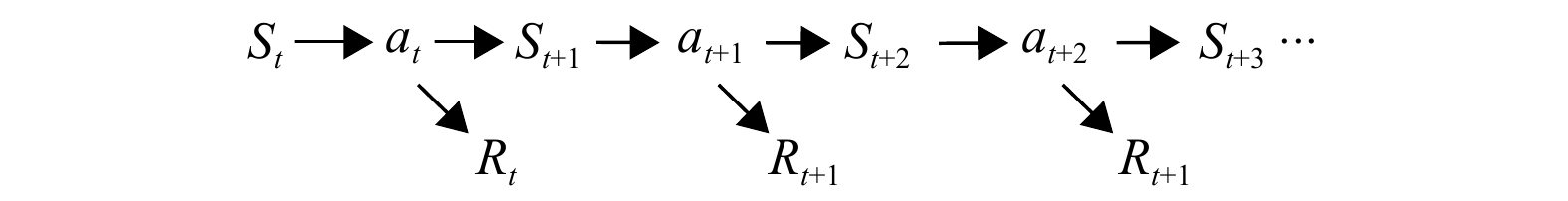Using deep reinforcement learning with smooth constraint to invert magnetotelluric data
-
摘要:
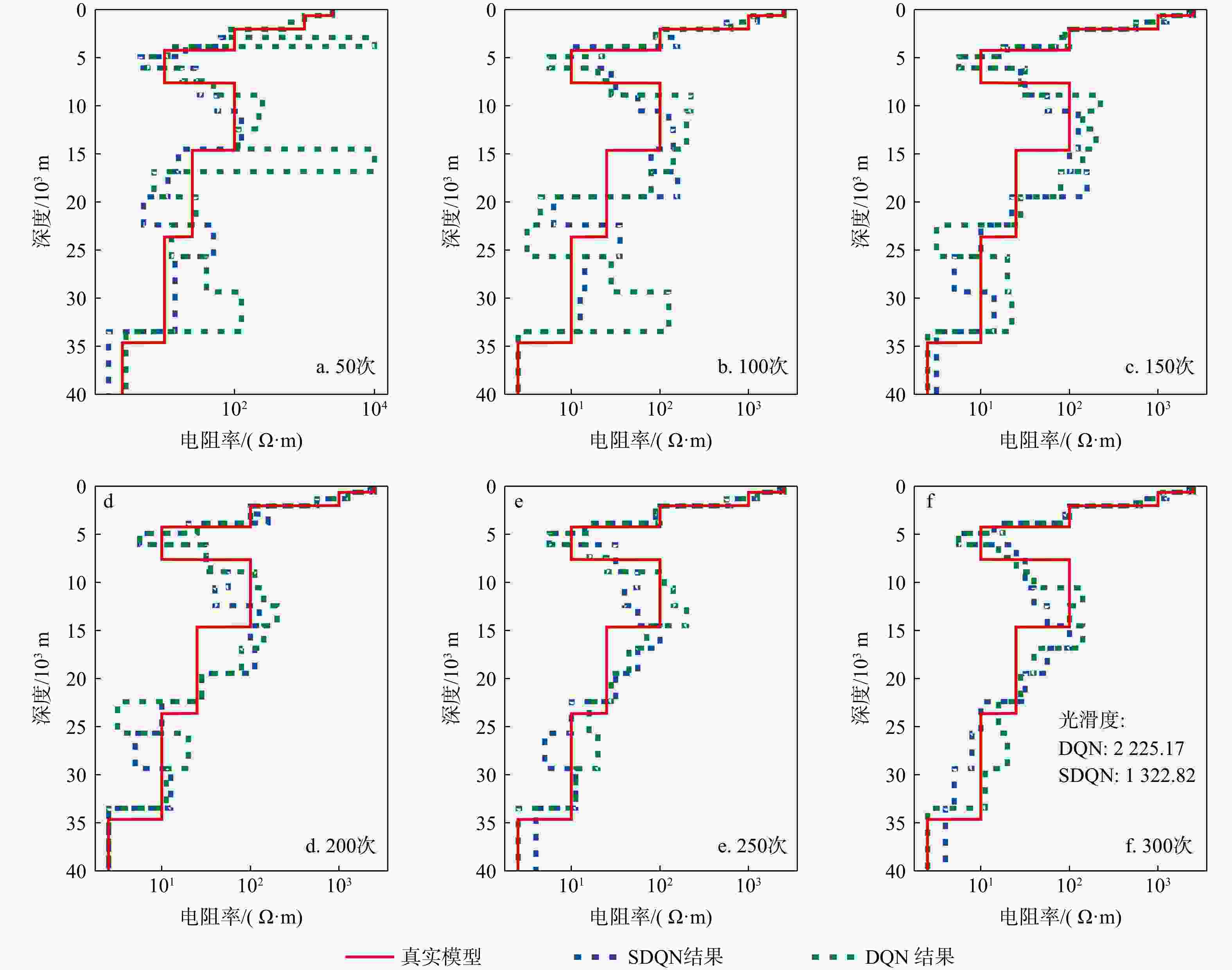
反演是处理大地电磁测深数据的关键步骤之一,得到了学者的广泛研究。其中基于数据驱动的反演方法主要包括带监督反演和半监督反演,对无监督反演的研究较少。DQN(deep Q-network)是一种经典的深度强化学习算法,作为无监督反演方法最近被用于解决一维大地电磁反演问题。该方法具有不需要训练数据集、对初始模型依赖较小、多次反演能够得到反演结果的概率分布等优点,但存在反演结果不集中的问题。提出了带光滑约束的大地电磁强化学习反演方法(Smooth DQN,简称SDQN)。本方法基于强化学习框架,将反演问题看成马尔可夫决策问题,并分别定义环境、奖励、智能体等术语;然后将正则化反演的模型约束项引入到奖励中来,从而引导智能体不断调整预测模型的电阻率参数以得到更符合模型约束的结果。理论模型反演结果表明,相较于DQN反演和Occam反演方法,在相同反演次数情况下SDQN方法反演不同噪声水平的观测数据时结果更稳定。西藏扎西康矿集区的大地电磁实测数据反演结果与Occam反演结果基本吻合并与已有的地质解释资料一致。SDQN方法具有反演结果更集中、对观测数据的抗噪能力更强的优点,是解决大地电磁反演问题的新工具。
Abstract:Inversion is one of the key steps in processing magnetotelluric sounding data and has been widely studied by scholars. The data-driven approaches mainly include supervised inversion and semi-supervised inversion,
but there is limited research on unsupervised inversion .Objective Deep Q-network (DQN) is a classical deep reinforcement learning algorithm,
which is an unsupervised inversion approach that has recently been applied to invert one-dimensional magnetotelluric data. It has the advantages of not requiring a training dataset,being less dependent on the initial model, and being able to obtain the probability distribution of inversion results through multiple inversions.However, it suffers from the issue that the inversion results are not concentrated.Method To address this issue,
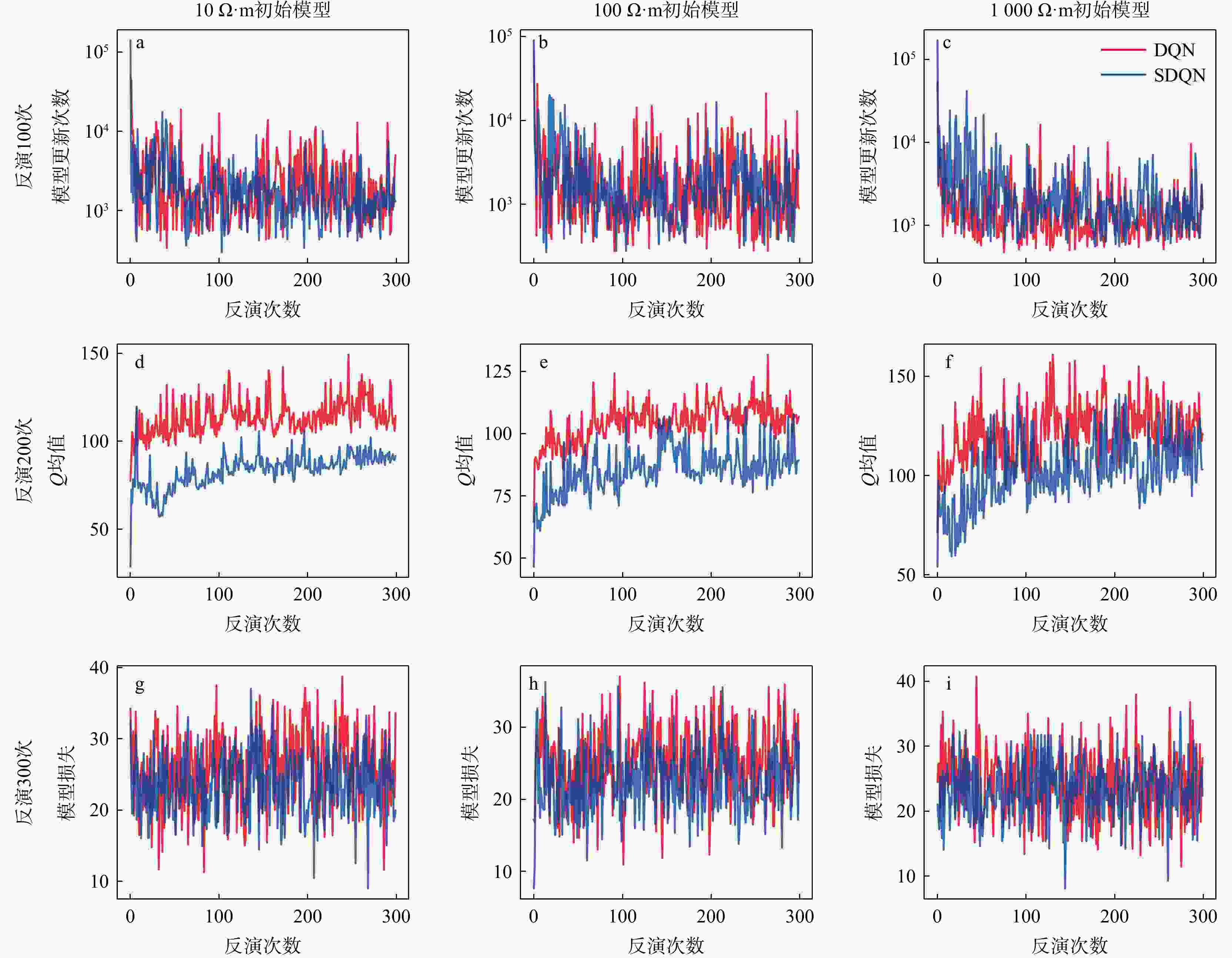
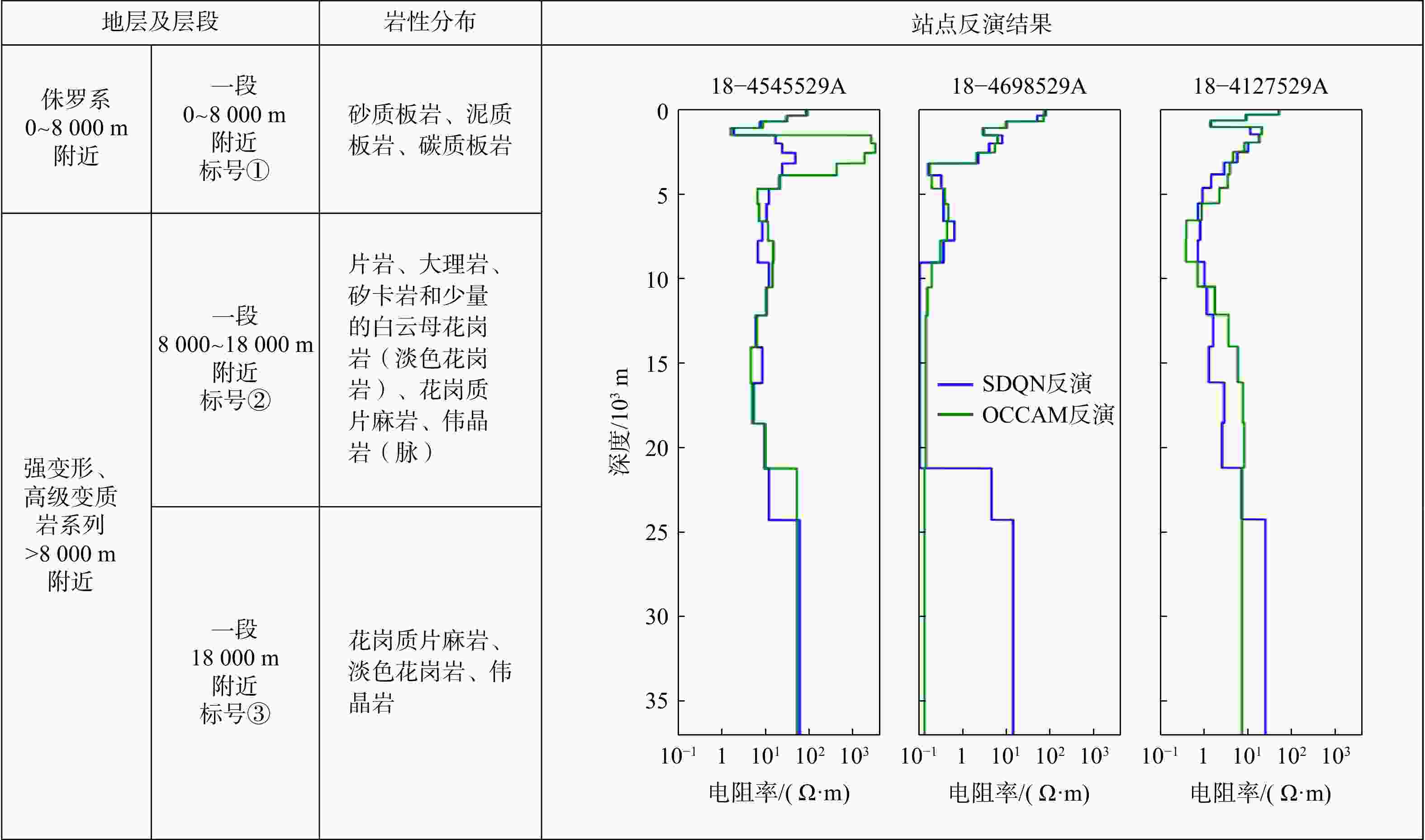
this paper proposes the use of deep reinforcement learning with a smooth constraint to invert magnetotelluric data (Smooth DQN, SDQN) . This method is based on the framework of reinforcement learning,considers the inversion problem as a Markov decision problem, and defines the termsenvironment ,reward ,agent , and so on. Then, the model constraint term of regularized inversion is introduced into the reward function,guiding the agent to continuously adjust the resistivity parameters of the prediction model to obtain results that are more consistent with the model constraints.Results The experimental results of the theoretical model inversion show that, compared with the DQN inversion and Occam inversion methods, the results of the proposed method are more stable when the observed data are inverted with the same number of iterations and different noise levels. The inversion results of the magnetotelluric measured data in the Tashi Kang Mine area of Tibet are
largely consistent with the Occam inversion results and align with the existing geological interpretations.Conclusion The experimental results show that this method has the advantages of more concentrated inversion results and stronger anti-noise capability for the observed data, and it is a new tool for solving the problem of magnetotelluric inversion.
-
Key words:
- Deep Reinforcement Learning /
- Magnetotelluric Inversion /
- Smooth Constraints /
- DQN
-
表 1 SDQN算法超参数设置
Table 1. Hyperparameters in the network.
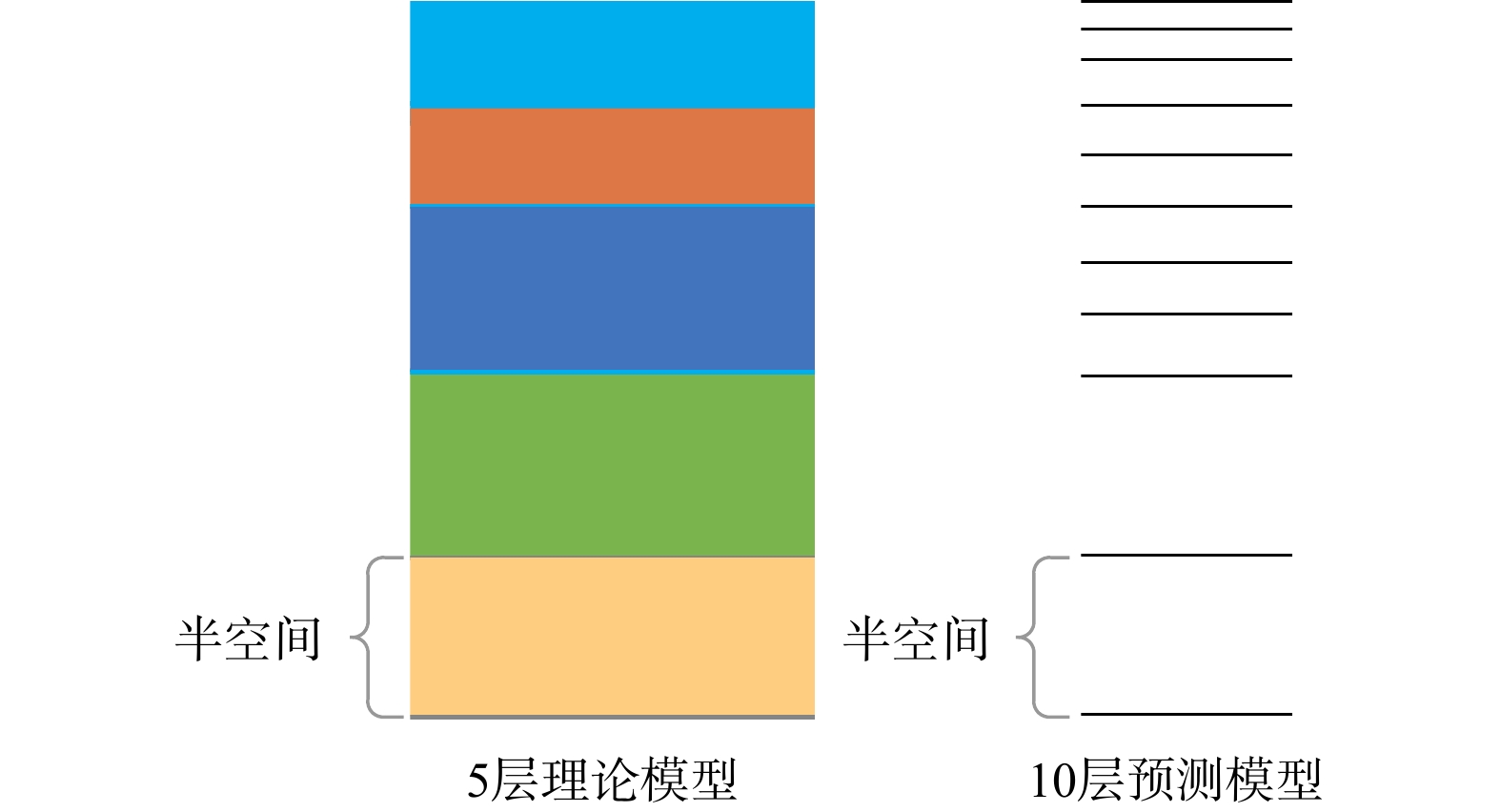
超参数 数值 小批量大小 32 经验池大小 2,500,000 约束网络更新频率 500 折扣因子 0.95 预测网络更新频率 5 学习率 0.0013 探索因子 0.1 表 2 5层理论模型
Table 2. Five-layer synthetic model.
层号 电阻率/(Ω·m) 厚度/m 1 200 1820 2 20 1900 3 100 4535 4 10 2150 5 100 − 表 3 10层预测模型3种初始模型参数设置
Table 3. Three initial model parameter settings for the predictive model
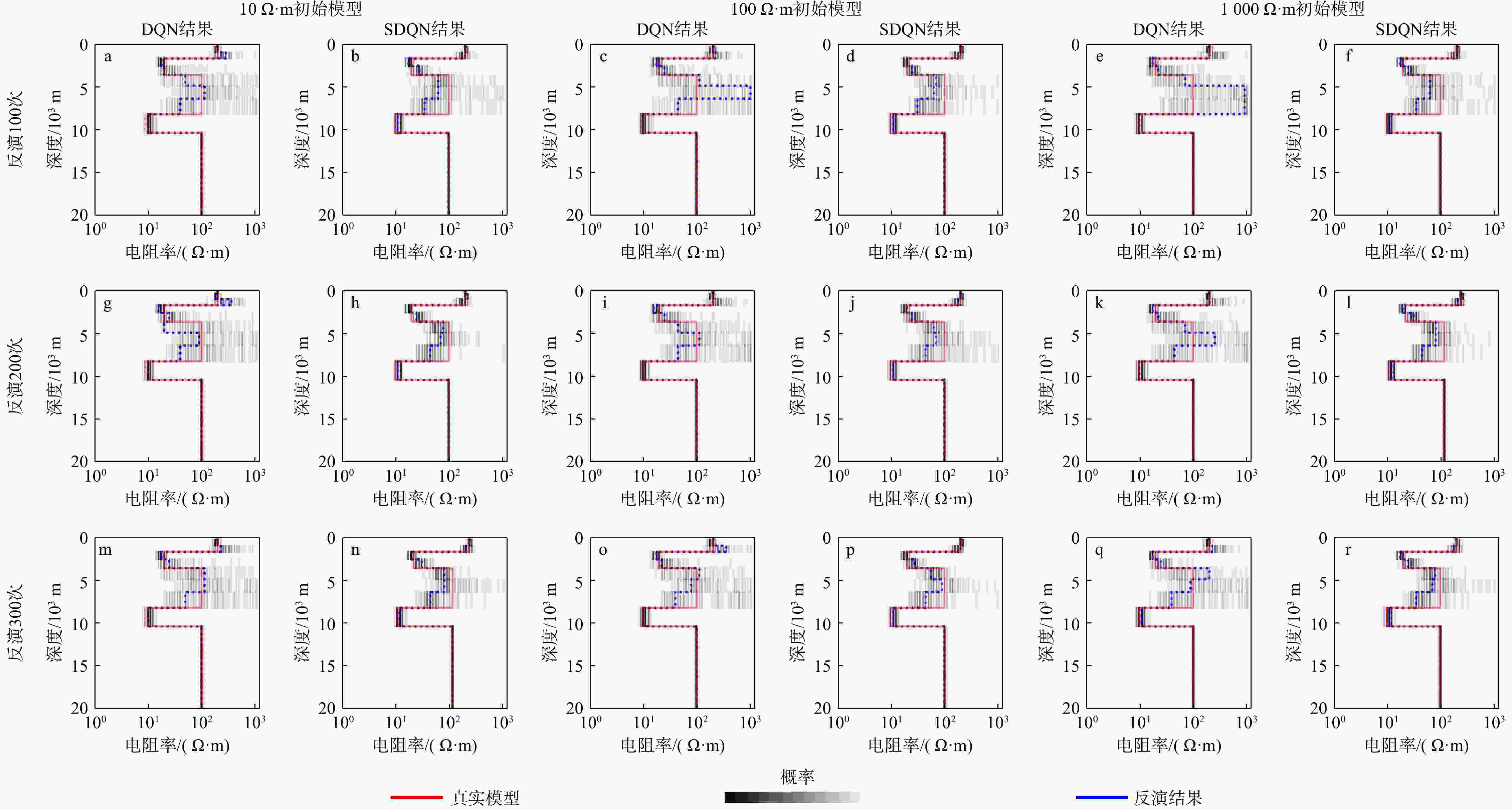
层号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 电阻率/(Ω·m) 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 电阻率/(Ω·m) 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 电阻率/(Ω·m) 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 厚度/m 500 600 720 865 1035 1245 1495 1795 2150 − 表 4 初始模型在100 Ω·m下反演结果的误差和方差
Table 4. Error and variance of the initial model inversion results at 100 Ω·m
反演次数 最终结果的均方误差 所有结果的均方误差的方差 DQN SDQN DQN SDQN 100 99.97 14.23 2532.45 296.60 200 13.355 15.094 3019.32 427.82 300 25.332 12.0845 2134.51 201.47 表 5 8层理论模型电阻率和厚度
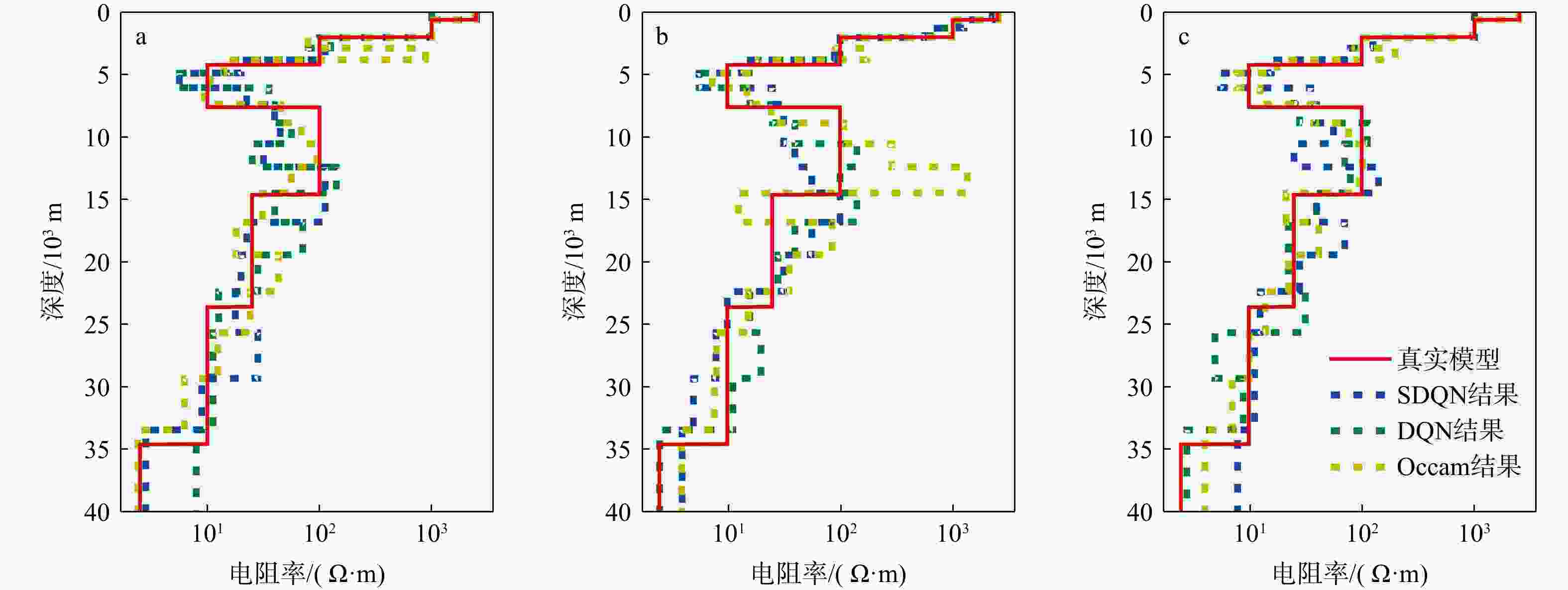
Table 5. Eight-layer synthetic model.
层号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 电阻率/(Ω·m) 2500 1000 100 10 100 25 10 2.5 厚度/m 600 1400 2200 3400 7000 9000 11000 − 表 6 20层预测模型三种初始模型参数设置
Table 6. Three initial model parameter settings for the predictive model
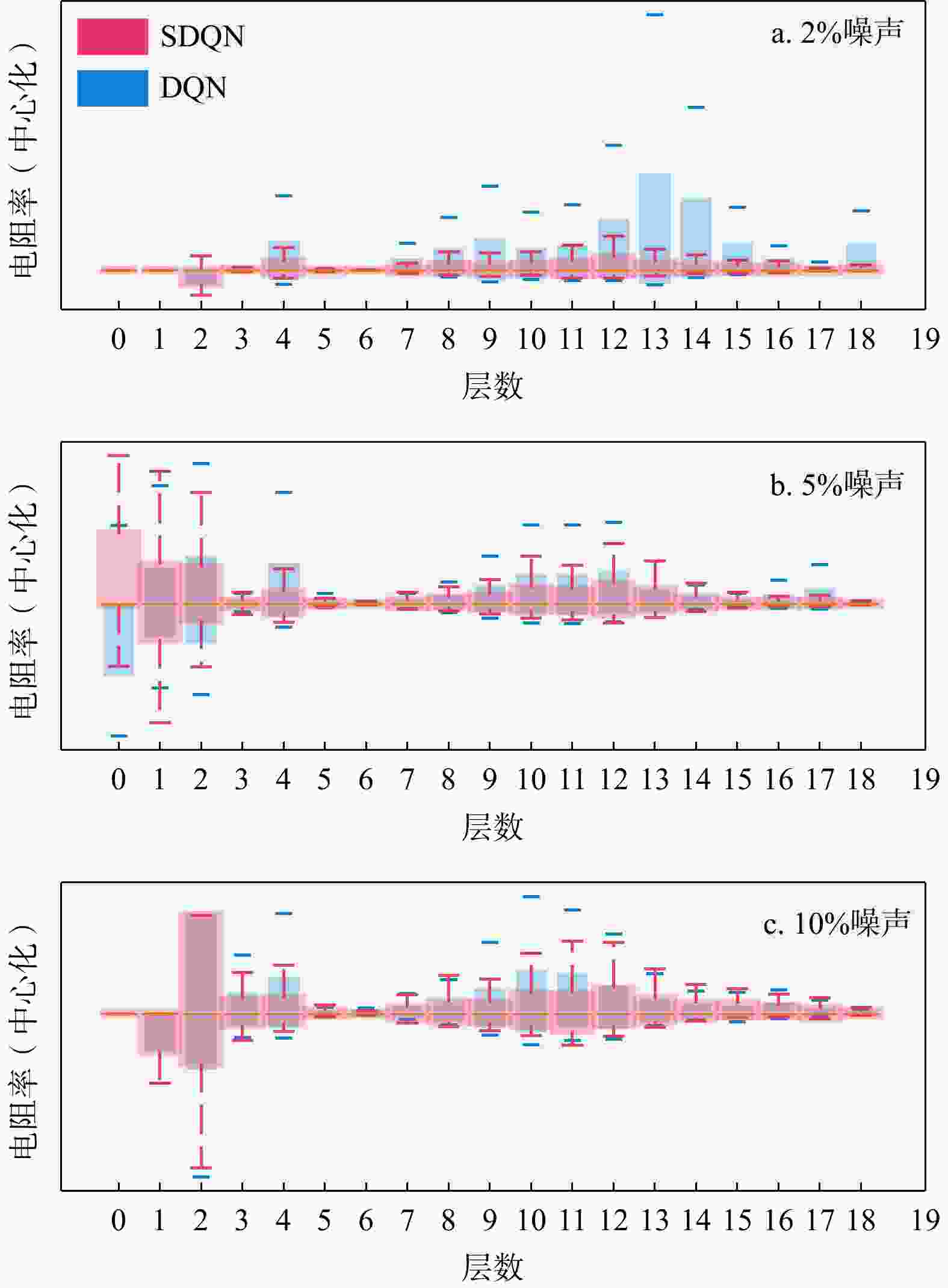
层号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 电阻率/(Ω·m) 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 厚度/m 600 672 752 842 944 1057 1184 1326 1485 1663 1863 2087 2337 2618 2932 3284 3678 4119 4613 − 表 7 5%噪声水平下DQN和SDQN方法的反演时间
Table 7. Inversion time of DQN and SDQN methods at 5% noise level
迭代次数 反演时间/s DQN SDQN 50 3287.29 3562.45 100 4164.09 4520.86 150 4918.86 5144.10 200 5628.15 5745.47 250 6304.54 6299.31 300 6944.33 6841.33 -
[1] 秦策, 刘幸飞, 王绪本, 等. 基于自适应有限元正演的大地电磁法三维反演算法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2022, 65(6): 2311-2325. doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0141QIN C, LIU X F, WANG X B, et al. Three-dimensional inversion of magnetotelluric based on adaptive finite element method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2022, 65(6): 2311-2325. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0141 [2] 董珮瑶, 杜利, 赵磊, 等. 机器学习模型在地热开发水温预测中的应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(3): 388-398. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240063DONG P Y, DU L, ZHAO L, et al. Application of machine learning models for groundwater temperature prediction in geothermal development[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(3): 388-398. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240063 [3] 喻国, 肖骑彬, 李满. 大地电磁二维各向异性反演及其在青藏高原北部的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2021, 64(6): 2108-2126.YU G, XIAO Q B, LI M. Two-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion with anisotropy and its application in the northern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(6): 2108-2126. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 唐荣江, 王绪本, 甘露. 一种利用特征值性质的MT阻尼最小二乘反演[J]. 石油物探, 2017, 56(6): 898-904. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2017.06.016TANG R J, WANG X B, GAN L. A damped least square inversion for MT utilizing eigenvalue property[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2017, 56(6): 898-904. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2017.06.016 [5] 吴小平, 徐果明. 大地电磁数据的Occam反演改进[J]. 地球物理学报, 1998, 41(4): 547-554.WU X P, XU G M. Improvement of Occam's inversion for MT data[J]. Acta Geophysica Sinica, 1998, 41(4): 547-554. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 姜奋勇, 叶益信, 陈海文, 等. 基于非结构网格的带地形MT二维Occam反演及应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(2): 482-489. doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2022.1397JIANG F Y, YE Y X, CHEN H W, et al. Application of 2D inversion of magnetotelluric data bearing terrain information based on an unstructured mesh[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(2): 482-489. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2022.1397 [7] 徐凤姣, 谢兴兵, 郭全仕. 不同极化模式的二维大地电磁非线性共轭梯度反演及应用研究[J]. 石油物探, 2022, 61(1): 174-182.XU F J, XIE X B, GUO Q S. Study and application on the nonlinear conjugate gradient inversion method for 2D Magnetotelluric with different polarization modes[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2022, 61(1): 174-182. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 管贻亮, 李予国, 胡祖志, 等. 大地电磁非线性共轭梯度一维反演[J]. 石油物探, 2014, 53(6): 752-759.GUAN Y L, LI Y G, HU Z Z, et al. Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 1D magnetotelluric inversion[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2014, 53(6): 752-759. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 彭勃, 强思远, 施小清. 基于贝叶斯实验设计优化跨孔高密度电阻率法监测四维水文地质过程[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(5): 293-301. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230600PENG B, QIANG S Y, SHI X Q. Optimizing 4D hydrogeological process monitoring using cross-hole electrical resistivity tomography(CHERT) via Bayesian experimental design[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(5): 293-301. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230600 [10] SEILLÉ H, VISSER G. Bayesian inversion of magnetotelluric data considering dimensionality discrepancies[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2020, 223(3): 1565-1583. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggaa391 [11] LIU X, ZHENG F W. Axis anisotropic Occam's 3D inversion of tensor CSAMT in data space[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2025, 22(2): 252-263. doi: 10.1007/s11770-024-1076-9 [12] NÁDASI E, GRIBENKO A V, ZHDANOV M S. Large-scale inversion of magnetotelluric data using regularized Gauss-Newton method in the data space[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2022, 179(10): 3785-3806. doi: 10.1007/s00024-022-03147-0 [13] 梁生贤, 吾守艾力·肉孜, 廖国忠, 等. 大地电磁线性反演算法比较[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2014, 29(6): 2702-2707.LIANG S X, WUSHOUAILI R Z, LIAO G Z, et al. Comparison and aanalysis of two-dimensional linear algorithm inversion for magnetotelluric[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2014, 29(6): 2702-2707. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 周俊杰, 胡英才, 刘祜, 等. 考虑先验信息的大地电磁模拟退火反演[J]. 地质论评, 2023, 69(增刊1): 465-467. doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2023.s1.201ZHOU J J, HU Y C, LIU H, et al. Inversion of magnetotelluric simulated annealing considering prior information[J]. Geological Review, 2023, 69(S1): 465-467. (in Chinese) doi: 10.16509/j.georeview.2023.s1.201 [15] 潘新朋, 刘志顺, 高大维, 等. 岩石物理驱动的储层物性参数非线性地震反演方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2024, 67(3): 1237-1254.PAN X P, LIU Z S, GAO D W, et al. Rock-physics-driven nonlinear seismic inversion for petrophysical parameters of reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2024, 67(3): 1237-1254. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 熊杰, 孟小红, 刘彩云, 等. 基于差分进化的大地电磁反演[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(3): 448-451.XIONG J, MENG X H, LIU C Y, et al. Magnetotelluric inversion based on differential evolution[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(3): 448-451. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 丁鑫, 郭乙霏, 方宏远, 等. 基于蚁群算法的层状结构介电特性反演方法[J]. 人民黄河, 2019, 41(6): 107-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2019.06.024DING X, GUO Y F, FANG H Y, et al. The inversion method of dielectric properties in layered structure based on ant colony algorithm[J]. Yellow River, 2019, 41(6): 107-110. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2019.06.024 [18] 李丽丽, 李长伟, 程勃, 等. 基于改进粒子群算法的大地电磁反演[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2023, 23(26): 11098-11107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.26.006LI L L, LI C W, CHENG B, et al. Magnetotelluric inversion based on improved particle swarm optimization algorithm[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2023, 23(26): 11098-11107. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2023.26.006 [19] LI R H, GAO L, YU N, et al. Memetic strategy of particle swarm optimization for one-dimensional magnetotelluric inversions[J]. Mathematics, 2021, 9(5): 519. doi: 10.3390/math9050519 [20] 刘高村, 王绪本, 袁崇鑫, 等. Transformer网络在大地电磁反演成像中的应用[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2023, 45(4): 484-496. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2023.04.09LIU G C, WANG X B, YUAN C X, et al. Application of transformer network in magnetotelluric inversion imaging[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 45(4): 484-496. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2023.04.09 [21] XU K J, LIANG S Y, LU Y, et al. Magnetotelluric data inversion based on deep learning with the self-attention mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5917910. [22] GAO C, LI Y B, WANG X Q. AUTL: An attention U-Net transfer learning inversion framework for magnetotelluric data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2024, 21: 3004505. [23] JEVINANI M R, DEHKORDI B H, FERGUSON I J, et al. Correction to: Deep learning-based 1-D magnetotelluric inversion: Performance comparison of architectures[J]. Earth Science Informatics, 2024, 17(2): 1679-1680. doi: 10.1007/s12145-024-01254-1 [24] LIAO X L, ZHANG Z H, YAN Q X, et al. Inversion of 1-D magnetotelluric data using CNN-LSTM hybrid network[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2022, 15(17): 1430. doi: 10.1007/s12517-022-10687-1 [25] CONWAY D, HEINSON G, REES N, et al. Time-lapse inversion of one-dimensional magnetotelluric data[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 2018, 70(1): 27. [26] 李思平, 刘彩云, 熊杰, 等. 基于改进残差网络的大地电磁反演研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(6): 1508-1518. doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2023.0186LI S P, LIU C Y, XIONG J, et al. Magnetotelluric inversion based on an improved residual network[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1508-1518. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11720/wtyht.2023.0186 [27] 王方, 熊杰, 田慧潇, 等. 基于深度学习的大地电磁二维反演方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 344-354. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220471WANG F, XIONG J, TIAN H X, et al. Two-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion method based on deep learning[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 344-354. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220471 [28] 廖晓龙, 张志厚, 姚禹, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的大地电磁反演[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 51(9): 2546-2557.LIAO X L, ZHANG Z H, YAO Y, et al. Magnetotelluric inversion based on convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2020, 51(9): 2546-2557. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 韩盈, 安志国, 底青云, 等. 基于循环神经网络的大地电磁信号噪声压制研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2023, 66(10): 4317-4331. doi: 10.6038/cjg2023R0123HAN Y, AN Z G, DI Q Y, et al. Research on noise suppression of magnetotelluric signal based on recurrent neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2023, 66(10): 4317-4331. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg2023R0123 [30] LI G, GU X J, CHEN C J, et al. Low-frequency magnetotelluric data denoising using improved denoising convolutional neural network and gated recurrent unit[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2024, 62: 5909216. [31] 王永昌, 刘彩云, 熊杰, 等. 基于生成对抗网络的半监督地震波阻抗反演[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(6): 1585-1593.WANG Y C, LIU C Y, XIONG J, et al. Semi-supervised seismic wave impedance inversion based on generative adversarial networks[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(6): 1585-1593. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] YANG B, XU K J, LIU Z. Fuzzy constrained inversion of magnetotelluric data using guided fuzzy C-means clustering[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2021, 42(2): 399-425. doi: 10.1007/s10712-020-09628-y [33] WANG H, LIU Y H, YIN C C, et al. Stochastic inversion of magnetotelluric data using deep reinforcement learning[J]. Geophysics, 2022, 87(1): 49-61. doi: 10.1190/geo2020-0425.1 [34] ZHU X Y, DONG H F. Shear wave velocity estimation based on deep-Q network[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(17): 8919. doi: 10.3390/app12178919 [35] DELL'AVERSANA P. Reinforcement learning in optimization problems. Applications to geophysical data inversion[J]. AIMS Geosciences, 2022, 8(3): 488-502. doi: 10.3934/geosci.2022027 [36] JANG B, KIM M, HARERIMANA G, et al. Q-learning algorithms: A comprehensive classification and applications[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 133653-133667. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2941229 [37] VAN HASSELT H, GUEZ A, SILVER D. Deep reinforcement learning with double Q-learning[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2016, 30(1): 2094-2100. [38] KAMINSKY A. ZondMT1D[CP/OL]. [2025-11-20]. http://zond-geo.com/english/zond-software/electromagnetic-sounding/zondmt1d/. [39] 梁生贤. 扎西康矿集区大地电磁测深数据(2018-2022)[DB/OL]. [2025-11-20]. https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/data/b55ce907-6829-46de-9548-c58f539e69c4/.LIANG S X. Magnetotelluric data of Zhaxikang ore district (2018-2022)[DB/OL]. [2025-11-20]. https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/zh-hans/data/b55ce907-6829-46de-9548-c58f539e69c4/. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 焦彦杰, 黄旭日, 李光明, 等. 藏南扎西康矿集区深部结构与成矿: 来自地球物理的证据[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(6): 2117-2128.JIAO Y J, HUANG X R, LI G M, et al. Deep structure and mineralization of zhaxikang ore-concentration area, south Tibet: Evidence from geophysics[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(6): 2117-2128. (in Chinese with English abstract -




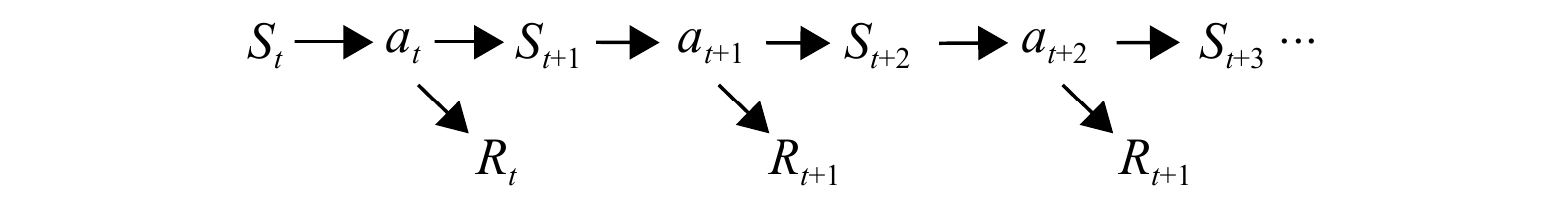
 下载:
下载: