Geochemical characteristics and genesis mechanisms of Kawu geothermal water in Tibet
-
摘要:
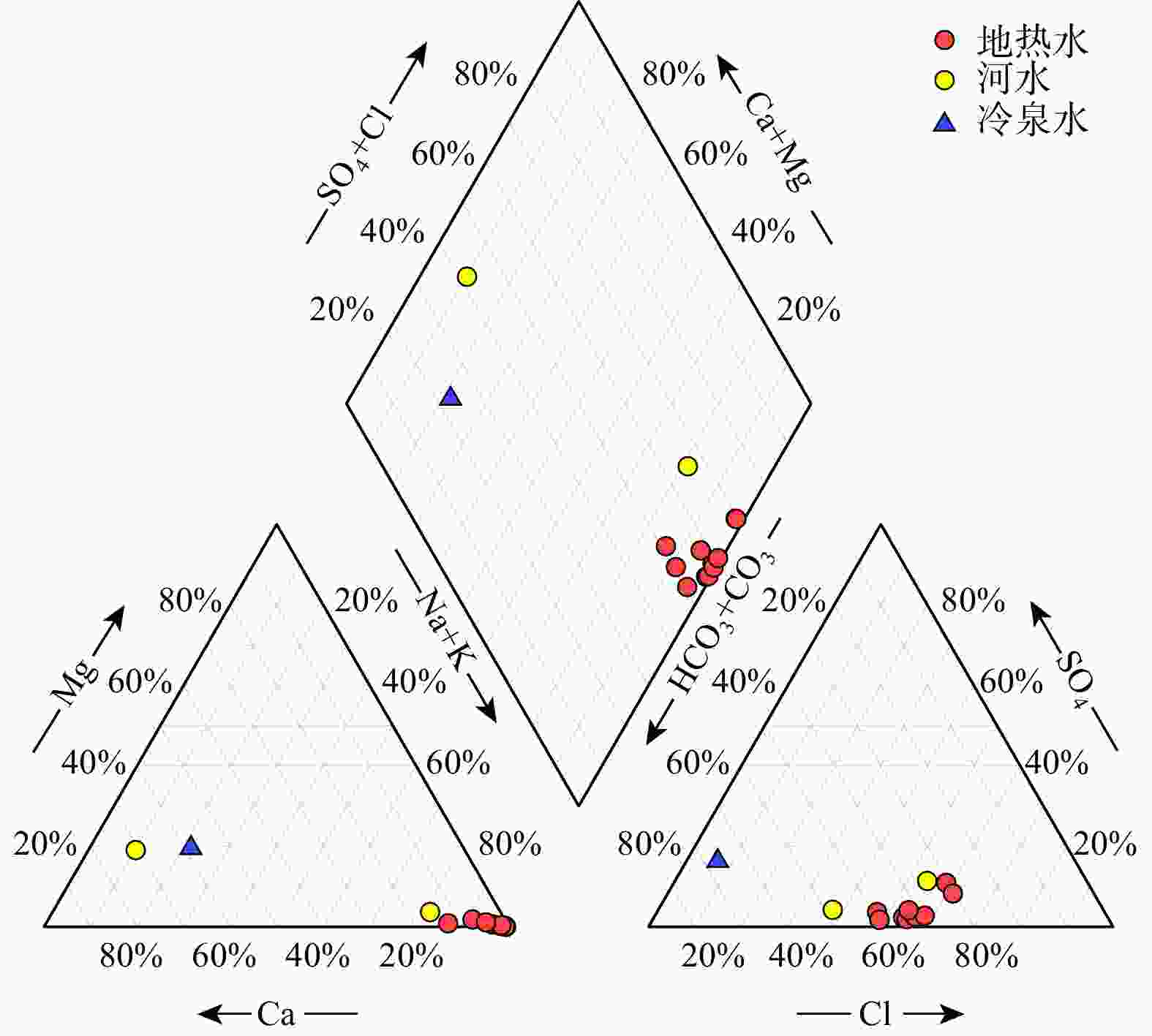
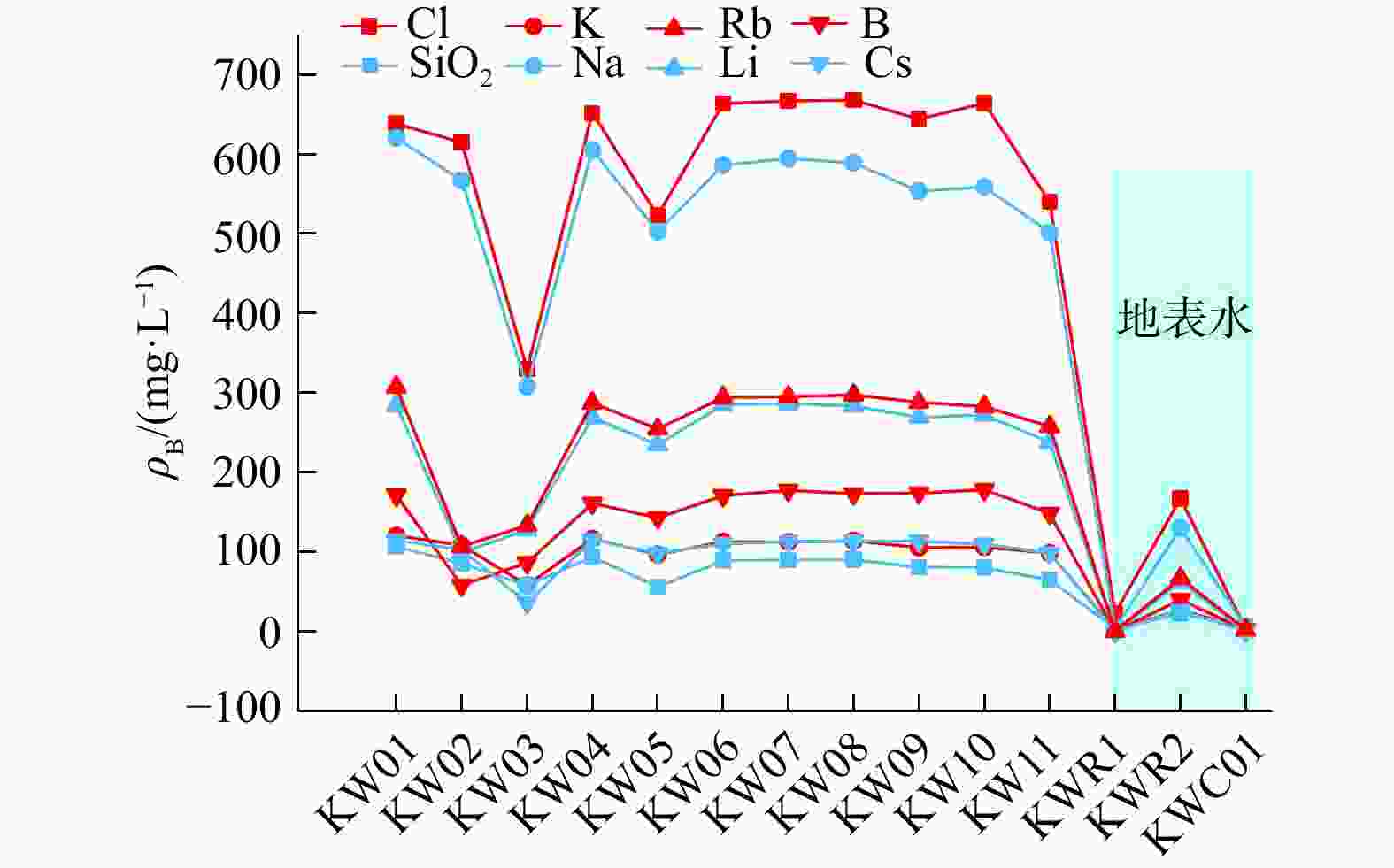
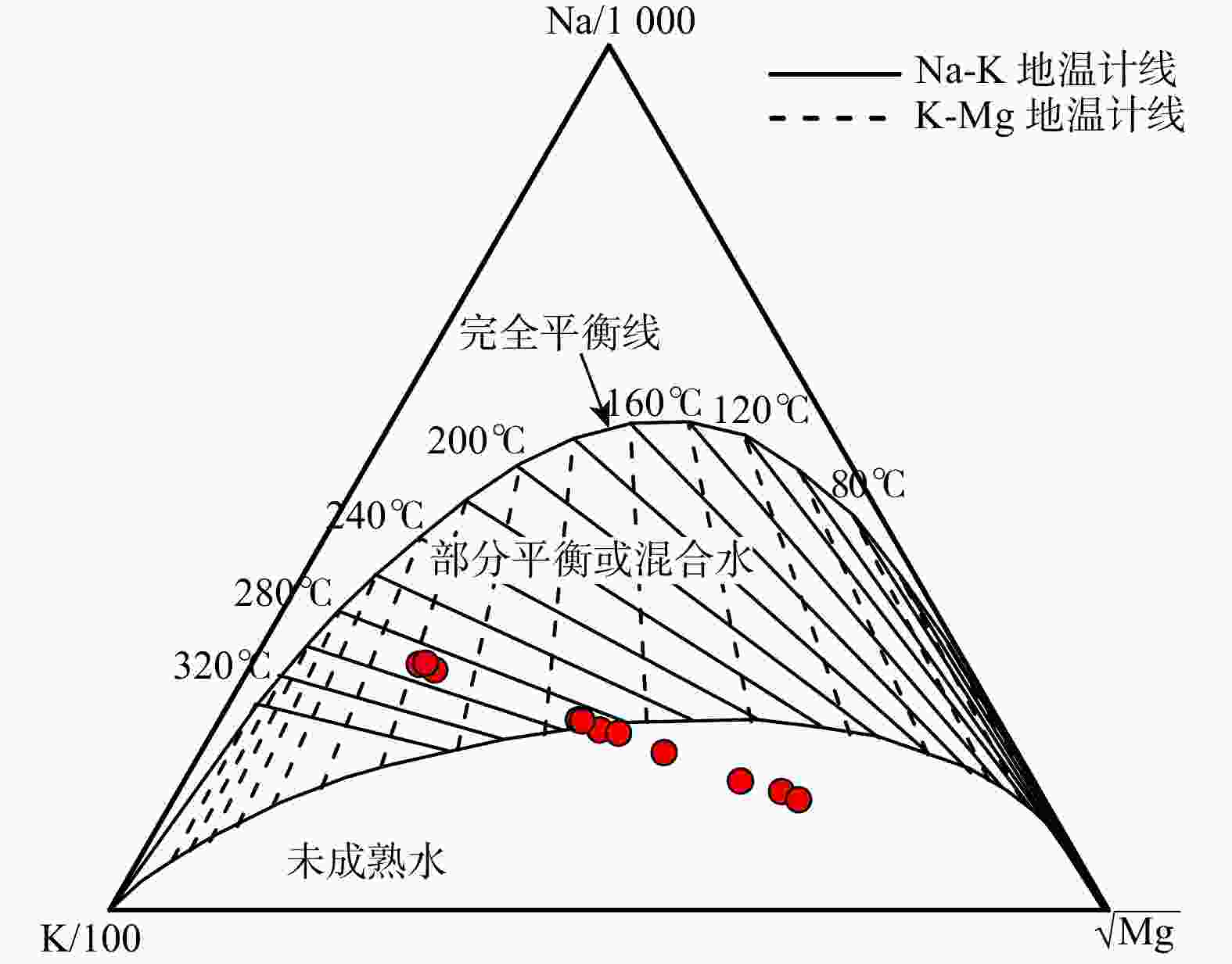
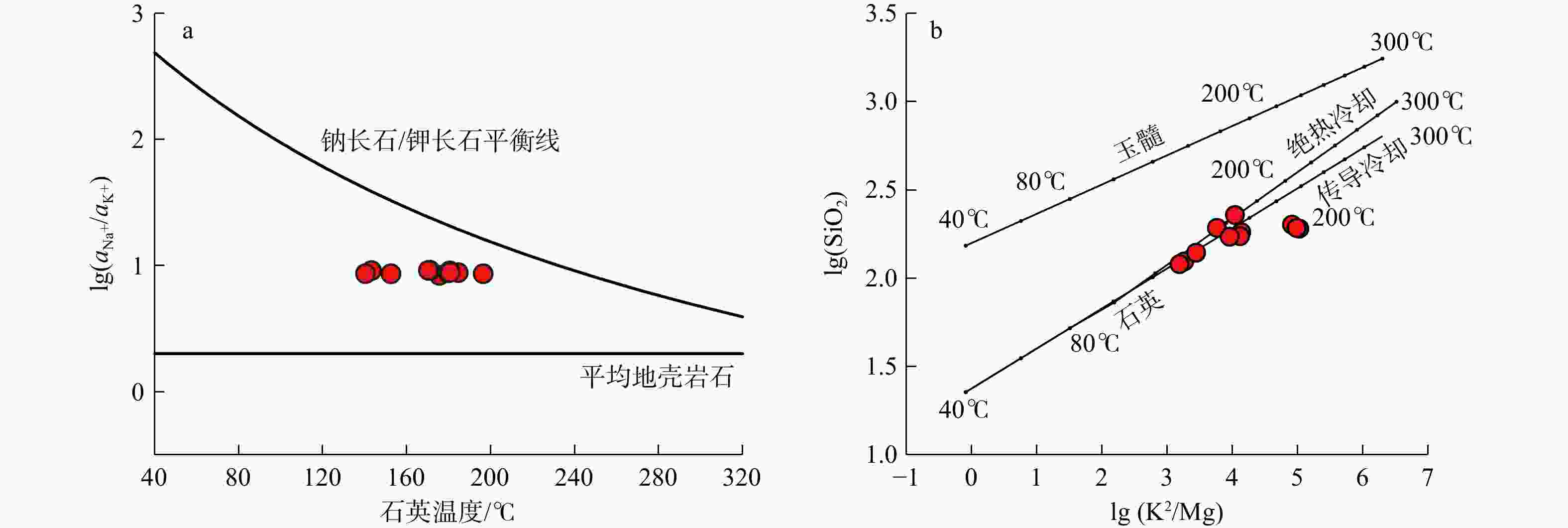
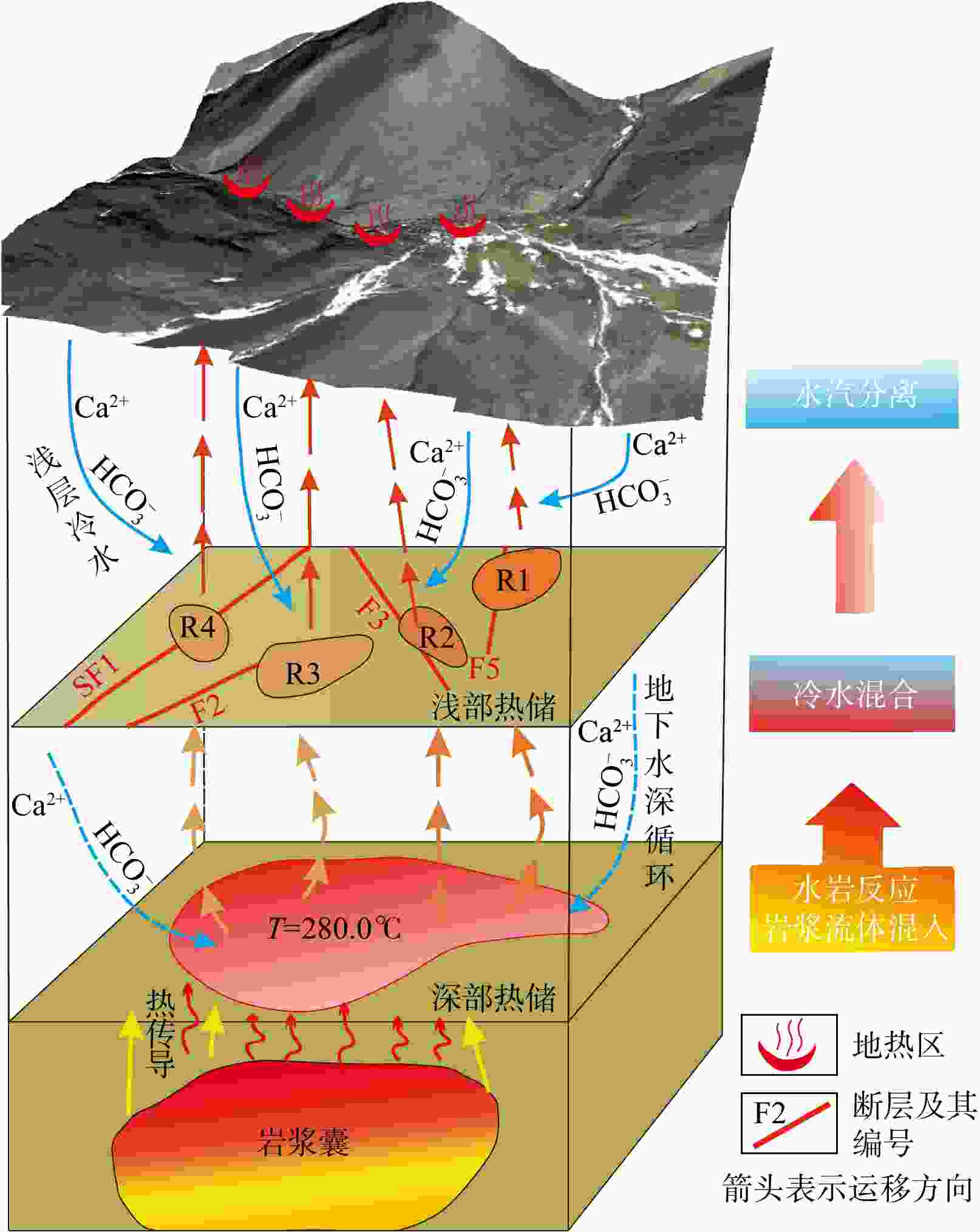
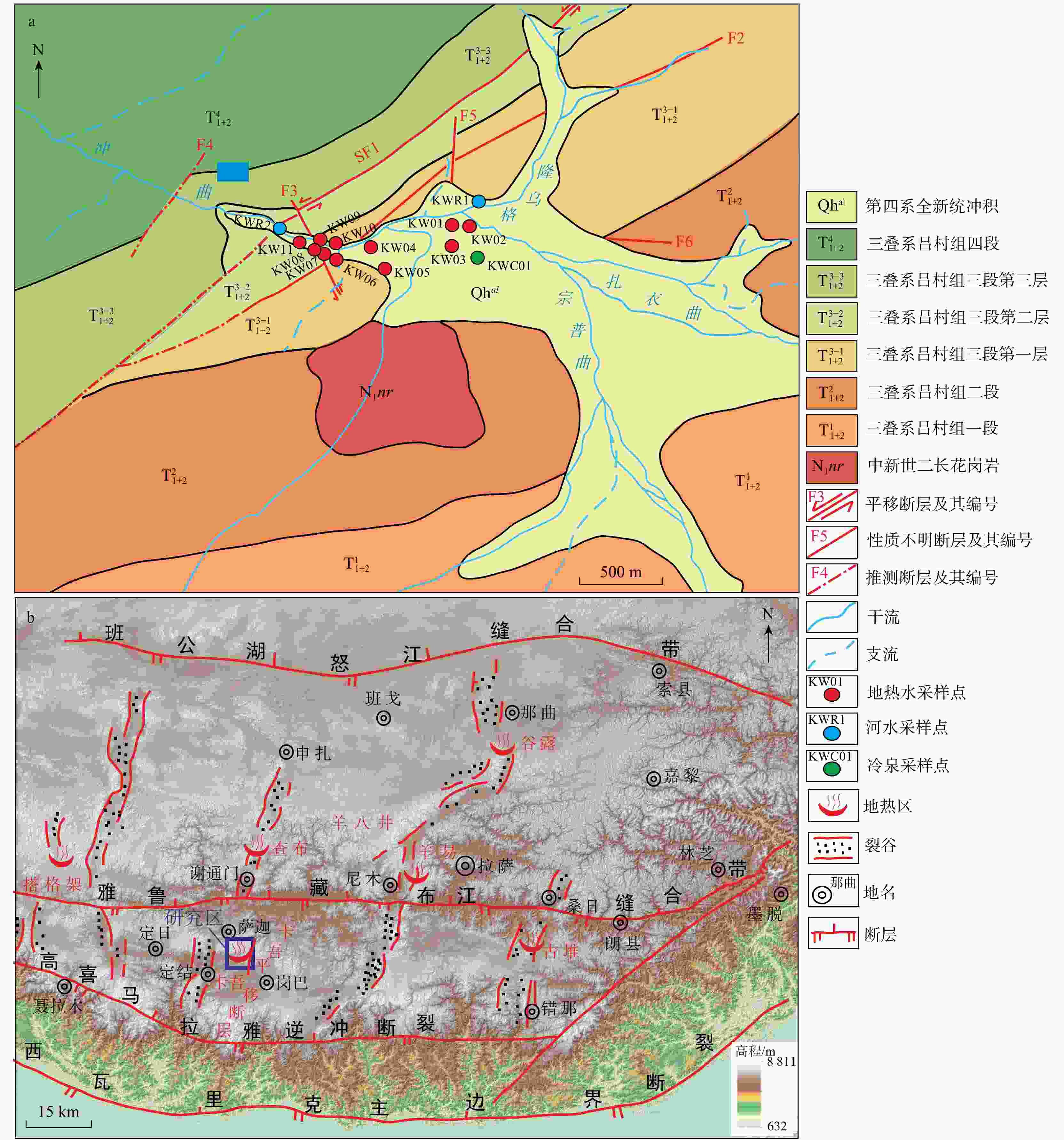
卡吾是藏南地区典型的高温水热系统,具有较大的开采潜力,而现阶段对其成因机制还远未充分认识,限制了地热资源的进一步开发利用。为了进一步探究卡吾地热区地热成因及热源,基于卡吾地热区地热水和浅层冷水的水文地球化学和氢氧同位素特征,评估了地热系统的热储温度,探讨了地热水形成过程中的水文地球化学过程(水-岩反应、冷水混合、水-汽分离等),识别了地热系统的深部热源,进而揭示了地热系统的成因机制。结果表明:地热水水化学类型主要为HCO3-Cl-Na 型,Na-K温标计算的深层统一热储温度为280℃,K-Mg温标和石英温标计算的浅层热储温度约175℃,冷水混合比例为50%~76%,还原的深部热储氘氧同位素范围分别为−207.20‰~−185.25‰,−22.26‰~−17.74‰。基于以上认识,提出了卡吾地热系统的成因模式:卡吾为一具有岩浆热源的的地热系统,深部统一的母地热流体沿区域内不同断裂向上运移并经过不同水文地球化学过程形成4个不同分布的浅部热储,最终出露形成卡吾地热水。研究成果为卡吾地热区地热资源的合理开发和高效利用提供了重要的指导作用,并可为藏南地区同类型地热系统成因机制的研究提供借鉴思路。
Abstract:Objective The Kawu area is a typical high-temperature hydrothermal system in southern Tibet, with high potential for exploitation. However, the current understanding of its genesis mechanisms is still insufficient, which limits the further development and utilization of geothermal resources. This study aims to investigate the genesis and thermal sources of the Kawu geothermal region.
Methods Hydrogeochemical characteristics and hydrogen-oxygen isotope data of geothermal and shallow cold waters were analyzed to assess the thermal reservoir temperatures of the geothermal system. The hydrogeochemical processes involved in the formation of geothermal waters, including water-rock interactions, cold water mixing, and water-steam separation, were explored. Additionally, the deep thermal sources of the geothermal system were identified, shedding light on the genesis mechanisms of the system.
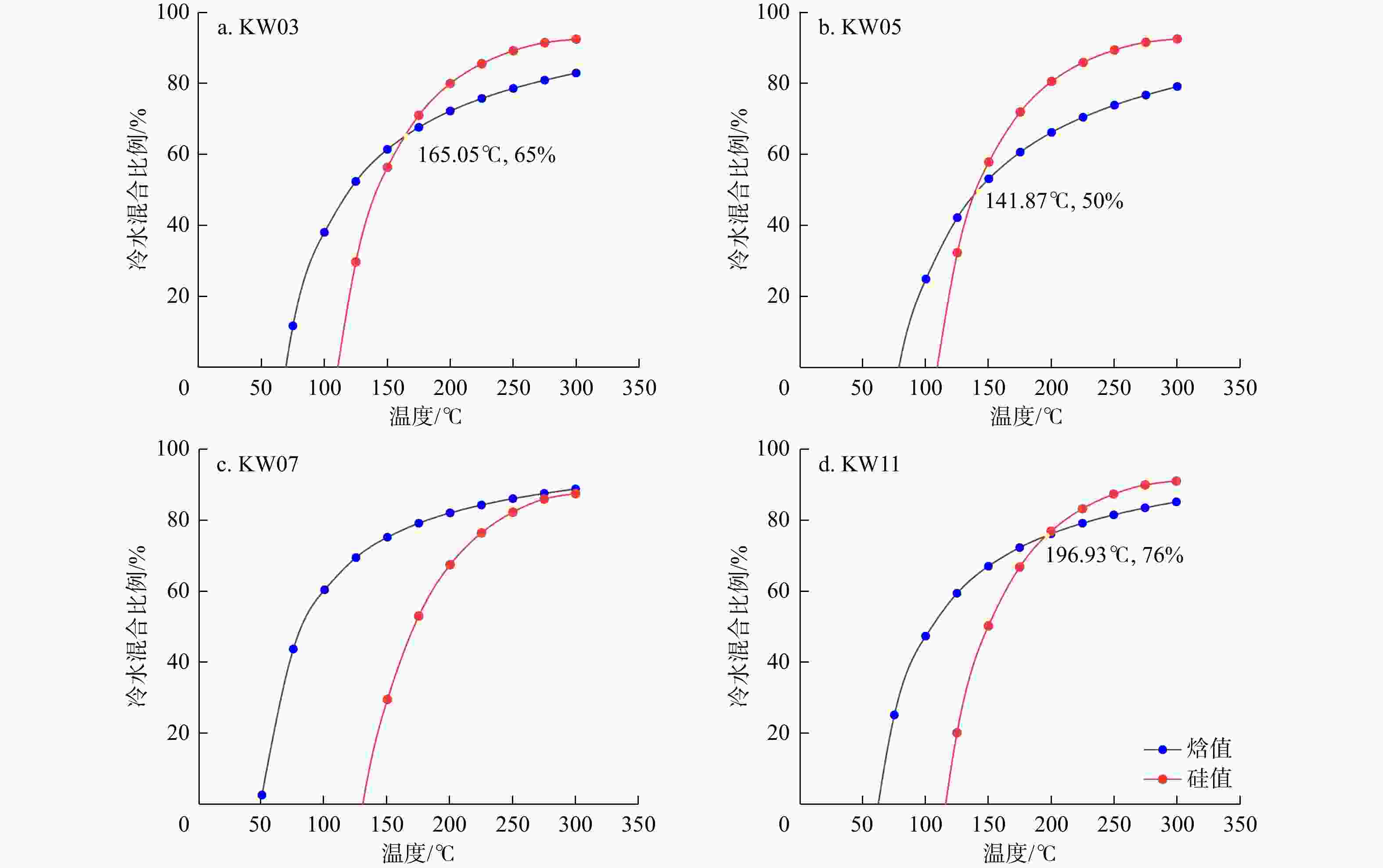
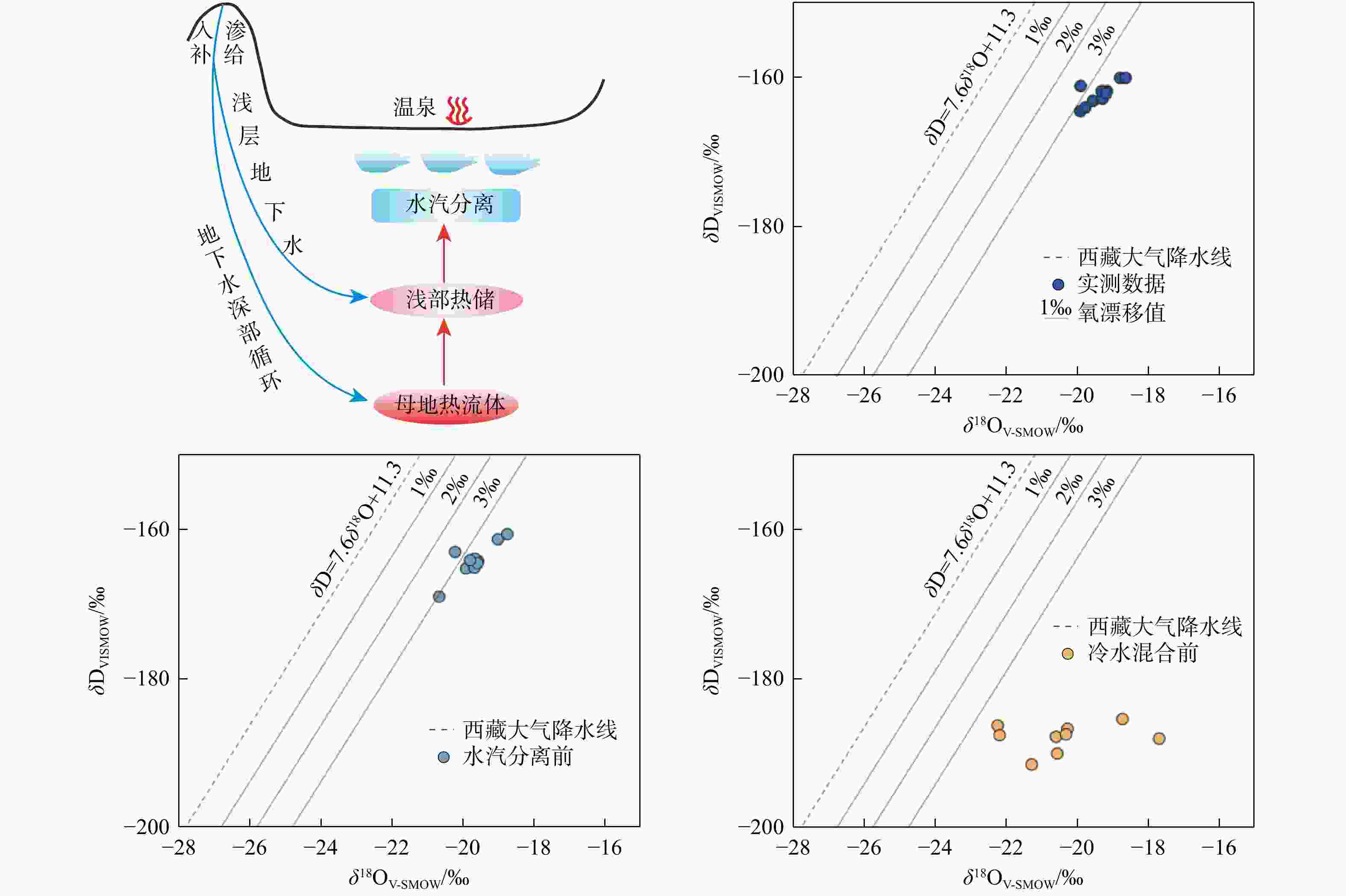
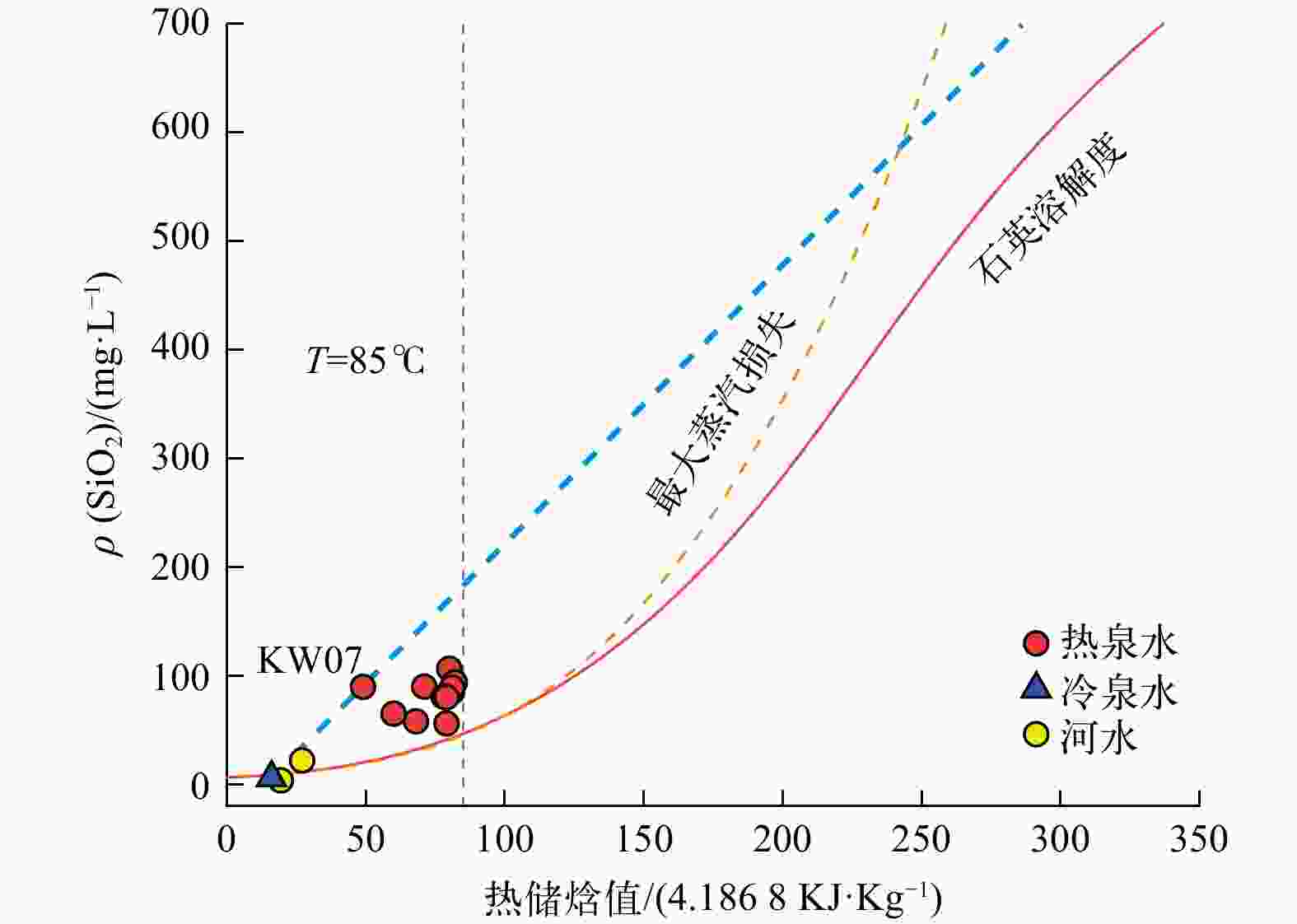
Results The results indicated that the geothermal waters primarily exhibited a neutral to weakly alkaline HCO3-Cl-Na chemical type. The Na-K geothermometer estimated the uniform deep thermal reservoir temperature at 280℃, while the K-Mg and quartz geothermometers estimated the shallow thermal reservoir temperature at approximately 175℃. The cold-water mixing ratio ranged from 50% to 76%. The deuterium and oxygen isotopic values of the reduced deep thermal reservoir ranged from −207.20‰ to −185.25‰ and −22.26‰ to −17.74‰, respectively. Based on these findings, a conceptual model for the Kawu geothermal system is proposed. It is suggested that Kawu area is a geothermal system with a magmatic heat source, where a uniform deep geothermal fluid rises along various regional fractures and undergoes different hydrogeochemical processes, resulting in the formation of four distinct shallow thermal reservoirs with varying distributions. This ultimately leads to the emergence of Kawu geothermal water.
Conclusion The study provides important guidance for the rational development and efficient utilization of geothermal resources in the Kawu geothermal region and offers valuable insights for studying the genesis mechanisms of similar geothermal systems in southern Tibet.
-
表 1 水-汽分离前地热水的热焓(H0)及蒸汽损失比例(fv)计算结果
Table 1. Calculation of geothermal water enthalpy (H0) and steam loss ratio (fv) before vapor separation
编号 KW01 KW02 KW03 KW04 KW05 KW06 KW08 KW09 KW10 KW11 H0/(kJ·kg−1) 438.55 515.39 478.63 494.33 654.31 505.63 392.39 492.23 513.84 359.68 fv/% 3.60 6.95 5.34 6.03 13.00 6.52 1.59 5.94 6.88 0.16 表 2 卡吾地区地热水氢氧同位素值偏移还原计算
Table 2. Calculation of geothermal water hydrogen and oxygen isotope deviations in Kawu area
编号 实测数据 水汽分离前 冷水混合前 δD/‰ δ18O/‰ δD/‰ δ18O/‰ δD/‰ δ18O/‰ KW01 −159.9 −18.8 −161.14 −19.00 −185.25 −18.77 KW02 −161.7 −19.17 −164.09 −19.57 −186.58 −20.31 KW03 −161 −19.91 −162.84 −20.21 −186.11 −22.26 KW04 −163 −19.56 −165.07 −19.90 −191.33 −21.31 KW05 −164.4 −19.92 −168.86 −20.66 −187.43 −22.21 KW06 −162.7 −19.29 −164.94 −19.66 −189.87 −20.60 KW08 −159.9 −18.65 −160.45 −18.74 −187.88 −17.74 KW09 −161.7 −19.32 −163.74 −19.66 −187.63 −20.63 KW10 −162 −19.19 −164.36 −19.58 −187.30 −20.35 KW11 −163.9 −19.78 −163.96 −19.79 −207.20 −21.94 -
[1] GUO Q,PANG Z H,WANG Y C,et al. Fluid geochemistry and geothermometry applications of the Kangding high-temperature geothermal system in eastern Himalayas[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2017,81:63-75. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.03.007 [2] 朱颖,甘建军,鹿淇瑞,等. 降雨型花岗岩残积土滑坡碎屑流运动过程分析:以湖北黄梅县袁山村为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2025,44(3):268-279.ZHU Y,GAN J J,LU Q R,et al. Analysis of rainfall induced-movement of landslide debris flows in granite residual soil:A case study of Yuanshan Village, Huangmei County, Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2025,44(3):268-279. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 王贵玲,张薇,梁继运,等. 中国地热资源潜力评价[J]. 地球学报,2017,38(4):449-450. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.02WANG G L,ZHANG W,LIANG J Y,et al. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2017,38(4):449-450. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.04.02 [4] ZHANG X B,HU Q H. Development of geothermal resources in China:A review[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2018,29(2):452-467. doi: 10.1007/s12583-018-0838-9 [5] MUTHER T,SYED F I,LANCASTER A T,et al. Geothermal 4.0:AI-enabled geothermal reservoir development-current status,potentials,limitations,and ways forward[J]. Geothermics,2022,100:102348. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2022.102348 [6] MORAGA J,DUZGUN H S,CAVUR M,et al. The geothermal artificial intelligence for geothermal exploration[J]. Renewable Energy,2022,192:134-149. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2022.04.113 [7] 邹俊,武斌,马昭雄,等. 西藏谢通门县卡嘎地热成因与资源潜力分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(3):207-216.ZOU J,WU B,MA Z X,et al. Geothermal genesis and resource potential of Kaga in Xietongmen County in Tibet[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(3):207-216. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 周鹏,孙明露,张云辉,等. 藏南隆子县模麓温泉群水文地球化学特征及成因机制研究[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2023,43(2):322-339.ZHOU P,SUN M L,ZHANG Y H,et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genetic mechanism of the Molu geothermal springs in the Longzi County,southern Tibet[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,2023,43(2):322-339. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] WANG Y C,GU H Y,LI D,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and genesis analysis of geothermal fluid in the Zhaxikang geothermal field in Cuona County,southern Tibet[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2021,80(11):415. doi: 10.1007/s12665-021-09577-8 [10] ERBAŞ H A,BOZDAĞ A. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and evaluation of the geothermal fluids in the Gazlıgöl geothermal field (Afyonkarahisar),western Anatolia,Turkey[J]. Geothermics,2022,105:102543. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2022.102543 [11] 王贵玲,刘彦广,朱喜,等. 中国地热资源现状及发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘,2020,27(1):1-9.WANG G L,LIU Y G,ZHU X,et al. The status and development trend of geothermal resources in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2020,27(1):1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 蔺文静,刘志明,王婉丽,等. 中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J]. 中国地质,2013,40(1):312-321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021LIN W J,LIU Z M,WANG W L,et al. The assessment of geothermal resources potential of China[J]. Geology in China,2013,40(1):312-321. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021 [13] 郭清海. 岩浆热源型地热系统及其水文地球化学判据[J]. 地质学报,2020,94(12):3544-3554. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.12.002GUO Q H. Magma-heated geothermal systems and hydrogeochemical evidence of their occurrence[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2020,94(12):3544-3554. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.12.002 [14] 佟伟,章铭陶,张知非. 西藏地热 [M]. 北京:科学出版社,1981:192.Tong W,Zhang M T,Zhang Z F. Geothermals Beneath Xizang (Tibetan) Plateau [M]. Beijing:Science Press,1981:192.(in Chinese) [15] 佟伟. 西藏温泉志[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2000.TONG W. Thermal springs in Tibet[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2000. (in Chinese) [16] WANG Y C,LI L,WEN H G,et al. Geochemical evidence for the nonexistence of supercritical geothermal fluids at the Yangbajing geothermal field,southern Tibet[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2022,604:127243. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.127243 [17] SU J B,TAN H B. The genesis of rare-alkali metal enrichment in the geothermal anomalies controlled by faults and magma along the northern Yadong-Gulu rift[J]. Ore Geology Reviews,2022,147:104987. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.104987 [18] LI J X,WANG X Y,RUAN C X,et al. Enrichment mechanisms of lithium for the geothermal springs in the southern Tibet,China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2022,612:128022. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128022 [19] GUO Q H,PLANER-FRIEDRICH B,LIU M L,et al. Magmatic fluid input explaining the geochemical anomaly of very high arsenic in some southern Tibetan geothermal waters[J]. Chemical Geology,2019,513:32-43. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.03.008 [20] SHI H J, LIU M L, WEI X, et al. Fluid geochemical constraints on the geological genesis of carbonate geothermal systems: A case study of Quzhuomu in southern Tibet, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2024, 177: 106222. [21] 师红杰,刘明亮,卫兴,等. 西藏玛旁雍错地热水地球化学特征及其成因机制分析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2023,43(2):311-321.SHI H J,LIU M L,WEI X,et al. Geochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms of the geothermal waters from the Mapamyumco,Tibet[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,2023,43(2):311-321. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 尚建波,卫兴,曹园园,等. 不同类型地热水硼的地球化学特征及对地热系统成因机制的指示[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(1):288-297.SHANG J B,WEI X,CAO Y Y,et al. Boron geochemical characteristics in different types of geothermal water and its indications for the genesis mechanism of geothermal systems[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(1):288-297. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 牛新生,刘喜方,吕苑苑,等. 西藏当雄错流域热泉成因机制及其对盐湖成矿物质(Li-Rb-Cs)的供给[J]. 中国地质,2023,50(4):1163-1175. doi: 10.12029/gc20220527001NIU X S,LIU X F,LYU Y Y,et al. Origin mechanism of thermal springs and their supply of minerals to the salt lake(Li-Rb-Cs) in the Tangqung Co watershed of Tibet[J]. Geology in China,2023,50(4):1163-1175. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12029/gc20220527001 [24] 周艺颖,欧阳正平,徐子东,等. 琼西南九所地热田水文地球化学特征及成因[J]. 地质科技通报,2025,44(1):216-228.ZHOU Y Y,OUYANG Z P,XU Z D,et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and genesis of Jiusuo geothermal field in southwestern Hainan,China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2025,44(1):216-228. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 卫兴,师红杰,陈松,等. 水文地球化学方法在地热资源勘查中的应用:以湖北省应城市为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):68-80.WEI X,SHI H J,CHEN S,et al. Application of hydrogeochemical methods in geothermal resource exploration:A case study of Yingcheng City,Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):68-80. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] PANG Z H,KONG Y L,LI J,et al. An isotopic geoindicator in the hydrological cycle[J]. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science,2017,17:534-537. doi: 10.1016/j.proeps.2016.12.135 [27] ZHOU R,ZHOU X C,LI Y,et al. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic characteristics of the hot springs in the Litang fault zone,Southeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Water,2022,14(9):1496. doi: 10.3390/w14091496 [28] PÉREZ-ZÁRATE D,PROL-LEDESMA R M,RODRÍGUEZ-DÍAZ A A,et al. Soil gas flux,hydrogeochemistry and multicomponent geothermometry of thermal springs in the La Escalera geothermal prospect,Mexico[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2022,139:105256. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105256 [29] GUDALA M,GOVINDARAJAN S K,YAN B C,et al. Numerical investigations of the PUGA geothermal reservoir with multistage hydraulic fractures and well patterns using fully coupled thermo-hydro-geomechanical modeling[J]. Energy,2022,253:124173. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.124173 [30] 郭镜,夏时斌. 川东褶皱带地热系统的空间载体:相互连通的断裂系统:以四川广安牟家镇地热井为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,2022,42(4):642-652.GUO J,XIA S B. Spatial carrier of geothermal system in eastern Sichuan fold zone:Interconnected fault system:A case study of geothermal well in Moujia Town,Guang'an,Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,2022,42(4):642-652. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] CHENG Y Z,PANG Z H,KONG Y L,et al. Imaging the heat source of the Kangding high-temperature geothermal system on the Xianshuihe fault by magnetotelluric survey[J]. Geothermics,2022,102:102386. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2022.102386 [32] 李义曼,陈凯,天娇,等. 广东丰顺汤坑地热田热水中稀土元素特征及其影响因素[J]. 地质论评,2022,68(3):993-1005.LI Y M,CHEN K,TIAN J,et al. REE characteristics and their influencing factors of the geothermal water in Tangkeng geothermal field,Fengshun,Guangdong Province[J]. Geological Review,2022,68(3):993-1005. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] LUO J,LI Y M,TIAN J,et al. Geochemistry of geothermal fluid with implications on circulation and evolution in Fengshun-Tangkeng geothermal field,South China[J]. Geothermics,2022,100:102323. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2021.102323 [34] 马昭雄,邹俊,谢伟,等. 西藏自治区萨迦县卡吾地热地质构造特征及成因初步分析[J]. 四川地质学报,2023,43(4):597-601. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2023.04.004MA Z X,ZOU J,XIE W,et al. Preliminary analysis on the geological structure characteristics and genesis of the geothermal in Kawu,Sakya County,Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan,2023,43(4):597-601. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2023.04.004 [35] 郭清海. 岩浆热源型地热系统释义[J]. 地质学报,2022,96(1):208-214. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.01.017GUO Q H. Definition of magma-impacted geothermal system[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2022,96(1):208-214. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.01.017 [36] 张庆,谭红兵,张文杰,等. 西藏萨迦县卡乌地热水的水环境效应[J]. 水资源保护,2015,31(2):45-49. doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2015.02.009ZHANG Q,TAN H B,ZHANG W J,et al. Water environmental effects of Kawu geothermal water in Sajia County,Tibet[J]. Water Resources Protection,2015,31(2):45-49. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3880/j.issn.1004-6933.2015.02.009 [37] 孙会肖,郎旭娟,男达瓦,等. 西藏萨迦冲曲流域地下热水成因及工程效应分析[J]. 安全与环境工程,2021,28(3):147-155.SUN H X,LANG X J,NAN D W,et al. Geothermal water genesis and engineering effect in Saga Chongqu Basin,Tibet[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering,2021,28(3):147-155. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] PANDEY V,CHOTALIYA B,BIST N,et al. Geochemical analysis and quality assessment of geothermal water in Gujarat,India[J]. Energy Geoscience,2023,4(1):59-73. doi: 10.1016/j.engeos.2022.08.001 [39] GUO Q H. Hydrogeochemistry of high-temperature geothermal systems in China:A review[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2012,27(10):1887-1898. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2012.07.006 [40] GIGGENBACH W F. Geothermal solute equilibria. derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1988,52(1):2749-2765. [41] GUO Q H,WANG Y X,LIU W. Hydrogeochemistry and environmental impact of geothermal waters from Yangyi of Tibet,China[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,2009,180(1):9-20. [42] GEMICI Ü,FILIZ Ş. Hydrochemistry of the Çeşme geothermal area in western Turkey[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,2001,110(1/2):171-187. [43] SANTOYO E,DÍAZ-GONZÁLEZ L. A new improved proposal of the Na/K geothermometer to estimate deep equilibrium temperatures and their uncertainties in geothermal systems[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the Proceedings world geothermal congress. Bali,Indonesia:[s.n.],2010:25-29. [44] FOURNIER R. Interpretation of Na-K-Mg relations in geothermal waters[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 1990 International Symposium on Geothermal Energy. Davis,CA,United States:[s.n.]. 1990:1421-1425. [45] LIU M L,GUO Q H,ZHANG X B,et al. Geochemistry of geothermal waters from the Gonghe region,northwestern China:Implications for identification of the heat source[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,75(8):682. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-5508-6 [46] FOURNIER R O. Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems[J]. Geothermics,1977,5(1/2/3/4):41-50. [47] LI X,HUANG X,LIAO X,et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics and conceptual model of the geothermal waters in the Xianshuihe fault zone,southwestern China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2020,17(2):500. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17020500 [48] GIGGENBACH W F. Isotopic shifts in waters from geothermal and volcanic systems along convergent plate boundaries and their origin[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1992,113(4):495-510. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(92)90127-H [49] GIGGENBACH W F,STEWART M K. Processes controlling the isotopic composition of steam and water discharges from steam vents and steam-heated pools in geothermal areas[J]. Geothermics,1982,11(2):71-80. doi: 10.1016/0375-6505(82)90009-8 [50] HORITA J,WESOLOWSKI D J. Liquid-vapor fractionation of oxygen and hydrogen isotopes of water from the freezing to the critical temperature[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1994,58(16):3425-3437. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90096-5 [51] WANG W D,WEI H Z,JIAN S Y,et al. The origin of rare alkali metals in geothermal fluids of southern Tibet,China:A silicon isotope perspective[J]. Scientific Reports,2019,9(1):7918. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44249-5 [52] KLEMPERER S L,ZHAO P,WHYTE C J,et al. Limited underthrusting of India below Tibet:3He/4He analysis of thermal springs locates the mantle suture in continental collision[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2022,119(12):e2113877119. [53] SHI D N,KLEMPERER S L,SHI J Y,et al. Localized foundering of Indian lower crust in the India-Tibet collision zone[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2020,117(40):24742-24747. -




 下载:
下载: