Identification of active landslides and analysis of deformation influencing factors in the Baihetan Reservoir area
-
摘要:
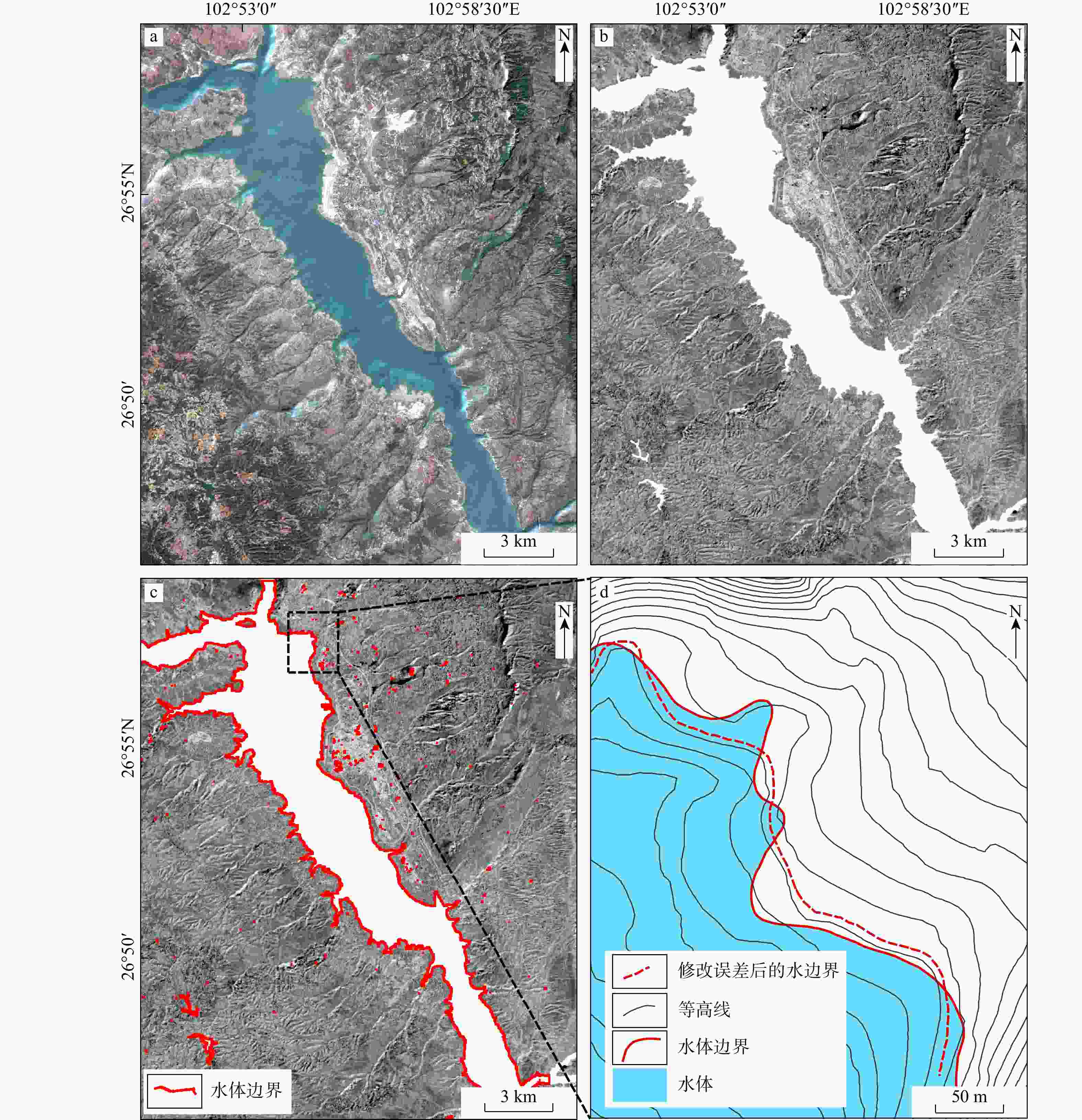
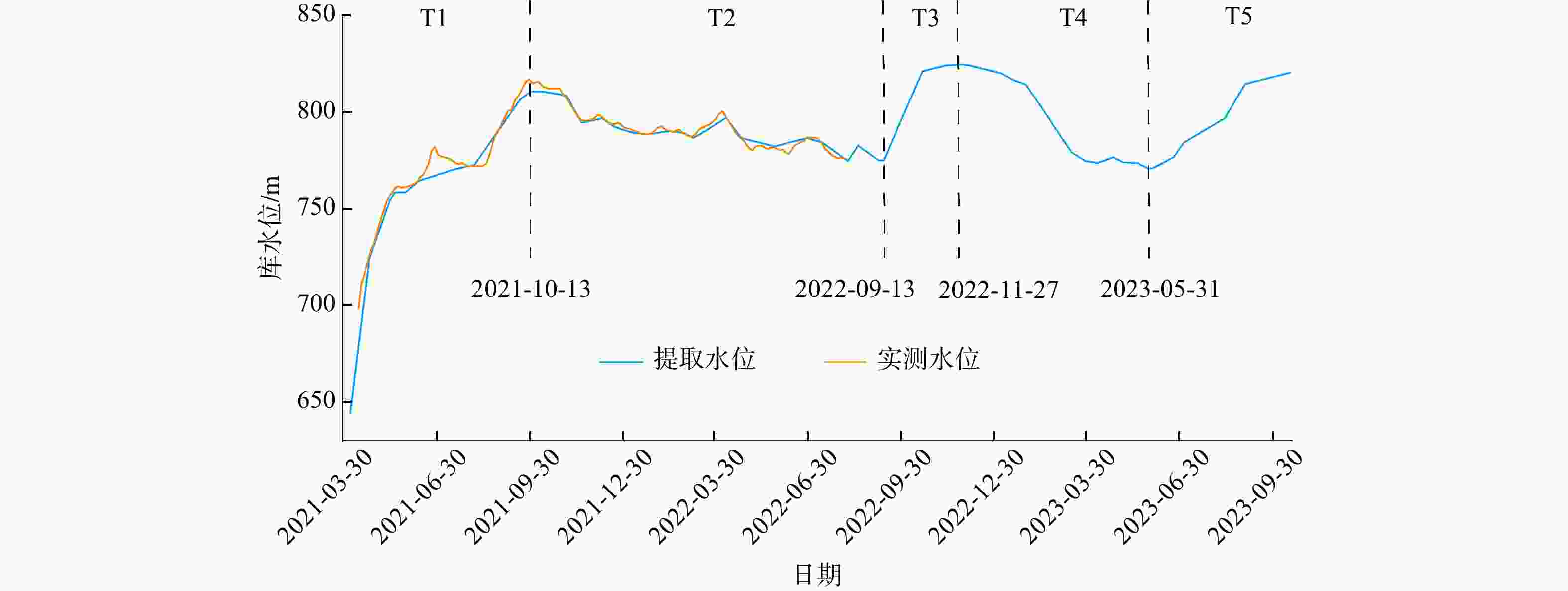
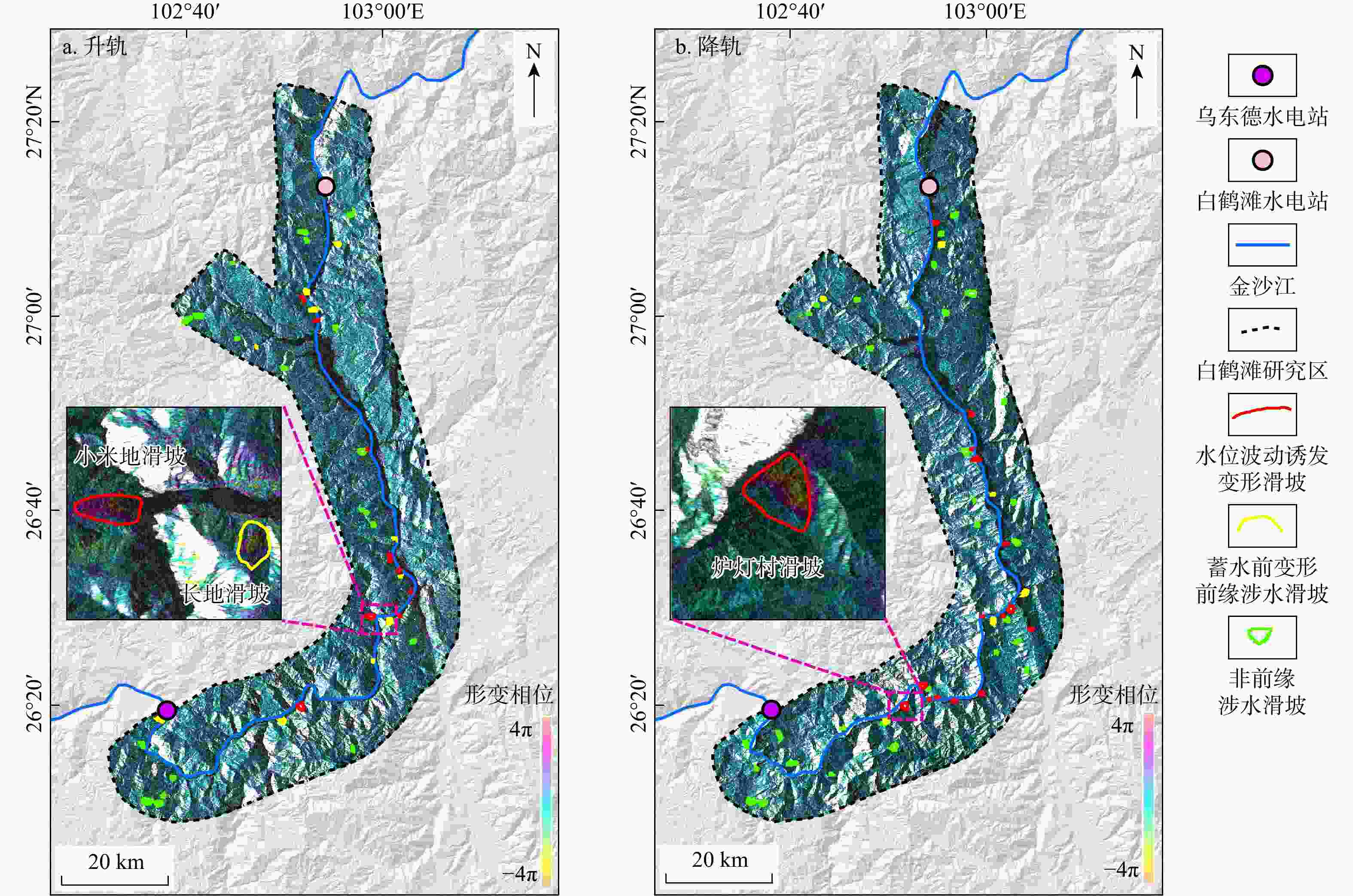
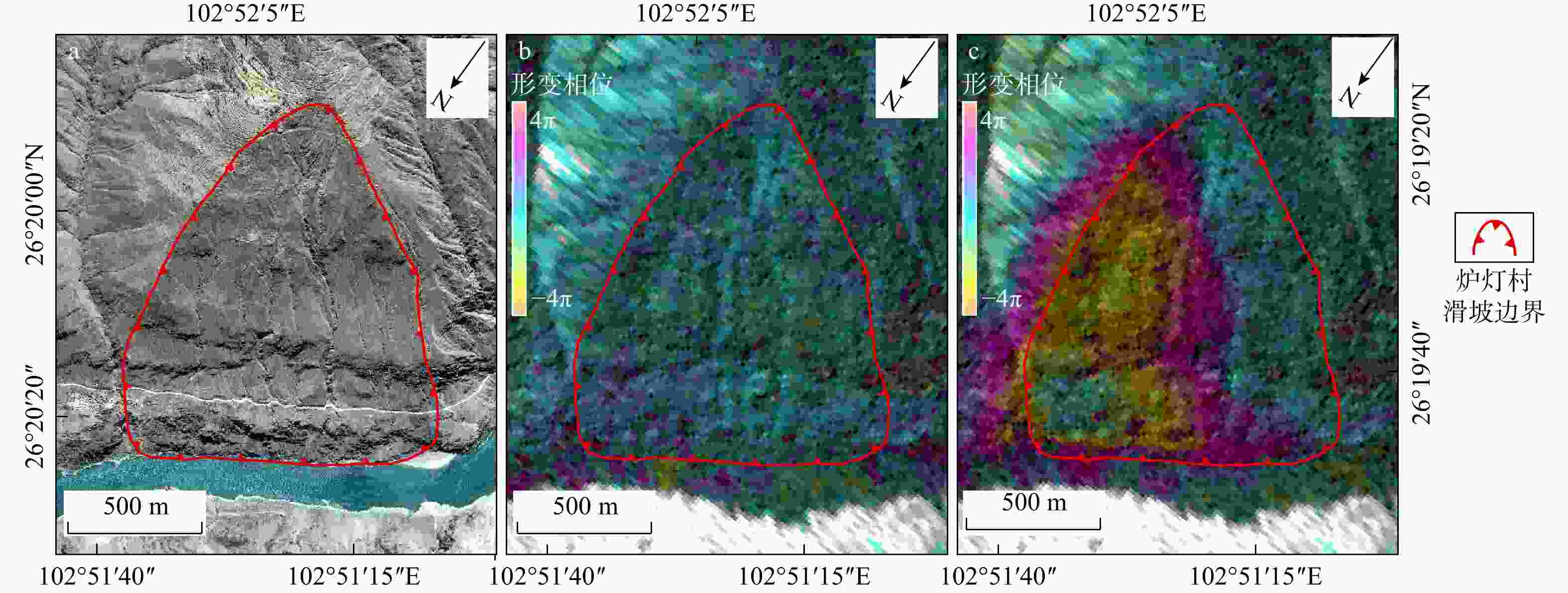
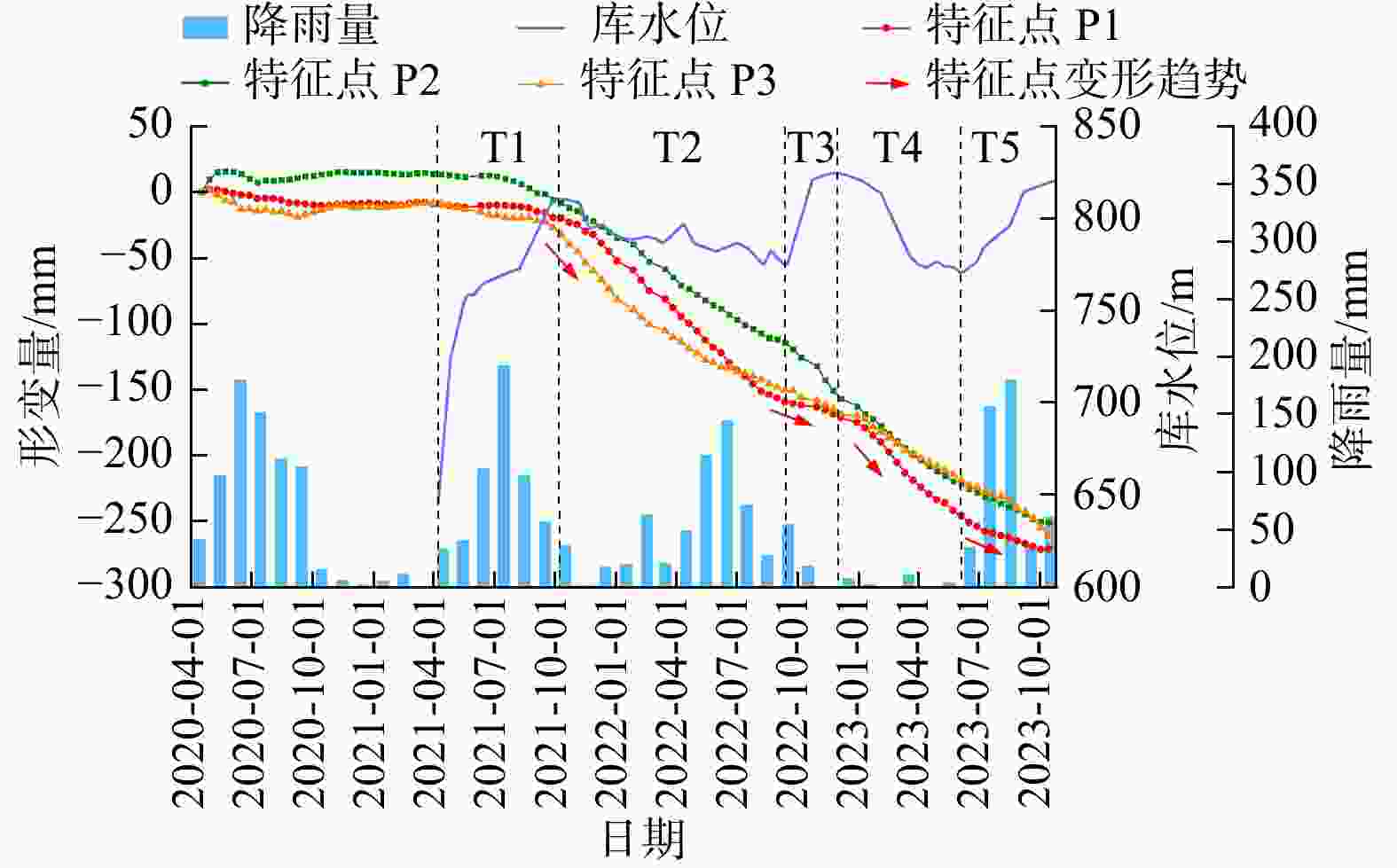
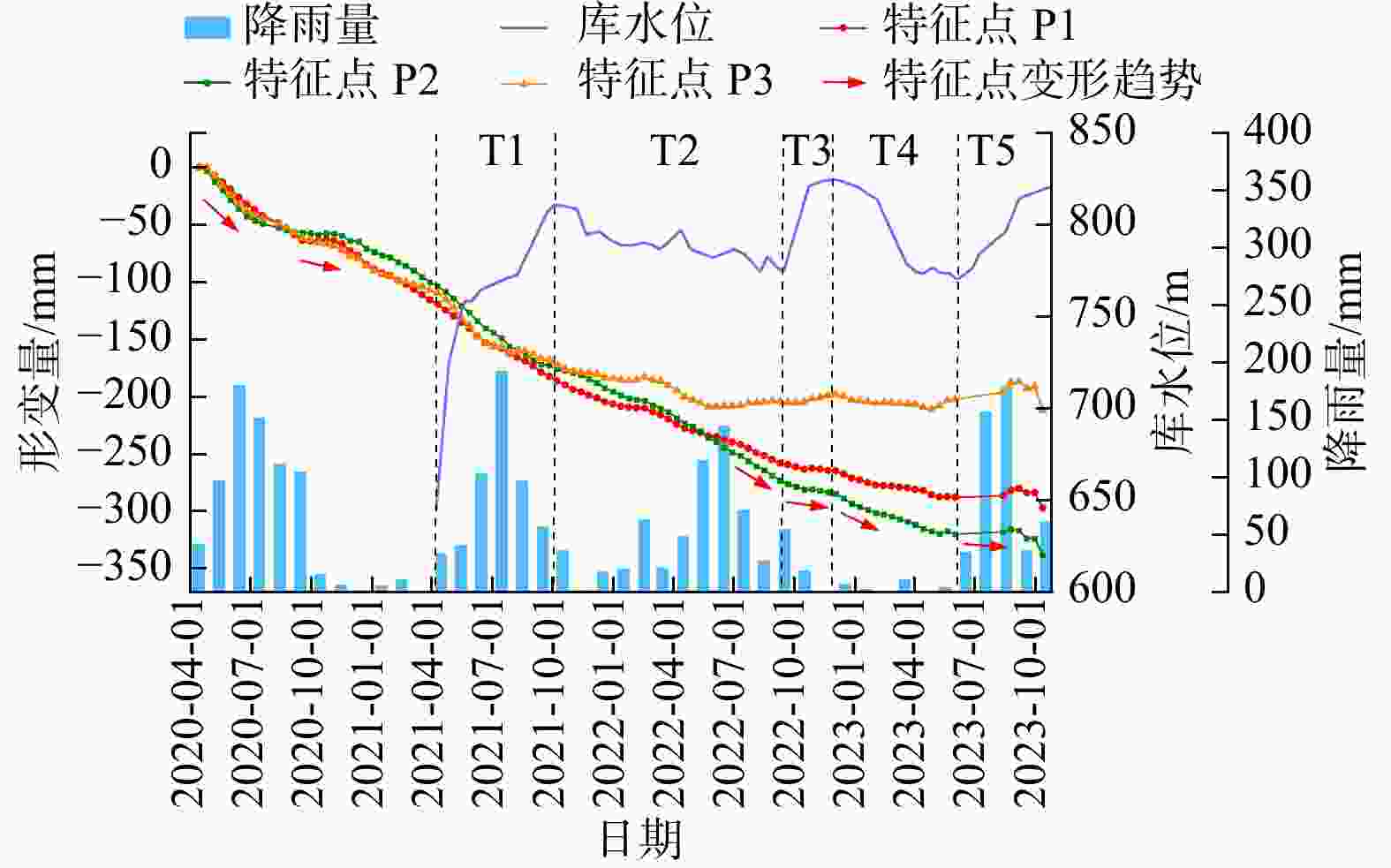
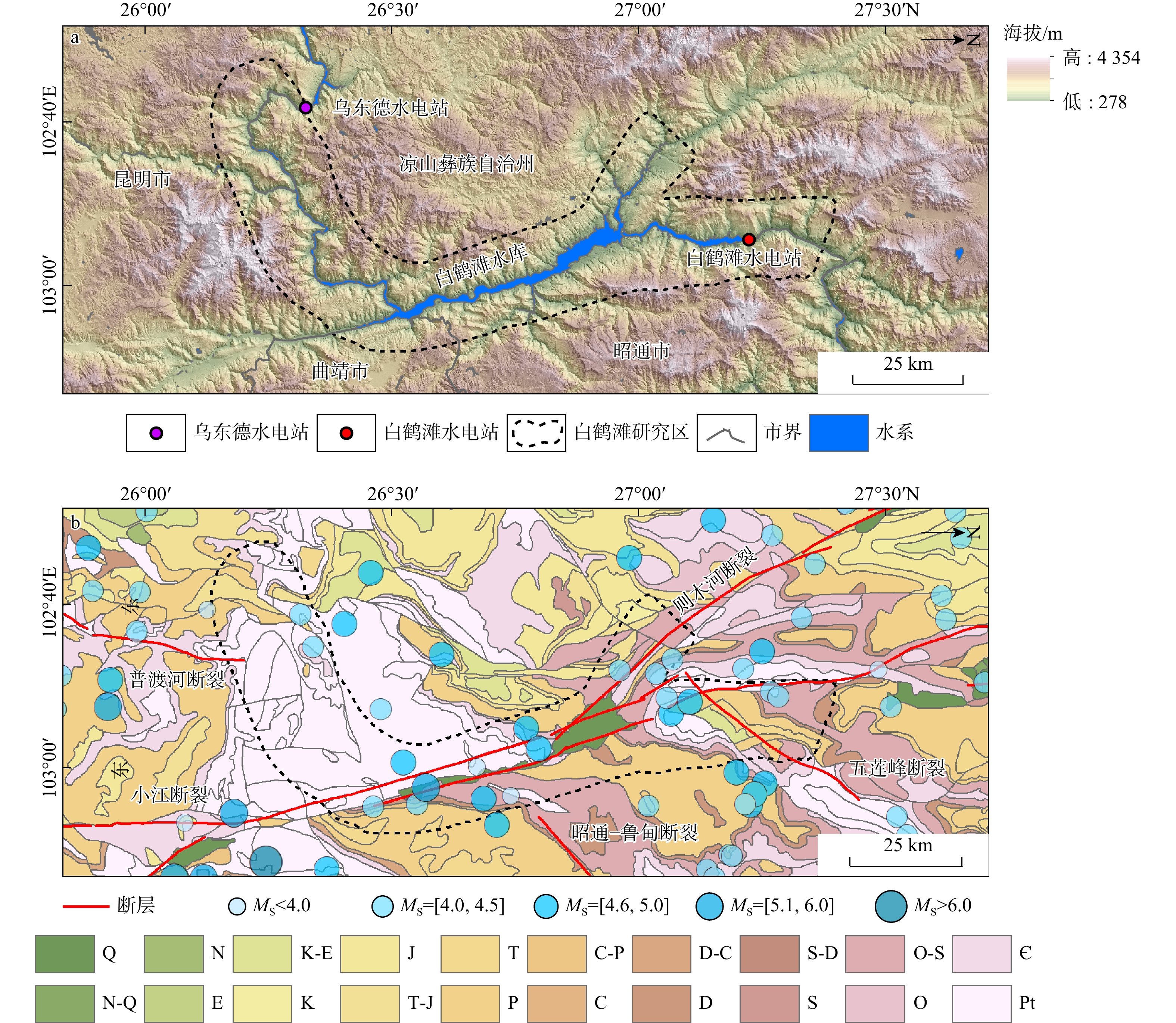
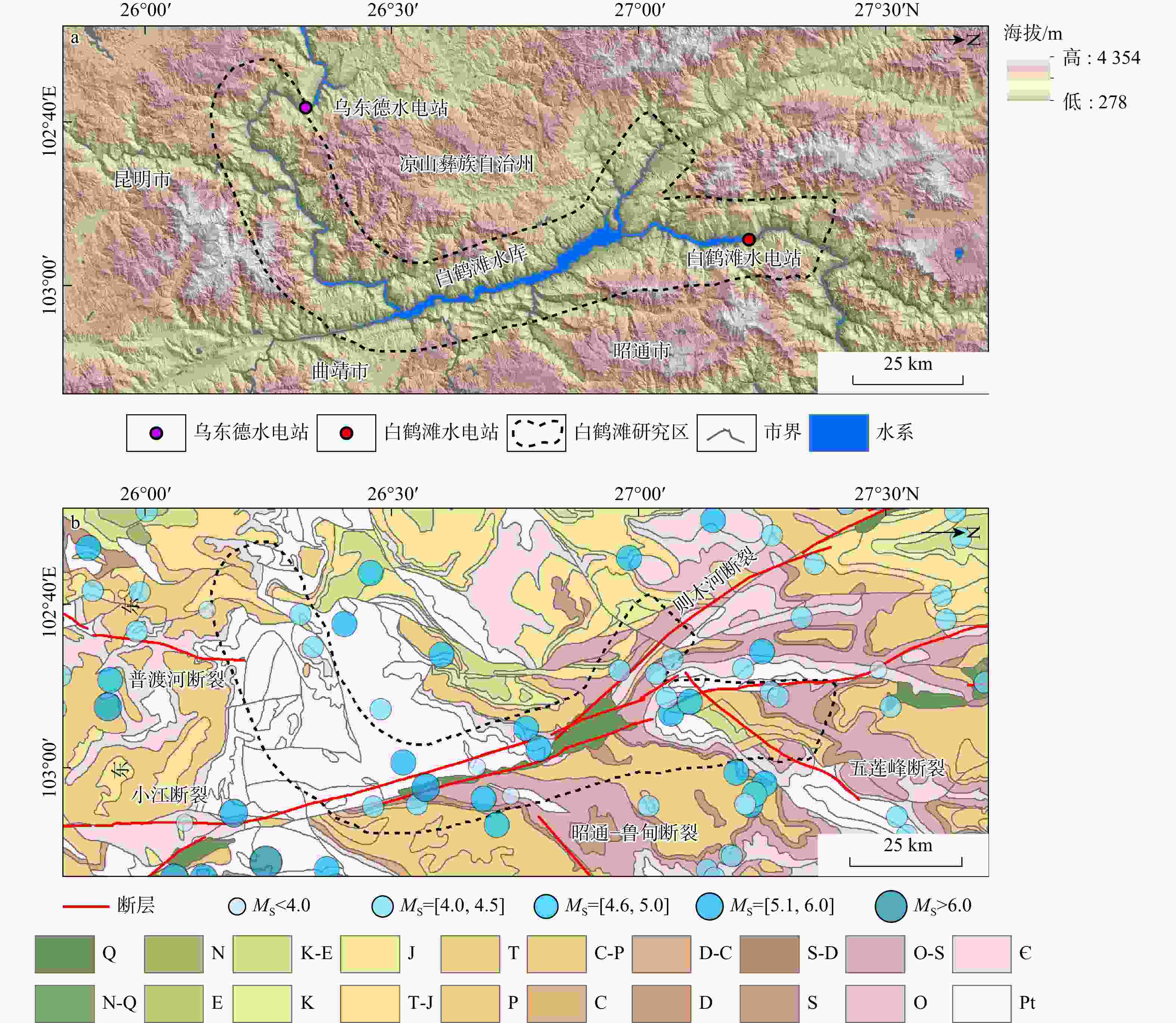
水库滑坡是水电工程建设中一种常见的地质灾害,当滑坡滑入库区中可能会引起涌浪、江河堵塞甚至溃坝,从而造成巨大的经济损失和人员伤亡,因此,研究水库滑坡形变特征对如何高效及时地开展对水库滑坡早期识别与监测具有重要意义。以白鹤滩库区为研究区域,基于哨兵一号(Sentinel-1)雷达影像,采用干涉堆叠法(stacking interferometry synthetic aperture radar,简称Stacking-InSAR)、小基线集干涉测量(small baseline subset interferometry synthetic aperture radar,简称SBAS-InSAR)方法开展了广域的活动滑坡灾害识别并获取了白鹤滩库区滑坡蓄水前后的形变信息,结合哨兵二号(Sentinel-2)影像利用自动水体提取指数(automated water extraction index,简称AWEI)提取库区水位数据,选取了形变较大的上升型、下降型、蓄水前形变型滑坡各一个作为典型滑坡,探讨了水库水位波动和降雨与滑坡变形的关系。研究表明:结合Sentinel-2影像利用AWEI提取库区水位数据的方法在研究区的应用效果较好,提取水位与实测水位平均误差为0.89 m,该方法对无水位数据的区域具有研究价值。白鹤滩库区在观测期内升轨、降轨影像共探测出活动滑坡共103个,其中前缘涉水活动滑坡37个,由水位波动引起形变的滑坡有23个。库岸滑坡变形与水位波动有较强相关性,与降雨量相关性较弱,且水位下降对库岸滑坡形变的影响较大。
Abstract:Objective Landslides in reservoir areas represent one of the most prevalent geological hazards in hydropower engineering construction. Landslides in reservoir area, they can generate surge waves, obstruct river channels, and even trigger dam breaches, resulting in significant economic losses and casualties. Therefore, understanding the deformation behavior of reservoir landslides is critical for early identification and monitoring.
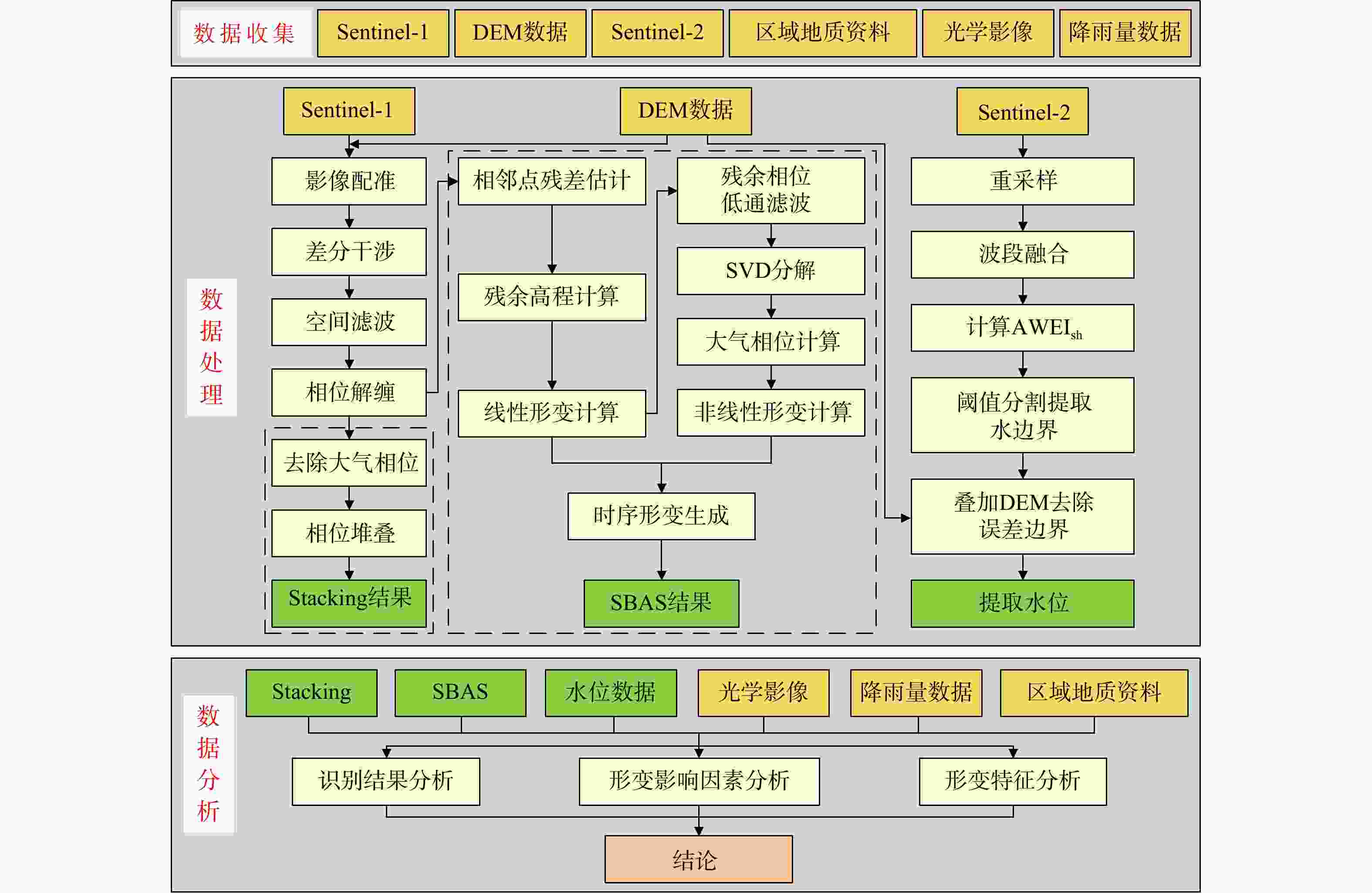
Methods This study employs Stacking Interferometry Synthetic Aperture Radar (Stacking-InSAR) and Small Baseline Subset Interferometry Synthetic Aperture Radar (SBAS-InSAR) techniques with Sentinel-1 data to identify active landslides and analyze deformation patterns in the Baihetan Reservoir area before and after impoundment. In addition, Sentinel-2 imagery and the Automated Water Extraction Index (AWEI) were used to derive reservoir water level variations. Representative landslides exhibiting substantial deformation were selected—one each from asceding-track, descending-track, and pre-impoundment datasets—to analyze the influence of water level fluctuations and rainfall on deformation behavior.
Results and Conclusion The results demonstrate that the AWEI- based water level extraction method using Sentinel-2 imagery achieved robust performance in the study area. The extracted water levels exhibited a mean error of 0.89 m compared to measured values, confirming the method's reliability for data-scarce regions. A total of 103 active landslides were identified in the Baihetan Reservoir area during the monitoring period through analysis of both ascending and descending orbit images. A total of 103 active landslides were detected in the Baihetan reservoir area during the obervation period, 37 exhibited submergence of their front edges, while 23 demonstrated clear deformation responses to water level fluctuations. Reservoir bank landslides showed significantly stronger correlation with water level changes than with rainfall. Notably, drawdown conditions exerted particularly pronounced effects on bank stability, with deformation rates increasing during lowering phases compared to rising water levels.
-
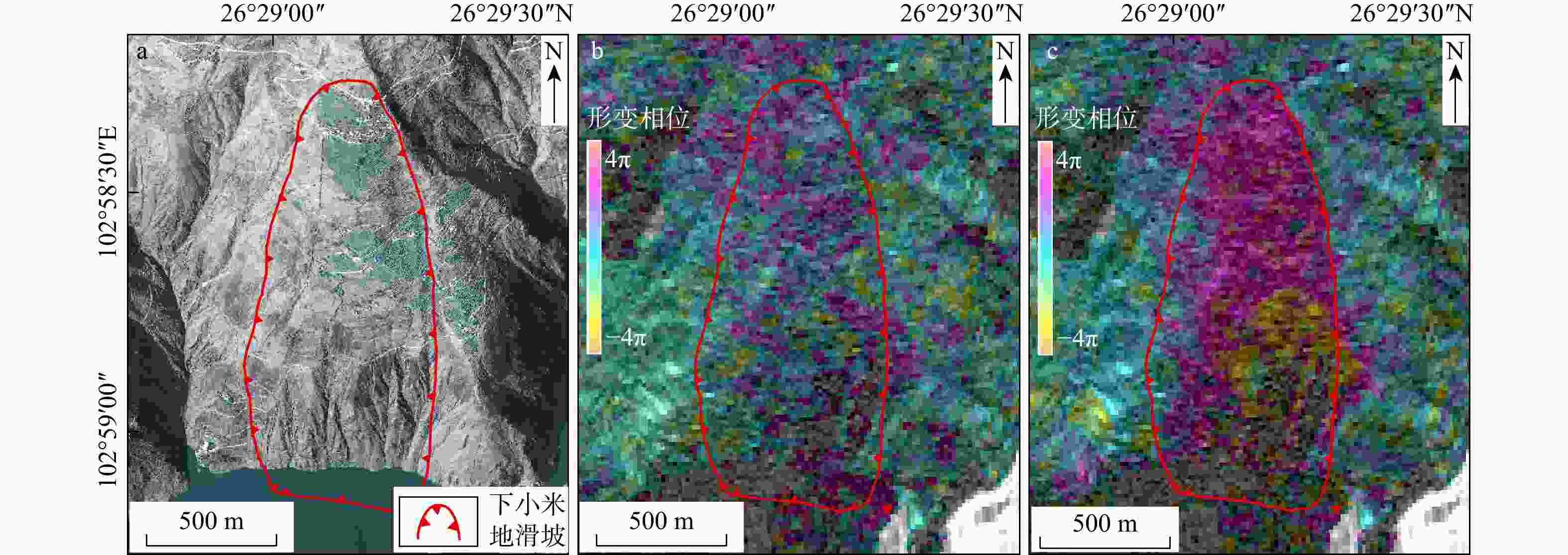
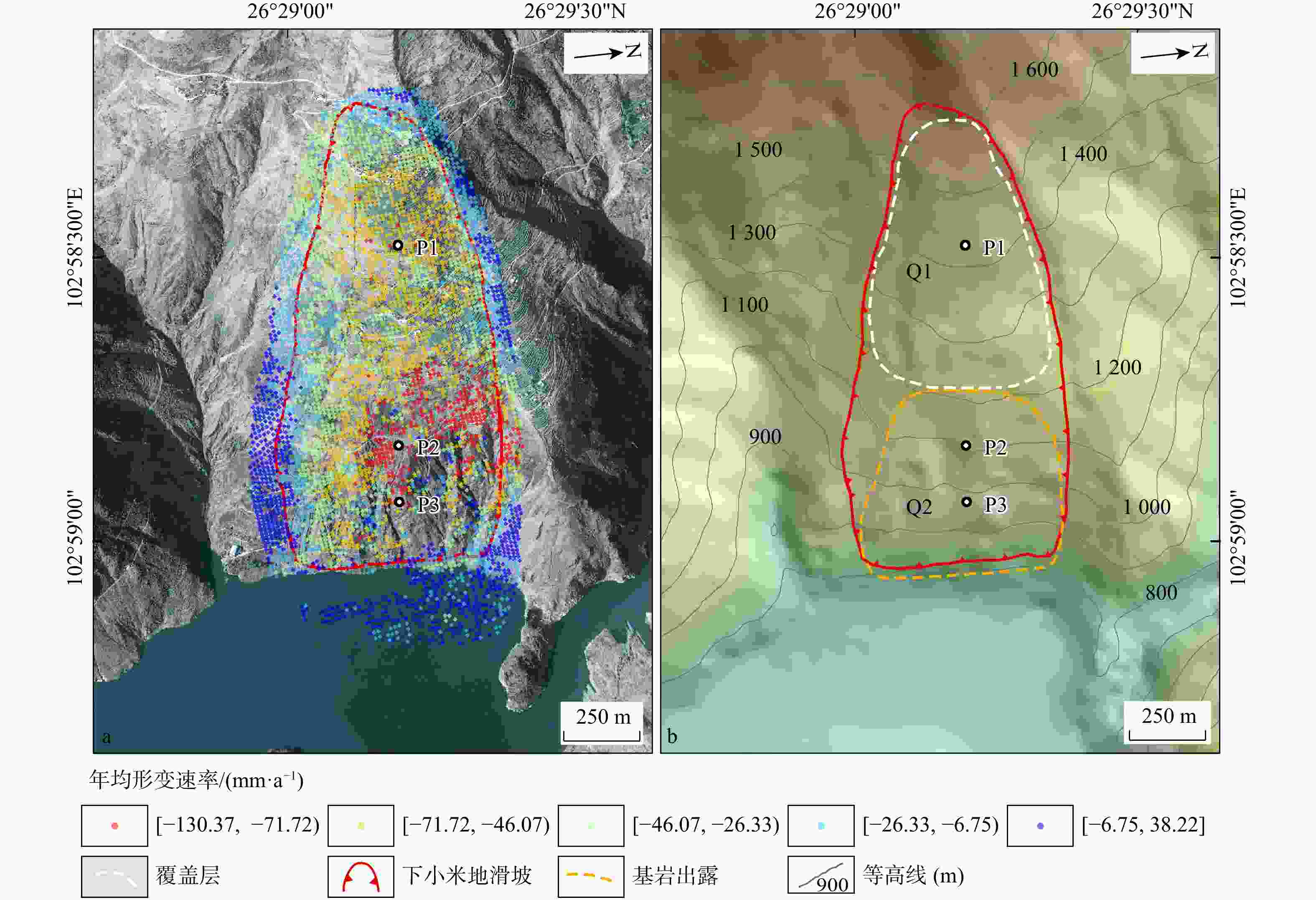
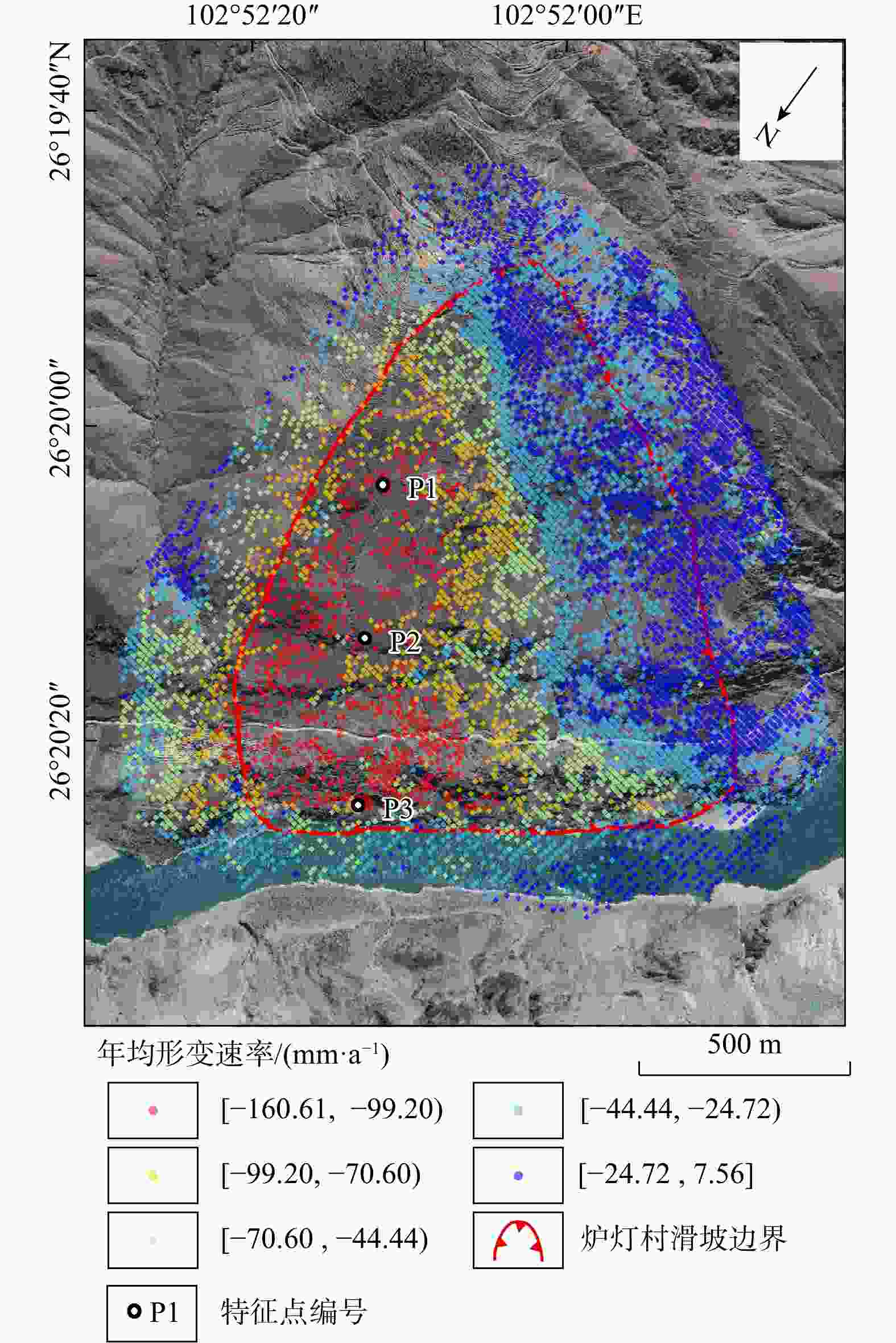
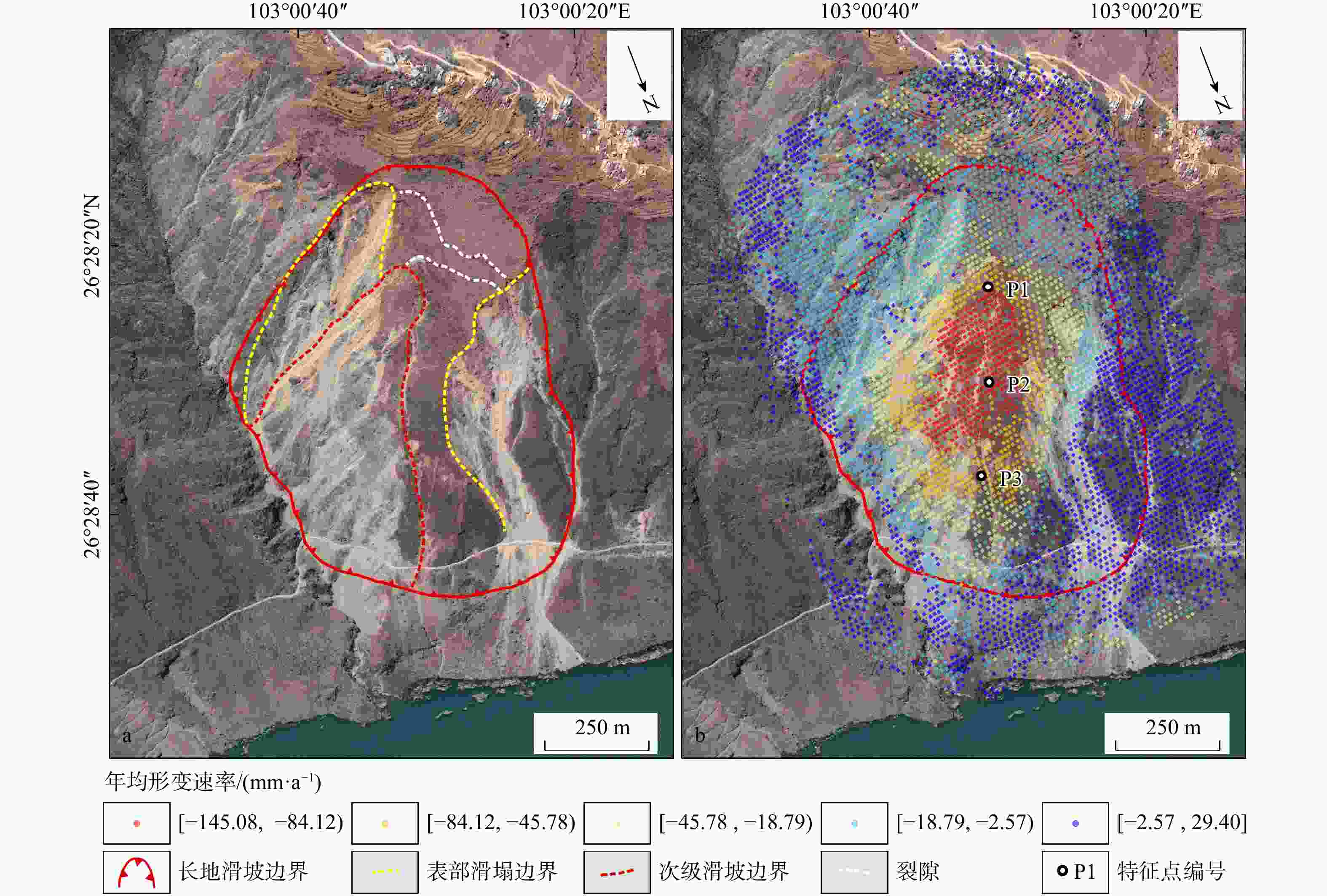
图 11 下小米地滑坡形变特征图
a. 年均形变速率图;b. 滑坡变形特征分区图(据文献[25]修改;Q1,Q2为滑坡分区编号;P1,P2,P3为滑坡特征点编号,下同)
Figure 11. Deformation characteristics map of Xiaxiaomidi landslide
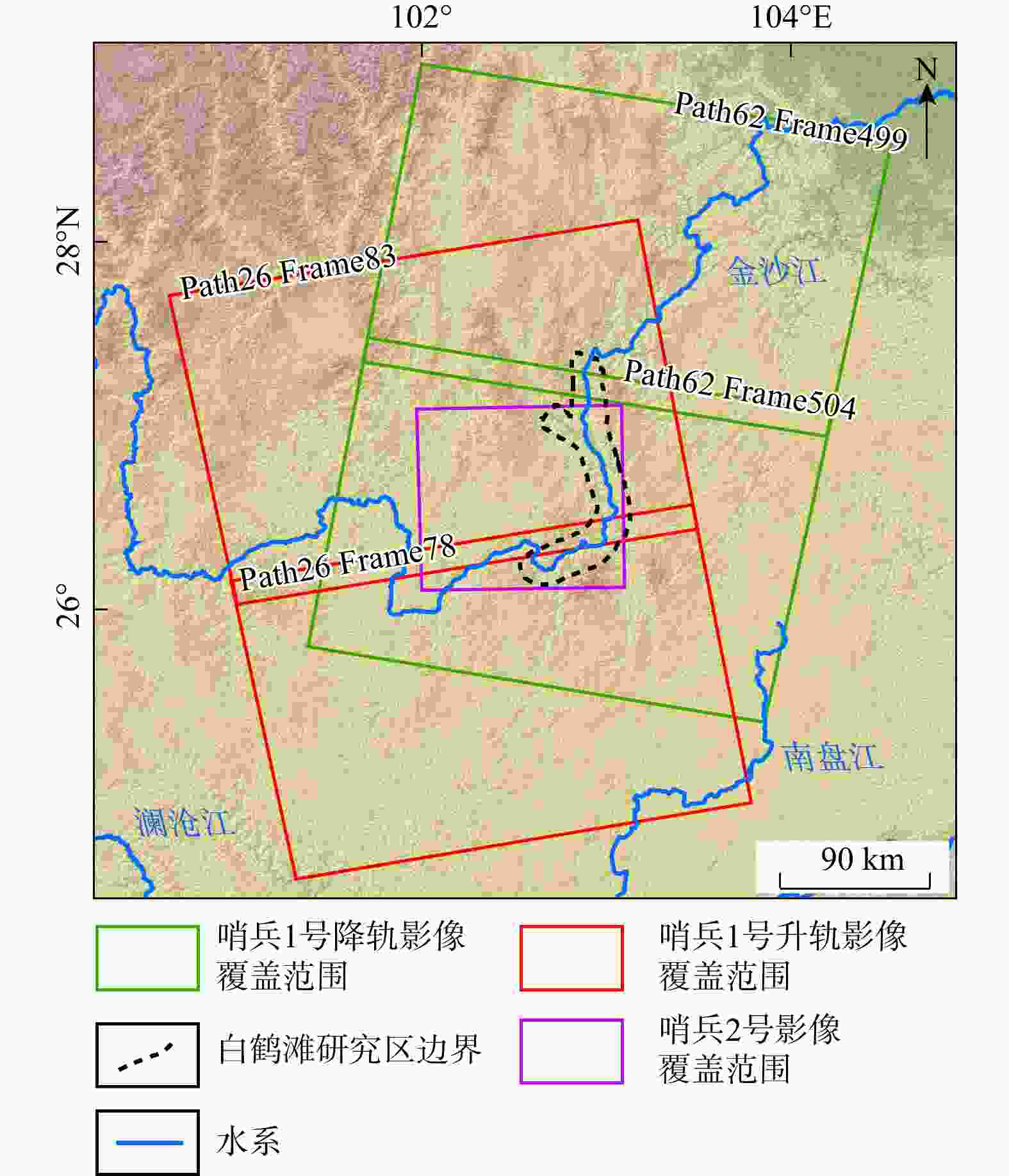
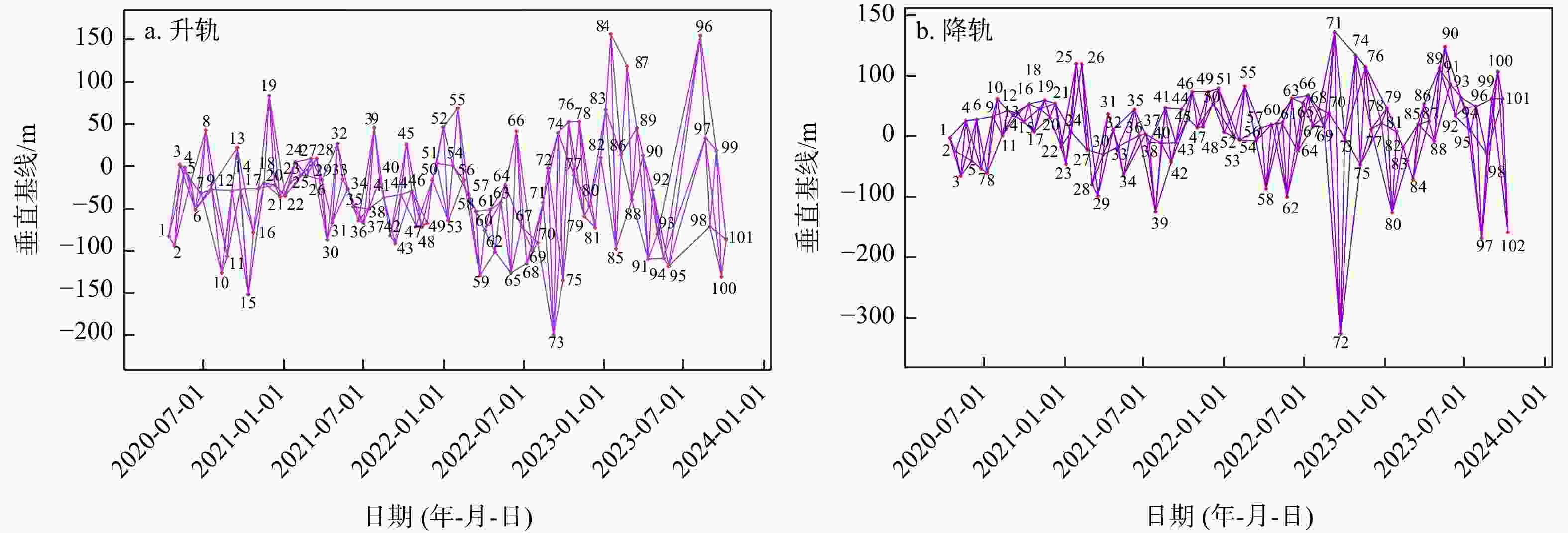
表 1 研究区Sentinel-1数据参数表
Table 1. Sentinel-1 data parameters of the study area
轨道 Path 入射角/(°) Frame 影像获取时间 影像数量 升轨 26 41.7 78 2020.04.14—2023.10.08 101 83 101 降轨 62 39.3 499 2020.04.16—2023.10.10 102 504 102 表 2 研究区水位表
Table 2. Water levels in the study area
序号 日期 水位/m 序号 日期 水位/m 序号 日期 水位/m 1 2021-04-07 644.5 19 2022-02-15 790.0 37 2023-01-19 816.5 2 2021-04-26 724.5 20 2022-02-28 789.0 38 2023-01-26 815.0 3 2021-05-16 754.5 21 2022-03-10 786.5 39 2023-01-31 814.0 4 2021-05-21 758.5 22 2022-03-22 790.0 40 2023-02-18 800.0 5 2021-05-31 758.5 23 2022-04-11 797.0 41 2023-03-07 786.5 6 2021-06-13 764.5 24 2022-04-26 786.5 42 2023-03-17 779.0 7 2021-07-20 770.5 25 2022-05-29 782.0 43 2023-03-30 774.5 8 2021-08-07 772.5 26 2022-06-30 786.5 44 2023-04-11 773.5 9 2021-09-21 806.5 27 2022-07-15 784.0 45 2023-04-26 776.5 10 2021-10-01 810.5 28 2022-08-09 774.5 46 2023-05-06 774.0 11 2021-10-13 810.5 29 2022-08-19 782.5 47 2023-05-21 773.5 12 2021-11-05 808.5 30 2022-09-08 775.0 48 2023-05-31 770.5 13 2021-11-20 794.5 31 2022-09-13 775.0 49 2023-06-05 771.0 14 2021-12-10 796.5 32 2022-10-21 821.0 50 2023-06-25 776.5 15 2021-12-22 792.5 33 2022-11-12 824.0 51 2023-07-05 784.0 16 2022-01-01 790.5 34 2022-11-27 824.5 52 2023-08-14 796.5 17 2022-01-11 789.0 35 2022-12-07 824.0 53 2023-09-03 814.5 18 2022-01-24 788.5 36 2023-01-06 820.0 54 2023-10-18 820.5 表 3 水位−形变各阶段相关系数表
Table 3. Correlation coefficients between water level and deformation at different stages
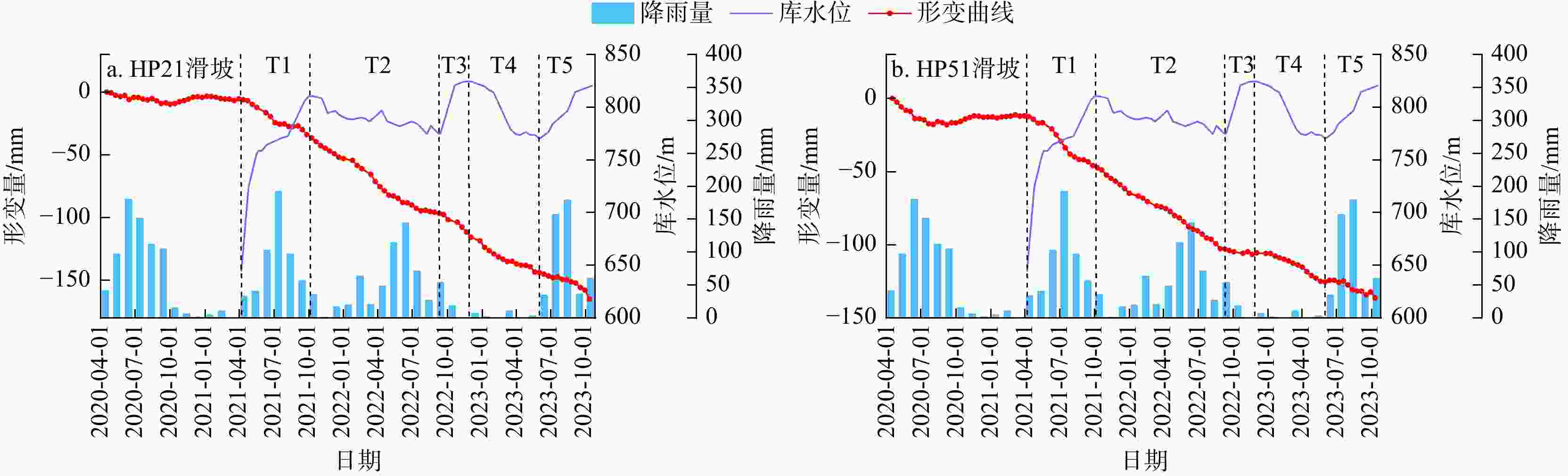
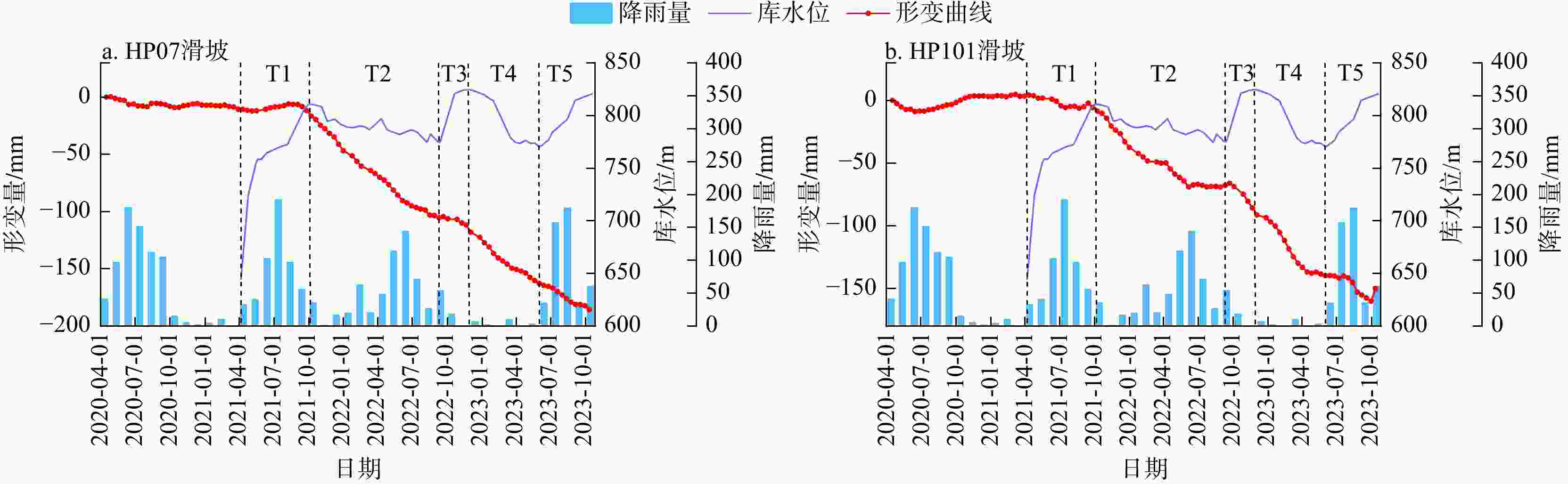
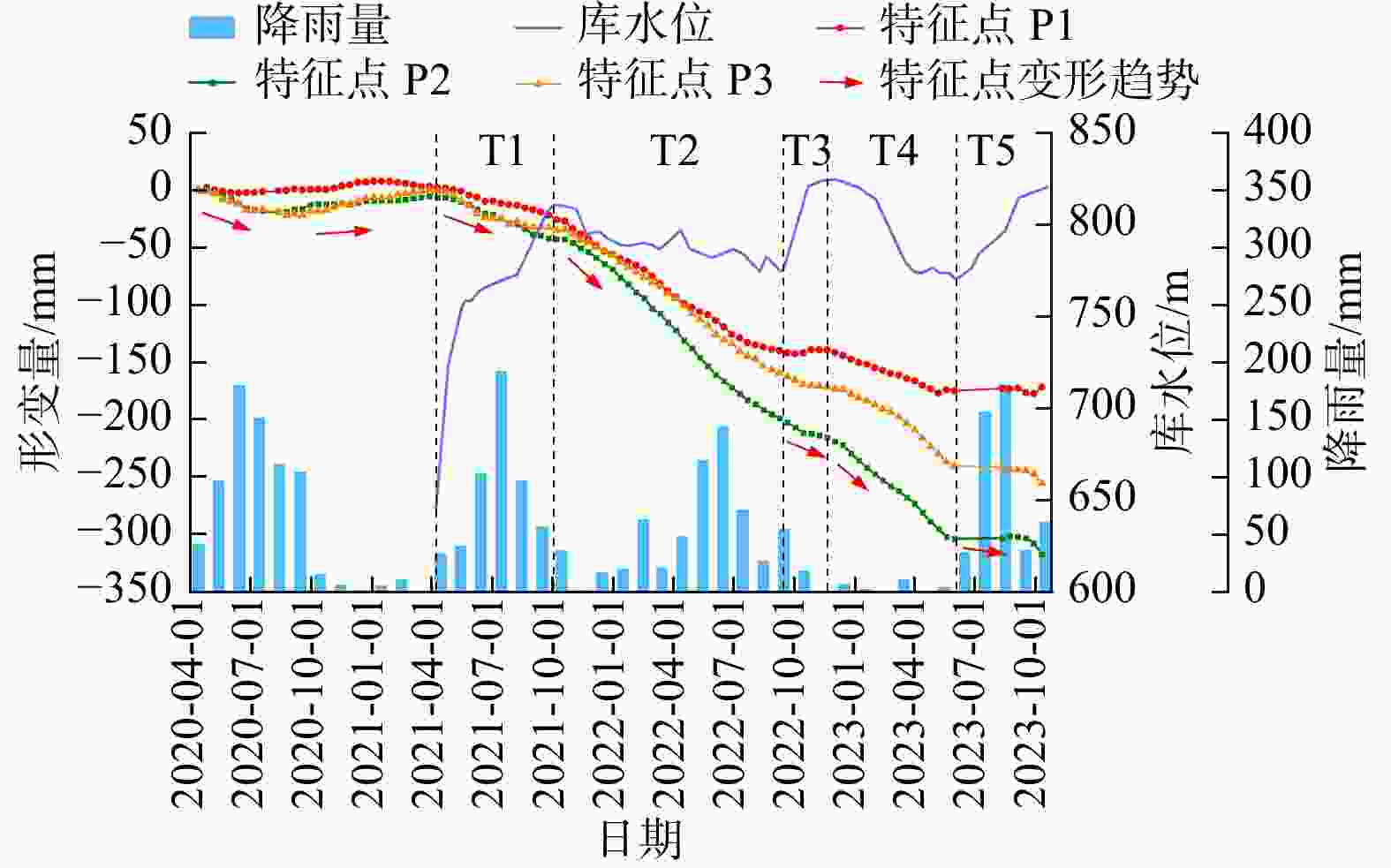
滑坡 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 下小米地滑坡 0.767 0.827 0.997 0.919 0.505 炉灯村滑坡 0.577 0.851 0.730 0.983 0.929 长地滑坡 0.853 0.841 0.868 0.910 0.478 表 4 降雨−形变相关系数表
Table 4. Correlation coefficients between rainfall and deformation
滑坡 2020年 2021年 2022年 2023年 下小米地滑坡 0.355 0.011 0.165 0.550 炉灯村滑坡 0.412 0.258 0.179 0.587 长地滑坡 0.186 0.251 0.266 0.180 -
[1] 姚鑫,邓建辉,刘星洪,等. 青藏高原泛三江并流区活动性滑坡InSAR初步识别与发育规律分析[J]. 工程科学与技术,2020,52(5):16-37.YAO X,DENG J H,LIU X H,et al. Primary recognition of active landslides and development rule analysis for pan three-river-parallel territory of Tibet Plateau[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2020,52(5):16-37. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] SHI X G,HU X,SITAR N,et al. Hydrological control shift from river level to rainfall in the reactivated Guobu slope besides the Laxiwa Hydropower Station in China[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2021,265:112664. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112664 [3] ZHAO N H,HU B,YI Q L,et al. The coupling effect of rainfall and reservoir water level decline on the Baijiabao landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area,China[J]. Geofluids,2017,2017(1):3724867. [4] 肖诗荣,魏瑞琦,李莹,等. 意大利瓦依昂滑坡研究综述[J]. 人民长江,2023,54(4):130-140.XIAO S R,WEI R Q,LI Y,et al. Review on Vaiont landslide in Italy[J]. Yangtze River,2023,54(4):130-140. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 汪发武,宋琨. 库水位涨落条件下不同结构边坡的变形破坏机制分析:以千将坪滑坡和树坪滑坡为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2021,29(3):575-582.WANG F W,SONG K. Analysis of deformation and failure mechanism of bank slopes with different structures under reservoir water level fluctuation:Taking Qianjiangping landslide and Shuping landslide as examples[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2021,29(3):575-582. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 周家文,陈明亮,瞿靖昆,等. 水库滑坡灾害致灾机理及防控技术研究与展望[J]. 工程科学与技术,2023,55(1):110-128.ZHOU J W,CHEN M L,QU J K,et al. Research and prospect on disaster-causing mechanism and prevention-control technology of reservoir landslides[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences,2023,55(1):110-128. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 单云锋,李为乐,周胜森,等. 长江上游区域滑坡灾害生态风险评估[J]. 生态学报,2024,44(24):11437-11449.SHAN Y F,LI W L,ZHOU S S,et al. Ecological risk assessment of landslide hazards in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River region[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2024,44(24):11437-11449. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 朱赛楠,殷跃平,王猛,等. 金沙江结合带高位远程滑坡失稳机理及减灾对策研究:以金沙江色拉滑坡为例[J]. 岩土工程学报,2021,43(4):688-697. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202104011ZHU S N,YIN Y P,WANG M,et al. Instability mechanism and disaster mitigation measures of long-distance landslide at high location in Jinsha River junction zone:Case study of Sela landslide in Jinsha River,Tibet[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021,43(4):688-697. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11779/CJGE202104011 [9] 佘金星,许强,杨武年,等. 九寨沟地震地质灾害隐患早期识别与分析研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2023,31(1):207-216.SHE J X,XU Q,YANG W N,et al. Early identification and analysis of earthquake and geological hazards in Jiuzhaigou[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2023,31(1):207-216. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] MALET J P,MAQUAIRE O,CALAIS E. The use of Global Positioning System techniques for the continuous monitoring of landslides:Application to the Super-Sauze earthflow (Alpes-de-Haute-Provence,France)[J]. Geomorphology,2002,43(1/2):33-54. [11] DUN J W,FENG W K,YI X Y,et al. Detection and mapping of active landslides before impoundment in the Baihetan Reservoir area (China) based on the time-series InSAR method[J]. Remote Sensing,2021,13(16):3213. doi: 10.3390/rs13163213 [12] 李振洪,宋闯,余琛,等. 卫星雷达遥感在滑坡灾害探测和监测中的应用:挑战与对策[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):967-979.LI Z H,SONG C,YU C,et al. Application of satellite radar remote sensing to landslide detection and monitoring:Challenges and solutions[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):967-979. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 谢云轩,汪洋,王梦瑶,等. 基于物理模型试验的库岸滑坡水阻力系数研究[J]. 地质科技通报,2025,44(2):59-66.XIE Y X,WANG Y,WANG M Y,et al. Water resistance coefficient of bank slope landslides via physical model experiments[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2025,44(2):59-66. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 许强,李为乐,董秀军,等. 四川茂县叠溪镇新磨村滑坡特征与成因机制初步研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2017,36(11):2612-2628.XU Q,LI W L,DONG X J,et al. The Xinmocun landslide on June 24,2017 in Maoxian,Sichuan:Characteristics and failure mechanism[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2017,36(11):2612-2628. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 陆会燕,李为乐,许强,等. 光学遥感与InSAR结合的金沙江白格滑坡上下游滑坡隐患早期识别[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(9):1342-1354.LU H Y,LI W L,XU Q,et al. Early detection of landslides in the upstream and downstream areas of the Baige landslide,the Jinsha River based on optical remote sensing and InSAR technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(9):1342-1354. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 许强,董秀军,李为乐. 基于天−空−地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):957-966.XU Q,DONG X J,LI W L. Integrated space-air-ground early detection,monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):957-966. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] ZHOU S S,CHEN B L,LU H Y,et al. Analysis of the spatial distribution and deformation types of active landslides in the upper Jinsha River,China,using integrated remote sensing technologies[J]. Remote Sensing,2024,16(1):100. [18] SHAN Y F,XU Z,ZHOU S S,et al. Landslide hazard assessment combined with InSAR deformation:A case study in the Zagunao River Basin,Sichuan Province,southwestern China[J]. Remote Sensing,2024,16(1):99. [19] LI L J,WEN B P,YAO X,et al. InSAR-based method for monitoring the long-time evolutions and spatial-temporal distributions of unstable slopes with the impact of water-level fluctuation:A case study in the Xiluodu Reservoir[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2023,295:113686. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2023.113686 [20] LOWRY B W,BAKER S,ZHOU W. A case study of novel landslide activity recognition using ALOS-1 InSAR within the ragged mountain western hillslope in Gunnison County,Colorado,USA[J]. Remote Sensing,2020,12(12):1969. doi: 10.3390/rs12121969 [21] 屈鹏鑫,谢婉丽,刘琦琦,等. 基于机器学习方法改进IVM-RF耦合模型的崩滑灾害危险性评价:以延安市志丹县为例[J]. 地质科技通报,2025,44(3):280-295.QU P X,XIE W L,LIU Q Q,et al. Collapse and landslide risk assessment based on machine learning improved IVM-RF coupling method:A case study of Zhidan County,Yan'an City[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2025,44(3):280-295. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] REYES-CARMONA C,GALVE J P,MORENO-SÁNCHEZ M,et al. Rapid characterisation of the extremely large landslide threatening the Rules Reservoir (southern Spain)[J]. Landslides,2021,18(12):3781-3798. doi: 10.1007/s10346-021-01728-z [23] LIU P,LI Z H,HOEY T,et al. Using advanced InSAR time series techniques to monitor landslide movements in Badong of the Three Gorges region,China[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,2013,21:253-264. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2011.10.010 [24] 康亚,赵超英,张勤,等. InSAR滑坡探测技术研究:以金沙江乌东德水电站段为例[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学,2018,38(10):1053-1057.KANG Y,ZHAO C Y,ZHANG Q,et al. Research on the InSAR technique of landslide detection:A case study of Wudongde Hydropower Station section,Jinshajiang[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics,2018,38(10):1053-1057. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 戴可人,沈月,吴明堂,等. 联合InSAR与无人机航测的白鹤滩库区蓄水前地灾隐患广域识别[J]. 测绘学报,2022,51(10):2069-2082. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220305DAI K R,SHEN Y,WU M T,et al. Identification of potential landslides in Baihetan Dam area before the impoundment by combining InSAR and UAV survey[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2022,51(10):2069-2082. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2022.20220305 [26] 史先琳,居安华,戴可人,等. 多源遥感揭示白鹤滩库区五里坡滑坡蓄水期形变演化与复活机制[J]. 北京理工大学学报,2023,43(11):1164-1175.SHI X L,JU A H,DAI K R,et al. Deformation evolution and reactivation mechanism of landslide revealed based on multi-source remote sensing during impoundment period for Wulipo landslide in Baihetan Reservoir area[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology,2023,43(11):1164-1175. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] ZHOU Z K,YAO X,LI R J,et al. Deformation characteristics and mechanism of an impoundment-induced toppling landslide in Baihetan Reservoir based on multi-source remote sensing[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2023,20(12):3614-3630. doi: 10.1007/s11629-023-7903-2 [28] YANG Z R,XI W F,YANG Z Q,et al. Time-lag response of landslide to reservoir water level fluctuations during the storage period:A case study of Baihetan Reservoir[J]. Water,2023,15(15):2732. doi: 10.3390/w15152732 [29] ZHAO S F,ZENG R Q,ZHANG H X,et al. Impact of water level fluctuations on landslide deformation at Longyangxia Reservoir,Qinghai Province,China[J]. Remote Sensing,2022,14(1):212. doi: 10.3390/rs14010212 [30] 王大钊,王思梦,黄昌. Sentinel-2和Landsat 8影像的四种常用水体指数地表水体提取对比[J]. 国土资源遥感,2019,31(3):157-165.WANG D Z,WANG S M,HUANG C. Comparison of Sentinel-2 imagery with Landsat 8 imagery for surface water extraction using four common water indexes[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources,2019,31(3):157-165. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 吴明堂,房云峰,卓冠晨,等. 白鹤滩库区三家村库岸地质灾害隐患综合遥感识别[J]. 昆明理工大学学报(自然科学版),2023,48(3):53-61.WU M T,FANG Y F,ZHUO G C,et al. Comprehensive remote sensing identification of potential geohazards in Sanjiacun Reservoir bank of Baihetan[J]. Journal of Kunming University of Science and Technology (Natural Science),2023,48(3):53-61. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 庞健峰,丁孝忠,韩坤英,等. 1∶100万中华人民共和国数字地质图空间数据库[J]. 中国地质,2017,44(增刊1):8-18.PANG J F,DING X Z,HAN K Y,et al. The national 1∶ 1000000 geological map spatial database[J]. Geology in China,2017,44(S1):8-18. (in Chinese with English abstract[33] 陈俊伊,李为乐,陆会燕,等. 基于InSAR技术的澜沧江卡贡乡−如美镇段崩滑隐患探测[J]. 中国地质调查,2022,9(4):134-143.CHEN J Y,LI W L,LU H Y,et al. Detection of potential landslides in the section from Kagong County to Rumei Town of Lancang River based on InSAR technology[J]. Geological Survey of China,2022,9(4):134-143. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 周胜森,李为乐,陆会燕,等. “三查” 体系在高植被山区地质灾害隐患识别与监测中的应用:以四川省乐山市为例[J/OL]. 自然资源遥感,2024:1-11. (2024-08-02). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/10.1759.p.20240731.1703.024.html.ZHOU S S,LI W L,LU H Y,et al. Application of 'space-air-ground investigation system' for geohazard id entification and monitoring in mountainous areas with high vegetation cover:A case of Leshan City,Sichuan Province[J/OL]. Remote Sensing for Natural Resources,2024:1-11. (2024-08-02). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/10.1759.p.20240731.1703.024.html.(in Chinese with English abstract [35] 付豪,李为乐,陆会燕,等. 基于“三查” 体系的丹巴县滑坡隐患早期识别与监测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2024,49(5):734-746.FU H,LI W L,LU H Y,et al. Early detection and monitoring of potential landslides in Danba County based on the space-air-ground investigation system[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2024,49(5):734-746. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] FEYISA G L,MEILBY H,FENSHOLT R,et al. Automated water extraction index:A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment,2014,140:23-35. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2013.08.029 [37] 许强,陆会燕,李为乐,等. 滑坡隐患类型与对应识别方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2022,47(3):377-387.XU Q,LU H Y,LI W L,et al. Types of potential landslide and corresponding identification technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2022,47(3):377-387. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 李松林. 三峡库区涉水滑坡对库水位变动的变形响应及其自适应性研究[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2020.LI S L. Study on the reactivation characteristic and deformation self-adaptive of landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] ZHOU C,CAO Y,YIN K L,et al. Characteristic comparison of seepage-driven and buoyancy-driven landslides in Three Gorges Reservoir area,China[J]. Engineering Geology,2022,301:106590. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106590 [40] 李松林,汤明高,许强,等. 库水位上升条件下浮托减重型滑坡离心模型试验[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版),2020,41(5):616-622.LI S L,TANG M G,XU Q,et al. Centrifugal model tests on buoyancy-induced weight loss landslides influenced by rising reservoir water level[J]. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science),2020,41(5):616-622. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: