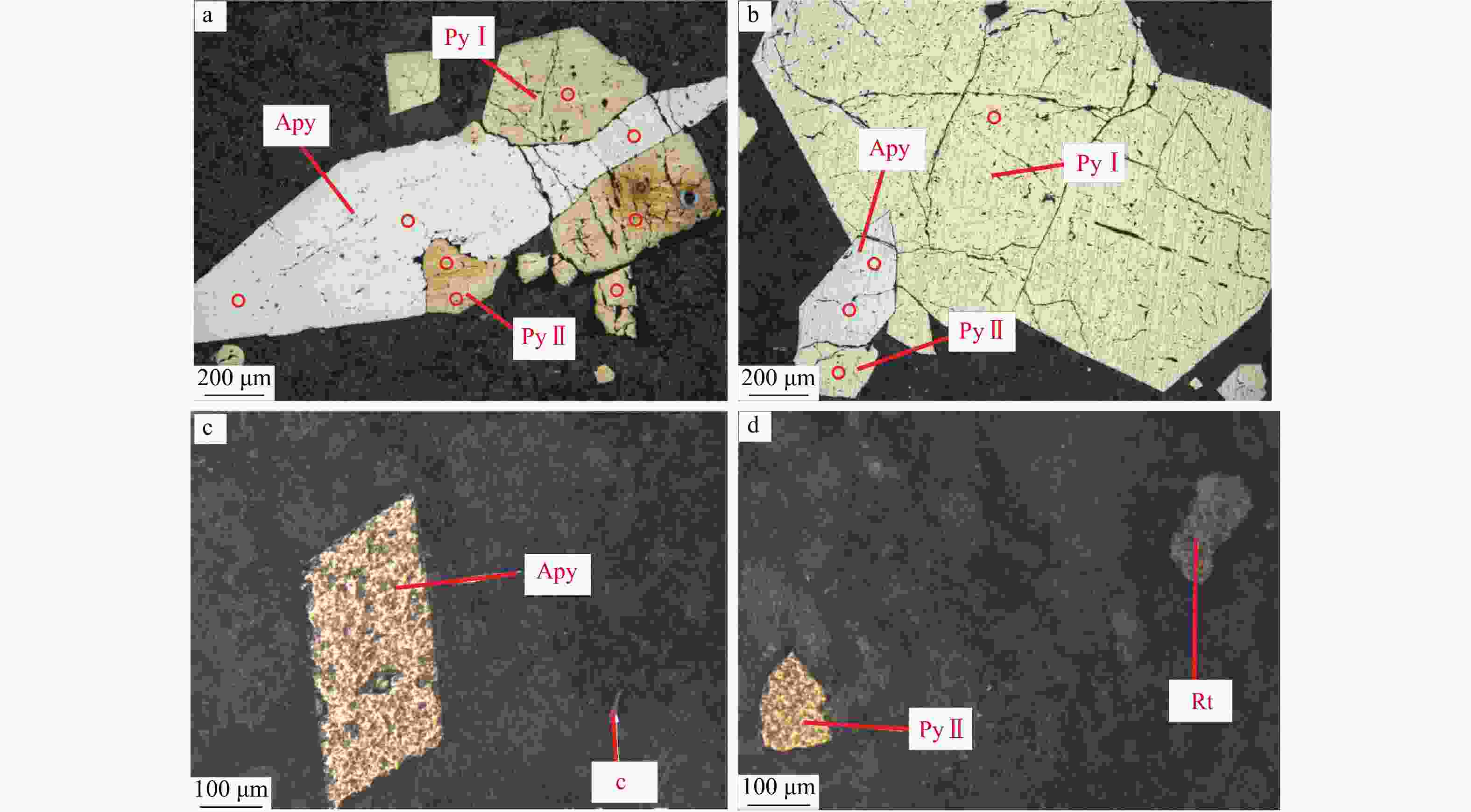
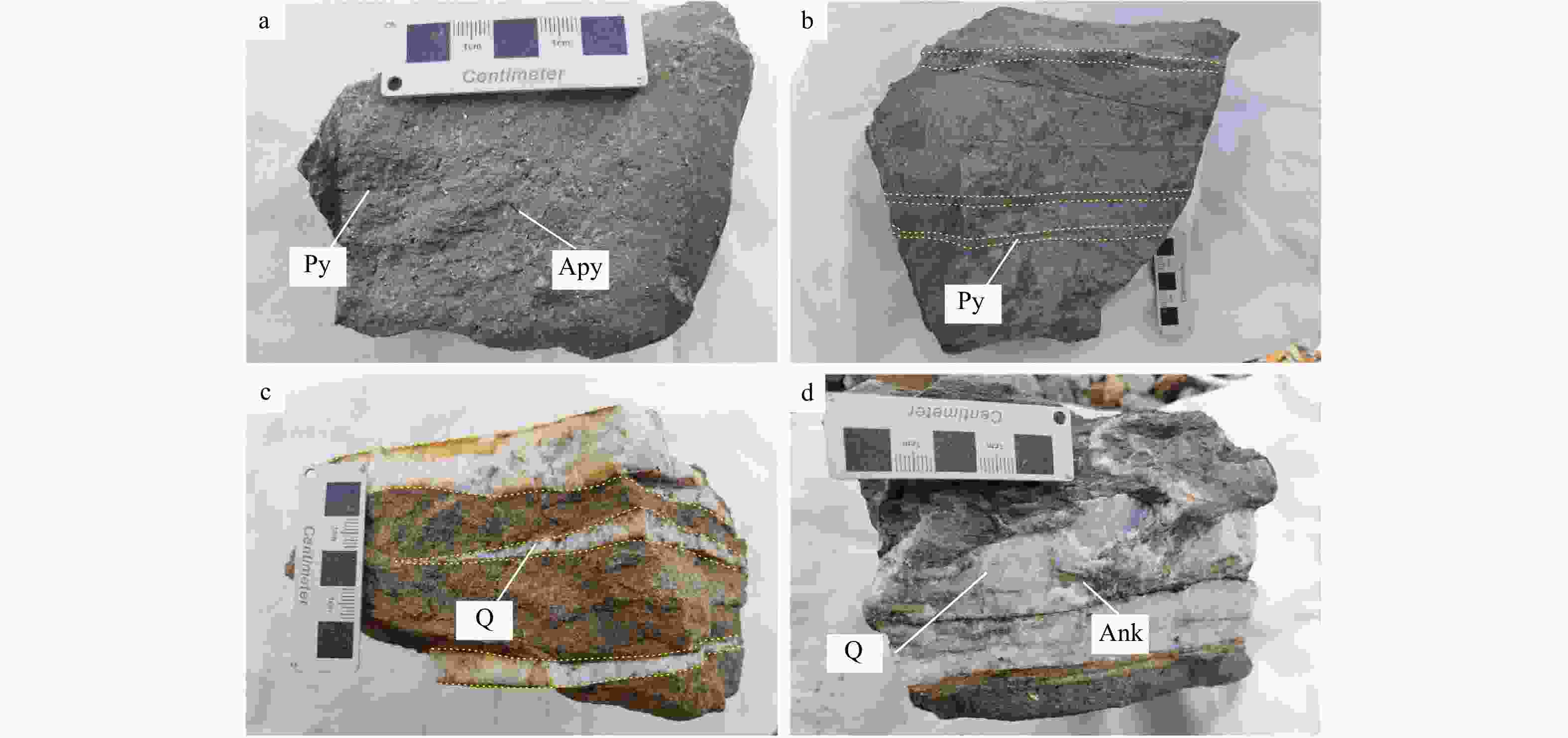
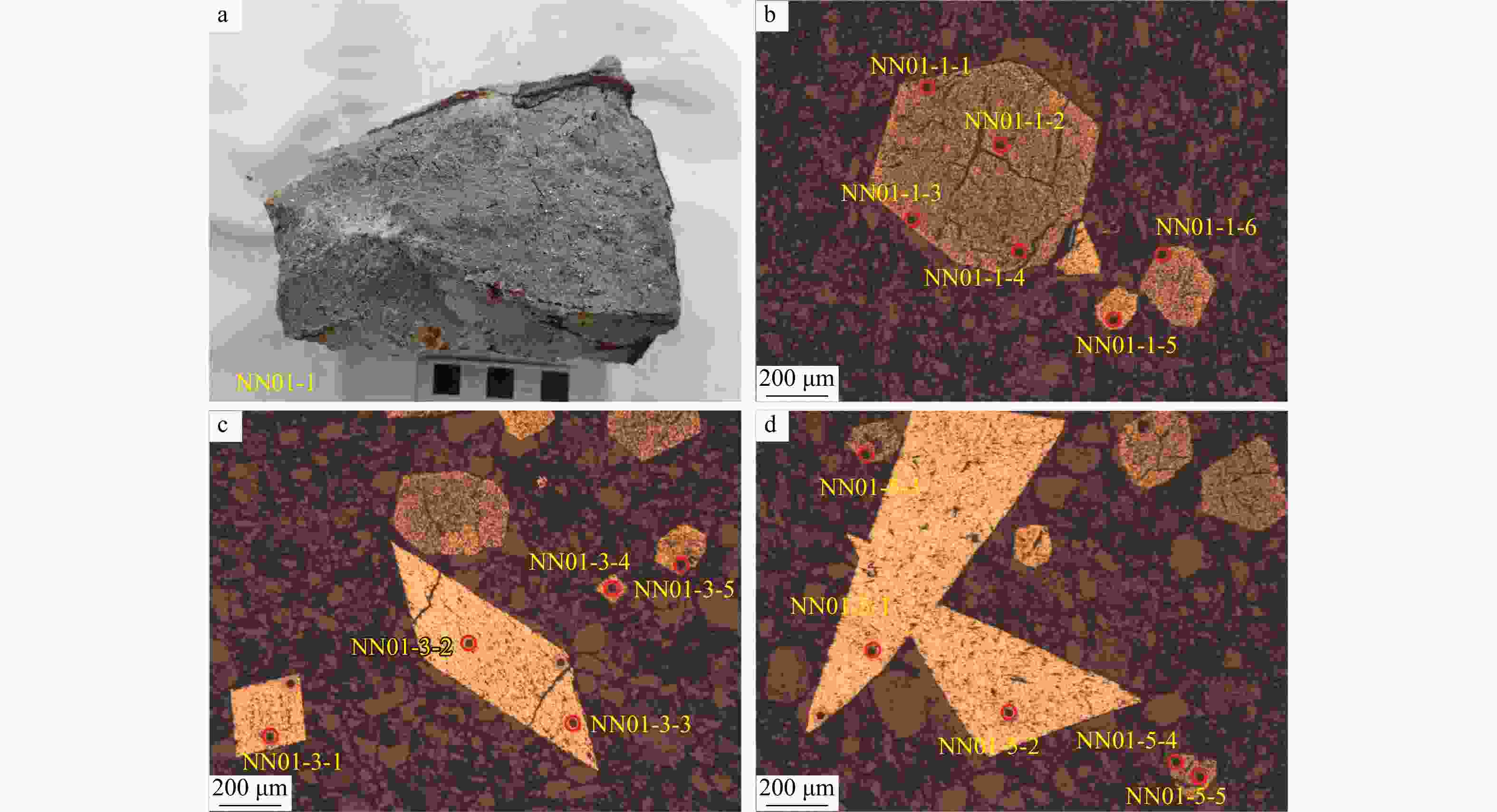
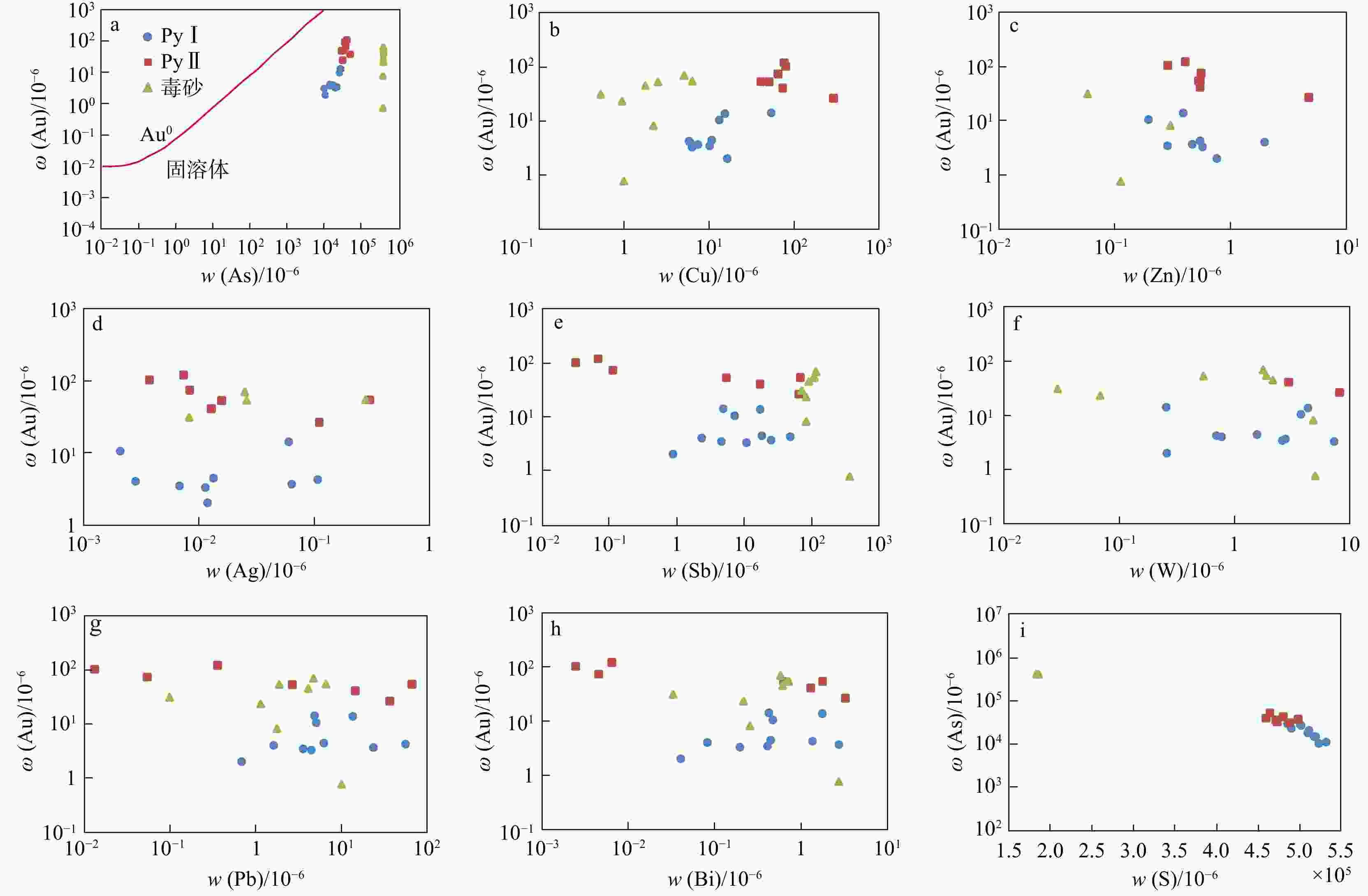
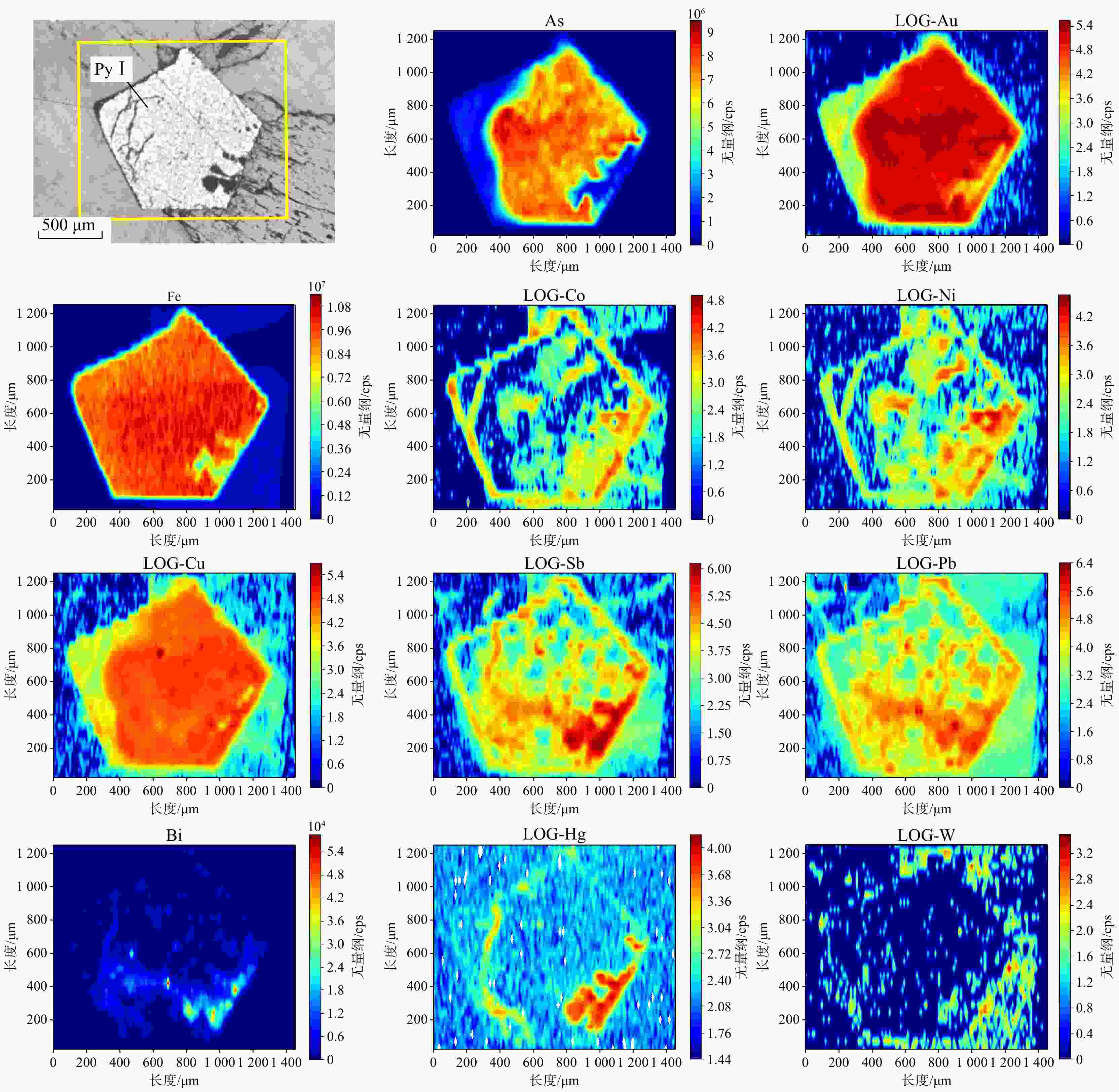
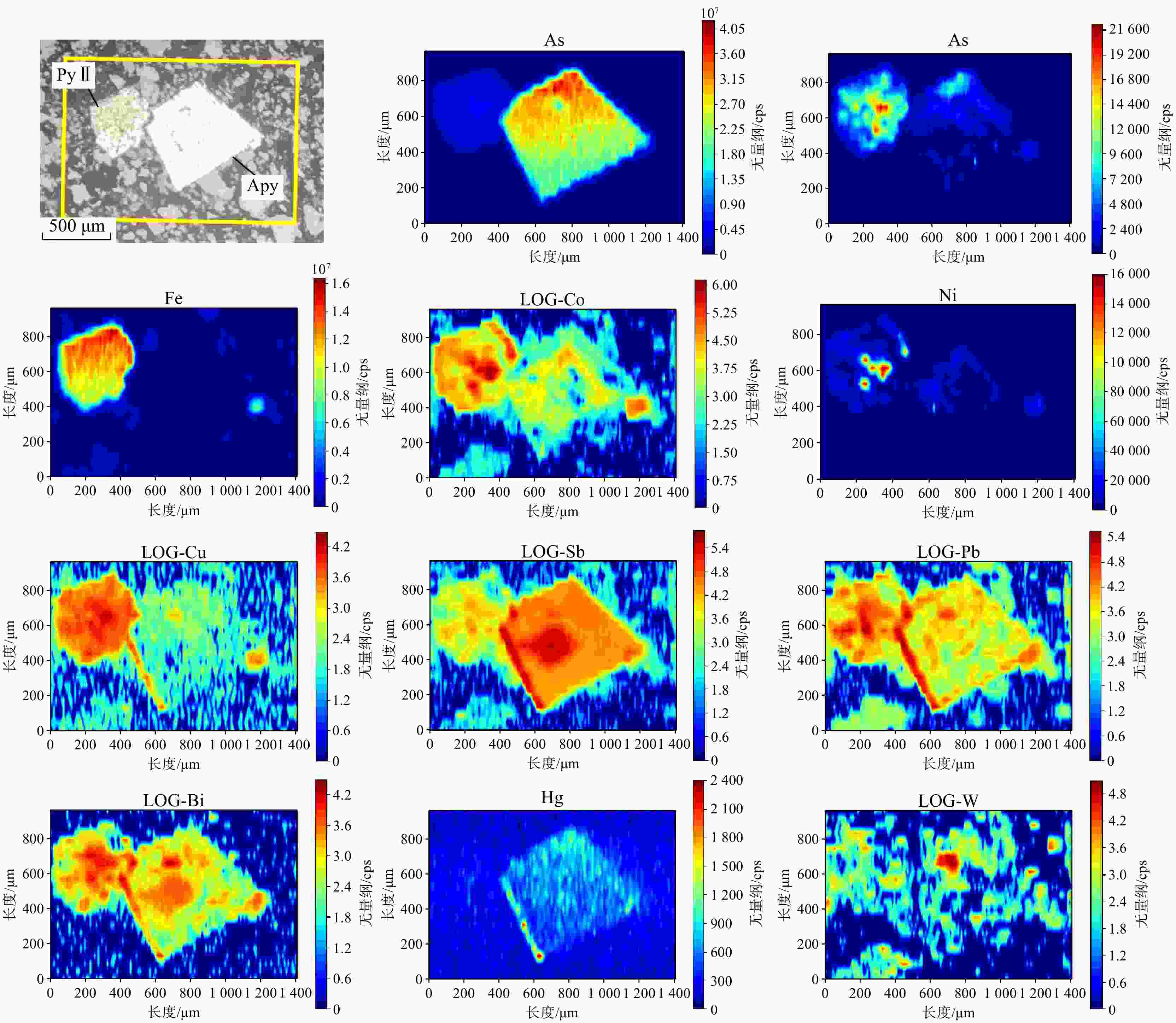
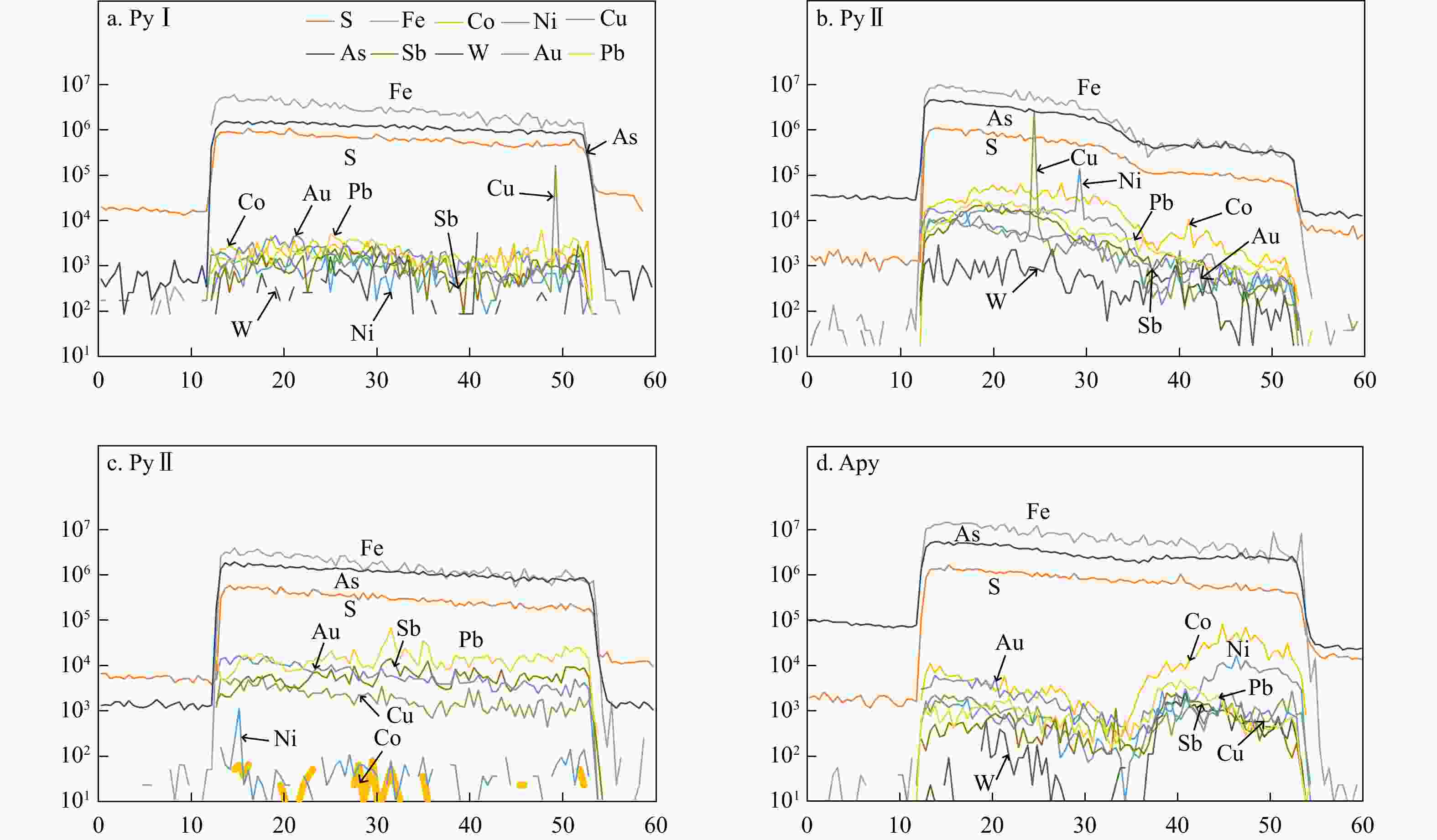
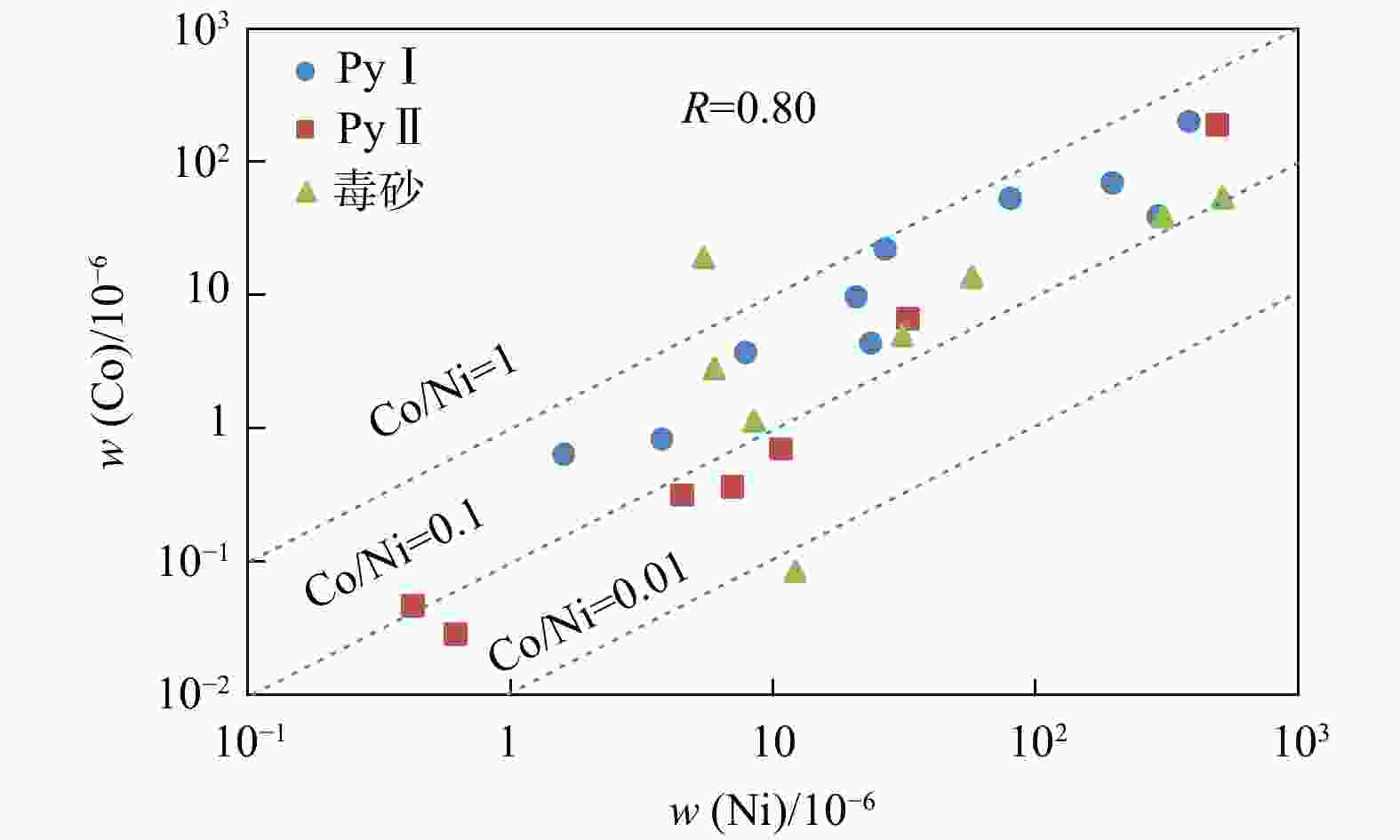
那能金矿床是滇东南地区一个重要的中型卡林型金矿,研究其矿床成因对在滇东南地区寻找此类金矿床具有重要意义。详细的野外调研和室内观察表明那能金矿发育2个世代黄铁矿(PyI和PyII),利用LA-ICP-MS技术对载金矿物黄铁矿和毒砂进行了原位微量元素和硫同位素分析,探讨了成矿物质来源和矿床成因。LA-ICP-MS分析结果显示PyⅠ含有一定量的Au(质量分数均值6.37×10−6),主要富集Co、Ni、Se、W等元素;与PyⅠ相比,PyⅡ微量元素分布特征相似,但Au质量分数(均值68.02×10−6)偏高,相对富集Au、As、Sb、Cu等元素;毒砂中Au质量分数均值为36.02×10−6,主要富集As、Ni、Sb、Se、Au等元素,Zn、Ag、Hg、Tl元素含量较低。载金矿物
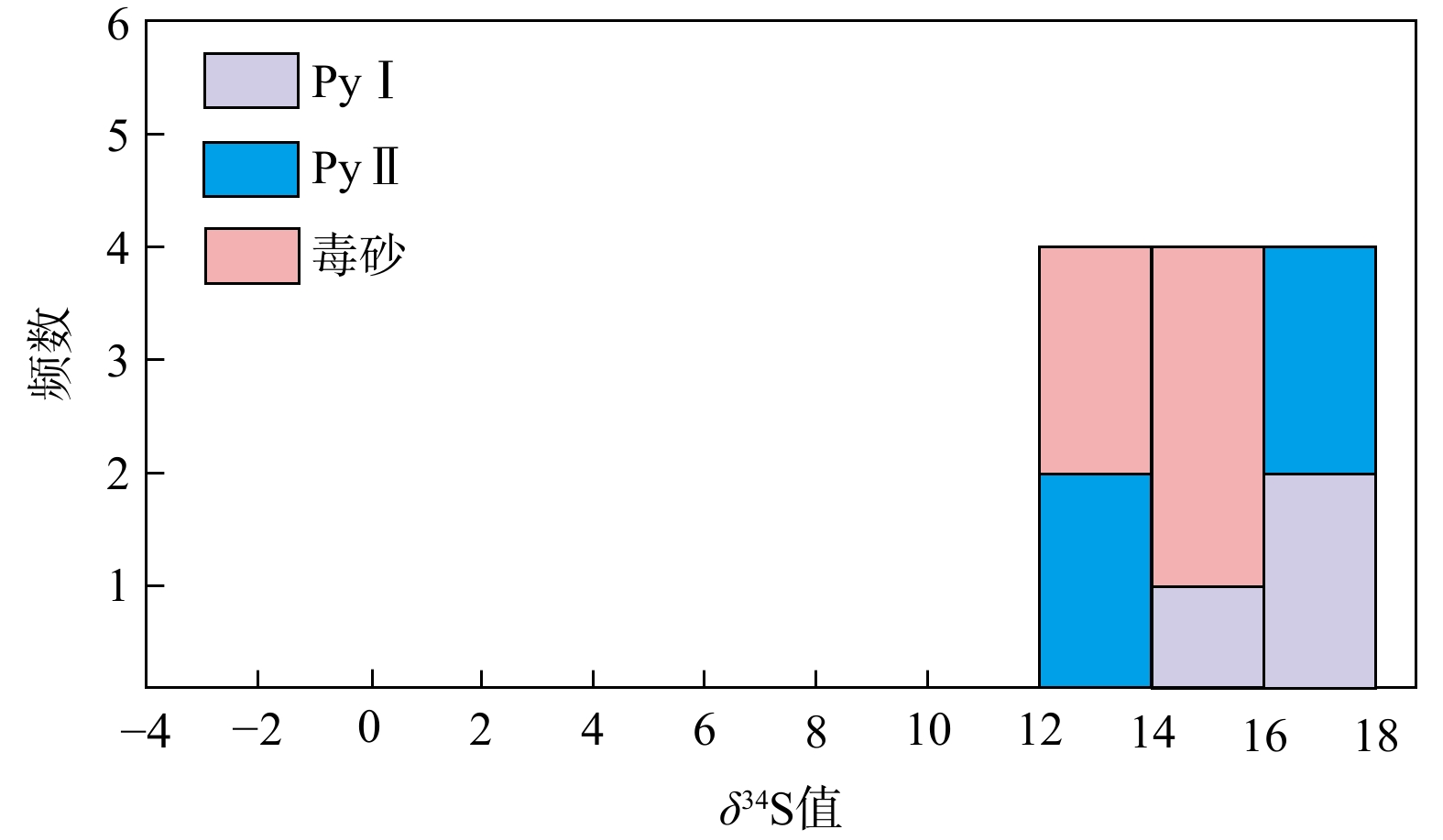
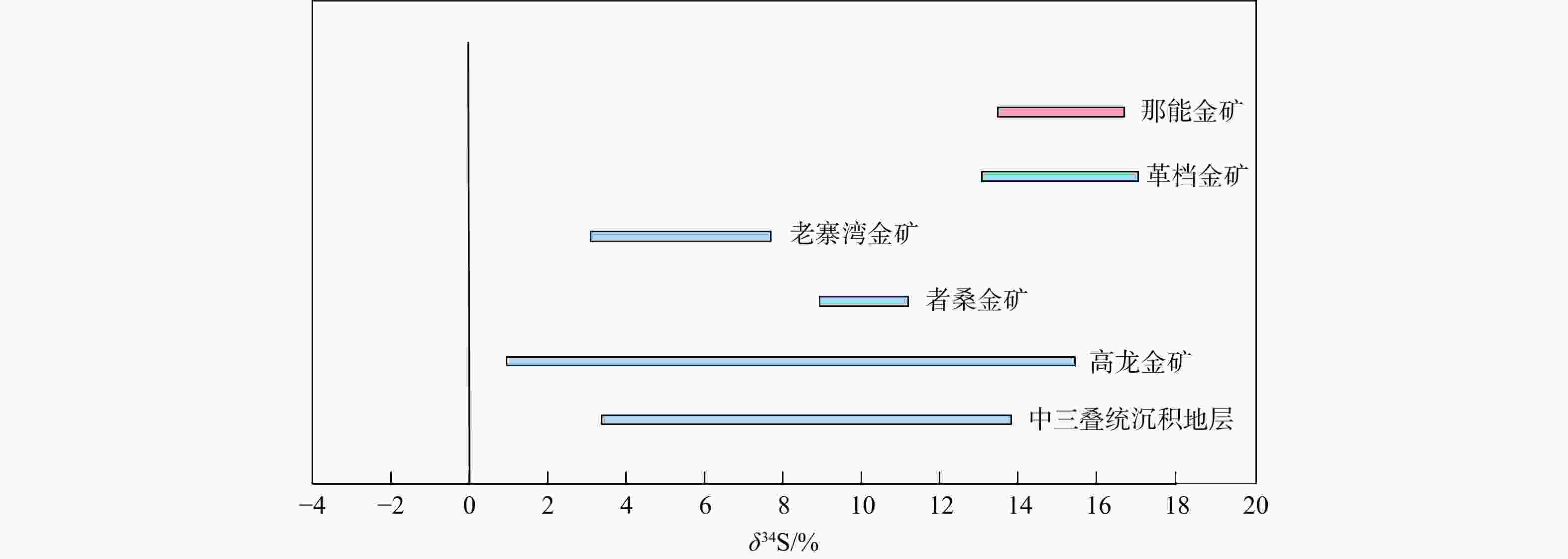
δ 34S值分布范围较为一致,主要集中在13.7‰~16.5‰,暗示载金矿物的S可能主要来自于围岩地层。初步分析表明在那能金矿形成过程中,富含Au、As、Sb等微量元素的中低温热液流体,在相对稳定的环境中形成PyⅠ黄铁矿,少量Au以固溶体(Au+)形式与PyⅠ同时沉淀,在PyⅡ阶段,区内强烈的构造活动使得成矿流体上涌,与围岩地层发生硫化反应后,流体中H2S浓度降低,Au-HS络合物失稳,Au过饱和沉淀后以纳米级包裹体(Au0)形式在PyⅡ黄铁矿中大量富集。Abstract:Objective The Naneng gold deposit is an important medium-sized Carlin type gold deposit in southeastern Yunnan, and studying its genesis is of great significance for searching for such gold deposits in southeastern Yunnan.
Methods Two generations of pyrite (PyI and PyII) were found to develop in the Naneng gold deposit during detailed field survey and indoor observation, and trace elements and sulfur isotopes of gold-bearing minerals are analyzed by LA-ICP-MS to constrain the source of ore-forming materials and ore genesis.
Results LA-ICP-MS analyses show that PyI contains a small amount of Au (mean 6.37×10−6), which is relatively enriched in elements such as Co, Ni, Se, W; The distribution characteristics of trace elements in PyII and PyI are similar, but the content of Au (mean 68.02×10−6) is relatively high, and As, Sb, Cu elements are enriched in PyII; The average Au content of arsenopyrite is 36.02×10−6, and arsenopyrite is mainly enriched in elements such as As、Ni、Sb、Se、Au, while Zn, Ag, Hg and Tl elements are low. In addition, gold-bearing minerals in the Naneng gold deposit have consistent in situ
δ 34S values, ranging from 13.7‰ to 16.5‰, indicating that the S of gold-bearing minerals mainly come from the surrounding rocks.Conclusion It is preliminarily concluded that PyI was formed in a relatively stable environment by medium to low temperature hydrothermal fluid from the same source rich in trace elements such as Au、As、Sb, and a small amount of Au precipitated simultaneously with PyI in the form of solid solution (Au+). In the PyII stage, the intense tectonic activity in the area caused ore-forming fluid to upswell, and after sulfidation reaction with surrounding rock strata, the concentration of H2S in the fluid decreased, Au-HS complex became unstable, and Au supersaturated precipitation was enriched in PyII in the form of nanoscale inclusions (Au0).
-
Key words:
- gold-bearing mineral /
- LA-ICP-MS /
- in situ sulfur isotope /
- ore genesis /
- Naneng gold
-
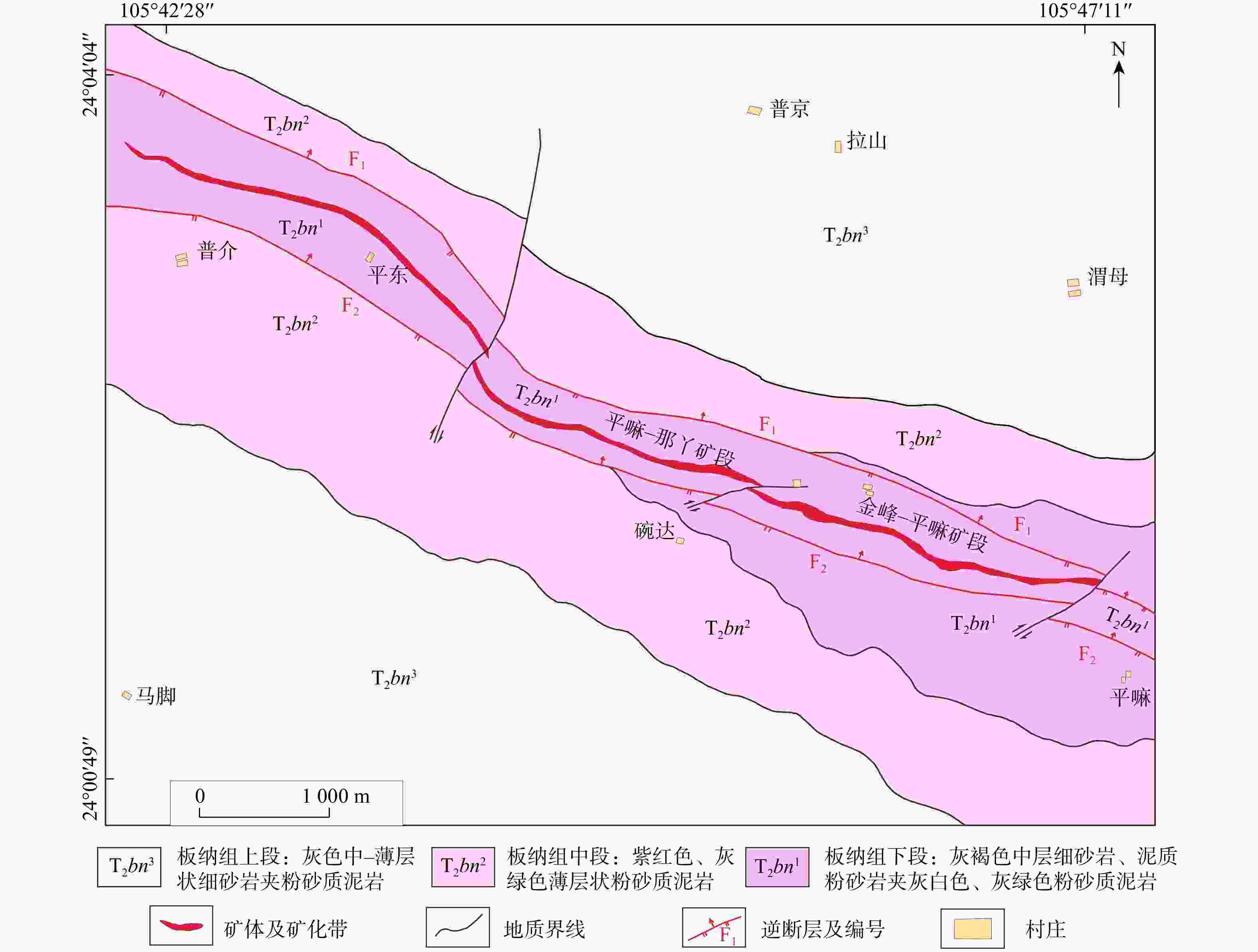
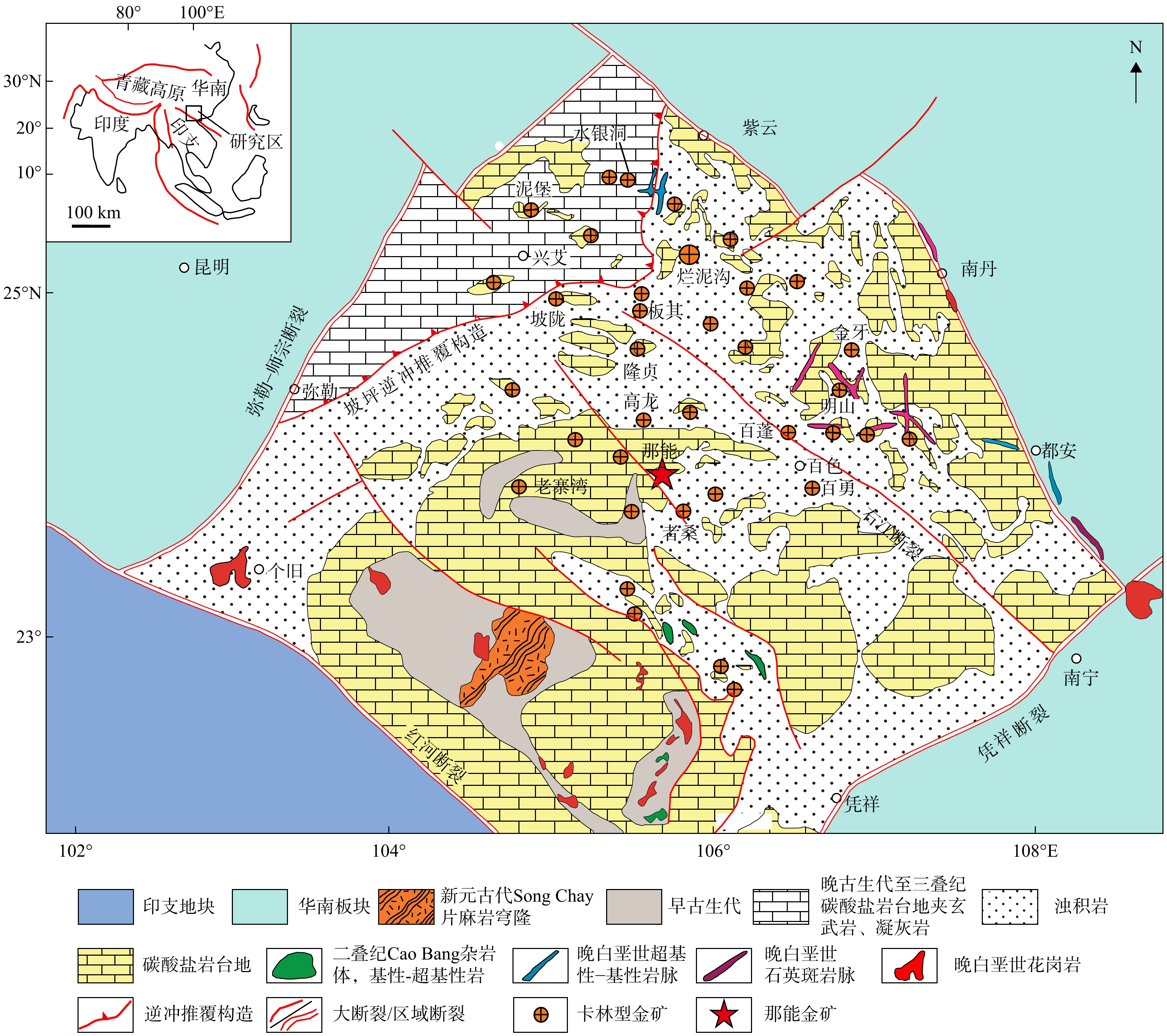
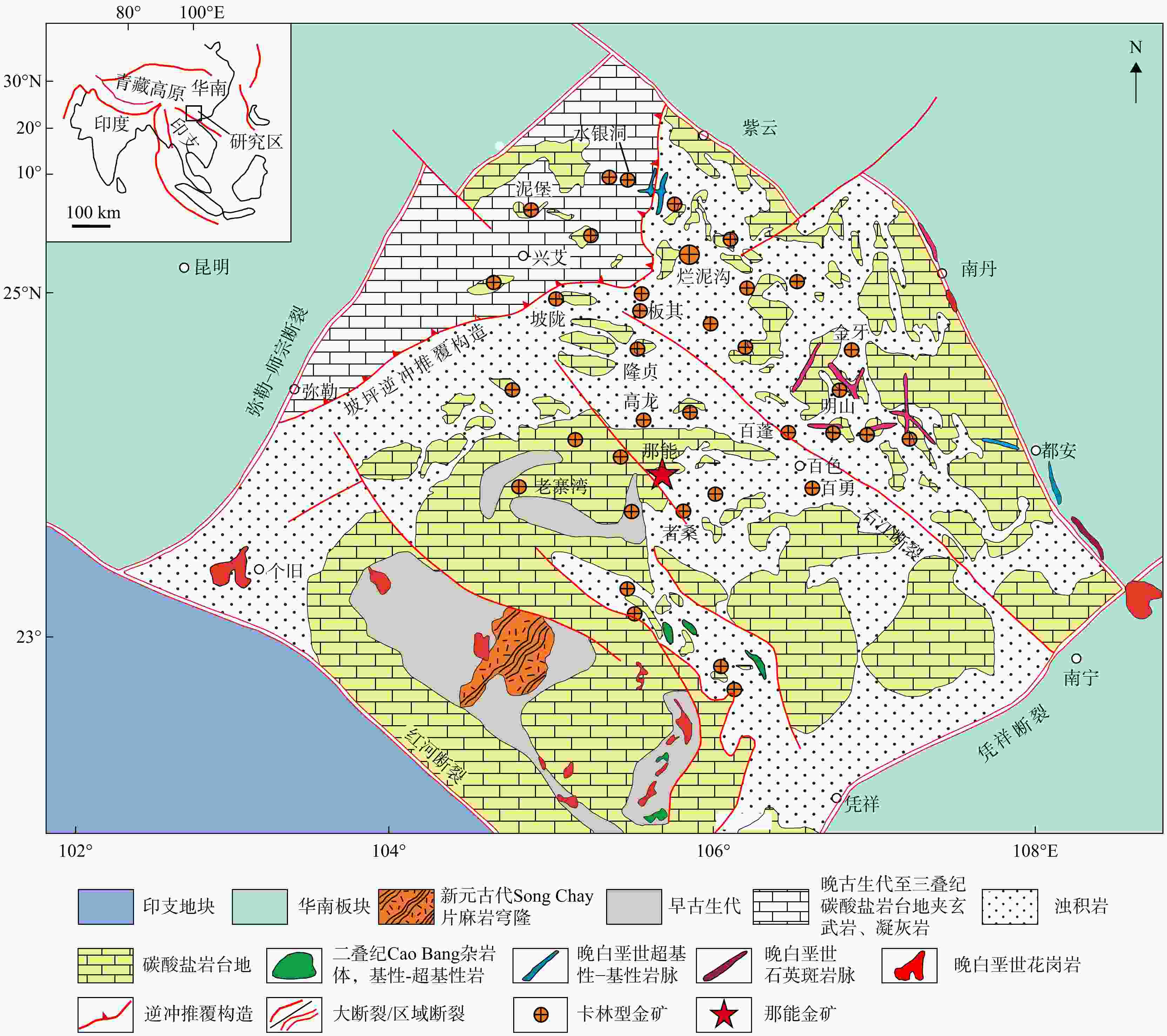
图 1 滇黔桂“金三角”卡林型金矿分布图(据文献[19]修改)
Figure 1. Distribution map of Carlin-type gold deposits in the "Golden Triangle" of Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi
表 1 那能金矿床载金矿物LA-ICP-MS 微量元素分析结果
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis results of gold-bearing mineral in Naneng gold deposit
wB/10−6 点号 矿物 Fe S Co Ni Cu Zn As Se Ag Sn Sb W Au Hg Tl Pb Bi NN01-1-1 PyⅠ 452352 516974 0.66 1.57 10.78 0.00 14668 1.78 0.01 0.18 18.32 1.57 4.43 0.26 0.70 6.21 0.45 NN01-1-2 437831 500378 40.20 285.82 54.16 0.00 28345 1.18 0.06 0.06 4.89 0.26 14.27 0.07 0.00 4.84 0.43 NN01-1-3 453960 518812 3.80 7.71 6.03 1.96 14800 1.48 0.00 0.02 2.36 0.77 4.02 0.06 0.01 1.62 0.08 NN01-1-4 457154 522461 0.85 3.71 6.35 0.58 10291 3.05 0.01 0.36 10.88 7.33 3.29 0.10 0.01 4.46 0.20 NN01-4-1 465036 531470 22.61 26.21 16.41 0.76 11014 3.09 0.01 0.00 0.88 0.26 2.02 0.04 0.00 0.68 0.04 NN01-4-2 438836 501526 54.46 78.42 13.24 0.20 26739 0.00 0.00 0.33 7.23 3.77 10.53 0.00 0.01 5.08 0.47 NN01-2-1 445704 509376 9.91 20.33 5.81 0.55 18089 2.29 0.11 0.00 48.35 0.70 4.24 0.13 0.04 55.66 1.36 NN01-2-2 424530 485178 204.96 375.30 15.42 0.39 29374 2.68 0.00 0.16 17.35 4.33 13.78 0.00 0.01 13.49 1.76 NN01-2-3 428482 489694 70.93 191.76 7.43 0.47 23041 0.00 0.06 0.11 25.07 2.77 3.67 0.05 0.01 23.50 2.74 NN01-2-4 446820 510651 4.46 23.07 10.18 0.29 20612 8.60 0.01 0.25 4.61 2.60 3.45 0.05 0.01 3.57 0.41 平均值 445070 508652 41.29 101.39 14.58 0.52 19697 2.41 0.03 0.15 13.99 2.44 6.37 0.07 0.08 11.91 0.79 NN01-1-5 PyⅡ 435574 497800 0.05 0.42 80.24 0.29 37430 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.03 0.00 103.59 0.04 0.00 0.01 0.00 NN01-1-6 419809 479781 0.37 6.88 76.51 0.41 42446 1.97 0.01 0.05 0.07 0.00 121.72 0.03 0.02 0.36 0.01 NN01-5-3 426610 487554 0.03 0.61 50.98 0.53 30805 0.16 0.02 0.00 5.44 0.00 53.80 0.11 0.08 2.67 0.63 NN01-5-4 412026 470887 0.32 4.44 40.75 0.55 36272 0.99 0.30 0.00 68.19 0.00 54.46 0.10 0.05 66.16 1.77 NN01-5-5 401748 459140 0.72 10.50 64.70 0.56 39901 0.57 0.01 0.06 0.11 0.00 74.63 0.03 0.00 0.05 0.00 NN01-3-4 413568 472649 193.44 482.13 292.36 4.73 32930 0.76 0.11 1.70 65.20 8.15 26.62 0.24 0.12 36.52 3.25 NN01-3-5 405897 463883 6.84 32.09 73.71 0.55 52533 0.00 0.01 0.25 17.22 2.96 41.31 0.08 0.00 14.49 1.29 平均值 416462 475956 28.83 76.72 97.04 1.09 38902 0.64 0.07 0.30 22.32 1.59 68.02 0.09 0.04 17.18 0.99 NN01-3-1 毒砂 322414 184236 5.07 30.44 6.37 0.00 417457 0.00 0.28 0.17 110.69 1.89 55.03 0.42 0.04 6.58 0.72 NN01-3-2 322840 184480 54.94 504.74 2.51 0.00 415697 13.27 0.03 0.00 106.42 0.54 53.87 0.35 0.00 1.88 0.69 NN01-3-3 321162 183521 13.89 56.13 1.78 0.00 419960 0.00 0.00 0.30 90.98 2.16 45.56 0.33 0.01 4.08 0.62 NN01-4-1 324695 185540 2.87 5.88 0.95 0.00 413464 1.42 0.00 0.14 83.93 0.07 23.39 0.15 0.01 1.14 0.22 NN01-4-2 323804 185031 39.35 298.57 5.10 0.00 413584 4.53 0.03 0.00 116.35 1.78 70.17 0.34 0.01 4.72 0.58 NN01-4-3 324423 185385 0.09 11.95 0.53 0.06 413218 21.16 0.01 0.00 71.89 0.03 31.16 0.01 0.02 0.10 0.03 NN01-5-1 324981 185703 19.50 5.34 1.00 0.11 405414 6.18 0.00 0.41 368.90 5.02 0.77 0.14 0.05 9.97 2.73 NN01-5-2 326103 186345 1.16 8.30 2.21 0.30 405725 6.05 0.00 0.37 83.34 4.82 8.20 0.13 0.02 1.76 0.26 平均值 323803 185030 17.11 115.17 2.56 0.06 413065 6.58 0.04 0.17 129.06 2.04 36.02 0.23 0.02 3.78 0.73 表 2 那能金矿载金矿物硫同位素组成
Table 2. Sulfur isotope composition of gold-bearing minerals in Naneng gold deposit
样品编号 矿物 δ34S/‰ 2α/‰ NN01 - 1 黄铁矿(PyⅠ) 16.2 0.1 NN01 - 2 黄铁矿(PyⅠ) 16.2 0.1 NN01 - 9 黄铁矿(PyⅠ) 14.8 0.1 NN01 - 6 黄铁矿(PyⅡ) 13.9 0.1 NN01 - 7 黄铁矿(PyⅡ) 16.3 0.1 NN01 - 8 黄铁矿(PyⅡ) 16.5 0.1 NN01 - 12 黄铁矿(PyⅡ) 15.1 0.1 NN01 - 3 毒砂 13.9 0.1 NN01 - 4 毒砂 13.7 0.1 NN01 - 5 毒砂 15.8 0.1 NN01 - 10 毒砂 14.7 0.1 NN01 - 11 毒砂 15.8 0.1 注:α.标准差。 -
[1] HU R Z, SU W C, BI X W, et al. Geology and geochemistry of Carlin-type gold deposits in China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2002, 37(3-4): 378-392. doi: 10.1007/s00126-001-0242-7 [2] 吕世琨, 李爱平, 杨绍文, 等. 滇东南那能金矿带之断裂控矿[J]. 云南地质, 2003(1): 47-55.LYU S K, LI A P, YANG S W, et al. The ore control of fault in Naneng gold deposit zone, Southeast Yunnan[J]. Yunnan Geology, 2003(1): 47-55. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 罗刚. 滇东南地区微细粒浸染型金矿床地质特征和成矿规律研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2010.LUO G. Study for the micro-disseminate gold deposit, geological and metallogenic in southeastern Yunnan area[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 张继安. 云南省富宁县那能金矿床地质特征及控矿规律[J]. 黄金, 2011, 32(7): 26-29.ZHANG J A. Geological feature and ore-controlling regulation of Naneng gold deposit in Funing County, Yunnan[J]. Gold, 2011, 32(7): 26-29. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] LARGE R R, BULL S W, MASLENNIKOV V V. A carbonaceous sedimentary source-rock model for Carlin-type and orogenic gold deposits[J]. Economic Geology and the Bulletin of the Society of Economic Geologists, 2011, 106(3): 331-358. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.106.3.331 [6] CIOBANU C L, COOK N J, PRING A, et al. 'Invisible gold' in bismuth chalcogenides[J]. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(7): 1970-1999. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2009.01.006 [7] COOK N J, CIOBANU C L, GEORGE L, et al. Trace element analysis of minerals in magmatic- hydrothermal ores by laser ablation inductively- coupled plasma mass spectrometry: Approaches and opportunities[J] Minerals, 2016, 4(6): 111. [8] LI W, COOK N J, XIE G Q, et al. Textures and trace element signatures of pyrite and arsenopyrite from the Gutaishan Au-Sb deposit, South China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2019, 54(4): 591-610. doi: 10.1007/s00126-018-0826-0 [9] 张红雨, 赵青青, 赵刚, 等. 黄铁矿微量元素LA-ICP-MS原位微区分析方法及其在金矿床研究中的应用[J]. 矿床地质, 2022, 41(6): 1182-1199.ZHANG H Y, ZHAO Q Q, ZHAO G, et al. In situ LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis of pyrite and its application in study of Au deposit[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2022, 41(6): 1182-1199. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 周涛发, 张乐骏, 袁峰, 等. 安徽铜陵新桥Cu-Au-S矿床黄铁矿微量元素LA-ICP-MS原位测定及其对矿床成因的制约[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(2): 306-319.ZHOU T F, ZHANG L J, YUAN F, et al. LA-ICP-MS in situ trace element analysis of pyrite from the Xinqiao Cu-Au-S deposit in Tongling, Anhui, and its constraints on the ore genesis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(2): 306-319. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] DEDITIUS P A, REICH M, KESLER E S, et al. The coupled geochemistry of Au and As in pyrite from hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Geochimica et Cosmo chimica Acta, 2014, 140(1): 644-670. [12] YANG L, WANG Q, LARGE R R, et al. Texture and geochemistry of pyrite from the Jinya, Nakuang and Gaolong gold deposits in the Youjiang Basin: Implications for basin-scale gold mineralization[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2022, 57(8): 1367-1390. doi: 10.1007/s00126-022-01115-1 [13] LARGE R R, DANYUSHEVSKY L, HOLLIT C, et al. Gold and trace element zonation in pyrite using a laser imaging technique: Implications for the timing of gold in orogenic and Carlin-style sediment-hosted deposits[J]. Economic Geology and the Bulletin of the Society of Economic Geologists, 2009, 104(5): 635-668. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.104.5.635 [14] 范宏瑞, 李兴辉, 左亚彬, 等. LA-(MC)-ICPMS和(Nano)SIMS硫化物微量元素和硫同位素原位分析与矿床形成的精细过程[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(12): 3479-3496.FAN H R, LI X H, ZUO Y B, et al. In situ LA-(MC)-ICPMS and ( Nano) SIMS trace elements and sulfur isotope analyses on sulfides and application to confine metallogenic process of ore deposit[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(12): 3479-3496. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 周伶俐, 曾庆栋, 孙国涛, 等. LA-ICPMS原位微区面扫描分析技术及其矿床学应用实例[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(7): 1964-1978. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.07.02ZHOU L L, ZENG Q D, SUN G T, et al. Laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICPMS) elemental mapping and its applications in ore geology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(7): 1964-1978. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.07.02 [16] GREGORY D D, CRACKNELL J M, LARGE R R, et al. Distinguishing ore deposit type and barren sedimentary pyrite using Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry trace element data and statistical analysis of large data sets[J]. Economic Geology, 2019, 114(4): 771-786. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.4654 [17] STEADMAN J A, LARGE R R, OLIN P H, et al. Pyrite trace element behavior in magmatic- hydrothermal environments: An LA-ICPMS imaging study[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 218. 103878. [18] 邓军, 李文昌, 符德贵, 等. 西南三江南段新生代金成矿系统[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. 2012.DENG J, LI W C, FU D G, et al. Cenozoic gold metallogenic system in the southern section of Sanjiang region, Southwest China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House. 2012. (in Chinese [19] 马克忠, 陈懋弘. 桂西北百勇金矿、百蓬金矿粗粒黄铁矿和毒砂的矿物学特征[J]. 矿物学报, 2020, 40(5): 601-614.MA K Z, CHEN M H. Mineralogical characteristics of coarse-grained pyrites and arsenopyrites in the Baiyong and Baipeng gold deposits, Northwest Guangxi, China[J]. Acta Mineralogical Sinica, 2020, 40(5): 601-614. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] COOK N J, CIOBANU L C, MERIA D, et al. Arsenopyrite-pyrite association in an orogenic gold ore: Tracing mineralization history from textures and trace elements[J]. Economic Geology and the Bulletin of the Society of Economic Geologists, 2013, 108(6): 1273-1283. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.108.6.1273 [21] TANG L, ZHAO Y, ZHANG S T, et al. Origin and evolution of a porphyry-breccia system: Evidence from zircon U-Pb, molybdenite Re-Os geochronology, in situ sulfur isotope and trace elements of the Qiyugou deposit, China[J]. Gondwana Research (International Geoscience Journal), 2021(89): 88-104. [22] SHENG Y M , TANG L , ZHANG S T, et al. Distal gold mineralization associated with porphyry system: The case of Hongzhuang and Yuanling deposits, East Qinling, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2022, 142: 104701. [23] 李增胜, 朱笑青, 卢焕章, 等. 硫化物中“不可见金”的赋存状态研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(3): 81-86.LI Z S, ZHU X Q, LU H Z, et al. Advances and current problems in the study of the occurrence of "Invisible Gold" in sulfides[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(3): 81-86. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] REICH M, KESLER E S, UTSUNOMIYA S, et al. Solubility of gold in arsenian pyrite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(11): 2781-2796. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.01.011 [25] HU X, GONG Y, ZENG G, et al. Multistage pyrite in the Getang sediment-hosted disseminated gold deposit, southwestern Guizhou Province, China: Insights from textures and in situ chemical and sulfur isotopic analyses[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 99: 16. [26] ZHOU Z, YONEZU K, IMAI A, et al. Trace elements mineral chemistry of sulfides from the Woxi Au Au-Sb-W deposit, southern China[J]. Resource Geology, 2021, 72(1): 16. [27] AGANGI A, HOFMANN A, WOHLGEMUTHU- EBERWASSER C C. Pyrite zoning as a record of mineralization in the Ventersdorp Contact Reef, Witwatersrand Basin, South Africa[J]. Economic Geology, 2013, 108: 1243-1272. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.108.6.1243 [28] 高振敏, 杨竹森, 李红阳, 等. 黄铁矿载金的原因和特征[J]. 高校地质学报, 2000(2): 156-62.GAO Z M, YANG Z S, LI H Y , et al. Genesis and characteristics of gold hosted by pyrite[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2000(2): 156-62. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] KESLER S E, RICIPUTI L C, YE Z. Evidence for a magmatic origin for Carlin-type gold deposits: isotopic composition of sulfur in the Betze- Post-Screamer deposit, Nevada, USA[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2005, 40(2): 127-136. doi: 10.1007/s00126-005-0477-9 [30] CHANG Z, LARGE R R, MASLENNIKOV V. Sulfur isotopes in sediment-hosted orogenic gold deposits: Evidence for an early timing and a seawater sulfur source[J]. Geology, 2008, 36(12): 971-974. doi: 10.1130/G25001A.1 [31] RIELLI A, TOMKINS A G, NEBEL O, et al. Sulfur isotope and PGE systematics of metasomatised mantle wedge[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2018, 497: 181-192. [32] 韩小梦, 郭云成, 段留安, 等. 胶莱盆地东北缘前垂柳金矿床S、Pb同位素组成: 对成矿物质来源的指示[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(3): 210-221.HAN X M, GUO Y C, DUAN L A, et al. S and Pb isotopic compositions of the Qianchuiliu gold deposit on the northeastern margin of the Jiaolai Basin: Implication on the source of ore-forming materia[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(3): 210-221. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] OHMOTO H. Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 1972, 67(5): 551-578. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.67.5.551 [34] 赵静, 梁金龙, 李军, 等. 贵州太平洞金矿床载金黄铁矿的矿物学特征及原位微区硫同位素分析[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2019, 43(2): 258-270.ZHAO J, LIANG J L, LI J, et al. Mineralogical characteristics and in situ sulfur isotopic compositions of Au-bearing pyrites in the Taipingdong gold deposit, Guizhou Province[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2019, 43(2): 258-270. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 严子清, 石文杰, 张鹏涛, 等. 胶东大尹格庄金矿成矿流体时空演化及矿床成因: 来自流体包裹体、成矿元素和H-O-S-Pb同位素证据[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 156-174.YAN Z Q, SHI W J, ZHANG P T, et al. Ore genesis and vertical variations of ore-forming fluids in the Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Constraints from fluid inclusions, ore forming elements, and H-O-S-Pb isotopes[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 156-174. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 陈履安, 周琦. 热化学硫酸盐还原作用(TSR) 与贵州汞(金锑)矿床成因机制再探讨: 从黔东锰矿古天然气渗漏沉积成矿理论得到的启示[J]. 地质论评, 2019, 65(2): 431-437.CHEN L A, ZHOU Q. Sulfate thermochemical reduction (TSR) and rediscussion on the formation mechanism of mercury (gold / antimony) deposits in Guizhou: Inspiration from the theory of paleo-gas seepage- sedimentary mineralization of manganese deposits in eastern Guizhou[J]. Geological Review, 2019, 65(2): 431-437. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 林清, 刘德汉. 黔西南金矿有机质地球化学研究[J]. 地球化学, 1995(4): 402-408.LIN Q, LIU D H. Organic geochemical study of gold deposits in southwestern Guizhou province[J]. Geochimica, 1995(4): 402-408. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 章永梅, 顾雪祥, 摆祥, 等. 云南富宁者桑金矿床硫铅同位素地球化学特征与成矿物质来源[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(1): 32-39.ZHANG Y M, GU X X, BAI X, et al. Sulfur and lead isotopic composition characteristics of the Zhesang gold deposit in Funing County, Yunnan[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(1): 32-39. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 魏震环, 李连生, 敬成贵. 云南革档金矿地质特征及成因[J]. 黄金地质科技, 1993(03): 22-28.WEI Z H, LI L S, JING C G. Geological characteristics and genesis of Gedang gold deposit in Yunnan Province[J]. Gold Geological Science and Technology, 1993(03): 22-28. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 陈翠华, 赵德坤, 顾雪祥, 等. 云南老寨湾金矿床成矿物质来源探讨[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2014, 33(1): 23-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2014.01.003CHEN C H, ZHAO D K, GU X X, et al. Discussion on ore-forming material sources of the Laozhaiwan gold deposit, Yunan[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2014, 33(1): 23-30. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2014.01.003 [41] 张永忠, 李蘅, 刘悟辉, 等. 广西高龙微细浸染型金矿床同位素地球化学研究[J]. 地球学报, 2008, 29(6): 697-702.ZHANG Y Z, LI H, LIU W H, et al. Isotope geochemistry of the Gaolong micro-disseminated gold deposit in Guangxi[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2008, 29(6): 697-702. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] 李存有. 高龙金矿同位素地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 贵金属地质, 1994(02): 123-130.LI C Y. The isotope earth chemical feature of the Gaolong gold deposit and its geology significance[J]. Journal of Precious Metallic Geology, 1994(02): 123-130. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] 宋学信, 张景凯. 中国各种成因黄铁矿的微量元素特征[C]//佚名, 中国地质科学院矿床地质研究所文集(18). 北京: 矿床地质研究所, 19860.SONG X X, ZHANG J K. Minor elements in pyrites of various genetic types from China[C]//Anon. Bulletin of the Institute of Mineral Deposits, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences. Beijing: Institute of Mineral Derosits, 1986: 10. (in Chinese) [44] 严育通, 李胜荣, 贾宝剑, 等. 中国不同成因类型金矿床的黄铁矿成分标型特征及统计分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(4): 214-226.YAN Y T, LI S R, JIA B J, et al. Composition typomorphic characteristic and statistic analysis of pyrite in gold deposits of different genetic types[J]. Earrh Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(4): 214-226. (in Chinese with English abstract [45] LARGE R R, HALPIN A J, DANYUSHEVSKY V L, et al. Trace element content of sedimentary pyrite as a new proxy for deep-time ocean-atmosphere evolution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2014, 389: 209-220. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2013.12.020 [46] HOU L, PENG H J, DING J, et al. Textures and in situ chemical and isotopic analyses of pyrite, Huijiabao trend, Youjiang Basin, China: Implications for paragenesis and source of sulfur[J]. Economic Geology and the Bulletin of the Society of Economic Geologists, 2016, 111(2): 331-353. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.111.2.331 [47] KUSEBAUCH C, GLEESON A S, OELZE M. Coupled partitioning of Au and As into pyrite controls formation of giant Au deposits[J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(5): 5891. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aav5891 [48] 陈威鸿, 刘玉平, 杨昌毕, 等. 滇东南茶花寨金矿床载金黄铁矿LA-ICPMS原位微量元素组成与地质意义[J]. 矿物学报, 2024, 44(1): 122-132.CHEN W H, LIU Y P, YANG C B, et al. LA-ICPMS trace element compositions of gold-bearing pyrite in the Chahuazhai gold deposit, SE Yunnan: Implications for ore genesis[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2024, 44(1): 122-132. (in Chinese with English abstract [49] 陈懋弘, 毛景文, 陈振宇, 等. 滇黔桂“金三角”卡林型金矿含砷黄铁矿和毒砂的矿物学研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, 28(5): 539-557.CHEN M H, MAO J W, CHEN Z Y, et al. Mineralogy of arsenian pyrites and arsenopyrites of Carlin-type gold deposits in Yunnan-Guizhou- Guangxi "golden triangle" area, southwestern China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2009, 28(5): 539-557. (in Chinese with English abstract [50] 胡瑞忠, 付山岭, 肖加飞. 华南大规模低温成矿的主要科学问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(11): 3239-3251.HU R Z, FU S L, XIAO J F. Major scientific problems on low-temperature metallogenesis in South China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(11): 3239-3251. (in Chinese with English abstract [51] PI Q H, HU R Z, XIONG B, et al. In situ SIMS U-Pb dating of hydrothermal rutile: Reliable age for the Zhesang Carlin-type gold deposit in the golden triangle region, SW China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2017, 52(8): 1179-1190. doi: 10.1007/s00126-017-0715-y -




 下载:
下载: