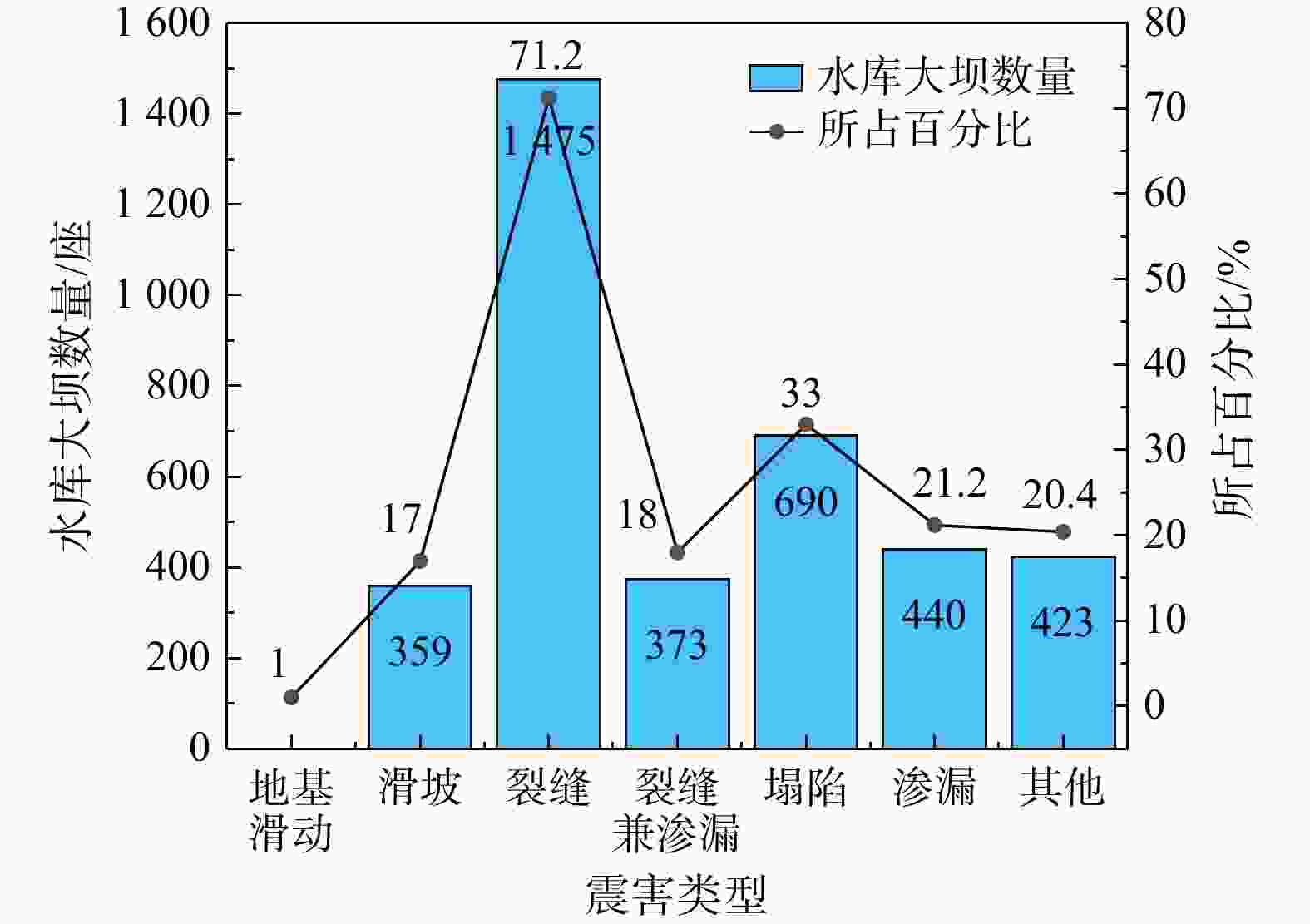
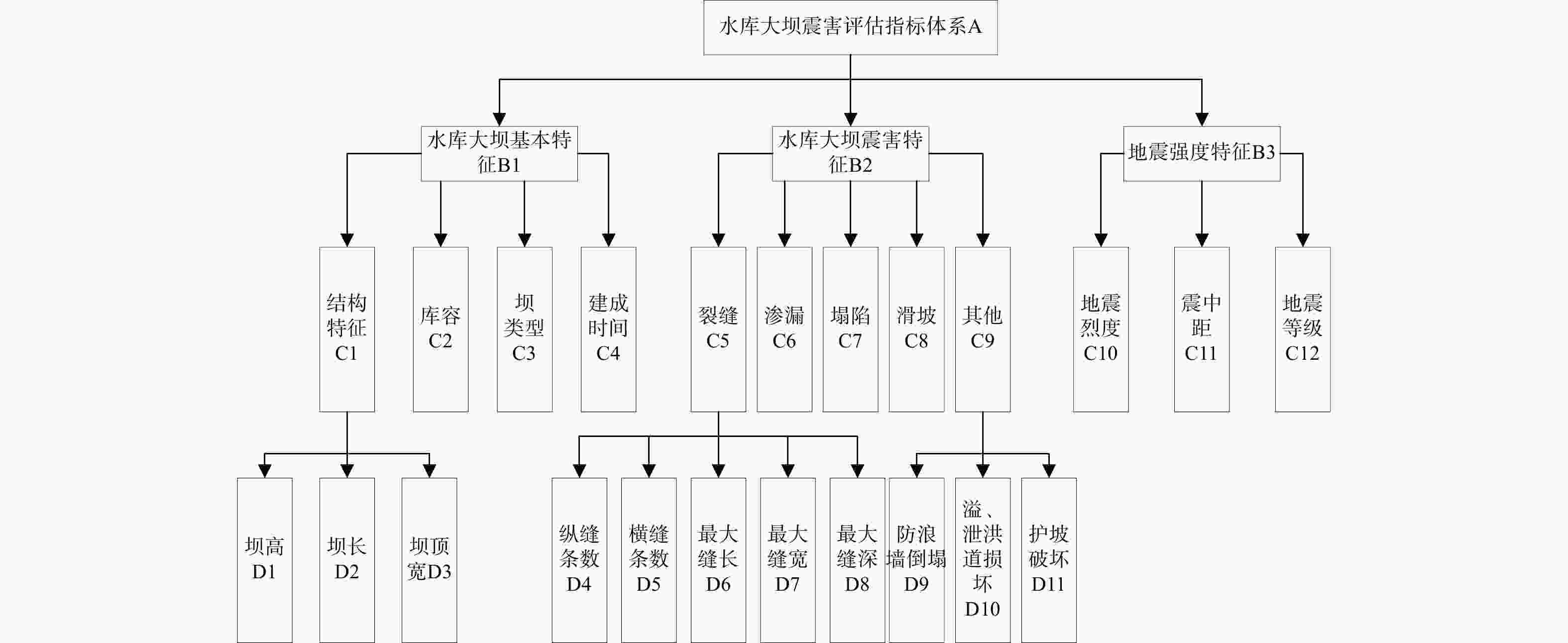
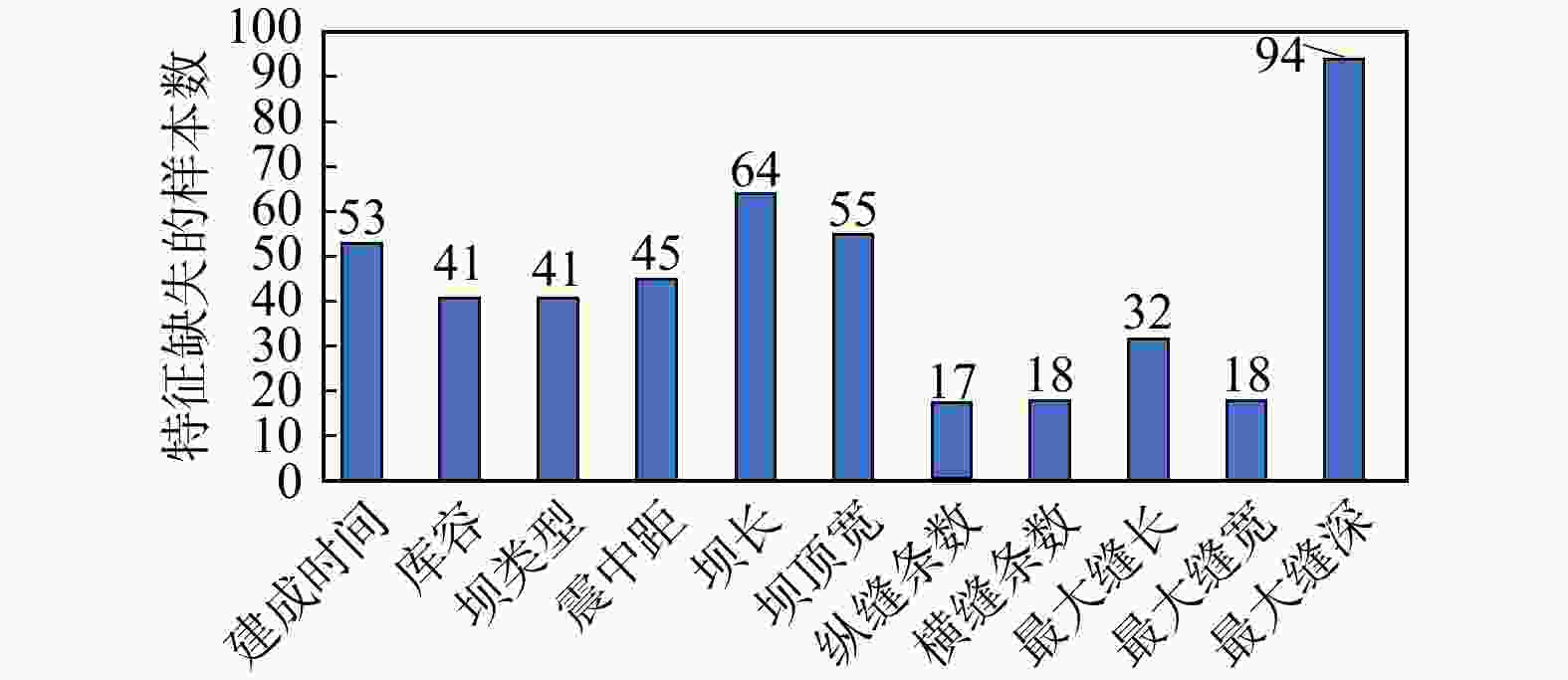
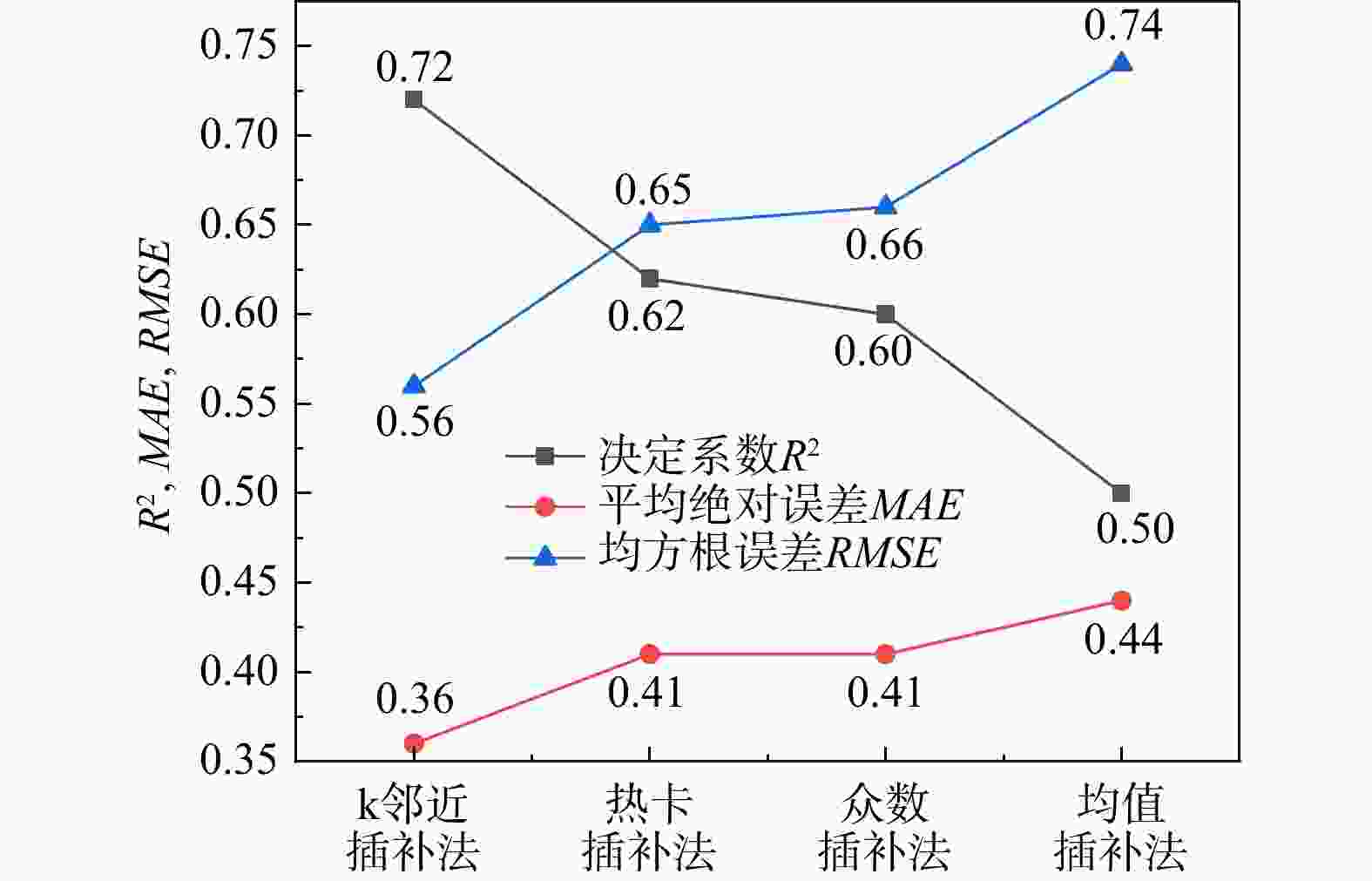
-
摘要:
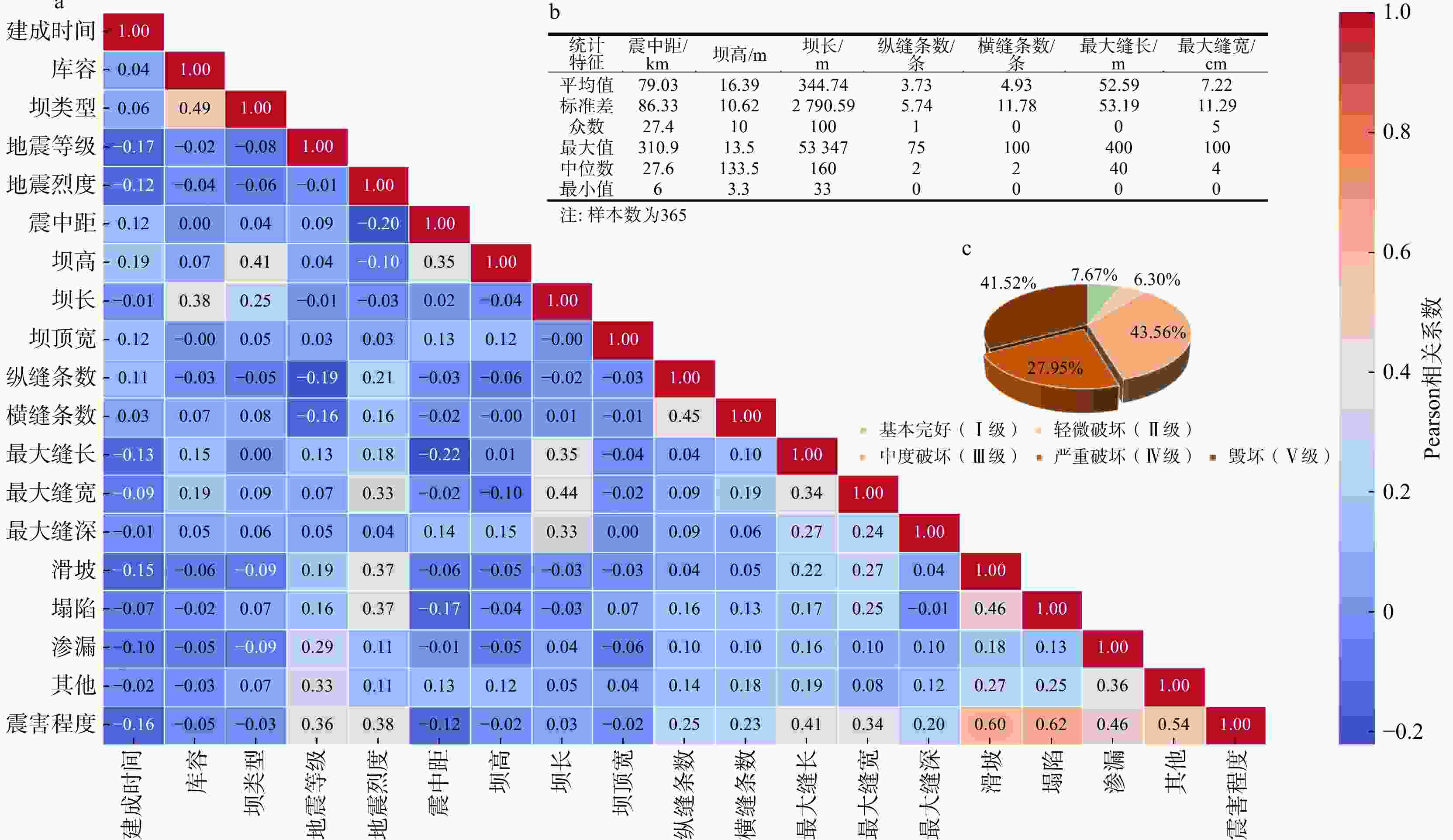
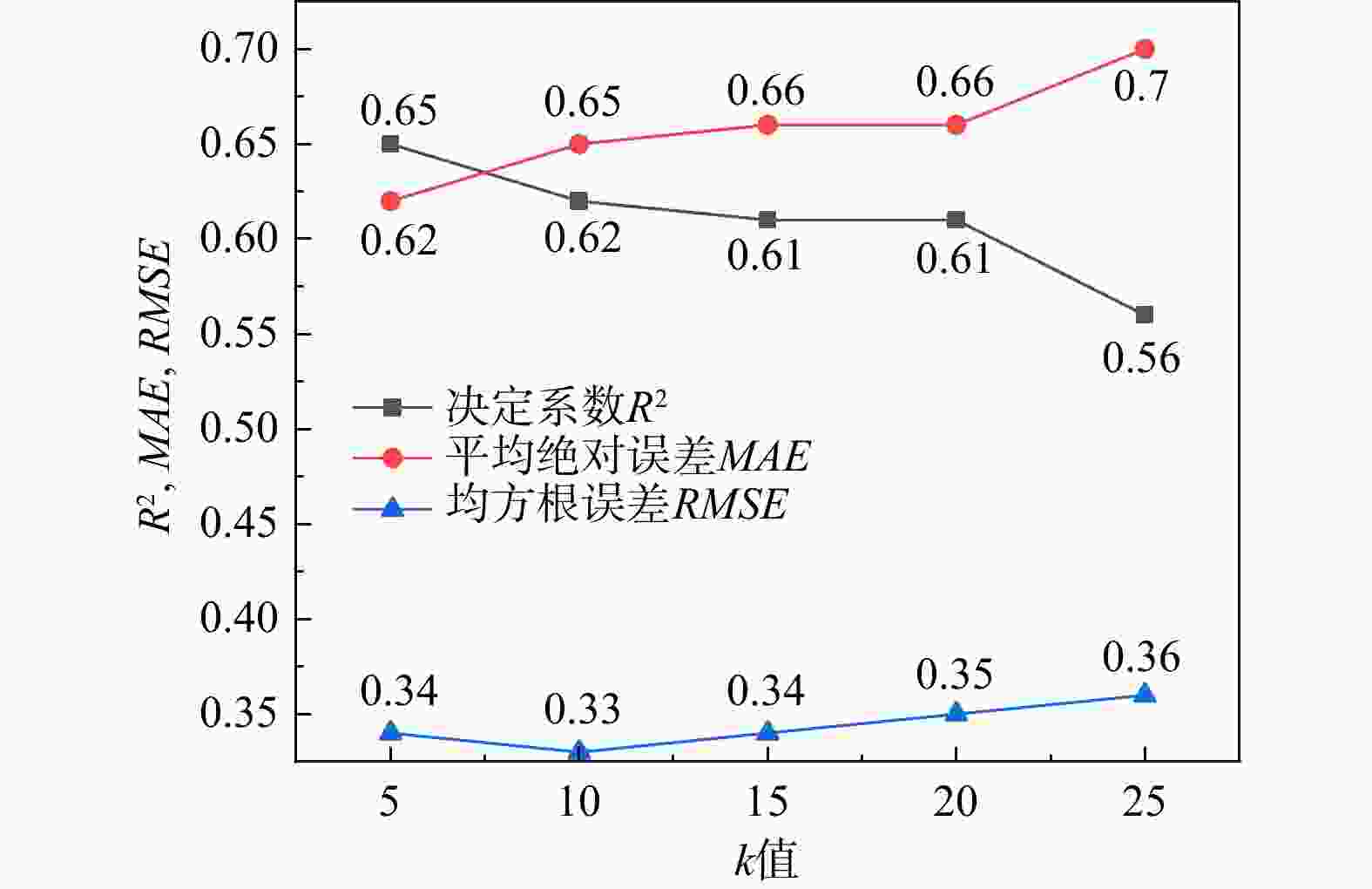
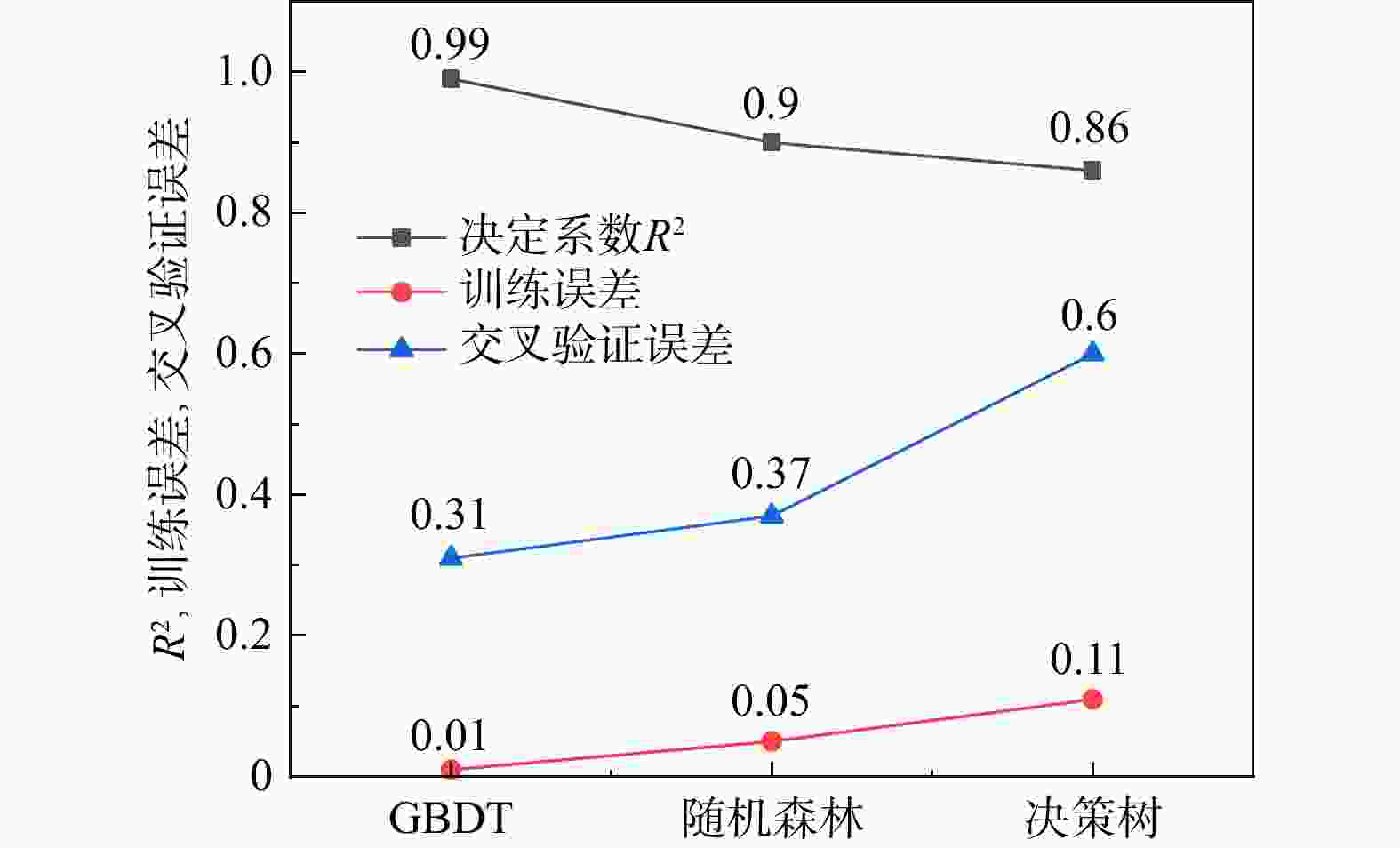
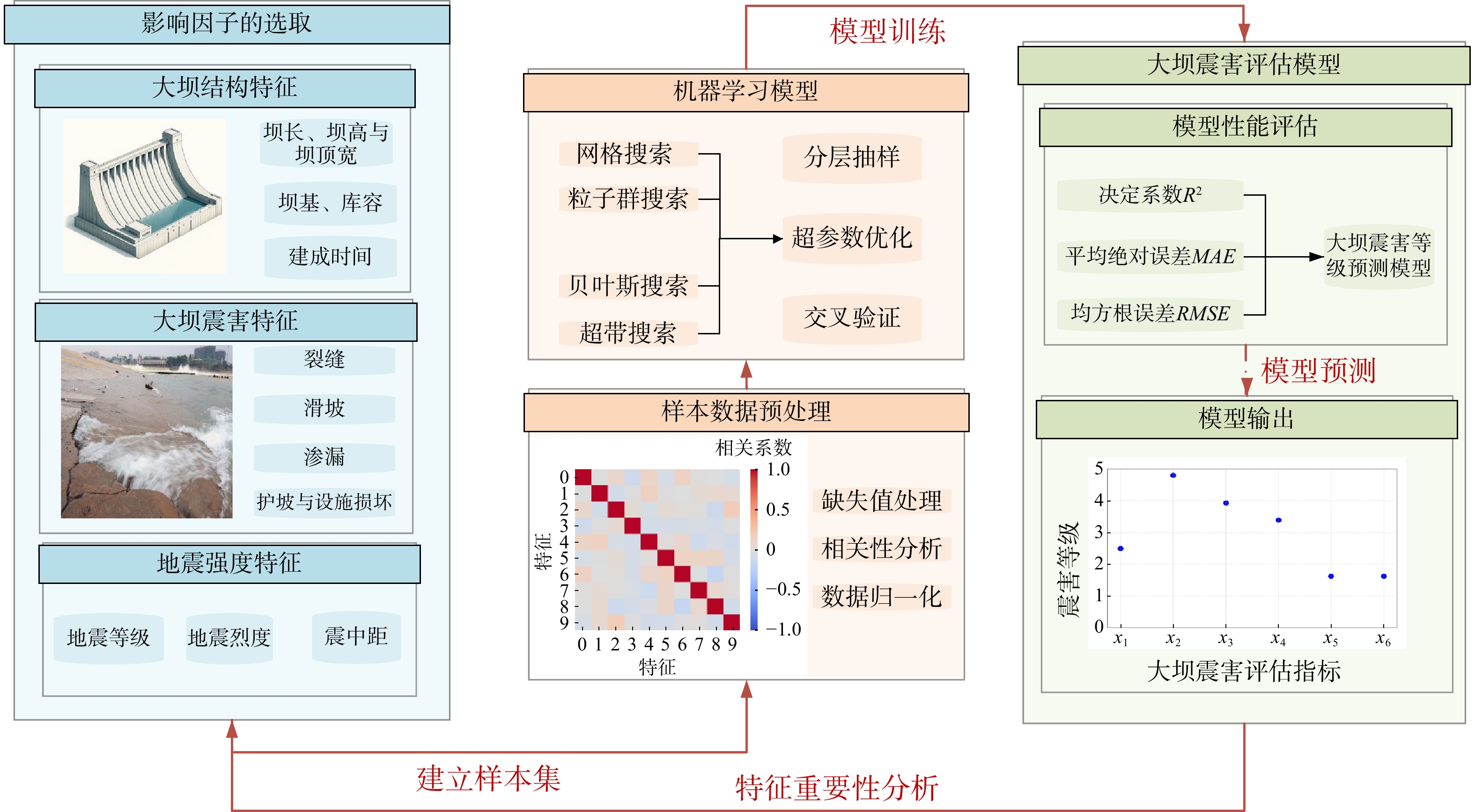
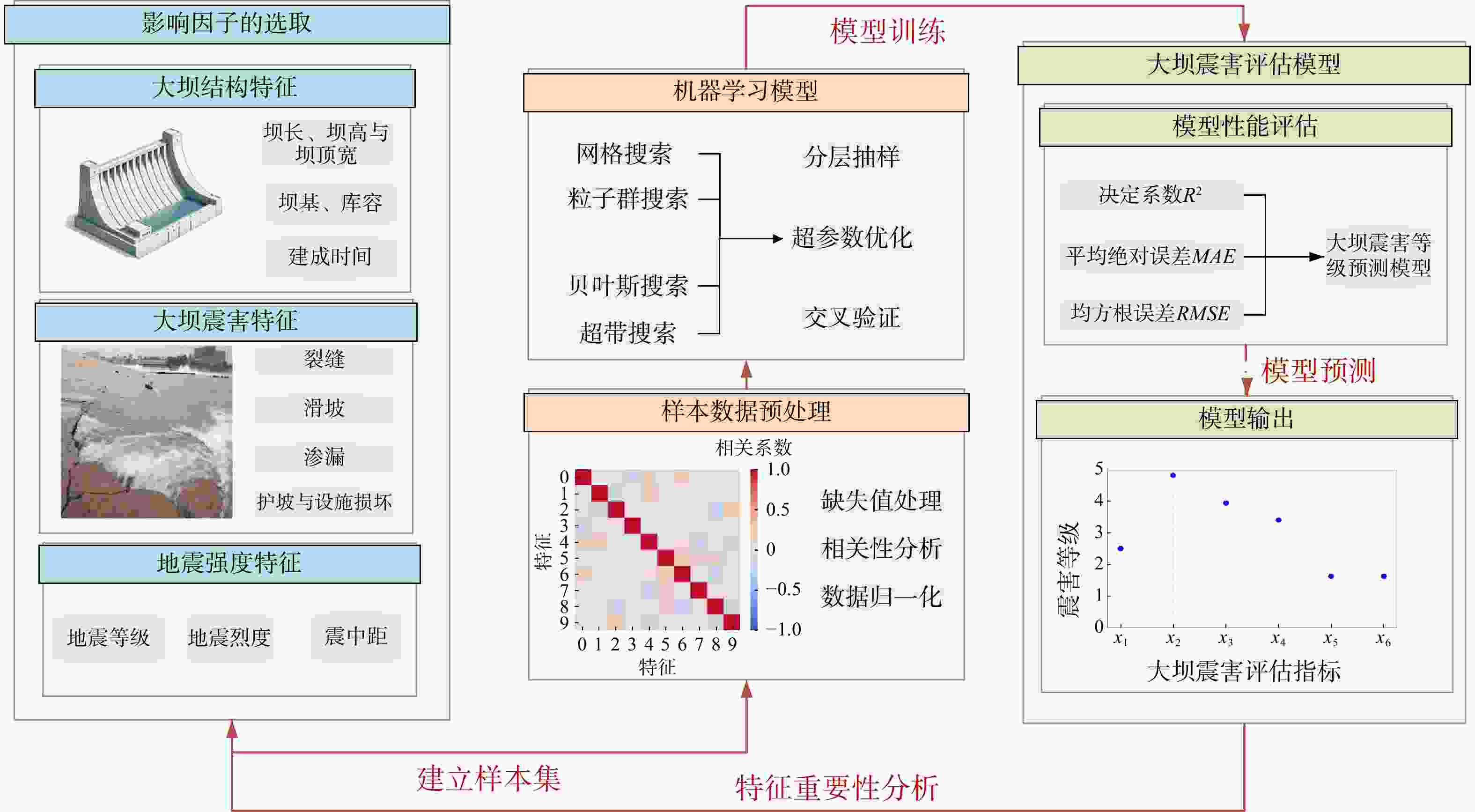
水库大坝是重大生命线工程,地震发生后如何快速有效地进行水库大坝的震害评估,对抢险方案制定和灾后修复重建意义重大。为了快速准确地对遭受地震侵袭的水库大坝破坏程度进行评估,选取汶川8.0级大地震各水库大坝的震损详情,结合大坝的结构特点和地震强度构建了评估指标体系和数据集,使用k邻近插补法对样本的缺失值进行了处理,并判断样本特征相关性,提出了一种基于梯度提升树算法的水库大坝震害快速评估模型。使用网格搜索(grid search,简称GS)、粒子群搜索(particle swarm optimization,简称PSO)、贝叶斯搜索(Bayesian optimization,简称BO)和超带搜索(hyperband search,简称HS)4种超参数优化方法对梯度提升树(gradient boosting decision tree,简称GBDT)回归算法进行了参数优化,根据各模型的性能指标(决定系数
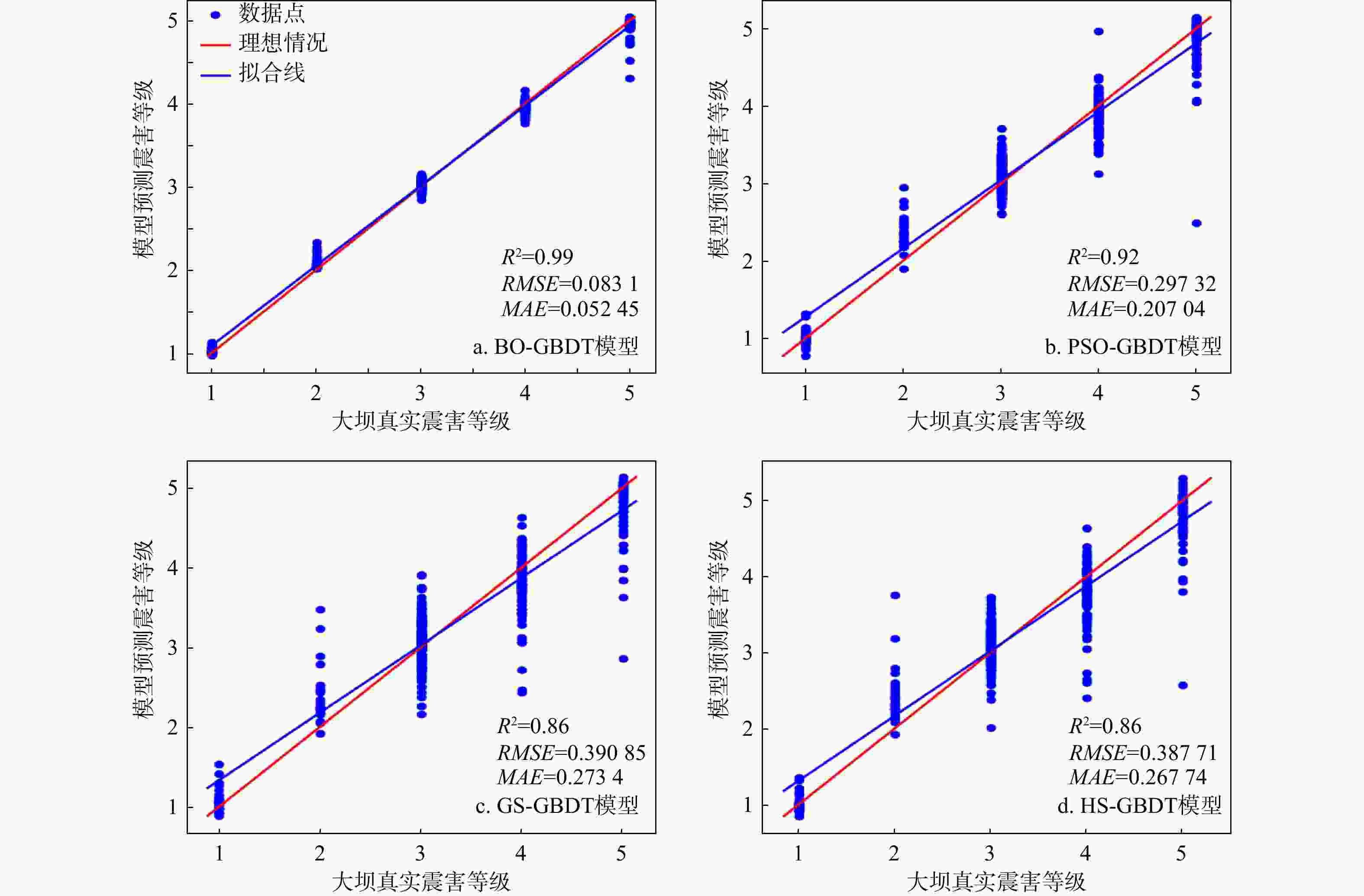
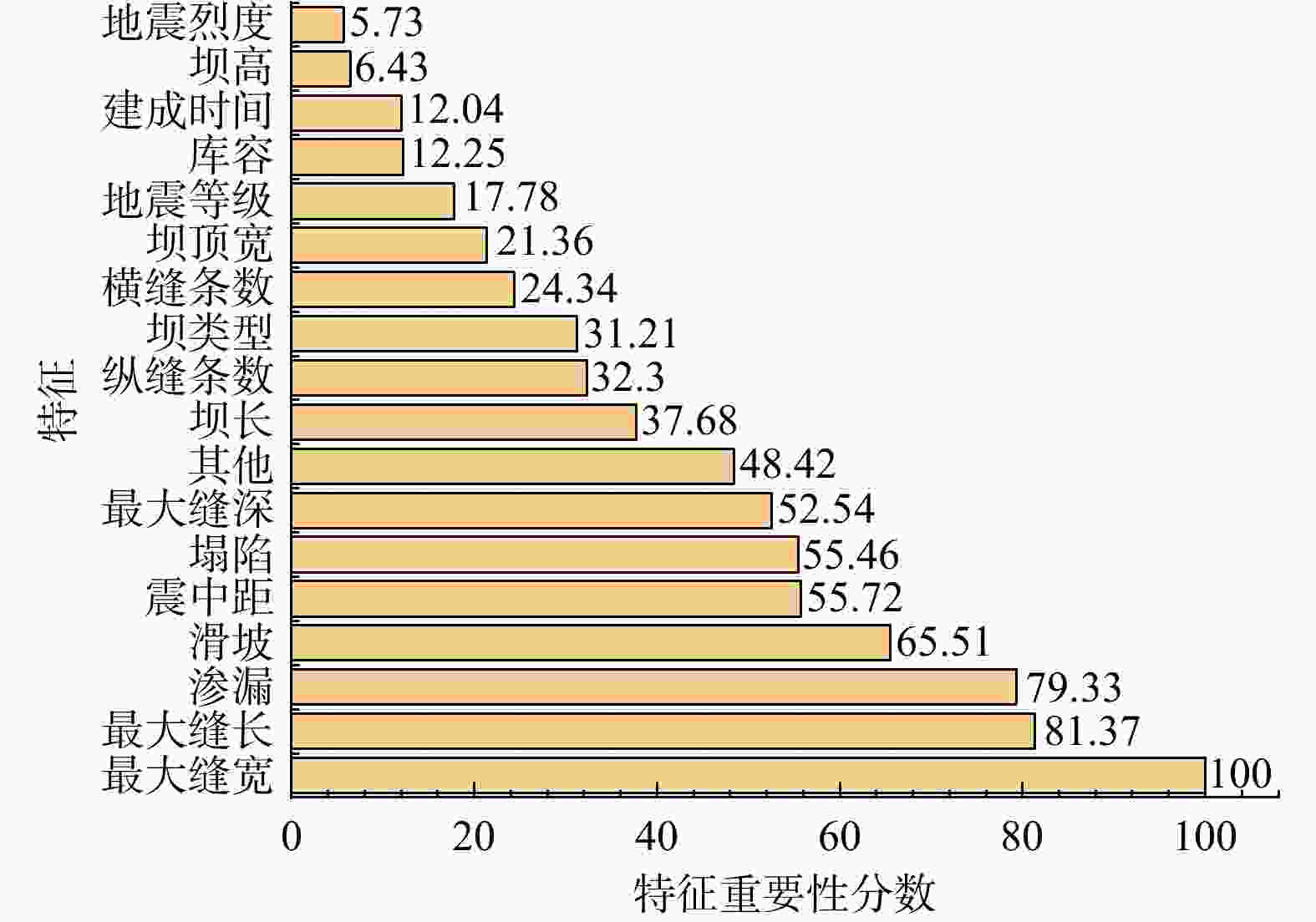
R 2、均方根误差RMSE 、平均绝对误差MAE )进行了对比,并对最优模型的特征重要性进行了排序。结果表明:BO-GBDT模型能以最短耗时以及较高精度对水库大坝震害程度进行评估,其决定系数R 2高达0.99,特征重要性分数表明最大缝宽是影响最大的因素。使用该模型与基于改进经验统计模型的土坝震害评估模型评估结果对比,准确度有进一步提高,验证了该模型在水库大坝震后震害快速调查评估应用中的可靠性。研究成果为水库大坝的震害评估提供了参考依据。Abstract:Objective Reservoir dams are critical infrastructure, and accurately assessing the extent of earthquake-induced damage is crucial for developing rescue operations and post-disaster restoration. This study aims to achieve rapid and accurate assessment of post-earthquake damage in reservoir dam.
Methods Focusing on earthquake damage data from the Wenchuan
M s8.0 earthquake, this research integrates dam structural characteristics and seismic intensity parameters to establish an assessment index system and dataset. The study employs k-nearest-neighbor interpolation for missing values processing and feature correlation analysis. A rapid assessment model for reservoir dam earthquake damage is proposed using gradient boosting algorithm. To optimize parameters of the gradient boosted tree (GBDT) regression algorithm, four hyperparameter optimization methods are implemented: Grid search (GS), particle swarm optimization (PSO), Bayesian optimization (BO), and hyperband search (HS). The models are compared based on performance metrics, including the coefficient of determination (R 2), root mean square error (RMSE ), and mean absolute error (MAE ), and the feature importance of the optimal models is ranked.Results The results demonstrate that the BO-GBDT model provides the most rapid and accurate assessment of earthquake damage to reservoir dams, achieving a high
R 2 of 0.99. Feature importance analysis shows that the maximum crack width is the most influential factor. The model demonstrates superior accuracy compared to earth dam damage assessment models based on improved empirical statistical methods, confirming its reliability for rapid post-earthquake damage evaluation of reservoir dams.Conclusion The research results provide a reference for the earthquake damage assessment of reservoir dams.
-
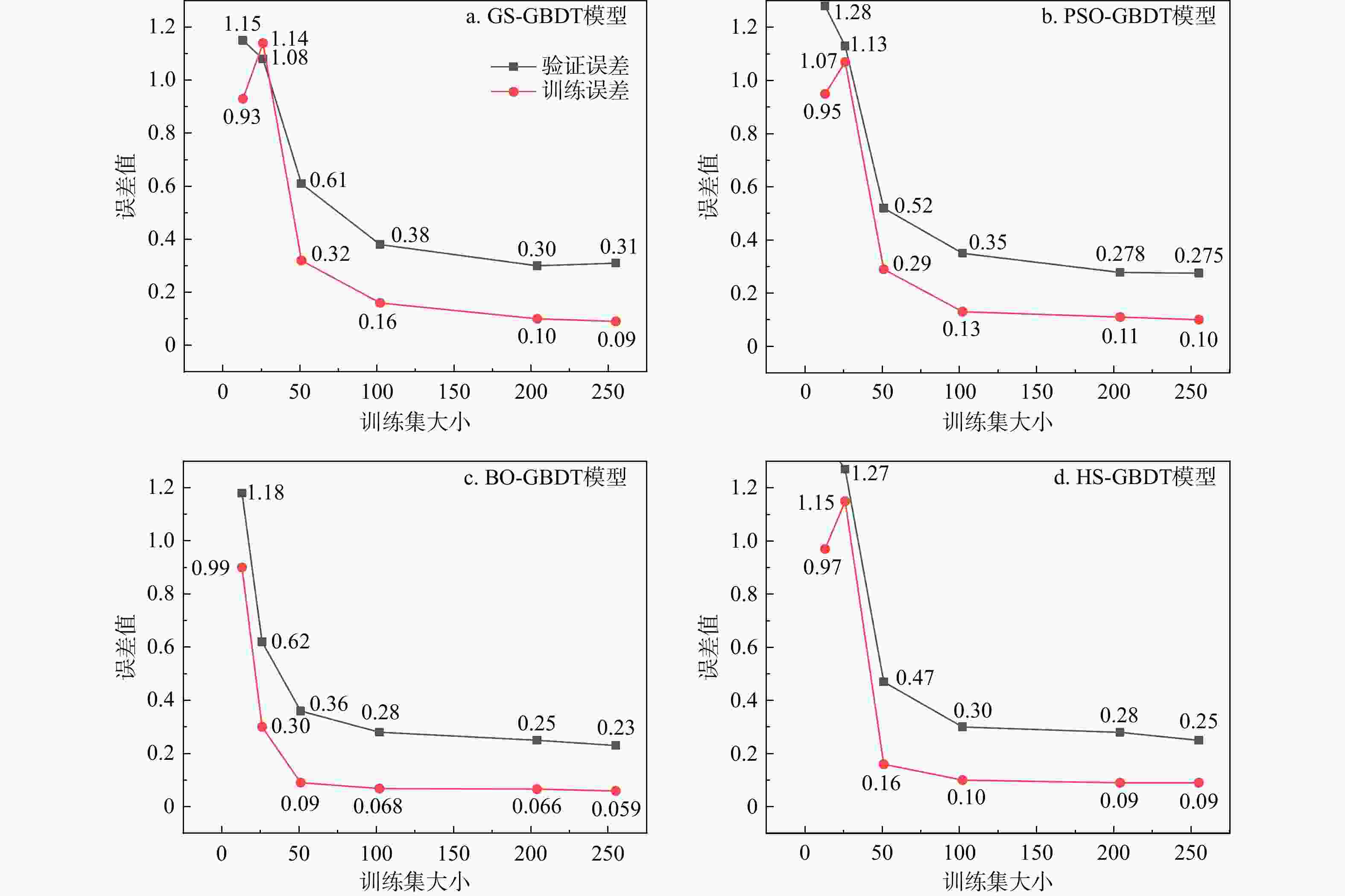
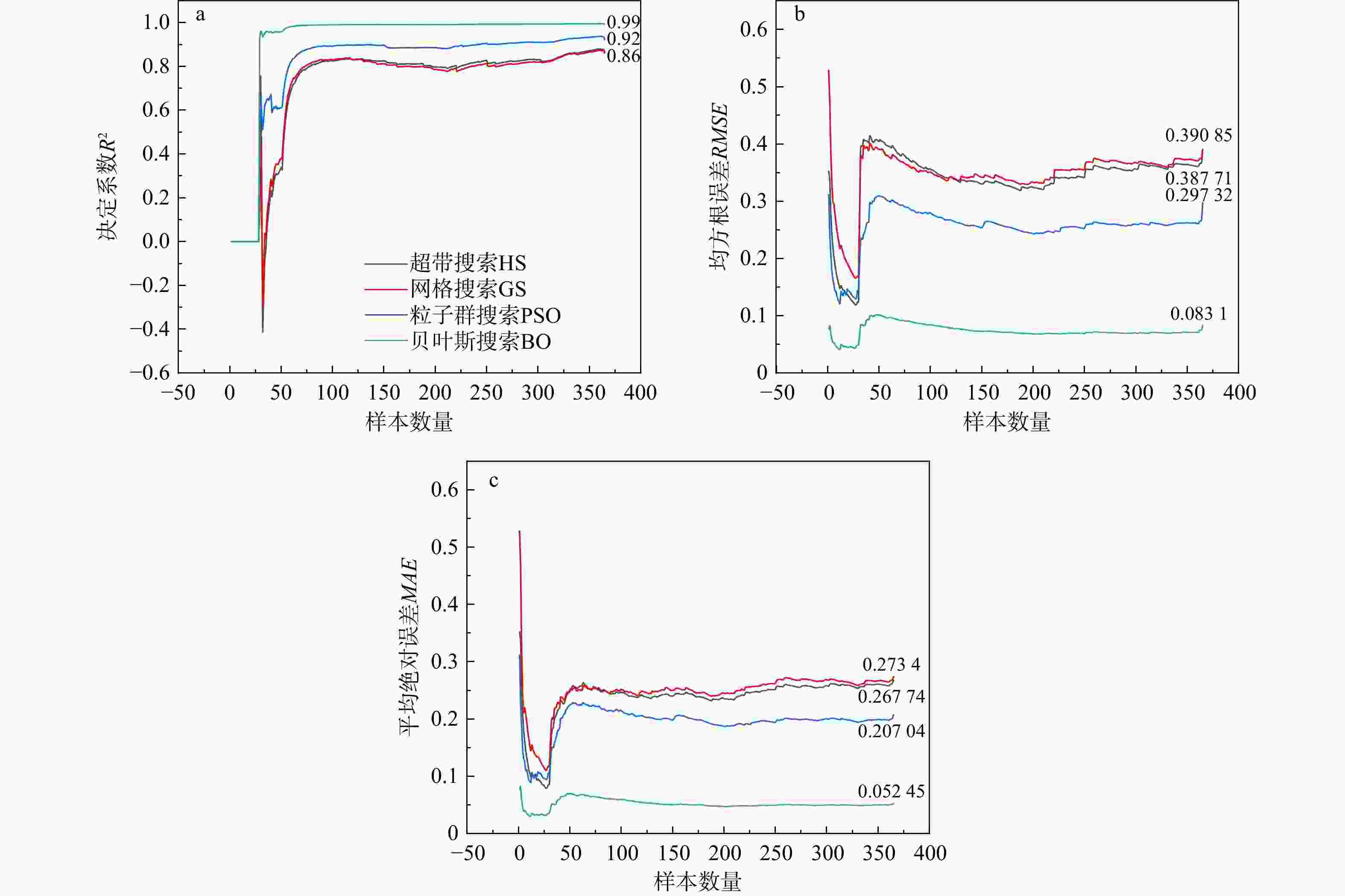
表 1 4种超参数优化算法参数设定、训练完成时间及最佳模型参数组合和交叉验证误差
Table 1. Parameter settings, training time, optimal parameter combinations and cross-validation errors for four optimization algorithms and models
优化算法 优化算法参数 最佳模型参数组合 训练完成
时间/s交叉验
证误差网格搜索 迭代次数:256 迭代次数:80
最大树深度:40
最小分割节点:5
特征分割数:386.52 0.40 粒子群
搜索迭代次数:30
粒子群数量:30
随机种子数:42迭代次数:76
最大树深度:63
最小分割节点:7
特征分割数:126.52 0.39 贝叶斯
搜索迭代次数:30
初始化参数:30
随机参数集:1000
随机种子数:42迭代次数:74
最大树深度:62
最小分割节点:7
特征分割数:369.23 0.38 超带搜索 最大预算:81
保留参数组合:3
随机种子数:42迭代次数:86
最大树深度:95
最小分割节点:8
特征分割数:2462.35 0.36 表 2 部分水库大坝震害因子取值与震害等级预测结果
Table 2. Values of seismic damage factors and predicted seismic damage levels of some reservoir dams
序号 坝名 建成时间/年 地震烈度/(°) 坝类型 坝长/m 坝高/m 坝顶宽/m 震害等级 Y1 Y2 1 上坝水库 1978 8 1 120 28.0 8 3 3.06 3.27 2 龙泉水库 1957 8 1 174 18.9 3.5 2 2.08 2.45 3 团结水库(玉皇) 1977 7 1 168 30.05 4 3 2.99 3.33 4 红刺藤水库 1962 9 1 156 12.0 6 4 4.07 2.33 5 民乐水库 1957 9 1 167 10.0 2 4 3.94 4.04 6 众力水库 1969 9 1 1095 9.3 2 2 2.09 2.67 7 新坪水库 1959 7 1 106 17.4 2 3 3.03 3.33 8 太平水库 1959 6 1 294 10.2 3.6 3 2.99 3.58 9 庆丰水库 1958 7 2 247 15.1 3 3 2.95 2.72 10 跃进水库 1958 7 1 284 11.3 3 3 2.99 2.45 11 拦沟堰水库 1960 6 1 234 5.0 3 1 1.45 1.29 12 八一水库 1975 7 1 130 10.5 2.5 4 3.83 3.82 13 罗家湾水库 1957 7 1 246 12.8 3.7 3 2.96 2.99 14 团结水库(百善) 1971 7 1 118 11.2 1 3 3.14 3.28 15 一根松水库 1973 7 1 167 9.8 3.3 3 3.00 3.82 16 尖梁子水库 1972 7 1 167 10 1.5 3 2.99 2.45 17 长岭水库 1957 7 1 256 10.6 3.3 3 3.00 2.99 18 新桥水库 1956 7 1 107 17 3.2 3 2.91 2.23 19 五七水库 1979 8 1 110 21.6 2.8 3 2.98 2.43 20 观音堂水库 1958 8 1 148 9 4 4 4.03 4.07 21 吴家大堰水库 1978 8 1 124 8 4 4 3.94 4.07 22 狮儿河水库 1958 8 1 131 17.4 4 4 3.89 4.07 23 合作水库 1975 8 1 120 20 2.5 4 3.93 4.07 24 岐山水库 1959 8 1 314 21 4 4 3.95 4.07 25 大田水库 1956 8 1 100.3 7.55 3 4 3.81 4.07 26 幸福水库 1971 8 1 101 14 4.5 3 3.03 2.23 27 牛角埝水库 1974 8 1 37 6 7 3 2.87 2.43 28 上游水库 1973 7 1 470 22 54 3 2.96 2.45 29 洞子沟水库 1985 8 1 182 18 2.2 3 3.00 2.97 30 火烧坡水库 1976 8 1 45 9 4 3 3.14 2.97 31 漆树坝水库 1974 8 1 38 10 3 3 3.09 2.97 32 三要水库 1975 7 1 400 7.4 13.52 3 2.92 3.33 33 和平水库 1977 8 1 175 24.4 3 3 2.91 2.67 34 金花水库 1957 8 1 240 18.6 3.14 3 3.13 2.67 35 崇林水库 1977 8 1 150 10 4.5 4 3.89 2.67 36 向阳水库 1964 7 1 405 20 4 3 3.01 2.99 37 朝阳水库 1985 7 1 130 18 10 3 2.90 3.33 38 红旗水库 1959 7 1 420 11.4 3 2 2.03 2.45 注:坝类型1表示均质坝;坝类型2表示黏土心墙坝;Y1为BO-GBDT模型预测的震害结果,Y2为改进的大坝震害经验统计模型预测的震害结果[10] 表 3 模型对比分析
Table 3. Comparison between different models
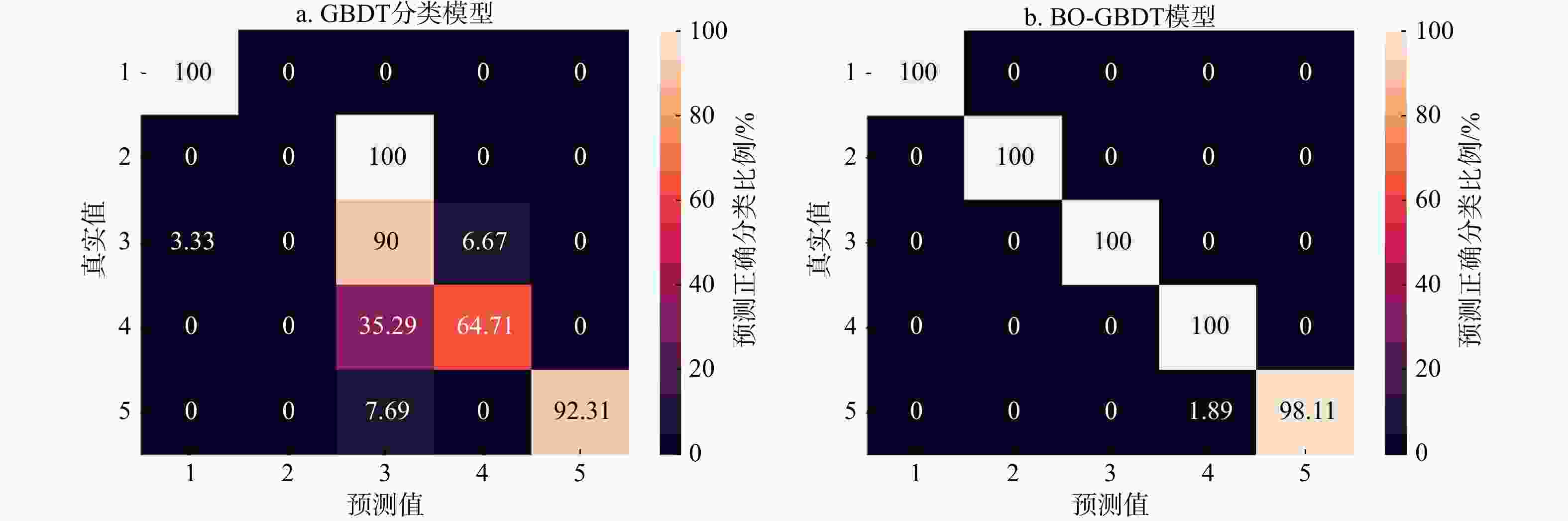
模型 震害等级正确分类的土坝 震害等级错误分类的土坝 平均误差 相关系数 数量/座 比例/% 数量/座 比例/% 改进的土坝震害经验统计模型 26 68.4 12 31.6 0.363 0.908 BO-GBDT模型 38 100 0 0 0.070 0.972 -
[1] 颜婷,肖鸿,林鹏智. 芦山地震水库震害考察及灾区大坝总风险评估[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版),2015,47(增刊1):41-47.YAN T,XIAO H,LIN P Z. Investigation of seismic damage to reservoirs and total risk assessment of dams in earthquake-stricken area during Lushan earthquake[J]. ournal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition),2015,47(S1):41-47. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] JING L P,LIANG H A,LI Y Q,et al. Characteristics and factors that infl uenced damage to dams in the Ms8.0 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration,2011,10:349-358. [3] 梁海安. 土石坝震害预测及快速评估方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨:中国地震局工程力学研究所,2012.LIANG H A. Seismic damage prediction and emergency assessment of earth-rock dam[D]. Harbin:Insititute of Engineering Mechanics,China Earthquake Administration,2012.(in Chinese with English abstract [4] PEKAU O A,CUI Y Z. Failure analysis of fractured dams during earthquakes by DEM[J]. Engineering Structures,2004,26(10):1483-1502. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2004.05.019 [5] SINGH R,ROY D,JAIN S K. Analysis of earth dams affected by the 2001 Bhuj earthquake[J]. Engineering Geology,2005,80(3/4):282-291. [6] DOAN N P,NGUYEN B P,PARK S S. Seismic deformation analysis of earth dams subject to liquefaction using UBCSAND2 model[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2023,172:108003. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2023.108003 [7] WANG G H,LU W B,ZHOU C B,et al. The influence of initial cracks on the crack propagation process of concrete gravity dam-reservoir-foundation systems[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering,2015,19(6):991-1011. doi: 10.1080/13632469.2015.1021407 [8] GHAEDI K,HEJAZI F,IBRAHIM Z,et al. Flexible foundation effect on seismic analysis of roller compacted concrete (RCC) dams using finite element method[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering,2018,22(4):1275-1287. doi: 10.1007/s12205-017-1088-6 [9] 饶为胜,杜成斌,江守燕,等. 土坝震害分类快速预测的模糊概率方法[J]. 灾害学,2017,32(2):206-209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2017.02.036RAO W S,DU C B,JIANG S Y,et al. Fuzzy probability method for fast predicting earthquake damage type of earth dam[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2017,32(2):206-209. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2017.02.036 [10] 郭恩栋,张丽娜,王亚东,等. 土坝震害评估模型研究[J]. 岩土力学,2011,32(12):3667-3671. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.12.022GUO E D,ZHANG L N,WANG Y D,et al. Study of evaluation model of earthquake damage to earth dams[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2011,32(12):3667-3671. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2011.12.022 [11] 吴云星,谷艳昌,王士军,等. 基于信息熵−变权模糊模型的土石坝震损评估[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2018(4):38-45.WU Y X,GU Y C,WANG S J,et al. Assessment of seismic damage for earth-rockfill dam based on information entropy variable weight fuzzy model[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering,2018(4):38-45. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 陆耀波,欧阳志勇. 灰关联分析与BP人工神经网络在土石坝震害群体预测中的运用[J]. 华南地震,2014,34(增刊1):90-94.LU Y B,OUYANG Z Y. Forecasting seismic damage to buildings based on grey relation and artificial neural network model[J]. South China Journal of Seismology,2014,34(S1):90-94. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 杨灿,刘磊磊,张遗立,等. 基于贝叶斯优化机器学习超参数的滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):228-238.YANG C,LIU L L,ZHANG Y L,et al. Machine learning based on landslide susceptibility assessment with Bayesian optimized the hyperparameters[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):228-238. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 郭衍昊,窦杰,向子林,等. 基于优化负样本采样策略的梯度提升决策树与随机森林的汶川同震滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):251-265.GUO Y H,DOU J,XIANG Z L,et al. Optimized negative sampling strategy of gradient boosting decision tree and random forest for evaluating Wenchuan coseismic landslides susceptibility mapping[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):251-265. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 林琴,郭永刚,吴升杰,等. 基于梯度提升的优化集成机器学习算法对滑坡易发性评价:以雅鲁藏布江与尼洋河两岸为例[J]. 西北地质,2024,57(1):12-22. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023031LIN Q,GUO Y G,WU S J,et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility by optimization integrated machine learning algorithm based on gradient boosting:Take both banks of Yarlung Zangbo River and Niyang River as examples[J]. Northwestern Geology,2024,57(1):12-22. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023031 [16] LIU X,LIANG Y Q,FU X,et al. Assessment of typhoon disaster loss based on the factor analysis-random forest model[J]. Journal of Physics (Conference Series),2024,2718(1):012043. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2718/1/012043 [17] ZHANG Y X,ZHANG T Y,SHEN W Q,et al. Economic loss assessment of typhoon-induced storm surge disasters in the South China Sea based on GSA-BP model[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2023,11:1258524. [18] 邓日朗,张庆华,刘伟,等. 基于改进两步法采样策略和卷积神经网络的崩塌易发性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(2):186-200.DENG R L,ZHANG Q H,LIU W,et al. Collapse susceptibility evaluation based on an improved two-step sampling strategy and a convolutional neural network[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(2):186-200. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 赵军,汪峻宇,赖强,等. 基于XGBoost 算法的走滑断裂内部特征带的精细识别[J/OL]. 地质科技通报,1-13(2024-04-19)[2024-09-17]. https://doi. org/10.19509/j. cnki. dzkq. tb20230583.ZHAO J,WANG J Y,LAI Q,et al. Fine-grained identification of internal characteristic zones within the strike-slip fault using the XGBoost algorithm [J/OL]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,1-13(2024-04-19)[2024-09-17]. https://doi.org/10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230583. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] FRIEDMAN J H. Greedy function approximation:A gradient boosting machine[J]. The Annals of Statistics,2001,29(5):1189-1232. doi: 10.1214/aos/1013203450 [21] BREIMAN L,FRIEDMAN J,OLSHEN R,et al. Classification and regression tree[M]. New York:Chapman,1984. [22] 林森,郭桂祯,刘蓓蓓. 基于梯度提升决策树(GBDT) 算法的南方洪涝灾害房屋倒损评估模型[J]. 灾害学,2020,35(1):109-112.LIN S,GUO G Z,LIU B B. A model of house damage assessment for southern China based on gradient boosting decision three (GBDT) algorithm[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2020,35(1):109-112. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 王昭栋,王自法,李兆焱,等. 基于机器学习−网格搜索优化的砂土液化预测[J]. 振动与冲击,2024,43(5):82-92.WANG Z D,WANG Z F,LI Z Y,et al. Prediction of sandy soil liquefaction based on machine learning GridSearch CV[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock,2024,43(5):82-92. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] BERGSTRA J,BARDENET R,BENGIO Y,et al. Algorithms for hyper-parameter optimization[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems ,2011:2546-2554. [25] BONYADI M R,MICHALEWICZ Z. Particle swarm optimization for single objective continuous space problems:A review[J]. Evolutionary Computation,2017,25(1):1-54. doi: 10.1162/EVCO_r_00180 [26] UNGREDDA J,BRANKE J. Bayesian optimisation for constrained problems[J]. ACM Transactions on Modeling and Computer Simulation,2024,34(2):1-26. [27] LI L S,JAMIESON K G,DESALVO G,et al. Hyperband:A novel bandit-based approach to hyperparameter optimization[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research,2016,18:1-52. [28] ZHANG Y Z,MA J,LIANG S L,et al. An evaluation of eight machine learning regression algorithms for forest aboveground biomass estimation from multiple satellite data products[J]. Remote Sensing,2020,12(24):4015. doi: 10.3390/rs12244015 [29] 叶亚三,陈国兴,王志华,等. 汶川大地震中广元市水库震害调查与分析[J]. 世界地震工程,2011,27(4):73-85.YE Y S,CHEN G X,WANG Z H,et al. Investigation and analysis of seismic damage of reservoirs in Guangyuan City during Wenchuan great earthquake[J]. World Earthquake Engineering,2011,27(4):73-85. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 陈国兴,景立平,汤皓,等. 汶川地震中绵竹市水库土坝震损调查与分析[J]. 南京工业大学学报(自然科学版),2009,31(9):15-23.CHEN G X,JING L P,TANG H,et al. Investigation and analysis of earthquake-induced earth dam damages in Mianzhu City during Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2009,31(9):15-23. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] CHEN G X,JIN D D,MAO J,et al. Seismic damage and behavior analysis of earth dams during the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2014,180:99-129. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.06.001 [32] LASHGARI A,MOSS R E S. Displacement and damage analysis of earth dams during the 2023 Turkiye earthquake sequence[J]. Earthquake Spectra,2024,40(2):939-976. doi: 10.1177/87552930231223749 [33] 叶亚三,陈国兴,王志华. 汶川大地震中土坝破坏程度与坝体几何形状的关系分析[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,2012,32(1):146-153.YE Y S,CHEN G X,WANG Z H. Relationships between damage extent and geometry of reservoir’s earth dams in Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics,2012,32(1):146-153. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] SOYSAL B F,ARICI Y. Crack width-seismic intensity relationships for concrete gravity dams[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering,2024,28(2):565-581. doi: 10.1080/13632469.2023.2220048 [35] TANI S,NAKASHIMA M. Earthquake damage to earth dams in Japan-Maximum epicentral distance to cause damage as a function of magnitude[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,1999,18(8):593-602. doi: 10.1016/S0267-7261(99)00017-2 [36] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中国国家标准化管理委员会. 生命线工程地震破坏等级划分:GB/T24336-2009[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2009.General Administration of Quality Supervision,Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China,Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Classification of earthquake damage to lifeline engineering:GB/T24336-2009[S]. Beijing:Standards Press of China,2009. (in Chinese) [37] 陈国兴,景立平,李永强. 汶川地震中小型水库震害与数据库[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2014.CHEN G X,JING L P,LI Y Q. Seismic damage of small and medium-sized reservoirs in the Wenchuan earthquake and databas[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2014. (in Chinese) [38] 冒进,陈国兴,王志华,等. 绵阳市东南部区域水库汶川地震典型震害分析[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2015,35(1):137-144.MAO J,CHEN G X,WANG Z H,et al. Analysis of representative seismic damage to reservoirs in the southeast of Mianyang City during Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Disaster Preventtion and Mitigation Engineering,2015,35(1):137-144. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 单锐,杨婧,朱文元,等. 不同缺失比例下的缺失值插补方法比较[J]. 信息技术,2023,47(12):52-56.SHAN R,YANG J,ZHU W Y,et al. Comparison of missing value interpolation methods under different missing ratios[J]. Information Technology,2023,47(12):52-56. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 仉文岗,唐理斌,陈福勇,等. 基于4种超参数优化算法及随机森林模型预测TBM掘进速度[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报,2021,29(5):1186-1200.ZHANG W G,TANG L B,CHEN F Y,et al. Prediction for TBM penetration rate using four hyperparameter optimization methods and random forest model[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering,2021,29(5):1186-1200. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 黄鹏辉,高勇. 分层抽样在电梯检验报告抽查中的应用[J]. 中国特种设备安全,2017,33(8):13-15.HUANG P H,GAO Y. Application of stratified sampling method in the sample survey of elevator inspection reports[J]. China Special Equipment Safety,2017,33(8):13-15. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] YATES L,ANDAHL Z,RICHARDS S. et al. Cross validation for model selection:A review with examples from ecology[J]. Ecological Monographs,2023,93(1):1-24. [43] LIU P F,CHEN J Y,XU Q,et al. Seismic stability analysis of CSG dams considering the effect of tension crack based on genetic algorithm with an improved initial population strategy[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2023,175:108210. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2023.108210 [44] 郝伟,宋宁宁. 高烈度区铁路桥梁地震灾害生命年损失评估方法[J]. 自然灾害学报,2022,31(6):86-94.HAO W,SONG N N. Evaluation method of earthquake disaster lifeyears loss of railway bridges in high intensity areas[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2022,31(6):86-94. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: