Elements, types, and risk zoning of marine geohazards in the Qizhou Islands offshore
-
摘要:
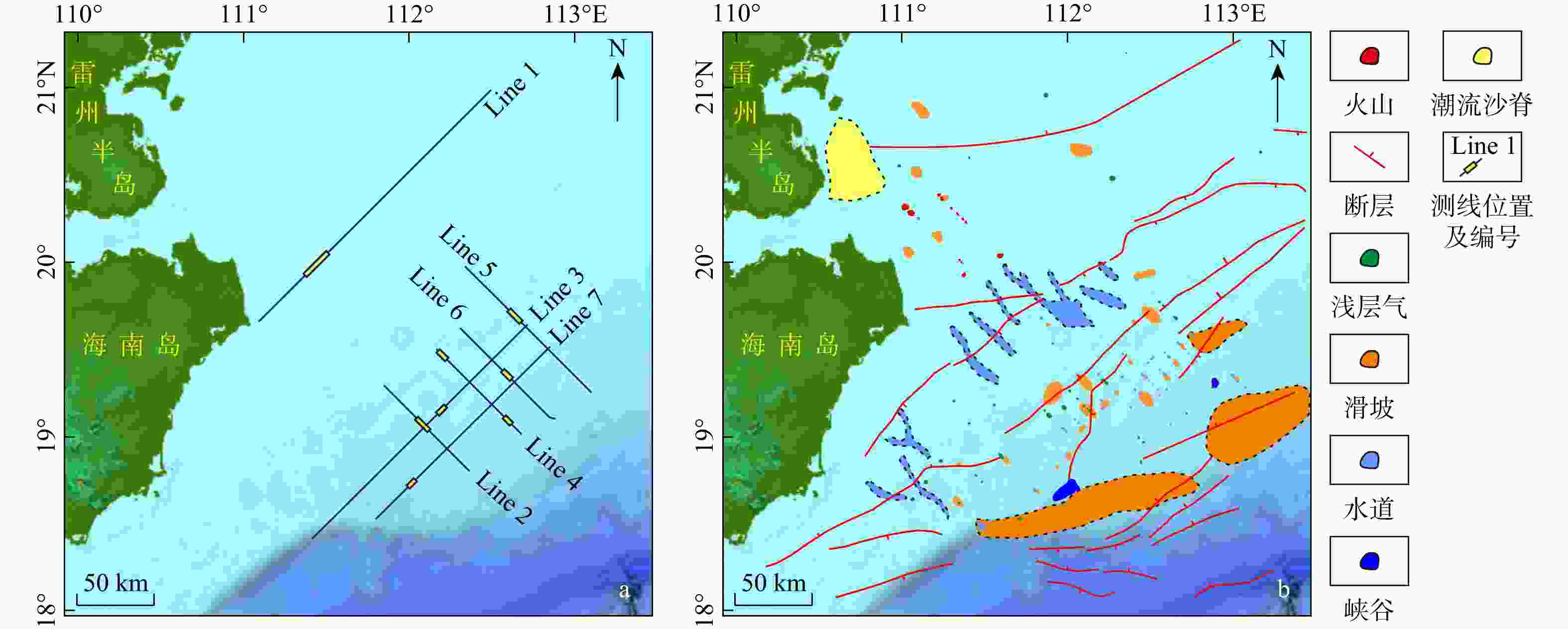
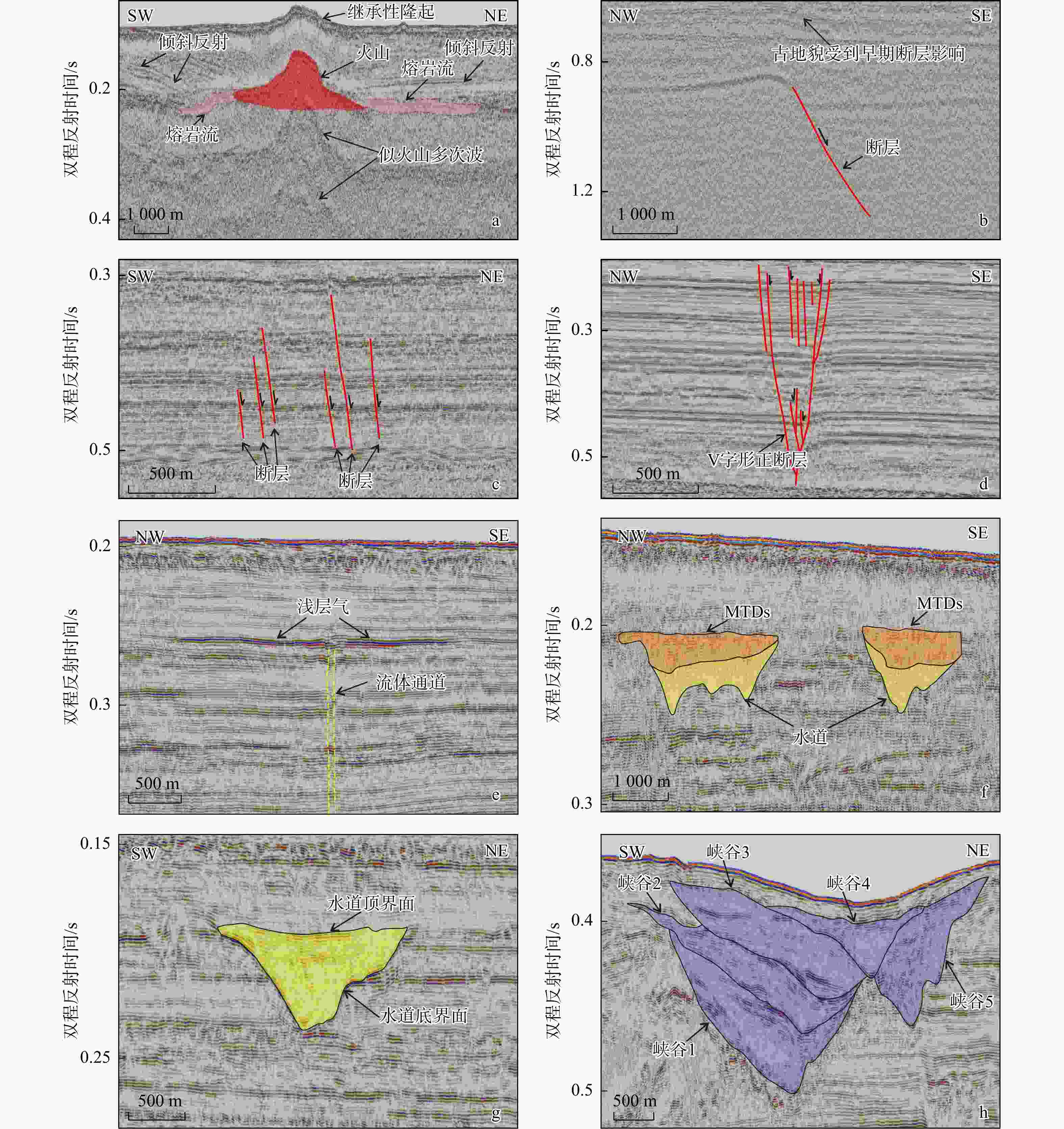
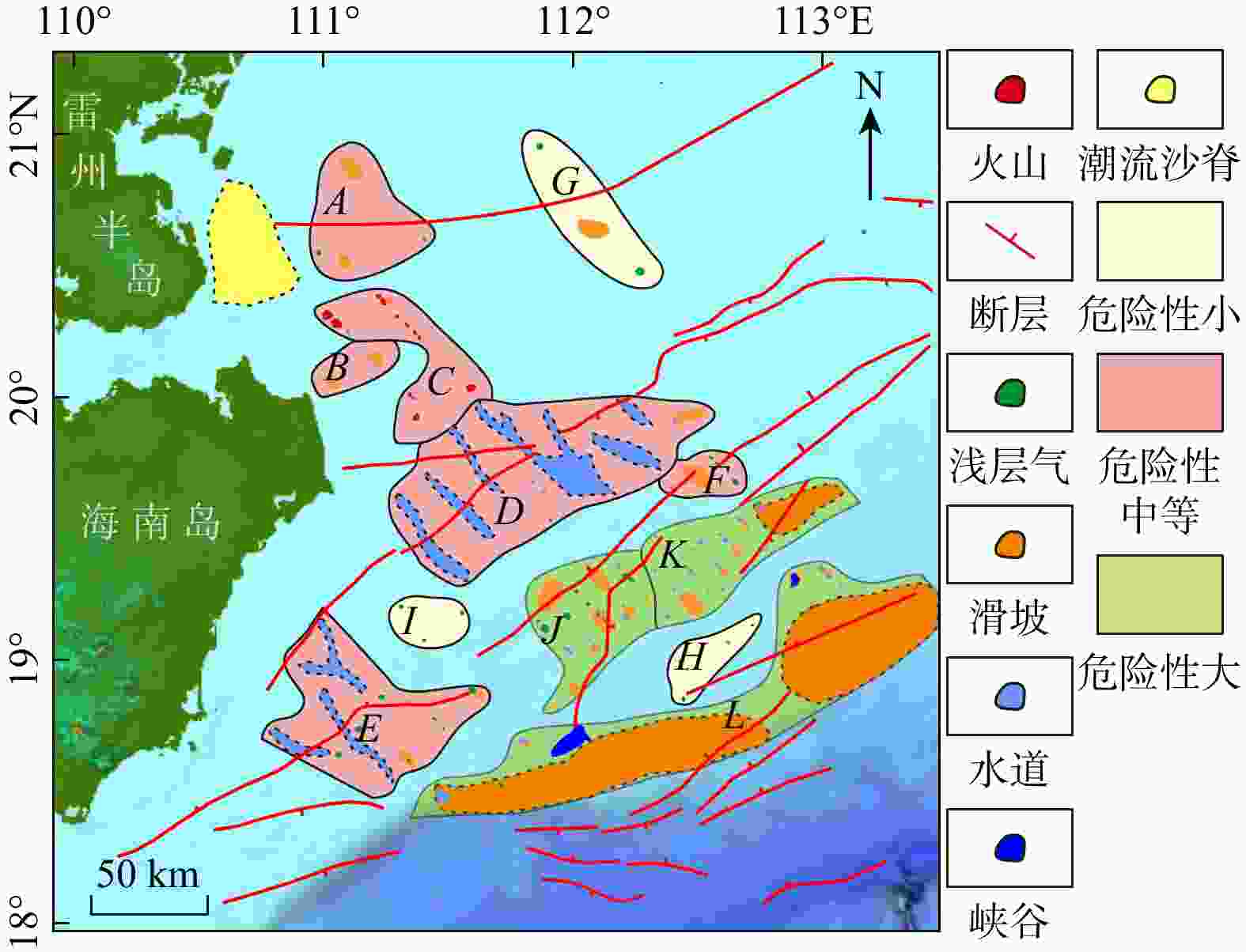
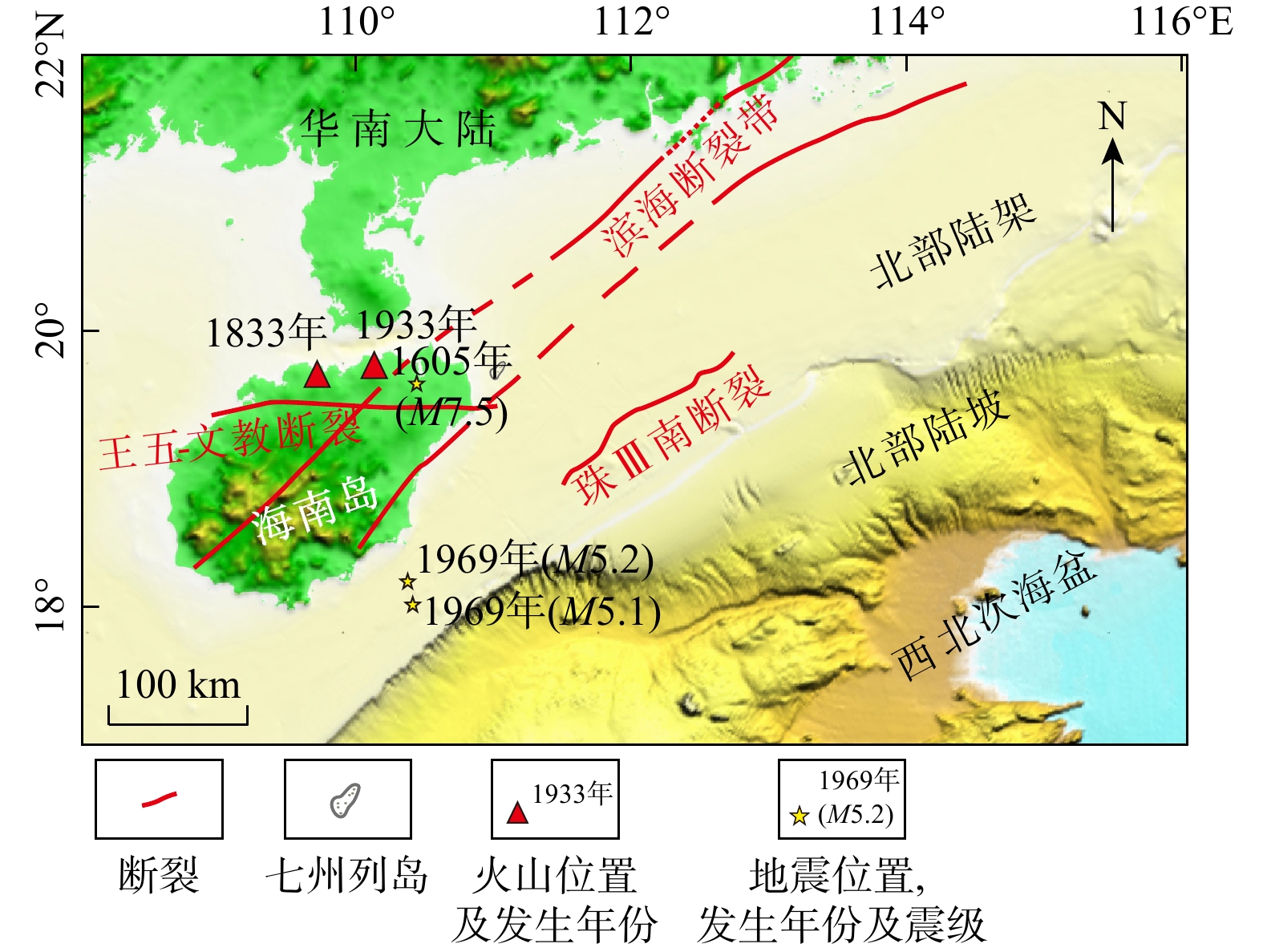
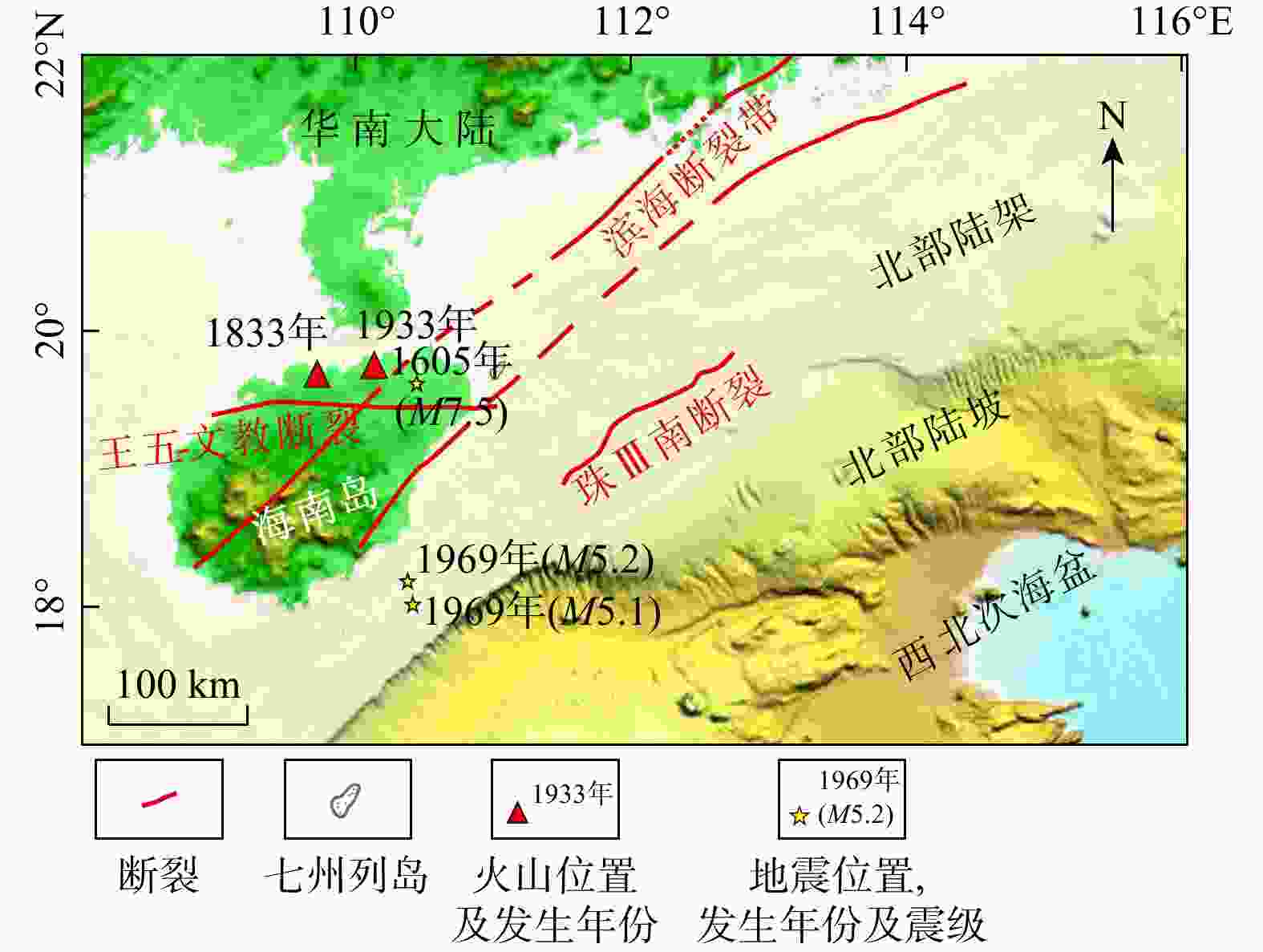
七洲列岛海域受活动断裂带、海南地幔柱等构造作用影响地震频发,南部靠近陆架边缘,古水道和峡谷较为发育,易发生海底失稳,威胁该区域工程设施的安全。目前对该海域的地质灾害研究较少,灾害要素的发育特征尚不明确。利用二维地震资料,识别出了火山、断层、浅层气、块状搬运沉积体系(MTDs)、峡谷、水道6种灾害要素,依据其数量、规模和分布特征,划分出了3个危险等级(危险性小、危险性中等、危险性大),共12个区块,结合不同区域的地形地貌和构造活动特征,对该海域海洋地质灾害防治提出了参考建议。研究成果对海洋地质灾害的防灾减灾工作具有重要意义。
Abstract:Objective The Qizhou Islands, located on the east side of Hainan Island, is an area with a high risk of geohazards due to the influence of tectonic processes (e.g., active fault zones and the Hainan mantle plume) and related earthquakes. The southern part of the Qizhou Islands is close to the edge of the continental shelf, with well-developed canyons and ancient channels, which weaken seabed stability and threaten the safety of engineering facilities in the area. Therefore, studying marine geohazards is of great significance for disaster prevention and mitigation in the Qizhou Islands area. However, research on geohazards in the sea area is limited, and the development characteristics of geohazard elements are unclear.
Objective To clarify the potential risks of marine geohazards in the offshore Qizhou Islands,
Methods based on 2D seismic data,
Results this study identified six geohazard elements (volcanoes, faults, shallow gas, mass-transport deposits (MTDs), canyons, and channels) offshore from the Qizhou Islands. According to their quantity, scale, and distribution characteristics, three risk levels (low risk, medium risk, and high risk) were assigned to 12 blocks.
Conclusion Combined with the geomorphological and tectonic characteristics, suggestions for geohazard prevention and control were proposed for the offshore Qizhou Islands area.
-
Key words:
- Qizhou Islands /
- marine geohazards /
- distribution regularities /
- risk zoning
-
表 1 七洲列岛周缘海洋地质灾害风险区域划分表
Table 1. Locations and main geohazard elements of risk zoning of geohazards in the Qizhou Islands offshore
区域编号 东经/(°) 北纬/(°) 主要灾害类型 灾害危险性 A 110.94~111.45 20.43 ~20.96 滑坡 中等 B 110.95~111.31 19.99 ~ 20.21 滑坡 中等 C 110.96~111.68 19.81 ~ 20.40 海底火山 中等 D 111.26~112.57 19.27 ~ 19.98 水道浊流 中等 E 110.75~111.67 18.46 ~ 19.19 水道浊流/滑坡/
浅层气中等 F 112.35~112.69 19.61 ~ 19.78 滑坡/浅层气 中等 G 111.80~112.36 20.41 ~ 21.01 滑坡/浅层气 小 H 112.38~112.76 18.82 ~ 19.17 浅层气 小 I 111.27~111.59 19.03 ~ 19.23 浅层气 小 J 111.81~112.33 18.79 ~ 19.41 水道浊流/滑坡/
浅层气大 K 112.28~113.15 19.11 ~ 19.69 水道浊流/滑坡 大 L 111.34~113.47 18.39 ~ 19.37 峡谷浊流/滑坡 大 -
[1] 冯志强, 冯文科, 薛万俊, 等. 南海北部地质灾害及海底工程地质条件评价[M]. 南京: 河海大学出版社, 1996.FENG Z Q. Evaluation of marine geologic hazards and engineering geological conditions in the northern South China Sea[M]. Nanjing: Hohai University Press, 1996. (in Chinese) [2] 陈俊仁, 李廷桓. 南海地质灾害类型与分布规律[J]. 地质学报, 1993, 67(1): 76-85.CHEN J R, LI T H. Types and distribution of geological hazards in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 1993, 67(1): 76-85. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 陈泓君, 彭学超, 朱本铎, 等. 南海1∶100万海南岛幅海洋区域地质调查与编图成果综述[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2014, 34(6): 83-96.CHEN H J, PENG X C, ZHU B D, et al. A brief review of 1∶ 1000000 marine geological survey and mapping results of the Hainan sheet in the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2014, 34(6): 83-96. (in Chinese with English abstract[4] 吴时国, 鲁向阳, 李刚, 等. 海南岛周邻新生代沉积盆地构造与差异性演化特征[J]. 地质学报, 2024, 98(1): 16-30. doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2023168WU S G, LU X Y, LI G, et al. Tectonics and discrepant evolution of Cenozoic sedimentary basins adjacent Hainan Island[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2024, 98(1): 16-30. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19762/j.cnki.dizhixuebao.2023168 [5] 吴太霏, 王华, 刘恩涛, 等. 珠三坳陷珠江组一段沉积体系演化过程及其控制因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 111-122. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220484WU T F, WANG H, LIU E T, et al. Evolutionary and controlling factors of sedimentary system in the First Member of the Zhujiang Formation in the Zhu Ⅲ Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 111-122. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220484 [6] 王福国, 张向涛, 梅廉夫, 等. 珠江口盆地白云东区古近纪挤压−伸展变形模式及勘探意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 246-252.WANG F G, ZHANG X T, MEI L F, et al. Characteristics of Paleogene compression-extension deformation and exploration significance in the Baiyun East area, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 246-252. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 王鹏程, 李三忠, 郭玲莉, 等. 南海打开模式: 右行走滑拉分与古南海俯冲拖曳[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(4): 294-319. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.yx.2017-4-3WANG P C, LI S Z, GUO L L, et al. Opening of the South China Sea(SCS): Ajoint effect of dextral strike-slip pull-apart and proto-SCS slab pull[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(4): 294-319. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.13745/j.esf.yx.2017-4-3 [8] 詹文欢, 孙宗勋, 唐诚, 等. 华南滨海断裂带及其对台湾海峡地震活动的控制作用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2004, 23(4): 19-24.ZHAN W H, SUN Z X, TANG C, et al. Littoral active fault belt of South China and its control on seismic activity in Taiwan strait[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2004, 23(4): 19-24. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 龚再升. 中国近海含油气盆地新构造运动与油气成藏[J]. 地球科学, 2004, 29(5): 513-517. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2004.05.002GONG Z S. Neotectonics and petroleum accumulation in offshore Chinese basins[J]. Earth Science, 2004, 29(5): 513-517. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2004.05.002 [10] 赵明辉, 丘学林, 夏戡原, 等. 南海东北部滨海断裂带的研究现状与展望[J]. 华南地震, 2003, 23(1): 20-27.ZHAO M H, QIU X L, XIA K Y, et al. The situation and prospect of the research on the Binhai fault of NE South China Sea[J]. South China Journal of Seismology, 2003, 23(1): 20-27. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 李志刚, 张培震, 惠格格, 等. 南海北部滨海断裂带的深部结构探测现状和展望[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版)(中英文), 2022, 61(1): 55-62. doi: 10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.2021D045LI Z G, ZHANG P Z, HUI G G, et al. Current status and prospect of the deep structure exploration of the littoral fault zone in the northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2022, 61(1): 55-62. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.13471/j.cnki.acta.snus.2021D045 [12] HO K S, CHEN J C, JUANG W S. Geochronology and geochemistry of late Cenozoic basalts from the Leiqiong area, southern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2000, 18(3): 307-324. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00059-0 [13] 石学法, 鄢全树. 南海新生代岩浆活动的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2011, 31(2): 59-72. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1140.2011.02059SHI X F, YAN Q S. Geochemistry of Cenozoic magmatism in the South China Sea and its tectonic implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2011, 31(2): 59-72. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1140.2011.02059 [14] LIN J N, XIA S H, WANG X Y, et al. Seismogenic crustal structure affected by the Hainan mantle plume[J]. Gondwana Research, 2022, 103: 23-36. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2021.10.029 [15] CHEN D X, ZHANG G X, WANG X J, et al. Seismic features and origin of fluid escape pipes offshore Hainan Island on the northern slope of South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 133: 105276. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105276 [16] SUN Q L, ALVES T. Petrophysics of fine-grained mass-transport deposits: A critical review[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 192: 104291. [17] 沈奥, 孙启良, 蔡砥柱, 等. 海底麻坑的特征、分类与成因机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 204-217. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0144SHEN A, SUN Q L, CAI D Z, et al. Characteristics, classification and genetic mechanism of pockmarks[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 204-217. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0144 [18] 马云, 李三忠, 夏真, 等. 南海北部神狐陆坡区灾害地质因素特征[J]. 地球科学, 2014, 39(9): 1364-1372. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.119MA Y, LI S Z, XIA Z, et al. Characteristics of hazardous geological factors on Shenhu continental slope in the northern South China Sea[J]. Earth Science, 2014, 39(9): 1364-1372. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.119 [19] 李勇航, 牟泽霖, 倪玉根, 等. 海南东方近岸海底活动沙波的地球物理特征及其迁移机制[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(4): 27-35.LI Y H, MU Z L, NI Y G, et al. Geophysical characteristics and migration mechanism of active submarine sand waves off the coast of Dongfang, Hainan[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(4): 27-35. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 仝长亮, 王华强, 覃茂刚, 等. 琼州海峡东口潮流沙脊表层沉积物特征及沉积环境划分[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2022, 41(4): 625-636.TONG C L, WANG H Q, QIN M G, et al. Surface sediment characteristics and sedimentary environment division of tidal sand ridge at the east entrance of Qiongzhou strait[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2022, 41(4): 625-636. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] YAN P, DENG H, LIU H L, et al. The temporal and spatial distribution of volcanism in the South China Sea region[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 27(5): 647-659. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.06.005 [22] 夏少红, 范朝焰, 孙金龙, 等. 南海北部晚新生代岩浆活动的发育特征与构造意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(6): 25-33. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2017.06.003XIA S H, FAN C Y, SUN J L, et al. Characteristics of Late Cenozoic magmatic activities on the northern margin of South China Sea and their tectonic implications[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(6): 25-33. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2017.06.003 [23] 张峤, 吴时国, 吕福亮, 等. 南海西北陆坡火成岩体地震识别及分布规律[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2014, 38(4): 919-938.ZHANG Q, WU S G, LYU F L, et al. The seismic characteristics and the distribution of the igneous rocks in the northernwest slope of the South China Sea[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2014, 38(4): 919-938. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] SUN Q L, MAGEE C, JACKSON C A L, et al. How do deep-water volcanoes grow[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2020, 542: 116320. [25] 朱友生. 南海北部陆架边缘区域地质灾害类型特征及分布规律[J]. 中国海上油气, 2017, 29(3): 107-115. doi: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2017.03.018ZHU Y S. Features and distribution pattern of the geological hazards in the northern continental shelf margins of South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2017, 29(3): 107-115. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11935/j.issn.1673-1506.2017.03.018 [26] 孙启良, 解习农, 吴时国. 南海北部海底滑坡的特征、灾害评估和研究展望[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(2): 258-270.SUN Q L, XIE X N, WU S G. Submarine landslides in the northern South China Sea: Characteristics, geohazard evaluation and perspectives[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(2): 258-270. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 庞雄, 陈长民, 朱明, 等. 南海北部陆坡白云深水区油气成藏条件探讨[J]. 中国海上油气, 2006, 18(3): 145-149.PANG X, CHEN C M, ZHU M, et al. A discussion about hydrocarbon accumulation conditions in Baiyun deep-water area, the northern continental slope, South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2006, 18(3): 145-149. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] KUANG Z G, COOK A, REN J F, et al. A flat-lying transitional free gas to gas hydrate system in a sand layer in the Qiongdongnan Basin of the South China Sea[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2023, 50(24): e2023GL105744. doi: 10.1029/2023GL105744 [29] 郭玉贵. 中国近海及邻域环境地质稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1998, 9(2): 51-62.GUO Y G. Analysis on environmental geology stability of China offshore and its adjacent areas[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1998, 9(2): 51-62. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 李萍, 杜军, 刘乐军, 等. 我国近海海底浅层气分布特征[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2010, 21(1): 69-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.01.015LI P, DU J, LIU L J, et al. Distribution characteristics of the shallow gas in Chinese offshore seabed[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2010, 21(1): 69-74. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2010.01.015 [31] 苏海霞, 刘姗, 张莉, 等. 南海南部北康盆地晚中新世以来深水沉积单元时空分布特征及其控制因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(6): 129-139.SU H X, LIU S, ZHANG L, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution characteristics and controlling factors of deep-water sediments in the Beikang Basin since the Late Miocene, southern South China Sea[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(6): 129-139. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 王大伟, 吴时国, 吕福亮, 等. 南海深水块体搬运沉积体系及其油气勘探意义[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 35(5): 14-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2011.05.003WANG D W, WU S G, LYU F, L, et al. Mass transport deposits and its significance for oil & gas exploration in deep-water regions of South China Sea[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2011, 35(5): 14-19. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2011.05.003 [33] 何健, 梁前勇, 马云, 等. 南海北部陆坡天然气水合物区地质灾害类型及其分布特征[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(1): 15-28. doi: 10.12029/gc20180102HE J, LIANG Q Y, MA Y, et al. Geohazards types and their distribution characteristics in the natural gas hydrate area on the northern slope of the South China Sea[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(1): 15-28. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12029/gc20180102 [34] 田冬梅. 南海西北部晚中新世深水水道沉积水动力学模拟[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2022.TIAN D M. Hydrodynamic simulation of Late Miocence submarine channels in the northwestern South China Sea[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] HARRIS P T, MACMILLAN-LAWLER M, RUPP J, et al. Geomorphology of the oceans[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 352: 4-24. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2014.01.011 [36] 陈珊珊, 王中波, 张勇, 等. 东海北部外陆架及邻区灾害地质体特征及成因研究[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(5): 1512-1529. doi: 10.12029/gc20200516CHEN S S, WANG Z B, ZHANG Y, et al. Characteristics and origin of disaster geological bodies in the northern outer shelf of the East China Sea and its adjacent areas[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(5): 1512-1529. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12029/gc20200516 [37] 胡久常. 海南火山的监测与灾害预防[C]//佚名. 火山作用与地球层圈演化: 全国第四次火山学术研讨会论文摘要集. [出版地不详]: [出版者不详], 2005: 32-34.HU J C. Monitoring and disaster prevention of Hainan volcanoes[C]//Anon. Volcanic activity and the Evolution of Earth's Lithosphere: Abstracts of the 4th National Volcanological Conference. [S. l. ]: [s. n. ], 2005: 32-34. (in Chinese) [38] 谢卓娟. 中国海域及邻区地震区划中的地震活动性研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所, 2020.XIE Z J. Study on seismic activities in seismic zoning of China'seas and adjacent[D]. Harbin: Institute of Engineering Mechanics, China Earthquake Administration, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 杨晓东, 张锦昌, 邱强, 等. 南海北缘钻探选址: 滨海断裂带大型海洋地质灾害研究[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(8): 2853-2865. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.08.017YANG X D, ZHANG J C, QIU Q, et al. Oceanic drilling into the northern margin of the South China Sea: Investigating the great marine geohazards along the littoral fault zone[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(8): 2853-2865. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.08.017 -




 下载:
下载: