CO2-EOR Numerical simulation for cores in 3rd Member of Funing Formation, Zhangjiaduo oilfield, Subei Basin
-
摘要:
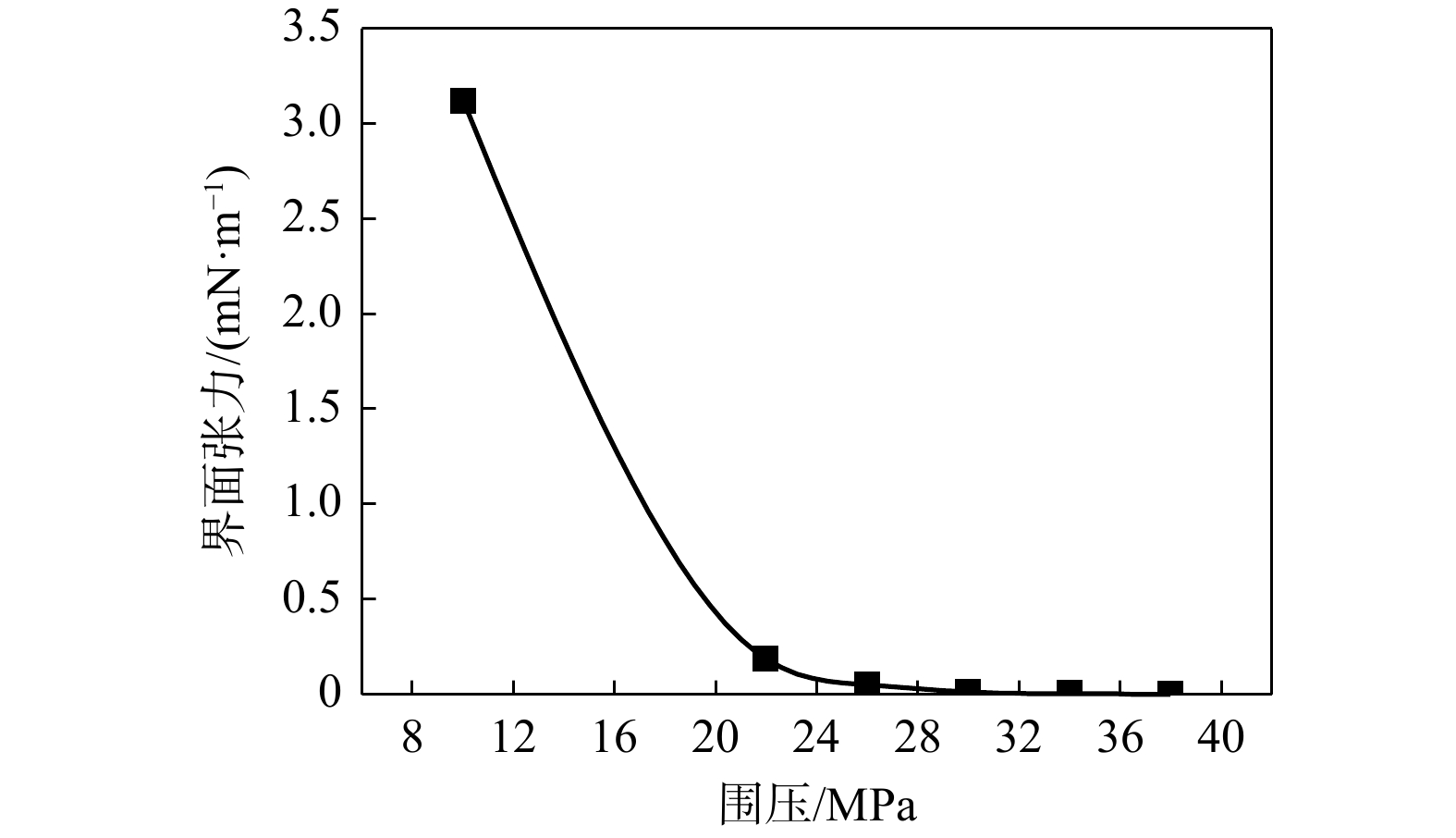
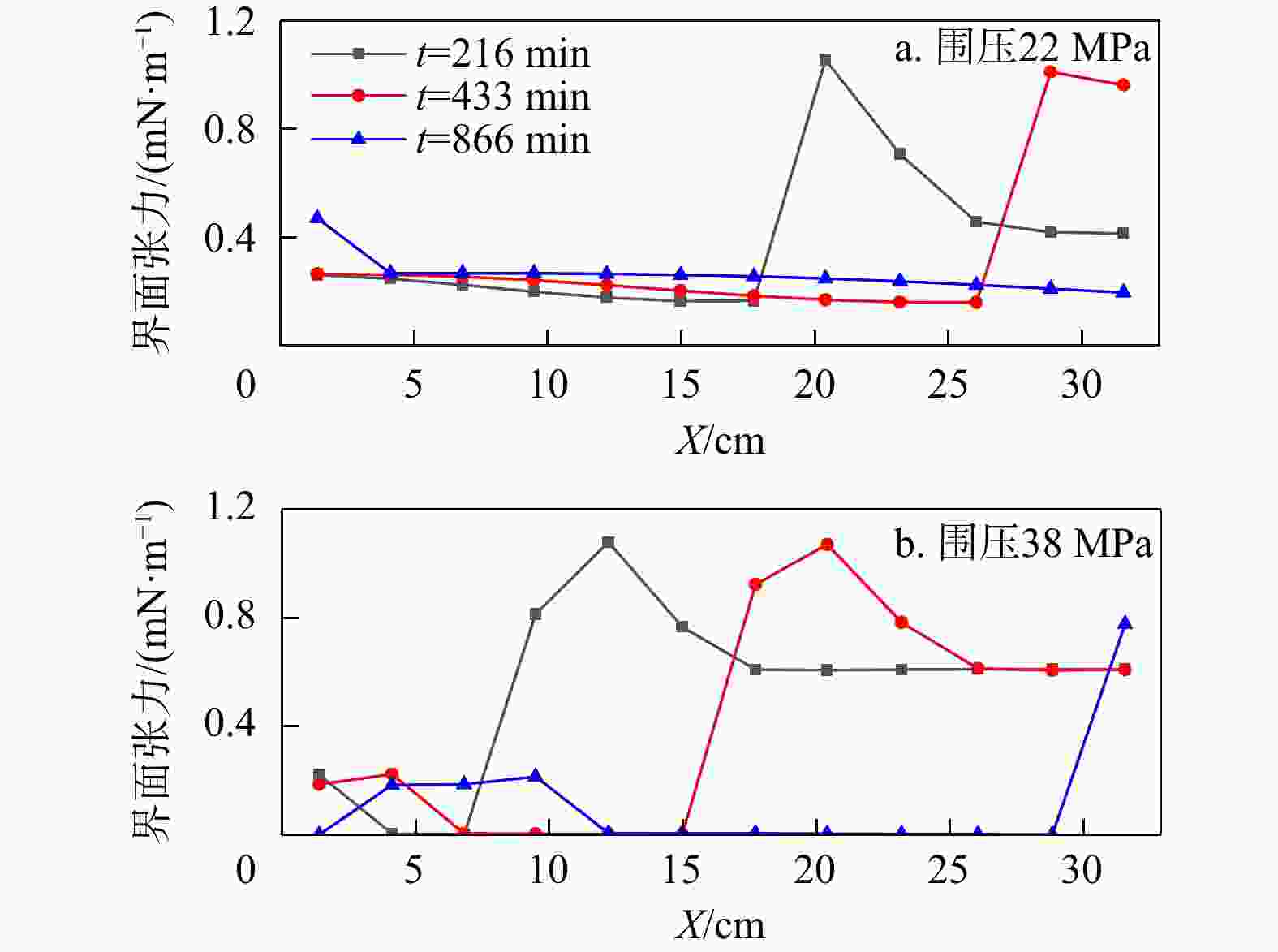
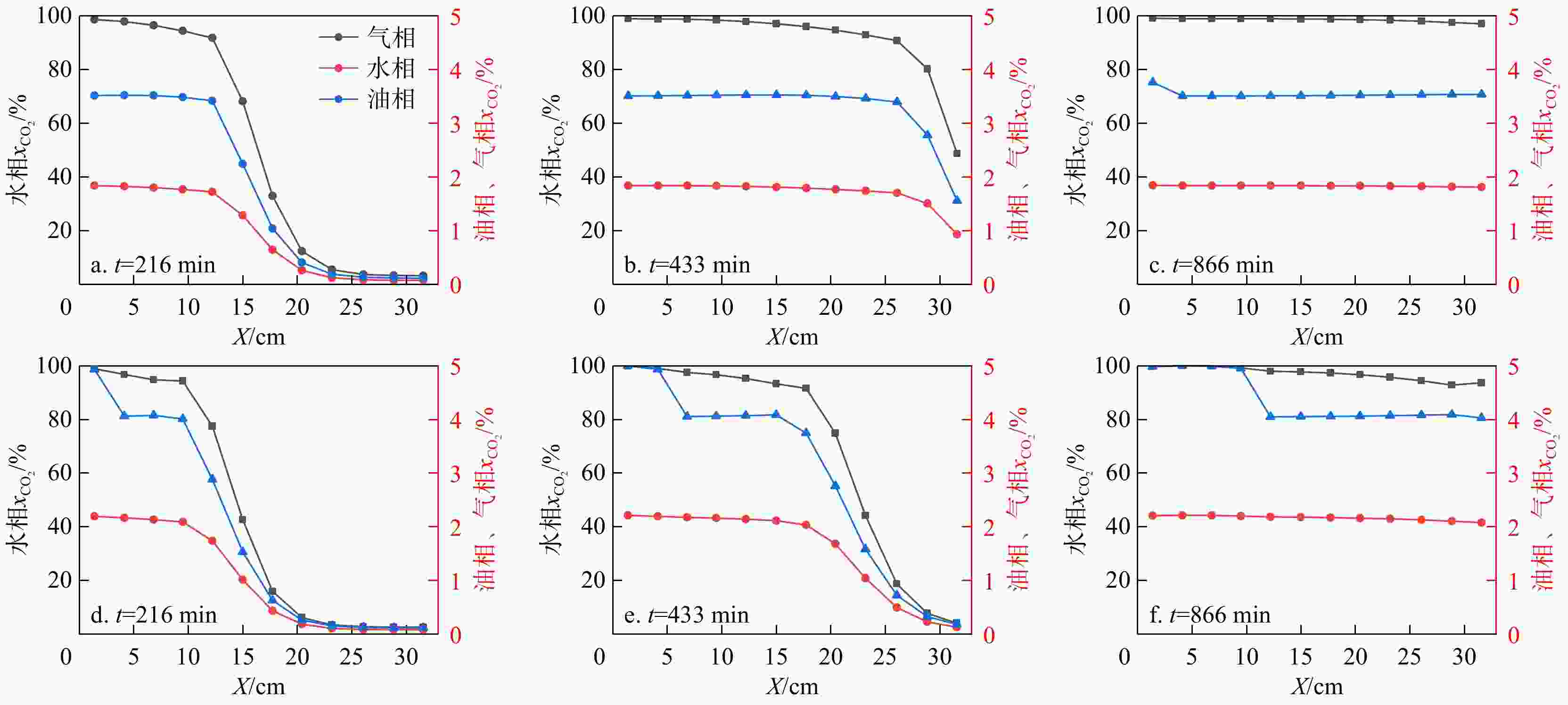
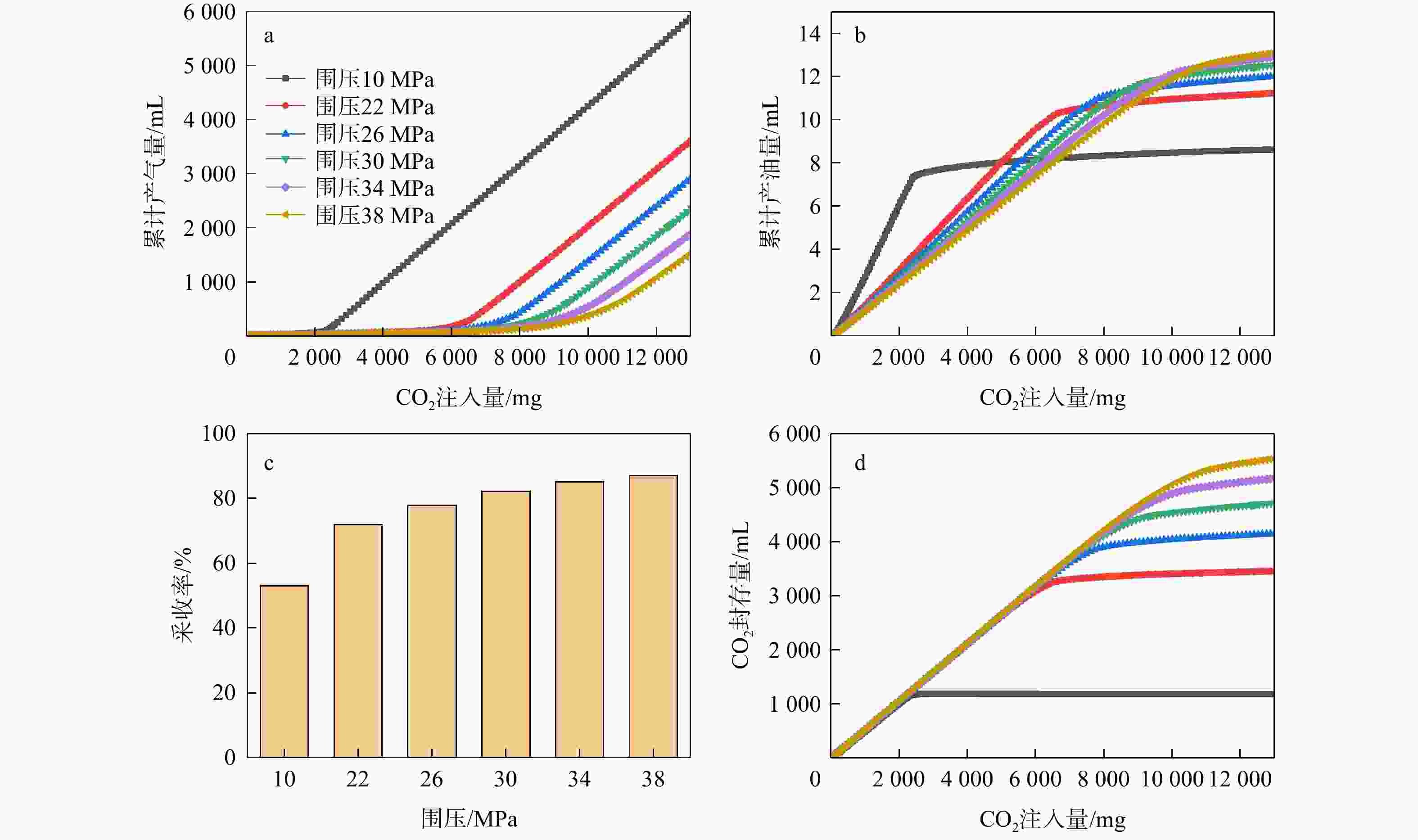
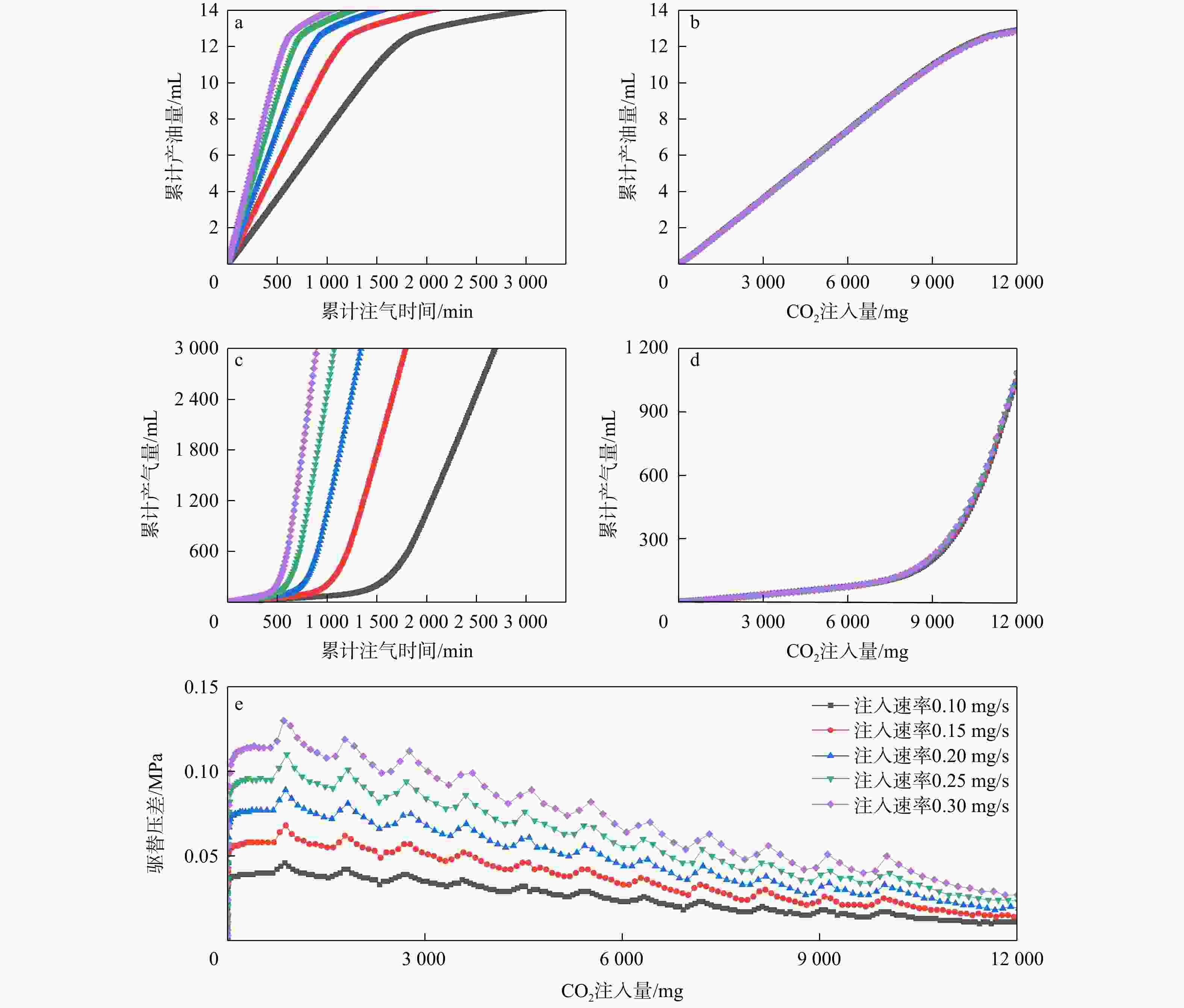
二氧化碳强化石油开采(CO2-EOR)是目前全球广泛应用的油田增产和碳封存技术之一。“双碳”目标导向下,CO2-EOR数值模拟需要考虑非独立水相对相间传质的影响,实现CO2多相溶解分布的刻画。基于苏北盆地张家垛阜三段油藏实际储层条件,采用多相流数值模拟软件TOGA建立岩心驱替模型,实现三相全组分互溶模拟。通过模拟不同压力和注气速率下CO2与油藏流体的相互作用,实现了研究区储层条件下CO2在水、气、油三相中溶解性的差异性刻画,揭示了混相驱油机理。模拟结果表明,研究区发生混相驱的最小混相压力为30 MPa,此时油气界面张力接近0。混相驱替显著提高了石油采收率,如38,10 MPa围压下的采收率分别为80%,52%。CO2在油相中的溶解性远大于其在水相中的溶解性,随着围压的增加CO2在油水两相中的摩尔百分数均提高,在22,38 MPa的围压下,水相中迁移的CO2摩尔百分数分别为1.8%,2.1%,油相中迁移的CO2摩尔百分数分别为65%,80%。研究区储层条件能够实现混相驱油,同时也有利于碳封存;加快注气速率可以提高生产效率,但对采收率和CO2贮存量的影响较小,还会导致气窜风险加大。研究成果为张家垛阜三段油藏的场地模拟和泄漏风险评估提供了技术参考。
-
关键词:
- 二氧化碳强化石油开采(CO2-EOR) /
- 数值模拟 /
- 溶解迁移 /
- 苏北盆地 /
- 驱油机理
Abstract:Objective CO2-enhanced oil recovery (CO2-EOR) is currently one of the most widely used techniques for oilfield production enhancement and carbon sequestration worldwide. Under the "dual carbon" goals, numerical simulation of CO2-EOR needs to consider the impact of interphase mass transfer of the non-independent water phase to accurately depict the multiphase dissolution distribution of CO2.
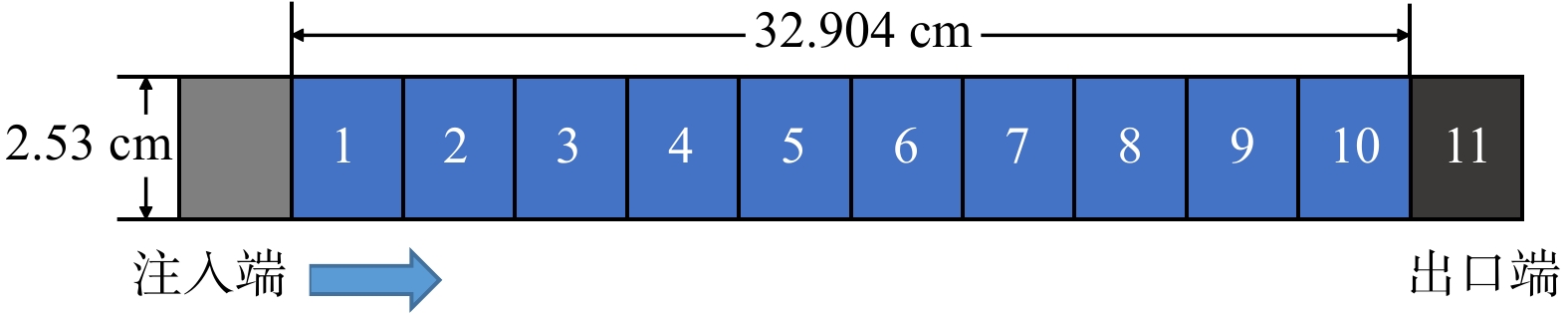
Methods Based on the actual reservoir conditions of the 3rd member of the Funing Formation in the Zhangjiaduo Oilfield, Subei Basin, this study uses the multiphase flow numerical simulation software TOGA to establish a core displacement model, achieving three-phase full-component mutual solubility simulation. By simulating the interaction between CO2 and reservoir fluids under different pressures and gas injection rates, the differences in CO2 solubility in water, gas, and oil phases under the reservoir conditions of the study area are characterized, revealing the miscible flooding mechanism.
Results The simulation results indicate that the minimum miscible pressure for miscible flooding in the study area is 30 MPa, at which the oil-gas interfacial tension approaches zero. Miscible displacement significantly improves oil recovery, with recovery rates of 80% and 52% under confining pressures of 38 MPa and 10 MPa, respectively. CO2 solubility in the oil phase is much greater than in the water phase, and with increasing confining pressure, the mole fraction of CO2 in both oil and water phases increases. At confining pressures of 22 MPa and 38 MPa, the mole fractions of CO2 migrating in the water phase are 1.8% and 2.1%, respectively, while those in the oil phase are 65% and 80%, respectively.
Conclusion The reservoir conditions in the study area can achieve miscible flooding, which is also conducive to carbon sequestration. Accelerating the gas injection rate can improve production efficiency, but it has little effect on total oil recovery and carbon dioxide storage, and may increase the risk of gas breakthrough. This study provides technical references for field simulations and leakage risk assessments of the 3rd member of the Funing Formation, Zhangjiaduo Oilfield.
-
Key words:
- CO2-EOR /
- Numerical Simulation /
- Solubility Trapping /
- Subei Basin /
- Displacement Mechanism
-
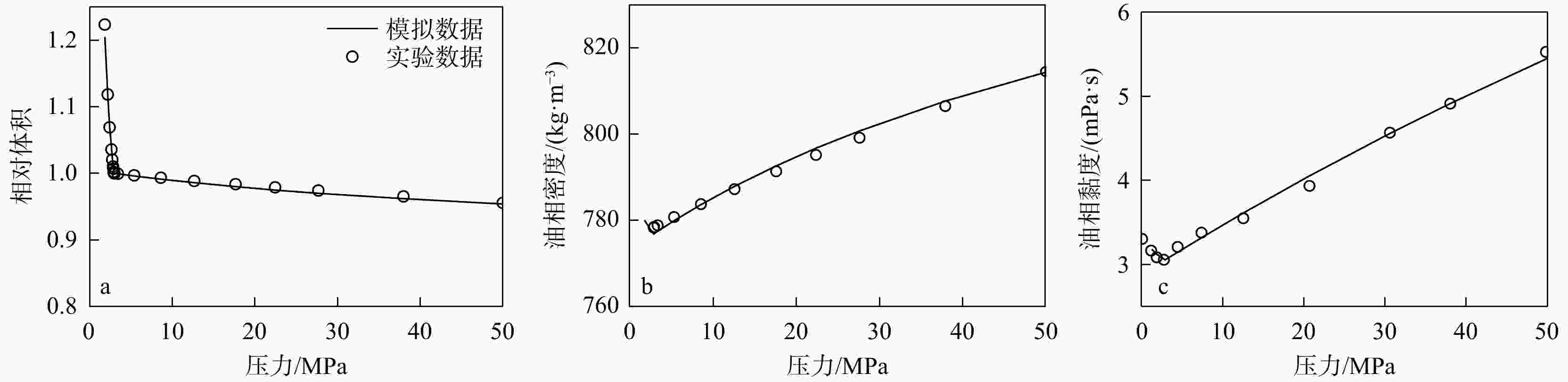
表 1 模型中原油组分及其摩尔百分数
Table 1. Crude oil components and proportions in the model
组分 摩尔百分数/% CO2 2.25 C1 5.92 C2 1.99 C3 3.27 C4 3.41 C5 1.41 C6 3.22 C7 4.39 C8 4.73 C9+ 69.41 表 2 情景设置
Table 2. Scenario settings
编号 CO2注入速率/
(mg·s−1)围压/
MPa编号 围压/
MPaCO2注入速率/
(mg·s−1)Test1 0.20 10 Test7 38 0.10 Test2 22 Test8 0.15 Test3 26 Test9 0.20 Test4 30 Test10 0.25 Test5 34 Test11 0.30 Test6 38 -
[1] HILL L B, LI X C, WEI N. CO2-EOR in China: A comparative review[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2020, 103: 103173. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2020.103173 [2] SAIRA, JANNA F, LE-HUSSAIN F. Effectiveness of modified CO2 injection at improving oil recovery and CO2 storage: Review and simulations[J]. Energy Reports, 2020, 6: 1922-1941. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2020.07.008 [3] 刘世奇, 皇凡生, 杜瑞斌, 等. CO2地质封存与利用示范工程进展及典型案例分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2023, 51(2): 158-174.LIU S Q, HUANG F S, DU R B, et al. Progress and typical case analysis of demonstration projects of the geological sequestration and utilization of CO2[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2023, 51(2): 158-174. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] ZHU Q L, WANG C, FAN Z H, et al. Optimal matching between CO2 sources in Jiangsu Province and sinks in Subei-Southern South Yellow Sea Basin, China[J]. Greenhouse Gases: Science and Technology, 2019, 9(1): 95-105. [5] 朱前林, 陈东宝, 龚懿杰, 等. 江苏省及近海区域CO2地质封存储层条件分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 2023, 29(1): 25-36.ZHU Q L, CHEN D B, GONG Y J, et al. Analysis of CO2 geological storage condition in Jiangsu Province and offshore area[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2023, 29(1): 25-36. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 陈祖华. 低渗透油藏CO2驱油开发方式与应用[J]. 现代地质, 2015, 29(4): 950-957.CHEN Z H. Application and utilization of CO2 flooding in low-permeability reservoir[J]. Geoscience, 2015, 29(4): 950-957. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 陈祖华, 吴公益, 钱卫明, 等. 苏北盆地复杂小断块油藏注CO2提高采收率技术及应用[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(1): 152-162.CHEN Z H, WU G Y, QIAN W M, et al. EOR technology and application of CO2 injection for small complex fault block reservoirs in Subei Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(1): 152-162. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 刘伟, 陈祖华. 苏北复杂断块小型油藏CO2驱油先导性试验研究[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2008, 30(2): 147-149.LIU W, CHEN Z H. Pilot test on CO2 flooding in complex and fault block small reservoirs of North Jiangsu oilfield[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2008, 30(2): 147-149. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 杨鹏, 丁晓琪, 张哨楠, 等. 张家垛油田阜三段湖相滩坝砂储层特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(3): 456-462.YANG P, DING X Q, ZHANG S N, et al. Characteristics of lacustrine beach-bar sandstone reservoirs in the 3rd Member of the Funing Formation in Zhangjiaduo oilfield[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(3): 456-462. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 刘莉. 张家垛阜三段油藏注CO2膨胀实验研究[J]. 化工管理, 2019(19): 223-224.LIU L. Experimental study on CO2 swelling in the Third Member of Zhangjiaduofu reservoir[J]. Chemical Engineering Management, 2019(19): 223-224. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 任柏璋. 张家垛油田阜三段油藏CO2驱油机理分析[J]. 石化技术, 2020, 27(4): 97-98.REN B Z. Analysis of CO2 displacement mechanism in the Third Member of Fujiang Formation in Zhangjiaduo oilfield[J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 2020, 27(4): 97-98. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 计秉玉, 何应付. 中国石化低渗透油藏CO2驱油实践与认识[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2021, 11(6): 805-811.JI B Y, HE Y F. Practice and understanding about CO2 flooding in low permeability oil reservoirs by Sinopec[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2021, 11(6): 805-811. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 李士伦, 孙雷, 陈祖华, 等. 再论CO2驱提高采收率油藏工程理念和开发模式的发展[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2020, 10(3): 1-14.LI S L, SUN L, CHEN Z H, et al. Further discussion on reservoir engineering concept and development mode of CO2 flooding-EOR technology[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2020, 10(3): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 任俊帆, 薛亮, 聂捷, 等. 基于随机森林算法的二氧化碳驱油与封存主控因素研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(3): 147-156.REN J F, XUE L, NIE J, et al. Research on the main control factors of carbon dioxide flooding and storage based on random forest algorithm[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(3): 147-156. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 唐建东, 王智林, 葛政俊. 苏北盆地江苏油田CO2驱油技术进展及应用[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2024, 14(1): 18-25.TANG J D, WANG Z L, GE Z J. CO2 flooding technology and its application in Jiangsu oilfield in Subei Basin[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2024, 14(1): 18-25. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 周新平, 邓秀芹, 李士祥, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组下组合地层水特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(1): 109-120.ZHOU X P, DENG X Q, LI S X, et al. Characteristics of formation water and its geological significance of lower combination of Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(1): 109-120. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] XUE L, LIU P C, ZHANG Y. Status and prospect of improved oil recovery technology of high water cut reservoirs[J]. Water, 2023, 15(7): 1342. [18] PERERA M S A, GAMAGE R P, RATHNAWEERA T D, et al. A review of CO2-enhanced oil recovery with a simulated sensitivity analysis[J]. Energies, 2016, 9(7): 481. [19] WEI B, GAO H, PU W F, et al. Interactions and phase behaviors between oleic phase and CO2 from swelling to miscibility in CO2-based enhanced oil recovery (EOR) process: A comprehensive visualization study[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 232: 277-284. [20] REZK M G, FOROOZESH J, ZIVAR D, et al. CO2 storage potential during CO2 enhanced oil recovery in sandstone reservoirs[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2019, 66: 233-243. [21] ZHANG L H, ZHANG T, ZHAO Y L, et al. A review of interaction mechanisms and microscopic simulation methods for CO2-water-rock system[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2024, 51(1): 223-238. [22] CUI G D, ZHANG L, TAN C Y, et al. Injection of supercritical CO2 for geothermal exploitation from sandstone and carbonate reservoirs: CO2-water-rock interactions and their effects[J]. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2017, 20: 113-128. [23] 高志豪, 赵锐锐, 成建梅. 砂岩含水层CO2封存中考虑盐沉淀反馈作用的数值模拟: 以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 269-277.GAO Z H, ZHAO R R, CHENG J M. Numerical simulation of CO2 sequestration in sandstone aquifers with feedback effect of salt precipitation: A case study of Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 269-277. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 鞠斌山, 杨怡, 杨勇, 等. 高含水油藏CO2驱油与地质封存机理研究现状及待解决的关键问题[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2023, 30(2): 53-67.JU B S, YANG Y, YANG Y, et al. Present research situation and key pending issues of CO2 flooding and geological storage mechanism in high water-cut reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2023, 30(2): 53-67. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] SANDVE T H, SÆVAREID O, AAVATSMARK I. Dynamic PVT model for CO2-EOR black-oil simulations[J]. Computational Geosciences, 2022, 26(4): 1029-1043. [26] VULIN D, GAĆINA M, CROATIA I D D L Z, et al. Slim-tube simulation model for CO2 injection eor[J]. Rudarsko-Geološko-Naftni Zbornik, 2018, 33(2): 37-48. [27] WEI J G, ZHOU X F, ZHOU J M, et al. Experimental and simulation investigations of carbon storage associated with CO2 EOR in low-permeability reservoir[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 2021, 104: 103203. [28] 高冉, 吕成远, 伦增珉, 等. 二氧化碳驱替与埋存一体化数值模拟[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(2): 102-107.GAO R, LYU C Y, LUN Z M, et al. Integrated numerical simulation of carbon dioxide displacement and sequestration[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(2): 102-107. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 康宇龙, 汪心雯, 李超跃, 等. 化子坪长6储层长岩心CO2驱替实验及数值模拟评价[J]. 地球学报, 2024, 45(2): 243-251.KANG Y L, WANG X W, LI C Y, et al. Long core testing and numerical simulation investigations of CO2-EOR and geological storage in the 6th section of the Yanchang Formation in the Huaziping oil reservoir[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2024, 45(2): 243-251. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] UMEOBI H I, LI Q, XU L, et al. Flow and structural analysis of sedimentary rocks by core flooding and nuclear magnetic resonance: A review[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2021, 92(7): 071501. [31] PRUESS K. Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) using CO2 as working fluid: A novel approach for generating renewable energy with simultaneous sequestration of carbon[J]. Geothermics, 2006, 35(4): 351-367. [32] CAI Z S, ZHANG K N, GUO C B. Development of a novel simulator for modelling underground hydrogen and gas mixture storage[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2022, 47(14): 8929-8942. [33] PAN L H, OLDENBURG C M. TOGA: A TOUGH code for modeling three-phase, multi-component, and non-isothermal processes involved in CO2-based enhanced oil recovery[C]. 2016: LBNL--1006472, 1332134. [34] 俞亮亮. 苏北盆地张家垛油田阜三段储层特征研究[J]. 中国石油和化工标准与质量, 2013, 33(9): 164-165.YU L L. Study on reservoir characteristics of 3rd Member of Funing Formation in Zhangjiaduo oilfield, Subei Basin[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Standard and Quality, 2013, 33(9): 164-165. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] HARTONO K F, PERMADI A K, SIAGIAN U W R, et al. The impacts of CO2 flooding on crude oil stability and recovery performance[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 2024, 14(1): 107-123. -




 下载:
下载: