-
摘要:
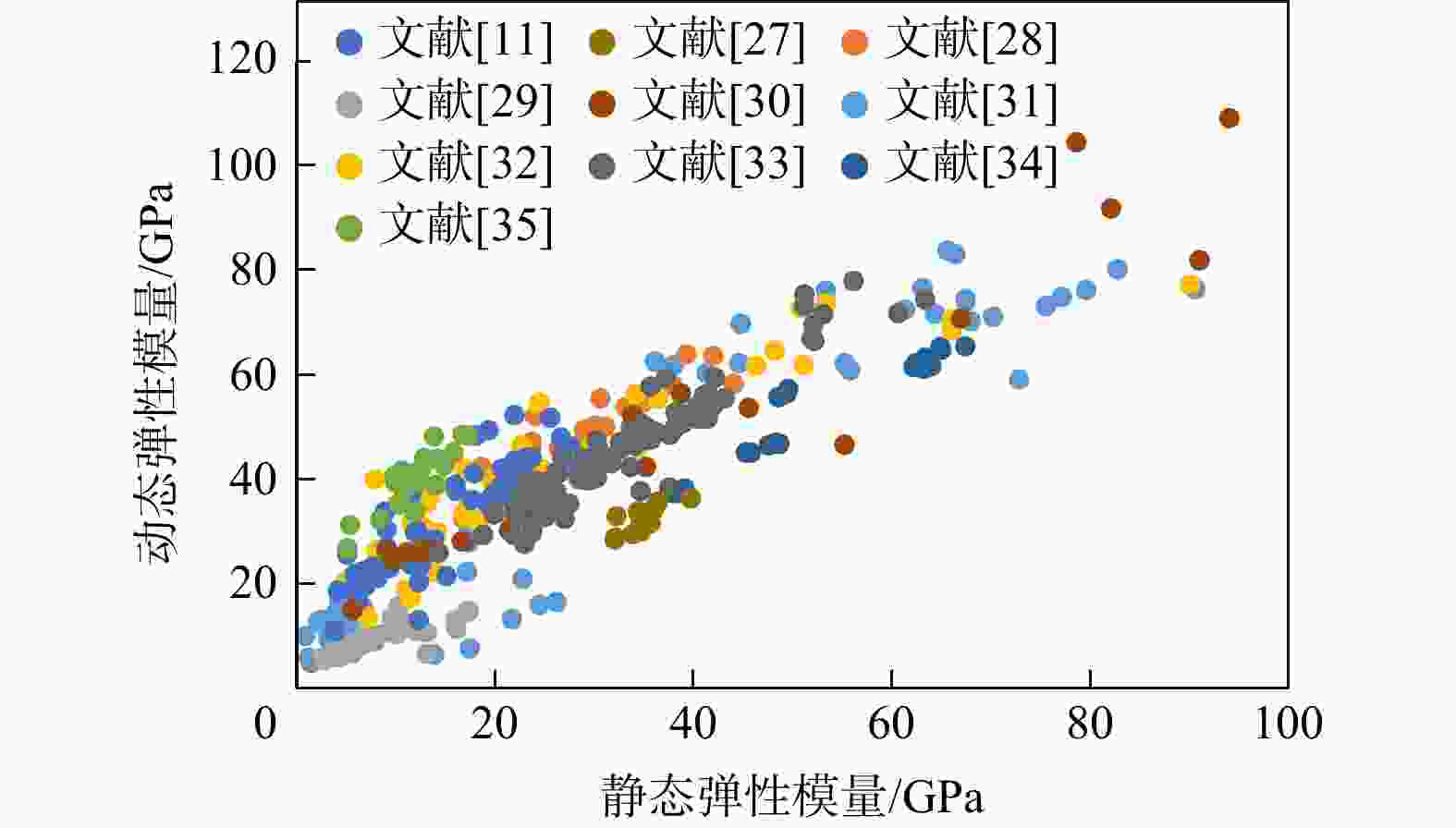
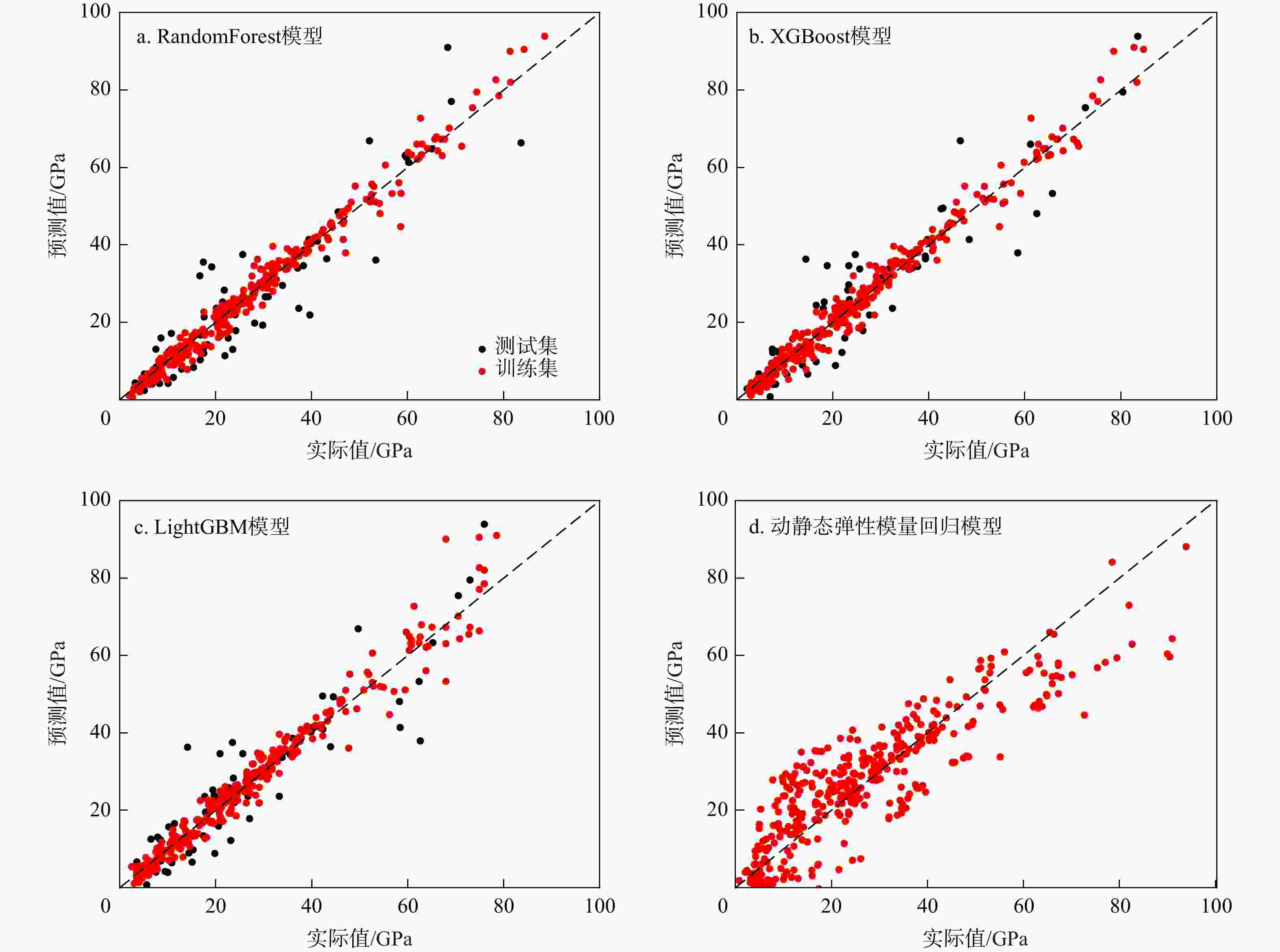
油气工程中常利用地球物理资料获取地层弹性模量并结合小样本的岩心实验数据进行校正,但这种方法在复杂地质条件下往往表现不佳。为提高岩石弹性模量的预测精度和泛化能力,提出了一种利用基本岩石物性参数的弹性模量智能预测模型。分别采用3种集成学习算法(RandomForest,XGBoost,LightGBM)构建了岩石弹性模量智能预测模型,并采用TPE方法对模型进行超参数优化,最后利用SHAP归因分析探讨了各输入变量对模型的贡献。结果表明:①提出的智能预测模型明显优于传统模型,能够实现弹性模量的精确预测并具有较强的泛化能力,其中XGBoost模型表现最佳(决定系数
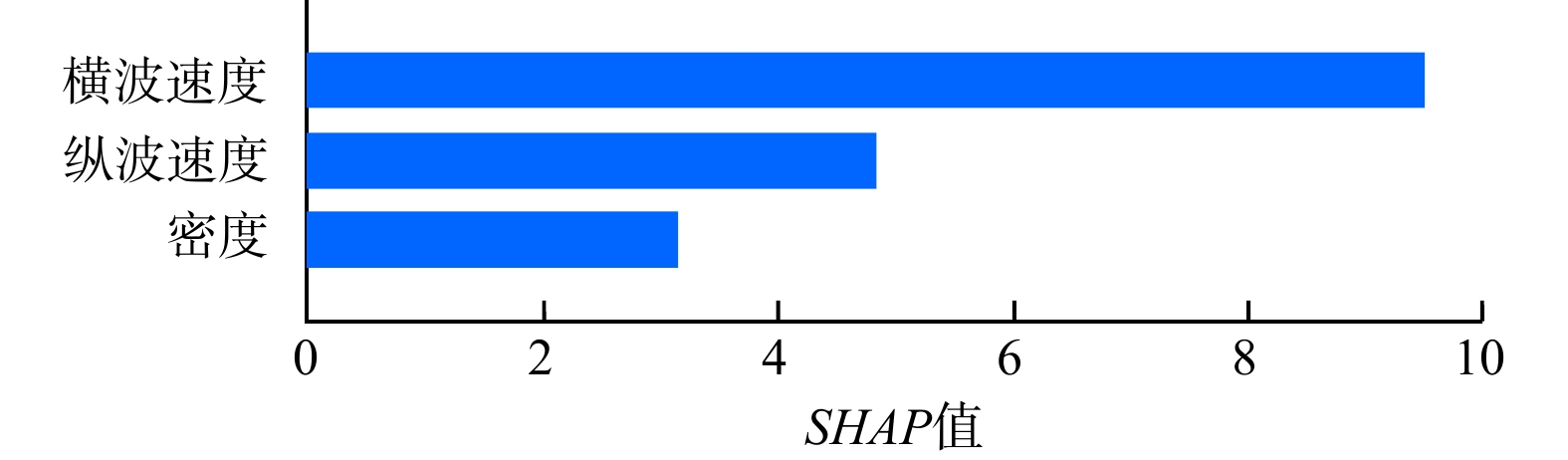
R 2=0.87,均方根误差RMSE =6.94,平均绝对误差MAE =4.96);②横波速度对模型贡献最大,纵波速度次之,密度最小,精确横波波速对弹性模量预测有重要意义。该方法无需对工区及地层进行预先识别即可实现弹性模量的精准预测,研究成果对油气工程设计及实施有重要参考意义。Abstract:Objective Geophysical data is often used to determine the elastic modulus of formations in oil and gas engineering, with experimental data from small core samples used for calibration. However, acquiring core samples from every stratum is impractical and often leads to inadequate performance under complex geological settings. To improve the predictive accuracy and generalizability of the rock elastic modulus, an intelligent prediction model based on fundamental rock physical properties is proposed.
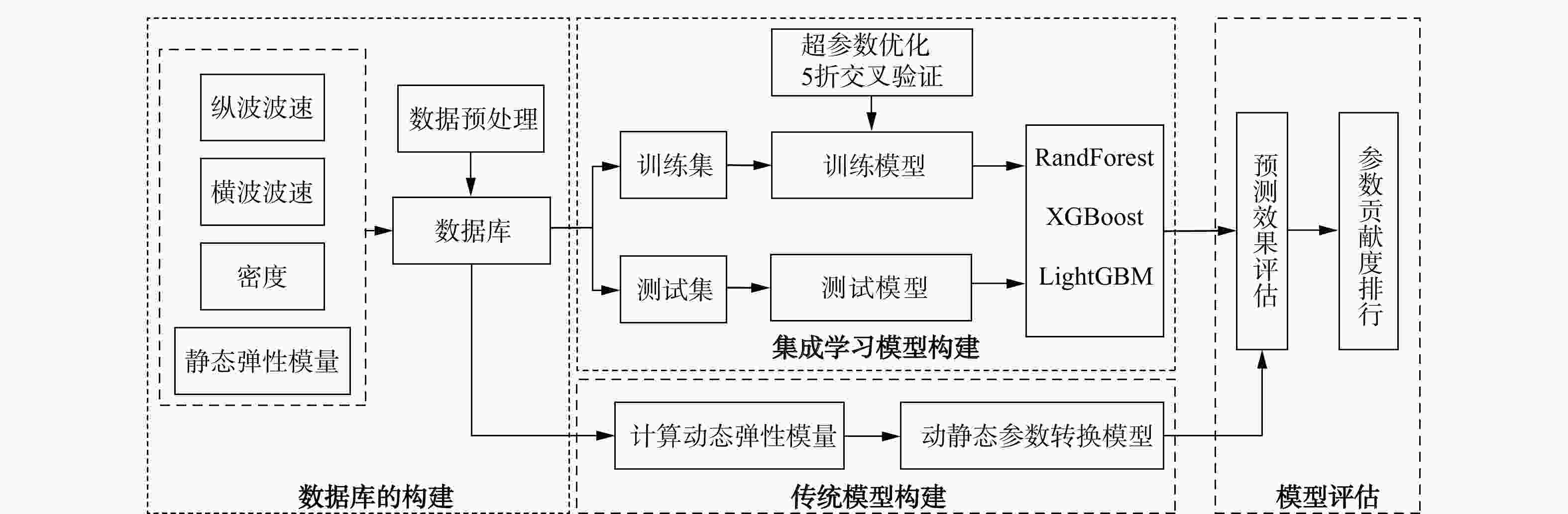
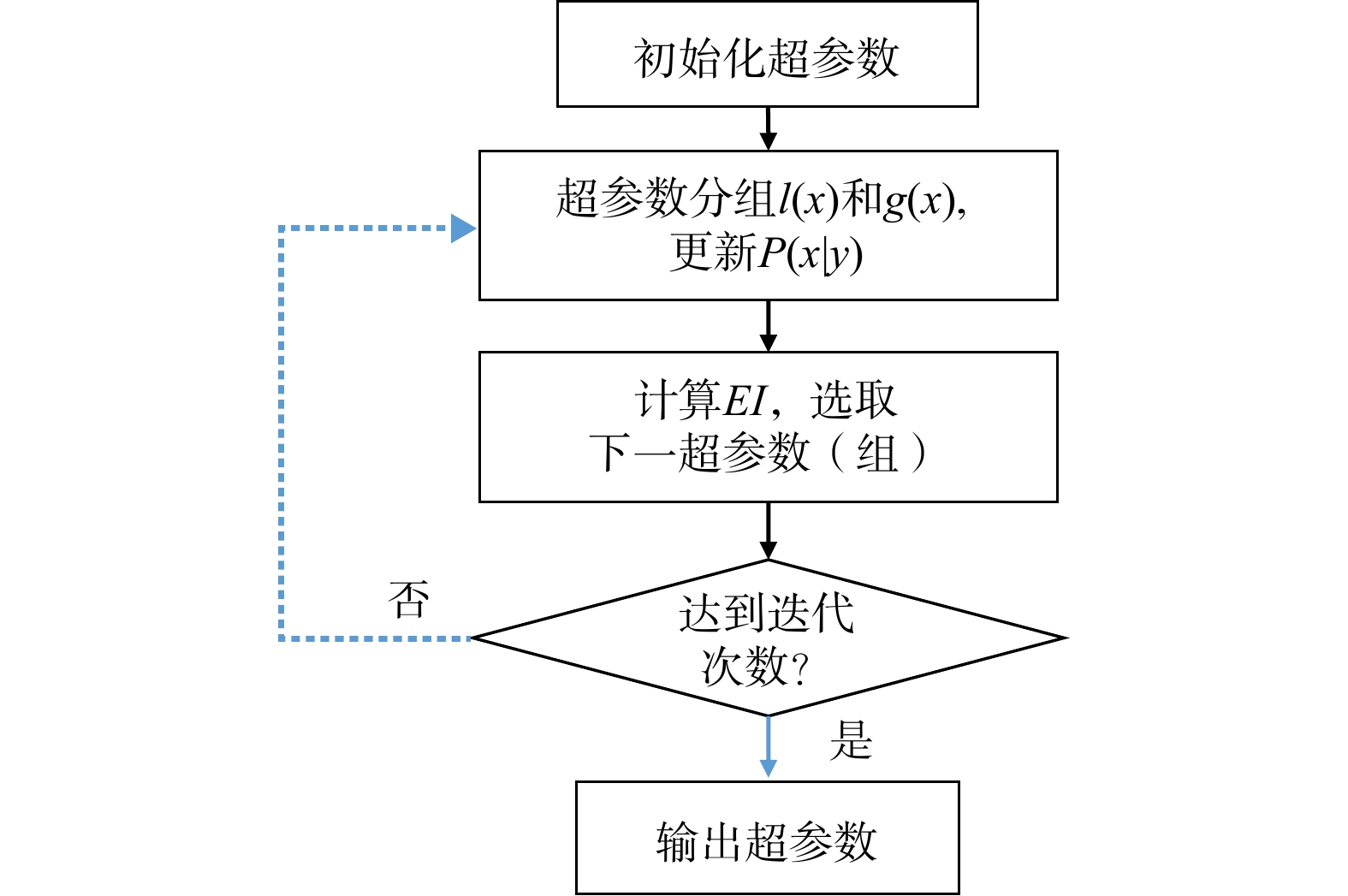
Methods Using 397 sets of core experimental data from diverse sources, with compressional and shear wave velocities and density as input variables, intelligent prediction models for rock elastic modulus were developed based on three ensemble learning algorithms (Random Forest, XGBoost, LightGBM). The TPE method was employed to optimize the models. The dynamic and static elastic modulus regression models were constructed based on current methods used in petroleum engineering to provide a comprehensive assessment of the performance of the intelligent predictive model using statistical indicators. Additionally, the SHAP attribution analysis was utilized to assess the contribution of each input variable to the model.
Results The research findings indicated that: ① The proposed intelligent prediction model using TPE was significantly better than traditional statistical regression models, achieving accurate predictions of the elastic modulus without distinguishing geological layers, with strong generalization ability. Among the three models, the XGBoost model performed the best (
R 2=0.87,RMSE =6.94,MAE =4.96). ②Shear wave velocity made the greatest contribution to the model, followed by compressional wave velocity, with density having the least impact. Accurate shear wave velocity was crucial for predicting the elastic modulus.Conclusion This method allows for the precise prediction of elastic modulus without the need for prior identification of the work area and strata, providing valuable insights for the design and implementation of oil and gas engineering projects.
-
Key words:
- elastic modulus /
- TPE /
- ensemble learning /
- SHAP /
- shear wave
-
表 1 数据来源
Table 1. Data sources
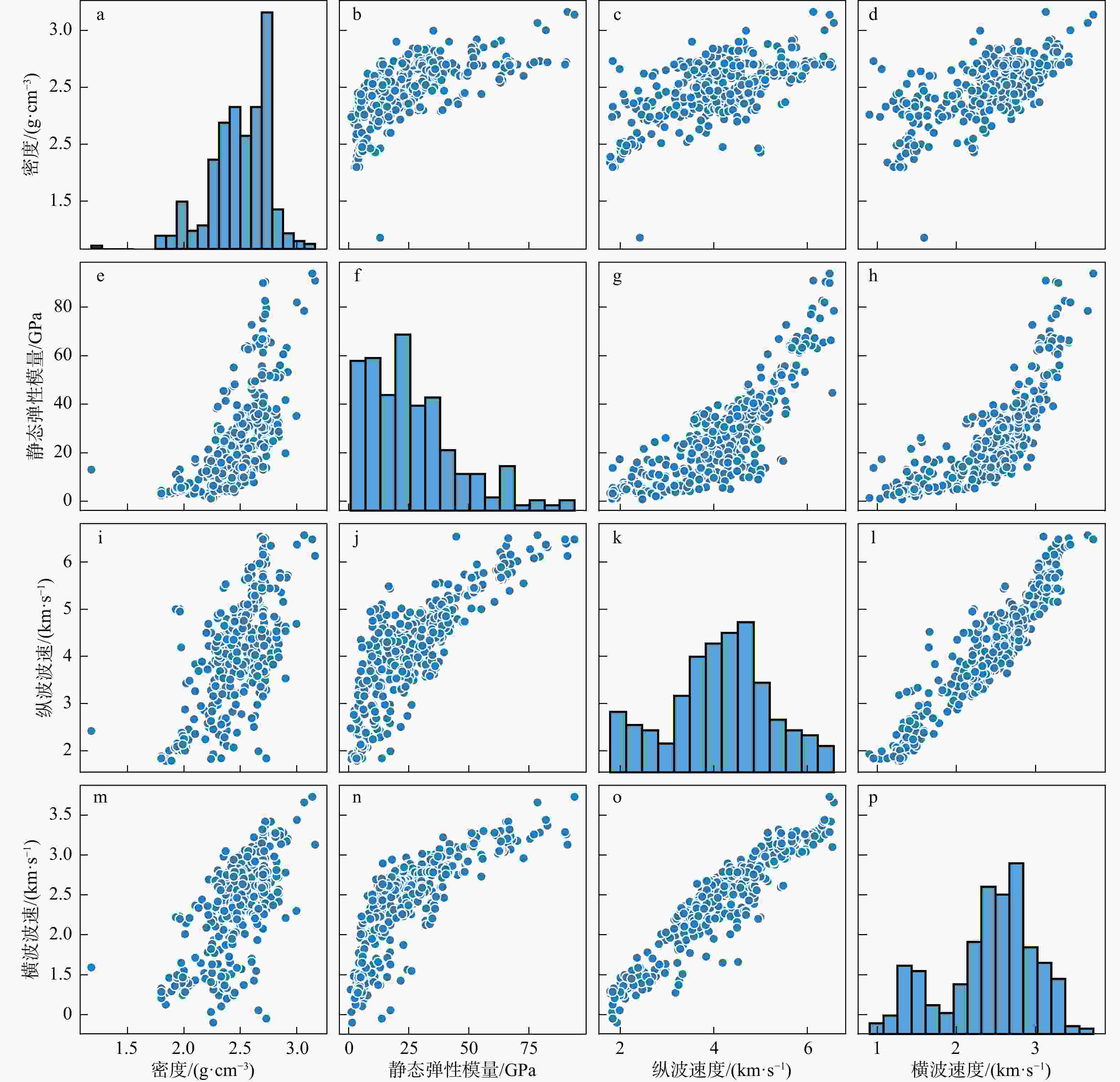
表 2 数据分布情况
Table 2. Data distribution
参数 密度/
(g·cm−3)静态弹性模量/
GPa纵波速度/
(km·s−1)横波速度/
(km·s−1)平均值 2.49 26.64 4.13 2.41 标准差 0.25 18.99 1.10 0.58 中位数 2.53 12.00 3.51 2.13 最大值 3.16 93.9 6.57 3.73 最小值 1.18 0.77 1.78 0.90 表 3 优化后的超参数
Table 3. Optimized hyperparameters
LightGBM
超参数取值 XGBoost
超参数取值 RandomForest
超参数取值 alpha 11.05 alpha 9.23 max_depth 25 learning_rate 0.19 learning_rate 0.09 n_estimators 1011 max_depth 36 max_depth 35 min_data_in_leaf 16 subsample 0.46 n_estimators 310 n_estimators 163 num_leaves 43 num_leaves 93 reg_lambda 1.71 reg_lambda 2.86 eta 0.02 表 4 预测模型的性能对比
Table 4. Performance comparison of prediction models
预测模型 RandomForest XGBoost LightGBM 统计回归模型 R2 训练集 0.98 0.98 0.97 0.78 测试集 0.86 0.87 0.86 交叉验证集 0.86 0.86 0.85 RMSE 训练集 2.54 2.70 3.41 9.11 测试集 7.16 6.87 7.14 交叉验证集 6.90 6.94 7.04 MAE 训练集 1.78 1.88 2.27 6.80 测试集 4.93 4.94 5.00 交叉验证集 4.87 4.96 5.19 注:R2. 决定系数;RMSE. 均方根误差;MAE. 平均绝对误差 -
[1] 蔡美峰. 岩石力学与工程[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002.CAI M F. Rock mechanics and engineering[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002. (in Chinese) [2] 李红斌, 王贵文, 庞小娇, 等. 苏北盆地古近系阜宁组页岩工程品质测井评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(3): 311-322. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20210692LI H B, WANG G W, PANG X J, et al. Logging evaluation of the engineering quality of the Paleogene Funing Formation oil shales in the Subei Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(3): 311-322. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20210692 [3] 舒红林, 仇凯斌, 李庆飞, 等. 页岩气地质力学特征评价方法: 中国南方海相强改造区山地页岩地质力学特征[J]. 天然气工业, 2021, 41(增刊1): 1-13.SHU H L, QIU K B, LI Q F, et al. A method for evaluating the geomechanical characteristics of shale gas: The geomechanical characteristics of the mountain shale in the intensively reworked marine area of South China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2021, 41(S1): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 葛洪魁, 陈颙, 林英松. 岩石动态与静态弹性参数差别的微观机理[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 25(4): 34-36.GE H K, CHEN Y, LIN Y S. Microscopic mechanism of difference between static and dynamic elastic parameters of rock[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum, China, 2001, 25(4): 34-36. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 尤明庆, 苏承东, 申江. 岩石材料的非均质性与动态参数[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 20(4): 492-494.YOU M Q, SU C D, SHEN J. Effect of heterogeneity on the dynamic parameters of rock[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science Edition), 2001, 20(4): 492-494. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] FJÆR E. Relations between static and dynamic moduli of sedimentary rocks[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2019, 67(1): 128-139. doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.12711 [7] 陈勉, 金衍, 张广清. 石油工程岩石力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008.CHEN M, JIN Y, ZHANG G Q. Rock mechanics of petroleum engineering[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008. (in Chinese) [8] LOZOVYI S, BAUER A. From static to dynamic stiffness of shales: Frequency and stress dependence[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(12): 5085-5098. doi: 10.1007/s00603-019-01934-1 [9] 蔡文军, 邓金根, 冯永存, 等. 泥页岩地层区域三维地质力学建模与应用[J]. 钻采工艺, 2023, 46(1): 8-14. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2023.01.02CAI W J, DENG J G, FENG Y C, et al. Three-dimensional geomechanical modeling and application in shale formation[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 2023, 46(1): 8-14. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1006-768X.2023.01.02 [10] 杨宝刚, 潘仁芳, 赵丹, 等. 四川盆地长宁示范区龙马溪组页岩岩石力学特性及脆性评价[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(4): 183-188.YANG B G, PAN R F, ZHAO D, et al. Mechanical properties and brittleness evaluation of Longmaxi shale rock of Changning demonstration area in Sichuan Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(4): 183-188. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 王文文, 李诺, 韩建强, 等. 基于多基因遗传规划的储层岩石静态模量预测[J]. 应用声学, 2020, 39(2): 300-305.WANG W W, LI N, HAN J Q, et al. Static modulus prediction for reservoir rocks based on multi-gene genetic programming[J]. Journal of Applied Acoustics, 2020, 39(2): 300-305. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] ELKATATNY S, MAHMOUD M, MOHAMED I, et al. Development of a new correlation to determine the static Young's modulus[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 2018, 8(1): 17-30. doi: 10.1007/s13202-017-0316-4 [13] NASIRI H, HOMAFAR A, CHELGANI S C. Prediction of uniaxial compressive strength and modulus of elasticity for Travertine samples using an explainable artificial intelligence[J]. Results in Geophysical Sciences, 2021, 8: 100034. doi: 10.1016/j.ringps.2021.100034 [14] 杨剑锋, 乔佩蕊, 李永梅, 等. 机器学习分类问题及算法研究综述[J]. 统计与决策, 2019, 35(6): 36-40. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2019.06.008YANG J F, QIAO P R, LI Y M, et al. A review of machine-learning classification and algorithms[J]. Statistics & Decision, 2019, 35(6): 36-40. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2019.06.008 [15] 徐继伟, 杨云. 集成学习方法: 研究综述[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 40(6): 1082-1092. doi: 10.7540/j.ynu.20180455XU J W, YANG Y. A survey of ensemble learning approaches[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2018, 40(6): 1082-1092. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7540/j.ynu.20180455 [16] 肖立志. 机器学习数据驱动与机理模型融合及可解释性问题[J]. 石油物探, 2022, 61(2): 205-212.XIAO L Z. The fusion of data-driven machine learning with mechanism models and interpretability issues[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2022, 61(2): 205-212. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 李超, 汪磊, 陈洋, 等. 基于贝叶斯集成学习算法的土体先期固结压力预测模型[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(5): 1780-1792.LI C, WANG L, CHEN Y, et al. Prediction model of soils' preconsolidation pressure based on Bayesian ensemble learning algorithm[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(5): 1780-1792. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] SUN J L, ZHANG R, ZHANG A L, et al. Rock strength prediction based on machine learning: A study from prediction model to mechanism explanation[J]. Measurement, 2024, 238: 115373. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2024.115373 [19] BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45: 5-32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 [20] CHEN T Q, GUESTRIN C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. San Francisco California USA: ACM, 2016: 785-794. [21] KE G, MENG Q, FINLEY T, et al. LightGBM: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree[C]//Anon. Neural Information Processing Systems. [S. 1. ]: [s. n. ], 2017: 3146-3154. [22] 李阳, 代宗仰, 张洁伟, 等. 基于无监督学习的多参数储层评价: 以蒲包山地区下三叠统飞仙关组礁滩储层为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(5): 285-292.LI Y, DAI Z Y, ZHANG J W, et al. Multiparameter reservoir evaluation method based on unsupervised learning: A case study of the reef beach reservoir of the Lower Triassic Feixianguan Formation in the Pubaoshan area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(5): 285-292. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] BERGSTRA J S, BARDENET R, BENGIO Y, et al. Algorithms for hyper-parameter optimization[C]//Anon. Neural Information Processing Systems. [S. 1. ]: [s. n. ], 2011: 2546-2554. [24] LUNDBERG S M and LEE S I. A unified approach to interpreting model predictions[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. [S. 1. ]: [s. n. ], 2017: 4765-4774. [25] LUNDBERG S M, ERION G, CHEN H, et al. From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2020, 2(1): 56-67. [26] 陈曦泽, 贾俊峰, 白玉磊, 等. 基于XGBoost-SHAP的钢管混凝土柱轴向承载力预测模型[J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2023, 57(6): 1061-1070.CHEN X Z, JIA J F, BAI Y L, et al. Prediction model of axial bearing capacity of concrete-filled steel tube columns based on XGBoost-SHAP[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2023, 57(6): 1061-1070. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 李新林. 川南深层页岩气储层地应力测井评价方法研究[D]. 武汉: 长江大学, 2022.LI X L. Study on logging evaluation method of in-situ stress for deep shale gas reservoir in southern Sichuan[D]. Wuhan: Yangtze University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 江昊焱. X地区致密砂岩储层岩石力学特性及体积压裂甜点研究[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2020.JIANG H Y. Study on rock mechanical characteristics and volume fracturing "sweet spot"of tight sandstone reservoir in area X[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an Shiyou University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 王艳梅. 岩石力学动、静态参数关系研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2012.WANG Y M. Study on the relationship between dynamic and static parameters of rock mechanics[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] LAMA R D, VUTUKURI V S. Handbook on mechanical properties of rocks: Testing techniques and results[M]. Clausthal, Bay Village, Ohio : Trans. Tech. Publications, 1978. [31] MORADIAN Z A, BEHNIA M. Predicting the uniaxial compressive strength and static Young's modulus of intact sedimentary rocks using the ultrasonic test[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics, 2009, 9(1): 14-19. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)1532-3641(2009)9:1(14) [32] NAJIBI A R, GHAFOORI M, LASHKARIPOUR G R, et al. Empirical relations between strength and static and dynamic elastic properties of Asmari and Sarvak limestones, two main oil reservoirs in Iran[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2015, 126: 78-82. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2014.12.010 [33] YALE D P, JAMIESON W H. Static and dynamic rock mechanical properties in the Hugoton and Panoma fields, Kansas[C]//Anon. SPE Mid-Continent Gas Symposium. Richardson: Society of Petroleum Engineers, 1994: SPE 27939-MS. [34] ABD EL-AAL A K, SALAH M K, KHALIFA M A. Acoustic and strength characterization of Upper Cretaceous dolostones from the Bahariya Oasis, western Desert, Egypt: The impact of porosity and diagenesis[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 187: 106798. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106798 [35] SHARIFI J, NOORAIEPOUR M, AMIRI M, et al. Developing a relationship between static Young's modulus and seismic parameters[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology, 2023, 13(1): 203-218. doi: 10.1007/s13202-022-01546-6 [36] NAJIBI A R, GHAFOORI M, LASHKARIPOUR G R, et al. Reservoir geomechanical modeling: In situ stress, pore pressure, and mud design[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2017, 151: 31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.01.045 [37] HARRYPERSAD-DANIEL A M, BLAKE O O, RAMSOOK R. Determining the static Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio, and compressive strength of the friable Erin Formation rocks using P-wave velocity[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2022, 198: 104557. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2022.104557 [38] QIN X, ZHANG Y H, WANG Y, et al. Experimental study on the static and dynamic elastic stiffness of rock samples from a shale oil reservoir[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2023, 170: 105446. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2023.105446 [39] 伍顺伟, 高阳, 胡俊, 等. 玛湖地区横波预测方法优选及其对岩石力学参数计算的影响[J]. 特种油气藏, 2021, 28(3): 9-14.WU S W, GAO Y, HU J, et al. Prediction method optimization for S-wave in Mahu area and its influence on calculation of rock mechanics parameters[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2021, 28(3): 9-14. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 赵旭阳, 郭海敏, 李紫璇, 等. 基于测井横波预测的地应力场及岩石力学参数建模[J]. 断块油气田, 2021, 28(2): 235-240. doi: 10.6056/dkyqt202102016ZHAO X Y, GUO H M, LI Z X, et al. Modeling of in situ stress field and rock mechanics parameters based on logging shear wave prediction[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2021, 28(2): 235-240. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6056/dkyqt202102016 -




 下载:
下载: