Empirical prediction model for the runout distance of rainfall-induced group-occurring shallow soil landslides
-
摘要:
降雨诱发的群发浅层土质滑坡具有突发性强和危险性高等特点,构建运动距离预测模型对滑坡风险防控具有重要意义。以福建省武平县“5·27”群发滑坡事件为研究对象,基于灾前灾后遥感影像、数字高程模型、无人机三维模型和野外调查,获取了131个滑坡特征数据。根据剪出口位置和地形特征,将滑坡分为坡脚剪出型、坡中剪出型和切坡剪出型,通过相关性分析确定了影响群发浅层土质滑坡运动距离的主要因素,采用逐步非线性回归分析方法建立了3类滑坡运动距离的最优预测模型。研究表明,滑源区高差是降雨型群发浅层土质滑坡运动距离的主要影响因素;建立的最优预测模型残差平方和较小,调整
R 2值大于0.9,显示出较高的可信度和精度。模型验证表明,预测值与实际值的相对误差较小,坡脚剪出型、坡中剪出型和切坡剪出型的最大相对误差分别为15.6%、13.5%和12.4%。建立的基于统计分析的降雨型群发浅层土质滑坡运动距离预测模型为类似地区的滑坡灾害防治提供了科学依据。尽管该模型在不同类型的滑坡中表现出较高的预测精度,但研究数据主要来源于特定区域,在其他地区的适用性仍需进一步验证;未来研究可以考虑增加样本量和影响因子,进一步完善模型。Abstract:Objective Rainfall-induced group-occurring shallow soil landslides have the characteristics of strong and sudden occurrence and high risk. It is of great significance to build a runout distance prediction model for landslide risk prevention and control.
Methods This study focuses on the "5·27" group-occurring landslide event in Wuping County, Fujian Province, and obtains 131 landslide characteristic data based on pre-disaster and post-disaster remote sensing images, digital elevation model, drone-derived 3D model and field investigation. According to the location of the slip-out point and topographic characteristics, the landslides are divided into the foot slip-out type, the middle slope slip-out type and the cut slope slip-out type. The main factors affecting the runout distance of group-occurring shallow soil landslides were determined by correlation analysis, and the optimal prediction model for the runout distance of three types of landslides was established using stepwise nonlinear regression analysis.
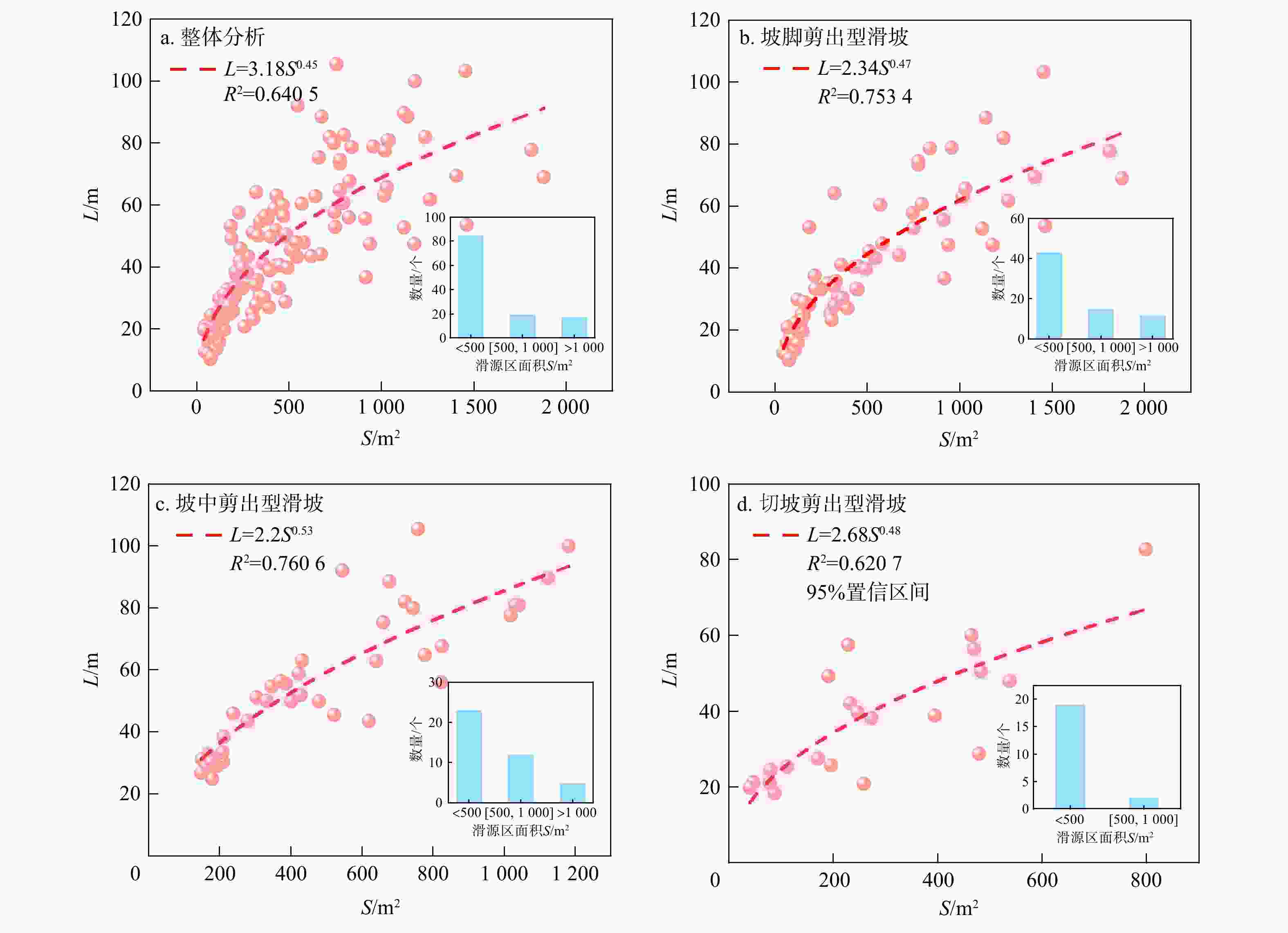
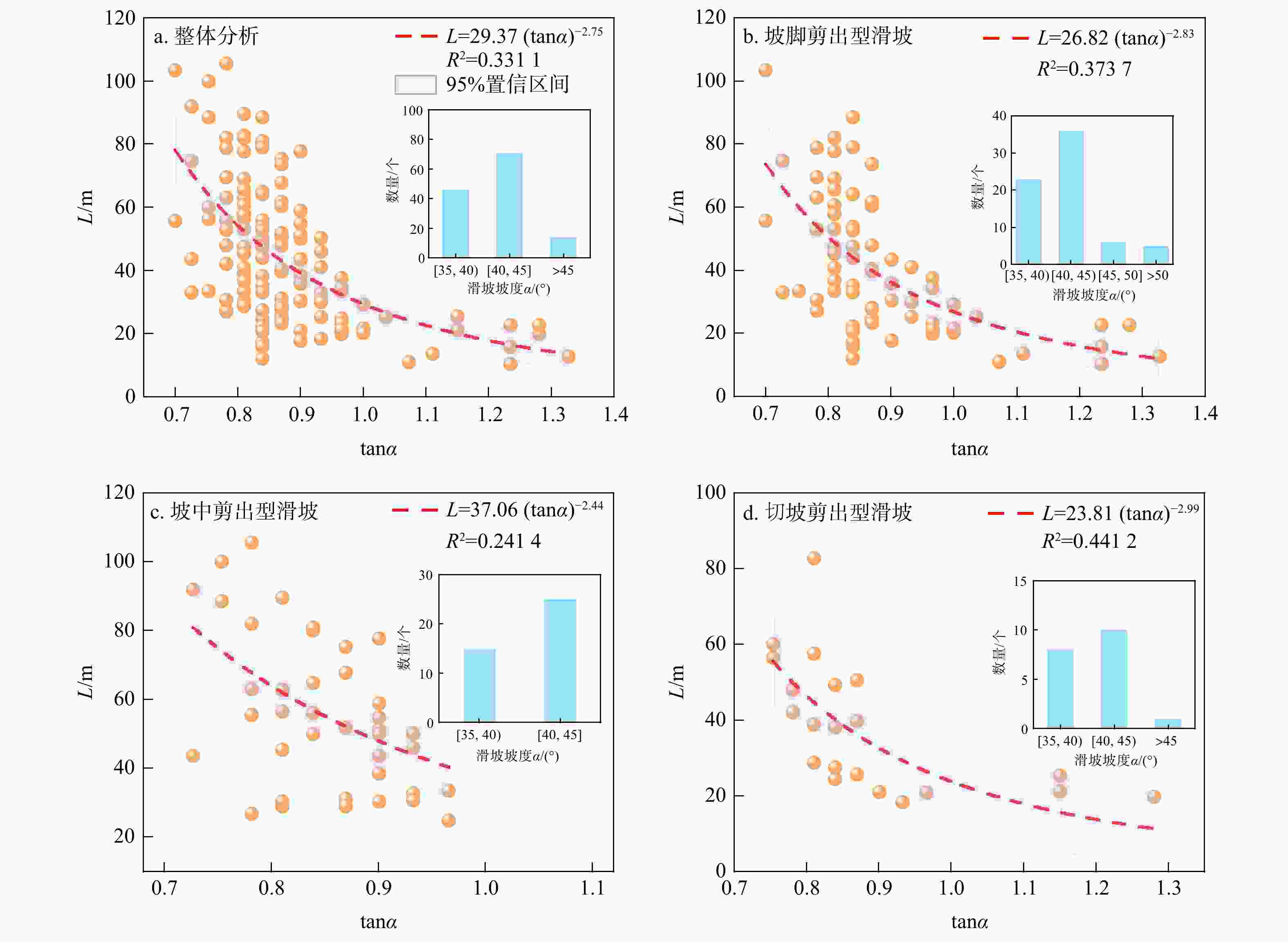
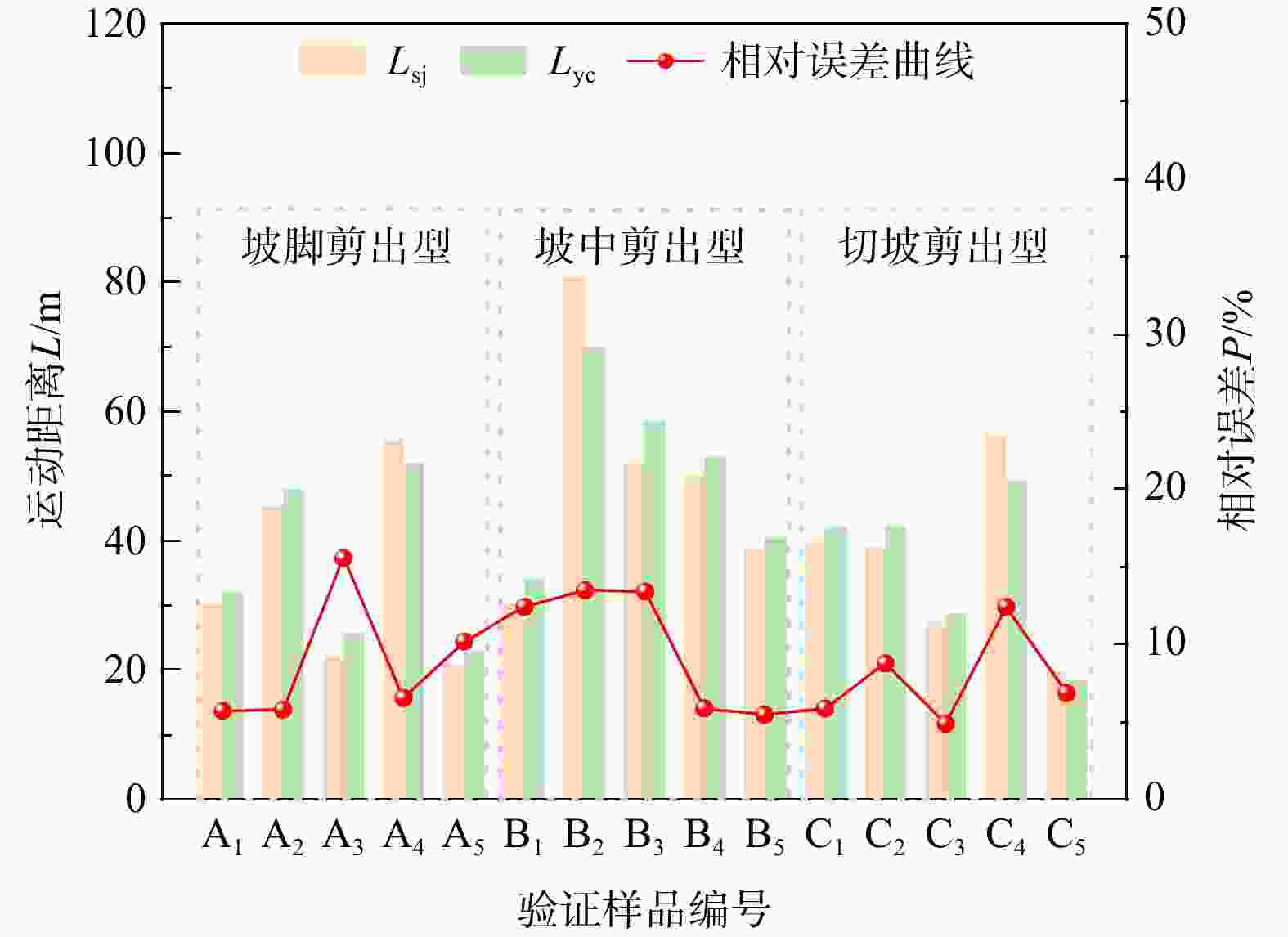
Results Correlation analysis shows that the height of the sliding source area is the main influencing factor of the runout distance of rainfall-induced group-occurring shallow soil landslides. The established optimal predictive models exhibited a low residual sum of squares (
RSS ) and an adjustedR 2 value greater than 0.9, indicating high reliability and precision. Model validation showed that the relative errors between the predicted and actual values were small, with maximum relative errors of 15.6%, 13.5%, and 12.4% for foot slip-out, middle slope slip-out, and cut slope slip-out types, respectively.Conclusion This study established a predictive model for the runout distance of rainfall-induced group-occurring shallow soil landslides based on statistical analysis, providing a scientific basis for landslide disaster prevention in similar regions. While the models exhibit high accuracy, their applicability might be limited by the localized data source. Future research should expand sample diversity and incorporate additional influencing factors to enhance model generalizability.
-
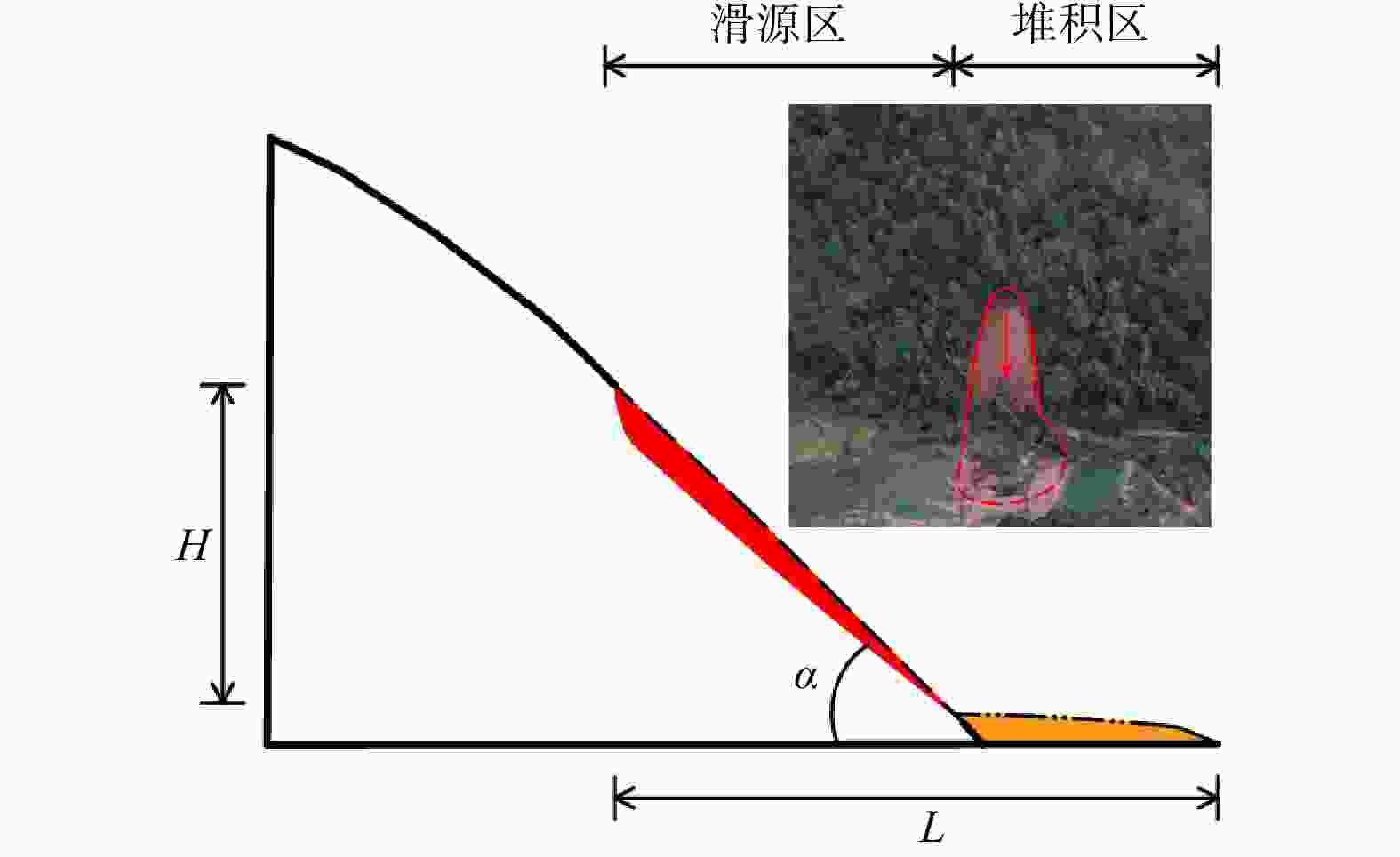
表 1 用于坡脚剪出型预测模型构建的滑坡训练数据
Table 1. Landslide training data for constructing the prediction model of the foot slip-out type
序号 L/m H/m α/(°) λ S/m2 序号 L/m H/m α/(°) λ S/m2 1 37.5 12.6 44 1.2 215 34 20.3 10.1 45 1.5 118 2 64.1 20.4 40 2.9 321 35 65.7 27.7 39 2.0 1028 3 24.6 8.0 41 0.5 154 36 19.8 8.4 44 1.0 147 4 69.5 26.6 38 1.1 1404 37 25.3 7.8 43 1.0 145 5 43.4 19.5 42 1.2 541 38 30.0 11.8 43 2.0 121 6 60.7 23.6 39 1.5 794 39 77.8 34.0 39 1.7 1810 7 78.7 26.2 38 2.4 837 40 37.5 12.6 44 1.2 360 8 33.1 13.5 36 1.0 448 41 53.2 22.0 39 1.3 1185 9 82.0 32.2 39 1.7 1236 42 52.7 21.9 40 0.9 1121 10 78.9 26.1 40 1.7 957 43 47.5 22.5 40 1.2 938 11 88.5 36.5 40 2.2 1140 44 40.4 19.2 41 2.0 430 12 60.4 25.9 41 2.5 567 45 57.8 24.9 39 1.7 745 13 73.5 29.1 41 1.9 774 46 40.7 19.8 39 2.1 452 14 69.0 27.5 39 1.0 1879 47 61.8 30.6 41 1.6 1262 15 53.7 22.1 40 0.9 1461 48 23.3 11.9 44 0.9 306 16 47.5 22.6 39 1.2 1176 49 39.7 14.7 41 0.9 492 17 47.9 22.4 41 2.4 580 50 12.1 5.1 40 0.9 58 18 22.7 11.1 51 1.3 135 51 15.8 8.0 51 1.0 124 19 16.0 6.5 40 1.4 64 52 22.6 9.9 52 0.9 115 20 27.1 11.3 38 0.7 390 53 74.6 19.9 36 1.2 735 21 13.6 7.8 48 1.0 108 54 33.1 13.5 40 1.5 247 22 36.7 18.0 39 1.1 915 55 10.3 5.2 51 0.4 74 23 28.1 10.5 41 1.2 186 56 33.5 9.5 37 1.0 219 24 30.7 12.0 38 1.1 340 57 35.8 13.8 42 1.7 330 25 44.1 21.0 40 1.5 673 58 103.3 32.1 35 2.2 1452 26 35.2 11.7 40 1.2 285 59 23.4 7.5 41 0.8 146 27 17.7 8.6 42 1.8 81 60 21.2 9.2 44 1.7 76 28 63.1 26.8 38 2.2 1014 61 29.1 12.7 45 1.0 158 29 25.2 12.4 46 0.9 300 62 34.3 17.8 44 1.7 319 30 33.4 13.3 39 1.1 441 63 27.9 12.6 41 1.1 323 31 52.9 24.0 38 1.7 750 64 10.9 5.5 47 0.6 80 32 12.7 7.0 53 1.7 44 65 21.6 7.0 45 0.9 104 33 17.3 7.2 40 1.2 95 λ. 滑坡长宽比;S. 滑坡面积;下同 表 2 用于坡中剪出型预测模型构建的滑坡训练数据
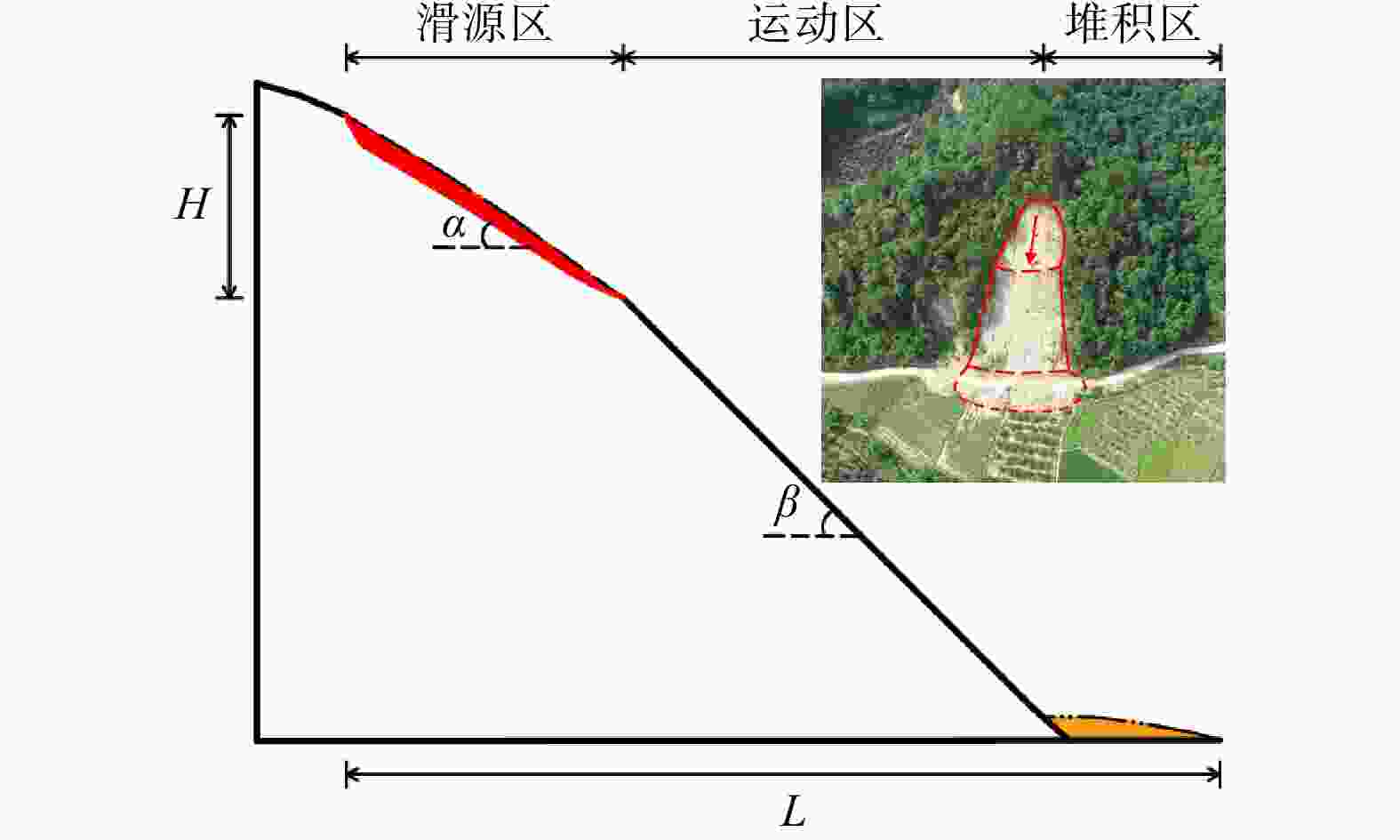
Table 2. Landslide training data for constructing the prediction model of the middle slope slip-out type
序号 L/m H/m α/(°) λ S/m2 β/(°) 序号 L/m H/m α/(°) λ S/m2 β/(°) 1 56.5 15.7 39 1.5 371 28 19 63.1 17.1 38 1.1 432 42 2 51.1 14.3 42 1.5 302 31 20 30.7 8.1 43 0.7 159 43 3 46.0 15.7 43 1.6 237 31 21 32.7 10.1 43 1.2 166 43 4 105.6 29.8 38 2.9 757 31 22 33.5 12.7 44 1.8 207 43 5 100.0 24.2 37 1.3 1181 32 23 54.8 16.2 42 2.0 345 43 6 56.0 19.2 40 1.1 823 33 24 62.8 19.6 39 1.6 641 44 7 75.3 19.1 41 1.3 660 33 25 80.9 22.1 40 1.0 1042 45 8 80.0 20.2 40 1.2 743 34 26 29.0 10.9 41 1.2 192 45 9 89.6 25.8 39 1.5 1123 34 27 64.9 22.8 40 1.6 776 45 10 88.5 21.5 37 1.6 677 34 28 26.9 8.5 38 1.1 148 46 11 45.5 12.9 39 0.8 521 36 29 82.0 22.9 38 1.8 720 46 12 50.2 12.9 43 1.4 331 36 30 43.6 14.3 36 1.0 619 47 13 92.0 17.6 36 1.6 545 36 31 28.9 9.0 39 1.1 163 48 14 43.6 15.5 42 2.6 278 39 32 50.0 15.3 40 1.3 480 48 15 58.9 15.7 42 1.3 422 40 33 24.8 9.9 44 1.1 178 50 16 77.6 27.2 42 1.9 1018 40 34 67.8 23.7 41 1.5 825 51 17 31.1 10.4 41 1.4 150 41 35 30.3 11.0 42 1.3 209 58 18 55.6 14.0 40 1.4 385 40 表 3 用于切坡剪出型预测模型构建的滑坡训练数据
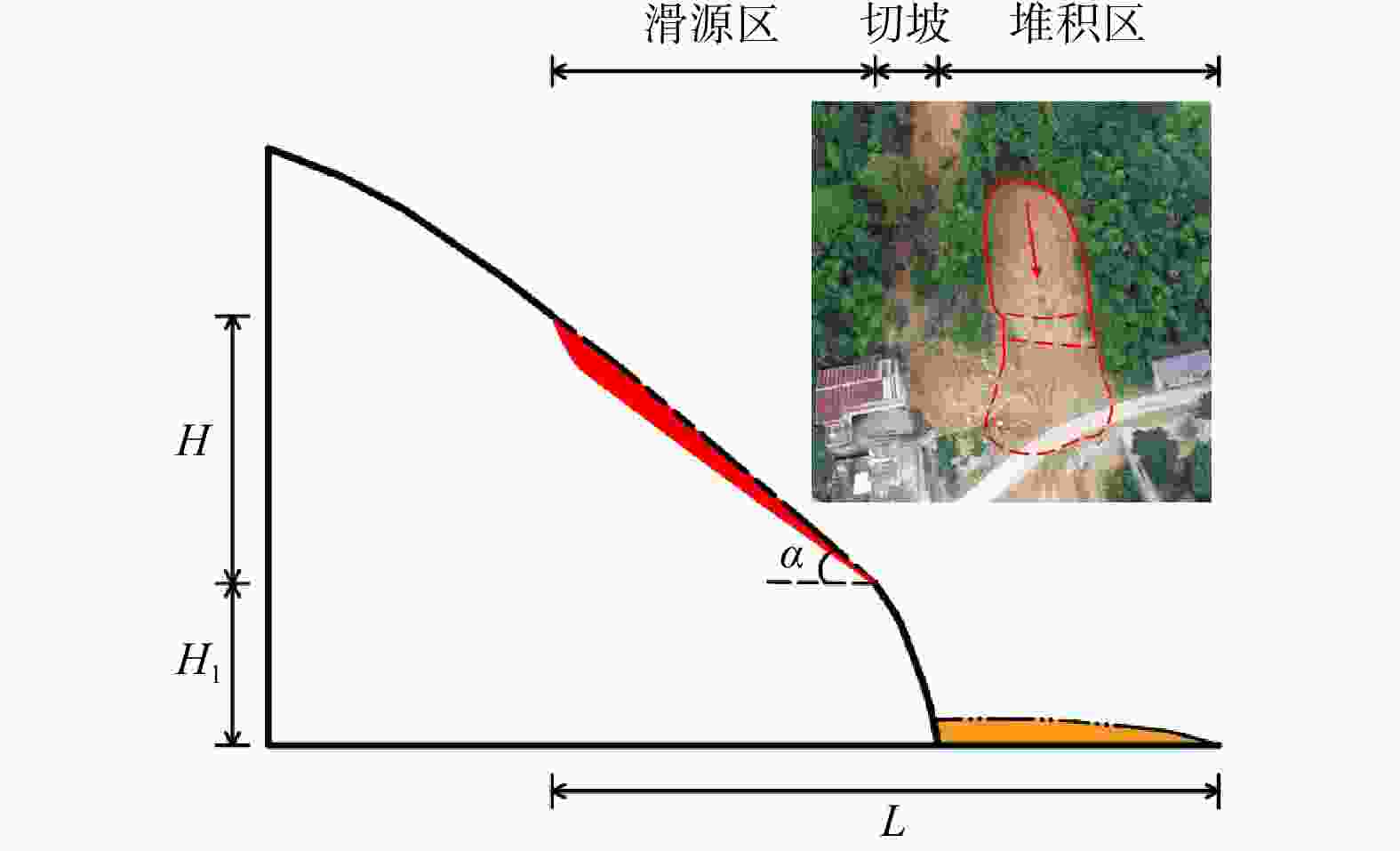
Table 3. Landslide training data for constructing the prediction model of the cut slope slip-out type
序号 L/m H/m α/(°) λ S/m2 H1/m 序号 L/m H/m α/(°) λ S/m2 H1/m 1 50.5 14.6 41 1.1 483 3.0 9 28.7 11.5 39 0.8 479 5.2 2 21.2 7.3 49 1.7 47 3.0 10 21.0 5.8 42 0.7 78 6.1 3 25.8 9.5 41 0.8 196 3.6 11 24.5 9.3 40 0.9 80 6.8 4 48.0 18.3 38 1.4 538 3.6 12 60.1 18.8 37 1.3 464 8.0 5 25.4 9.7 49 1.5 111 4.0 13 38.2 16.2 40 1.9 272 9.4 6 20.8 6.5 44 1.0 258 4.5 14 42.0 11.3 38 1.3 232 9.6 7 49.3 15.8 40 1.7 190 4.5 15 82.7 24.8 39 2.0 798 9.8 8 18.3 7.9 43 1.3 88 4.6 16 57.6 14.0 39 1.7 228 18.2 表 4 坡脚剪出型滑坡运动距离预测回归模型
Table 4. Regression model for predicting the foot slip-out type landslides runout distance
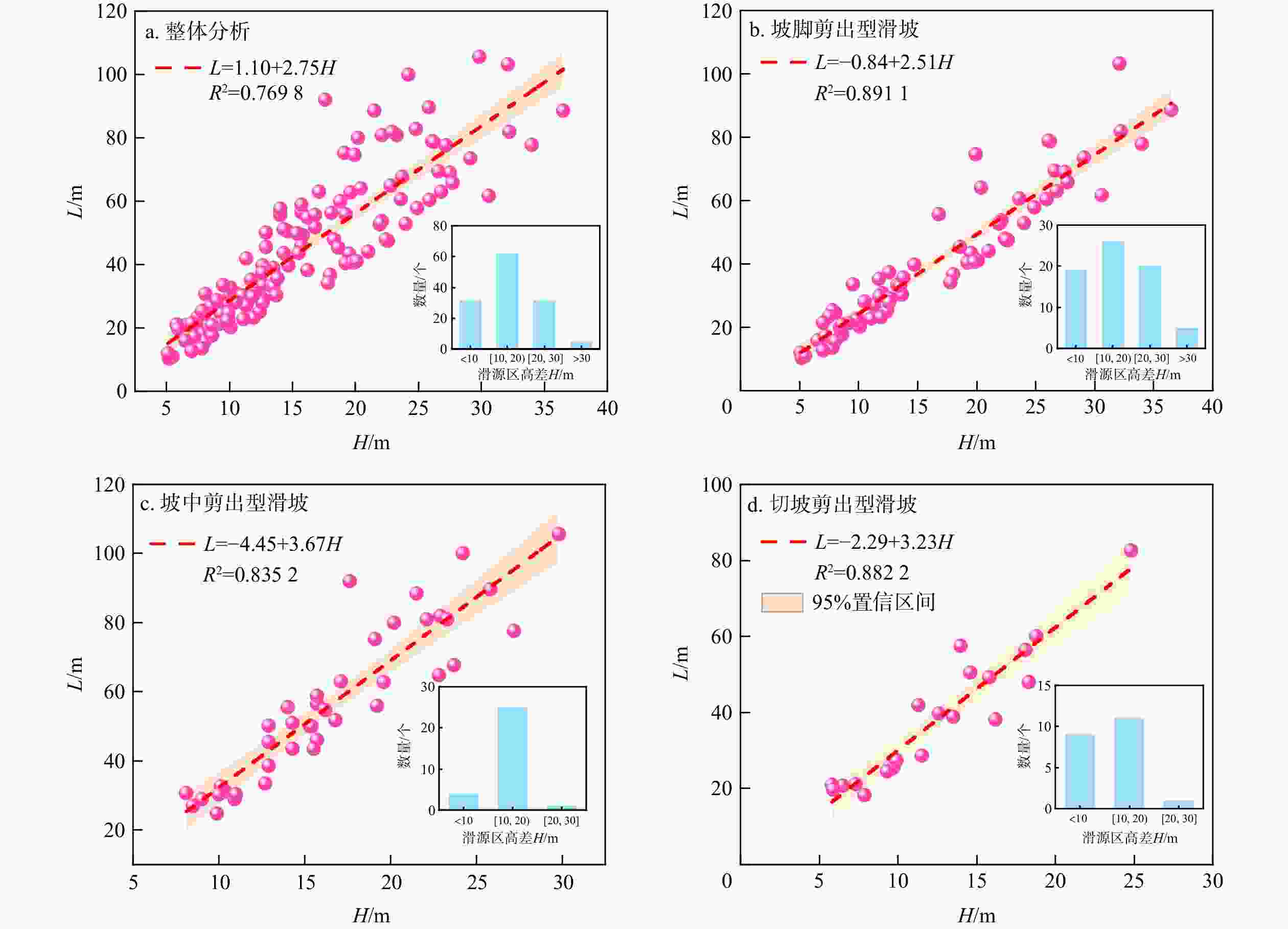
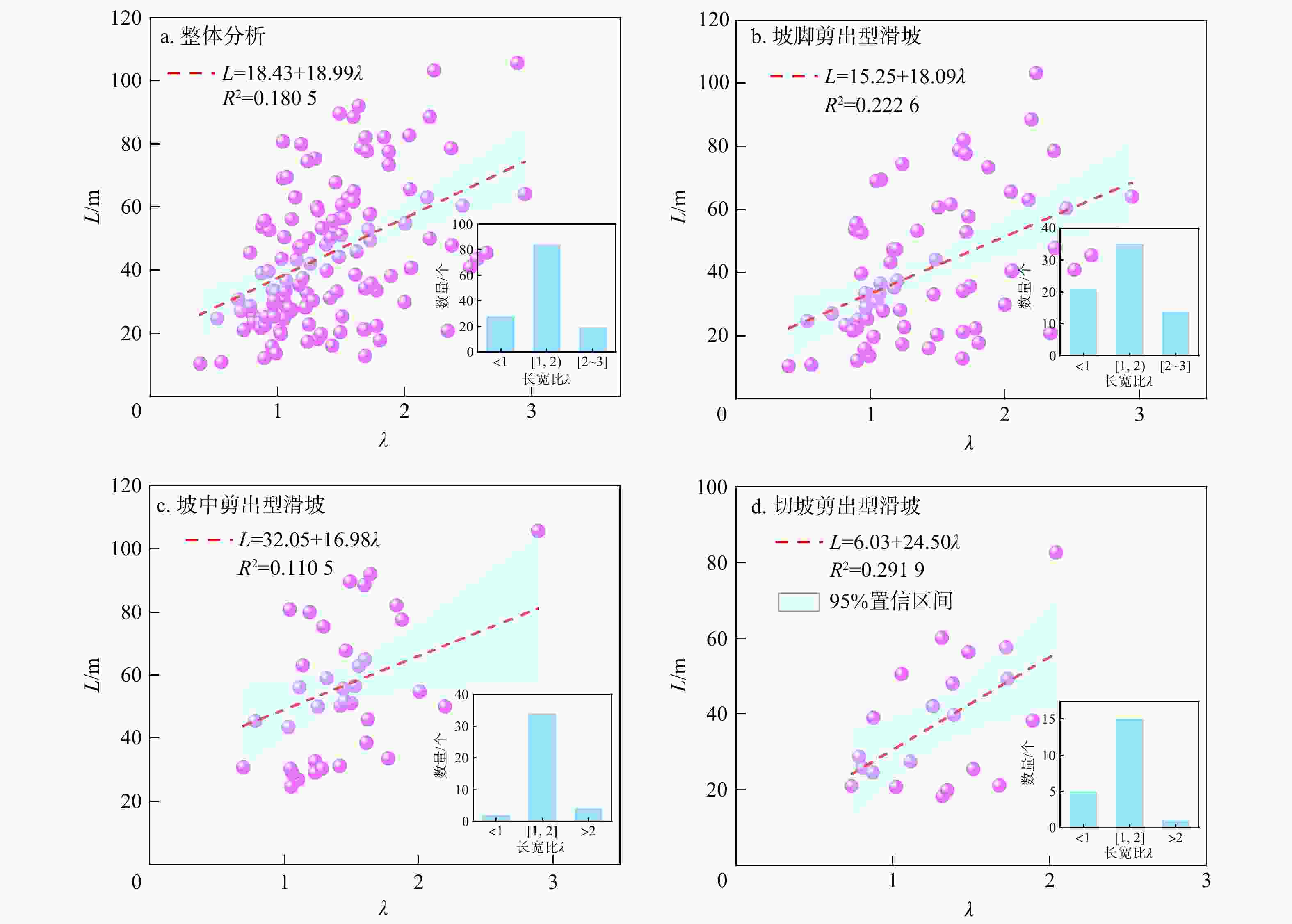
序号 类型 预测模型 RSS 调整R2 F值 1 L(H) L=2.23H1.03 3295 0.8928 1336 2 L(H, S) L=2.15H0.98S0.03 3276 0.8917 881 3 L(H, α) L=2.67H0.91(tanα)−1.19 2289 0.9243 1270 4 L(H, α, λ) L=2.86H0.87(tanα)−1.21λ0.07 2240 0.9247 958 表 5 坡中剪出型滑坡运动距离预测回归模型
Table 5. Regression model for predicting the middle slope slip-out type landslides runout distance
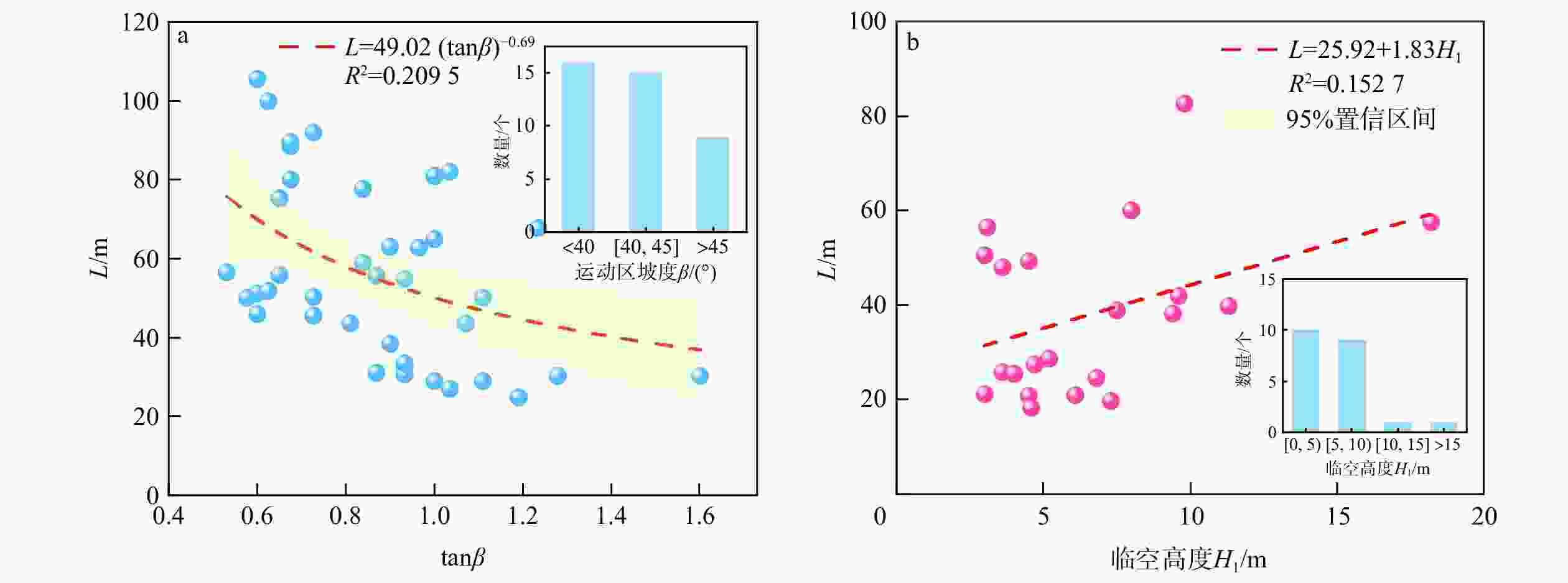
序号 类型 预测模型 RSS 调整R2 F值 1 L(H) L=3.063H1.04 3159 0.8162 679 2 L(H, S) L=2.46H0.81S0.14 2993 0.8204 463 3 L(H, α) L=3.09H0.95(tanα)−1.42 1958 0.8825 714 4 L(H, S, α) L=2.93H0.91S0.03(tanα)−1.39 1952 0.8791 520 5 L(H, α, β) L=3.55H0.89(tanα)−1.29(tanβ)−0.24 1571 0.9027 648 6 L(H, α, β, λ) L=3.29H0.93(tanα)−1.24(tanβ)−0.24λ−0.07 1533 0.9019 514 表 6 切坡剪出型滑坡运动距离预测回归模型
Table 6. Regression model for predicting the cut slope slip-out type landslides runout distance
序号 类型 预测模型 RSS 调整R2 F值 1 L(H) L=2.35H1.1 563 0.8817 349 2 L(H, S) L=2.4H1.05S0.02 662 0.8502 183 3 L(H, α) L=2.5H1.06(tanα)−0.27 553 0.8749 220 4 L(H, λ) L=2.65H1.04λ0.12 543 0.8770 224 5 L(H, H1) L=2.13H1.01H10.18 367 0.9168 333 -
[1] 伍宇明,兰恒星,高星,等. 台风暴雨型滑坡降雨阈值曲线研究:以福建地区为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(2):255-262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2014.02.015WU Y M,LAN H X,GAO X,et al. Rainfall threshold of storm-induced landslides in typhoon areas:A case study of Fujian Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014,22(2):255-262. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2014.02.015 [2] BAI H L,FENG W K,YI X Y,et al. Group-occurring landslides and debris flows caused by the continuous heavy rainfall in June 2019 in Mibei Village,Longchuan County,Guangdong Province,China[J]. Natural Hazards,2021,108(3):3181-3201. doi: 10.1007/s11069-021-04819-1 [3] 庞海松,谢骏锦,张小明,等. 基于RAMMS数值模拟的短时强降雨型泥石流危险性评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(2):215-225.PANG H S,XIE J J,ZHANG X M,et al. Hazard assessment of debris flow induced by short-time heavy rainfall based on RAMMS numerical simulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(2):215-225. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] HEIM A,BERGSTURZ M. Bergsturz und Menschenleben[M]. Zütich:Naturforschenden Gesellschaft,1932:120-133. [5] SCHEIDEGGER A E. On the prediction of the reach and velocity of catastrophic landslides[J]. Rock Mechanics,1973,5(4):231-236. doi: 10.1007/BF01301796 [6] ZHANG Z L,ZENG R Q,MENG X M,et al. Estimating landslide sliding distance based on an improved Heim sled model[J]. Catena,2021,204:105401. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2021.105401 [7] 江晓禹,乔建平. 典型滑坡危险性的接触力学预测模型[J]. 工程力学,2006,23(8):106-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2006.08.020JIANG X Y,QIAO J P. Contact mechanics model for risk predication of typical landslides[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2006,23(8):106-109. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4750.2006.08.020 [8] LIU Z Y,SU L J,ZHANG C L,et al. Investigation of the dynamic process of the Xinmo landslide using the discrete element method[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2020,123:103561. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103561 [9] WANG H J,SUN P,ZHANG S,et al. Evolutionary and dynamic processes of the Zhongzhai landslide reactivated on October 5,2021,in Niangniangba,Gansu Province,China[J]. Landslides,2022,19(12):2983-2996. doi: 10.1007/s10346-022-01966-9 [10] 刘悦,黄强兵. 一种黄土滑坡滑距预测模型[J]. 灾害学,2001,16(3):6-11.LIU Y,HUANG Q B. A forecast pattern of the side distance of loess landslides[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2001,16(3):6-11. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 常晁瑜,薄景山,李孝波,等. 地震黄土滑坡滑距预测的BP神经网络模型[J]. 地震工程学报,2020,42(6):1609-1614. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2020.06.1609CHANG C Y,BO J S,LI X B,et al. A BP neural network model for forecasting sliding distance of seismic loess landslides[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2020,42(6):1609-1614. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2020.06.1609 [12] WAN J C,XUE X H. Application of the group method of data handling (GMDH) approach for travel distance prediction of landslides[J]. Landslides,2023,20(3):645-661. doi: 10.1007/s10346-022-01991-8 [13] 樊晓一,胡晓波,张睿骁,等. 开阔型地形条件对滑坡运动距离的影响研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2018,27(5):188-196.FAN X Y,HU X B,ZHANG R X,et al. Study on the open topography influence on the moving distances of landslides[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2018,27(5):188-196. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 陆盟,张洁,文思成. 地震作用下滑坡水平运动距离概率预测模型[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2020,40(1):92-99.LU M,ZHANG J,WEN S C. Probabilistic model for prediction of seismic landslide travel distance[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2020,40(1):92-99. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 刘红岩,阎锡东,张小趁,等. 滑坡运动距离预测的统计模型及其改进[J]. 灾害学,2022,37(4):6-10.LIU H Y,YAN X D,ZHANG X C,et al. The statistical model for the movement distance forecast of the landslide and its improvement[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2022,37(4):6-10. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 翟淑花,于家烁,齐干,等. 降雨入渗条件下堆积体边坡致灾因子试验分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(3):9-15.ZHAI S H,YU J S,QI G,et al. Triggering factor analysis of deposit slope under rainfall infiltration based on laboratory experiments[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(3):9-15. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 郑德凤,潘美伊,高敏,等. 集中降雨影响下辽南仙人洞国家级自然保护区滑坡灾害多因子风险评价[J]. 地质科技通报,2025,44(2):48-58.ZHENG D F,PAN M Y,GAO M,et al. Multi-factor risk assessment of landslide disasters under concentrated rainfall in Xianrendong national nature reserve in southern Liaoning Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2025,44(2):48-58. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] WALLACE C S,SANTI P M,WALTON G. Scoring system to predict landslide runout in the Pacific Northwest,USA[J]. Landslides,2022,19(6):1449-1461. doi: 10.1007/s10346-021-01839-7 [19] 孟华君,姜元俊,张树轩,等. 汶川地震前后都江堰山区滑坡滑动距离影响因素变化分析[J]. 地质力学学报,2017,23(6):904-913.MENG H J,JIANG Y J,ZHANG S X,et al. Analysis on the change of influence factors on slipping displacement of landslides in Dujiangyan area before and after the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2017,23(6):904-913. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 吴博,赵法锁,贺子光,等. 基于BA-LSSVM模型的黄土滑坡致灾范围预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(5):1-6.WU B,ZHAO F S,HE Z G,et al. Prediction of the disaster area of loess landslide based on least square support vector machine optimized by bat algorithm[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(5):1-6. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 杨明钰,陈红旗,祁小博,等. 基于可靠度理论的地震滑坡运动距离预测模型[J]. 中国地质调查,2023,10(3):102-109.YANG M Y,CHEN H Q,QI X B,et al. Prediction model for the landslide movement distance induced by earthquake based on the reliability theory[J]. Geological Survey of China,2023,10(3):102-109. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 钟兴荣. 基于功能定理的高位滑坡运动距离预测方法研究[J/OL]. 工程地质学报,2024:1-11. (2024-03-11). https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2023-0185.ZHONG X R. The study of movement distance forecast method of the rock avalanche based on work-energy principle[J/OL]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2024:1-11. (2024-03-11). https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2023-0185.(in Chinese with English abstract [23] 段俊杰,李孝波,周兴浩,等. 黄土地震滑坡运动特征研究:以海原特大地震诱发滑坡为例[J]. 地震工程学报,2024,46(5):1151-1159.DUAN J J,LI X B,ZHOU X H,et al. Kinematic characteristics of loess seismic landslides:A case study of landslides triggered by the Haiyuan great earthquake[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2024,46(5):1151-1159. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 董建辉,钱珂江,赵建军,等. 基于深度神经网络的高位滑坡范围预测[J]. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文),2021,19(5):972-981.DONG J H,QIAN K J,ZHAO J J,et al. Prediction of high landslide range based on deep neural network[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2021,19(5):972-981. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 王冉,王学良,袁鸿鹄,等. 基于统计分析和数值模拟方法的滑坡视摩擦系数影响因素及特征研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(3):825-833.WANG R,WANG X L,YUAN H H,et al. Influence factors and characteristics of apparent friction coefficient of landslide based on statistical analysis and numerical simulation[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(3):825-833. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 郑光,许强,彭双麒. 岩质滑坡−碎屑流的运动距离计算公式研究[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(12):4897-4906.ZHENG G,XU Q,PENG S Q. Calculation model of the long-runout distance of rock avalanche[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(12):4897-4906. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] ROMAN QUINTERO D C,ORTIZ CONTRERAS J D,TAPIAS CAMACHO M A,et al. Empirical estimation of landslide runout distance using geometrical approximations in the Colombian north-east Andean region[J]. Sustainability,2024,16(2):793. doi: 10.3390/su16020793 [28] 吴伟乐,贺凯,高杨,等. 强降雨条件下碎屑岩滑坡远程运动模拟分析:以牛儿湾滑坡为例[J]. 地质力学学报,2022,28(6):1115-1126.WU W L,HE K,GAO Y,et al. Long-runout fluidization disaster simulation analysis of clastic landslide under heavy rainfall:A case study of the Niuerwan landslide[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2022,28(6):1115-1126. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 宋德光,吴瑞安,马德芹,等. 四川泸定昔格达组滑坡灾害运动过程模拟分析[J]. 地质通报,2023,42(12):2185-2197. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2023.12.014SONG D G,WU R A,MA D Q,et al. Simulation analysis of landslide disaster movement process in Xigeda Formation,Luding County,Sichuan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2023,42(12):2185-2197. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2023.12.014 [30] 邵葆蓉,孙即超,朱月琴,等. 基于多元回归的黄土滑坡滑动距离预测模型探讨:以甘肃天水地区为例[J]. 地质通报,2020,39(12):1993-2003. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2020.12.013SHAO B R,SUN J C,ZHU Y Q,et al. Research on gliding distance estimation of loess landslide based on multiple regression:A case study of Tianshui region,Gansu Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2020,39(12):1993-2003. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2020.12.013 [31] 康孟羽,朱月琴,陈晨,等. 基于多元非线性回归和BP神经网络的滑坡滑动距离预测模型研究[J]. 地质通报,2022,41(12):2281-2289.KANG M Y,ZHU Y Q,CHEN C,et al. Research on landslide sliding distance prediction model based on multiple nonlinear regression and BP neural network[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2022,41(12):2281-2289. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 王佳佳,陈浩军,肖莉丽,等. 滑坡−碎屑流运动堆积特征与能量耗散规律[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2024,56(11):63-71.WANG J J,CHEN H J,XIAO L L,et al. Motion and accumulation characteristics and energy dissipation laws of landslide-debris flow[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2024,56(11):63-71. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 吴越,刘东升,周忠浩. 考虑滑动过程内部崩解耗散的滑坡体运动模型[J]. 岩土工程学报,2015,37(1):35-46.WU Y,LIU D S,ZHOU Z H. Mobility assessment model for landslide mass considering disintegration energy consumption in slipping process[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2015,37(1):35-46. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 李小琴,富海鹰,张迎宾,等. 地形起伏对滑坡运动的影响规律研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2020,40(6):867-877.LI X Q,FU H Y,ZHANG Y B,et al. Study on the influences of topography on landslide mobility[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2020,40(6):867-877. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 王贵洲,龚文平,邢磊,等. 考虑堆积区宽度影响的滑坡碎屑流运动与堆积过程物理模型试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2023,31(5):1637-1647.WANG G Z,GONG W P,XING L,et al. Model tests of run-out and deposition process of landslide debris considering influence of depositing zone width[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2023,31(5):1637-1647. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] KOMU M P,NEFESLIOGLU H A,GOKCEOGLU C. Modeling shallow landslide runout distance in Eocene flysch facies using empirical-statistical models (western black sea region of Türkiye)[J]. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information,2024,13(3):84. doi: 10.3390/ijgi13030084 [37] 樊晓一,李天话,田述军,等. 未完全受阻地震滑坡运动距离的影响因素及机制分析[J]. 地震地质,2017,39(4):754-767. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.04.010FAN X Y,LI T H,TIAN S J,et al. Controlling factors and mechanisms of incomplete obstruction seismic landslide mobility[J]. Seismology and Geology,2017,39(4):754-767. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.04.010 [38] ZHAN W W,FAN X M,HUANG R Q,et al. Empirical prediction for travel distance of channelized rock avalanches in the Wenchuan earthquake area[J]. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences,2017,17(6):833-844. doi: 10.5194/nhess-17-833-2017 [39] 杨海龙,裴向军,樊晓一. 坡脚型滑坡运动特征分析及运动距离预测[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(6):1379-1388.YANG H L,PEI X J,FAN X Y. Numerical inversion analysis of movement characteristics and distance prediction of slope-toe landslides[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(6):1379-1388. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] ROBERT I,KABACOFF. R in Action,Third Edition:Data analysis and graphics with R and Tidyverse[M]. Manning,2022. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2024.107474 -




 下载:
下载: