Identification and prediction of gravity flow channel interlayers under deep water and few wells conditions
-
摘要:
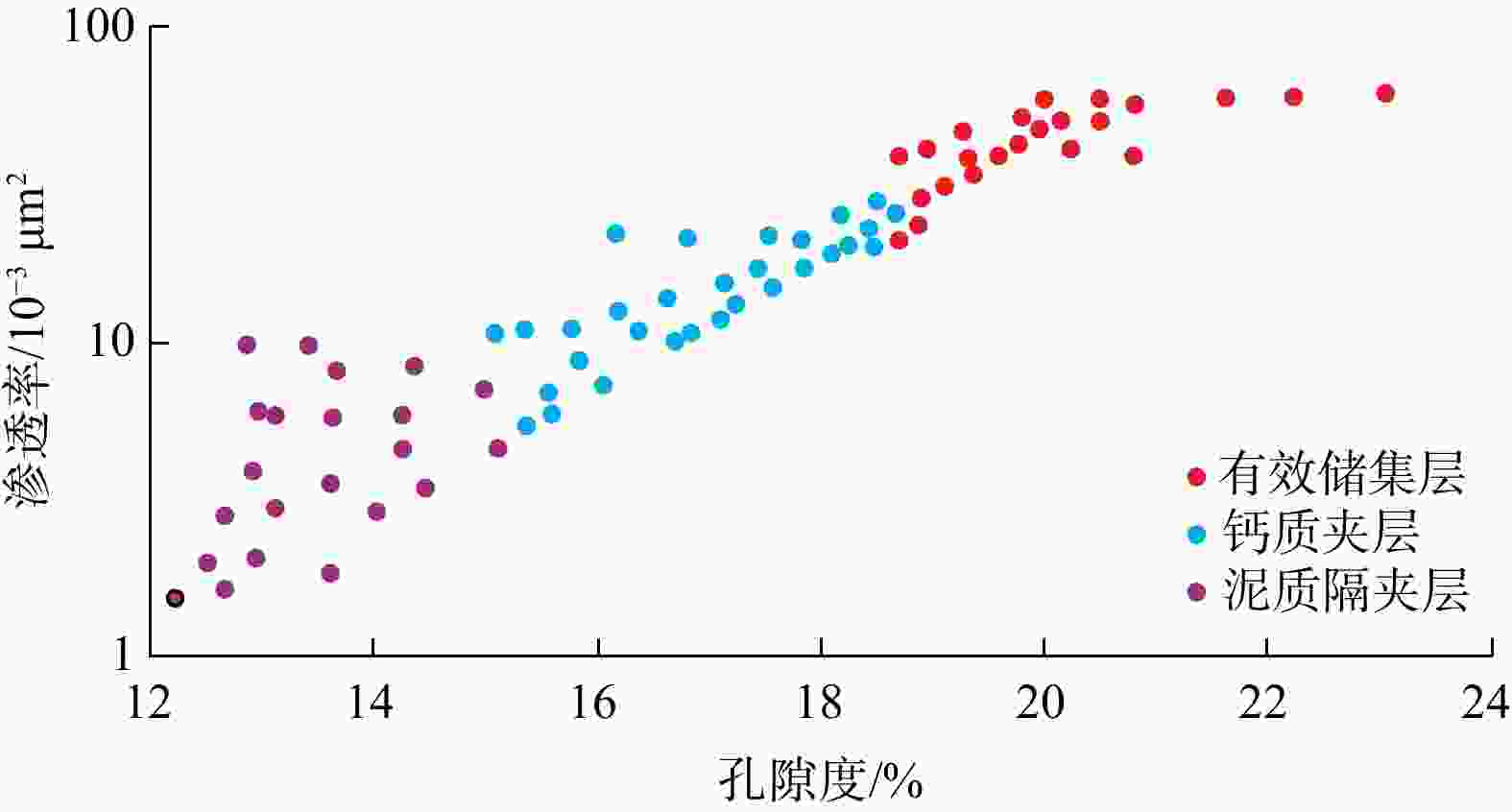
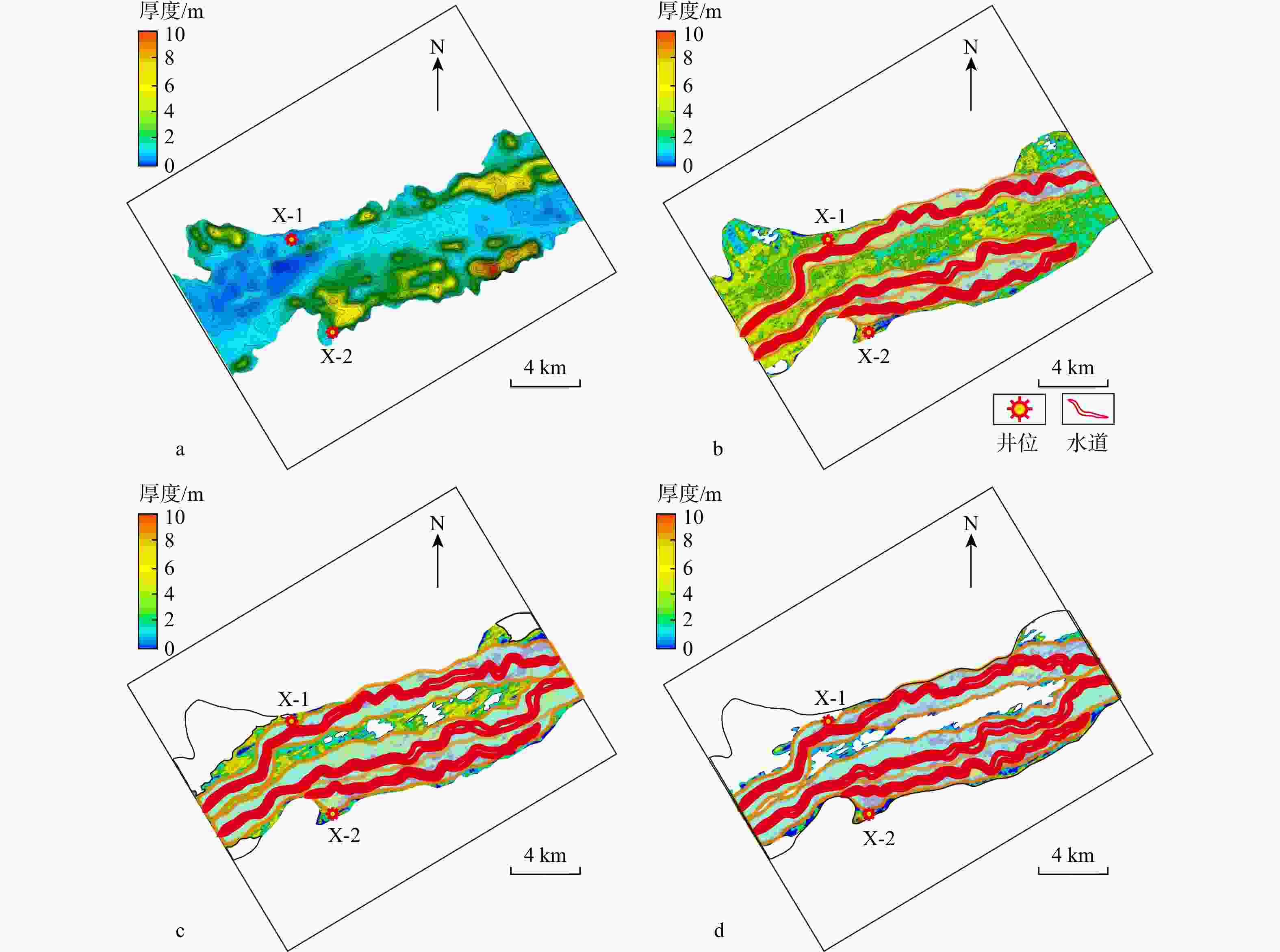
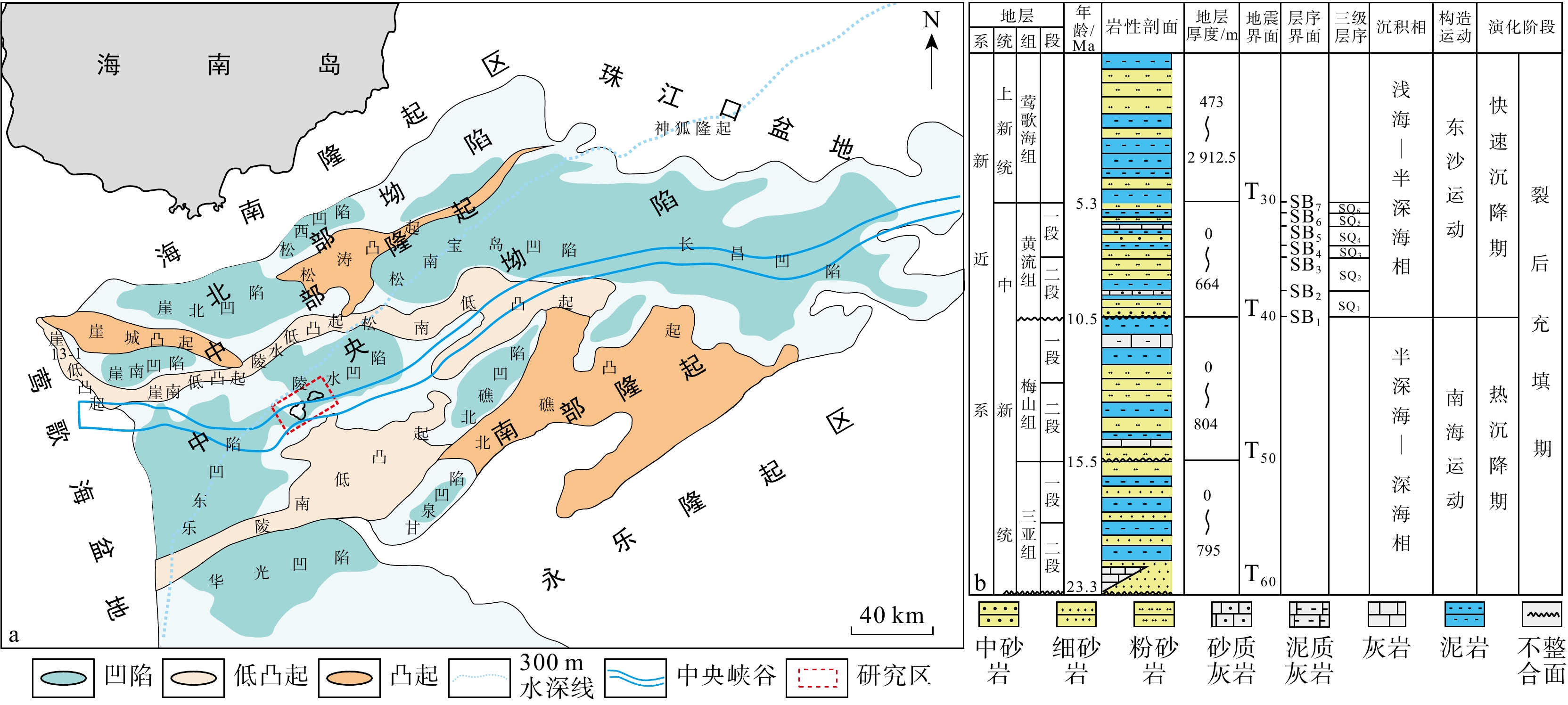
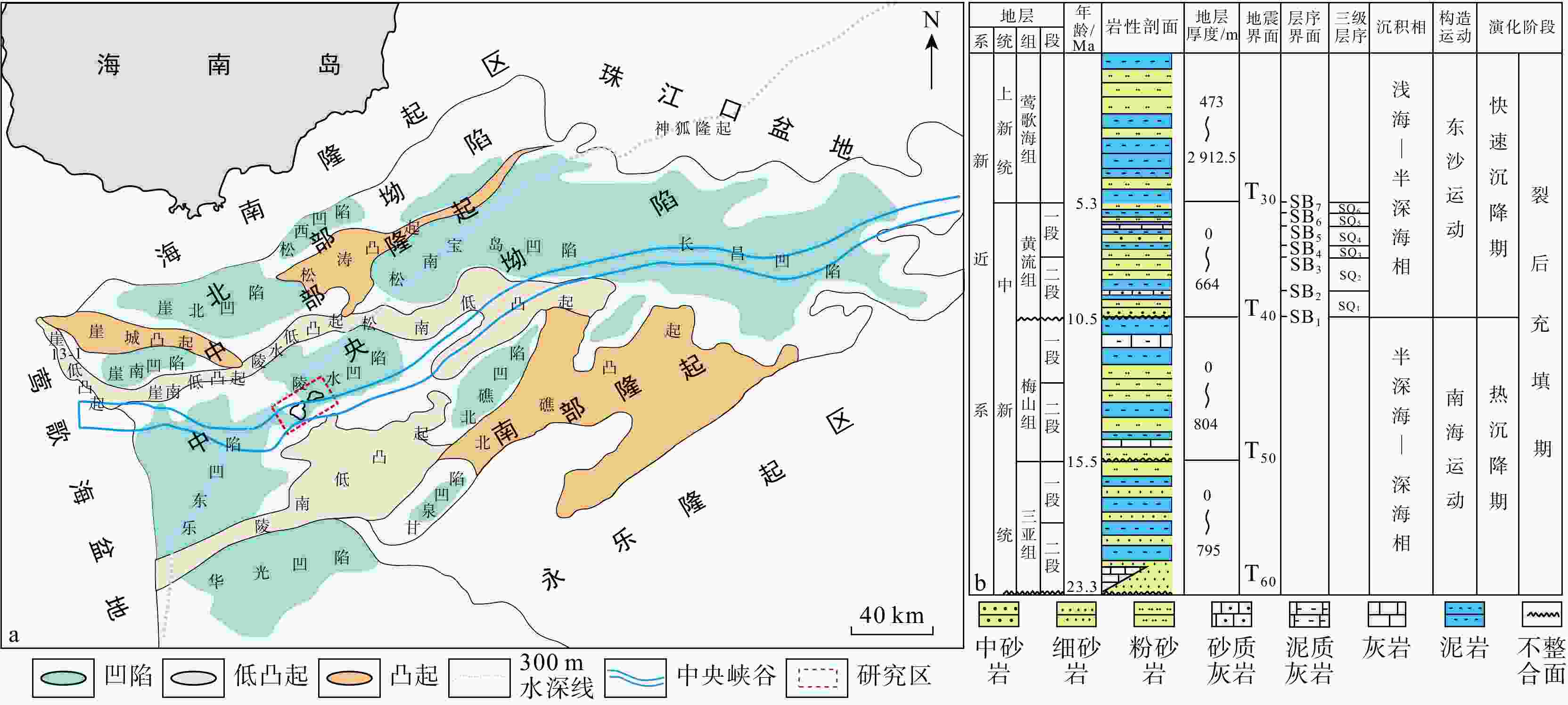
琼东南盆地陵水X气田已探明天然气地质储量128.09亿m3,但受限于海域盆地水体深度大,钻井资料少、地震资料分辨率低、隔夹层识别不清,无法满足油气勘探需求。基于岩心、测井和地震资料,建立了隔夹层识别标准,并结合拓频与反演技术,揭示了黄流组重力流水道中不同成因隔夹层展布规律及对油气开发方案部署优化。结果表明:①研究区整体为峡谷水道沉积体系,发育重力流水道、水道-堤岸、席状砂、滑塌沉积和深海泥5种微相。②黄流组发育泥质隔层、泥质夹层和钙质夹层。其中,泥质隔夹层具有高自然伽马、高密度、高速度和高波阻抗特征;钙质夹层则表现为中等自然伽马、低密度及高电阻。③泥质隔层主要分布在峡谷中部及边缘,呈大规模稳定分布;泥质夹层在峡谷内部水道两翼小规模局限分布;钙质夹层分布面积小且稳定性差。④隔夹层发育受沉积微相控制,重力流能量强时,隔夹层多出现在水道两侧堤岸泥沉积区,能量弱时则以深水原地沉积为主。⑤优化新开发井A-1部署方案及其井轨迹,形成了一套隔夹层半定量预测技术。研究成果可为研究区和类似深水气田隔夹层识别及预测、后续油气开发提供理论指导和技术支撑。
Abstract:Objective The Lingshui X gas field in the Qiongdongnan Basin has proven natural gas geological reserves of 12.809 billion cubic meters. However, exploration and development efforts have been hindered by challenges such as the large water depths of the offshore basin, limited well data, low resolution of seismic data, and unclear identification of interbedded layers, which are critical for optimizing oil and gas exploration strategies. This study aims to address these challenges by establishing a methodology for identifying interbedded layers and optimizing the oil and gas development plan for the Lingshui X gas field.
Methods This research
utilizes core samples, well logging, and seismic data, which areused to create a set of criteria for identifying interbedded layers in the Huangliu Formation’s gravity flow channels. Additionally, frequency extension and inversion techniques are employed to enhance the resolution of seismic data and to reveal the distribution patterns of interbedded layers with different origins. These results contribute to the optimization of exploration and development strategies.Results The results indicate that: (1) The overall sedimentary system in the study area is a canyon-channel system, characterized by the development of five distinct microfacies: gravity flow channels, channel-levee complexes, sheet sands, slump deposits, and deep-sea mud. (2) The Huangliu Formation contains mudstone interlayers, mudstone interbeds, and calcareous interbeds. The mudstone interlayers exhibit high natural gamma ray, high density, high velocity, and high impedance characteristics, whereas the calcareous interbeds are distinguished by moderate natural gamma values, low density, and high resistivity. (3) Mudstone interlayers predominantly occur in the central and marginal areas of the canyon, forming large-scale stable distributions, while mudstone interbeds are confined to smaller, localized areas on the flanks of the canyon channels. Calcareous interbeds have limited distribution areas and are less stable in nature. (4) The development of these interbedded layers is influenced by the sedimentary microfacies. When the gravity flow energy is strong, interbedded layers are more commonly found in the levee mud deposits along the channel sides. Conversely, when the energy is weaker, interbeds are more likely to occur in deep-water in-situ deposits. (5) Based on these observations, an optimized deployment plan for a newly developed well, A-1, was proposed, along with its well trajectory. This plan incorporates a semi-quantitative prediction method for identifying interbedded layers, which will improve the precision of future exploration and development.
Conclusion In conclusion, the results of this study provide significant theoretical and technical support for the identification, prediction, and subsequent oil and gas development in the Lingshui X gas field and similar deep-water gas fields. The methodology established in this research is expected to contribute to enhancing the exploration efficiency and optimizing development strategies for deep-water hydrocarbon reservoirs.
-
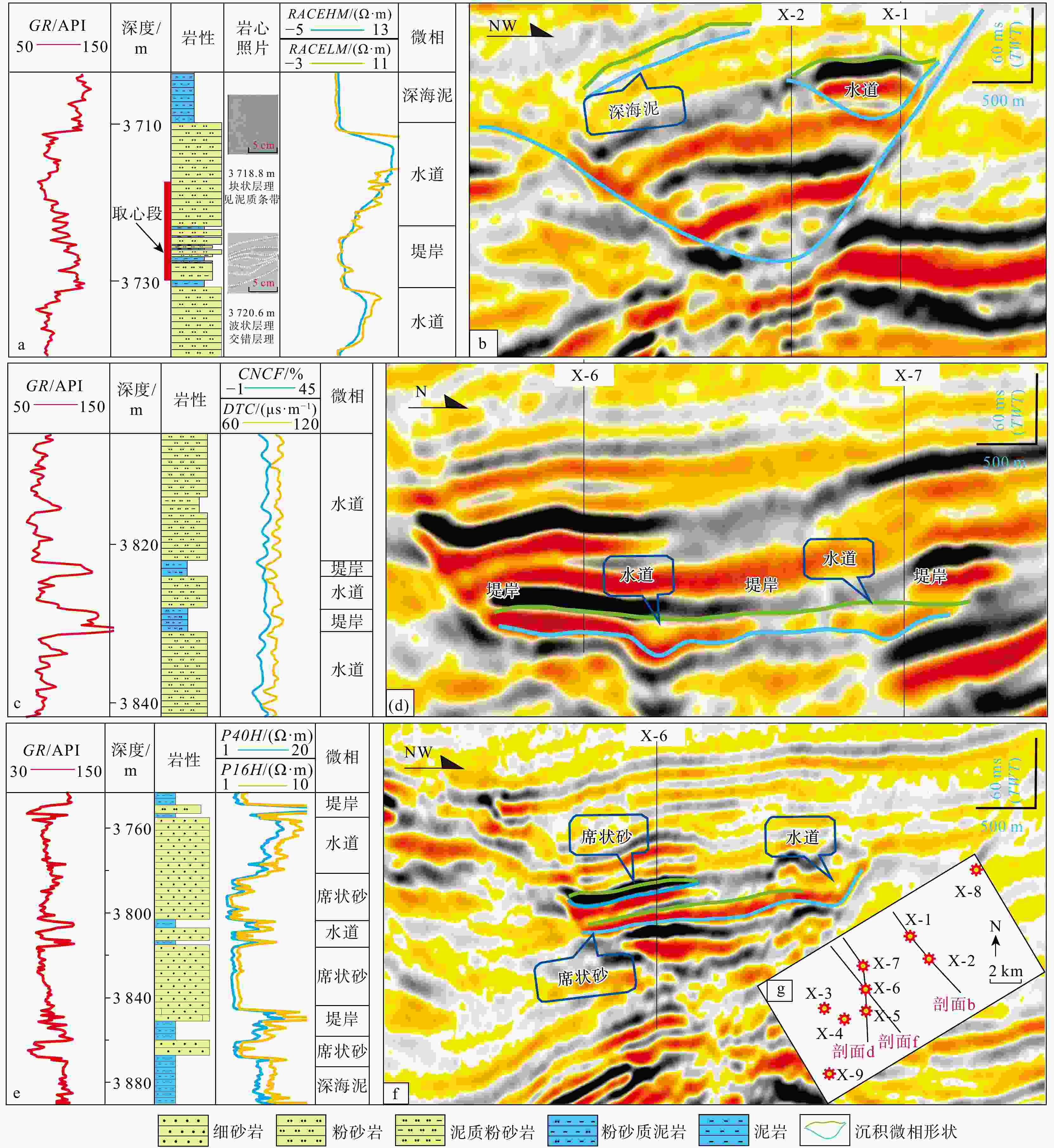
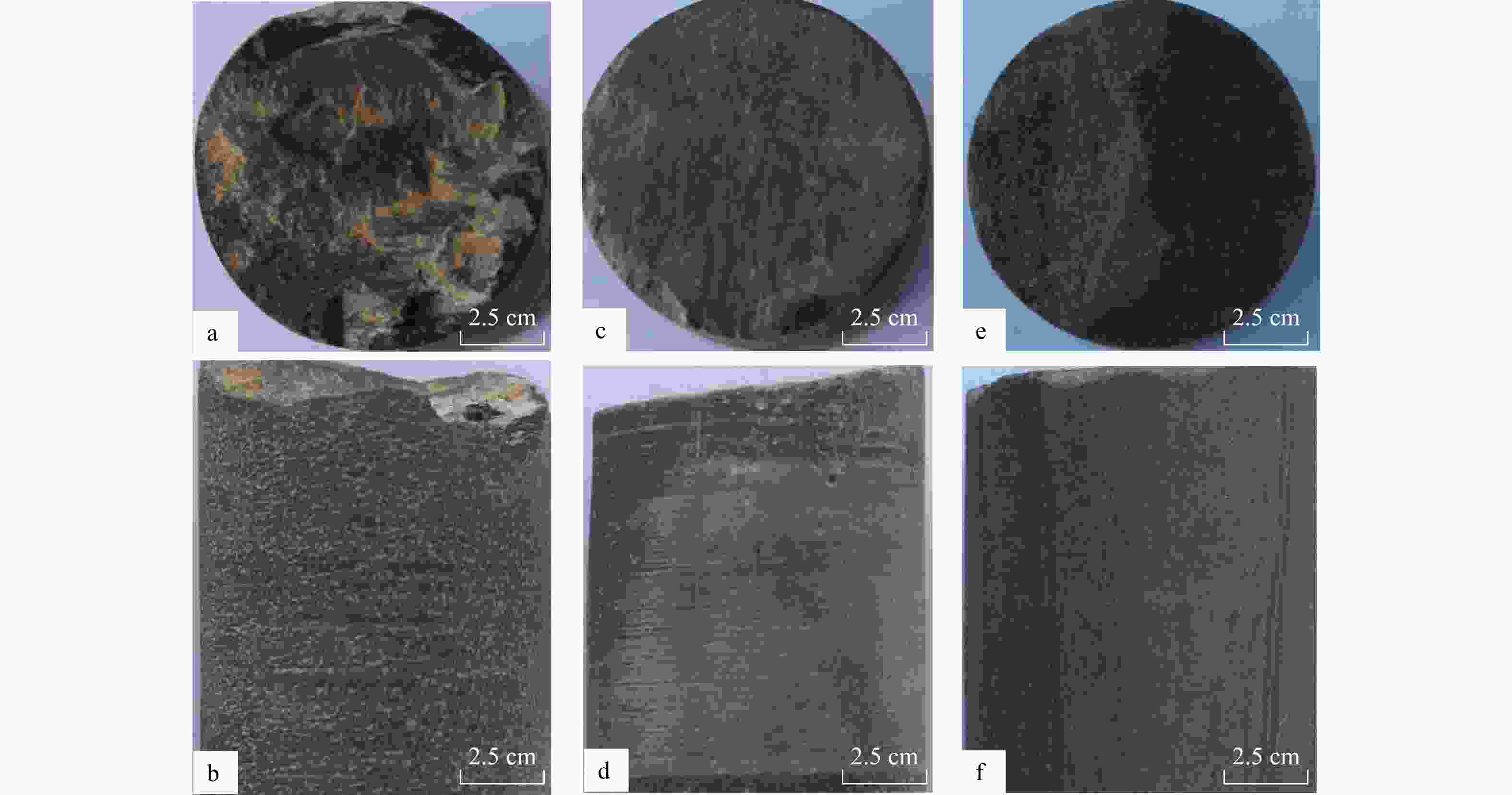
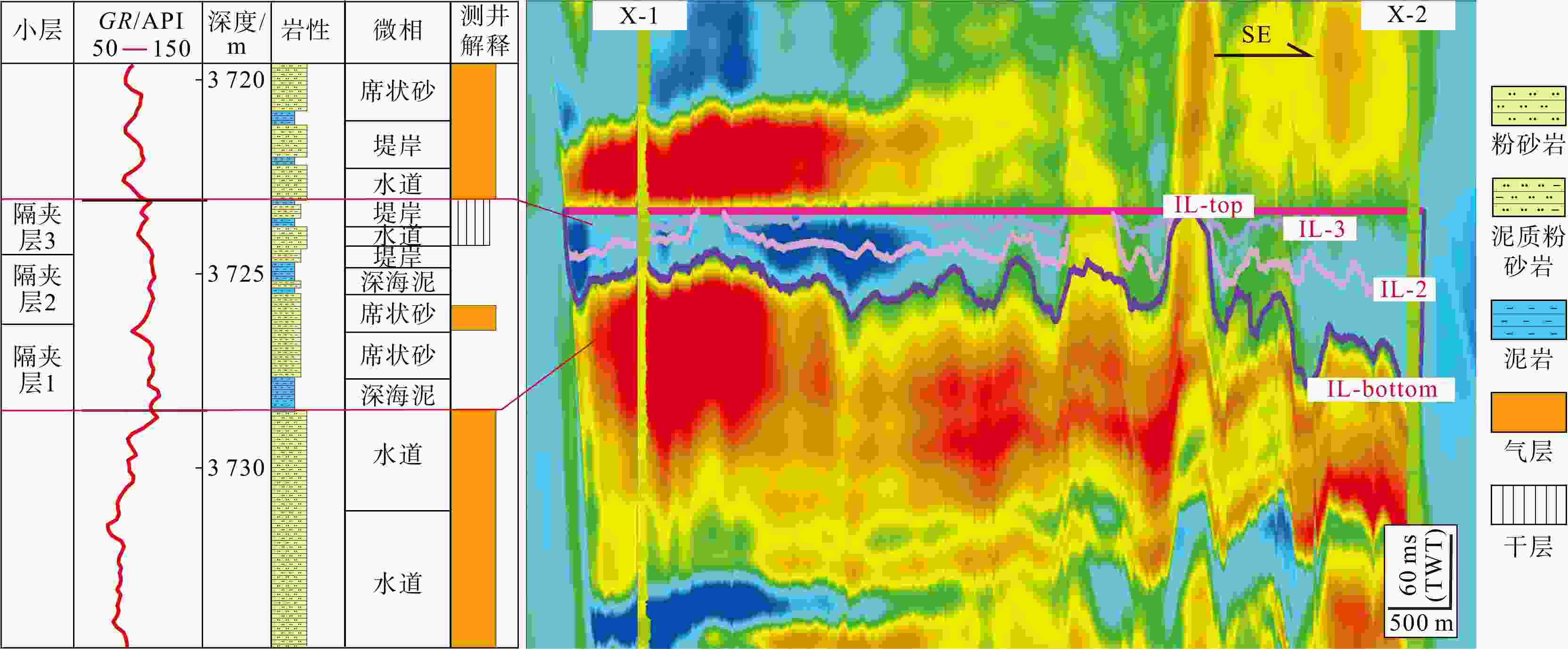
图 5 泥质隔层、泥质夹层和钙质夹层测井响应图版
a.X-1井,泥质隔层;b. X-1井,泥质夹层;c. X-2井,钙质夹层(井位见图2g)
Figure 5. Log response chart for mudstone barriers, mudstone interlayers, and calcareous interlayers
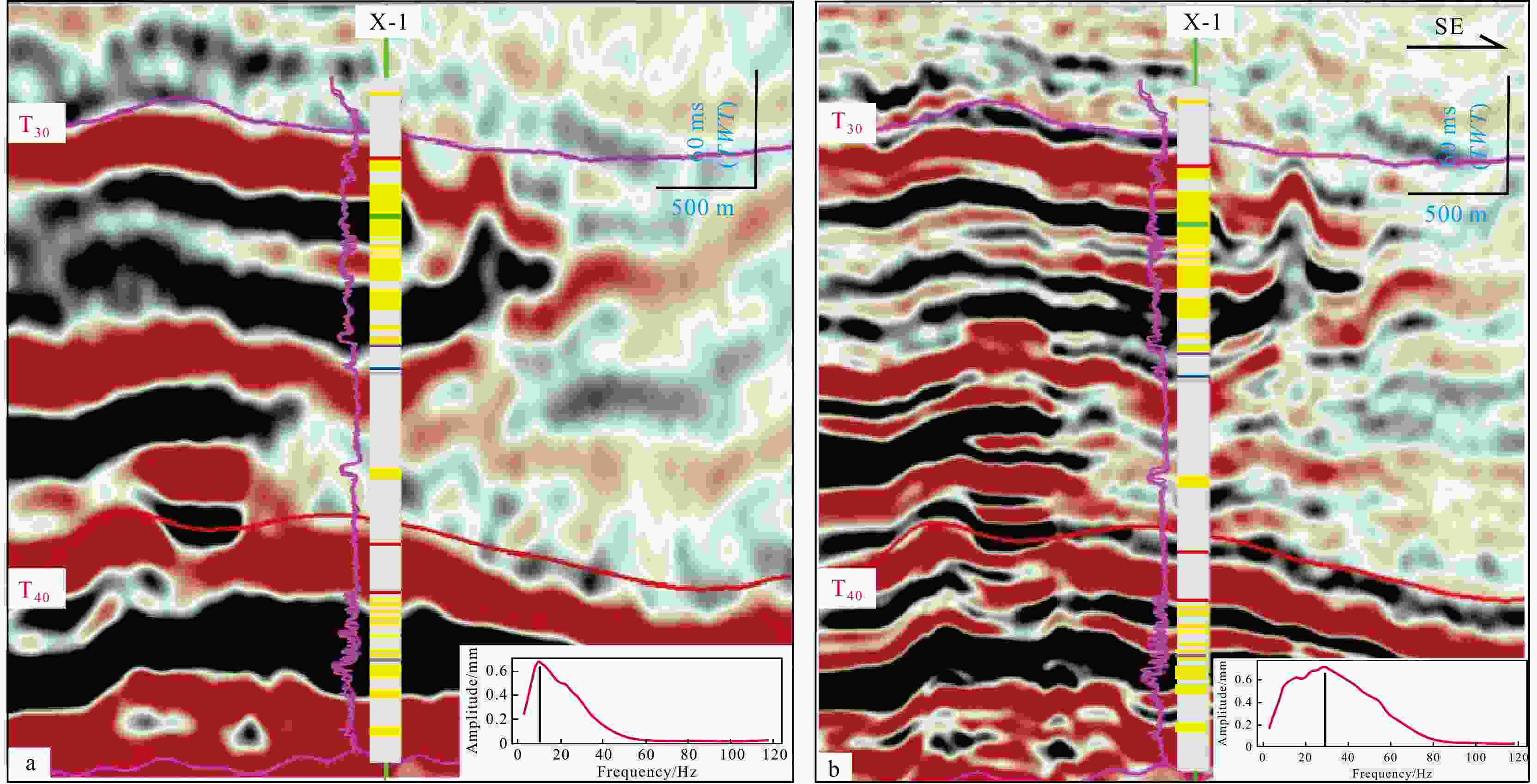
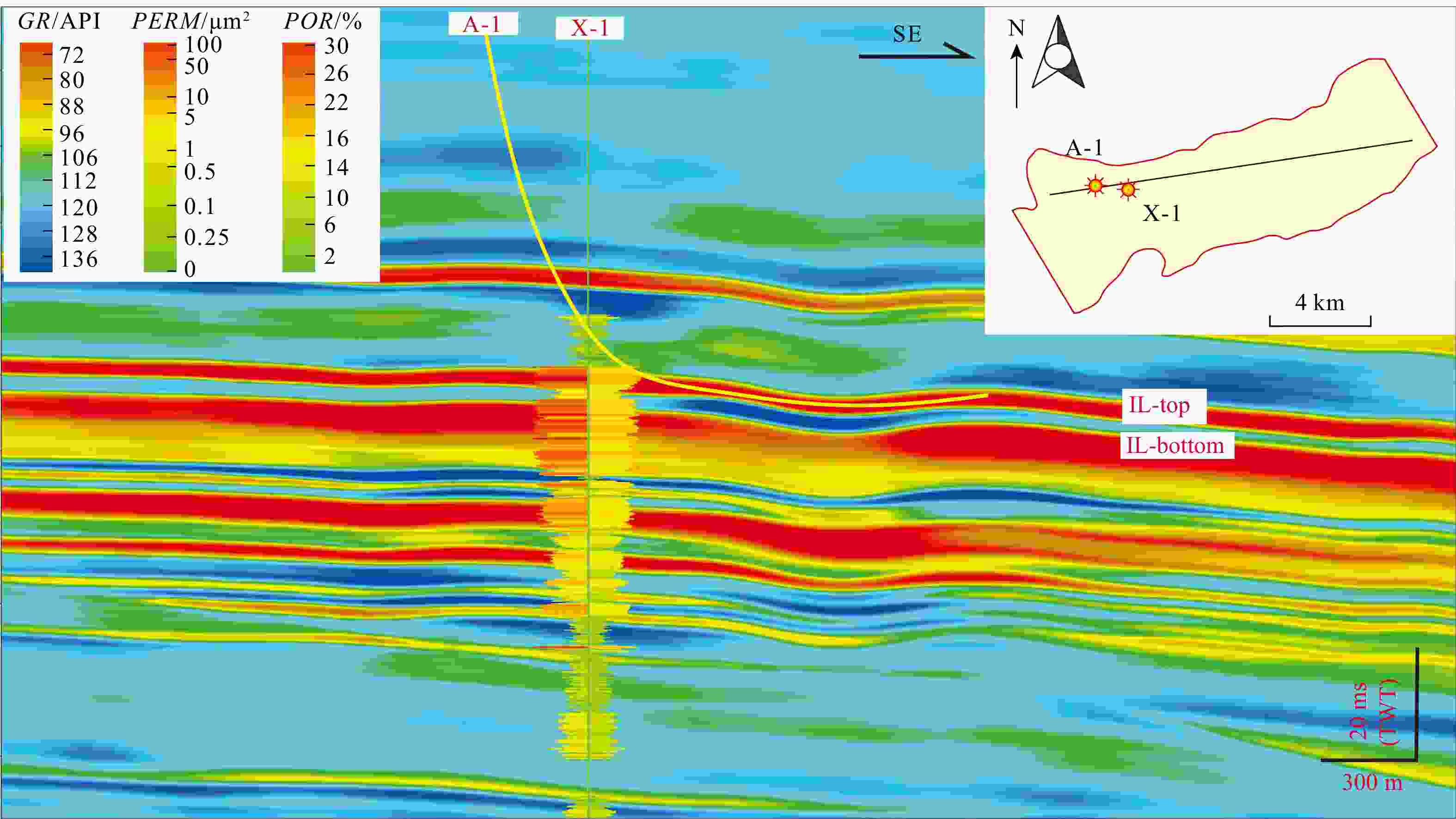
图 9 N-S-3连井反演剖面(剖面位置肩图2g)
Figure 9. N-S-3 cross-well inversion profile
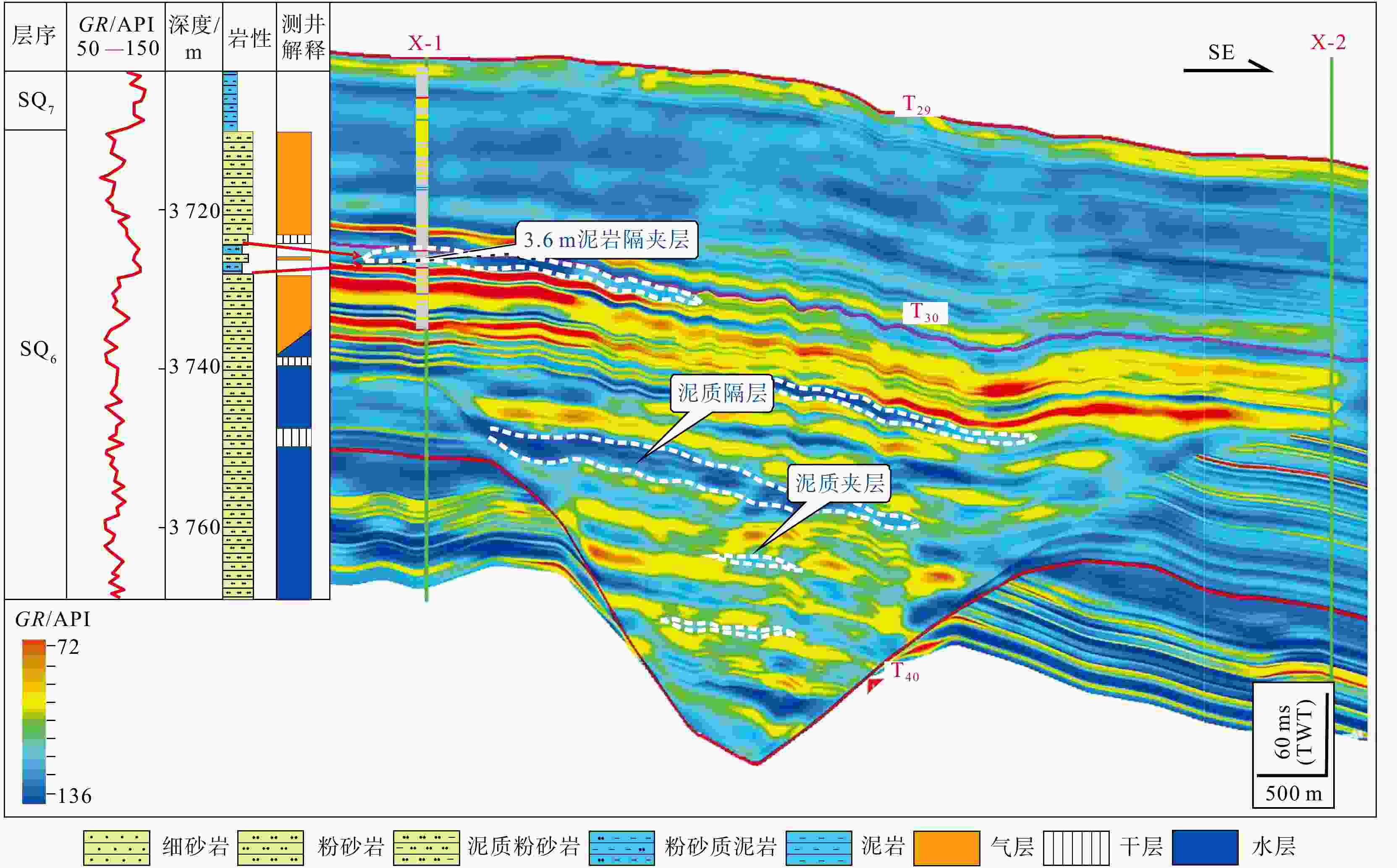
图 10 X-1井区隔夹层内部夹层划分(剖面位置见图2g)
Figure 10. Interlayer division within the X-1 well area
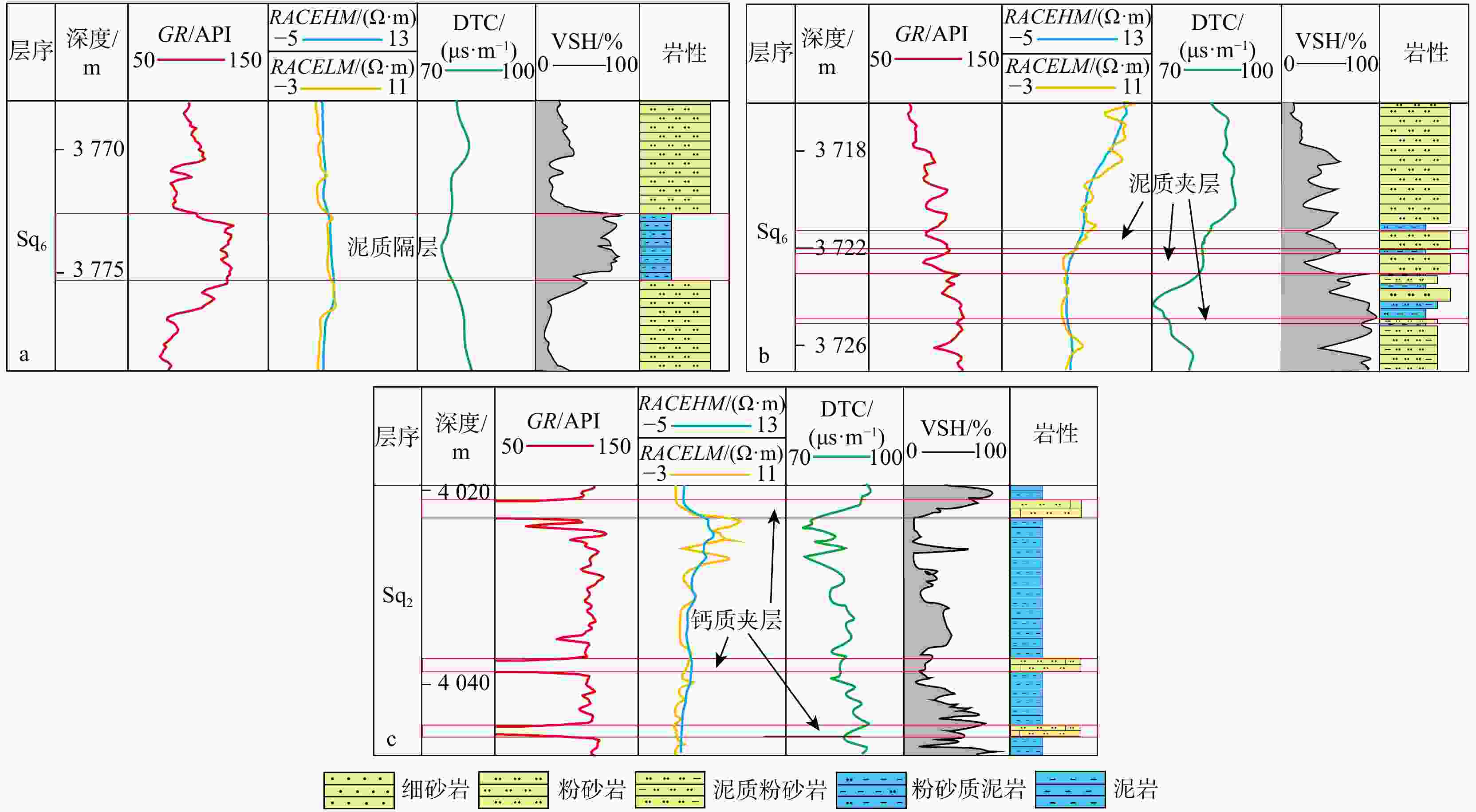
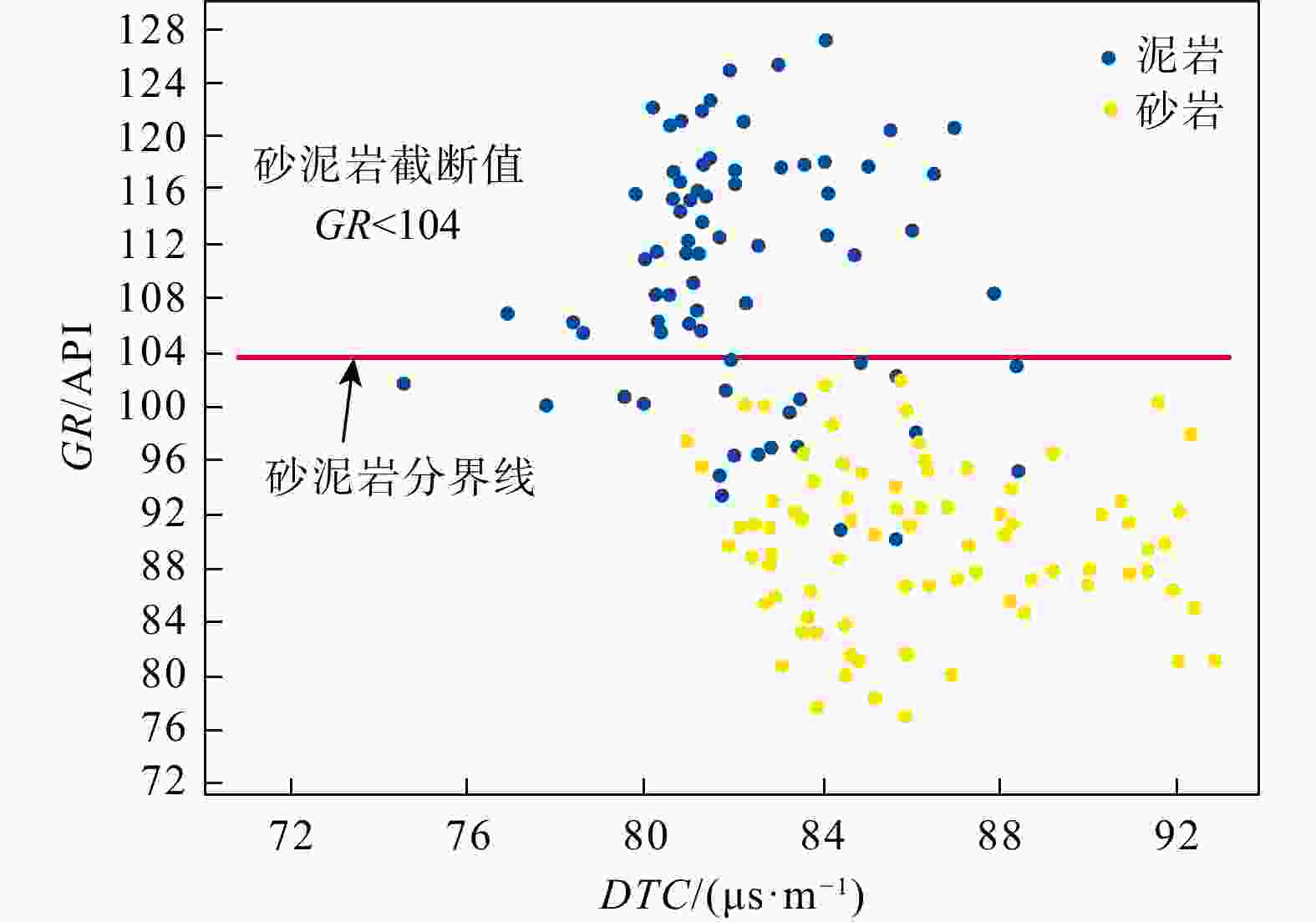
表 1 陵水X气田黄流组隔夹层定性识别标准
Table 1. Qualitative identification criteria for interlayers in the Huangliu Formation, Lingshui X gas field
测井曲线 隔夹层类型 泥质隔层 泥质夹层 钙质夹层 岩性 厚层泥岩 薄层泥岩、粉砂质泥岩 钙质粉砂岩 GR 高值,波动幅度差小 高值或略增加 低值 DTC 高值且变化不大 高值 低值 RACEHM、RACESHM 低值 中等 明显高值且呈尖峰状 VSH 高值 较高 低值 注:VSH. 泥质含量,下同 表 2 陵水X气田黄流组夹层定量识别标准
Table 2. Quantitative identification criteria for interlayers in the Huangliu Formation, Lingshui X gas field
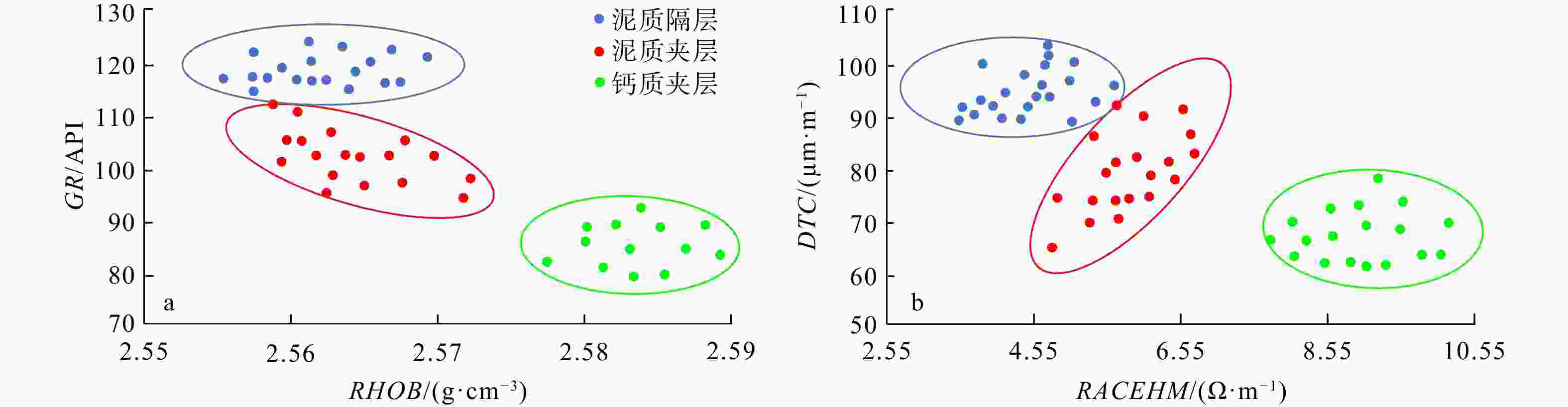
夹层分类 RHOB/(g·cm−3) DTC/(μs· m−1) GR/API RACEHM/(Ω·m−1) 范围 平均 范围 平均 泥质隔层 2.55~2.57 88.1~107.9 90.8 116.5~125 120 2.7~5 泥质夹层 2.56~2.575 63.4~91.3 76.8 92~110.9 104 4.5~7 钙质夹层 >2.58 61.2~76.1 71.01 76.3~90.6 88.2 7~10.55 注:RHOB. 密度,下同 -
[1] 谢玉洪. 中国海油近海油气勘探实践与思考[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(2): 1-13.XIE Y H. Practices and thoughts of CNOOC offshore oil and gas exploration[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(2): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 谢玉洪, 高阳东. 中国海油近期国内勘探进展与勘探方向[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2020, 25(1): 20-30.XIE Y H, GAO Y D. Recent domestic exploration progress and direction of CNOOC[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2020, 25(1): 20-30. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 张功成, 屈红军, 张凤廉, 等. 全球深水油气重大新发现及启示[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(1): 1-34. doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0042-6ZHANG G C, QU H J, ZHANG F L, et al. Major new discoveries of oil and gas in global deepwaters and enlightenment[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(1): 1-34. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1038/s41401-018-0042-6 [4] 付超, 谢玉洪, 王晖, 等. 深水峡谷复合浊积砂体内隔夹层发育类型与沉积成因: 以琼东南盆地中央峡谷为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2023, 43(5): 23-33.FU C, XIE Y H, WANG H, et al. Types and sedimentary genesis of barriers and interlayers in the composite turbidite sand bodies of deep-water canyon: A case study of the central canyon in the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2023, 43(5): 23-33. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 蔺鹏, 吴胜和, 胡光义. 被动陆缘盆地逆冲、底辟构造对深水层序结构的控制: 以尼日尔三角洲盆地某深水区为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(9): 21-34. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.09.003LIN P, WU S H, HU G Y. Control of thrust and diapir structures on deep-water sequence architectures in passive continental margin basins: A case study on a deep-water zone in the Niger Delta Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(9): 21-34. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2022.09.003 [6] 谢玉洪. 南海北部自营深水天然气勘探重大突破及其启示[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(10): 1-8.XIE Y H. A major breakthrough in deepwater natural gas exploration in a self-Run oil/gas field in the northern South China Sea and its enlightenment[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(10): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 朱建敏, 达丽亚, 高红立, 等. 海上稀井条件下砂质辫状河储层隔夹层识别: 以渤海LD2X油田为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2020, 27(6): 739-744. doi: 10.6056/dkyqt202006013ZHU J M, DA L Y, GAO H L, et al. Identification of interlayers in sandy braided river reservoirs under less well conditions: A case study of LD2X oilfield, Bohai, China[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2020, 27(6): 739-744. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6056/dkyqt202006013 [8] 叶云飞, 刘春成, 刘志斌, 等. 海上宽频地震反演方法及其在南海深水区的应用[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(2): 65-70.YE Y F, LIU C C, LIU Z B, et al. Analysis of marine broadband seismic data inversion and application in deep water of South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(2): 65-70. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 束青林. 孤岛油田馆陶组河流相储层隔夹层成因研究[J]. 石油学报, 2006, 27(3): 100-103. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.03.022SHU Q L. Interlayer characterization of fluvial reservoir in Guantao Formation of Gudao oilfield[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2006, 27(3): 100-103. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2006.03.022 [10] DING W J, HOU D J, ZHANG W W, et al. A new genetic type of natural gases and origin analysis in northern Songnan-Baodao Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2018, 50: 384-398. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2017.12.003 [11] MORAD S, AL-RAMADAN K, KETZER J M, et al. The impact of diagenesis on the heterogeneity of sandstone reservoirs: A review of the role of depositional facies and sequence stratigraphy[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2010, 94(8): 1267-1309. doi: 10.1306/04211009178 [12] ESCHARD R, LEMOUZY P, BACCHIANA C, et al. Combining sequence stratigraphy, geostatistical simulations, and production data for modeling a fluvial reservoir in the Chaunoy field (Triassic, France)[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1998, 82(1998): 545-568. [13] 吴兆徽, 刘显太, 杜玉山, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘哈山地区油藏夹层几何形态及空间散布建模[J]. 新疆地质, 2023, 41(3): 449-453. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2023.03.025WU Z H, LIU X T, DU Y S, et al. Geometric shape and spatial dispersion modeling of reservoir interbeds in hala'alta region at the northwest margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2023, 41(3): 449-453. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2023.03.025 [14] 李峰峰, 李蕾, 万继方, 等. 伊拉克X油田碳酸盐岩隔夹层隐蔽性特征及封隔性评价[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 48(4): 1-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2024.04.001LI F F, LI L, WAN J F, et al. Hidden characteristics and sealed property evaluation of carbonate baffles and barrier in X oilfield, Iraq[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2024, 48(4): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2024.04.001 [15] 苏明, 姜涛, 张翠梅, 等. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷体系东段形态-充填特征及其地质意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(6): 1805-1815.SU M, JIANG T, ZHANG C M, et al. Characteristics of morphology and infillings and the geological significances of the central canyon system in eastern Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2014, 44(6): 1805-1815. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 李冬, 王英民, 王永凤, 等. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷深水天然堤−溢岸沉积[J]. 沉积学报, 2011, 29(4): 689-694. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2011.04.008LI D, WANG Y M, WANG Y F, et al. The sedimentary and foreground of prospect for levee-overbank in central canyon, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2011, 29(4): 689-694. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2011.04.008 [17] 解习农, 陈志宏, 孙志鹏, 等. 南海西北陆缘深水沉积体系内部构成特征[J]. 地球科学, 2012, 37(4): 627-634. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2012.072XIE X N, CHEN Z H, SUN Z P, et al. Depositional architecture characteristics of deepwater depositional systems on the continental margins of northwestern South China Sea[J]. Earth Science, 2012, 37(4): 627-634. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2012.072 [18] 张道军, 王亚辉, 王振峰, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区中央峡谷沉积微相特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(6): 1114-1121.ZHANG D J, WANG Y H, WANG Z F, et al. Characteristics of sedimentary microfacies in the central canyon within the deep water area, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(6): 1114-1121. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 许怀智, 张迎朝, 林春明, 等. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷天然气成藏特征及其主控因素[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(9): 1741-1752.XU H Z, ZHANG Y Z, LIN C M, et al. Characteristics and key controlling factors of natural gas accumulation in the central submarine canyon, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(9): 1741-1752. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 党亚云. 莺歌海盆地东方区黄流组一段海底扇地震沉积学研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(6): 118-128. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220208DANG Y Y. Seismic sedimentology of submarine fan system in the 1st Member of the Huangliu Formation, Dongfang area, Yinggehai Basin, China[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(6): 118-128. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220208 [21] 孙海萱, 李磊, 丁晟, 等. 琼东南盆地L区中央峡谷沉积构型、演化及其主控因素[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2022, 38(1): 61-71.SUN H X, LI L, DING S, et al. Sedimentary architecture of the central canyon in L area of Qiongdongnan Basin and their evolution and controlling factors[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2022, 38(1): 61-71. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 刘巍, 胡林, 廖仪, 等. 南海深水中央峡谷下切水道识别及对储层非均质性影响[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2022, 36(2): 54-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2022.02.009LIU W, HU L, LIAO Y, et al. Identification of undercut channel in deep water central canyon of South China Sea and its influence on reservoir heterogeneity[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2022, 36(2): 54-61. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2022.02.009 [23] 周展, 杨朝强, 洪楚侨, 等. 深水少井区重力流薄泥岩隔夹层预测方法[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(12): 52-58. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.12.006ZHOU Z, YANG Z Q, HONG C Q, et al. A prediction method of thin mudstone interlayers with gravity flow in deep water areas with fewer wells[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(12): 52-58. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2020.12.006 [24] 李超, 陈国俊, 沈怀磊, 等. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷沉积充填特征与储层分布规律[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(增刊2): 74-82. doi: 10.7623/syxb2013S2009LI C, CHEN G J, SHEN H L, et al. Depositional filling and reservoir distribution patterns of the central canyon in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(S2): 74-82. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7623/syxb2013S2009 [25] MAO K N, XIE X N, XIE Y H, et al. Post-rift tectonic reactivation and its effect on deep-water deposits in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northwestern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2015, 36(2): 227-242. [26] 谭建财, 范彩伟, 任科英, 等. 琼东南盆地北部构造变换带及其油气地质意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2014, 21(2): 62-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2014.02.016TAN J C, FAN C W, REN K Y, et al. Structural transfer zone and significance for hydrocarbon geological in northern Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2014, 21(2): 62-65. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2014.02.016 [27] 任建业. 中国近海海域新生代成盆动力机制分析[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(10): 3337-3361.REN J Y. Genetic dynamics of China offshore Cenozoic basins[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(10): 3337-3361. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 江汝锋, 曹立成, 邓孝亮, 等. 琼东南盆地宝岛21-1区陵水组沉积特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(5): 31-44. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230329JIANG R F, CAO L C, DENG X L, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of the Lingshui Formation in the Baodao 21-1 area of the Qiongdongnan Basin and their significance in hydrocarbon exploration[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(5): 31-44. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230329 [29] ZHU W L, LEI C. Refining the model of South China Sea's tectonic evolution: Evidence from Yinggehai-Song Hong and Qiongdongnan basins[J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2013, 34(3): 325-339. [30] GONG C L, WANG Y M, ZHU W L, et al. The central submarine canyon in the Qiongdongnan basin, northwestern South China Sea: Architecture, sequence stratigraphy, and depositional processes[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(9): 1690-1702. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.06.005 [31] SHI W Z, XIE Y H, WANG Z F, et al. Characteristics of overpressure distribution and its implication for hydrocarbon exploration in the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 66: 150-165. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.037 [32] 王华, 陈思, 刘恩涛, 等. 南海北部莺-琼盆地典型重力流沉积特征与物源体系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 5-18.WANG H, CHEN S, LIU E T, et al. Typical gravity flow sedimentary features and provenance system in Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 5-18. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 朱继田, 杨希冰, 胡向阳, 等. 琼东南盆地北部中生代凹陷特征及油气成藏条件初探[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 83-93. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0219ZHU J T, YANG X B, HU X Y, et al. Characteristic and petroleum geology of the Mesozoic sags of the northern Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 83-93. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0219 [34] ZHU W L, ZHONG K, LI Y C, et al. Characteristics of hydrocarbon accumulation and exploration potential of the northern South China Sea deepwater basins[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 57(24): 3121-3129. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4940-y [35] ALPAK F O, BARTON M D, NARUK S J. The impact of fine-scale turbidite channel architecture on deep-water reservoir performance[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(2): 251-284. doi: 10.1306/04021211067 [36] 李华, 何幼斌, 谈梦婷, 等. 深水重力流水道-朵叶体系形成演化及储层分布: 以鄂尔多斯盆地西缘奥陶系拉什仲组露头为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2022, 43(4): 917-928.LI H, HE Y B, TAN M T, et al. Evolution of and reservoir distribution within deep-water gravity flow channel-lobe system: A case study of the Ordovician Lashenzhong Formation outcrop at western margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2022, 43(4): 917-928. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 李华, 王英民, 徐强, 等. 深水单向迁移水道-堤岸沉积体系特征及形成过程[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(3): 653-661. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.03.017LI H, WANG Y M, XU Q, et al. Characteristics and processes of deep water unidirectionally-migrating channel-levee system[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(3): 653-661. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2013.03.017 [38] 王文涛, 卢刚臣, 李冰玲, 等. 地震波形指示反演技术在埕海区块薄储层预测中的应用[J]. 石油地质与工程, 2022, 36(4): 7-11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2022.04.002WANG W T, LU G C, LI B L, et al. Application of seismic waveform indication inversion technology in prediction of thin reservoir in Chenghai block[J]. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2022, 36(4): 7-11. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8217.2022.04.002 [39] 顾雯, 徐敏, 王铎翰, 等. 地震波形指示反演技术在薄储层预测中的应用: 以准噶尔盆地B地区薄层砂岩气藏为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(11): 2064-2069.GU W, XU M, WANG D H, et al. Application of seismic motion inversion technology in thin reservoir prediction: A case study of the thin sandstone gas reservoir in the B area of Junggar Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(11): 2064-2069. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 陈奎, 王雯娟, 徐万兴, 等. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷“深海一号” 大气田周缘成藏条件与滚动勘探成效[J]. 石油实验地质, 2023, 45(5): 994-1006. doi: 10.11781/sysydz202305994CHEN K, WANG W J, XU W X, et al. Accumulation conditions and rolling exploration results in the periphery of "Deep Sea No. 1" giant gas field in central canyon of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2023, 45(5): 994-1006. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11781/sysydz202305994 [41] 张迎朝, 李绪深, 徐新德, 等. 琼东南盆地深水西区L25气田天然气成因、来源与成藏过程[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019, 24(3): 73-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2019.03.009ZHANG Y Z, LI X S, XU X D, et al. Genesis, origin, and accumulation process of the natural gas of L25 gas field in the western deepwater area, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2019, 24(3): 73-82. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2019.03.009 -




 下载:
下载: