Characteristics of dolomite in the first sub-member of the First Member of Longmaxi Formation shale in Tiangongtang area of Sichuan Basin and its influence on reservoir pore development
-
摘要:
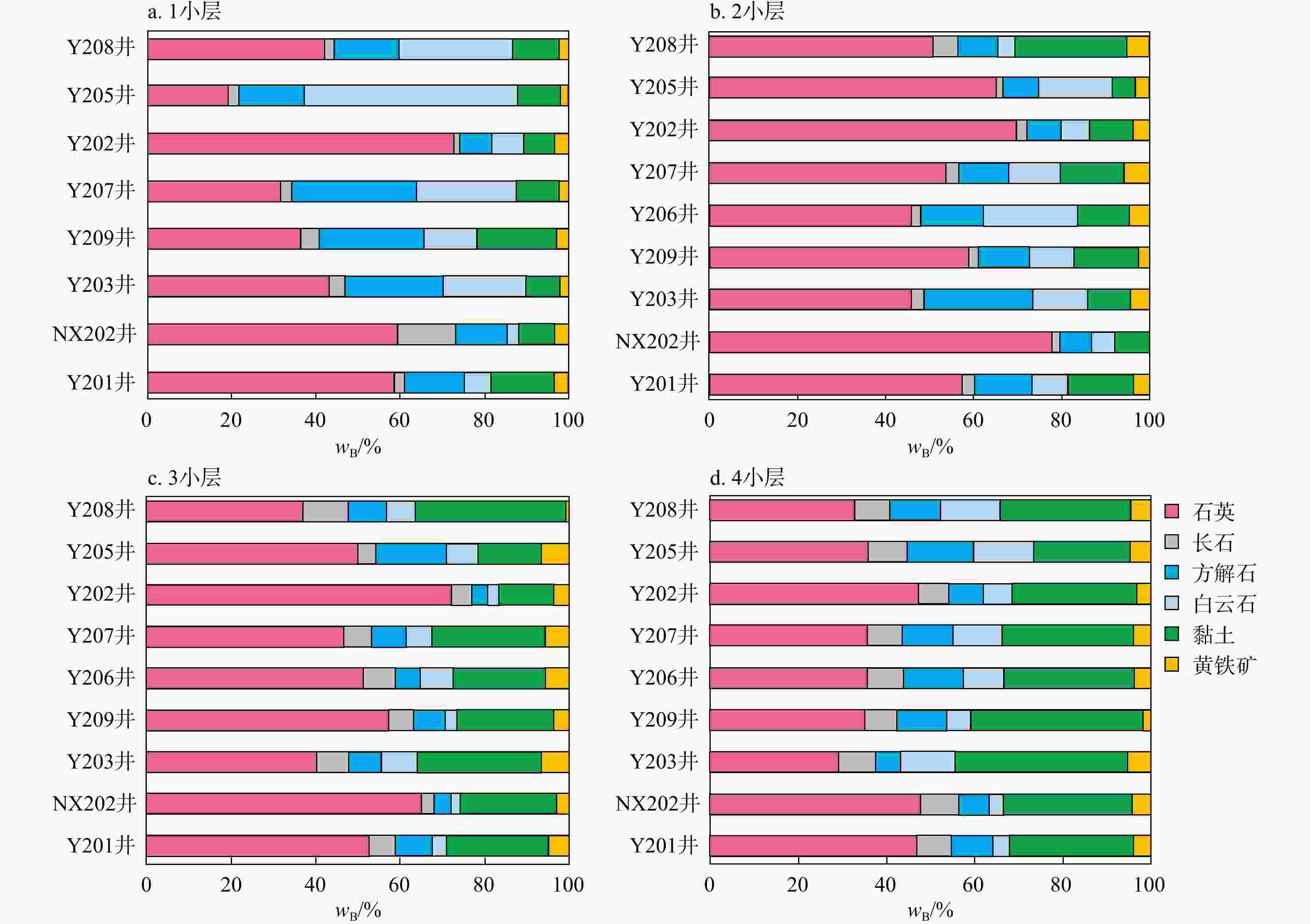
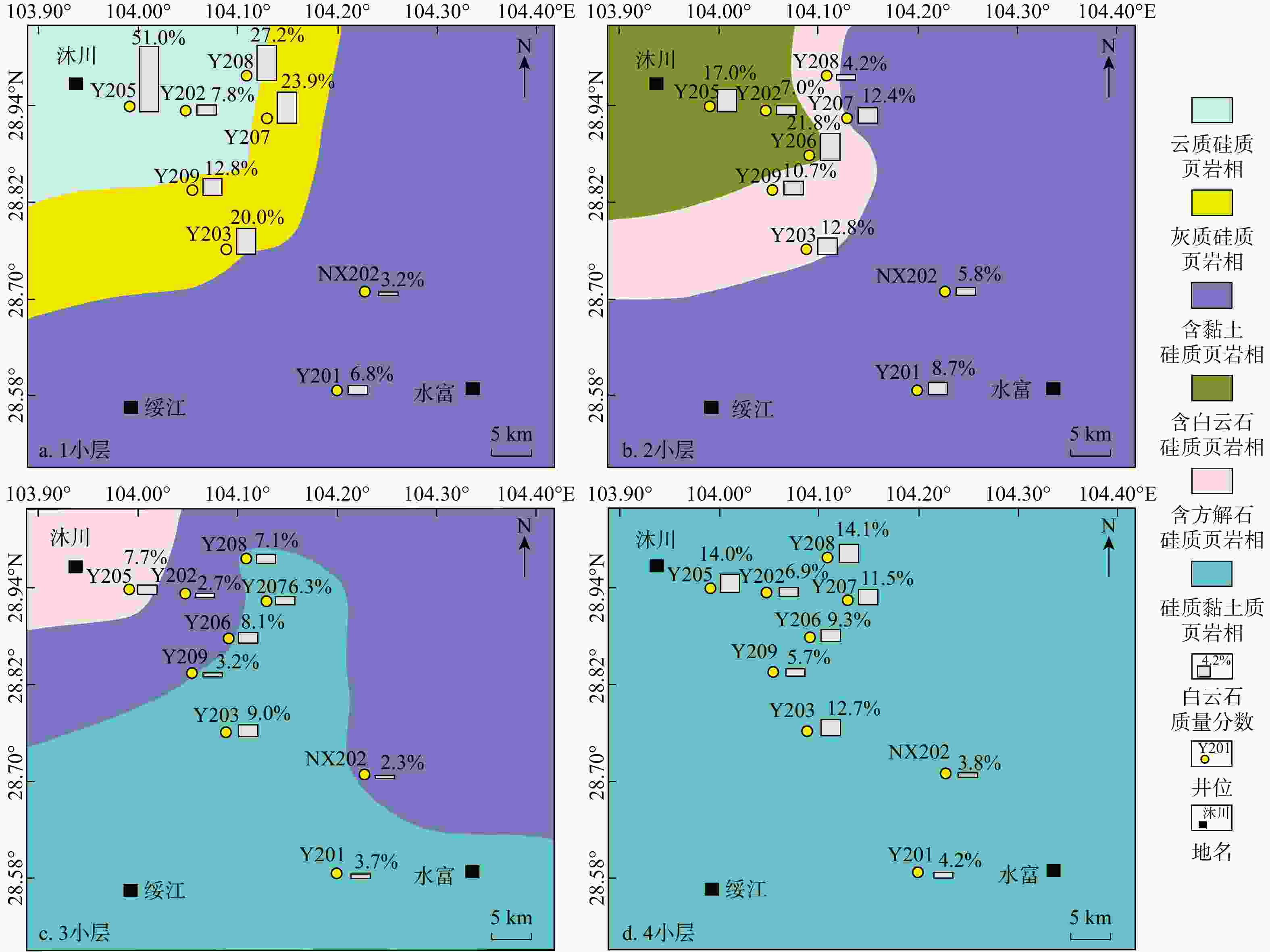
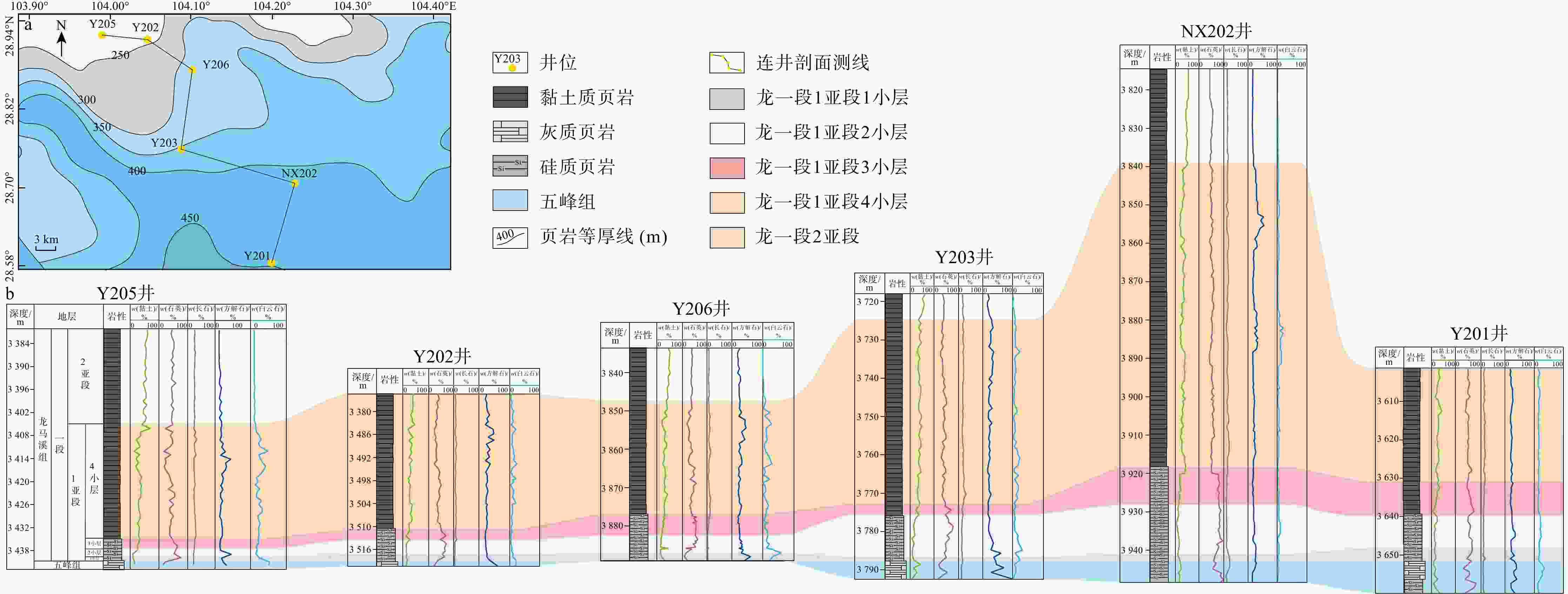
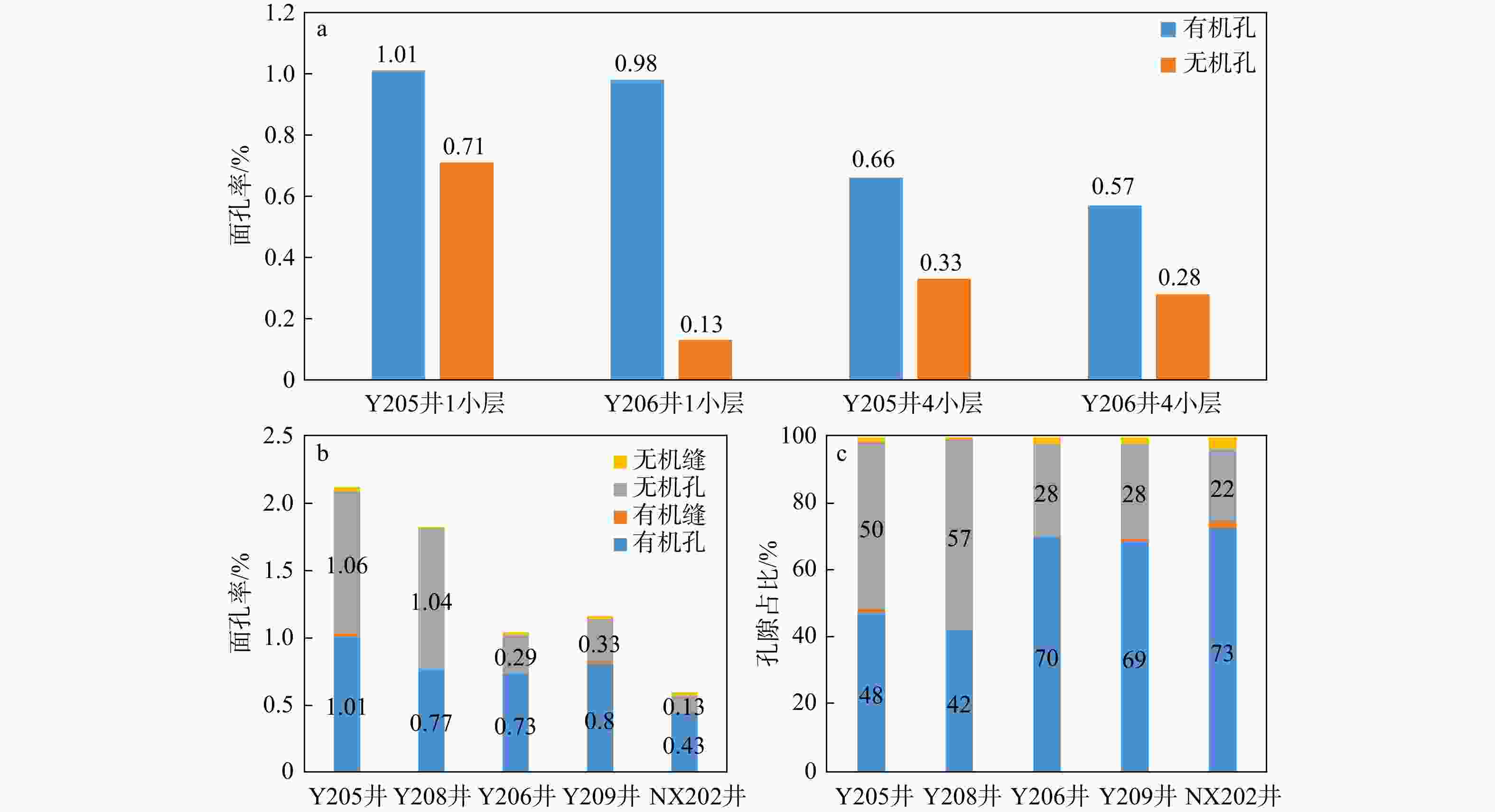
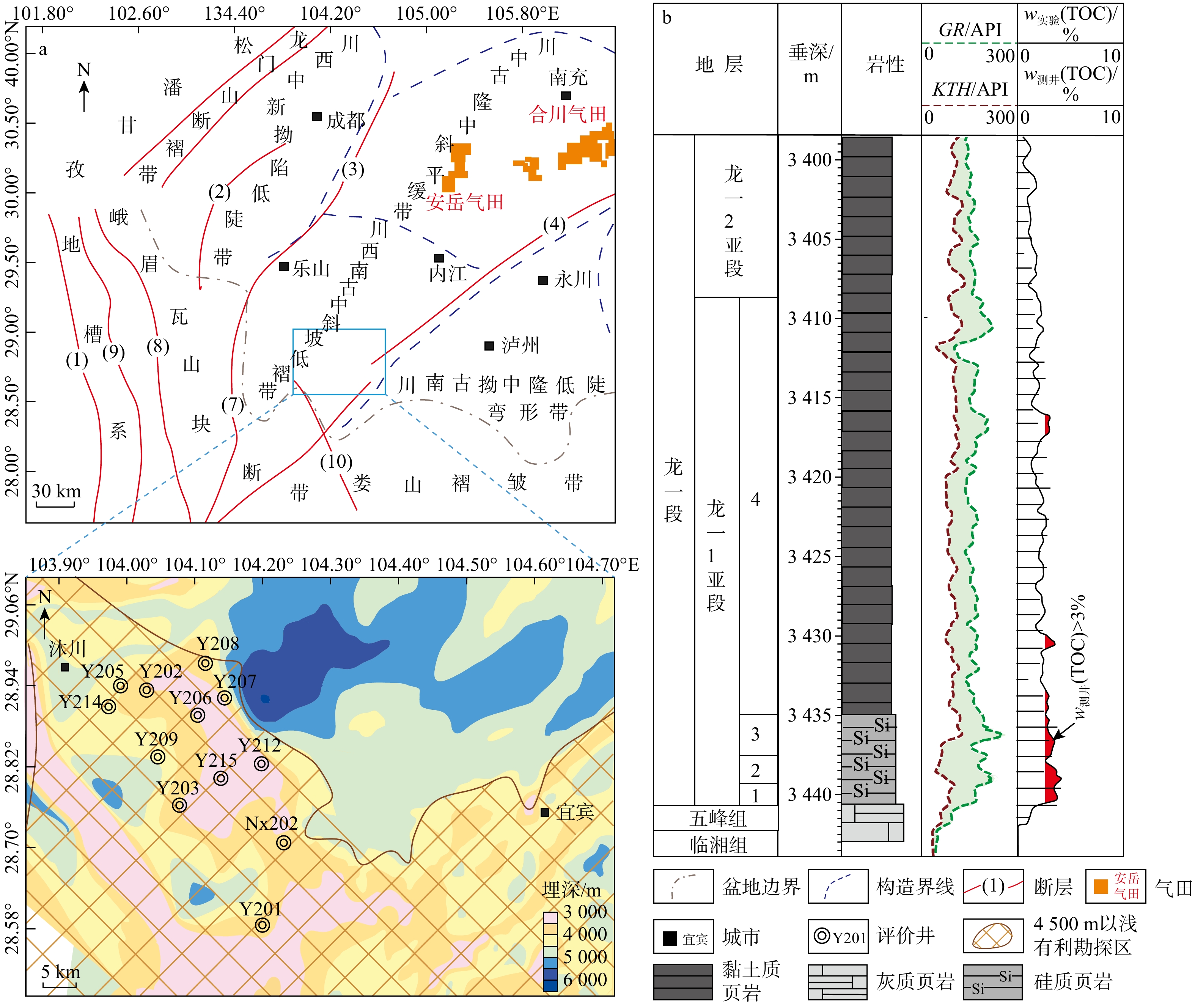
以四川盆地天宫堂地区龙马溪组一段1亚段海相页岩为研究对象,通过薄片观察、X射线衍射(X-Ray diffraction,简称XRD)、扫描电镜、电子探针等实验,分析海相富有机质页岩中白云石类型、成因、分布规律及其对储层物性的影响。根据矿物学特征,龙马溪组页岩中识别出分散状、纹层状和聚集状3种类型白云石。白云石具有菱形晶型,由白云石核心和环带组成。白云石核心结晶程度低,具有高镁高钙、几乎不含铁的特征,环带的自形程度高,具有高镁高钙高铁的特征。天宫堂地区龙马溪组页岩中西北部无机孔发育程度整体高于东南部,西北部的白云石含量也高于东南部。1小层无机孔发育程度优于4小层,1小层的白云石含量远高于4小层。白云石环带可能形成于成岩作用早期浅埋藏阶段的甲烷厌氧氧化作用带中,核心的磨圆特征表明其可能属于碎屑来源。天宫堂地区北部白云石含量的增加有利于无机孔的发育,白云石颗粒的抗压实能力较强,能有效改善页岩储层的储集物性。研究成果对页岩气的勘探和开发有一定指导作用。
Abstract:Objective and Methods This study investigates the types, origins, distribution, and impact on reservoir properties of dolomite in organic-rich marine shale of the first sub-member of the First Member of Longmaxi Formation in Tiangongtang area of the Sichuan Basin.
Results Utilizing thin-section observation, X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy, electron probe analysis, and other experiments, we have identified three dolomite types: Dispersed, layered, and aggregated dolomite. Dolomite crystals are rhombic, featuring a distinct core-ring structure. The core is poorly crystalline and compositionally characterized by high magnesium, high calcium, and almost no iron. In contrast, the ring is well-crystalline with high magnesium, high calcium, and high iron content. The distinct differential compaction boundaries and rhombic crystals at the edges of dolomite grains suggest that the ankerite ring may have formed in the methane anaerobic oxidation zone during the early shallow burial diagenesis. The rounding characteristics of the dolomite core suggest a detrital origin. Additionally, ankerite spots in the dolomite core may be due to the pore-filling cementation. The dolomite content in Tiangongtang area is highest in the first sub-member of the First Member of Longmaxi Formation shale, and gradually decreases upwards. The dolomite content shows a gradual increase from the deep-water area in the southeast to the shallow-water area in the northwest of the study area. Analysis of the dolomite content and visible porosity indicates that the development of inorganic pores in Longmaxi Formation shale in Tiangongtang area is closely related to the presence of dolomite. When the dolomite content is below 15%, it promotes the development of inorganic pores. When the dolomite content reaches about 15%~20%, its contribution to pore development peaks, and further increases in dolomite content no longer significantly affect reservoir pore development. Dolomite grains exhibit strong anti-compaction properties, retaining intergranular pores and effectively improving the reservoir properties of shale. In particular, the large number of intergranular pores between dolomite grains with layered and aggregated distributions makes a significant contribution to the reservoir space, whereas dispersed dolomite has little impact on pore development.
Conclusion The research results offer valuable insights for shale gas exploration and development.
-
Key words:
- dolomite /
- reservoir pore development /
- Longmaxi Formation shale /
- Tiangongtang area /
- Sichuan Basin
-
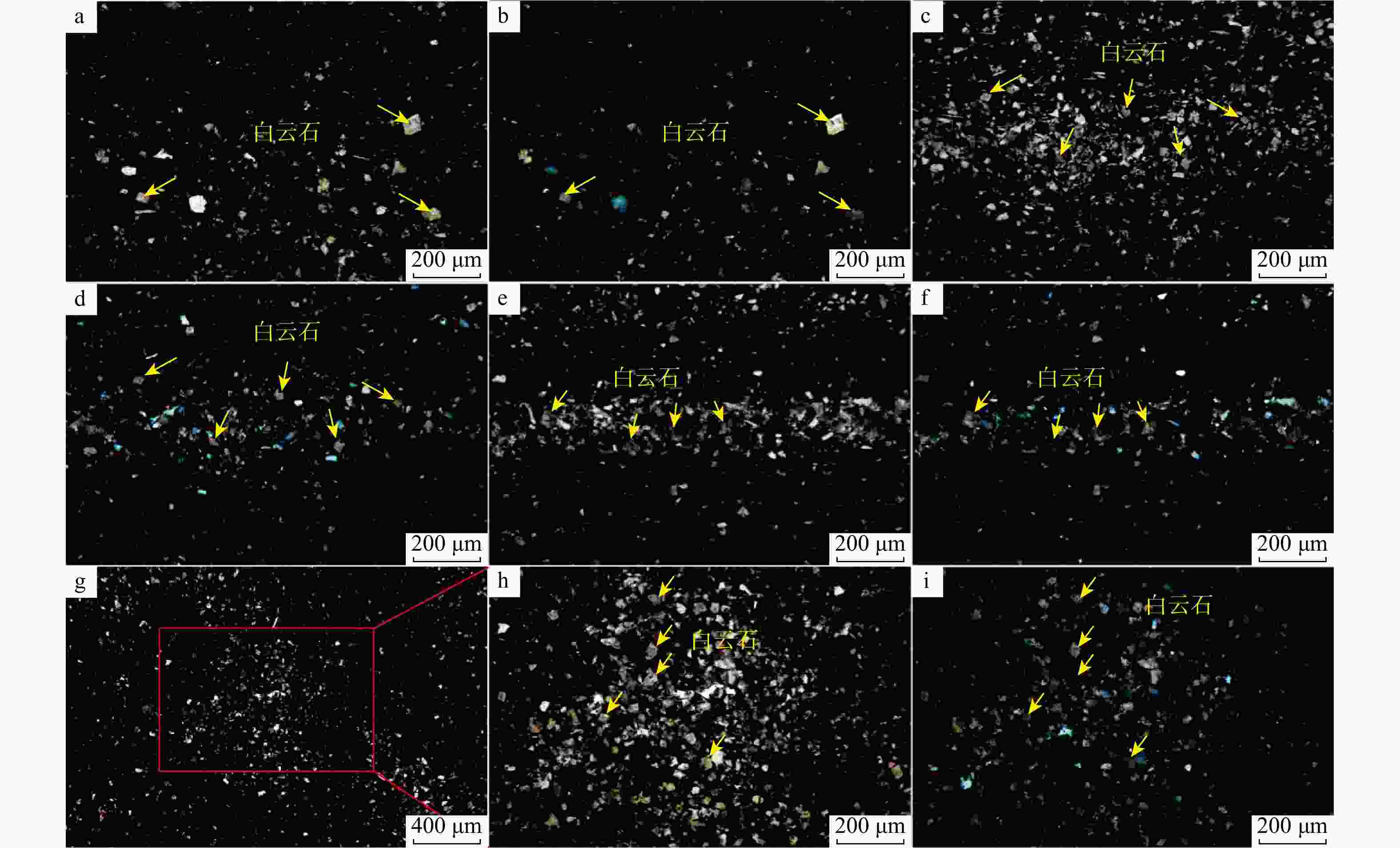
图 3 天宫堂地区龙一1亚段页岩光学显微镜特征
a. 少量白云石分散于泥质中,Y205井,
3413.45 m,4小层,单偏光;b. 少量白云石分散于泥质中,Y205井,3413.45 m,4小层,正交光;c. 大量白云石呈纹层状分布于暗色泥质中,Y205井,3424.45 m,4小层,单偏光;d. 大量白云石呈纹层状分布于暗色泥质中,Y205井,3424.45 m,4小层,正交光;e. 大量白云石呈纹层状分布于暗色泥质中,Y205井,3424.45 m,4小层,单偏光;f. 大量白云石呈纹层状分布于暗色泥质中,Y205井,3424.45 m,4小层,正交光;g, h. 大量白云石聚集分布,Y205井,3420.48 m,4小层,单偏光;i. 大量白云石聚集分布,Y205井,3420.48 m,4小层,正交光Figure 3. Optical microscopic characteristics in the first sub-member of the First Member of Longmaxi Formation shale in Tiangongtang area
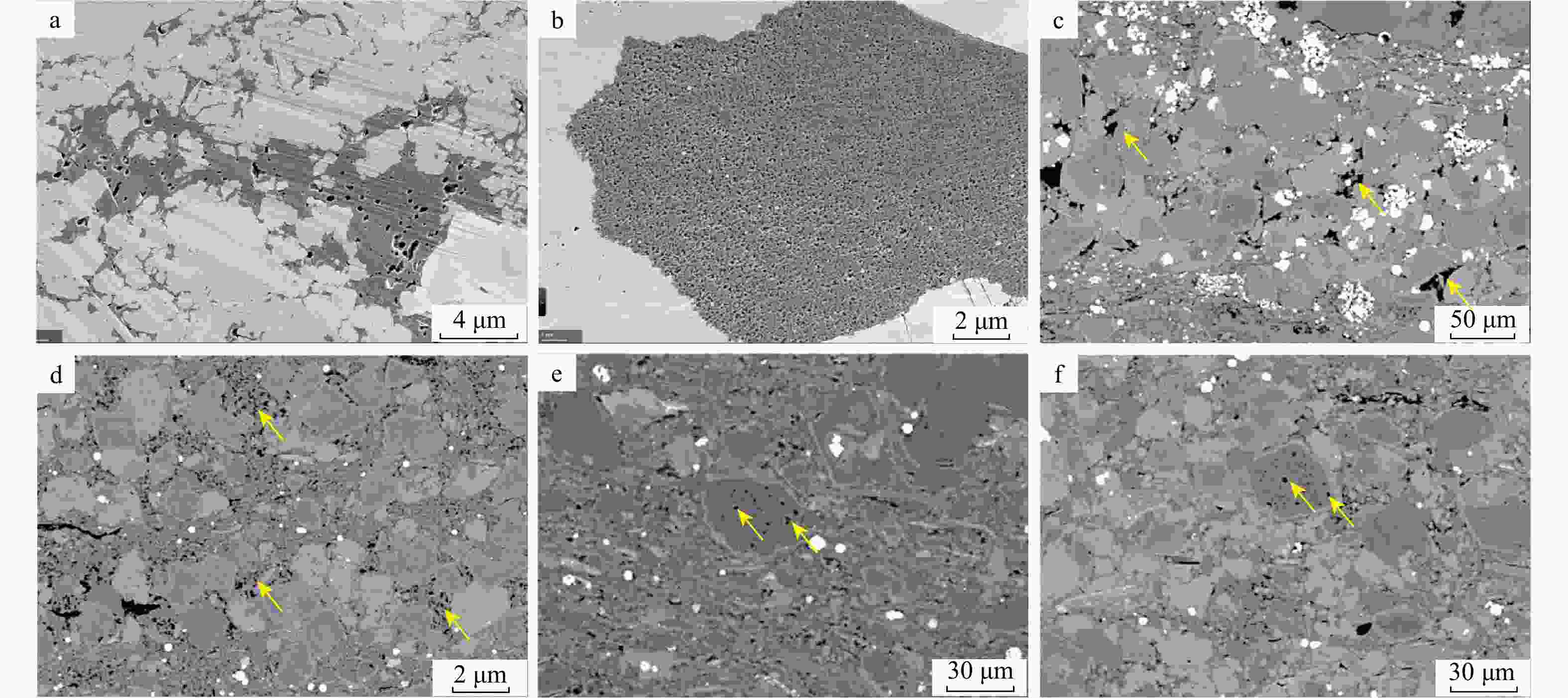
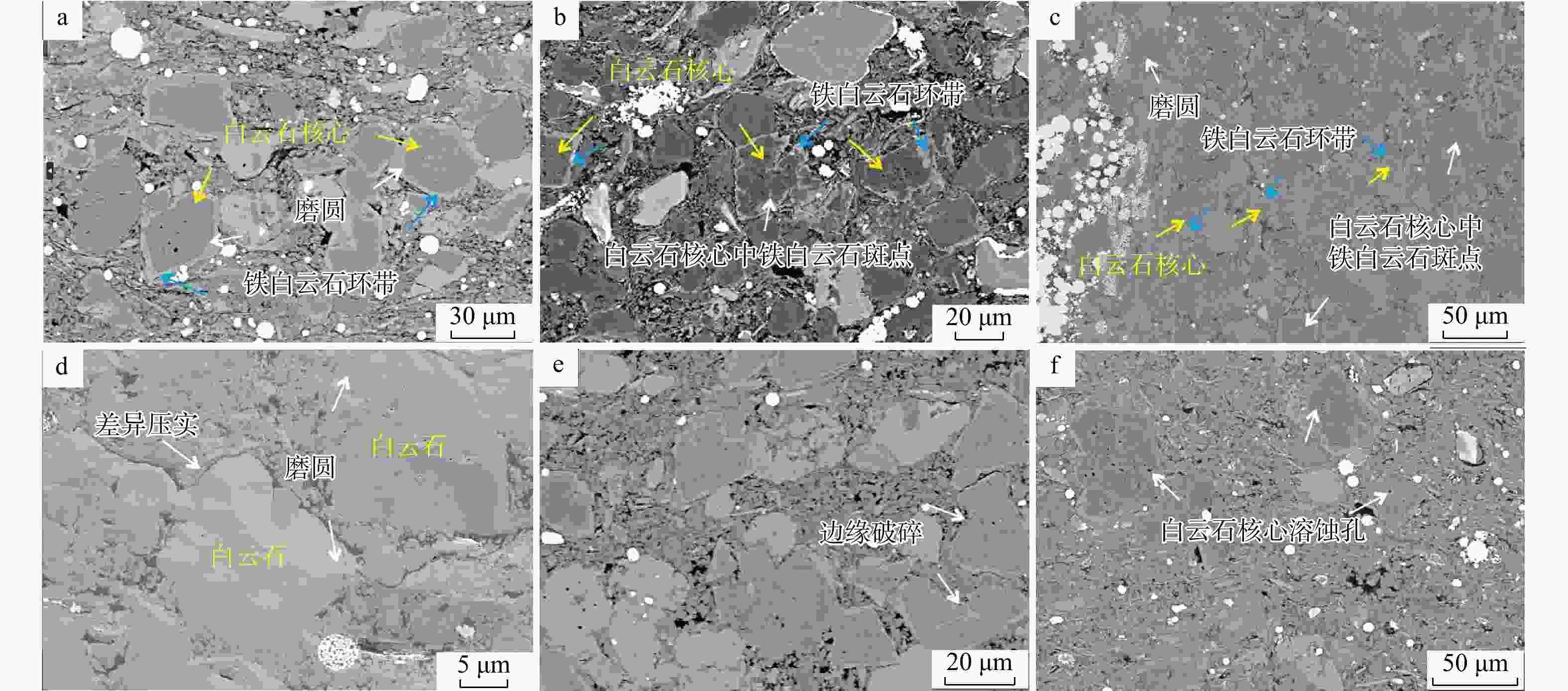
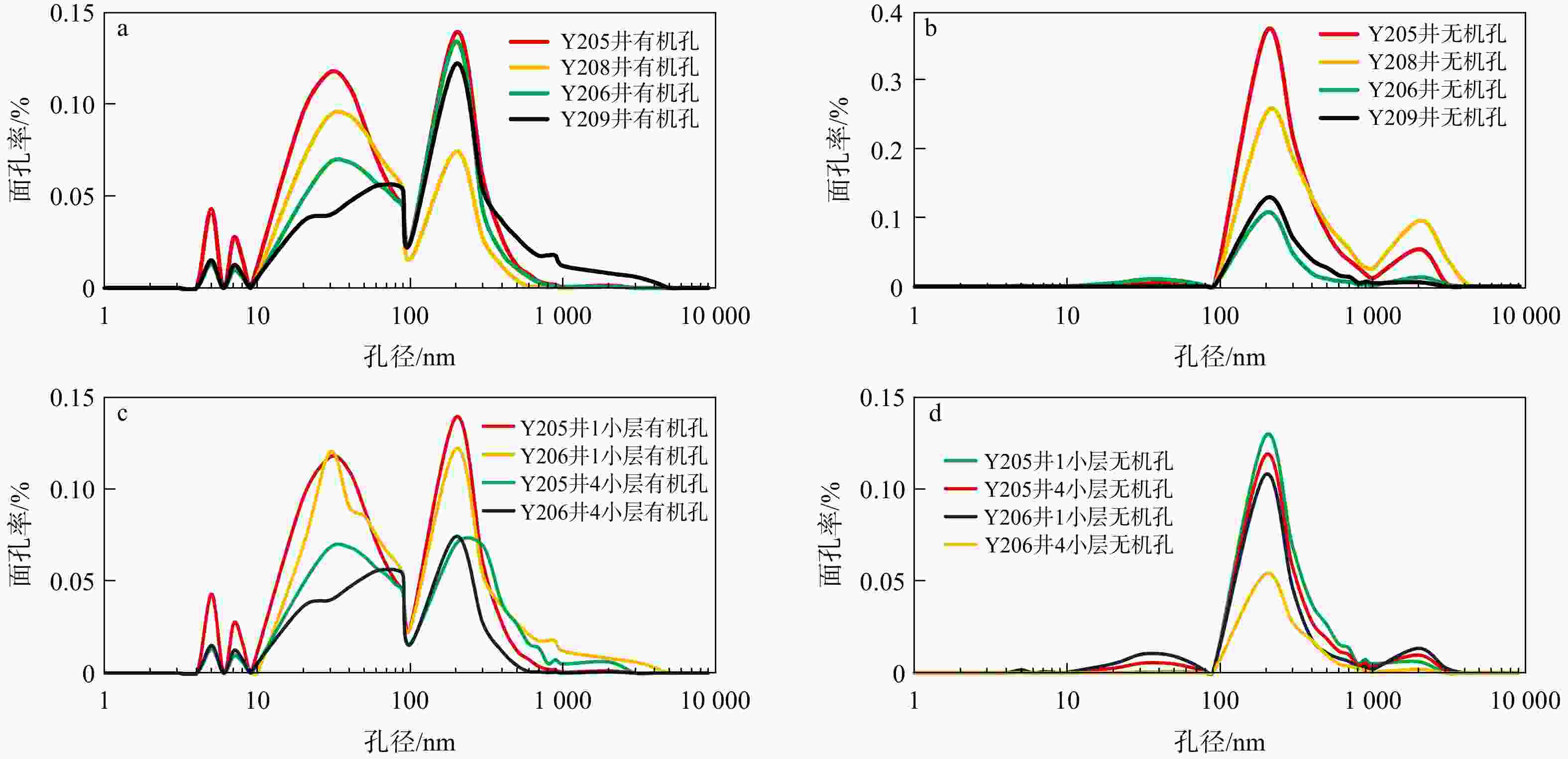
图 4 天宫堂地区龙一1亚段页岩中白云石扫描电镜特征
a.白云石的环带和核心,白云石核心的磨圆现象,Y205井,
3436.47 m,3小层;b. 白云石的环带和核心,白云石核心中的铁白云石斑点,Y206井,3875.2 m,4小层;c. 白云石的环带和核心,白云石核心的磨圆现象,白云石核心中的铁白云石斑点,Y205井,3436.47 m,3小层;d. 白云石边缘磨圆现象,白云石颗粒边缘的差异压实现象,L205井,4033.40 m,1小层;e. 纹层状白云石颗粒边缘的破碎现象,Y205井,3436.47 m,3小层;f. 白云石核心中的溶蚀孔,Y203井,3750.44 m,4小层Figure 4. Scanning electron microscopic characteristics of dolomite in the first sub-member of the First Member of Longmaxi Formation shale in Tiangongtang area
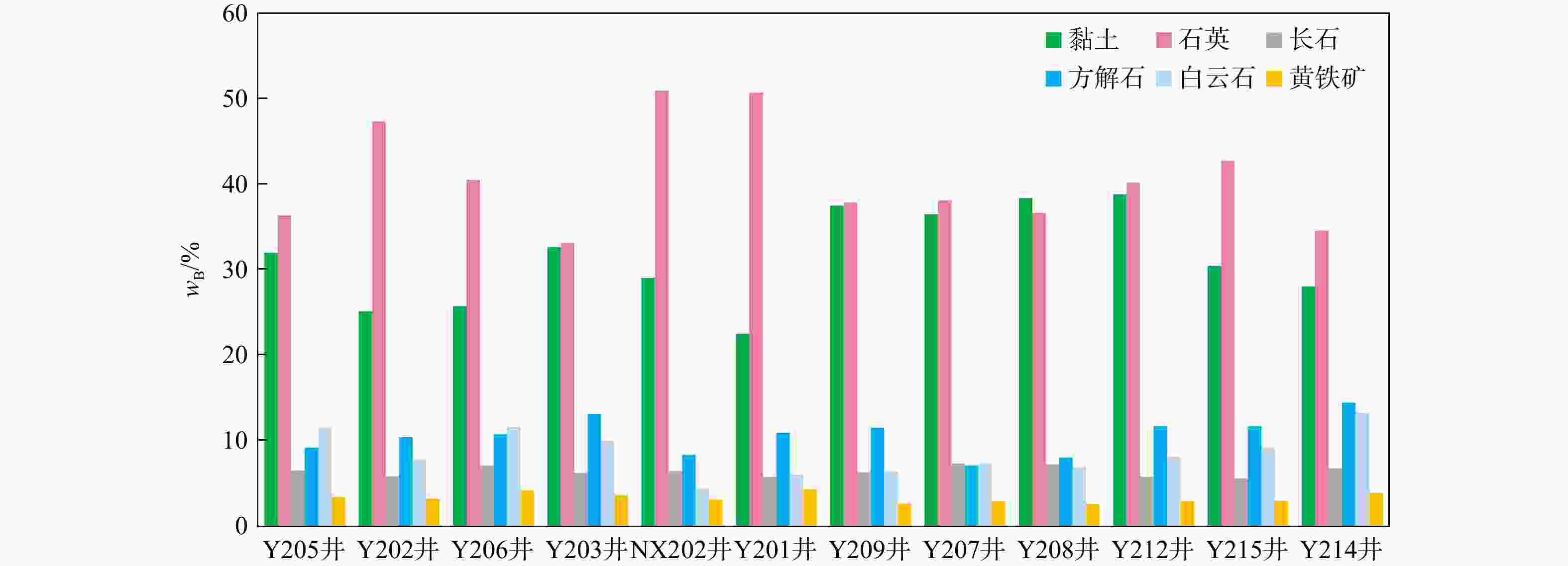
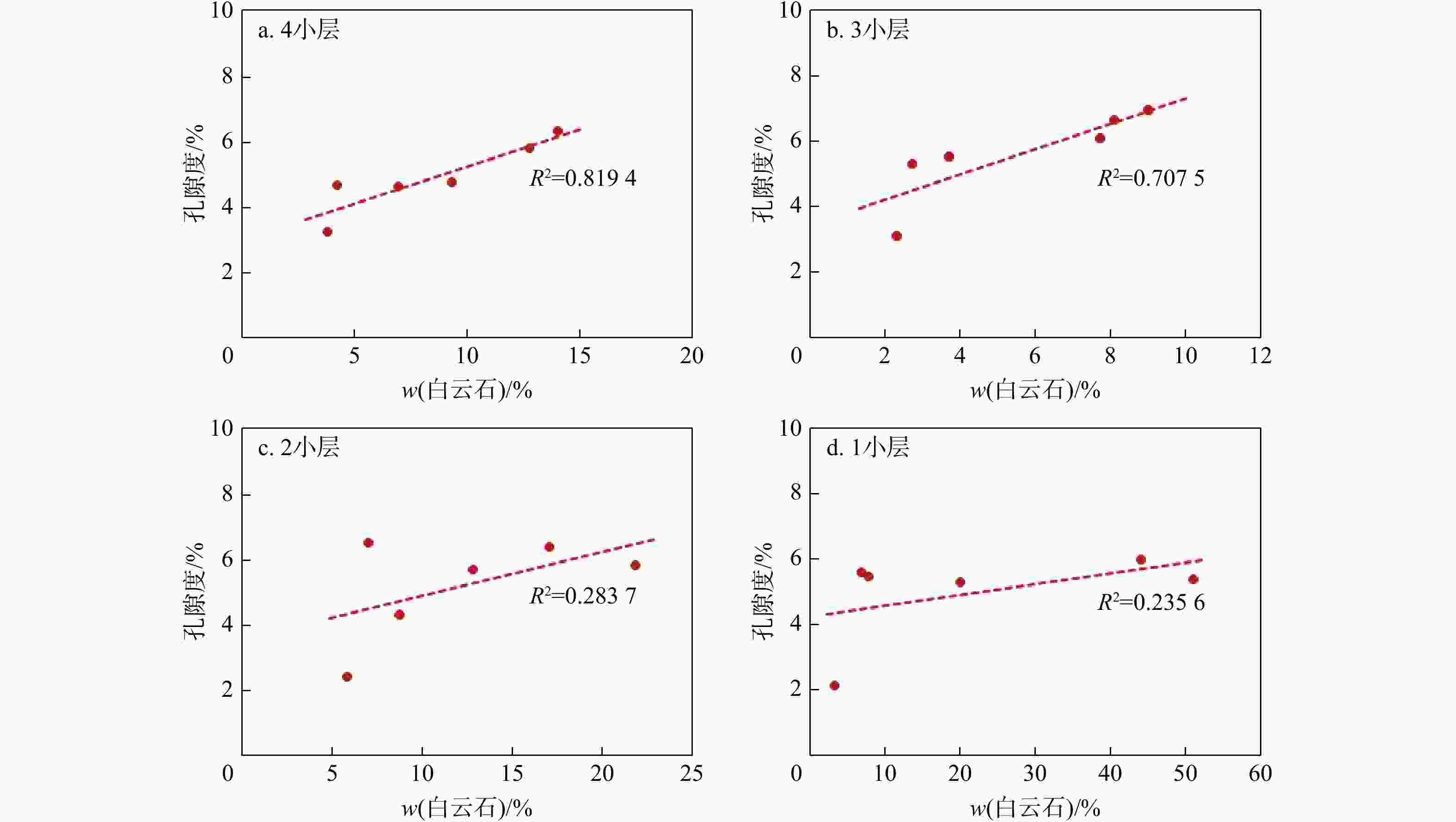
表 1 天宫堂地区五峰组−龙马溪组龙一1亚段各小层储层参数实验数据
Table 1. Test data of reservoir parameters for each small layer in the first sub-member of the First Member of Wufeng Formation and Longmaxi Formation in Tiangongtang area
区块 地层 地层厚度/m w(TOC)/% 孔隙度/% 脆性矿物质量分数/% 含气饱和度/% 天宫堂构造 龙一2亚段 6.7~46.1
27.30.1~1.7
0.51.0~5.5
3.035.4~59.0
48.511.3~66.1
40.6龙一1亚段 4小层 21.3~78.9
41.60.1~4.6
2.31.0~7.4
3.934.0~90.0
65.710.6~77.9
54.03小层 2.3~10.1
5.30.9~6.9
4.31.8~8.1
5.245.4~89.3
72.113.9~86.5
59.12小层 2.0~13.0
5.91.3~6.5
4.01.3~7.5
4.738.0~99.0
84.47.3~90.9
65.01小层 0.8~3.4
1.71.4~7.8
4.42.1~7.6
4.559.1~92.0
84.316.8~87.9
64.2五峰组 1.5~8.4
2.81.1~6.0
2.02.1~7.6
2.751.0~98.5
82.210.2~91.8
59.0注:数据来源于以下井:Y205、Y202、Y206、Y203、Y201、Y209、Y207、Y208;$\dfrac{6.7\sim 46.1}{27.3} $. $ \dfrac{最小值-最大值}{均值}$ 表 2 天宫堂地区Y205井龙一1亚段页岩白云石颗粒元素质量分数
Table 2. Element content of dolomite grains in the first sub-member of the First Member of Longmaxi Formation shale in Well Y205 in Tiangongtang area
分布形式 CaO MgO FeO 分布形式 CaO MgO FeO wB/% wB/% 白
云
石
核
心分
散
状30.92 18.58 0.25 白
云
石
核
心聚
集
状30.96 18.30 0.01 30.66 18.27 0.09 32.10 16.83 0.11 29.18 17.54 0.82 31.07 17.86 0.24 29.20 16.77 1.99 30.66 18.27 0.09 30.51 18.37 0.29 29.18 17.54 0.82 33.37 16.85 0.17 32.67 17.73 0.07 31.06 18.55 1.13 34.06 18.34 0.10 30.59 17.94 0.37 31.72 16.62 0.10 纹
层
状35.09 19.63 0.08 31.59 19.26 1.62 30.51 19.63 0.05 29.36 17.40 2.56 33.66 18.16 0.05 30.24 18.49 2.58 29.21 17.82 1.96 30.39 18.54 0.08 33.65 19.10 0.79 31.33 17.21 1.75 31.29 17.81 0.37 31.09 17.93 0.71 33.15 18.44 0.10 31.21 17.00 0.86 34.18 18.27 0.15 31.85 17.30 0.01 33.72 18.95 0.01 33.00 18.85 0.48 33.46 16.01 0.07 33.29 17.20 1.73 31.92 17.90 0.08 32.43 16.97 0.04 32.25 18.02 0.03 29.94 17.93 0.23 31.76 17.83 0.08 白
云
石
环
带纹
层
状28.07 14.71 8.81 33.27 19.00 0.18 28.61 15.60 8.36 34.73 18.95 0.09 27.56 16.10 5.24 34.68 18.28 0.07 27.39 18.28 6.49 30.92 18.58 0.25 28.79 15.37 8.01 31.62 17.80 0.09 29.15 15.94 4.90 31.27 17.50 0.08 28.76 15.70 7.31 31.99 17.01 0.07 29.28 16.20 6.32 31.46 16.15 1.00 26.89 11.95 12.02 30.96 18.30 0.01 26.21 15.26 3.74 32.10 16.83 0.11 29.68 15.50 4.21 31.07 17.86 0.24 27.77 14.38 8.95 30.66 18.27 0.09 聚
集
状29.47 14.74 4.51 29.18 17.54 0.82 25.65 13.91 9.40 29.20 16.77 1.99 28.20 12.15 9.87 32.30 17.93 0.09 28.07 14.71 8.81 32.45 16.01 2.84 28.61 15.60 8.36 32.28 16.76 0.08 27.56 16.10 5.24 32.00 17.01 0.06 27.39 18.28 6.49 29.90 16.01 2.27 28.79 15.37 8.01 -
[1] LOUCKS R G, RUPPEL S C. Mississippian Barnett shale: Lithofacies and depositional setting of a deep-water shale-gas succession in the Fort Worth Basin, Texas[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4): 579-601. doi: 10.1306/11020606059 [2] 邹才能, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型、特征、机理及展望: 以中国致密油和致密气为例[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(2): 173-187. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.203ZOU C N, ZHU R K, WU S T, et al. Types, characteristics, genesis and prospects of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon accumulations: Taking tight oil and tight gas in China as an instance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 173-187. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.203 [3] 刘超, 包汉勇, 万云强. 四川盆地东缘白马地区常压页岩气开发地质评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(4): 53-61. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230648LIU C, BAO H Y, WAN Y Q. Development geology avaluation of normal-pressured shale gas in the Baima area, eastern margin of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(4): 53-61. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230648 [4] LOUCKS R G, REED R M, RUPPEL S C, et al. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6): 1071-1098. doi: 10.1306/08171111061 [5] 舒志国, 舒逸, 陈绵琨, 等. 陆相页岩岩相非均质性及储层孔隙发育特征: 以四川盆地自流井组东岳庙段页岩为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 1-15. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220446SHU Z G, SHU Y, CHEN M K, et al. Lithofacies heterogeneity and reservoir pore development characteristics of continental shale: A case study of the Dongyuemiao shale of the Ziliujing Formation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 1-15. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20220446 [6] MATHIA E J, BOWEN L, THOMAS K M, et al. Evolution of porosity and pore types in organic-rich, calcareous, Lower Toarcian Posidonia shale[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 75: 117-139. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.04.009 [7] 袁俊亮, 邓金根, 张定宇, 等. 页岩气储层可压裂性评价技术[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(3): 523-527.YUAN J L, DENG J G, ZHANG D Y, et al. Fracability evaluation of shale-gas reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(3): 523-527. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] CHEN Y, ZHAO J H, HU Q H, et al. Origin of carbonate minerals and impacts on reservoir quality of the Wufeng and Longmaxi shale, Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Science, 2023, 20(6): 3311-3336. doi: 10.1016/j.petsci.2023.08.012 [9] WARTHMANN R, VAN LITH Y, VASCONCELOS C, et al. Bacterially induced dolomite precipitation in anoxic culture experiments[J]. Geology, 2000, 28(12): 1091. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<1091:BIDPIA>2.0.CO;2 [10] 王秀平, 牟传龙, 葛详英, 等. 川南及邻区龙马溪组黑色岩系矿物组分特征及评价[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(2): 150-162. doi: 10.7623/syxb201502003WANG X P, MOU C L, GE X Y, et al. Mineral component characteristics and evaluation of black rock series of Longmaxi Formation in Southern Sichuan and its periphery[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(2): 150-162. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7623/syxb201502003 [11] 郭芪恒, 金振奎, 耿一凯, 等. 四川盆地龙马溪组页岩中碳酸盐矿物特征及对储集性能的影响[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(5): 616-625.GUO Q H, JIN Z K, GENG Y K, et al. The characteristics of carbonate minerals in the Longmaxi Formation gas shale and its impact on the reservoir performance in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(5): 616-625. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 张梦琳, 李郭琴, 何嘉, 等. 川西南缘天宫堂构造奥陶系五峰组−志留系龙马溪组页岩气富集主控因素[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(2): 141-151.ZHANG M L, LI G Q, HE J, et al. Main controlling factors of Ordovician Wufeng-Silurian Longmaxi shale gas enrichment in Tiangongtang structure, southwestern margin of Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2022, 34(2): 141-151. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 何登发, 鲁人齐, 黄涵宇, 等. 长宁页岩气开发区地震的构造地质背景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(5): 993-1006. doi: 10.11698/PED.2019.05.19HE D F, LU R Q, HUANG H Y, et al. Tectonic and geological background of the earthquake hazards in Changning shale gas development zone, Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(5): 993-1006. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.2019.05.19 [14] 何骁, 吴建发, 雍锐, 等. 四川盆地长宁−威远区块海相页岩气田成藏条件及勘探开发关键技术[J]. 石油学报, 2021, 42(2): 259-272.HE X, WU J F, YONG R, et al. Accumulation conditions and key exploration and development technologies of marine shale gas field in Changning-Weiyuan block, Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2021, 42(2): 259-272. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] CHENG J R, MENG X Q, ZHANG E L, et al. An early Holocene primary dolomite layer of abiotic origin in Lake Sayram, central Asia[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(23): e2021GL096309. doi: 10.1029/2021GL096309 [16] BAKER P A, KASTNER M. Constraints on the formation of sedimentary dolomite[J]. Science, 1981, 213: 214-216. doi: 10.1126/science.213.4504.214 [17] COMPTON J S. Degree of supersaturation and precipitation of organogenic dolomite[J]. Geology, 1988, 16(4): 318. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1988)016<0318:DOSAPO>2.3.CO;2 [18] MA B B, CAO Y C, ERIKSSON K A, et al. Carbonate cementation patterns, potential mass transfer, and implications for reservoir heterogeneity in Eocene tight-oil sandstones, Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China: Evidence from petrology, geochemistry, and numerical modeling[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2019, 103(12): 3035-3067. doi: 10.1306/04101917330 [19] DUTTON S P. Calcite cement in Permian deep-water sandstones, Delaware Basin, West Texas: Origin, distribution, and effect on reservoir properties[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2008, 92(6): 765-787. doi: 10.1306/01280807107 [20] YANG T, CAO Y C, FRIIS H, et al. Genesis and distribution pattern of carbonate cements in lacustrine deep-water gravity-flow sandstone reservoirs in the Third Member of the Shahejie Formation in the Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression, eastern China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 92: 547-564. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.11.020 [21] SCHIEBER J, SHAO X H. Detecting detrital carbonate in shale successions: Relevance for evaluation of depositional setting and sequence stratigraphic interpretation[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 130: 105130. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105130 [22] DENNY A C, ORLAND I J, VALLEY J W. Regionally correlated oxygen and carbon isotope zonation in diagenetic carbonates of the Bakken Formation[J]. Chemical Geology, 2020, 531: 119327. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119327 [23] 曲红军. 试论古构造对轿顶山式锰矿的控制作用[J]. 地质与勘探, 1992, 28(6): 1-5.QU H J. On Palaeostructural of control the Jaiodingshan type Mn-deposits[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1992, 28(6): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 冯洪真, 王海峰, 方一亭, 等. 四川汉源五峰期地层中烷烃的某些分布特征[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 1994, 30(4): 662-669.FENG H Z, WANG H F, FANG Y T, et al. Some distributive characteristics of saturated hydrocarbons from Wufengian strata in Hanyuan area of Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Science), 1994, 30(4): 662-669. (in Chinese) [25] DAVIES P J, BUBELA B, FERGUSON J. Simulation of carbonate diagenetic processes: Formation of dolomite, huntite and monohydrocalcite by the reactions between nesquehonite and brine[J]. Chemical Geology, 1977, 19(1/2/3/4): 187-214. [26] MANSFIELD C F. A urolith of biogenic dolomite: Another clue in the dolomite mystery[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1980, 44(6): 829-839. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(80)90264-1 [27] MACHEL H G, MOUNTJOY E W. Chemistry and environments of dolomitization: A reappraisal[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1986, 23(3): 175-222. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(86)90017-6 [28] 牟传龙, 王秀平, 王启宇, 等. 川南及邻区下志留统龙马溪组下段沉积相与页岩气地质条件的关系[J]. 古地理学报, 2016, 18(3): 457-472. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2016.03.032MOU C L, WANG X P, WANG Q Y, et al. Relationship between sedimentary facies and shale gas geological conditions of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation in southern Sichuan Basin and its adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2016, 18(3): 457-472. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2016.03.032 [29] 姜在兴, 孔祥鑫, 杨叶芃, 等. 陆相碳酸盐质细粒沉积岩及油气甜点多源成因[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(1): 26-37. doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.01.03JIANG Z X, KONG X X, YANG Y P, et al. Multi-source genesis of continental carbonate-rich fine-grained sedimentary rocks and hydrocarbon sweet spots[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(1): 26-37. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.2021.01.03 [30] RICKMAN R, MULLEN M, PETRE E, et al. A practical use of shale petrophysics for stimulation design optimization: All shale plays are not clones of the Barnett shale[C]//Anon. SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition. [S. l. ]: SPE, 2008: SPE-115258-MS. [31] 邵红梅, 高波, 潘会芳, 等. 松辽盆地古龙页岩成岩: 孔隙演化[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2021, 40(5): 56-67. doi: 10.19597/J.ISSN.1000⁃3754.202107032SHAO H M, GAO B, PAN H F, et al. Diagenesis-pore evolution for Gulong shale in Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2021, 40(5): 56-67. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19597/J.ISSN.1000⁃3754.202107032 -




 下载:
下载: