Suitability and potential evaluation of geological storage of carbon dioxide in saline aquifers of Ying-Qiong Basin
-
摘要:
二氧化碳(CO2)过量排放造成全球气候多变,进而引发一系列生态环境问题,作为减少CO2排放的关键技术,碳捕集、利用和封存(CCUS)在实现CO2大规模减排中发挥重要作用。中国近海盆地咸水层CO2封存项目的应用前景广阔,封存潜力巨大。针对莺−琼盆地咸水层CO2封存有利层系和封存潜力认识不清等问题,基于莺−琼盆地的地质特征,通过计算指标组成权重和适宜性得分对莺−琼盆地开展了CO2地质封存适宜性评价。此外,结合数值模拟方法计算的不同层系CO2有效封存系数,采用不同的封存潜力计算方法,对莺−琼盆地咸水层的CO2封存潜力进行了评价。结果表明,欧盟(EC)方法计算的CO2封存容量要略小于美国能源部(USDOE)和碳收集领导人论坛(CSLF)方法得出的封存容量。由于CSLF方法考虑了构造封存、残余气封存和溶解封存等封存机制,其结果更符合实际情况。综上所述,莺歌海盆地和琼东南盆地咸水层的CO2封存潜力分别为7.96×1010和4.40×1010 t,莺−琼盆地咸水层总的CO2封存潜力为1.24×1011 t,进一步验证了莺−琼盆地咸水层CO2封存工业规模试点和示范项目的巨大潜力,为开展莺−琼盆地咸水层CO2地质封存场地选址提供了依据。
Abstract:Objective Excessive carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions have led to global climate variability, resulting in a series of environmental challenges. As a critical technology for reducing CO2 emissions, carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) plays a significant role in mitigating large-scale CO2 emissions. The application of CO2 storage in saline aquifers, particularly in offshore China, offers promising prospects with substantial technical and economic potential.
Methods To address the uncertainties regarding favorable areas and CO2 storage potential in saline aquifers of Ying-Qiong Basin, this study evaluates the geological suitability for CO2 storage by calculating the weights of key components and the suitability score based on the basin's geological characteristics. Additionally, the CO2 storage potential is assessed using effective CO2 storage coefficients obtained through numerical simulation and various storage potential calculation methods.
Results The results indicate that the storage capacity determined by the EC method is lower than that obtained using the USDOE and CSLF methods. Since the CSLF method accounts for storage mechanisms such as geological structure storage, residual gas storage, and dissolution storage, its results are more reasonable. The CO2 storage potential in saline aquifers of Ying-Qiong Basin and Qiongdongnan Basin is estimated to be 7.96×1010 and 4.40×1010 t, respectively. The total CO2 storage potential in Ying-Qiong Basin's saline aquifers is 1.24×1011 t, further confirming the significant potential for industrial-scale pilot and demonstration projects.
Conclusion This provides a solid foundation for future CO2 storage initiatives in saline aquifers of Ying-Qiong Basin.
-
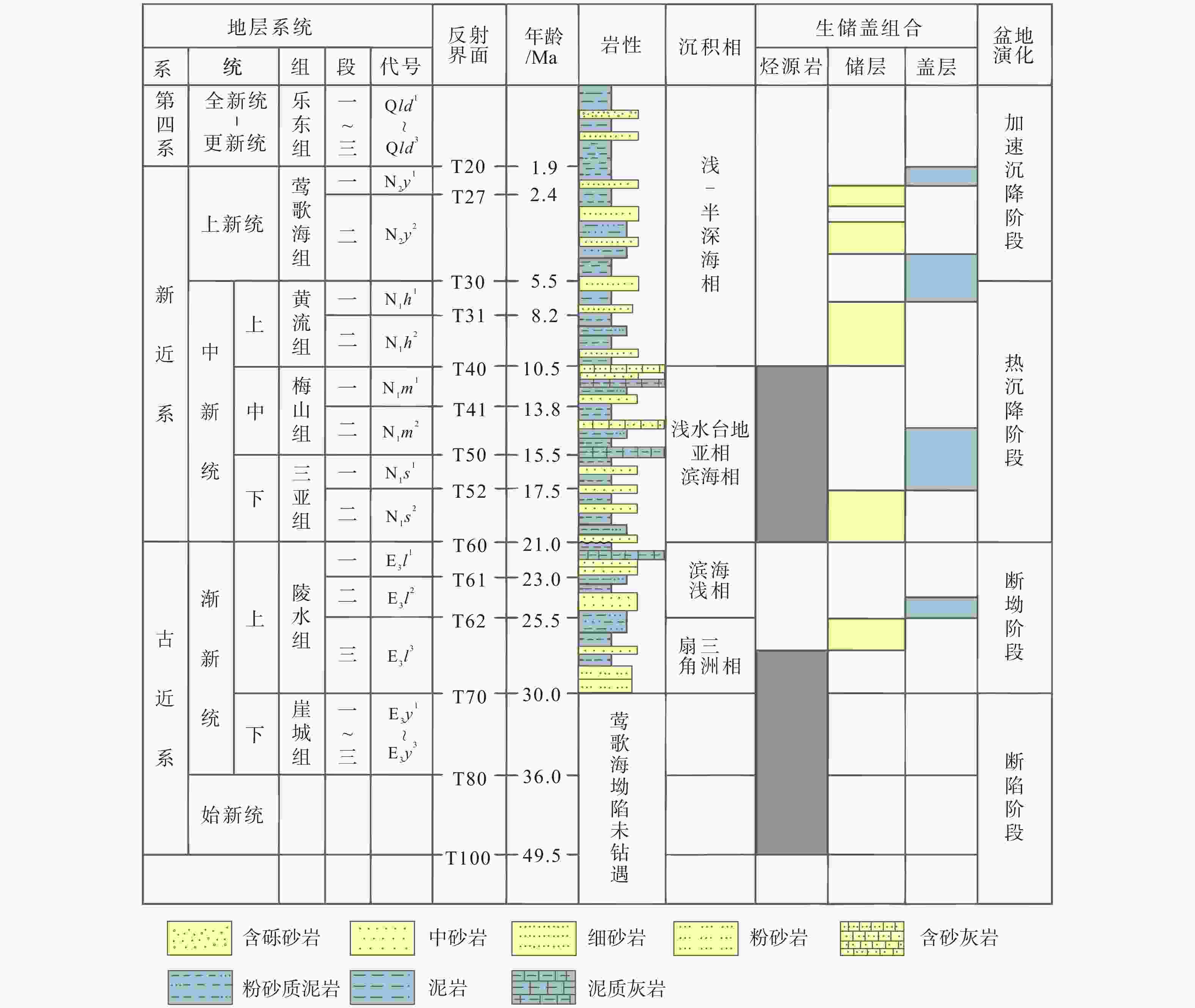
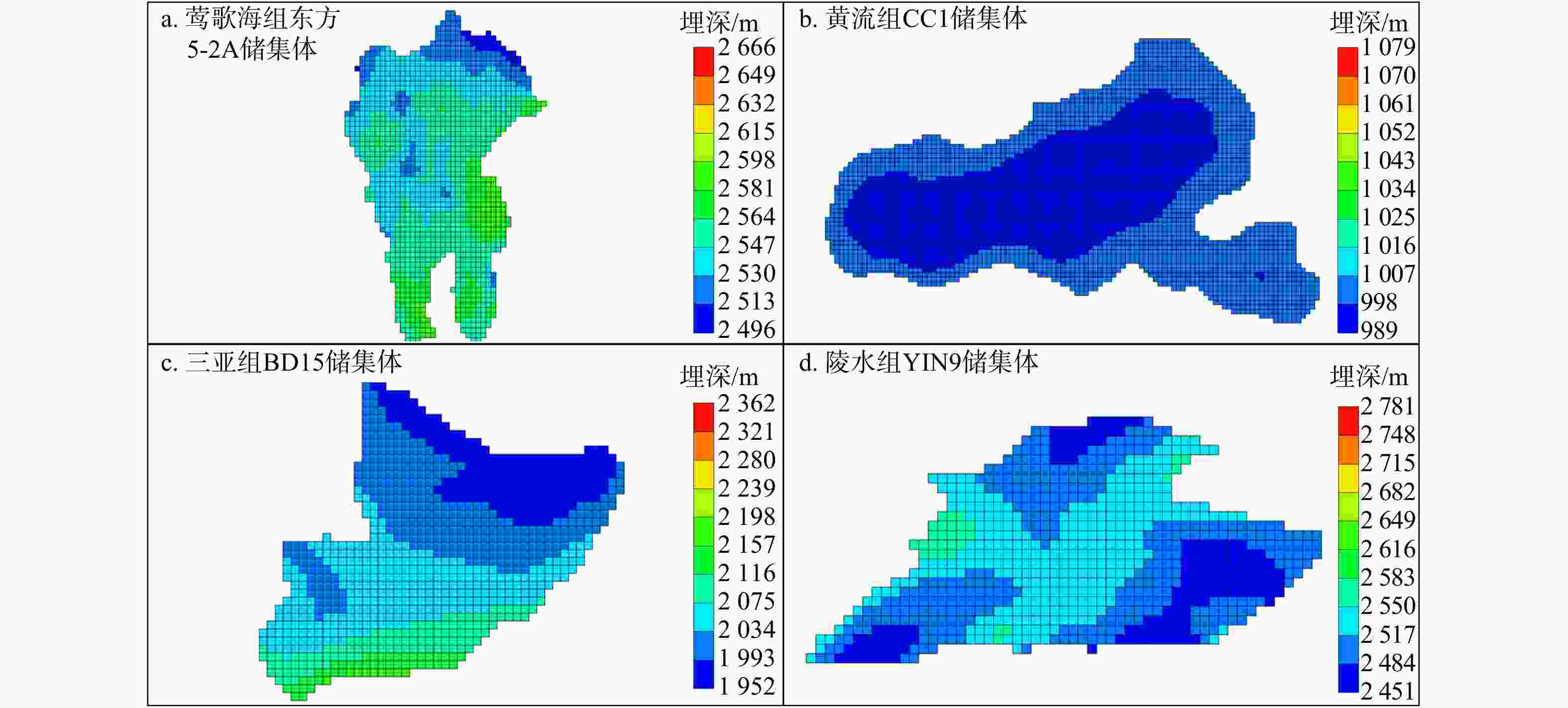
盆地 主要储层 平均孔隙度 平均渗透率/
10−3 μm2净毛比 地层厚度/m 莺歌海 莺歌海组 0.22~0.25 3.6~274.5 0.13 1270 ~3300 琼东南 莺歌海组−黄流组 0.15~0.225 11.7 0.13 473~ 3576 梅山组−三亚组 0.16~0.18 2.3~ 1000 0.26 200~ 3000 陵水组 0.13~0.16 69~111 0.28 100~ 4600 表 2 莺−琼盆地咸水层CO2地质封存适宜性评价[29-30]
Table 2. Suitability evaluation for CO2 geological storage in saline aquifers of Ying-Qiong Basin
指标层 权重 指标亚层 权重 指标组成 权重 地质特征 0.2164 地壳稳定性 1.0 断裂特征 0.1434 断裂封闭性 0.5246 地震 0.2390 火山 0.0930 储盖特征 0.6434 储层特征 0.4545 岩性 0.1111 储层深度 0.2222 储层厚度 0.2222 孔隙度 0.2222 渗透率 0.2223 储盖组合 0.0910 — — 盖层特征 0.4545 岩性 0.3333 分布连续性 0.3333 单层厚度 0.1667 累计厚度 0.1667 地温特征 0.0449 地温梯度 0.50 — — 地热流值 0.50 — — 社会经济特征 0.0953 勘探程度 0.50 — — 基础条件 0.50 — — 表 3 莺−琼盆地咸水层CO2地质封存适宜层系的封存量计算参数[25,28]
Table 3. Parameters of CO2 geological storage suitable formation in saline aquifers of Ying-Qiong Basin
计算参数 莺歌海盆地 琼东南盆地 莺歌海组 莺歌海组−
黄流组梅山组−
三亚组陵水组 净毛比 0.13 0.13 0.26 0.28 平均孔隙度 0.23 0.185 0.17 0.145 储层体积/km3 153069 46710 43135 4051 地层温度/℃ 92 80 100 120 地层压力/Mpa 21.6 24 30 36 CO2密度/(kg·m−3) 559.03 653.93 635.04 654.87 CO2溶解度/(mol·L−1) 1.032 1.178 1.270 1.362 表 4 莺−琼盆地CO2封存潜力评价结果
Table 4. Results of CO2 storage potential of Ying-Qiong Basin
盆地 有利层系 咸水层CO2总的有效封存量/t EC USDOE CSLF 莺歌海 莺歌海组 5.57×1010 7.16×1010 7.96×1010 琼东南 莺歌海组−黄流组 9.11×109 1.10×1010 1.30×1010 梅山组−三亚组 2.13×1010 2.30×1010 2.79×1010 陵水组 2.61×109 2.48×109 3.14×109 莺−琼 — 8.87×1010 1.08×1011 1.24×1011 注:EC. European Commission,欧盟计算方法;USDOE. United States Department of Energy,美国能源部计算方法;CSLF. Carbon Sequestration Leadership Forum,碳收集领导人论坛计算方法 -
[1] 李阳,黄文欢,金勇,等. 双碳愿景下中国石化不同油藏类型CO2驱提高采收率技术发展与应用[J]. 油气藏评价与开发,2021,11(6):793-804.LI Y,HUANG W H,JIN Y,et al. Different reservoir types of CO2 flooding in Sinopec EOR technology development and application under "dual carbon" vision[J]. Petroleum Reservoir Evaluation and Development,2021,11(6):793-804. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 张海龙. CO2混相驱提高石油采收率实践与认识[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2020,39(2):114-119.ZHANG H L. Practice and understanding of enhancing the oil recovery by CO2 miscible flooding[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing,2020,39(2):114-119. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 尹书郭,杨国栋,冯涛,等. 页岩储层物性参数对CO2不同封存机制及封存量的影响[J]. 高校地质学报,2023,29(1):37-46.YIN S G,YANG G D,FENG T,et al. Effects of physical parameters of shale on CO2 storage capacity with different mechanisms[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2023,29(1):37-46. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 杨红,赵习森,康宇龙,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地CO2地质封存适宜性与潜力评价[J]. 气候变化研究进展,2019,15(1):95-102.YANG H,ZHAO X S,KANG Y L,et al. Evaluation on geological sequestration suitability and potential of CO2 in Ordos Basin[J]. Climate Change Research,2019,15(1):95-102. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 赵晓亮,廖新维,王万福,等. 二氧化碳埋存潜力评价模型与关键参数的确定[J]. 特种油气藏,2013,20(6):72-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2013.06.018ZHAO X L,LIAO X W,WANG W F,et al. Evaluative model of CO2 geological sequestration and determination of key parameters[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs,2013,20(6):72-74. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6535.2013.06.018 [6] 任相坤,崔永君,步学朋,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地CO2地质封存潜力分析[J]. 中国能源,2010,32(1):29-32.REN X K,CUI Y J,BU X P,et al. Analysis on CO2 storage potentiality in Ordos Basin[J]. Energy of China,2010,32(1):29-32. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 米立军. 全球海上CO2封存现状及中国近海机遇与挑战[J]. 中国海上油气,2023,35(1):123-135.MI L J. Current status of global CO2 ocean sequestration and opportunities and challenges in China offshore areas[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,2023,35(1):123-135. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 赵金洲,郑建超,任岚,等. 海洋CO2地质封存研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2024,43(1):1-13.ZHAO J Z,ZHENG J C,REN L,et al. Research progress and development trend of marine CO2 geological storage[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing,2024,43(1):1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 夏翠梅,王楠,刘景昱,等. “碳中和” 目标下海洋黑碳的源汇过程及其意义[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(2):318-329.XIA C M,WANG N,LIU J Y,et al. Source-sink processes of marine black carbon in the context of “carbon neutrality”[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(2):318-329. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] GUO J Q,WEN D G,ZHANG S Q,et al. Potential and suitability evaluation of CO2 geological storage in major sedimentary basins of China,and the demonstration project in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition,2015,89(4):1319-1332. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12531 [11] 贺陆胜,万建华,张建强,等. CO2地质封存研究与中国CO2地质封存潜力评述[J]. 甘肃地质,2024,33(1):59-71.HE L S,WAN J H,ZHANG J Q,et al. CO2 geological sequestration and evaluation of CO2 geological sequestration potential in China[J]. Gansu Geology,2024,33(1):59-71. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] ZHANG K,LAU H C,CHEN Z X. Extension of CO2 storage life in the Sleipner CCS project by reservoir pressure management[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering,2022,108:104814. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2022.104814 [13] CAO W Z,SHI J Q,DURUCAN S,et al. Evaluation of shear slip stress transfer mechanism for induced microseismicity at in Salah CO2 storage site[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2021,107:103302. doi: 10.1016/j.ijggc.2021.103302 [14] 王永胜. CO2咸水层封存砂岩储层孔隙尺度变化规律及可注性研究:基于神华CCS示范工程[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2021.WANG Y S. Study on the variation of pore scale and injectability of CO2 saltwater sequestered sandstone reservoir:Based on Shenhua CCS demonstration project[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences (Wuhan),2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 闫华敏,李磊,李林涛,等. 基于层次分析法和模糊评价法的中国近海盆地CO2封存适宜性评价[J]. 海洋地质前沿,2024,40(1):79-93.YAN H M,LI L,LI L T,et al. Suitability assessment on CO2 storage in offshore basins of China based on AHP and fuzzy comprehensive evaluation[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers,2024,40(1):79-93. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 张振冬,杨正先,张永华,等. CO2捕集与封存研究进展及其在我国的发展前景[J]. 海洋环境科学,2012,31(3):456-459.ZHANG Z D,YANG Z X,ZHANG Y H,et al. Study progress on CO2 capture and storage and development prospect in China[J]. Marine Environmental Science,2012,31(3):456-459. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 李春峰,赵学婷,段威,等. 中国海域盆地CO2地质封存选址方案与构造力学分析[J]. 力学学报,2023,55(3):719-731.LI C F,ZHAO X T,DUAN W,et al. Strategic and geodynamic analysis of geo-sequestration of CO2 in China offshore sedimentary basins[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics,2023,55(3):719-731. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] 熊鹏飞,方小宇,乐文喜,等. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷咸水层CO2地质封存储盖优选及潜力评估[J]. 煤炭学报,2024,49(5):2405-2413.XIONG P F,FANG X Y,LE W X,et al. Reservoir-cap combination optimization and potential evaluation of CO2 geological storage in saline aquifer,in Wenxinan Sag of Beibu Gulf Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2024,49(5):2405-2413. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] QIN J Z,ZHONG Q H,TANG Y,et al. CO2 storage potential assessment of offshore saline aquifers in China[J]. Fuel,2023,341:127681. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.127681 [20] 谢玉洪,李绪深,徐新德,等. 莺−琼盆地高温高压领域天然气成藏与勘探大突破[J]. 中国石油勘探,2016,21(4):19-29.XIE Y H,LI X S,XU X D,et al. Gas accumulation and great exploration breakthroughs in HTHP formations within Yinggehai-Qiongdongnan basins[J],China petroleum exploration,2016,21(4):19-29. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 罗盼,高圆圆,王后金,等. 南海西南次海盆V型尖端地壳岩石圈最终裂解的特征及过程[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(2):234-246.LUO P,GAO Y Y,WANG H J,et al. Characteristics and process of the final breakup of the crustal lithosphere at the V-shaped tip of the Southwest Subbasin in South China Sea[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(2):234-246. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 王振峰,裴健翔,郝德峰,等. 莺−琼盆地中新统大型重力流储集体发育条件、沉积特征及天然气勘探有利方向[J]. 中国海上油气,2015,27(4):13-21.WANG Z F,PEI J X,HAO D F,et al. Development conditions,sedimentary characteristics of Miocene large gravity flow reservoirs and the favorable gas exploration directions in Ying-Qiong basins[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,2015,27(4):13-21. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 周杰,胡林,胡高伟,等. 莺歌海盆地莺东斜坡带南段中深层断裂特征及控藏作用[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(8):3021-30.ZHOU J,HU L,HU G W,et al. Characteristics of middle deep faults in the southern segment of the eastern belt of Yinggehai Basin and their controlling effect on natural gas accumulation[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(8):3021-3030. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 张旭友,范彩伟,郭小文,等. 莺歌海盆地中央底辟带乐东区莺歌海组超压成因及相对贡献定量化评价[J]. 地球科学,2024,49(10):3547-3558.ZHANG X Y,FAN C W,GUO X W,et al. Overpressure mechanisms and quantitative evaluation of the relative contribution for Yinggehai Formation in Ledong area of the central diapir zone,Yinggehai Basin[J]. Earth Science,2024,49(10):3547-3558. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] ZHANG C M,ZHOU D,LI P C,et al. CO2 storage potential of the Qiongdongnan Basin,northwestern South China Sea[J]. Greenhouse Gases:Science and Technology,2014,4(6):691-706. doi: 10.1002/ghg.1430 [26] 谢玉洪,刘平,黄志龙. 莺歌海盆地高温超压天然气成藏地质条件及成藏过程[J]. 天然气工业,2012,32(4):19-23.XIE Y H,LIU P,HUANG Z L. Geological conditions and pooling process of high-temperature and overpressure natural gas reservoirs in the Yinggehai Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2012,32(4):19-23. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 谢玉洪,李绪深,童传新,等. 莺琼盆地高温超压天然气成藏理论与勘探实践[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2015.XIE Y H,LI X S,TONG C X,et al. Theory and exploration practice of high temperature overpressure gas accumulation in Ying-Qiong Basin[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,2015. (in Chinese) [28] 霍传林. 我国近海二氧化碳海底封存潜力评估和封存区域研究[D]. 辽宁大连:大连海事大学,2014.HUO C L. Study on the potential evaluation and the storage areas of the carbon dioxide seabed storage in offshore China[D]. Dalian Liaoning:Dalian Maritime University,2014. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 祁生文,郑博文,路伟,等. 二氧化碳地质封存选址指标体系及适宜性评价研究[J]. 第四纪研究,2023,43(2):523-550. doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2023.02.19QI S W,ZHENG B W,LU W,et al. Investigation of indexes system and suitability evaluation for carbon dioxide geological storage site[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2023,43(2):523-550. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2023.02.19 [30] 文冬光,郭建强,张森琦,等. 中国二氧化碳地质储存研究进展[J]. 中国地质,2014,41(5):1716-1723. doi: 10.12029/gc20140525WEN D G,GUO J Q,ZHANG S Q,et al. The progress in the research on carbon dioxide geological storage in China[J]. Geology in China,2014,41(5):1716-1723. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12029/gc20140525 [31] 肖贝,陈磊,杨皝,等. 准噶尔盆地深部咸水层CO2地质封存适宜性及潜力评价[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2024,43(6):120-127.XIAO B,CHEN L,YANG H,et al. Suitability and potential evaluation of CO2 geological storage in deep saline aquifers of Junger Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing,2024,43(6):120-127. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] KOIDE H,TAKAHASHI M,TSUKAMOTO H,et al. Self-trapping mechanisms of carbon dioxide in the aquifer disposal[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,1995,36(6/7/8/9):505-508. [33] U. S. Department of Energy. Carbon sequestration atlas of the United States and Canada[M]. Washingto United States:U. S. Department of Energy,2008. [34] BACHU S,BONIJOLY D,BRADSHAW J,et al. CO2 storage capacity estimation:Methodology and gaps[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control,2007,1(4):430-443. doi: 10.1016/S1750-5836(07)00086-2 [35] WANG Y,ZHANG K N,WU N Y. Numerical investigation of the storage efficiency factor for CO2 geological sequestration in saline formations[J]. Energy Procedia,2013,37:5267-5274. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2013.06.443 [36] GUO B Y,WEI N,SONG J Z,et al. Prediction of the maximum allowable bottom hole pressure in CO2 injection wells[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2017,156:575-581. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.06.033 -




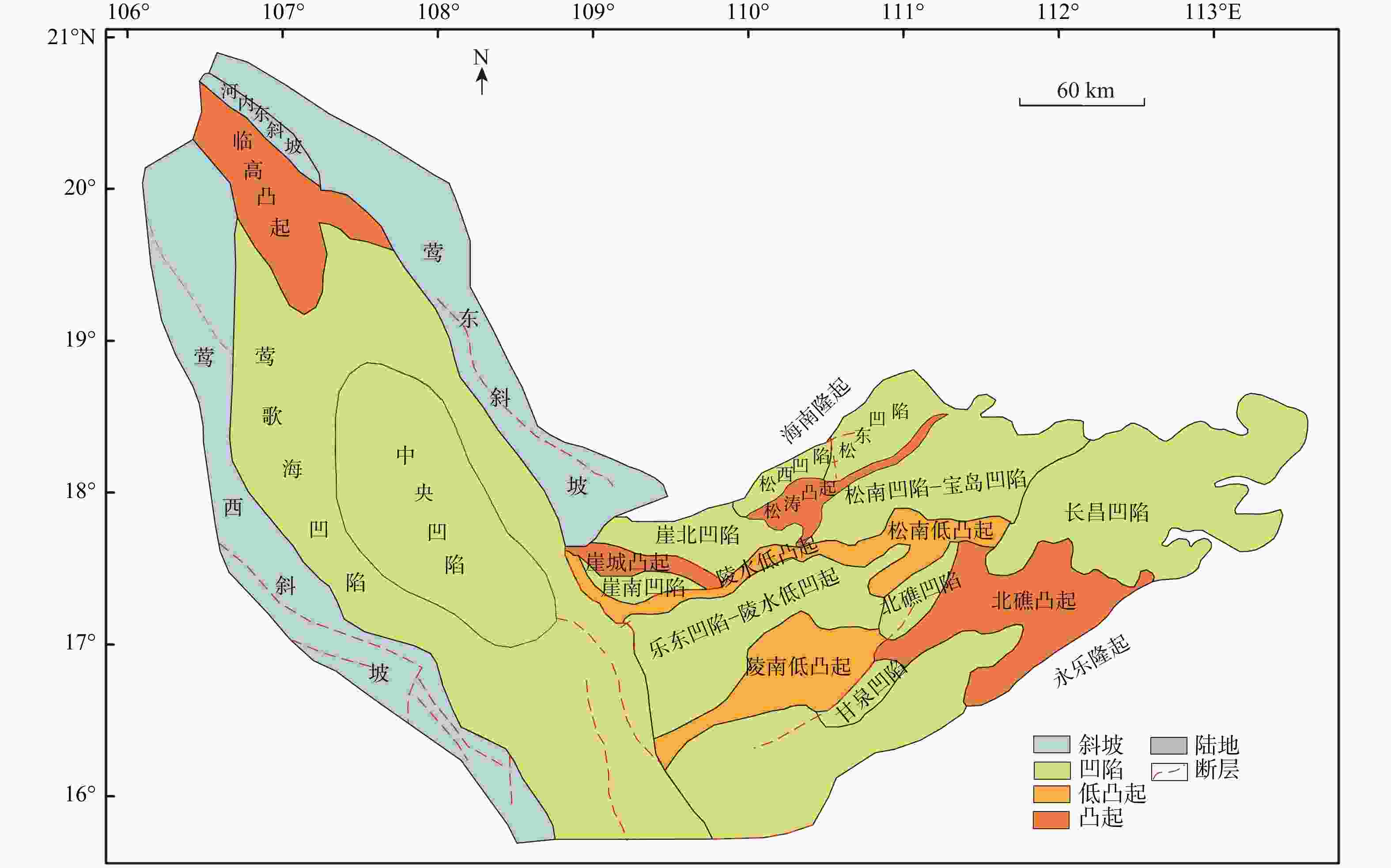
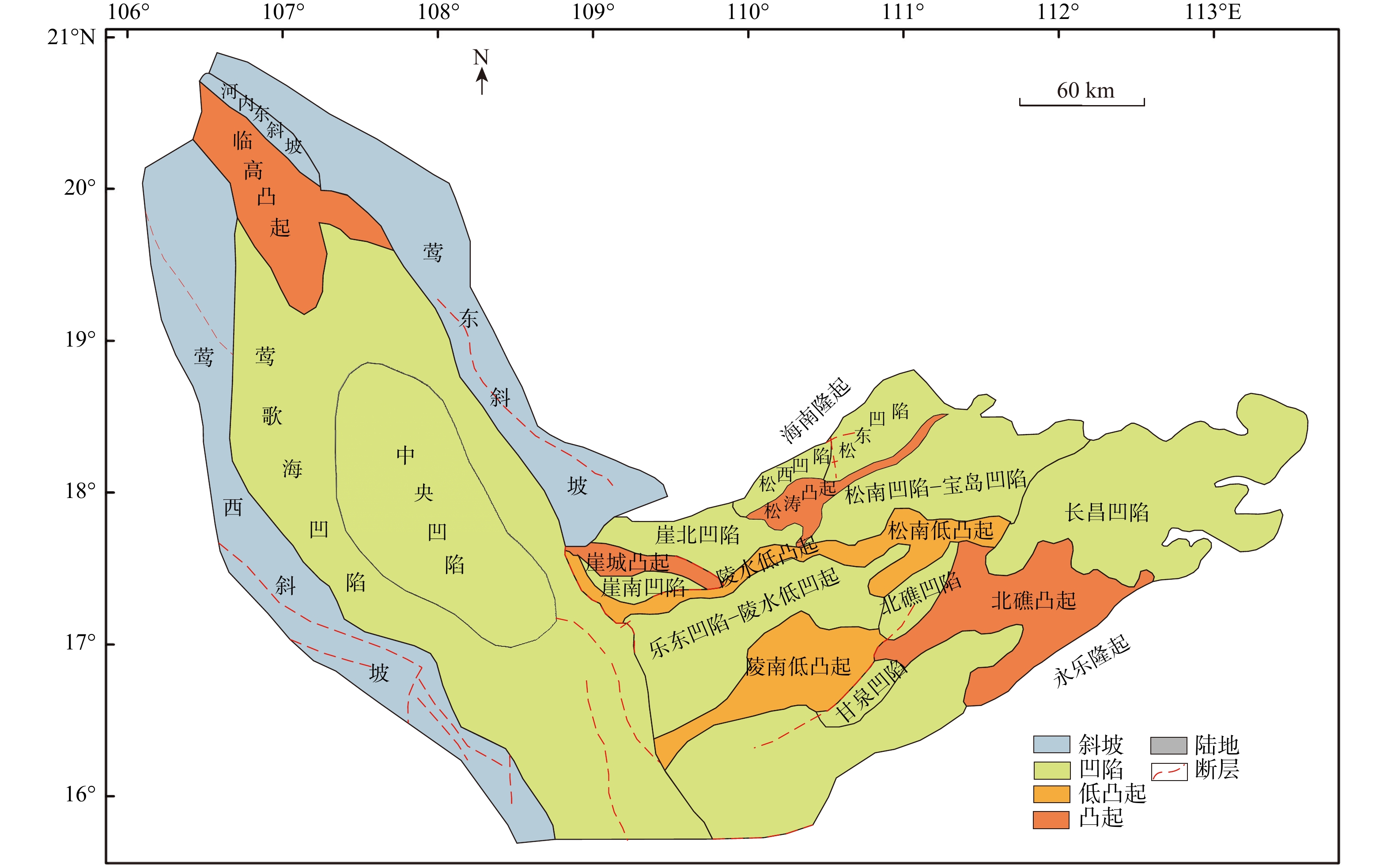
 下载:
下载: