Considering the effect of layered heterogeneity on CO2 migration processes and sequestration in marine saline aquifers
-
摘要:
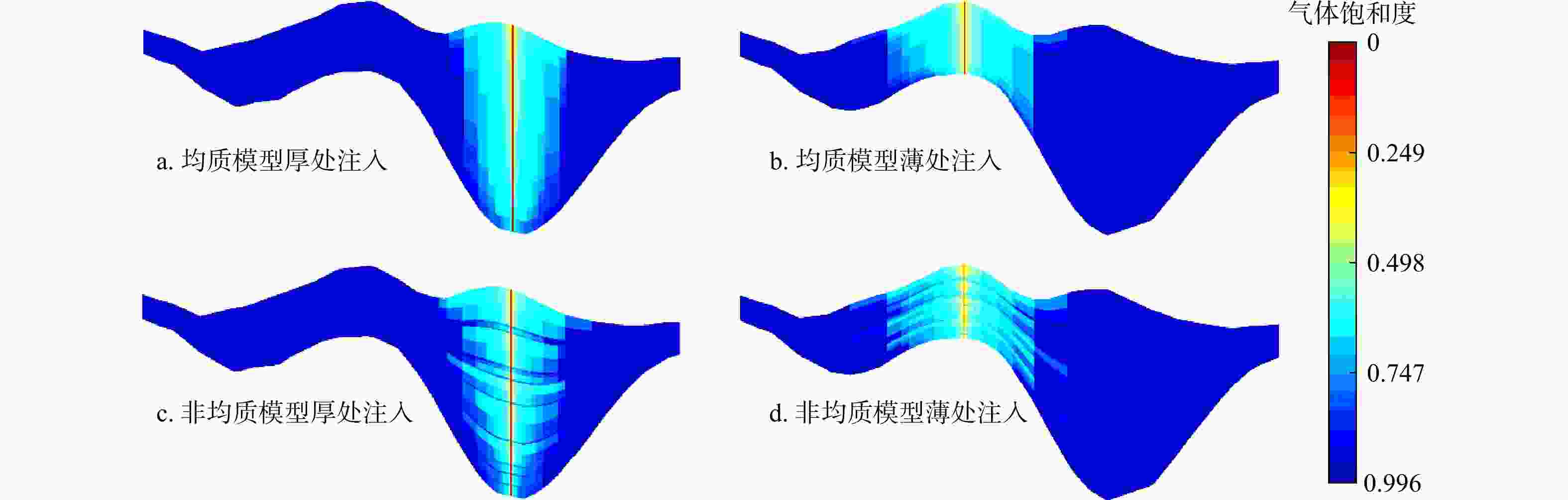
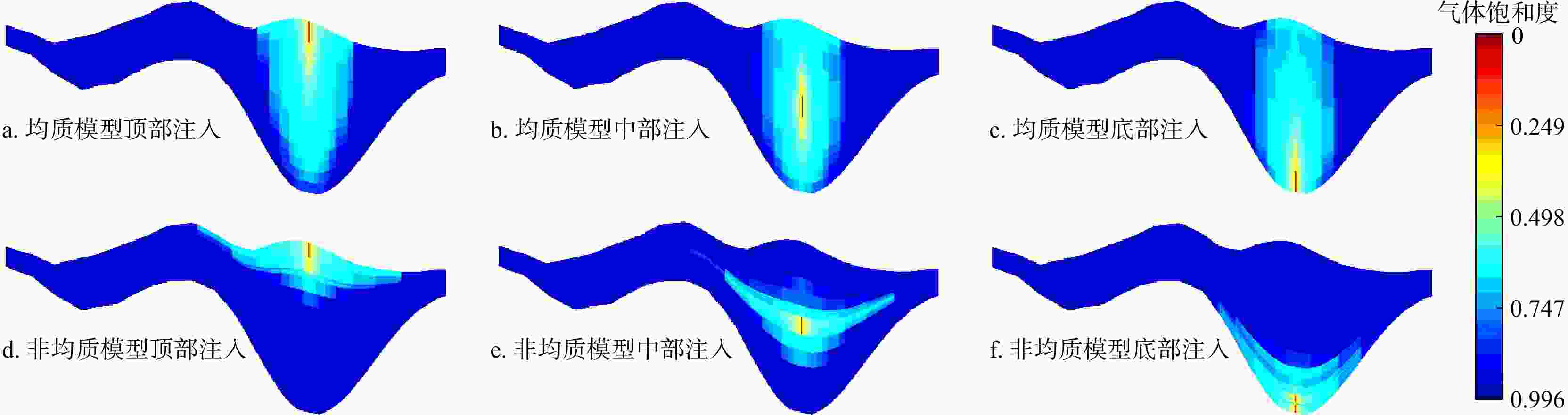
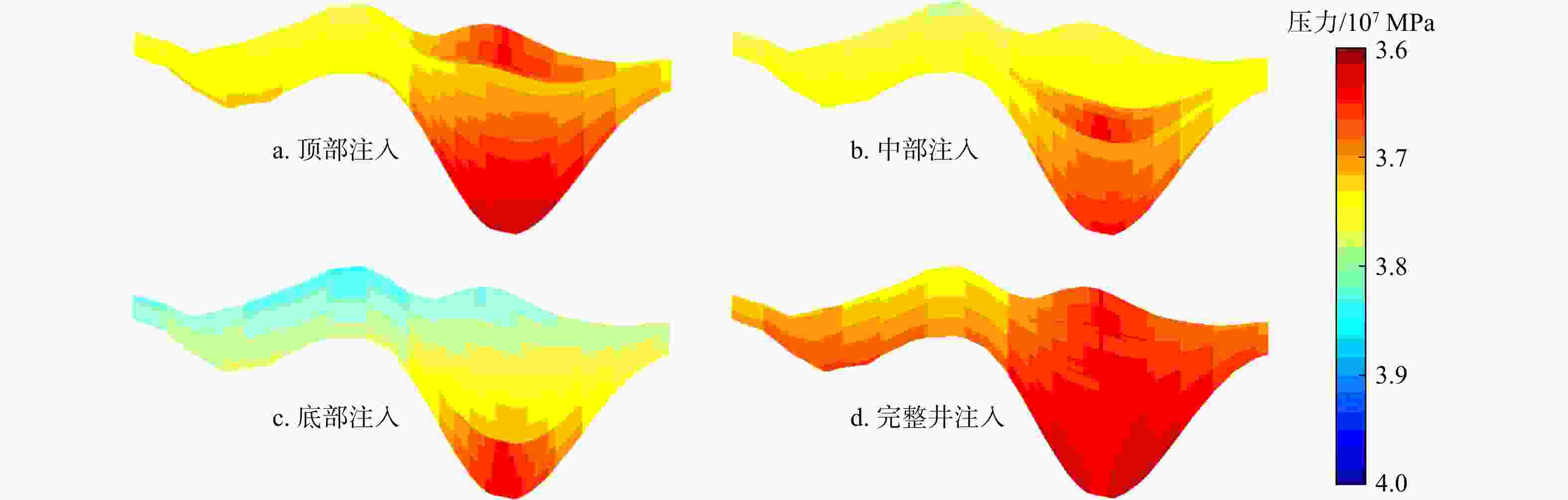
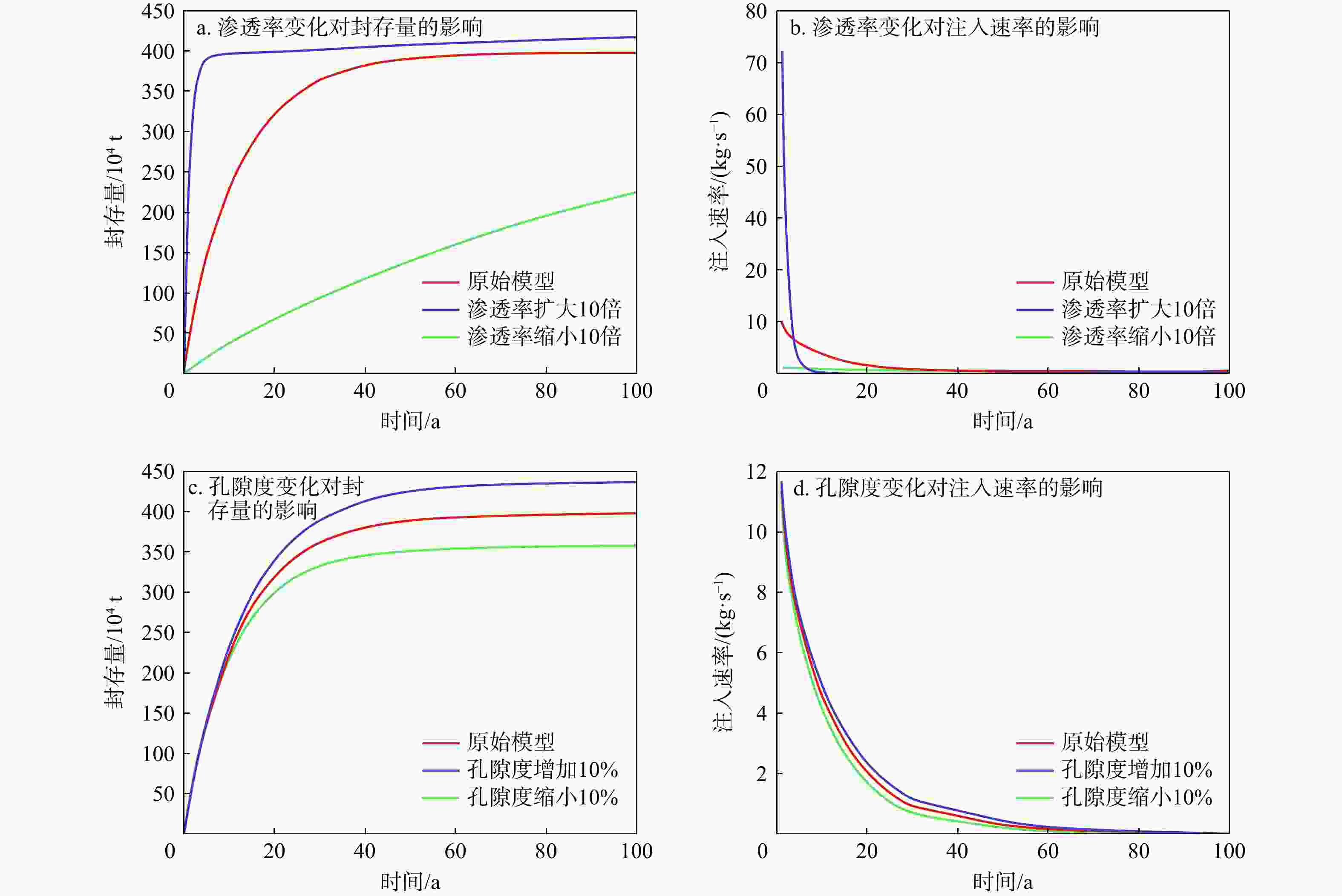
数值模拟是研究咸水层中CO2迁移机理及地质封存量的主要手段。然而,前人研究往往假设储层是规则且均质的长方体,并且关于CO2在海域咸水层中迁移过程的数值模拟研究鲜见报道。依托南海某储集体,考虑地层的非均质性与岩性圈闭的实际位置,利用地震反射特征和钻孔资料建立了非均质地质模型,采用TOUGHREACT软件模拟了不同注入位置对CO2在地层中迁移和封存的影响。结果表明:CO2向上迁移过程受到泥岩的阻挡,横向迁移更加显著。对于不同的注入方案,储层压力分布存在显著差异。在储层顶部注入时储层压力可达到40.1 MPa;在储层底部注入时,储层压力最高可达到39.7 MPa;当完整井注入时,储层的压力最高可达到40.3 MPa。因此完整井注入和顶部注入方案长期实行导致的压力积聚可能破坏储盖层结构, CO2泄露的风险更大,在储层底部和中部注入的方案更加安全。当持续注入100 a时,CO2以超临界相为主,占总封存量的77%以上。在相同的井口注入压力下,均质模型会高估储集体的封存量,非均质模型中在储层顶部注入和中部注入比底部注入分别多55.1%和49.3%。敏感性分析结果表明孔隙度和渗透率对结果的影响比毛管压力显著。研究查明了考虑储层的层状非均质性时注入井位置对CO2迁移机理和封存量的影响,可以为CO2封存的布井设计提供理论依据。
Abstract:Numerical modeling is a primary tool for studying the migration mechanisms and sequestration of CO2 in saline aquifers. However, previous studies often assume that reservoirs are regular rectangular shapes and homogeneous, with few reports on numerical simulations of CO2 migration in marine saline aquifers.
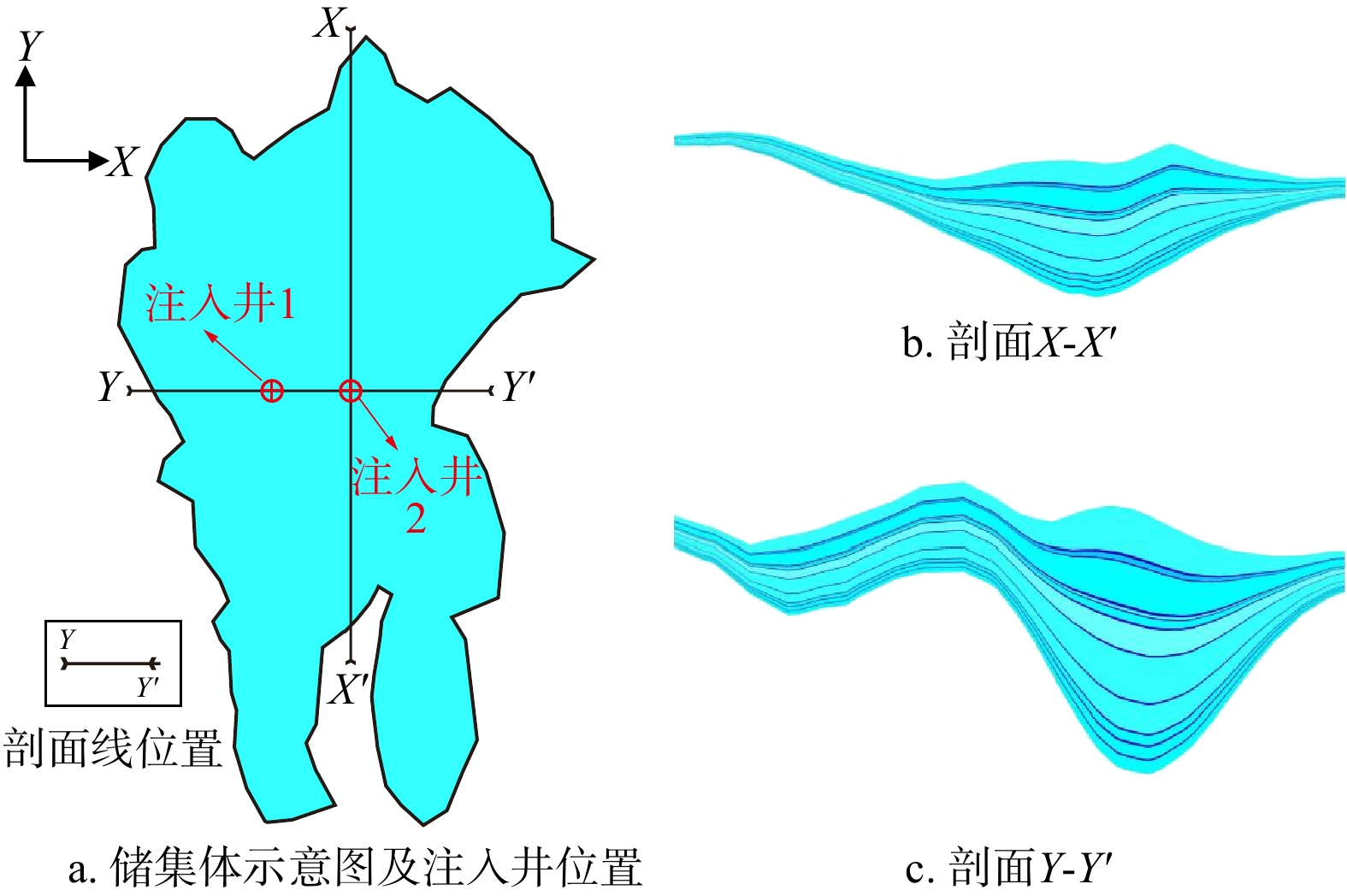
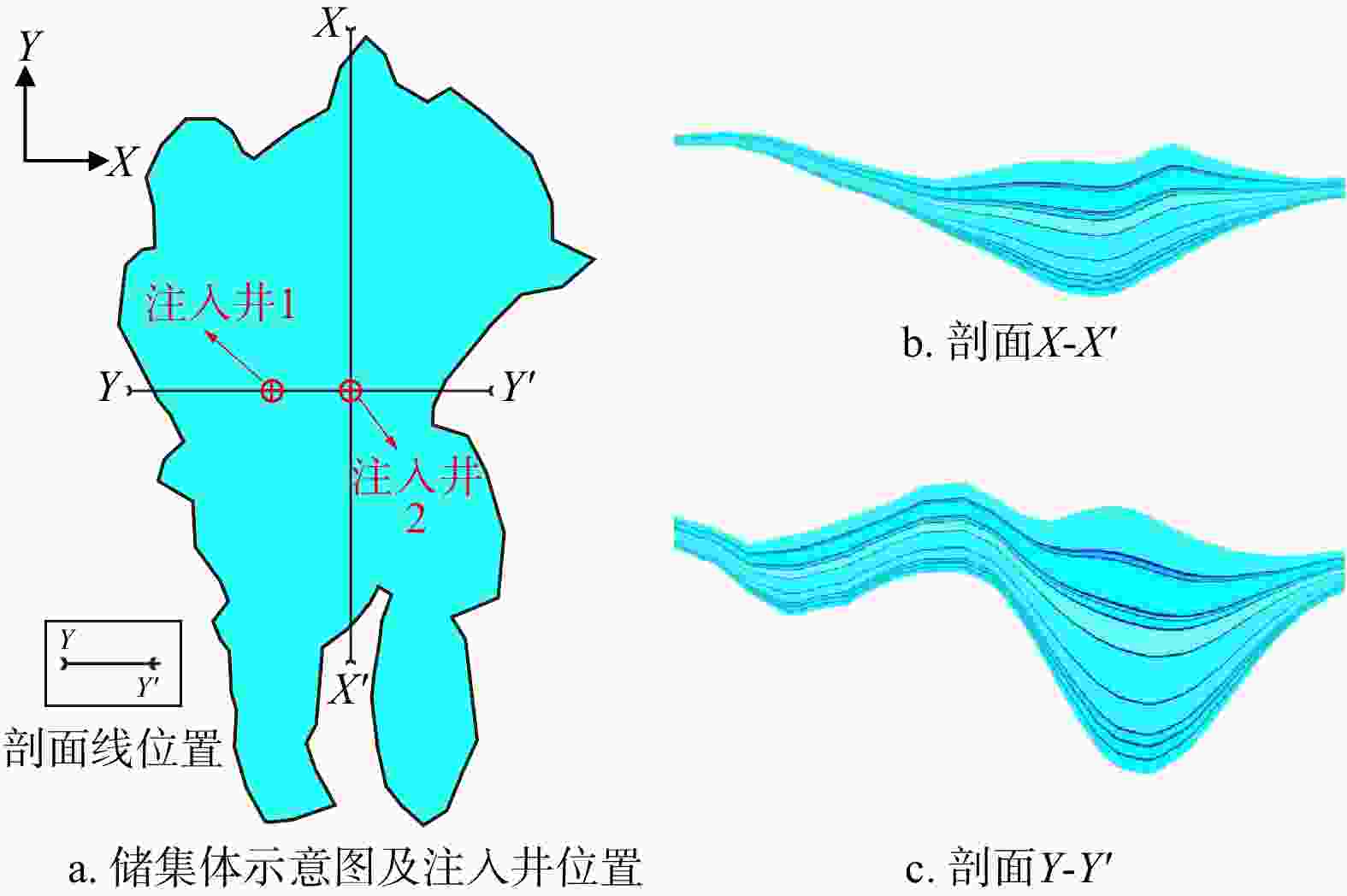
Objective & Methods This study focuses on a reservoir in the South China Sea, taking into account the heterogeneity of the formation and the actual location of the lithological traps. The study establishes a heterogeneous geological model based on seismic reflection characteristics and drilling data, using TOUGHREACT to simulate the effects of different injection locations on CO2 migration and sequestration in the formation.
Results The results indicate that the upward migration of CO2 is hindered by mudstone, while lateral migration is more pronounced. For different injection scenarios, significant variations in reservoir pressure distribution were observed. The reservoir pressure reaches 40.1 MPa when injecting at the top, 39.7 MPa at the bottom, and 40.3 MPa when injecting in a complete well. Therefore, the pressure buildup from long-term implementation of complete well injection and top injection schemes may damage the reservoir cap rock, increasing the risk of CO2 leakage. The bottom and middle injection schemes are safer. When injected continuously for 100 years, CO2 is predominantly in the supercritical phase, accounting for more than 77% of the total sequestration, with the dissolved phase making up less than 23%. At the same wellhead injection pressure, the homogeneous model overestimates the storage volume of the reservoir. The heterogeneous model injects 55.1% and 49.3% more CO2 at the top and middle, respectively, compared to the bottom. Sensitivity analysis results show that porosity and permeability have a more significant impact on the results than capillary pressure.
Conclusion This study aims to investigate the impact of injection well locations on CO2 migration mechanisms and storage capacity when considering the layered heterogeneity of the reservoir, with the aim of providing theoretical guidance for the design of well placement for CO2 storage.
-
表 1 模型中初始水化学离子浓度
Table 1. Initial water chemical ion concentrations in the model
指标 质量浓度/(mg·L−1) 指标 质量浓度/(mg·L−1) 矿化度 29509.89 Mn2+ 0.54 HCO3- 589.00 Sr2+ 21.88 Cl- 17843.32 Zn2+ 0.26 SO42- 24.00 Li+ 0.34 Ca2+ 361.10 Br- 0.17 K+ 78.90 As3+ 1.30 Mg2+ 83.57 I- 0.26 Na+ 10530.00 Fe3+ 0.18 Ba2+ 1.61 溶解氧 0.83 表 2 水文地质学及热力学参数
Table 2. List of hydrogeological and thermodynamic parameters
参数 砂岩 泥岩 水平渗透率/10−3 μm2 2.3~7 0.01 垂向渗透率/10−3 μm2 0.23~0.70 0.001 孔隙度 0.19~0.21 0.15 岩层热传导率/(W·m−1·K−1) 2.51 岩石颗粒特殊焓/(J·kg−1·K−1) 920.0 岩石密度/(kg·m−3) 2600 温度/℃ 75.0 压力/MPa 25~26.7 表 3 模型100 a封存量
Table 3. Model 100-year sequestration
104 t 方案 均质模型 非均质模型 顶部注入 415.28 386.00 中部注入 402.35 371.71 底部注入 387.35 248.89 厚层注入 407.38 398.57 薄处注入 409.09 401.50 -
[1] 赵金洲,郑建超,任岚,等. 海洋CO2地质封存研究进展与发展趋势[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发,2024,43(1):1-13.ZHAO J Z,ZHENG J C,REN L,et al. Research progress and development trend of marine CO2 geological storage[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing,2024,43(1):1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 赵改善. 二氧化碳地质封存地球物理监测:现状、挑战与未来发展[J]. 石油物探,2023,62(2):194-211. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2023.02.002ZHAO G S. Geophysical monitoring for geological carbon sequestration:Present status,challenges,and future development[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum,2023,62(2):194-211. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2023.02.002 [3] 桑树勋,袁亮,刘世奇,等. 碳中和地质技术及其煤炭低碳化应用前瞻[J]. 煤炭学报,2022,47(4):1430-1451.SANG S X,YUAN L,LIU S Q,et al. Geological technology for carbon neutrality and its application prospect for low carbon coal exploitation and utilization[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2022,47(4):1430-1451. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] SUN X,SHANG A R,WU P,et al. A review of CO2 marine geological sequestration[J]. Processes,2023,11(7):2206. doi: 10.3390/pr11072206 [5] KHUDAIDA K J,DAS D B. A numerical analysis of the effects of supercritical CO2 injection on CO2 storage capacities of geological formations[J]. Clean Technologies,2020,2(3):333-364. doi: 10.3390/cleantechnol2030021 [6] MARSHALL J P. A social exploration of the west Australian gorgon gas,carbon capture and storage project[J]. Clean Technologies,2022,4(1):67-90. doi: 10.3390/cleantechnol4010006 [7] ROCK L,O’BRIEN S,TESSAROLO S,et al. The quest CCS project:1st year review post start of injection[J]. Energy Procedia,2017,114:5320-5328. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.1654 [8] METCALFE R,THATCHER K,TOWLER G,et al. Sub-surface risk assessment for the endurance CO2 store of the white rose project,UK[J]. Energy Procedia,2017,114:4313-4320. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.1578 [9] 宋爽,韩建波,陈虹,等. “双碳” 目标下二氧化碳海底地质封存在中国的发展潜力及建议[J]. 科技导报,2023,41(22):30-37.SONG S,HAN J B,CHEN H,et al. Development potential and countermeasures of sub-seabed CO2 sequestration under the target of carbon peaking and carbon neutrality in China[J]. Science & Technology Review,2023,41(22):30-37. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] JHA N K,ALI M,SARMADIVALEH M,et al. Low salinity surfactant nanofluids for enhanced CO2 storage application at high pressure and temperature[M]. Utrecht,Netherlands:EAGE Publications BV,2018:1-4. [11] HE D,JIANG P X,XU R N. The influence of heterogeneous structure on salt precipitation during CO2 geological storage[J]. Advances in Geo-Energy Research,2023,7(3):189-198. doi: 10.46690/ager.2023.03.05 [12] 谢健,张可霓,胡立堂. 神华鄂尔多斯CO2地质封存场地多井并注模拟初探[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2015,51(6):636-642.XIE J,ZHANG K N,HU L T. Numerical investigation of geological CO2 storage with multiple injection wells for the Shenhua Ordos CCS Project[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science),2015,51(6):636-642. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] FLETT M,GURTON R,WEIR G. Heterogeneous saline formations for carbon dioxide disposal:Impact of varying heterogeneity on containment and trapping[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2007,57(1/2):106-118. [14] 赵锐锐,成建梅. 使用水力屏障控制单一倾斜储层中CO2羽的迁移[J]. 地球科学,2016,41(4):675-682.ZHAO R R,CHENG J M. Using hydraulic barrier control CO2 plume migration in sloping reservoir[J]. Earth Science,2016,41(4):675-682. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 高志豪,赵锐锐,成建梅. 砂岩含水层CO2封存中考虑盐沉淀反馈作用的数值模拟:以鄂尔多斯盆地为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(1):269-277.GAO Z H,ZHAO R R,CHENG J M. Numerical simulation of CO2 sequestration in sandstone aquifers with feedback effect of salt precipitation:A case study of Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(1):269-277. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 任俊帆,薛亮,聂捷,等. 基于随机森林算法的二氧化碳驱油与封存主控因素研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):147-156.REN J F,XUE L,N J,et al. Research on the main control factors of carbon dioxide flooding and storage based on random forest algorithm[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):147-156. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] QIN J Z,ZHONG Q H,TANG Y,et al. CO2 storage potential assessment of offshore saline aquifers in China[J]. Fuel,2023,341:127681. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.127681 [18] 马永法,周学军,董俊领,等. 黑龙江林甸地区深部咸水层CO2地质储存条件与潜力评估[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(6):179-189.MA Y F,ZHOU X J,DONG J L,et al. Geological storage conditions and potential assessment of CO2 in deep saline aquifers in Lindian of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(6):179-189. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 靖晶,苑艺琳,杨艳林,等. 地层倾角对CO2地质封存的影响研究:以鄂尔多斯CCS工程为例[J]. 工程勘察,2014,42(6):39-44.JING J,YUAN Y L,YANG Y L,et al. Influence of strata dip on CO2 geological storage: A case study of Ordos CCS Project[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2014,42(6):39-44. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 郑长远,雷宏武,崔银祥,等. 西宁盆地南部天然CO2泄漏和浅部含水层响应[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(6):223-232.ZHENG C Y,LEI H W,CUI Y X,et al. Natural CO2 leakage and responses of shallow aquifers in the southern Xining Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(6):223-232. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 李义连,房琦,柯怡兵,等. 高盐度卤水对CO2地质封存的影响:以江汉盆地潜江凹陷为例[J]. 地球科学,2012,37(2):283-288.LI Y L,FANG Q,KE Y B,et al. Effect of high salinity on CO2 geological storage:A case study of Qianjiang Depression in Jianghan Basin[J]. Earth Science,2012,37(2):283-288. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 卜繁婷,许天福,王福刚,等. 储层温度对CO2矿物封存的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2014,41(1):101-105.BU F T,XU T F,WANG F G,et al. The influence on CO2 mineral sequestration of reservoir temperature[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2014,41(1):101-105. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 盛丹娜,王惠民,盛金昌,等. CO2地质封存中随机裂隙网络走向对盖层密封性影响[J]. 地球科学,2025,50(1):349-360.SHENG D N,WANG H M,SHENG J C,et al. Effect of random fracture network orientations on sealing performance of caprock in CO2 geological sequestration[J]. Earth Science,2025,50(1):349-360. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] URYCH T,SMOLIŃSKI A. Numerical modeling of CO2 migration in saline aquifers of selected areas in the Upper Silesian Coal Basin in Poland[J]. Energies,2019,12(16):3093. [25] LI Y M,PANG Z H. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of deep saline aquifers in sedimentary basins in China and implications for CO2 geological storage with emphasis on total dissolved solids (TDS) and water type[J]. Greenhouse Gases (Science and Technology),2017,7(1):53-64. [26] 商松华. 海底沉积物甲烷冷泉泄漏的碳−硫循环过程与数值模拟研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2023.SHANG S H. Study on carbon-sulfur cycle process and numerical simulation for the leakage of methane cold seep in marine sediments[D]. Changchun:Jilin University,2023. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 谢建华. 南海新生代构造演化及其成因数值模拟[D]. 广州:中国科学院研究生院(广州地球化学研究所),2006.XIE J H. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the South China Sea and a numerical simulation study on its formation[D]. Guangzhou:Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry,Chinese Academy of Sciences,2006. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 刘晓涵. 中国南海常规油气资源潜力综合评价:以生烃潜力法为例[D]. 北京:中国石油大学(北京),2021.LIU X H. Comprehensive evaluation of conventional oil and gas resources potential in the South China Sea:Taking the method of hydro carbon generation potential as an example[D]. Beijing:China University of Petroleum (Beijing),2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 李海燕,彭仕宓,许明阳,等. CO2在深部咸水层中的埋存机制研究进展[J]. 科技导报,2013,31(2):72-79.LI H Y,PENG S M,XU M Y,et al. CO2 storage mechanism in deep saline aquifers[J]. Science & Technology Review,2013,31(2):72-79. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 廖晋,金澳涵,李才,等. 莺−琼盆地咸水层二氧化碳地质封存适宜性及潜力评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2025,44(3):344-352.LIAO J,JIN A H,LI C,et al. Suitability and potential evaluation of geological storage of carbon dioxide in saline aquifers of Ying-Qiong Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2025,44(3):344-352. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] GUO B Y,WEI N,SONG J Z,et al. Prediction of the maximum allowable bottom hole pressure in CO2 injection wells[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2017,156:575-581. [32] 李传亮. 油藏工程原理[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2011.LI C L. Principle of reservoir engineering[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,2011. (in Chinese) [33] MUALEM Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media[J]. Water Resources Research,1976,12(3):513-522. [34] VAN GENUCHTEN M T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,1980,44(5):892-898. [35] 王涛,于海洋,朱旭晨,等. 水气交替CO2咸水层地质封存数值模拟研究[J]. 中国海上油气,2023,35(4):198-204.WANG T,YU H Y,ZHU X C,et al. Numerical simulation study on geological storage of CO2 in saline aquifers assisted by water alternating gas[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,2023,35(4):198-204. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 刘阳,王媛. 深部咸水层CO2地质封存研究现状[J]. 水利水电科技进展,2011,31(6):74-79.LIU Y,WANG Y. State-of-the-art researches on CO2 geologic storage in deep saline aquifer[J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources,2011,31(6):74-79. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 郑展鹏. 多孔介质内CO2/盐水岩心驱替数值模拟研究[D]. 辽宁大连:大连理工大学,2018.ZHENG Z P. Numerical simulation study of CO2 and brine core flooding in porous media[D]. Dalian Liaoning:Dalian University of Technology,2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 靖晶. CO2储存过程多因素影响的数值模拟研究:以鄂尔多斯盆地石千峰组为例[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2021.JING J. Numerical simulation of multiple factors influence on CO2 storage process[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences (Wuhan),2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 孟庆亮. 超临界二氧化碳在盐水层多孔介质条件下迁移的数值模拟研究[D]. 合肥:中国科学技术大学,2014.MENG Q L. A numerical study of supercritical carbon dioxide migration in porous media under conditions of saline aquifers[D]. Hefei:University of Science and Technology of China,2014. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] KUMAR S,FOROOZESH J,EDLMANN K,et al. A comprehensive review of value-added CO2 sequestration in subsurface saline aquifers[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering,2020,81:103437. -




 下载:
下载: