Landslide susceptibility assessment in Shimian County based on time-series InSAR deformation
-
摘要:
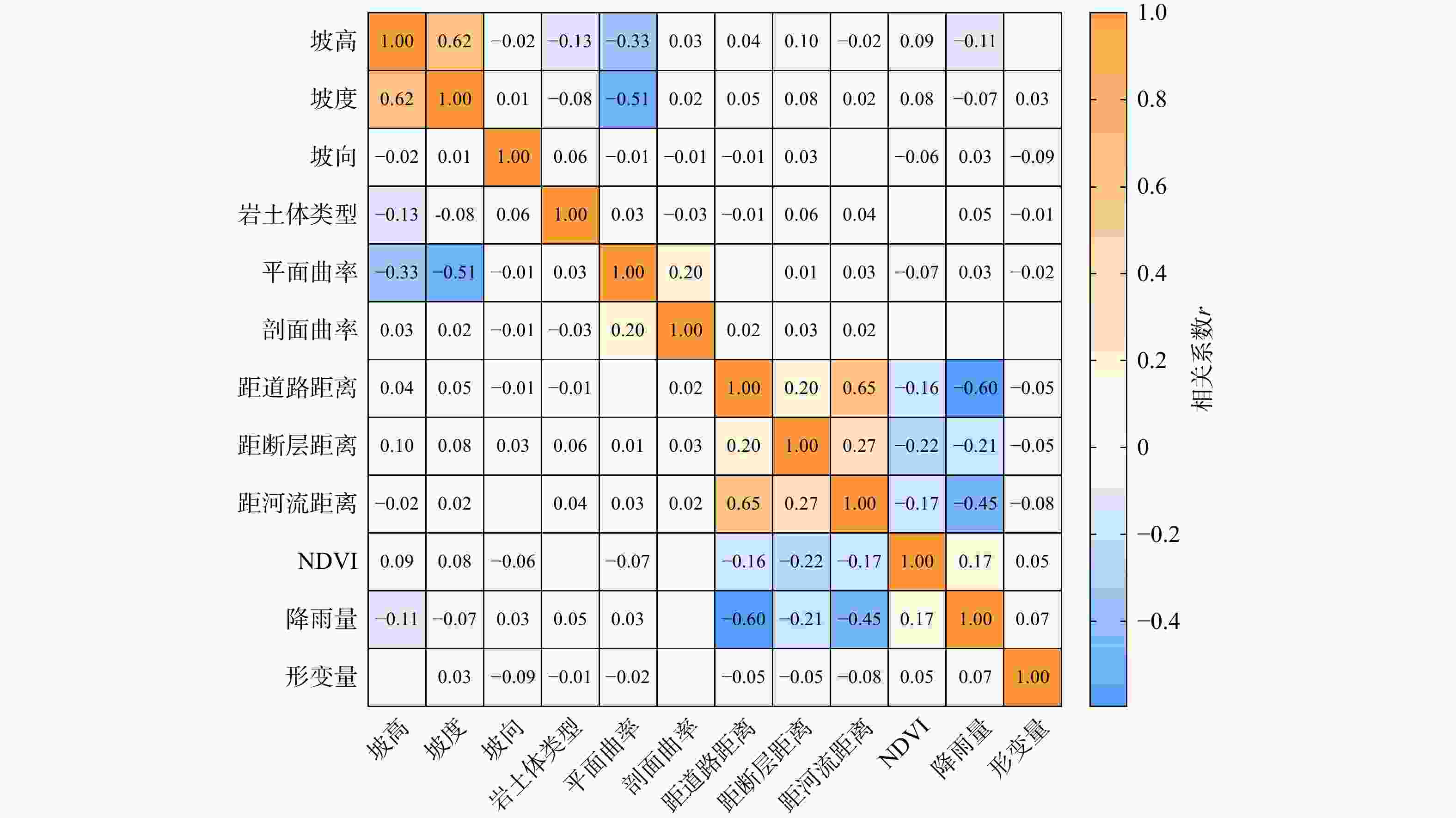
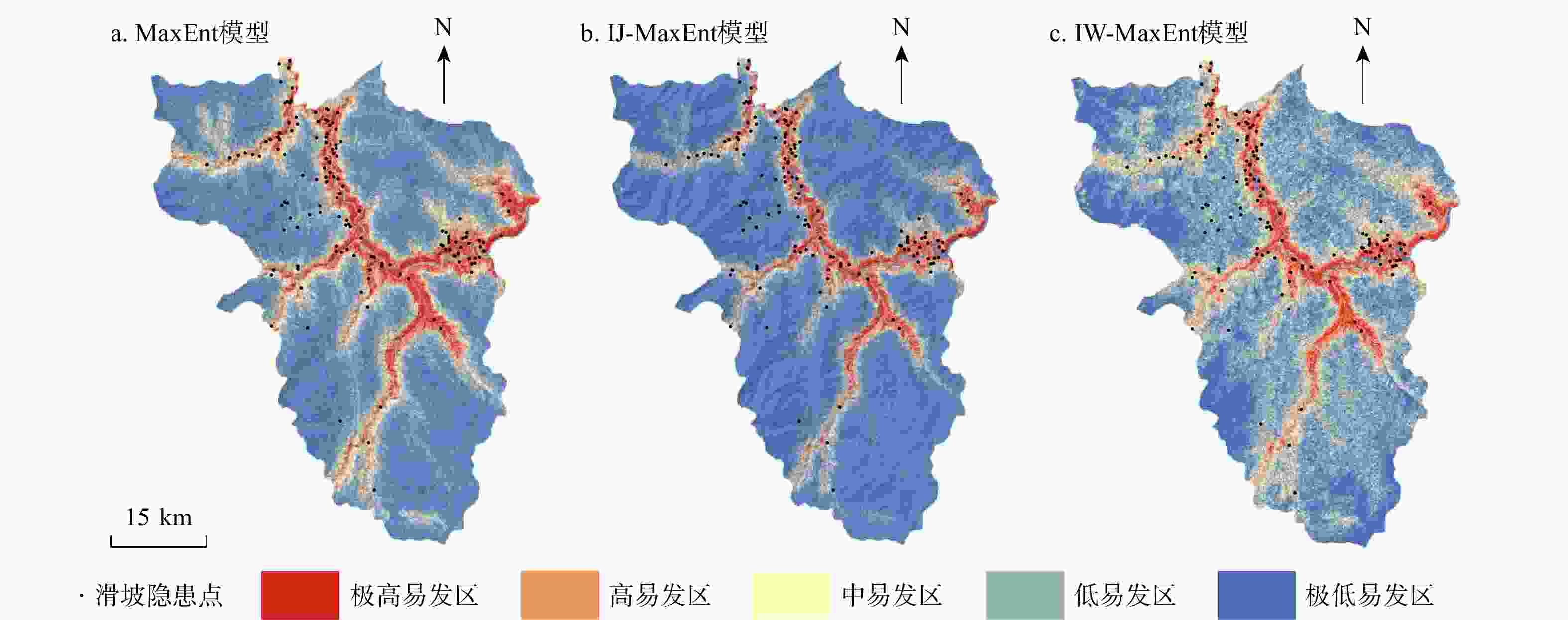
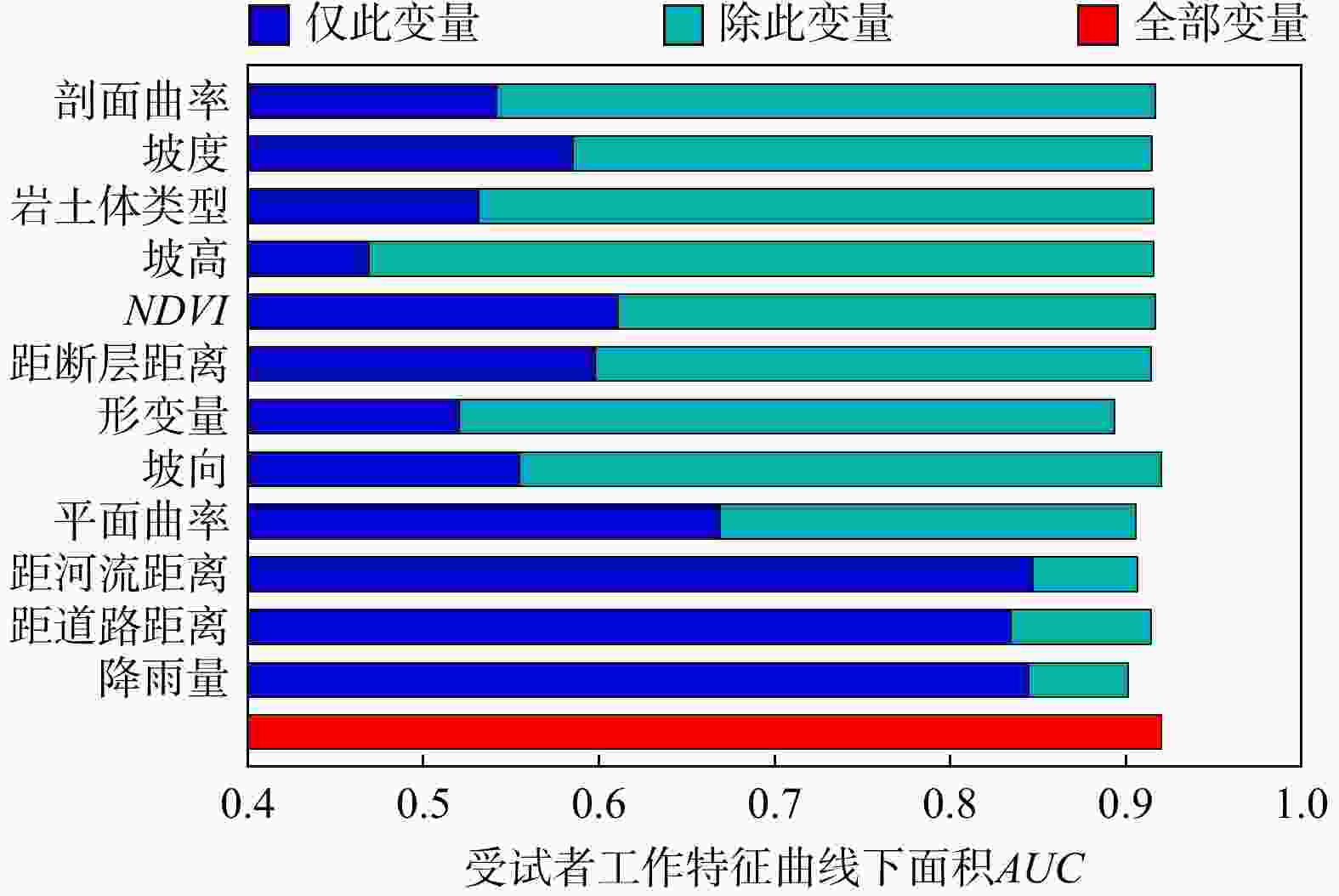
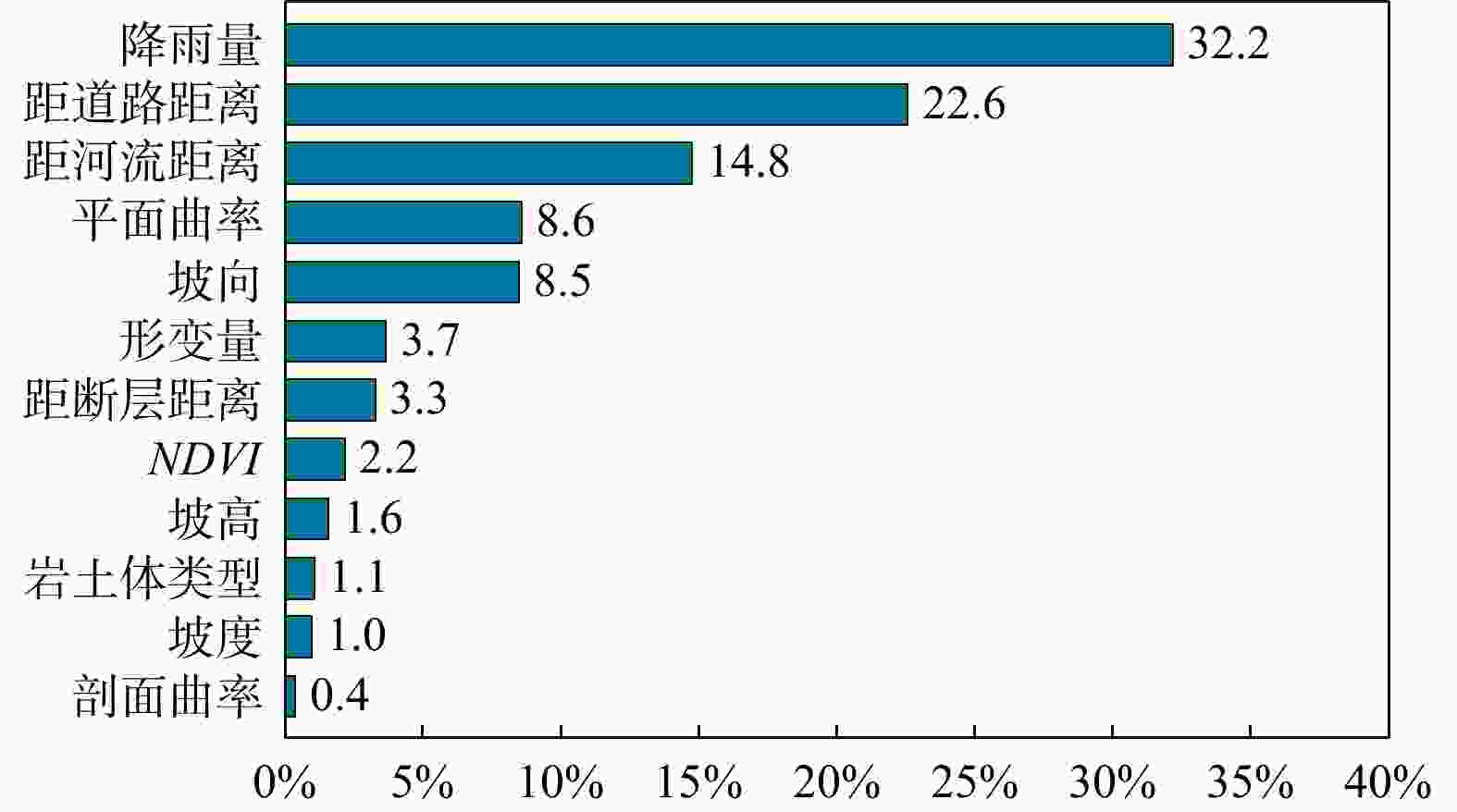
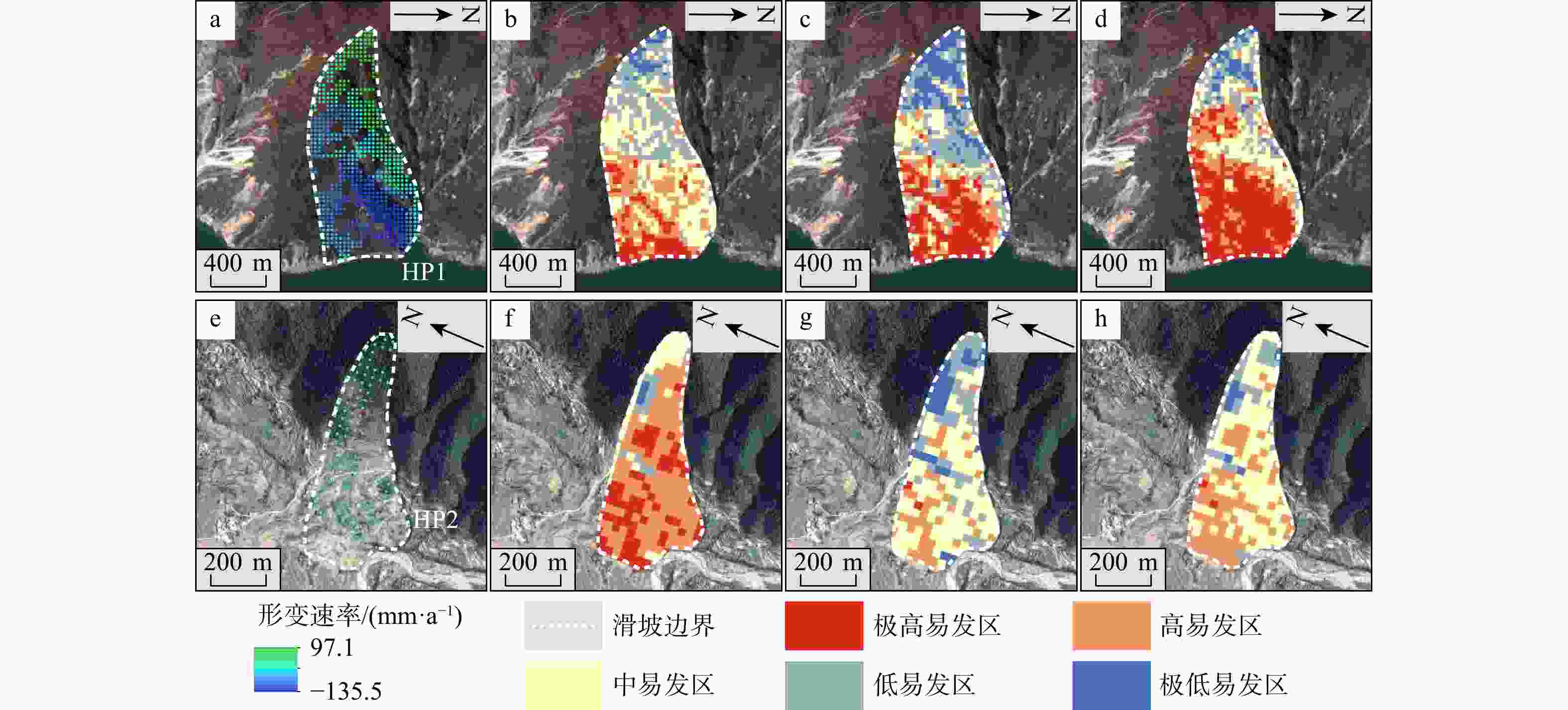
滑坡作为一种对自然和社会环境造成极大破坏的地质灾害,其易发性评价对防灾减灾至关重要。现有的滑坡数据库常作为滑坡易发性评价的数据基础,由于更新不及时,存在时效性差和不全面等问题。此外,传统的滑坡易发性评价方法主要依赖于静态数据(如地形、地质、水文),缺乏动态数据(如地表形变),难以全面捕捉正在变形的滑坡特征,导致评价的可靠性较差。结合光学遥感技术和合成孔径雷达干涉测量技术(interferometric synthetic aperture radar,简称InSAR)识别研究区滑坡并获取地表形变作为动态评价因子,结合静态评价因子,采用联合训练和加权叠加两种方法,耦合最大熵模型(maximum entropy,简称MaxEnt),并使用迭代自组织(Iterative Self-Organizing,简称ISO)聚类算法对石棉县进行了滑坡易发性评价及分区。结果表明:(1)综合光学遥感技术和InSAR技术两种方法,在研究区共识别出139处滑坡,石棉县滑坡灾害高易发区主要分布于河流和道路两侧,滑坡灾害点的分布与所划分区域有很好的吻合性。(2)补充InSAR形变因子在一定程度上提高了6.1%的易发性精度(受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)下面积
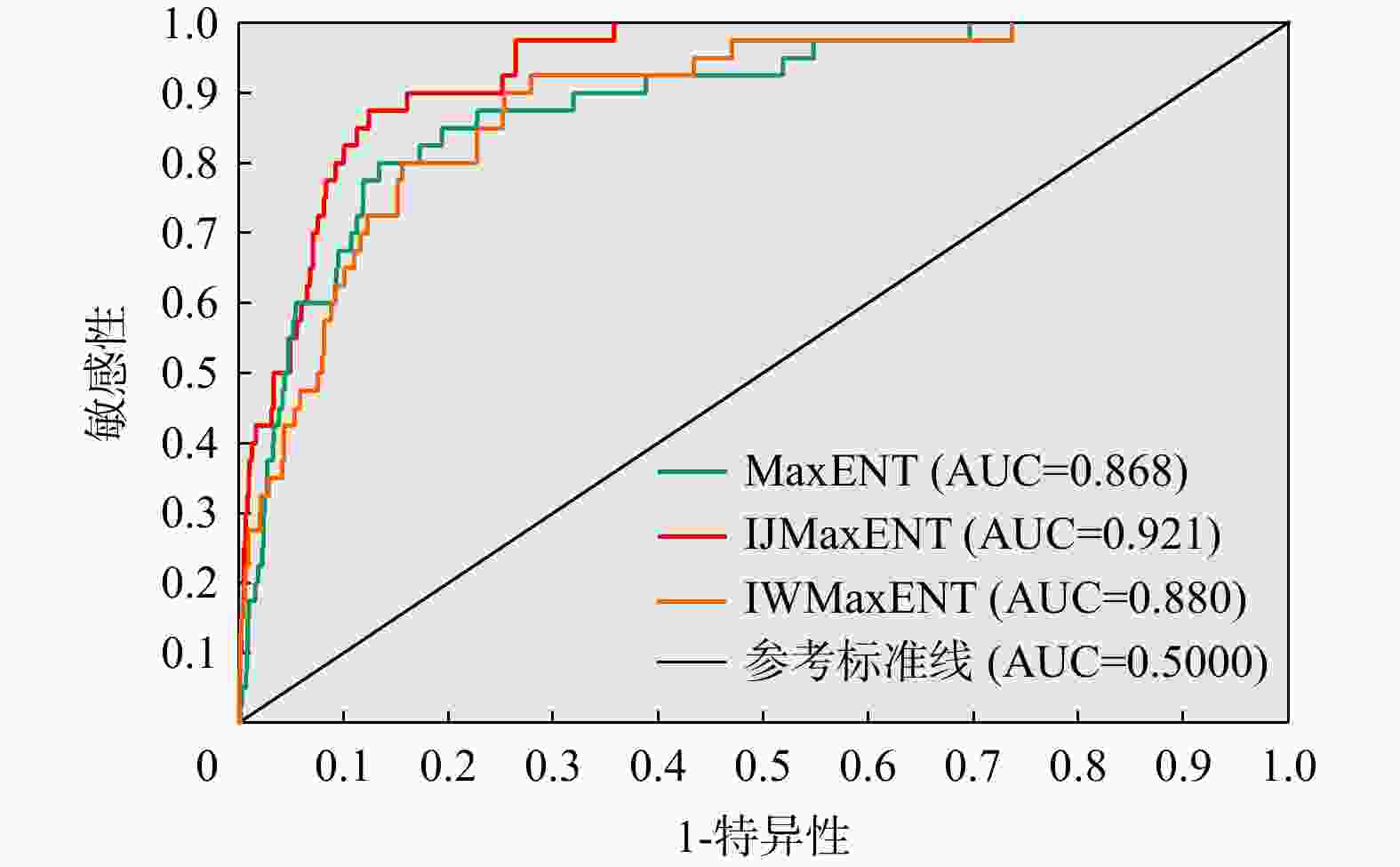
AUC =0.921),同时显著地降低了评估结果中出现假阳性和假阴性的情况,提高了模型的精确性。该研究突出了将InSAR形变信息融入滑坡易发性模型中的优势,可为石棉县滑坡灾害预防提供重要支撑。Abstract:Objective Landslides are geological disasters that cause significant damage to both natural and social environment. Effective landslide susceptibility assessment is crucial for disaster prevention and mitigation. Existing landslide databases are often used as the primary data source for susceptibility assessments. However, due to delays in updates, these databases suffer from issues such as poor timeliness and incompleteness. Moreover, traditional landslide susceptibility assessment methods primarily rely on static data (e.g., topography, geology, and hydrology) and lack dynamic data (e.g., surface deformation), making it difficult to fully characterize the deforming landslides and reducing assessment reliability.
Methods This study combined optical remote sensing technology and synthetic aperture radar interferometry (Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar, InSAR) to identify landslides in the study area and obtain surface deformation as a dynamic evaluation factor. In combination with static evaluation factors, two methods—joint training and weighted superposition—were employed, alongside the Maximum Entropy (MaxEnt) model and the Iterative Self-Organizing (ISO) clustering algorithm to assess and categorize landslide susceptibility in Shimian County.
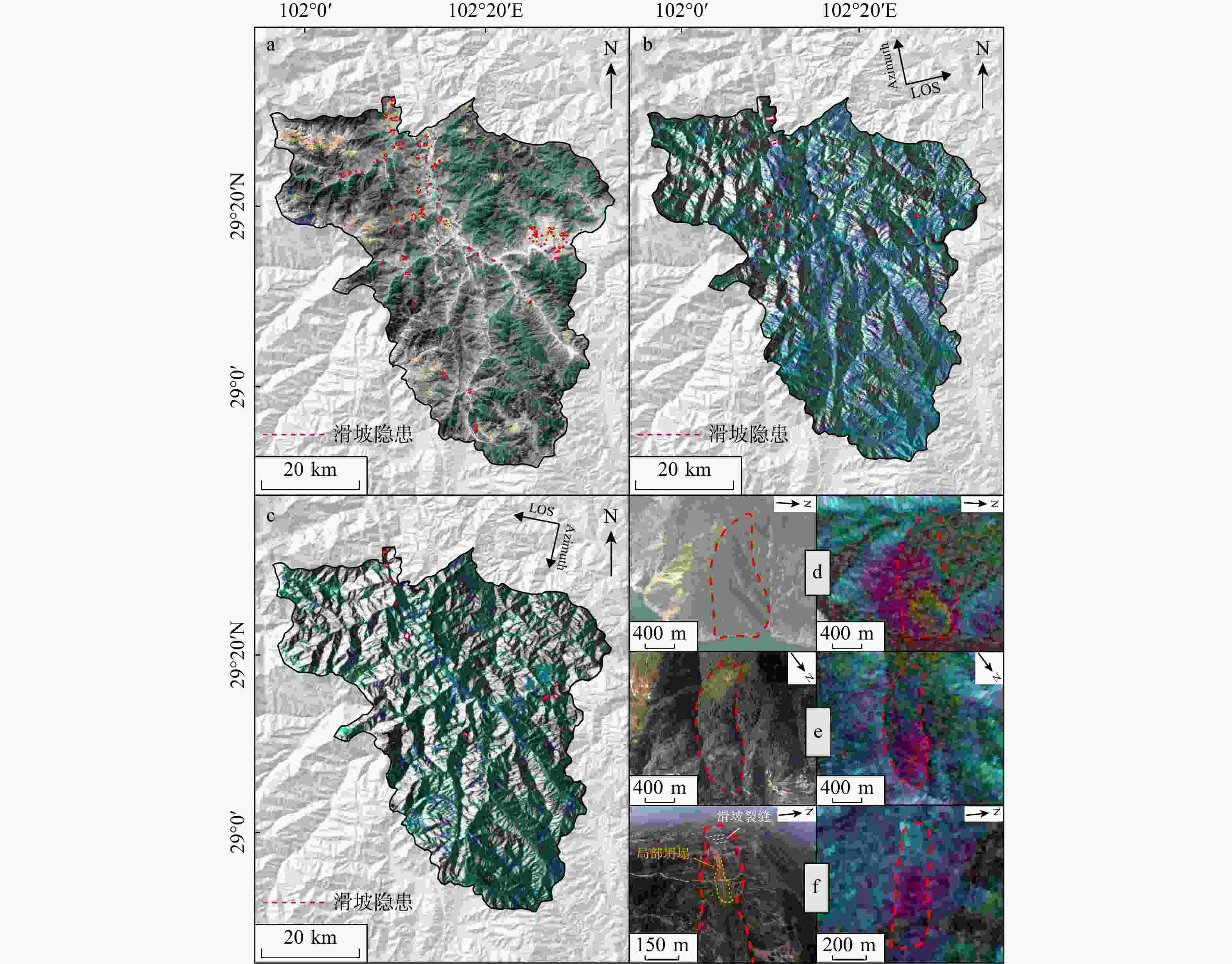
Results The findings are as follows: (1) By integrating optical remote sensing and InSAR technologies, 139 landslides are identified in the study area. High-risk landslide zones in Shimian County are predominantly located along riverbanks and roadsides. The distribution of landslide disaster points aligns well with the zoned areas. (2) Incorporating the InSAR deformation factor enhances the susceptibility accuracy by 6.1% (AUC=0.921) and substantially reduces the occurrence of false positives and false negatives, thereby improving overall model accuracy.
Conclusion This study demonstrates the advantages of incorporating InSAR deformation data into landslide susceptibility models, offering valuable support for landslide disaster prevention in Shimian County.
-
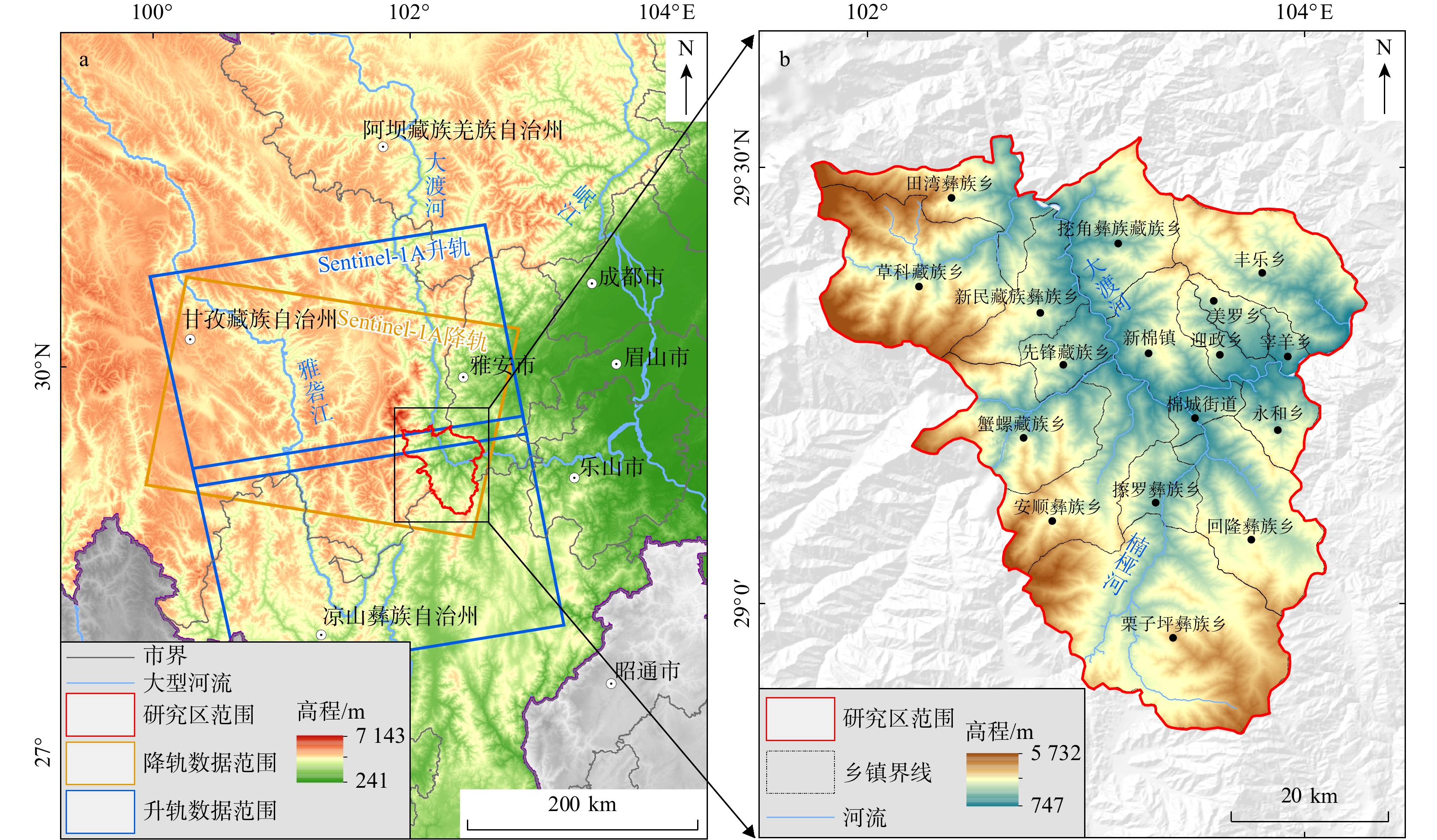
表 1 Sentinel-1A数据基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of Sentinel-1A data
主要参数 基本数据 波长/m 5.6 波段 C波段 轨道方向 升/降轨 重访周期/d 12 d 入射角/(°) 39.80/39.42 成像模式 IW 极化方式 VV 表 2 影响因子数据源
Table 2. Impact factor data source
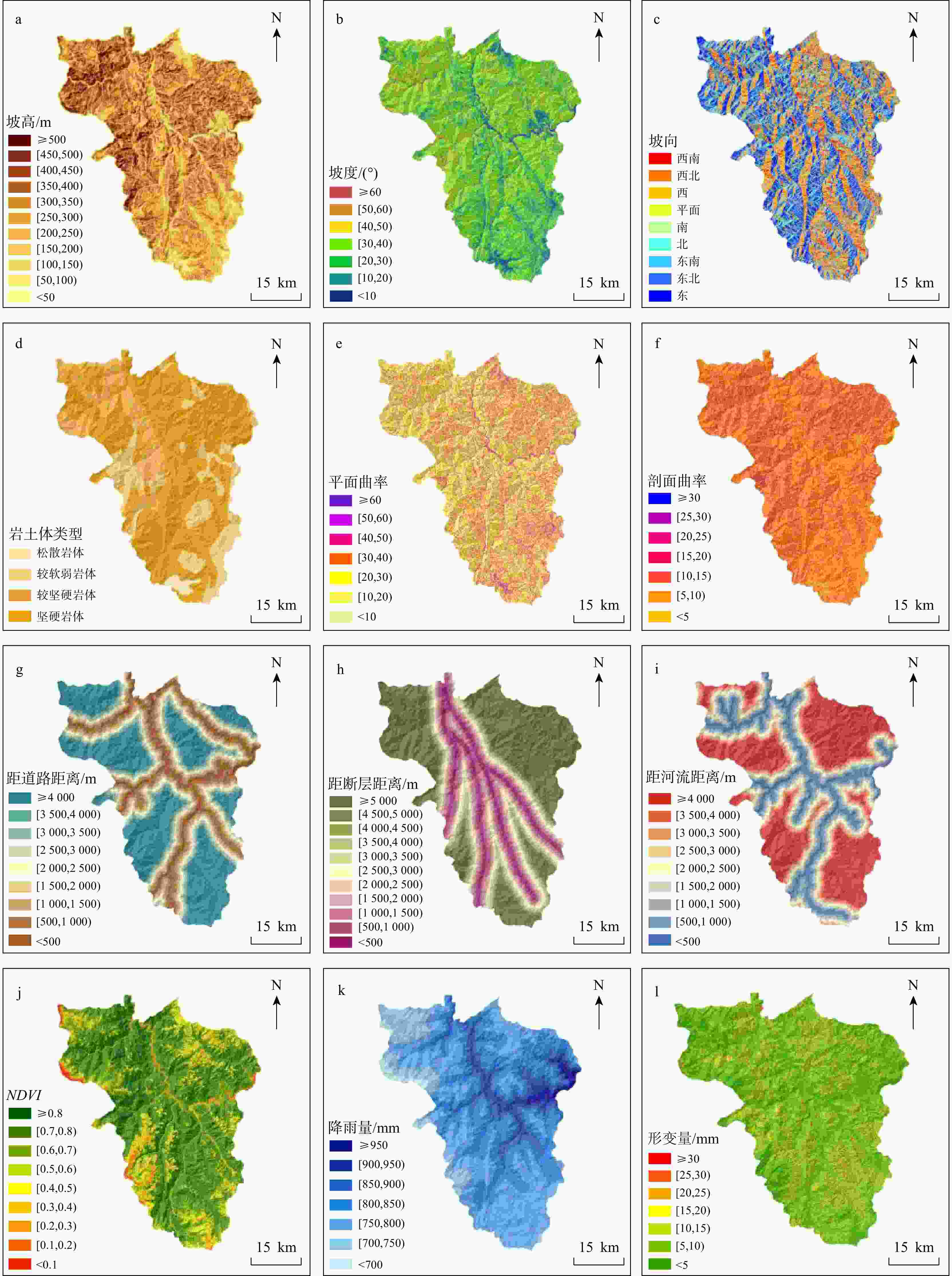
数据名称 类型 分辨率/比例尺 来源 DEM 栅格 30 m https://www.gscloud.cn 岩性 矢量 1∶25万 http://www.ngac.org.cn 断层 降雨量 栅格 30 m https://www.resdc.cn 水系 矢量 1∶25万 https://www.webmap.cn 道路 NDVI 栅格 30 m http://www.nesdc.org.cn SAR影像 栅格 5 m×20 m https://search.asf.alaska.edu 表 3 三种模型滑坡灾害点分布对比表
Table 3. Comparison of landslide hazard point distribution in three models.
模型 易发性等级 滑坡数
量/个滑坡比
例/%面积比
例/%单位面积内已有滑坡点
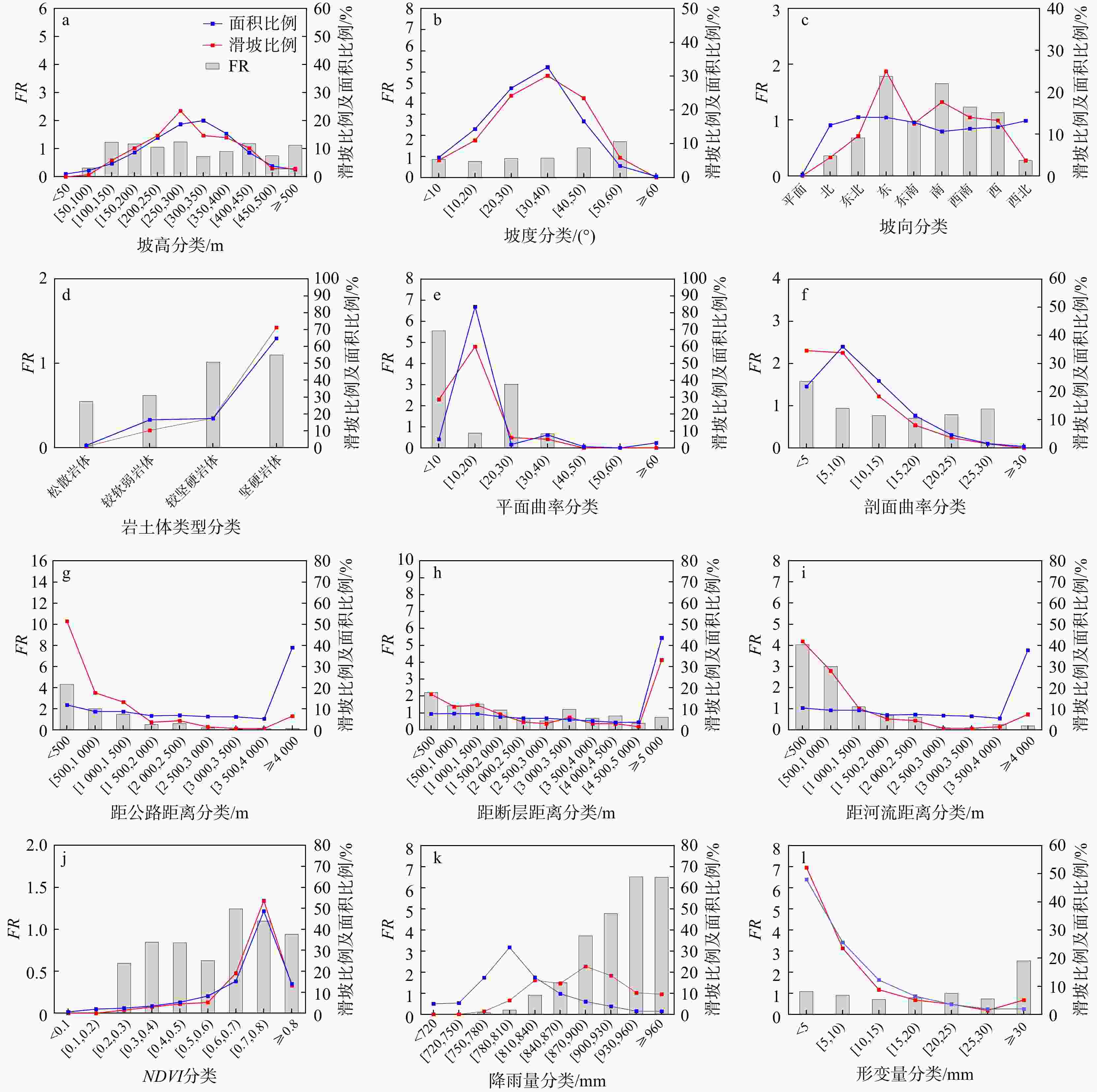
个数/(个·10−1 km−2)MaxEnt 极低易发性 8 5.76 49.30 0.1 低易发性 11 7.91 26.05 0.2 中易发性 9 6.47 10.51 0.3 高易发性 26 18.71 6.58 1.5 极高易发性 85 61.15 7.56 4.2 IJMaxEnt 极低易发性 11 7.91 72.62 0.1 低易发性 18 12.95 13.19 0.5 中易发性 15 10.79 5.12 1.1 高易发性 22 15.83 3.59 2.3 极高易发性 73 52.52 5.48 5.0 IWMaxEnt 极低易发性 6 4.32 40.67 0.0 低易发性 8 5.76 30.42 0.1 中易发性 16 11.51 15.99 0.4 高易发性 38 27.33 7.55 1.9 极高易发性 71 51.08 5.37 4.9 -
[1] 许强, 汤明高, 徐开祥, 等. 滑坡时空演化规律及预警预报研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(6): 1104-1112. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.06.003XU Q, TANG M G, XU K X, et al. Research on space-time evolution laws and early warning-prediction of landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(6): 1104-1112. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.06.003 [2] 许强, 董秀军, 李为乐. 基于天−空−地一体化的重大地质灾害隐患早期识别与监测预警[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(7): 957-966.XU Q, DONG X J, LI W L. Integrated space-air-ground early detection, monitoring and warning system for potential catastrophic geohazards[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 957-966. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 许强, 陆会燕, 李为乐, 等. 滑坡隐患类型与对应识别方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2022, 47(3): 377-387.XU Q, LU H Y, LI W L, et al. Types of potential landslide and corresponding identification technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2022, 47(3): 377-387. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 中华人民共和国应急管理部. 国家减灾委员会关于印发《“十四五”国家综合防灾减灾规划》的通知: 国减发〔2022〕1号[EB/OL]. (2022-06-19)[2024-06-05]. https://www.mem.gov.cn/gk/zfxxgkpt/fdzdgknr/202207/t20220721_418698.shtml.Ministry of Emergency Management of the People's Republic of China. The National Disaster Reduction Commission on the issuance of the "14th five year plan for national comprehensive disaster prevention and reduction": Guo Jian Fa [2022] No. 1 [EB/OL] (2022-06-19) [2024-06-05] https://www.mem.gov.cn/gk/zfxxgkpt/fdzdgknr/202207/t20220721_418698.shtml. (in Chinese [5] 戴岚欣, 许强, 范宣梅, 等. 2017年8月8日四川九寨沟地震诱发地质灾害空间分布规律及易发性评价初步研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2017, 25(4): 1151-1164.DAI L X, XU Q, FAN X M, et al. A preliminary study on spatial distribution patterns of landslides triggered by Jiuzhaigou earthquake in Sichuan on August 8th, 2017 and their susceptibility assessment[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(4): 1151-1164. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 盖侨侨, 孙倩, 张宁, 等. 融合时序InSAR形变的白银市地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2024, 49(8): 1434-1443.GAI Q Q, SUN Q, ZHANG N, et al. Evaluation of geological hazard susceptibility of Baiyin City based on MT-InSAR deformation measurements[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2024, 49(8): 1434-1443. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 张伟, 陈宏, 纪成亮, 等. 基于升降轨InSAR数据的高山峡谷区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(2): 94-103.ZHANG W, CHEN H, JI C L, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment in the alpine and canyon areas based on ascending and descending InSAR data[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(2): 94-103. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 郭衍昊, 窦杰, 向子林, 等. 基于优化负样本采样策略的梯度提升决策树与随机森林的汶川同震滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(3): 251-265.GUO Y H, DOU J, XIANG Z L, et al. Susceptibility evaluation of Wenchuan coseismic landslides by gradient boosting decision tree and random forest based on optimal negative sample sampling strategies[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(3): 251-265. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 田尤, 陈龙, 黄海, 等. 藏东察雅县城地质灾害风险评价及源头管控对策建议[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2024, 35(2): 146-154.TIAN Y, CHEN L, HUANG H, et al. Geological hazard risk assessment and suggestions for risk control in Chaya County, eastern Xizang[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2024, 35(2): 146-154. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 卢佳燕, 李为乐, 刘刚, 等. 米林震后地质灾害空间分布特征及易发性分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2019, 28(2): 183-190.LU J Y, LI W L, LIU G, et al. Spatial distribution and susceptibility analysis of geological disasters triggered by the Milin earthquake[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2019, 28(2): 183-190. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 陆会燕, 李为乐, 许强, 等. 光学遥感与InSAR结合的金沙江白格滑坡上下游滑坡隐患早期识别[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2019, 44(9): 1342-1354.LU H Y, LI W L, XU Q, et al. Early detection of landslides in the upstream and downstream areas of the Baige landslide, the Jinsha River based on optical remote sensing and InSAR technologies[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(9): 1342-1354. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 许强, 朱星, 李为乐, 等. “天−空−地” 协同滑坡监测技术进展[J]. 测绘学报, 2022, 51(7): 1416-1436. doi: 10.11947/j.issn.1001-1595.2022.7.chxb202207027XU Q, ZHU X, LI W L, et al. Technical progress of space-air-ground collaborative monitoring of landslide[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2022, 51(7): 1416-1436. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11947/j.issn.1001-1595.2022.7.chxb202207027 [13] 宋家苇, 杨莹辉, 许强, 等. 滑坡灾害InSAR早期识别关键技术方法研究[J/OL]. 工程地质学报, 2024, 32(3): 963-977.SONG J W, YANG Y H, XU Q, et al. Research on key theoretical methods for early landslide detection using InSAR technology[J/OL]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2024, 32(3): 963-977(in Chinese with English abstract [14] MWAKAPESA D S, LAN X J, MAO Y M. Landslide susceptibility assessment using deep learning considering unbalanced samples distribution[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(9): e30107. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30107 [15] LIU X K, SHAO S, SHAO S J. Landslide susceptibility prediction and mapping in Loess Plateau based on different machine learning algorithms by hybrid factors screening: Case study of Xunyi County, Shaanxi Province, China[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2024, 74(1): 192-210. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2024.03.074 [16] HUANG X H, GUO F, DENG M L, et al. Understanding the deformation mechanism and threshold reservoir level of the floating weight-reducing landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China[J]. Landslides, 2020, 17(12): 2879-2894. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01435-1 [17] 陈宝林, 李为乐, 陆会燕, 等. 基于SBAS-InSAR的黄河干流军功古滑坡形变分析[J/OL]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2024, 49(8): 1407-1421.CHEN B L, LI W L, LU H Y, et al. Deformation analysis of Jungong ancient landslide based on SBAS-InSAR technology in the Yellow River mainstream[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2024, 49(8): 1407-1421(in Chinese with English abstract [18] DAI C, LI W L, LU H Y, et al. Landslide hazard assessment method considering the deformation factor: A case study of Zhouqu, Gansu Province, northwest China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15(3): 596. doi: 10.3390/rs15030596 [19] SHAN Y F, XU Z, ZHOU S S, et al. Landslide hazard assessment combined with InSAR deformation: A case study in the Zagunao River Basin, Sichuan Province, southwestern China[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16(1): 99. [20] 于淼, 邢会歌, 胡士瑜. 基于信息量−逻辑回归模型的泥石流易发性评价: 以四川省石棉县为例[J]. 人民长江, 2021, 52(12): 107-114.YU M, XING H G, HU S Y. Debris flow susceptibility assessment based on information value and logistic regression coupled model: Case of Shimian County, Sichuan Province[J]. Yangtze River, 2021, 52(12): 107-114. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] HONG H Y, POURGHASEMI H R, POURTAGHI Z S. Landslide susceptibility assessment in Lianhua County (China): A comparison between a random forest data mining technique and bivariate and multivariate statistical models[J]. Geomorphology, 2016, 259: 105-118. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.02.012 [22] AYALEW L, YAMAGISHI H. The application of GIS-based logistic regression for landslide susceptibility mapping in the Kakuda-Yahiko Mountains, Central Japan[J]. Geomorphology, 2005, 65(1/2): 15-31. [23] SUN D L, GU Q Y, WEN H J, et al. Assessment of landslide susceptibility along mountain highways based on different machine learning algorithms and mapping units by hybrid factors screening and sample optimization[J]. Gondwana Research, 2023, 123: 89-106. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2022.07.013 [24] 段钊, 赵法锁, 陈新建. 陕北黄土高原区崩塌发育类型及影响因素分析: 以吴起县为例[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2012, 21(6): 142-149.DUAN Z, ZHAO F S, CHEN X J. Types and influencing factors of collapse development in Loess Plateau region of north Shaanxi: A case study of Wuqi County[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2012, 21(6): 142-149. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 吴昊, 裴向军, 崔圣华, 等. 强震山区滑坡发育分布的地形地质控制作用研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(5): 972-986.WU H, PEI X J, CUI S H, et al. Study of topographic and geological controls on landslide development and distribution within mountainous regions influenced by strong earthquakes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(5): 972-986. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 罗路广, 裴向军, 黄润秋. 强震山区地震滑坡发生概率研究: 以九寨沟国家地质公园为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2020, 39(10): 2079-2093.LUO L G, PEI X J, HUANG R Q. Earthquake-triggered landslide occurrence probability in strong seismically mountainous areas: A case study of Jiuzhaigou National Geopark[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(10): 2079-2093. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 杜国梁, 邹玲, 杨志华, 等. 雅鲁藏布江大拐弯地区滑坡发育分布特征及其对地貌演化的响应[J]. 地质学报, 2024, 98(10): 3062-3076.DU G L, ZOU L, YANG Z H, et al. A study on the development and distribution characteristics of landslides in the region of the Grand Bend of the Varlung Zangbo River and their response to geomorphic evolution[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2024, 98(10): 3062-3076. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 郭子正, 何俊, 黄达, 等. 降雨诱发浅层滑坡危险性的快速评估模型及应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(5): 1188-1201.GUO Z Z, HE J, HUANG D, et al. Fast assessment model for rainfall-induced shallow landslide hazard and application[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(5): 1188-1201. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 王高峰, 李浩, 田运涛, 等. 甘肃省白龙江流域典型高位堆积层滑坡成因机制研究及其危险性预测[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2023, 42(4): 1003-1018.WANG G F, LI H, TIAN Y T, et al. Study on the formation mechanism and risk prediction of high-level accumulation landslides in Bailongjiang River Basin, Gansu Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, 42(4): 1003-1018. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] KARIMZADEH S. Characterization of land subsidence in Tabriz Basin (NW Iran) using InSAR and watershed analyses[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Geophysica, 2016, 51(2): 181-195. doi: 10.1007/s40328-015-0118-4 [31] PHILLIPS S J, DUDÍK M, SCHAPIRE R E. A maximum entropy approach to species distribution modeling[C]//Anon. Twenty-First International Conference on Machine Learning - ICML '04. July 4-8, 2004. Banff, Alberta, Canada: ACM, 2004: 83. [32] PHILLIPS S J, ANDERSON R P, SCHAPIRE R E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions[J]. Ecological Modelling, 2006, 190(3/4): 231-259. [33] PHILLIPS S J, DUDÍK M. Modeling of species distributions with maxent: New extensions and a comprehensive evaluation[J]. Ecography, 2008, 31(2): 161-175. doi: 10.1111/j.0906-7590.2008.5203.x [34] FELICÍSIMO Á M, CUARTERO A, REMONDO J, et al. Mapping landslide susceptibility with logistic regression, multiple adaptive regression splines, classification and regression trees, and maximum entropy methods: A comparative study[J]. Landslides, 2013, 10(2): 175-189. doi: 10.1007/s10346-012-0320-1 [35] PARK N W. Using maximum entropy modeling for landslide susceptibility mapping with multiple geoenvironmental data sets[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 73(3): 937-949. doi: 10.1007/s12665-014-3442-z [36] KORNEJADY A, OWNEGH M, BAHREMAND A. Landslide susceptibility assessment using maximum entropy model with two different data sampling methods[J]. Catena, 2017, 152: 144-162. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2017.01.010 [37] DU B Y, WANG Z Q, LI X Y, et al. Adaptation of tree species in the greater khingan range under climate change: Ecological strategy differences between Larix gmelinii and quercus mongolica[J]. Forests, 2024, 15(2): 283. doi: 10.3390/f15020283 [38] LIU B X, LIU Z Q, CHEN Y, et al. Potential distribution of Crassostrea sikamea (Amemiya, 1928) along coastal China under global climate change[J]. Global Ecology and Conservation, 2024, 50: e02843. doi: 10.1016/j.gecco.2024.e02843 [39] DEVARA M, TIWARI A, DWIVEDI R. Landslide susceptibility mapping using MT-InSAR and AHP enabled GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis[J]. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 2021, 12(1): 675-693. doi: 10.1080/19475705.2021.1887939 [40] CAO C, ZHU K X, XU P H, et al. Refined landslide susceptibility analysis based on InSAR technology and UAV multi-source data[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 368: 133146. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133146 [41] WANG J, CHENG W M, ZHOU C H, et al. Automatic mapping of lunar landforms using DEM-derived geomorphometric parameters[J]. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2017, 27(11): 1413-1427. doi: 10.1007/s11442-017-1443-z [42] 王启盛, 熊俊楠, 程维明, 等. 耦合统计方法、机器学习模型和聚类算法的滑坡易发性评价方法[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2024, 26(3): 620-637. doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2024.230427WANG Q S, XIONG J N, CHENG W M, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping methods coupling with statistical methods, machine learning models and clustering algorithms[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2024, 26(3): 620-637. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2024.230427 [43] 曹文庚, 潘登, 徐郅杰, 等. 河南省滑坡灾害易发性制图研究: 多种机器学习模型的对比[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(1): 101-111.CAO W G, PAN D, XU Z J, et al. Landslide disaster vulnerability mapping study in Henan Province: Comparison of different machine learning models[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(1): 101-111. (in Chinese with English abstract [44] GAO H, QIAN Q Q, DENG X Q, et al. Predicting the distributions of morus notabilis C. K. schneid under climate change in China[J]. Forests, 2024, 15(2): 352. doi: 10.3390/f15020352 -




 下载:
下载: