Construction and application of earthquake disaster knowledge graph fusing with multimodal data
-
摘要:
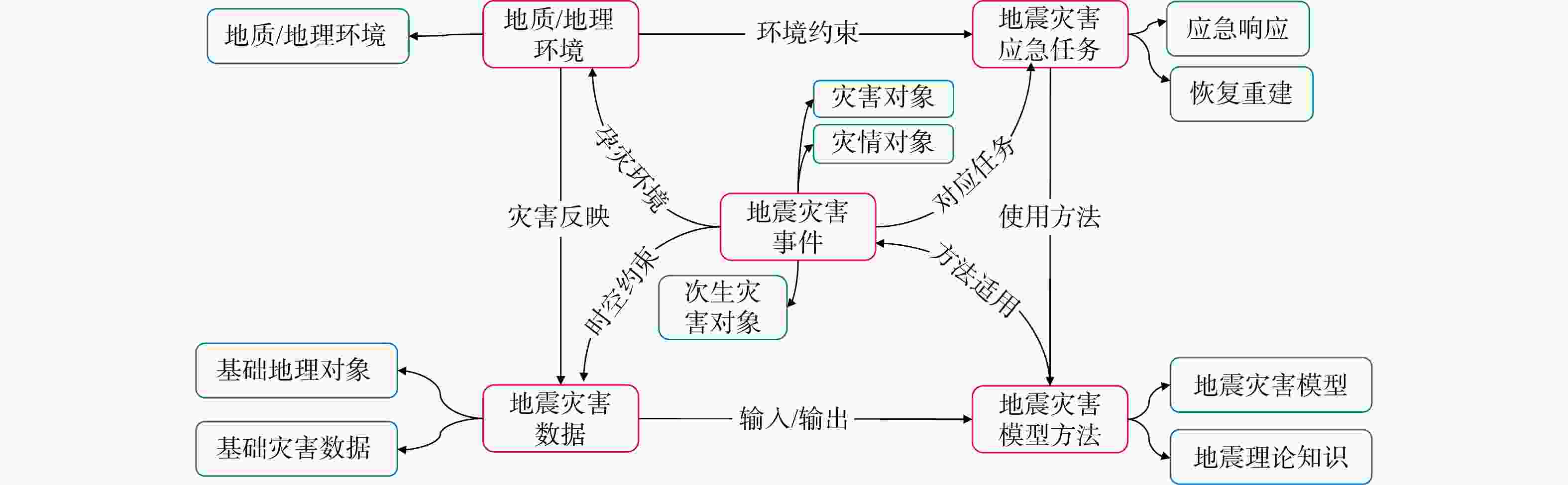
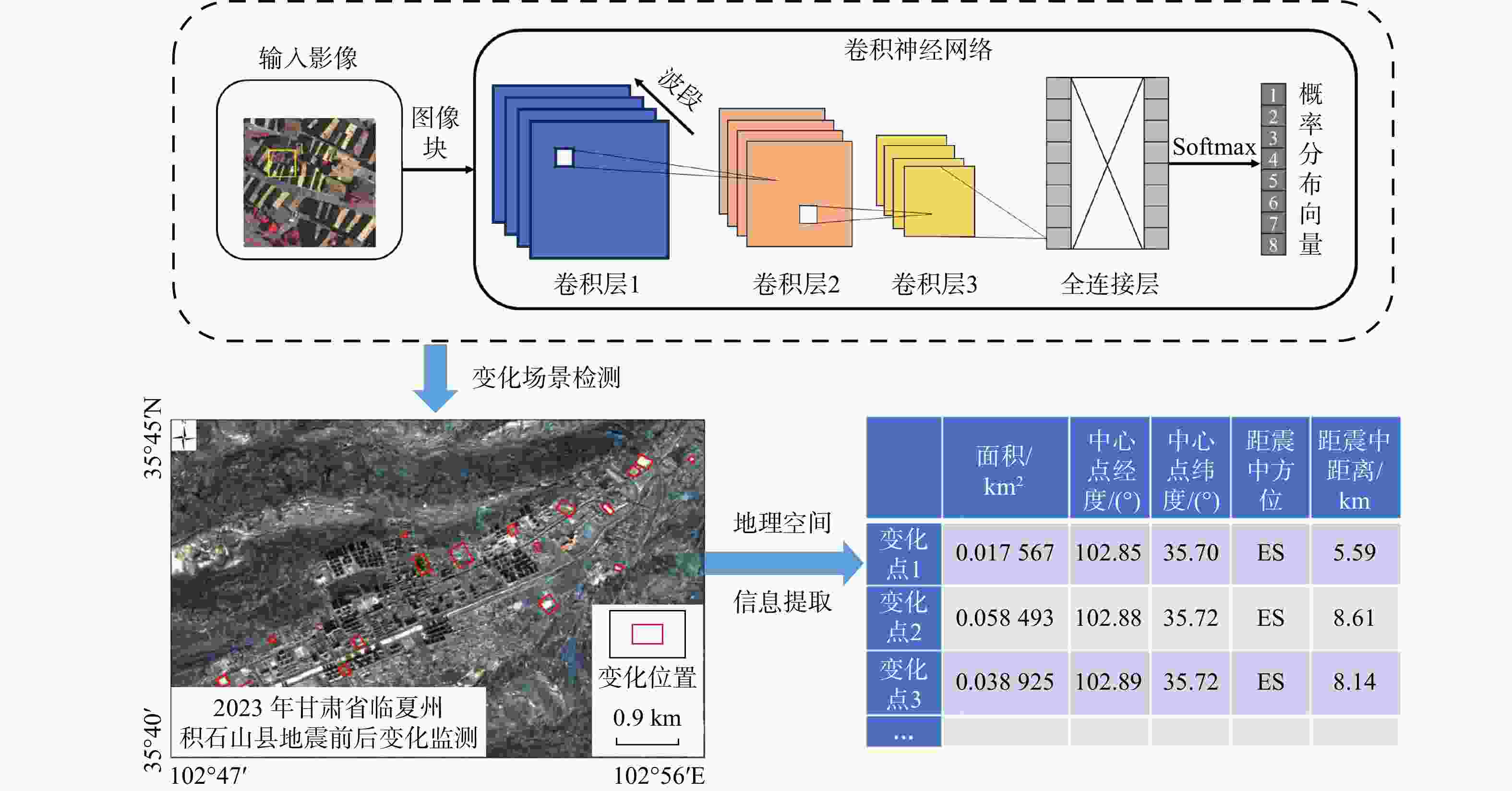
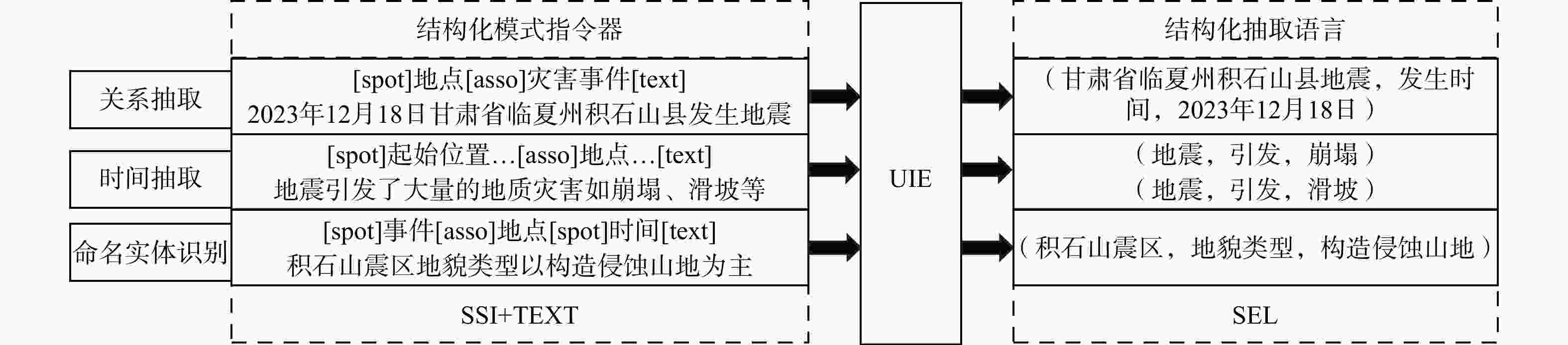
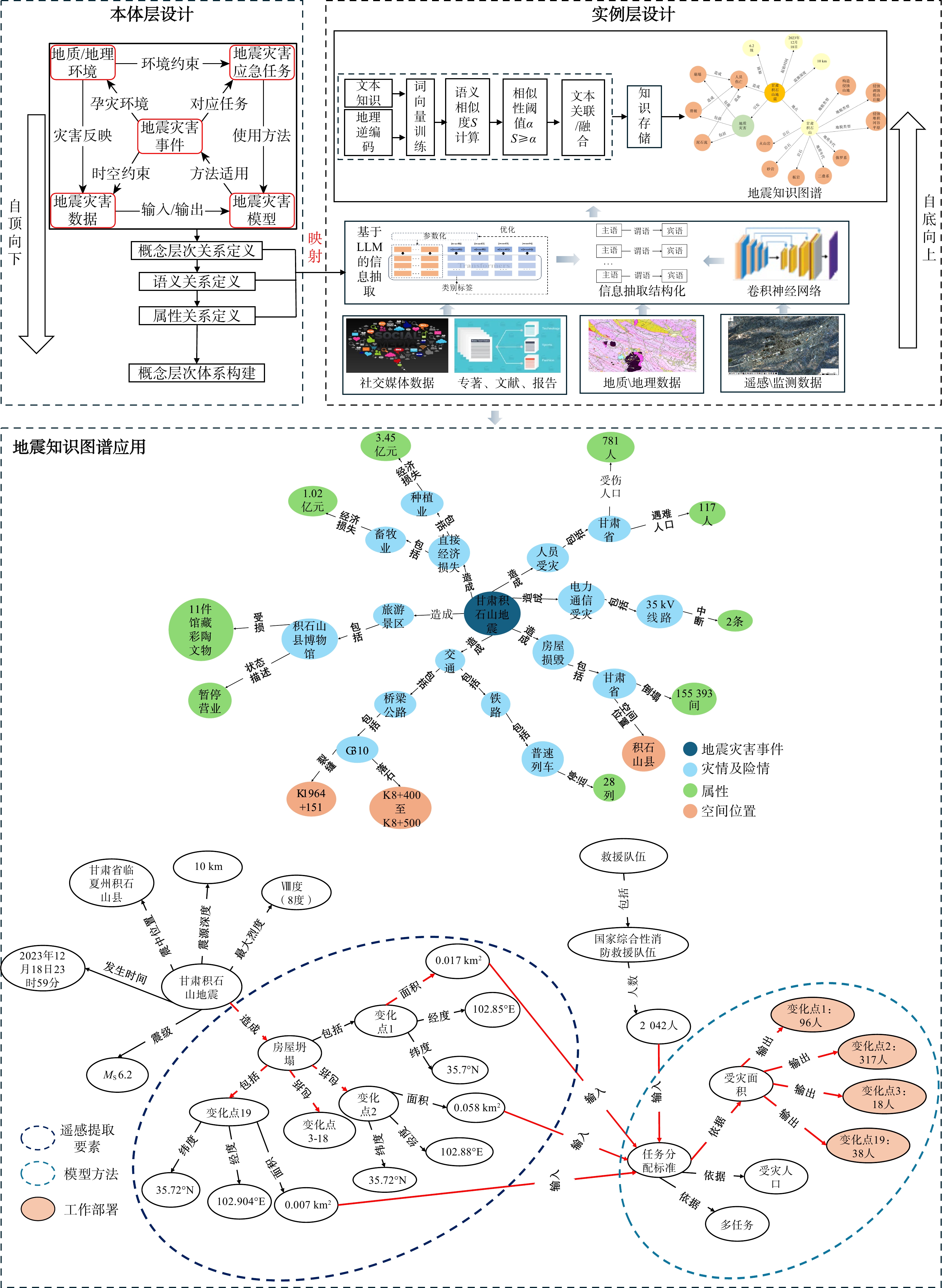
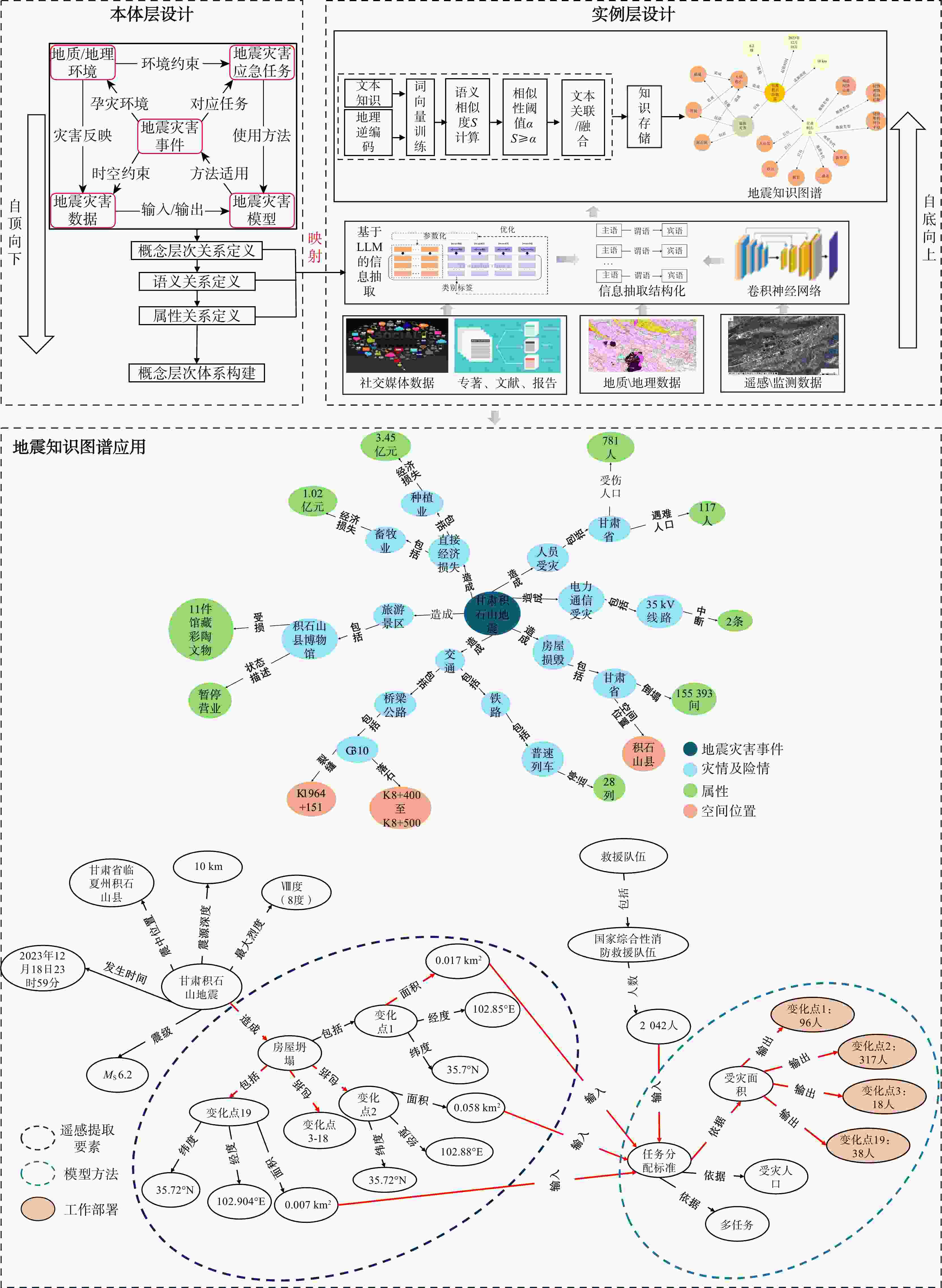
地震灾害观测数据多源异构、蕴含知识分散且关联程度低,导致难以高效利用数据进行信息整合和查询,进而提供风险评估、救援决策辅助支持。知识图谱是一种有效的数据关联和融合的手段。首先,基于自顶向下方法梳理地震灾害领域概念,构建地震灾害数据、地质/地理环境、地震灾害事件、地震灾害应急任务、地震灾害模型本体,形成地震灾害本体层;结合自底向上方法构建高质量数据层,通过卷积神经网络对遥感影像进行灾害前后变化识别,实现从影像信息到文本知识的智能结构化转换;融合微调后通用信息抽取框架(universal information extraction,简称UIE)预训练模型对文本数据进行命名实体及关系属性知识抽取,精确率分别为82.04%和70.66%。通过计算词向量语义相似度实现数据融合与统一表达。以2023年12月18日甘肃省临夏州积石山县地震为例,通过本体构建、数据抽取、统一表达形成高质量地震灾害知识图谱,实现地震灾害多源异构地震数据到统一知识表达的转化。基于所构建的地震灾害知识图谱实现了灾害损失、应急链决策支持的查询展示,及结合相关地质数据推理和查询潜在次生灾害。该方法结合深度学习与预训练技术,融合多模态数据,构建了地震灾害知识图谱构建,为快速准确的地震灾害信息查询与次生灾害发生提供辅助支撑。
Abstract:Objective Earthquake disaster observation data are multi-source and heterogeneous, with scattered knowledge and poor correlation, making it difficult to efficiently utilize the data for information integration and efficient querying, thereby limiting its effectiveness in supporting risk assessment and emergency decision-making.
Methods Knowledge graphs are an effective means of data association and fusion. Firstly, based on a top-down approach, the concepts in the earthquake disaster domain were sorted out, and the ontologies of earthquake disaster data, geological/geographical environment, earthquake disaster events, earthquake disaster emergency tasks, and earthquake disaster models were constructed to form the earthquake disaster ontology layer. Combined with a bottom-up approach, a high-quality data layer was built. Through convolutional neural networks, changes in remote sensing images before and after disasters were identified, achieving intelligent structured conversion from image information to textual knowledge. The fine-tuned UIE (universal information extraction) pre-training model was used to extract named entities and relationship attribute knowledge from text data, with precision rates of 82.04% and 70.66%, respectively. Data fusion and unified expression were achieved by calculating the semantic similarity of word vectors.
Results Taking the earthquake in Jishishan County, Linxia Prefecture, Gansu Province on December 18, 2023 as an example, a high-quality earthquake disaster knowledge graph was established through ontology construction, data extraction, and unified expression, achieving the transformation from multi-source heterogeneous earthquake data to unified knowledge representation.
Conclusion Based on the constructed earthquake disaster knowledge graph, queries and displays of disaster losses and emergency chain decision support are realized. Additionally, potential secondary disasters can be inferred and queried by integrating relevant geological data. This method combines deep learning and pre-training techniques with multi-modal data to construct an earthquake disaster knowledge graph, providing auxiliary support for rapid and accurate earthquake disaster information queries and the prediction of secondary disasters.
-
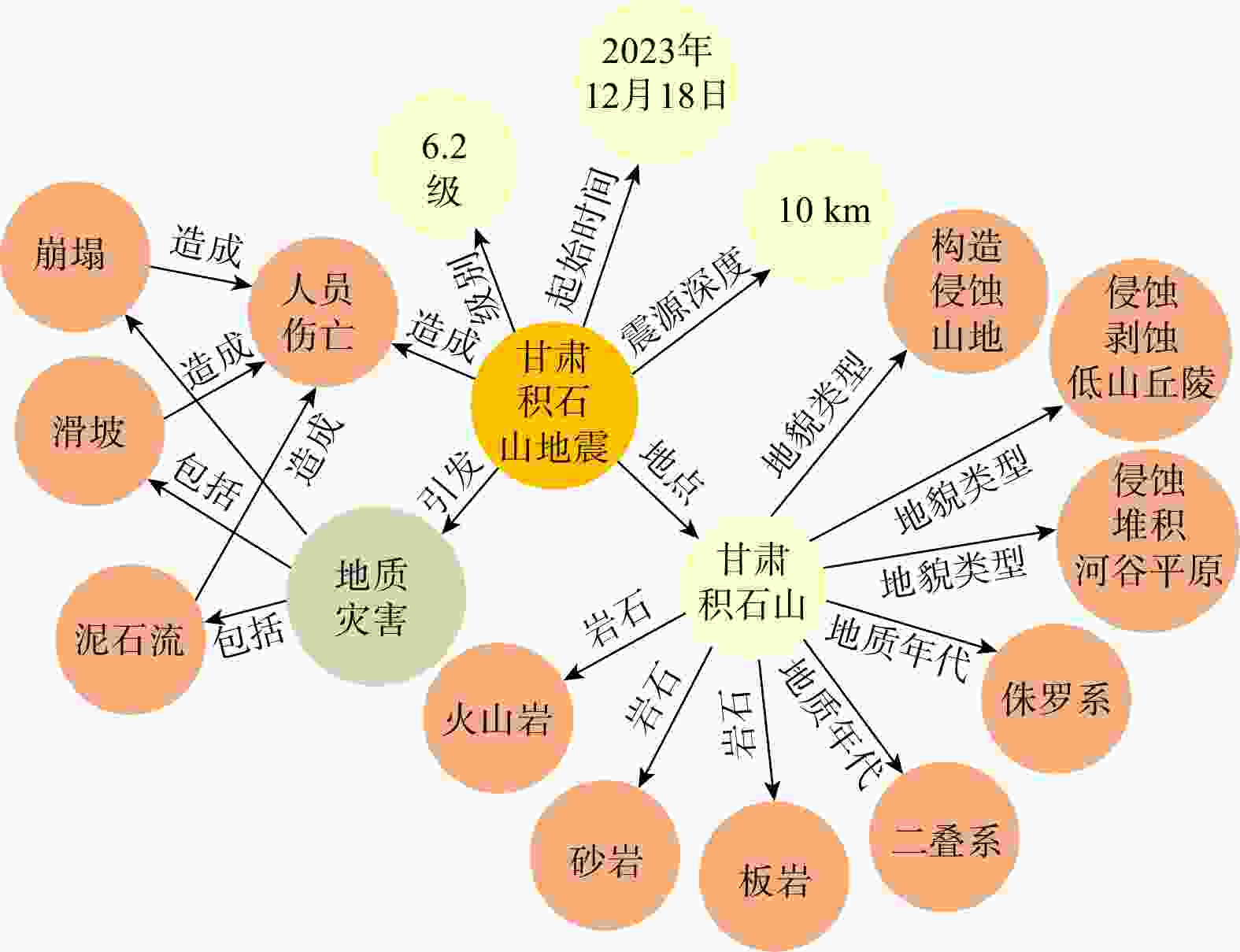
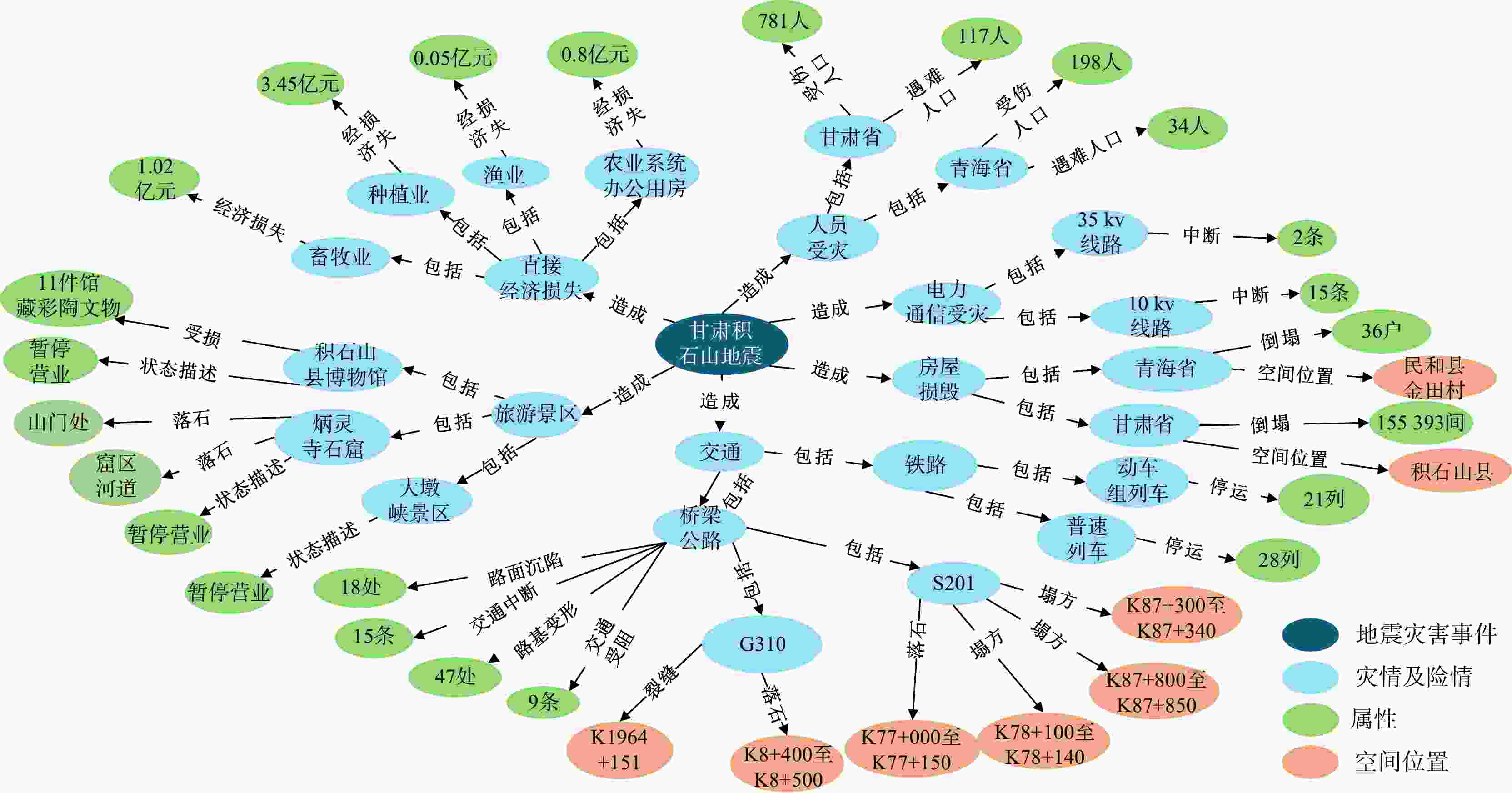
表 1 地震灾害对象实体类型分析
Table 1. Analysis of entity types of earthquake disaster objects
地震灾害本体 地震实体类型 二级分类实体 属性 地震灾害事件 灾害对象 震中位置、有感范围、影响范围、余震、断裂方向、震源深度 方位、面积、震级、深度 灾情对象 经济损失、死亡人口、失踪人口、受伤人口、受灾人口、受损建筑物、安置人口、灾区等级、灾害范围 损失金额、伤亡数目、受损程度、受损面积等 次生灾害对象 泥石流、崩塌、滑坡、水灾、火灾、爆炸、瘟疫、
地裂、毒气泄漏灾害级别、时间、地点、滑坡长度、滑坡体积、
毒气类型等地质/地理环境 地质/地理环境 地形地貌环境、地质构造环境、岩土体
工程地质环境山脉、平原、河流、湖泊、海洋、峡谷、沙漠、地壳、
地震带、断层、构造山脉、盆地、岩浆岩、地质构造图、
岩石、土壤、岩土体、岩土层、地下水位地震灾害数据 基础灾害数据 村镇基础信息、天气、土地覆被、历史地震等 时间、天气、最高气温、最低气温、风向、风速、特殊
天气、震级、发震时刻、纬度、经度、震源深度、距震中距离、
周边县城名称、人口、距震中方位、距震中距离、总面积、
林地、草地、水体、不透水面、裸地、耕地比例等基础地理对象 地形、天气、房屋、道路、河流、基础设施、
地名、居民地、机场、火车站方位、距离、风速、经度、纬度、气温、时间、名称等 地震灾害应急任务 地震灾害应急对象 大中型水库、群体性事件、医疗点、物资发放点、
应急避难场所、现场指挥部、撤退路线、救援路线响应等级、安置人数、物资数目、撤退人数等 地震预防策略 国家的法律法规、预防措施、震后处理措施、
抗震避灾手段措施内容、使用场景、注意事项、措施类型 地震灾害模型方法 地震灾害模型 地理信息系统、遥感、统计分析、模型模拟 方法名称、类别、功能、详细描述、应用效果和验证地区 地震理论知识 地震基础概念、地震成因、断层机制 定义、原理、地震波、烈度、震级、饱和现象 表 2 地震灾害实体间关系分析
Table 2. Analysis of relationships of earthquake disaster entities
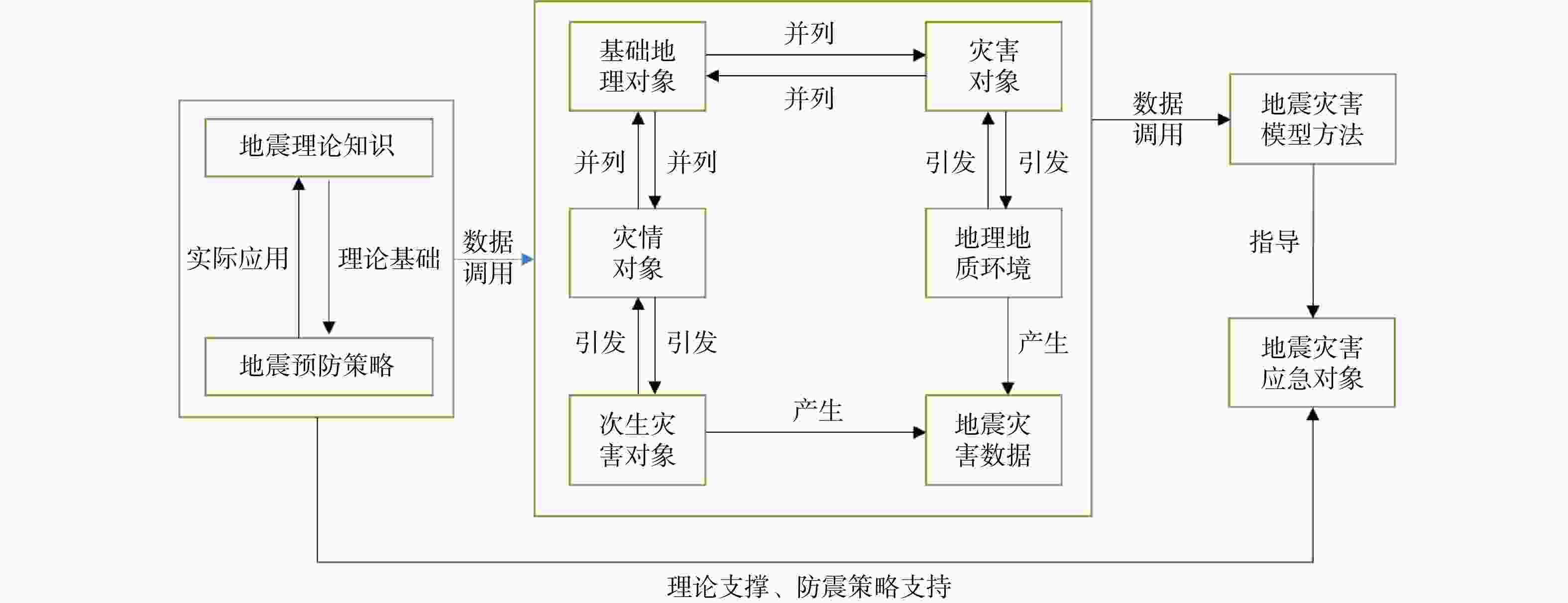
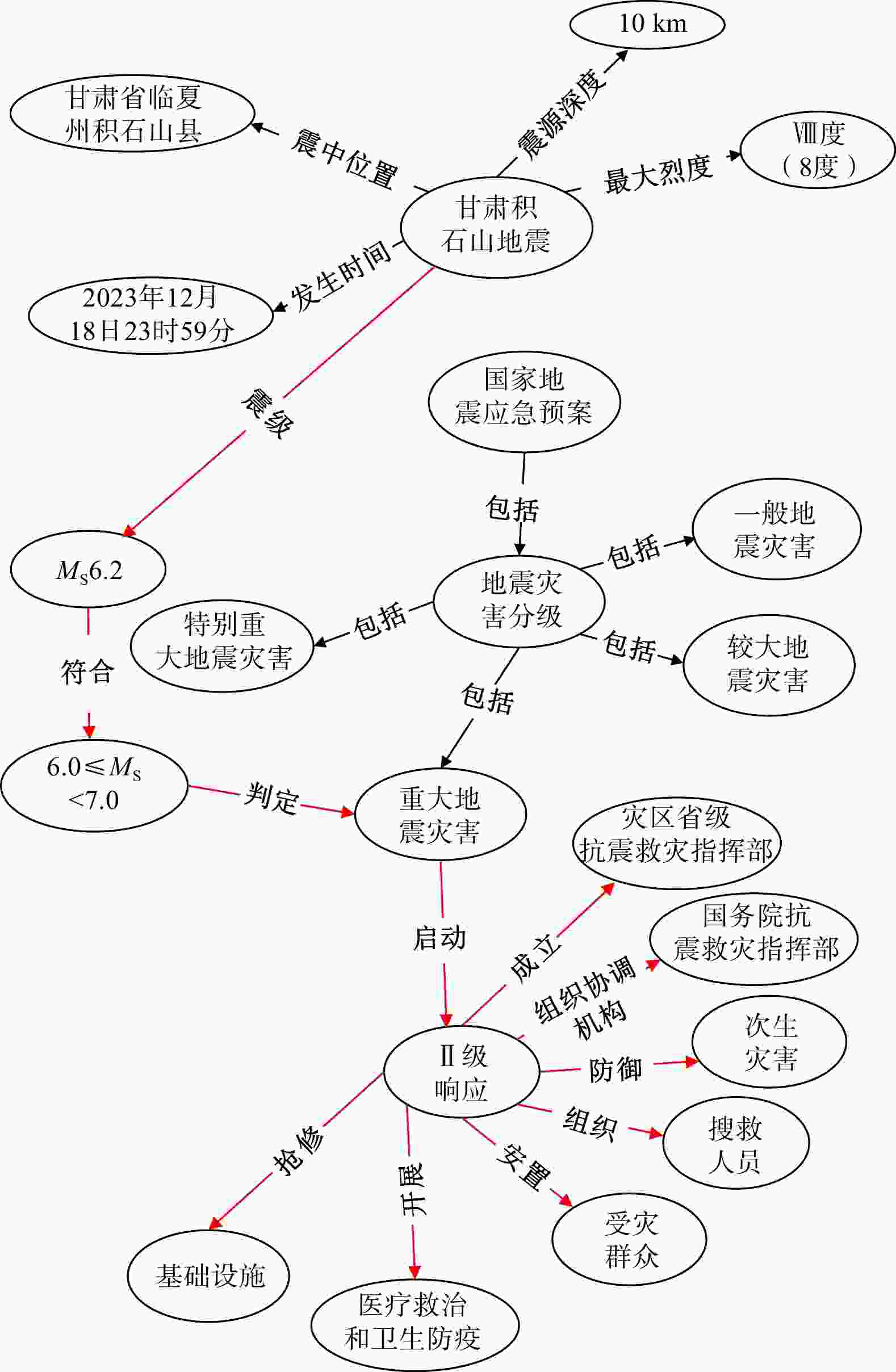
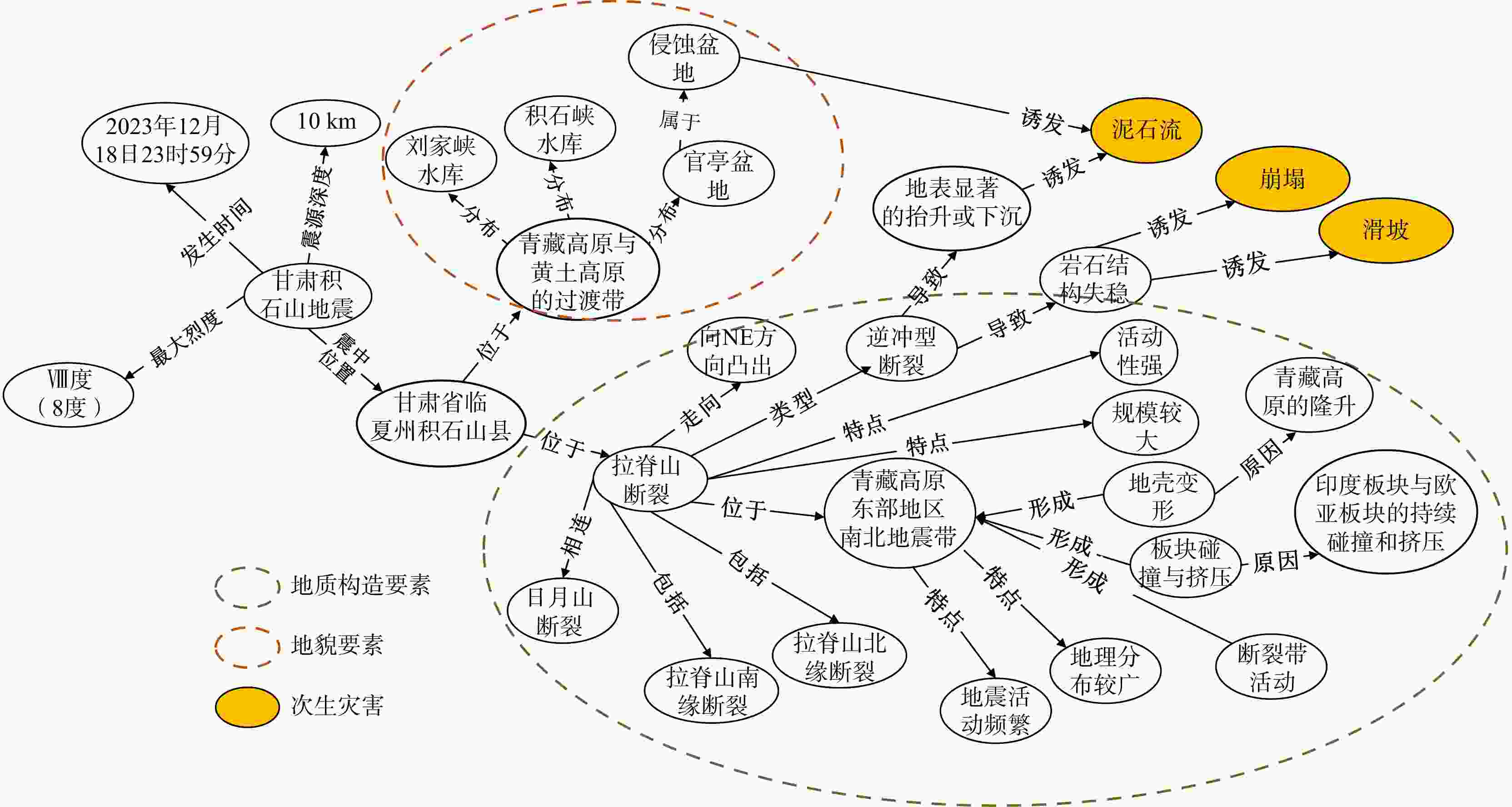
关系类型 关系定义 子类型 三元组 并列关系 如果在同一属概念之中存在同层次的种概念,
则这些种概念之间是并列关系伴随 (山脉,伴随,断裂) 并列 (居民地防震,并列,医院防震) 属性关系 对象的性质与对象之间关系的统称 致灾因子 (地震,致灾因子,逆冲型地震) 对应任务 (地震仪,对应任务,监测地震) 发生地点 (甘肃地震,发生地点,甘肃省临夏州积石山县) 因果关系 在地震灾害中一个事件和第二个事件之间的作用关系 引发 (断裂,引发,地震)
(地震,引发,泥石流)造成 (地震,造成,经济损失) 导致 (泥石流,导致,人员伤亡) 相关关系 存在逻辑关系的地震灾害实体之间的关系 隶属关系 (地震监测数据,来源,地震监测台站) 包含关系 (直接经济损失,包含,农牧渔业) 衍生关系 (防震减灾法,衍生,地方防震减灾规划) 时间关系 地震概念或实例在时间上的相互关系 起始时间 (甘肃地震,起始时间,2023年12月18日) 结束关系 (甘肃地震,结束时间,2023年12月28日) 先后关系 (地震释放,先于,地震发生)
(地震发生,先于,地震波传播)
(地震发生,先于,次生灾害)同时关系 (初级波,同时,次级波) 时间拓扑关系 包含关系 (震中时间,包含,余震) 相交关系 (A地余震发生时间,相交,B地余震发生时间) 相邻关系 (A地余震发生时间,相邻,B地余震发生时间) 空间关系 地震概念或地震实例在空间上的相互关系 空间拓扑关系 相等关系 (地震震源,相等,断层) 包含关系 (震中区域,包含,震源区域) 邻近关系 (地震震源,相邻,附近地质构造)
(A地震断层,相邻,B地震断层)相离关系 (震中区域,相离,非震中区域) 方位关系 (地球板块交界,上面,地震活动区域) 距离关系 (震源位置,距离,观测点) 接触关系 整合接触 (索拉克组,整合接触,中奥陶统环形组) 不整合接触 (索拉克组,不整合接触,下二叠统因格布拉克组) 断层接触 (索拉克组,断层接触,上奥陶统拉配泉群) 假整合接触 (童子岩组,假整合接触,茅口组) 组成关系 聚合关系系指弱的整体和部分关系,整体和部分可以
相互独立;组合关系系指一种强的整体和部分,
整体和部分具有相同的生命周期聚合关系 (A板块,聚合,B板块)
(A断层带,聚合,B断层带)组合关系 (地堑,组合,断裂) 作用关系 地震对象与形成原因之间的关系 成因关系 (断裂,导致,地层错位) 影响关系 (地震,影响,人民生活) 演化关系 地壳和地球内部岩石体系发生变化的过程 板块构造演化 (板块,碰撞,地震)
(岩石,拗断,断裂)岩浆活动 (岩浆,断裂,火山岩) 表 3 UIE模型抽取信息精度
Table 3. Accuracy of information extraction of UIE model
类型 类别 精确率 召回率 F1 实体 地震灾害事件 0.887 0.764 0.823 地质/地理环境 0.875 0.798 0.848 地震灾害数据 0.767 0.668 0.708 地震灾害应急任务 0.898 0.805 0.835 地震灾害模型方法 0.675 0.421 0.622 关系 并列关系 0.700 0.677 0.691 属性关系 0.621 0.61 0.652 因果关系 0.563 0.465 0.533 相关关系 0.785 0.671 0.726 时间关系 0.917 0.885 0.862 空间关系 0.879 0.758 0.841 组成关系 0.431 0.365 0.422 作用关系 0.752 0.698 0.673 演化关系 0.711 0.68 0.600 表 4 实体-关系类型数量统计
Table 4. Entity-relationship type quantity statistics
实体类型 实体数量 关系类型 关系数量 地震理论知识 360 并列关系 53 地震预防策略 366 属性关系 68178 地质/地理环境 12577 因果关系 132 基础灾害数据 282 相关关系 79 基础地理对象 38947 时间关系 122 灾害对象 24 空间关系 34627 灾情对象 72 组成关系 180 次生灾害对象 30 作用关系 28 地震灾害应急对象 230 演化关系 10 地震灾害模型 30 -
[1] HUSSAIN E, KALAYCıOĞLU S, MILLINER C W D, et al. Preconditioning the 2023 Kahramanmaraş (Türkiye) earthquake disaster[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2023, 4(5): 287-289. [2] LIN B C, LEE C H. Constructing an adaptability evaluation framework for community-based disaster management using an earthquake event[J]. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 2023, 93: 103774. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2023.103774 [3] ZHOU H X, CHE A L, SHUAI X H, et al. A spatial evaluation method for earthquake disaster using optimized BP neural network model[J]. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 2023, 14(1): 1-26. [4] 陈博, 宋闯, 陈毅, 等. 2023年甘肃积石山Ms 6.2地震同震滑坡和建筑物损毁情况应急识别与影响因素研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2025, 50(2): 322-332.CHEN B, SONG C, CHEN Y, et al. Emergency identification and influencing factor analysis of coseismic landslides and building damages induced by the 2023 Ms 6.2 Jishishan(Gansu, China) earthquake[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2025, 50(2): 322-332. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 黄观文, 景策, 李东旭, 等. 甘肃积石山Ms 6.2地震对滑坡易发区的变形影响分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2025, 50(2): 223-235.HUANG G W, JING C, LI D X, et al. Deformation analysis of the Ms 6.2 Jishishan(Gansu, China) earthquake on the landslide hazard areas[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2025, 50(2): 223-235. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 刘振江, 韩炳权, 能懿菡, 等. InSAR观测约束下的2023年甘肃积石山地震震源参数及其滑动分布[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2025, 50(2): 344-355.LIU Z J, HAN B Q, NENG Y H , et al. Source parameters and slip distribution of the 2023 MW 6.0 Jishishan(Gansu, China) earthquake constrained by InSAR observations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2025, 50(2): 344-355. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 杨九元, 温扬茂, 许才军. InSAR观测揭示的2023年甘肃积石山Ms 6.2地震发震构造[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2025, 50(2): 313-321.YANG J Y, WEN Y M, XU C J. Seismogenic fault structure of the 2023 Ms 6.2 Jishishan(Gansu, China)earthquake revealed by InSAR observations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2025, 50(2): 313-321. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] XU J H, NYERGES T L, NIE G Z. Modeling and representation for earthquake emergency response knowledge: Perspective for working with geo-ontology[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2014, 28(1): 185-205. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2013.845893 [9] ZHANG Y H, ZHU J, ZHU Q, et al. The construction of personalized virtual landslide disaster environments based on knowledge graphs and deep neural networks[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2020, 13(12): 1637-1655. doi: 10.1080/17538947.2020.1773950 [10] 宋静园, 刘洋, 董秀军, 等. “9·5” 泸定地震人口密集区域同震滑坡空间分布规律[J/OL]. 地质科技通报: 1-12. [2023-12-13]. https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230619.SONG J Y, LIU Y, DONG X J, et al. Spatial distribution of earthquake-induced landslide in densely populated area of the Luding 9·5 earthquake[J/OL]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology: 1-12. [2023-12-13]. https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230619. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 魏旭, 彭志忠, 刘兴臣, 等. 泸石高速公路沿线历史地震诱发滑坡遥感调查及发育分布规律[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 386-396.WEI X, PENG Z Z, LIU X C, et al. Remote sensing investigation and development distribution of historical earthquake-induced landslides along Lushi Expressway[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 386-396. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 陶坤旺, 赵阳阳, 朱鹏, 等. 面向一体化综合减灾的知识图谱构建方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2020, 45(8): 1296-1302.TAO K W, ZHAO Y Y, ZHU P, et al. Knowledge graph construction for integrated disaster reduction[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(8): 1296-1302. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 谢炎宏, 王亮, 董春, 等. 面向地震灾害防治的知识图谱构建方法研究[J]. 测绘科学, 2021, 46(10): 219-226.XIE Y H, WANG L, DONG C, et al. Research on the construction method of earthquake disaster prevention knowledge graph[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(10): 219-226. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 张雪英, 张春菊, 吴明光, 等. 顾及时空特征的地理知识图谱构建方法[J]. 中国科学(信息科学), 2020, 50(7): 1019-1032. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2019-0269ZHANG X Y, ZHANG C J, WU M G, et al. Spatiotemporal features based geographical knowledge graph construction[J]. Scientia Sinica (Informationis), 2020, 50(7): 1019-1032. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/SSI-2019-0269 [15] WANG B, WU L, XIE Z, et al. Understanding geological reports based on knowledge graphs using a deep learning approach[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2022, 168: 105229. [16] QIU Q J, XIE Z, ZHANG D, et al. Knowledge graph for identifying geological disasters by integrating computer vision with ontology[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2023, 34(5): 1418-1432. doi: 10.1007/s12583-022-1641-1 [17] 周成虎, 王华, 王成善, 等. 大数据时代的地学知识图谱研究[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2021, 51(7): 1070-1079. doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2020-0337ZHOU C H, WANG H, WANG C S, et al. Research on geo-knowledge map in the age of big data[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2021, 51(7): 1070-1079. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2020-0337 [18] 诸云强, 孙凯, 王曙, 等. 顾及复杂时空特征及关系的地球科学知识图谱自适应表达模型[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2023, 53(11): 2609-2622.ZHU Y Q, SUN K, WANG S, et al. An adaptive representation model for geoscience knowledge graphs considering complex spatiotemporal features and relationships[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2023, 53(11): 2609-2622. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 许强, 崔圣华, 黄维, 等. 面向工程地质领域的滑坡知识图谱构建方法研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2023, 48(10): 1601-1615.XU Q, CUI S H, HUANG W, et al. Construction of a landslide knowledge graph in the field of engineering geology[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2023, 48(10): 1601-1615. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] QIU Q J, HUANG Z, XU D X, et al. Integrating NLP and ontology matching into a unified system for automated information extraction from geological hazard reports[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2023, 34(5): 1433-1446. doi: 10.1007/s12583-022-1716-z [21] 田佳, 李萌, 罗浩. 基于U-Net神经网络的微地震有效事件自动拾取方法[J/OL]. 地质科技通报: 1-13. [2024-04-29]. https://link. cnki. net/doi/10.19509/j. cnki. dzkq. tb20230689.TIAN J, LI M, LUO H. Automatic pickup of effective microseismic events based on U-Net neural network[J/OL]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology: 1-13. [2024-04-29]. https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230689.(in Chinese with English abstract [22] 沈伟豪, 钟燕飞, 王俊珏, 等. 多模态数据的洪涝灾害知识图谱构建与应用[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2023, 48(12): 2009-2018.SHEN W H, ZHONG Y F, WANG J J, et al. Construction and application of flood disaster knowledge graph based on multi-modal data[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2023, 48(12): 2009-2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 刘晓. 基于文本挖掘的灾害多级联动分析与预测研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2021.LIU X. Research on prediction and analysis of cascading disasters based on text mining[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] RILOFF E. Automatically constructing a dictionary for information extraction tasks[C]//Anon. AAAI'93: Proceedings of the eleventh national conference on Artificial intelligence. [S. 1.]: [s. n.], 1993: 811-816. [25] KRUPKA G R, ISOQUEST K. Description of the nerowl extractor system as used for muc-7[C]//Anon. Proc. 7th Message Understanding Conf. [S. 1. ]: [s. n. ], 2005: 21-28. [26] DOAN S, XU H. Recognizing medication related entities in hospital discharge summaries using support vector machine[J]. Proceedings of COLING International Conference on Computational Linguistics, 2010, 2010: 259-266. [27] ASHKTORAB Z, BROWN C, NANDI M, et al. Tweedr: Mining twitter to inform disaster response[C]//Anon. Information Systems for Crisis Response and Management Association. [S. 1.]: [s. n.], 2014: 269-272. [28] IMRAN M, MITRA P, CASTILLO C. Twitter as a lifeline: Human-annotated twitter corpora for NLP of crisis-related messages[EB/OL]. (2016-05-31) [2025-06-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.05894v2. [29] 杜志强, 李钰, 张叶廷, 等. 自然灾害应急知识图谱构建方法研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2020, 45(9): 1344-1355.DU Z Q, LI Y, ZHANG Y T, et al. Knowledge graph construction method on natural disaster emergency[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(9): 1344-1355. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] QIU Q J, XIE Z, WU L, et al. BiLSTM-CRF for geological named entity recognition from the geoscience literature[J]. Earth Science Informatics, 2019, 12(4): 565-579. doi: 10.1007/s12145-019-00390-3 [31] QIU Q J, TIAN M, HUANG Z, et al. Chinese engineering geological named entity recognition by fusing multi-features and data enhancement using deep learning[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2024, 238: 121925. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.121925 [32] 谢雪景, 谢忠, 马凯, 等. 结合BERT与BiGRU-Attention-CRF模型的地质命名实体识别[J]. 地质通报, 2023, 42(5): 846-855.XIE X J, XIE Z, MA K, et al. Geological named entity recognition combined BERT and BiGRU-Attention-CRF model[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2023, 42(5): 846-855. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 王刘坤, 李功权. 基于GeoERNIE-BiLSTM-Attention-CRF模型的地质命名实体识别[J]. 地质科学, 2023, 58(3): 1164-1177.WANG L K, LI G Q. Geological named entity recognition based on GeoERNIE-BiLSTM-Attention-CRF model[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica), 2023, 58(3): 1164-1177. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] LEE S, AN J, KWAK B, et al. Learning korean named entity by bootstrapping with web resources[J]. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, 2004, 87(12): 2872-2882. [35] KEKLIK O, TUGLULAR T, TEKIR S. Rule-based automatic question generation using semantic role labeling[J]. IEICE Transactions on Information and Systems, 2019, E102. D(7): 1362-1373. [36] LI J, SUN A X, HAN J L, et al. A survey on deep learning for named entity recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2022, 34(1): 50-70. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2020.2981314 [37] ZHANG J, SHEN D, ZHOU G D, et al. Enhancing HMM-based biomedical named entity recognition by studying special phenomena[J]. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 2004, 37(6): 411-422. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2004.08.005 [38] ZHAO J, LIU F F. Product named entity recognition in Chinese text[J]. Language Resources and Evaluation, 2008, 42(2): 197-217. doi: 10.1007/s10579-008-9066-8 [39] SAHA S K, SARKAR S, MITRA P. Feature selection techniques for maximum entropy based biomedical named entity recognition[J]. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 2009, 42(5): 905-911. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2008.12.012 [40] HAO Z F, WANG H F, CAI R C, et al. Product named entity recognition for Chinese query questions based on a skip-chain CRF model[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2013, 23(2): 371-379. doi: 10.1007/s00521-012-0922-5 [41] LI Z N, LI Q, ZOU X T, et al. Causality extraction based on self-attentive BiLSTM-CRF with transferred embeddings[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 423: 207-219. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.08.078 [42] 谢腾, 杨俊安, 刘辉. 融合多特征BERT模型的中文实体关系抽取[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2021, 30(5): 253-261.XIE T, YANG J A, LIU H. Chinese entity relation extraction based on multi-feature BERT model[J]. Computer Systems & Applications, 2021, 30(5): 253-261. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] 陆亮, 孔芳. 面向对话的融入交互信息的实体关系抽取[J]. 中文信息学报, 2021, 35(8): 82-88.LU L, KONG F. Interactive information enhanced relation extraction from dialogue[J]. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2021, 35(8): 82-88. (in Chinese with English abstract [44] 马建红, 魏字默, 陈亚萌. 基于信息融合标注的实体及关系联合抽取方法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2021, 38(7): 159-166.MA J H, WEI Z M, CHEN Y M. Entity and relationship joint extraction method based on information fusion tagging[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2021, 38(7): 159-166. (in Chinese with English abstract [45] HOU J, XU S S. Near-real-time seismic human fatality information retrieval from social media with few-shot large-language models[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 20th ACM Conference on Embedded Networked Sensor Systems. Boston Massachusetts: ACM, 2022: 1141-1147. [46] MA K, TIAN M, TAN Y J, et al. Ontology-based BERT model for automated information extraction from geological hazard reports[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2023, 34(5): 1390-1405. doi: 10.1007/s12583-022-1724-z [47] 杜志强, 王叁, 张叶廷. 接入实时降雨数据的暴雨型洪涝灾害临灾预警方法[J]. 地理信息世界, 2017, 24(1): 97-102.DU Z Q, WANG S, ZHANG Y T. Temporary precaution method for rainstorm-type flood disaster with real-time rainfall data[J]. Geomatics World, 2017, 24(1): 97-102. (in Chinese with English abstract [48] 张航. 泥石流灾害领域知识图谱的构建与应用[D]. 昆明: 云南师范大学, 2021.ZHANG H. Construction and application of knowledge graph in the field of debris flow disaster[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Normal University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [49] 邱芹军, 吴亮, 马凯, 等. 面向灾害应急响应的地质灾害链知识图谱构建方法[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(5): 1875-1891.QIU Q J, WU L, MA K, et al. A knowledge graph construction method for geohazard chain for disaster emergency response[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(5): 1875-1891. (in Chinese with English abstract [50] 宁慧涵, 眭海刚, 王金地, 等. 顾及时空关系的事故灾难事理图谱构建方法研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2024, 49(5): 831-843.NING H H, SUI H G, WANG J D, et al. Construction of disaster event evolutionary graph based on spatiotemporal relationship[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2024, 49(5): 831-843. (in Chinese with English abstract [51] SINGHAL A. Introducing the knowledge graph: Things, notstrings[EB/OL]. (2012-05-16) [2022-05-02]. https://www.blog.google/products/search/introducing-knowledge-graph-thi-ngs-not/. [52] 林森, 刘蓓蓓, 李建文, 等. 基于BERT迁移学习模型的地震灾害社交媒体信息分类研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2024, 49(9): 1661-1671.LIN S, LIU B B, LI J W, et al. Social media information classification of earthquake disasters based on BERT transfer learning model[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2024, 49(9): 1661-1671. (in Chinese with English abstract [53] 谭剪梅. 顾及多类型用户需求的地震灾害场景知识图谱构建及应用[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2019.TAN J M. The construction and application of earthquake disaster scene knowledge graph concerned on the demands of multy-type users[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [54] 贺海霞, 刘涛, 杜萍. 地震灾害应急管理知识图谱构建研究[J]. 兰州交通大学学报, 2023, 42(3): 113-123.HE H X, LIU T, DU P. Study on the construction of knowledge graph of earthquake disaster emergency management[J]. Journal of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2023, 42(3): 113-123. (in Chinese with English abstract [55] 中华人民共和国应急管理部. 中华人民共和国防震减灾法[Z]. 北京: 中华人民共和国第十一届全国人民代表大会常务委员会, 2008.Ministry of Emergency Management of the People's Republic of China. Law of the People's Republic of China on seismic disaster prevention and mitigation[Z]. Beijing: Standing Committee of the Eleventh National People's Congress of the People's Republic of China, 2008. (in Chinese) [56] 中华人民共和国国务院办公厅. 国家地震应急预案[Z]. 北京: 国务院地震工作主管部门, 2012.General Office of the State Council of the People's Republic of China. National Earthquake Emergency Plan[Z]. Beijing: Competent Department of the State Council for Earthquake Work, 2012. (in Chinese) [57] 民政部国家减灾中心. 自然灾害承载体分类与代码: GB/T32572-2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.National Disaster Reduction Center of the Ministry of Civil Affairs. Classification and coding of natural disaster exposure: GB/T32572-201 [S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016. (in Chinese) [58] 中华人民共和国民政部. 自然灾害灾情统计: GB/T24438.1-2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009.Ministry of Civil Affairs of the People's Republic of China. Natural disaster information statistic: GB/T24438.1-2009[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2009. (in Chinese) [59] 中华人民共和国自然资源部. 地质灾害风险调查评价规范: DZ/T0438-2023[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2023.Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. Specification of geological hazard risk survey and assessment: DZ/T0438-2023[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2023. (in Chinese) -




 下载:
下载: