Geothermal genesis and hazard assessment for a fault-controlled kilometer-deep tunnel in Xinjiang
-
摘要:
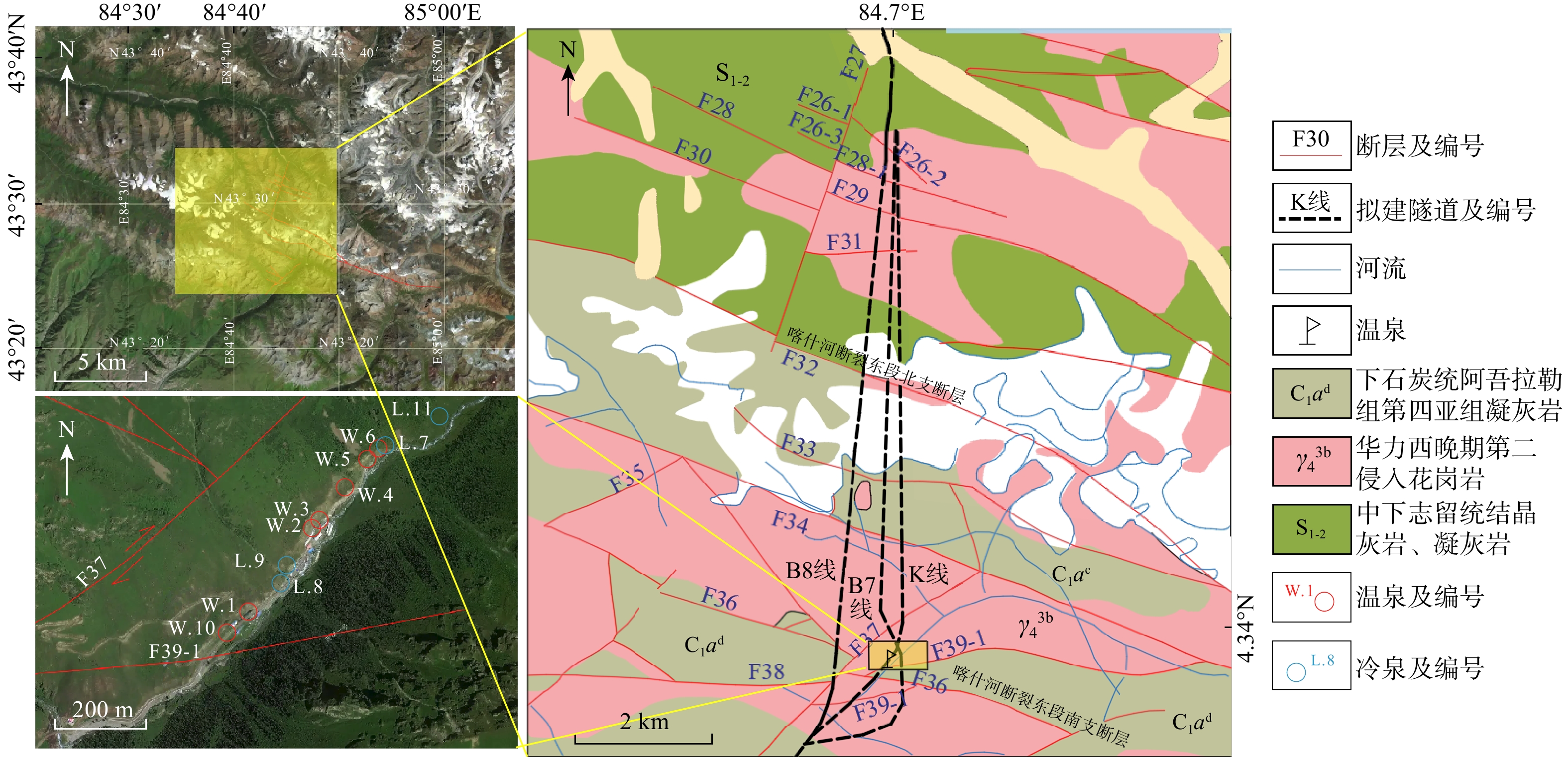
深部隧道建设受到各种地质活动的影响,其中地热活动严重影响了施工安全和效率,而目前研究缺乏对地热成因的实例研究。以拟建新疆某高速公路隧道(最大埋深
1348 m)为例,通过物探、钻探、水文地球化学、热红外遥感、无人机等方法得到该隧道工程地质、水文地质特征,对隧道附近温泉分布和高温等特征进行了研究。结果表明:温泉仅分布在F36与F37断裂交汇处EN方向的沟谷地区;研究区存在低电阻岩体破碎带,尤其分布在断层和温泉点附近;同时温泉水样矿化度与阿尔先河水相比相差很大,温度也略高于周围地层。研究得出研究区内地热水形成机制:地热水并非由较近的阿尔先河水补给,而是由大气降水和3000 m外的冰雪融水补给,地下水汇聚到F35、F36、F37断层交汇点附近在地下约200 m处遇深部热源加热,高温地下水沿2个断层交汇处裂隙向地表流动。同时采用了层次分析法对该隧道拟建线路开展热害评估,将断层、地温、隧道涌水、围岩岩性4个因素作为主要影响因子,评估结果表明,B8线路分值最低,说明其受热害影响程度最小,判断B8线为最优线路。本研究揭示了深埋隧道地热活动的形成机制与分布规律,为高寒山区隧道热害防治提供了科学依据。Abstract:Objective Deep tunnel construction is impacted by various geological processes, with geothermal activity significantly affecting construction safety and efficiency. However, case studies specifically revealing geothermal genesis remain scarce.
Methods An integrated approach employing geophysical exploration, drilling, hydrogeochemical analysis, thermal infrared remote sensing, and UAV surveys was utilized to characterize the engineering geological and hydrogeological conditions of a planned expressway tunnel in Xinjiang (maximum burial depth:
1348 m), with specific focus on adjacent hot springs and high-temperature phenomena.Results Results show that hot springs are exclusively distributed within the valley area northeast of the intersection between the F36 and F37 faults. Low-resistance fractured rock masses are presented within the study area, particularly concentrated near fault zones and hot spring locations. Additionally, hot spring water samples exhibit significantly higher mineralization compared to the Arxian River water, along with slightly elevated temperatures relative to the ambient strata.
Conclusion Based on aformentioned findings, the geothermal water formation mechanism within the study area is proposed. Recharge occurs not from the proximal Arxian River, but from atmospheric precipitation and meltwater sourced from distal glaciers/snowfields approximately 3 km away. These recharged groundwaters converge near the F35-F36-F37 fault intersection, where it is heated at about 200 m depth by a deep-seated heat source before ascending along fractures in the fault zone towards the surface. Furthermore, employing the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) for thermal hazard assessment of present planned tunnel alignments-considering faults, geothermal gradient, water inflow potential, and surrounding rock lithology as key factors-identified alignment B8 as optimal, evidenced by its lowest AHP score indicating minimal thermal hazard impact. This study elucidates the formation mechanisms and distribution patterns of geothermal activity in deep-buried tunnels, providing a scientific basis for thermal hazard mitigation in high-altitude permafrost regions.
-
Key words:
- deep-buried tunnel /
- geothermal genesis /
- fault control /
- thermal hazard /
- Xinjiang
-
图 4 阿尔先温泉物探结果图(剖面位置见图2)
Figure 4. Geophysical survey results for the hot springs in Arxan
表 1 钻孔温度表
Table 1. Borehole Temperature measurements
钻孔编号 孔深/m 孔内最高温度/℃ 地温梯度/(℃·100−1·m−1) ZK15-1 230 23.0 1.77 ZK15-2 110 21.5 1.39 ZK15-3 72 21.1 1.44 ZK18-4 323 24.6 1.46 表 2 最大埋深处温度值
Table 2. Temperature at the maximum buried depth
拟建线路 B8线 B7线 K线 左线 右线 左线 右线 左线 右线 最大埋深/m 1348 1339 1363 1348 1423 1442 计算最大埋深处温度/℃ 39.98 39.84 40.20 39.98 41.10 41.39 表 3 影响因子权重表
Table 3. Weighting of influencing factors
热害评估
影响因子决策层对目标
层的权重${w_i}$拟建线路 方案层对决策
层的权重${C_i}$断层 0.0633 B8线 0.1429 B7线 0.4286 K线 0.4286 地温 0.6558 B8线 0.1634 B7线 0.2970 K线 0.5396 隧道涌水 0.1744 B8线 0.4000 B7线 0.4000 K线 0.2000 岩性 0.1065 B8线 0.2000 B7线 0.6000 K线 0.2000 表 4 热害评估总得分
Table 4. Total score of thermal hazard assessment
拟建线路 得分 B8线 0.2073 B7线 0.3555 K线 0.4372 -
[1] 张家齐. 山岭铁路隧道施工塌方风险评估[D]. 石家庄:石家庄铁道大学,2021.ZHANG J Q. Risk assessment of collapse in mountain railway tunnel construction [D]. Shijiazhuang:Shijiazhuang Railway University,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 黄润秋,王贤能. 深埋隧道工程主要灾害地质问题分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,1998,25(4):21-24.HUANG R Q,WANG X N. The analysis of the main geological hazards in deep lying tunnels[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,1998,25(4):21-24. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 严金秀. 大埋深特长山岭隧道技术挑战及对策[J]. 现代隧道技术,2018,55(3):1-5.YAN J X. Technical challenges of super-long mountainous tunnels at great depth[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology,2018,55(3):1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 王建平. 高原高地热隧道热害防治安全施工技术[J]. 中小企业管理与科技(上旬刊),2014(4):125-126.WANG J P. Safety construction technology for prevention and control of thermal damage of high geothermal tunnel in plateau[J]. Management & Technology of SME,2014(4):125-126. (in Chinese) [5] 谢君泰,余云燕. 高海拔隧道工程热害等级划分[J]. 铁道工程学报,2013,30(12):69-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2013.12.015XIE J T,YU Y Y. Grades for heat damage in high altitude tunnel engineering[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society,2013,30(12):69-73. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2013.12.015 [6] 卢达. 拉日铁路雅江峡谷段隧道地热场模拟及地热分级研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2012.LU D. Geothermal field simulation and geothermal classification of tunnel in Yarlung Zangbo Gorge section of Luda-lari Railway [D]. Chengdu:Southwest Jiaotong University,2012. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 张杰. 拉月隧道地热场分布特征及热害防治措施研究[D]. 成都:西南交通大学,2021.ZHANG J. Research on the distribution characteristics of geothermal field and the prevention and control measures of heat damage in Layue Tunnel [D]. Chengdu:Southwest Jiaotong University,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 张宁,张文哲,李郎平,等. 青藏高原地温时空分布及某重大线性工程深部高地温风险分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(3):708-719.ZHANG N,ZHANG W Z,LI L P,et al. Geothermal characteristics of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and risk analysis of deep underground geothermal hazards for one major linear project[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(3):708-719. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 袁可. 高温隧道热害现象典型特点及影响因素权重分析[J]. 铁道建筑技术,2022(8):43-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4539.2022.08.010YUAN K. Typical characteristics and weight analysis of influencing factors of thermal damage in high temperature tunnels[J]. Railway Construction Technology,2022(8):43-47. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4539.2022.08.010 [10] LIN M, ZHOU P, JIANG Y F, et al. Numerical investigation on comprehensive control system of cooling and heat insulation for high geothermal tunnel: A case study on the highway tunnel with the highest temperature in China[J/OL]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2022, 173: 107385.LIN M,ZHOU P,JIANG Y F,et al. Numerical investigation on comprehensive control system of cooling and heat insulation for high geothermal tunnel:A case study on the highway tunnel with the highest temperature in China[J/OL]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences,2022,173:107385. [11] 李准. 玉磨铁路高地温隧道降温技术及其经济研究[J]. 铁道工程学报,2022,39(6):95-99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2022.06.017LI Z. Technical and economic research on the efficiency reduction and cooling measures in high geothermal tunnel in Yuxi-Mohan Railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society,2022,39(6):95-99. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2022.06.017 [12] 杨志勋,张兴权,王进. 新疆地下热水[J]. 新疆地质,1990,8(3):205-218.YANG Z X,ZHANG X Q,WANG J. Geothermal water of Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Geology,1990,8(3):205-218. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 侯代平,刘乃飞,余春海,等. 新疆布仑口高温引水隧洞几个设计与施工问题探讨[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2013,32(增刊2):3396-3403.HOU D P,LIU N F,YU C H,et al. Discussion on design and construction measures for a rock tunnel in high-temperature conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2013,32(S2):3396-3403. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 王贵玲,蔺文静. 我国主要水热型地热系统形成机制与成因模式[J]. 地质学报,2020,94(7):1923-1937. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.002WANG G L,LIN W J. Main hydro-geothermal systems and their genetic models in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2020,94(7):1923-1937. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.07.002 [15] GILLESPIE P A,HOLDSWORTH R E,LONG D,et al. Introduction:Geology of fractured reservoirs[J]. Journal of the Geological Society,2021,178(2):2020-2197. [16] TANG X C,ZHANG J,PANG Z H,et al. Distribution and genesis of the eastern Tibetan Plateau geothermal belt,western China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2016,76(1):31. [17] ZHANG B J,ZHAO T,LI Y Y,et al. The hydrochemical characteristics and its significance of geothermal water in both sides of large fault:Taking northern section of the Liaokao fault in North China as an example[J]. China Geology,2019,2(4):512-521. doi: 10.31035/cg2018132 [18] ZHOU X,ZHUO L Y,WU Y Q,et al. Origin of some hot springs as conceptual geothermal models[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2023,624:129927. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129927 [19] 庞忠和,杨峰田,袁利娟,等. 新疆塔县盆地地热显示与热储温度预测[J]. 地质论评,2011,57(1):86-88.PANG Z H,YANG F T,YUAN L J,et al. Geothermal display and thermal storage temperature prediction in Taxian Basin,Xinjiang[J]. Geological Review,2011,57(1):86-88. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] YUAN D,XIAO K,FENG T,et al. Geothermal characteristics of the Xianshuihe fault zone and their engineering influence on tunnel construction[J]. Thermal Science,2023,27(1 Part B):615-622. [21] 陈喆. 川藏铁路沿线及邻区地热异常区定量预测评价研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2021.CHEN Z. Quantitative prediction and evaluation of geothermal anomaly areas along the Sichuan-Tibet Railway and its adjacent areas[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences(Beijing),2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 杜宇本,蒋良文,陈明浩,等. 中国铁路隧道勘察技术的发展与展望[J]. 隧道建设(中英文),2021,41(11):1943-1952.DU Y B,JIANG L W,CHEN M H,et al. Development and prospect of geological surveying technology for railway tunnels in China[J]. Tunnel Construction,2021,41(11):1943-1952. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] LUO X,GONG S,HUO Z G,et al. Application of comprehensive geophysical prospecting method in the exploration of coal mined-out areas[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering,2019,2019(1):2368402. doi: 10.1155/2019/2368402 [24] ZHAO J Y,LI N,LIU F Y. Geological survey and drilling technology of karst land[J]. Desalination and Water Treatment,2020,187:144-153. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2020.25311 [25] YANG P H,DAN L,GROVES C,et al. Geochemistry and genesis of geothermal well water from a carbonate-evaporite aquifer in Chongqing,SW China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2019,78(1):33. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-8004-3 [26] YANG P H,LUO D,HONG A H,et al. Hydrogeochemistry and geothermometry of the carbonate-evaporite aquifers controlled by deep-seated faults using major ions and environmental isotopes[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2019,579:124116. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124116 [27] WANG C K,LIU Z Y,ZHANG F K,et al. Heat hazards in high-temperature tunnels:Influencing factors,disaster forms,the geogenetic model and a case study of a tunnel in Southwest China[J]. Sustainability,2024,16(3):1044. doi: 10.3390/su16031044 [28] 王争鸣. 拉日铁路地热地区综合选线研究[J]. 铁道工程学报,2015,32(9):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2015.09.001WANG Z M. Research on the integrated alignment of geothermal district of Lhasa Rikaze Railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society,2015,32(9):1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2015.09.001 [29] 李尚蔚,刘毅,李铜邦,等. 同仁地区地下热水水化学特征及演化过程分析[J]. 青海大学学报,2022,40(5):75-82.LI S W,LIU Y,LI T B,et al. Analysis of hydrochemical characteristics and evolution process of thermal groundwater in Tongren[J]. Journal of Qinghai University,2022,40(5):75-82. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 王思琪,张保建,李燕燕,等. 雄安新区高阳地热田东北部深部古潜山聚热机制[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(3):12-21.WANG S Q,ZHANG B J,LI Y Y,et al. Heat accumulation mechanism of deep ancient buried hill in the northeast of Gaoyang geothermal field,Xiongan New Area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(3):12-21. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 邵杰,李瑛,侯光才,等. 新疆伊犁河谷地下水循环演化特征[J]. 干旱区研究,2017,34(1):20-25.SHAO J,LI Y,HOU G C,et al. Evolution of groundwater circulation in the Yili River valley in Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research,2017,34(1):20-25. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 王长申,黄炳香,赵兴龙,等. 伊南煤田伊犁一矿侏罗纪煤系地下水化学特征与水循环演化[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报,2024,41(1):160-170.WANG C S,HUANG B X,ZHAO X L,et al. Chemistry and water cycle of the groundwater in the Jurassic confined fissured aquifers at Ili No. 1 Coal Mine,South Ili Coalfield,China[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2024,41(1):160-170. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 杜先利,王泓博,赵容生,等. 松辽盆地南部大情字井区青山口组地热水化学特征及成因模式[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(3):22-35.DU X L,WANG H B,ZHAO R S,et al. Geothermal chemical characteristics and genetic model of the Qingshankou Formation in the Daqingzijing area,southern Songliao Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(3):22-35. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] KUTASOV I M,李兰忠. 用经验公式估算地温梯度[J]. 国外油气勘探,1995,7(6):782-783.KUTASOV I M,LI L Z. Estimation of geothermal gradient by empirical formula[J]. Oil & Gas Prospecting Abroad,1995,7(6):782-783. (in Chinese) [35] 杨新亮. 拉日铁路吉沃希嘎隧道地热异常特征与防治措施分析[J]. 铁道标准设计,2014,58(7):107-112.YANG X L. Research on geothermal anomaly characteristics and control measures for Jiwoxiga tunnel on Lasa-Shigatse Railway[J]. Railway Standard Design,2014,58(7):107-112. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 张群,高明中,王新丰,等. 潘三煤矿地温分布规律分析[J]. 煤矿安全,2014,45(6):170-172.ZHANG Q,GAO M Z,WANG X F,et al. The geotherm regularities analysis in Pansan coal mine[J]. Safety in Coal Mines,2014,45(6):170-172. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 杨丹. 西卓井田5号煤层热害区分布及成因初步探讨[C]//佚名. 煤炭绿色开发地质保障技术研究:陕西省煤炭学会学术年(2019)暨第三届“绿色勘查科技论坛”论文集. 陕西省煤炭学会、重庆市煤炭学会、内蒙古煤炭工业协会、青海省煤炭会,2019:266-269.YANG D. Preliminary discussion on the distribution and causes of heat damage area of No. 5 coal seam in Xizhuo minefield [C]//Anon. Research on geological guarantee technology for green development of coal-Academic Annual Meeting of Shaanxi Coal Society ( 2019 ) and the third "Green Exploration Science and Technology Forum" Proceedings. Shaanxi Coal Society,Chongqing Coal Society,Inner Mongolia Coal Industry Association,Qinghai Coal Society,2019 :266-269. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 王林涛. 许疃煤矿地温分布特征与控制模式研究[D]. 安徽 淮南:安徽理工大学,2021.WANG L T. Study on the distribution characteristics and control mode of ground temperature in Xutuan coal mine[D]. Huainan Anhui:Anhui University of Science and Technology,2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 刘文连,利满霖,许模,等. 穿越小江断裂的登楼山隧址区水热活动特征分析及隧道热害评估[J]. 隧道建设(中英文),2023,43(9):1523-1532.LIU W L,LI M L,XU M,et al. Hydrothermal activity characterization and thermal hazard evaluation in Dengloushan tunnel crossing Xiaojiang fault[J]. Tunnel Construction,2023,43(9):1523-1532. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 刘星辰,黄锋,陈树汪,等. 水热活动带下的隧道热害特征与成因分析[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版),2024,43(3):35-44.LIU X C,HUANG F,CHEN S W,et al. Characteristics and causes of tunnel thermal damage in hydrothermal activity zones[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science),2024,43(3):35-44. (in Chinese with English abstract -





 下载:
下载: