Graptolite Biostratigraphy of the Ordovician to Silurian Renheqiao Formation in the Baoshan region, southern Yunnan, China
-
摘要:
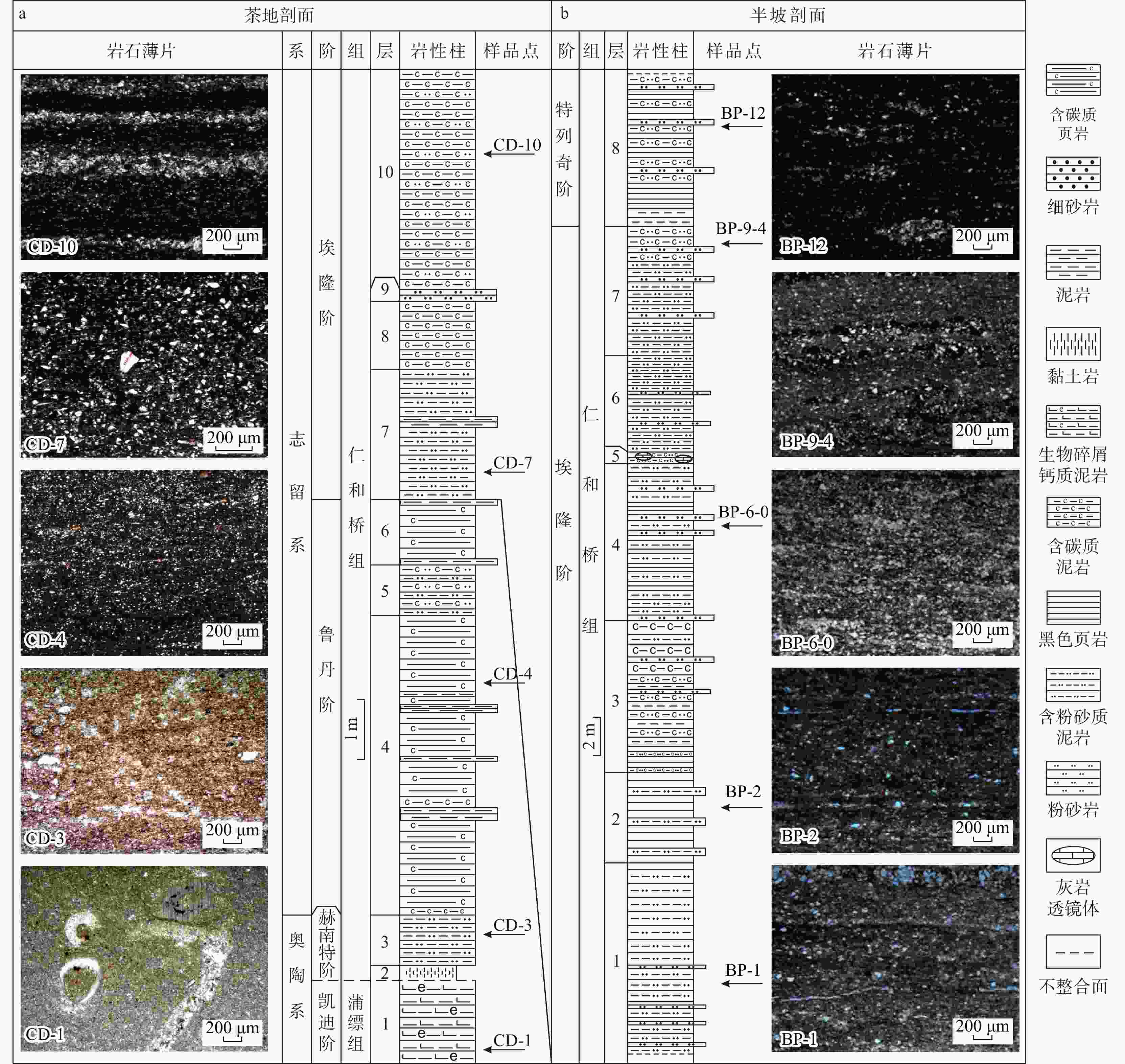
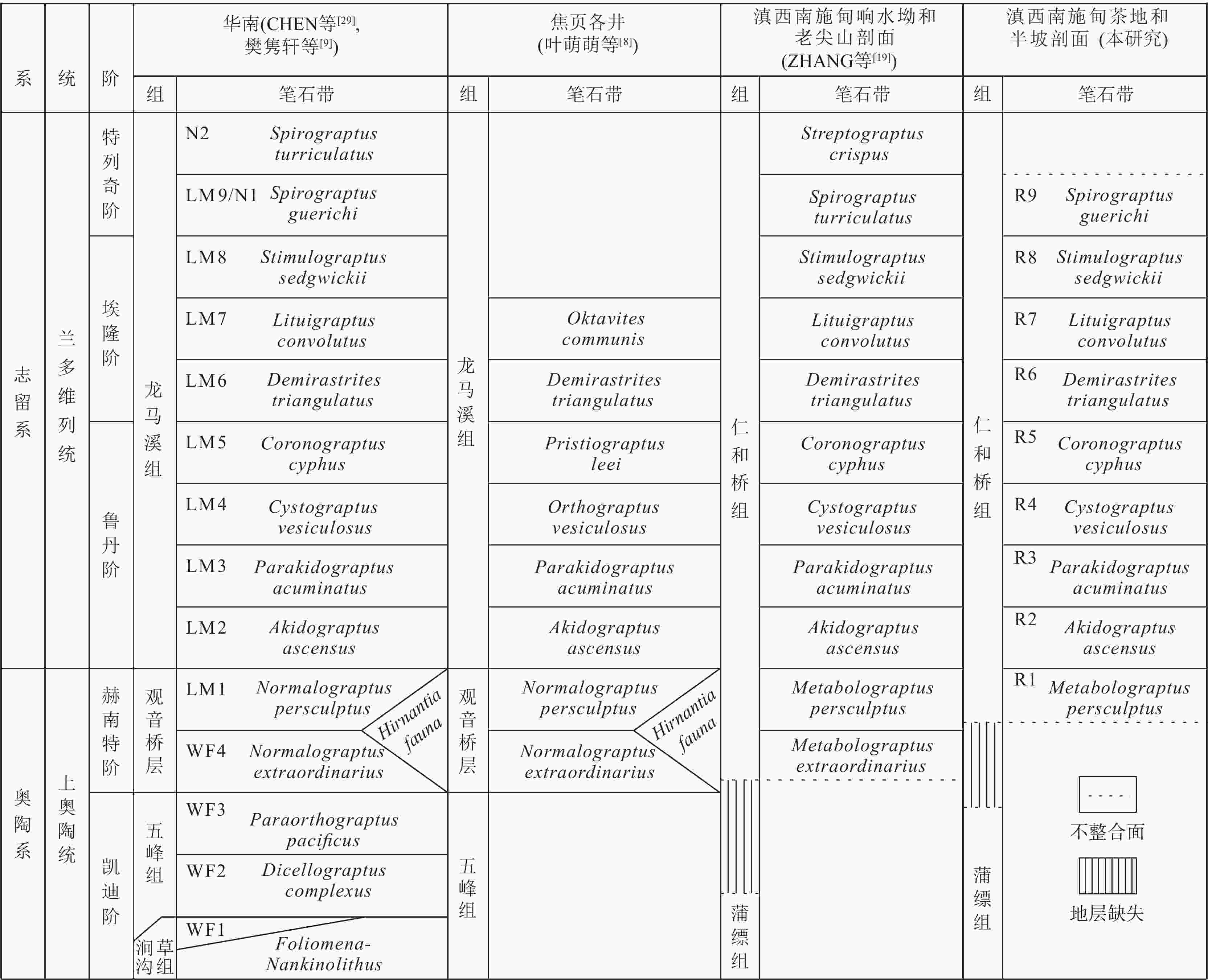
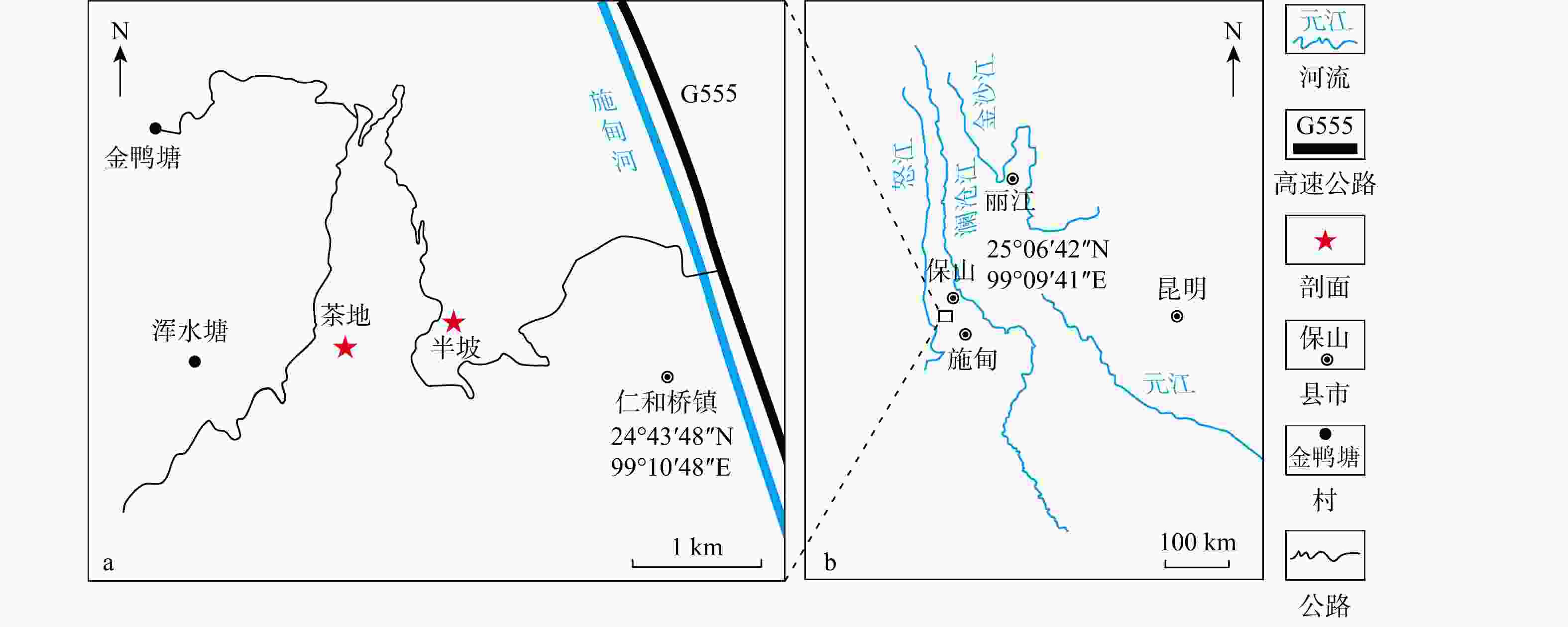
滇西保山地区广泛发育奥陶系−志留系仁和桥组黑色岩系。为了建立其笔石地层时空对比框架,以云南保山市施甸县半坡剖面和茶地剖面为研究对象,开展了生物地层学和岩石学研究。研究表明,研究区仁和桥组总厚度约71.6 m,底部发育一层厚约25 cm的古风化壳,与下伏蒲缥组呈平行不整合接触,证明研究区在晚奥陶世曾暴露于地表。基于高分辨率笔石化石调查,识别出了上奥陶统赫南特阶至志留系兰多维列统特列奇阶共9个笔石带,自下而上依次为
Metabolograptus persculptus 带(仁和桥组第1笔石带,后续简称R1)、Akidograptus ascensus 带(R2)、Parakidograptus acuminatus 带(R3)、Cystograptus vesiculosus 带(R4)、Coronograptus cyphus 带(R5)、Demirastrites triangulatus 带(R6),Lituigraptus convolutus 带(R7),Stimulograptus sedgwickii 带(R8)和Spirograptus guerichi 带(R9)。与扬子地区龙马溪组笔石生物地层对比表明,保山地区仁和桥组9个笔石带能够与龙马溪组LM1~LM9笔石带相对应。此研究成果为保山地区仁和桥组页岩气调查评价建立了良好的笔石生物地层学基础。Abstract:The Ordovician to Silurian Renheqiao Formation, characterized by a sequence of well-preserved black shales, is extensively developed in the Baoshan region, southwestern Yunnan Province, China.
Objective The primary goal of this study is to establish a graptolite biostratigraphic framework for the Renheqiao Formation. To achieve this, the research focuses on the Banpo and Chadi sections in Shidian County, Baoshan City, Yunnan Province, which are critical outcrops for biostratigraphic analysis in the area.
Methods A combination of high-resolution biostratigraphic and lithologic records was conducted to precisely define the stratigraphy and identify key biozones within the formation.
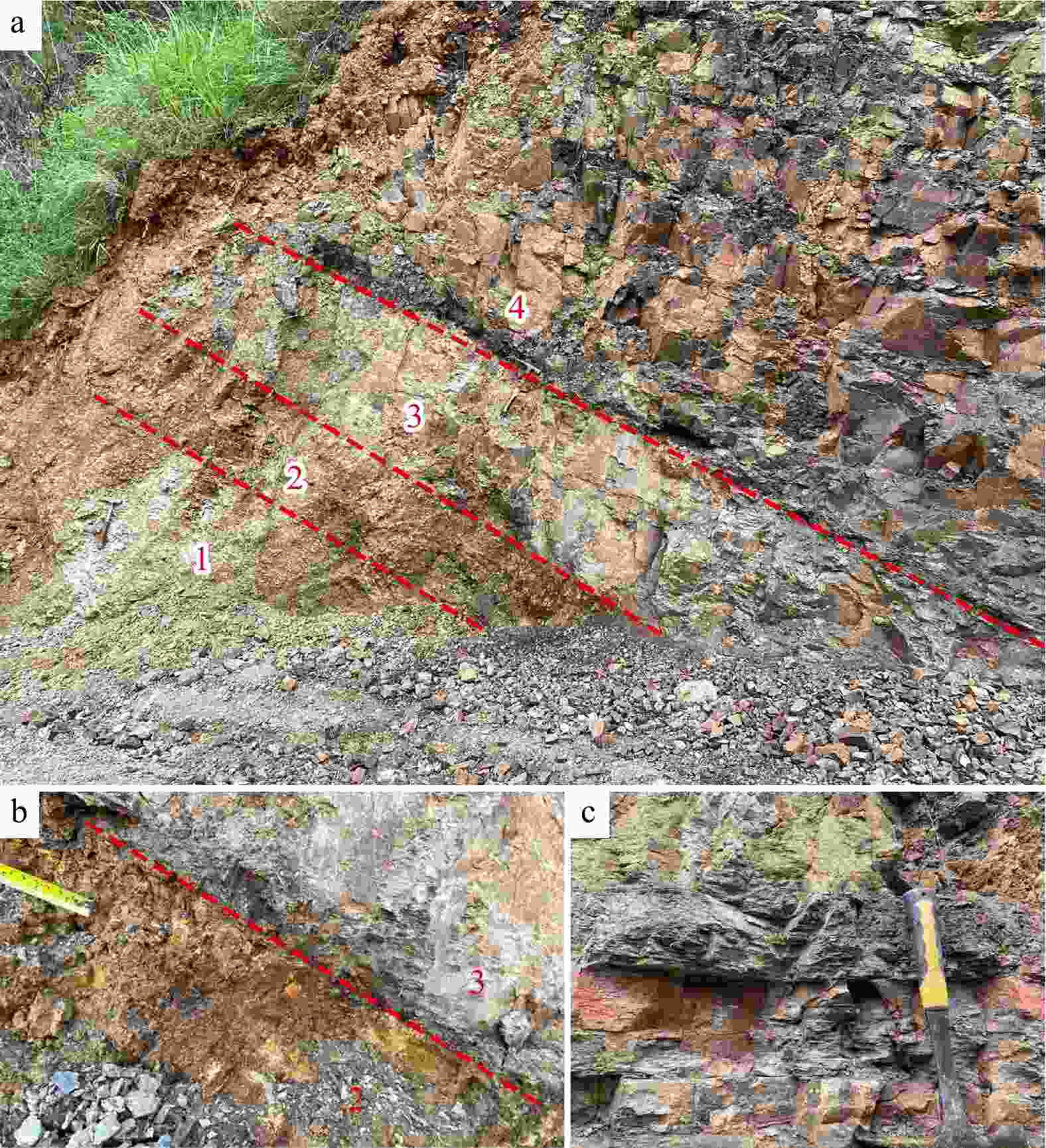
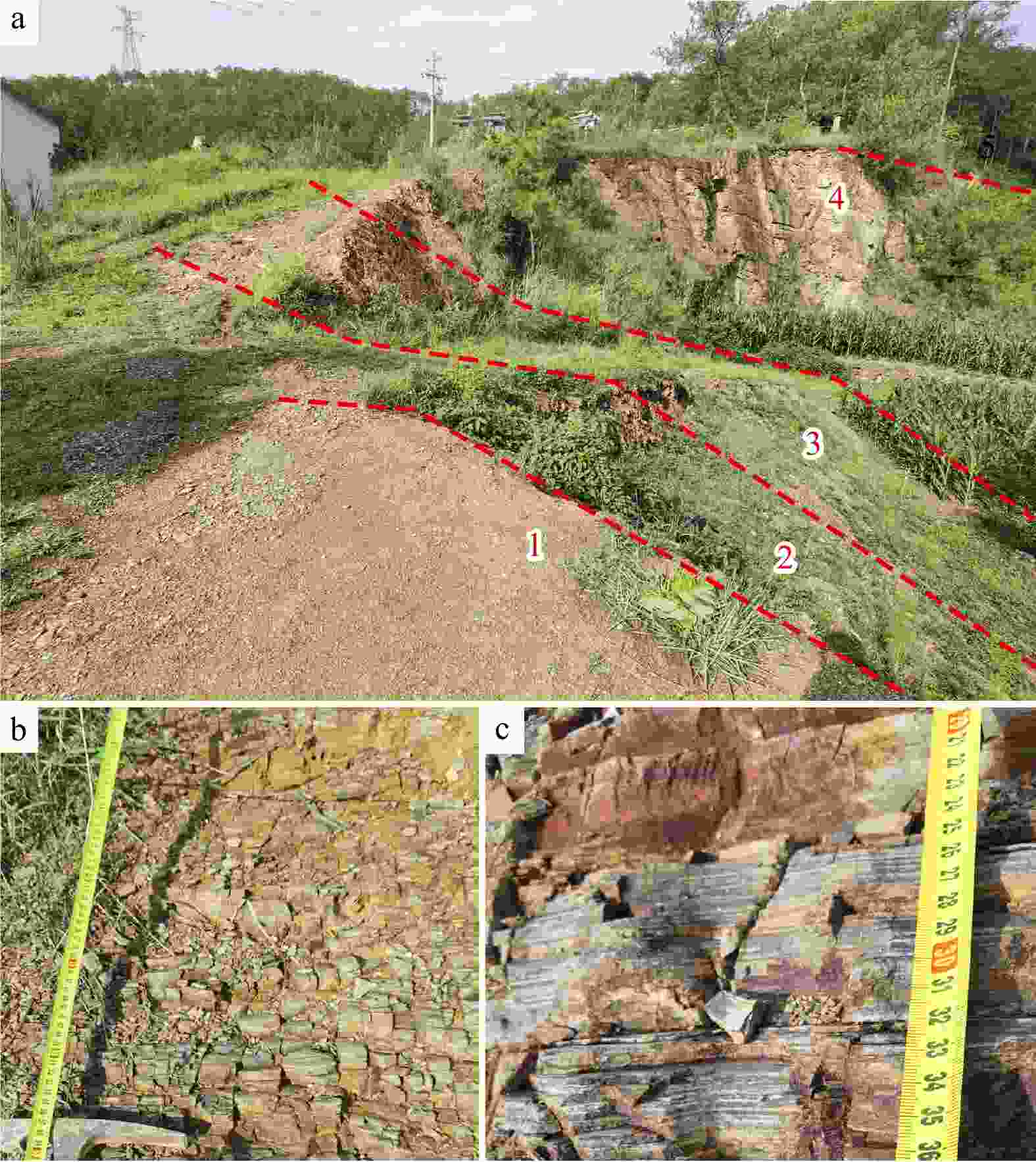
Results The Renheqiao Formation in the study area is approximately 71.6 meters thick, with a about 25 cm of paleo-weathering crust at the base. It unconformably overlies the Pupiao Formation, indicating that the study area was subaerially exposed during the Late Ordovician. Based on detailed fieldwork and high-resolution surveys, a total of nine graptolite zones were identified, spanning from the upper Hirnantian in the Ordovician to the Silurian Llandovery Telychian stage. These identified graptolite zones are in ascending order as follows: the
Metabolograptus persculptus zone (R1),Akidograptus ascensus zone (R2),Parakidograptus acuminatus zone (R3),Cystograptus vesiculosus zone (R4),Coronograptus cyphus zone (R5),Demirastrites triangulatus zone (R6),Lituigraptus convolutus zone (R7),Stimulograptus sedgwickii zone (R8), andSpirograptus guerichi zone (R9).Conclusion The nine graptolite zones of the Renheqiao Formation in the Baoshan region correlate well with those of the Longmaxi Formation (LM1–LM9) in the Yangtze region. This correlation not only strengthens the regional stratigraphic framework but also provides a solid basis for future shale gas exploration and assessment in the Baoshan region.
-
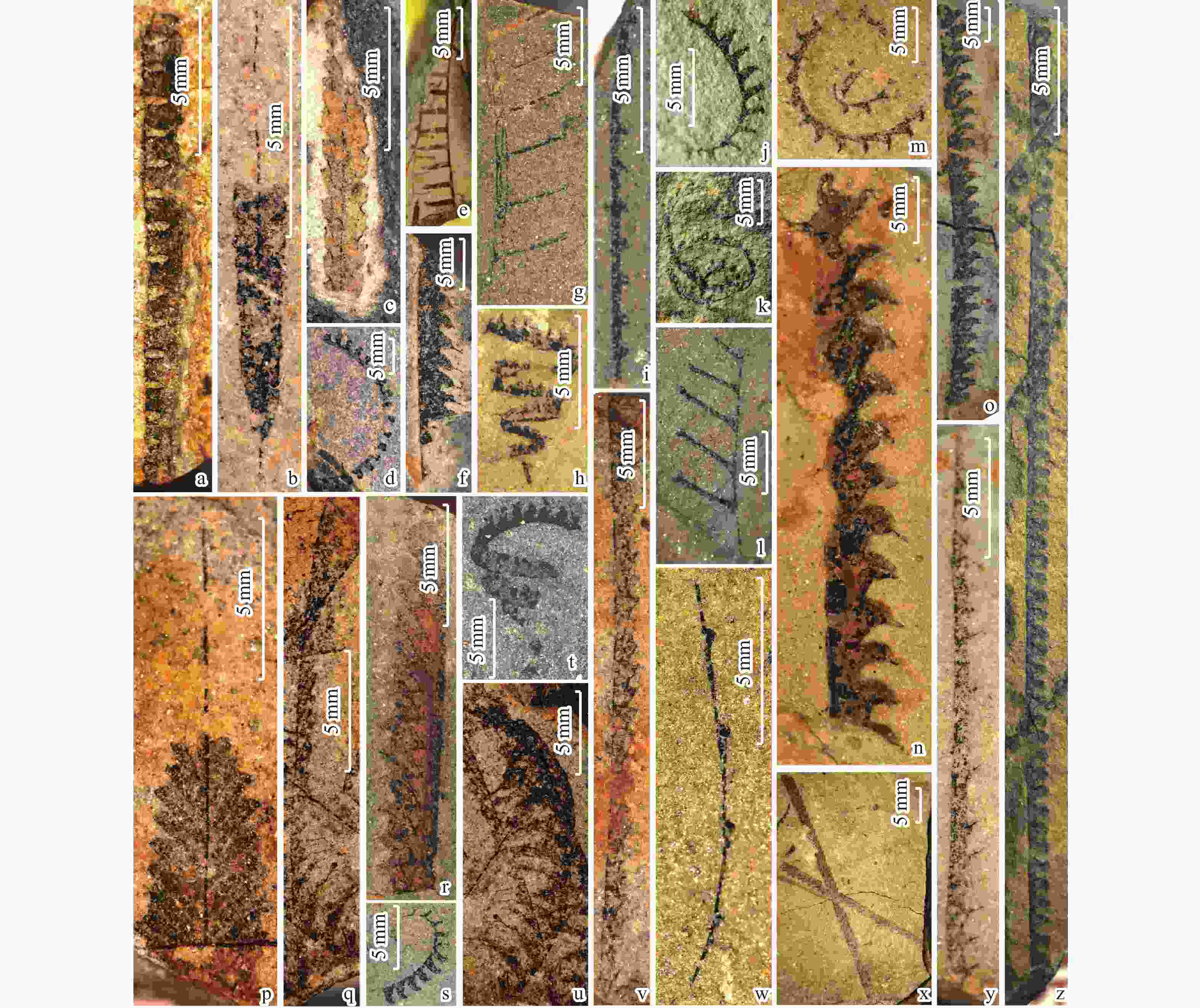
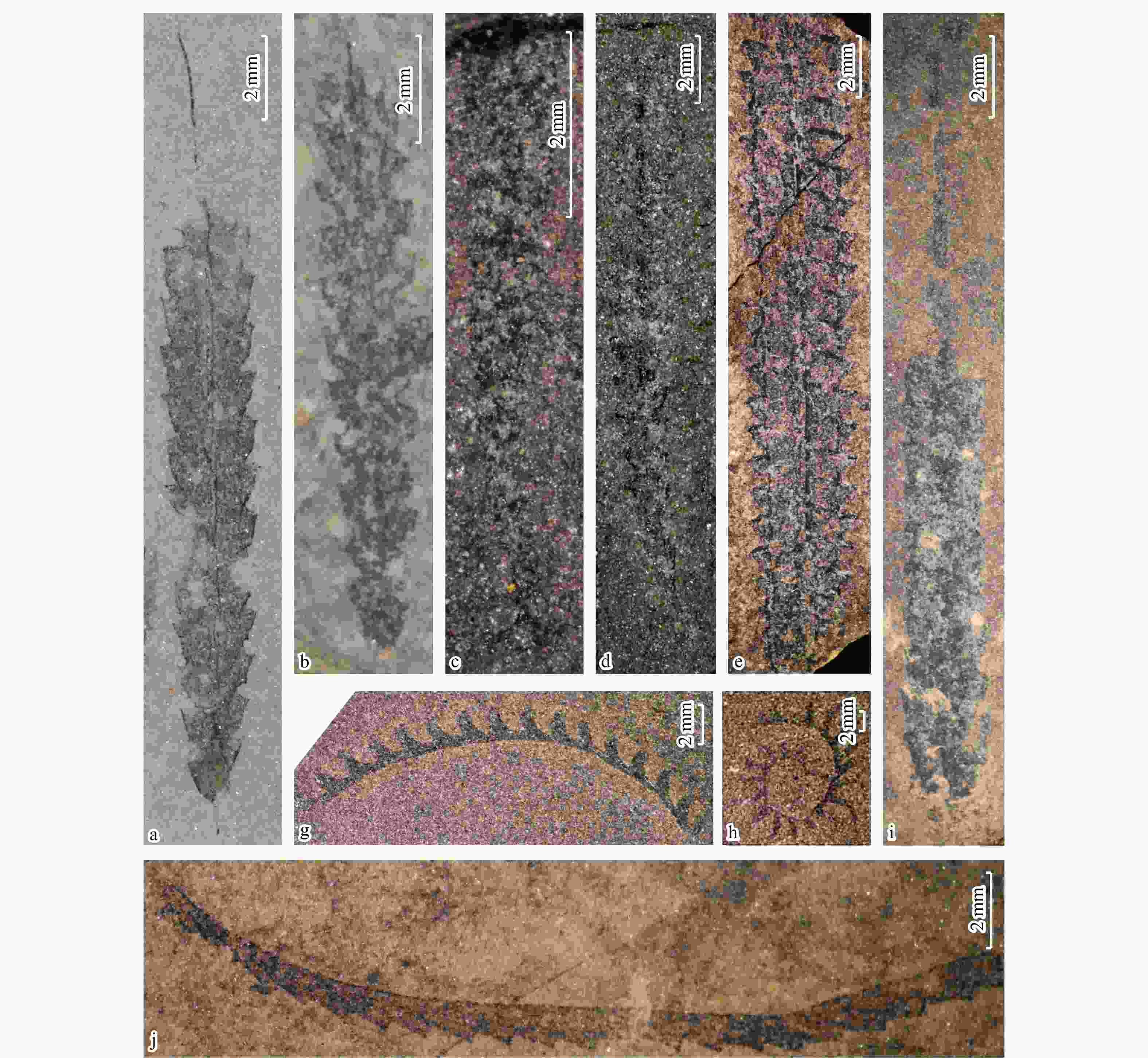
图 5 茶地剖面部分笔石照片
a. Metalograptus ojsuensis Koren' and Mikhaylova in Apollonov et al. 1980,样品点CD-3; b. Metabolograptus persculptus Elles and Wood 1907,样品点CD-3; c. Akidograptus ascensus Davies 1929,样品点CD-4; d. Parakidograptus acuminatus Nicholson 1867,样品点CD-4; e. Cystograptus vesiculosus Nicholson 1868,样品点CD-4; f. Cystograptus ancestralis Štorch 1972,样品点CD-4; g. Demirastrites triangulatus Harkness 1851,样品点CD-7; h. Rastrites guizhouensis Mu 2002,样品点CD-10; i. Coronograptus cyphus Lapworth 1876, 样品点CD-10
Figure 5. Graptolites photos form the Chadi section
图 6 半坡剖面部分笔石照片
a. Euclimacograptus Riva 1989,样品点BP-3;b.Normalograptus sp.,样品点BP-6;c. Glyptograptus sp.,样品点BP-7-0;d. Demirastrites magnificus Pribyl and Munch 1942,样品点BP-0;e. Rastrites peregrinus Barrande 1850,样品点BP-9-1;f, n, o. Stimulograptus sedgwickii Portlock 1843,样品点BP-9-1,BP-11,BP-12;g. Rastrites distans Lapworth 1876;h. Spirograptus guerichi Loydell et al. 1993,样品点BP-9-2;i. Monograptus yichangensis Ni 1987,样品点BP-0-7;j. Demirastrites triangulatus Harkness 1851,样品点BP-2-1;k. Spirograptus guerichi Loydell et al. 1993,样品点BP-12;l. Rastrites distans abbreviatus Lapworth 1876,样品点BP-2-1;m. Oktavites gracilis Wang 1978,样品点BP-6-1;p. Petalolithus sp.,样品点BP-7-1;q. Pribylograptus argutus Lapworth 1876,样品点BP-7-3;r. Pernerograptus Pribyl 1941,样品点BP-9-2;s. Demirastrites triangulatus,样品点BP-0-0;t. Spirograptus guerichi Loydell et al. 1993,样品点BP-9-2;u. Lituigraptus convolutus Hisinger 1837,样品点BP-7-3;v. Pernerograptus qijiangensis Ye 1978,样品点BP-8-1;w. Monograptus gemmatus Barrande 1850,样品点BP-9;x. Pristiograptus sp.,样品点BP-1;y. Pristiograptus sichuanensis Ye 1978,样品点BP-0-4;z. Monograptus xizangensis Mu and Ni 1975,样品点BP-6
Figure 6. Graptolites photos form the Banpo section
-
[1] 王洪浩,李江海,孙唯童,等. 志留纪全球古板块再造及岩相古地理[J]. 古地理学报,2016,18(2):185-196.WANG H H,LI J H,SUN W T,et al. Global Palaeo-plate reconstruction and lithofacies Palaeogeography in the Silurian[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition),2016,18(2):185-196. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] ZOU C N,DONG D Z,WANG S J,et al. Geological characteristics and resource potential of shale gas in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2010,37(6):641-653. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(11)60001-3 [3] LUČIĆ D,BOSWORTH W. Regional geology and petroleum systems of the main reservoirs and source rocks of north Africa and the middle east,the geology of the Arab world:An overview[M]. Cham:Springer Geology. 2019. [4] ALBRIKI K,WANG F Y,LI M J,et al. Silurian hot shale occurrence and distribution,organofacies,thermal maturation,and petroleum generation in Ghadames Basin,North Africa[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences,2022,189:104497. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2022.104497 [5] 李刚,赵迪斐,郭英海. 川东南地区龙马溪组页岩笔石与沉积环境的关系[J]. 科学技术与工程,2018,18(12):16-23.LI G,ZHAO D F,GUO Y H. The relationship between graptolite of Longmaxi shale and sedimentary environment in southeastern Sichuan[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2018,18(12):16-23. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] KHAN M Z,FENG Q L,ZHANG K,et al. Biogenic silica and organic carbon fluxes provide evidence of enhanced marine productivity in the Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian of South China[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2019,534:109278. [7] 郭伟. 渝东南地区五峰组−龙马溪组黑色岩系地球化学特征与有机质富集机制研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2019.Guo W. Geochemical Characteristics and Organic Matter enrichment mechanism:A case study of Wufeng-Longmaxi Black Shales in southeast of Chongqing[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences (Wuhan),2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 叶萌萌,潘安阳,张毅,等. 涪陵地区五峰组–龙马溪组黑色页岩有机质特征及成烃生物分析[J]. 微体古生物学报,2023,40(4):317-326.YE M M,PAN A Y,ZHANG Y,et al. Organic matter composition and hydrocarbon biogenic analysis on the black shale of the Wufeng–Longmaxi Formations in Fuling area[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica,2023,40(4):317-326. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 樊隽轩,MELCHIN M J,陈旭,等. 华南奥陶-志留系龙马溪组黑色笔石页岩的生物地层学[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2012,42(1):130-139. doi: 10.1360/zd-2012-42-1-130FAN J X,MELCHIN M J,CHEN X,et al. Biostratigraphy of black graptolite shale in Longmaxi Formation of Ordovician-Silurian in South China[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae),2012,42(1):130-139. (in Chinese) doi: 10.1360/zd-2012-42-1-130 [10] 陈旭,樊隽轩,张元动,等. 五峰组及龙马溪组黑色页岩在扬子覆盖区内的划分与圈定[J]. 地层学杂志,2015,39(4):351-358.CHEN X,FAN J X,ZHANG Y D,et al. Subdivision and delineation of the Wufeng and Lungmachi black shales in the subsurface areas of the Yangtze platform[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy,2015,39(4):351-358. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] FANG X,MA X,LI W J,et al. Biostratigraphical constraints on the disconformity within the Upper Ordovician in the Baoshan and Mangshi regions,western Yunnan Province,China[J]. Lethaia,2018,51(2):312-323. doi: 10.1111/let.12255 [12] 王红岩,施振生,孙莎莎. 四川盆地及周缘奥陶系五峰组:志留系龙马溪组页岩生物地层及其储集层特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2021,48(5):879-890.WANG H Y,SHI Z S,SUN S S. Biostratigraphy and reservoir characteristics of the Ordovician Wufeng-Silurian Longmaxi shale in the Sichuan Basin and surrounding areas,China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2021,48(5):879-890. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 聂海宽,陈清,李世臻,等. 重庆綦江观音桥剖面五峰组—龙马溪组地层特征及其对页岩气勘探开发的启示[J]. 地层学杂志,2022,46(3):271-285.NIE H K,CHEN Q,LI S Z,et al. Stratigraphic characteristics of Wufeng Formation-Lungmachi Formation in Guanyinqiao section of Qijiang,Chongqing,China and their implications for shale gas exploration and development[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy,2022,46(3):271-285. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 邹才能,赵群,张国生,等. 能源革命:从化石能源到新能源[J]. 天然气工业,2016,36(1):1-10.ZOU C N,ZHAO Q,ZHANG G S,et al. Energy revolution:From a fossil energy era to a new energy era[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2016,36(1):1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 李遇. 滇西地区下仁和桥组页岩气储层特征[C]//匿名:云南省首届青年地质科技论坛优秀学术论文集. [出版地不详]:[出版者不详],2017,168:13.Li Y. Shale Gas Reservoir Characteristics of Xiarenheqiao Formation in Western Yunnan [C]//Anon. Yunnan Exploration & Development (Ltd) of Coalbed Gas Resource. [S.L.]:[S.n.],2017,168:13. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] METCALFE I. Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion:Tectonic and Palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2013,66:1-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.020 [17] 云南省地质矿产局. 云南省区域地质志[M]. 北京:地质出版社,1990.Yunnan Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Regional Geology of Yunnan Province [M]. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,1990. (in Chinese) [18] 倪寓南,陈挺恩,蔡重阳,等. 云南西部的志留系[J]. 古生物学报,1982,21(1):119-132.NI Y N,CHEN T E,CAI C Y,et al. The Silurian rocks in western Yunnan[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica,1982,21(1):119-132. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] ZHANG Y,WANG Y,ZHAN R. Ordovician and Silurian Stratigraphy and Palaeontology of Yunnan,Southwest China[M]. Science Press,2014. [20] 苏柯又. 滇西−湾甸地区奥陶系沉积地层及沉积相特征研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2017.SU K Y. Study on characteristics of stratum and sedimentary of Ordovician sedimentary strata in wandian area of facies west Yunnan[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2017. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 全国地层委员会. 全国地层会议学术报告汇编:中国的志留系[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1962.Compilation of Academic Reports of the National Stratigraphic Conference:Silurian System of China [M]. Beijing:Science Press,1962. (in Chinese) [22] 尹赞勋. 志留纪时期的中国,西南地区区域地层表(云南省分册) [M]. 北京:地质出版社,1966.YIN Z X. China During the Silurian period,regional stratigraphic chart of southwestern China (Yunnan Volume) [M]. Beijing:Geological Press,1966.(in Chinese) [23] 陈旭,樊隽轩,陈清,等. 论广西运动的阶段性[J]. 中国科学(地球科学),2014,44(5):842-850.CHEN X,FAN J X,CHEN Q,et al. On the stages of Guangxi movement[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae),2014,44(5):842-850. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] SALTZMAN M R,YOUNG S A. Long-lived glaciation in the Late Ordovician? Isotopic and sequence-stratigraphic evidence from western Laurentia[J]. 2005,33(2):109-112. [25] HOLLAND S M,PATZKOWSKY M E. Sequence architecture of the Bighorn dolomite,Wyoming,USA:Transition to the late Ordovician icehouse[J]. 2012,82(8):599-615. [26] 陈旭,樊隽轩,王文卉,等. 黔渝地区志留系龙马溪组黑色笔石页岩的阶段性渐进展布模式[J]. 中国科学(地球科学),2017,47(6):720-732. doi: 10.1360/N072016-00186CHEN X,FAN J X,WANG W H,et al. Stage-progressive distribution pattern of the Lungmachi black graptolitic shales from Guizhou to Chongqing,Central China[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae),2017,47(6):720-732. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/N072016-00186 [27] 吕勇,山克强,谢运球,等. 滇西潞西(芒市)的奥陶系和志留系[J]. 地层学杂志,2014,38(2):161-169.LYU Y,SHAN K Q,XIE Y Q,et al. Ordovician-Silurian sequences in Luxi(Mangshi),western Yunnan,SW China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy,2014,38(2):161-169. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] CHEN X,CHEN Q,AUNG K P,et al. Latest Ordovician graptolites from the Mandalay Region,Myanmar[J]. Palaeoworld,2020,29(1):47-65. doi: 10.1016/j.palwor.2019.09.003 [29] CHEN X,RONG J Y,FAN J X,et al. The global boundary stratotype section and point (GSSP) for the base of the hirnantian stage (the uppermost of the Ordovician system)[J]. Episodes,2006,29(3):183-196. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/2006/v29i3/004 [30] ŠTORCH P,SCHÖNLAUB H P. Ordovician-Silurian boundary graptolites of the southern Alps,Austria[J]. Bulletin of Geosciences,2012:755-766. [31] CHEN X,FAN J X,MELCHIN M J,et al. Hirnantian (latest Ordovician) graptolites from the Upper Yangtze region,China[J]. Palaeontology,2005,48(2):235-280. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-4983.2005.00453.x [32] CHEN X,RONG J Y,MITCHELL C E,et al. Late Ordovician to earliest Silurian graptolite and brachiopod biozonation from the Yangtze region,South China,with a global correlation[J]. 2000,137(6):623-650. [33] ŠTORCH P. Graptolites from the rhuddanian-aeronian boundary interval (Silurian),Prague synform,Czech republic[J]. Bulletin of Geosciences,2015:841-891. [34] 武学进,陈清,李关访,等. 黔北习科1井五峰组−龙马溪组黑色页岩的地层划分与对比[J]. 地层学杂志,2020,44(1):1-11.WU X J,CHEN Q,LI G F,et al. Stratigraphic subdivision and correlation of the Wufeng and Lungmachi black shales from Xike-1 drillcore in northern Guizhou Province,South China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy,2020,44(1):1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 冯洪真,李明,李丽霞,等. 江南斜坡区早奥陶世笔石动物的生物分带与多样性变化[C]//佚名. 全国地层会议. 北京:中国地质学会,2013.FENG H Z,LI M,LI L X,et al. Biostratigraphy and diversity changes of early Ordovician graptolites in the Jiangnan slope area[C]//Anon. National Stratigraphic Conference. Beijing:Chinese Geological Society,2013. (in Chinese [36] 夏广胜. 安徽无为西部下志留统笔石[J]. 古生物学报,1979,18(1):92-121.XIA G S. Lower Silurian graptolites of Wuwei,Anhui Province[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica,1979,18(1):92-121. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 汪啸风,陈孝红,王传尚,等. 中国奥陶系和下志留统下部年代地层单位的划分[J]. 地层学杂志,2004,28(1):1-17.WANG X F,CHEN X H,WANG C S,et al. Ordovician to the Lowest Silurian chronostratigraphic subdivision in China[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy,2004,28(1):1-17. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 刘义生,金吉能,潘仁芳,等. 渝东南盆缘转换带五峰组−龙马溪组常压页岩气保存条件评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(1):253-263.LIU Y S,JIN J N,PAN R F,et al. Preservation condition evaluation of normal pressure shale gas in the Wufeng and Longmaxi Formations of basin margin transition zone,Southeast Chongqing[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(1):253-263. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 王川,董田,蒋恕,等. 中扬子地区上奥陶统−下志留统五峰组−龙马溪组页岩纵向非均质性及主控因素[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(3):108-121.WANG C,DONG T,JIANG S,et al. Vertical heterogeneity and the main controlling factors of the Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian Wufeng-Longmaxi shales in the Middle Yangtze region[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(3):108-121. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 蔡全升,陈孝红,王传尚,等. 上奥陶统五峰组−下志留统龙马溪组黑色岩系笔石赋存特征与堆积模式[J]. 地质科技通报,2020,39(2):43-53.CAI Q S,CHEN X H,WANG C S,et al. Occurrence characteristics and depositional model of graptolites from the black shale in the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation and Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2020,39(2):43-53. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 罗超,王兰生,石学文,等. 长宁页岩气田宁211井五峰组−龙马溪组生物地层[J]. 地层学杂志,2017,41(2):142-152.LUO C,WANG L S,SHI X W,et al. Biostratigraphy of the Wufeng to Longmaxi Formation at Well Ning 211 of Changning shale gas field[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy,2017,41(2):142-152. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] 樊隽轩,吴磊,陈中阳,等. 四川兴文县麒麟乡五峰组−龙马溪组黑色页岩的生物地层序列[J]. 地层学杂志,2013,37(4):513-520.FAN J X,WU L,CHEN Z Y,et al. Biostratigraphy of the Wufeng-lungmachi black shales at Qilin,Xingwen County,Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy,2013,37(4):513-520. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: