Source of CO2-rich fluid and its impact on reservoir quality of L gas field in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin
-
摘要:
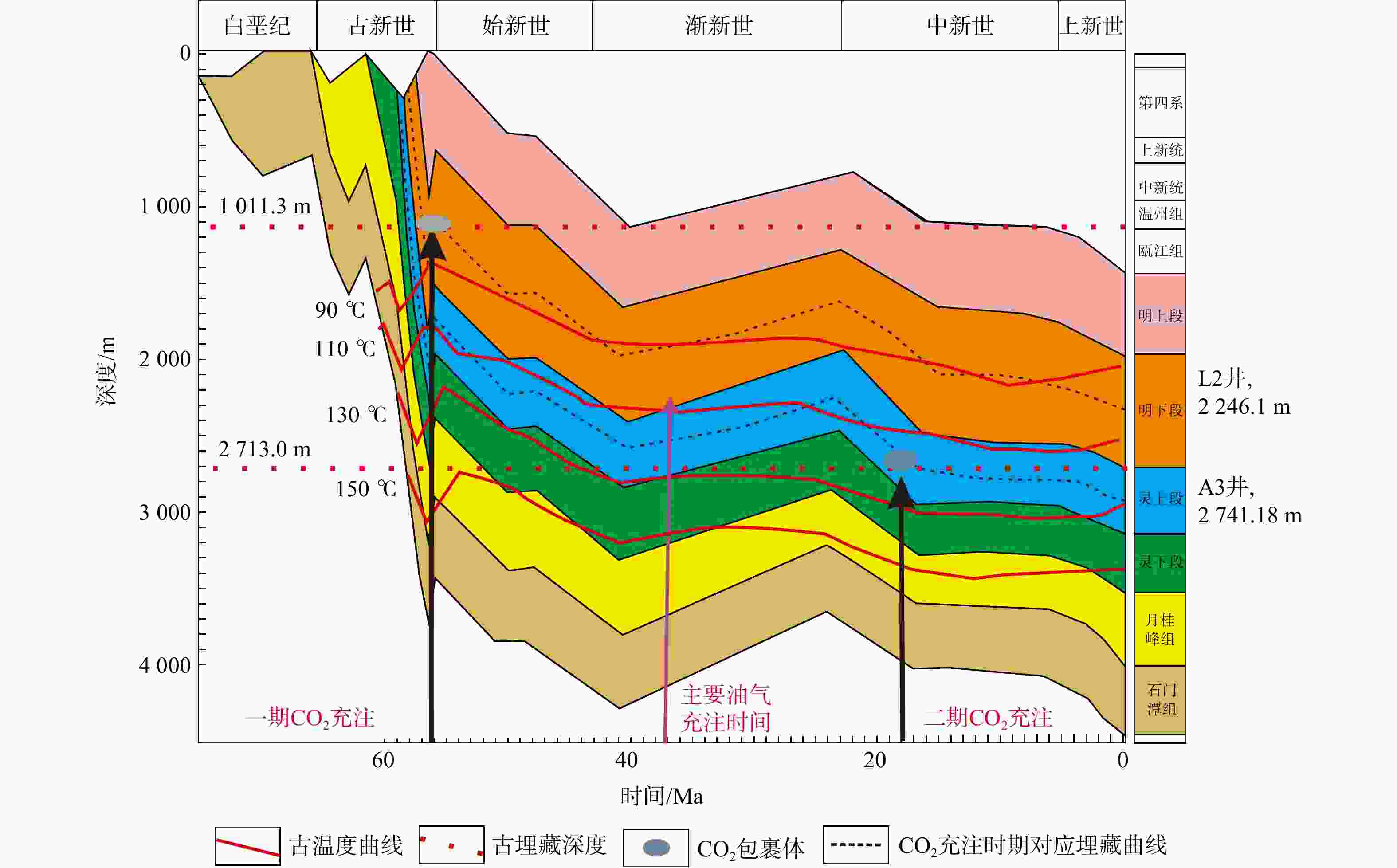
富CO2流体−砂岩相互作用是砂岩储层次生孔隙主要形成机制之一。L气田作为丽水凹陷已发现的商业性气田,其主要产层不仅CO2气体含量高,而且片钠铝石富集。为了揭示CO2来源、形成时间、充注强度,及其对储层的影响,对L气田的岩矿、物性、碳氧同位素和相关地球化学特征展开了系统分析。研究区储层中自生碳酸盐矿物主要为铁白云石、片钠铝石和铁方解石,其次为白云石、菱铁矿和方解石,片钠铝石纵向上集中分布于明下段的中下部(CO2高含量段)。CO2主要为无机来源,幔源与壳源成因各半,其充注有2期,第一期CO2充注时间为晚古新世,约57 Ma;第二期CO2充注时间为早中新世,约18 Ma,以第一期为主。CO2充注的时间、强度是决定其对储层影响是否有利的关键因素,L气田储层刚性颗粒含量不高,容易被压实致密,溶蚀也不强烈,加上地温梯度高有机酸生成的窗口窄,有机酸对储层的改善有限,而早期CO2的充注不仅会生成碳酸产生溶蚀孔,而且会增强砂体的抗压实能力,能够保存一定量的原生孔,从而有利优质储层的发育。研究成果可为气田发育盆地的油气勘探提供借鉴。
Abstract:Objective The interaction between CO2-rich fluids and sandstone is one of the main mechanisms of secondary pore generation in sandstone reservoirs. The L gas field, located in Lishui Sag, is not only characterized by high CO2 content but also by the enrichment of ammonium dawsonite in its main production layers.
Methods This study systematically analyzes the rock and mineral composition, physical properties, carbon and oxygen isotopes, and related geochemistry to reveal the source, formation time, filling intensity of CO2, and its influence on the reservoir in the L gas field.
Results The results are as follows: (1) In the reservoir of the study area, authigenic carbonate minerals are primarily iron dolomite, sodium aluminate, and iron calcite, followed by dolomite, siderite, and calcite. (2) Ammonium dawsonite is vertically concentrated in middle and lower parts of the Lower Member of Mingyuefeng Formation, where the CO2 content is high. (3) CO2 is mainly of inorganic origin, with contributions from both mantle and crust sources. (4) There were two phases of CO2 charging. The first filling event occurred around 57 Ma during the Late Paleocene and was the major charging period. The second filling event occurred during the Early Miocene, about 18 Ma. (5) The timing and intensity of CO2 charging are key factors determining its impact on the reservoir. Due to the low content of rigid particles in the L gas field, the reservoir is prone to compaction, and the dissolution is not strong. Additionally, the geothermal gradient is high, and the organic acid window is narrow, limiting the reservoir improvement by organic acids. Early CO2 filling not only generates carbonate dissolution pores but also enhances the anti-compaction ability of the sand bodies, preserving a certain amount of primary porosity. This process is beneficial for the development of high-quality reservoirs.
Conclusion The research results can provide reference for oil and gas exploration in the sedimentary basin of the gas field.
-
Key words:
- Lishui Sag /
- dawsonite /
- CO2 charging /
- carbon and oxygen stable isotopes /
- high-quality reservoir
-
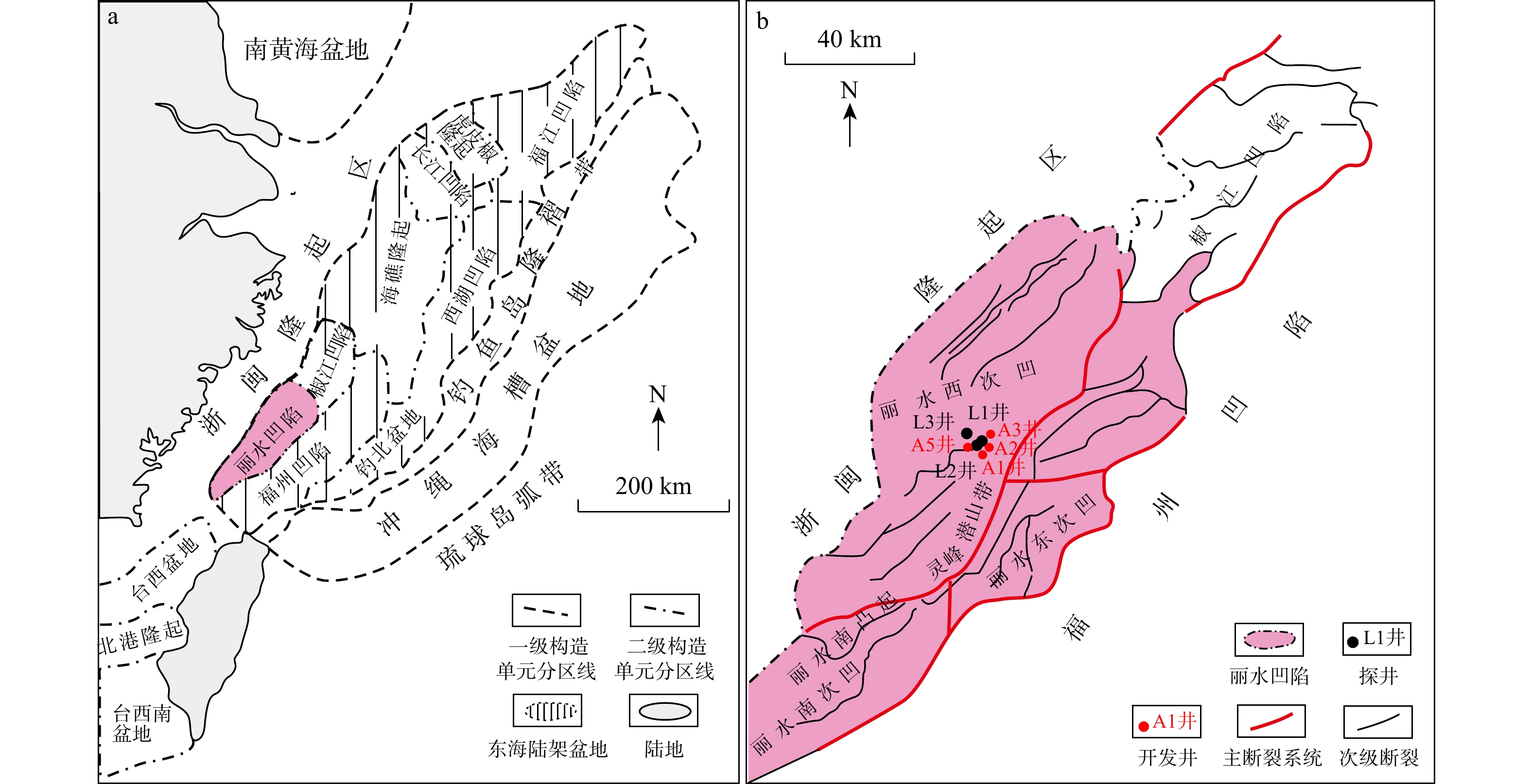
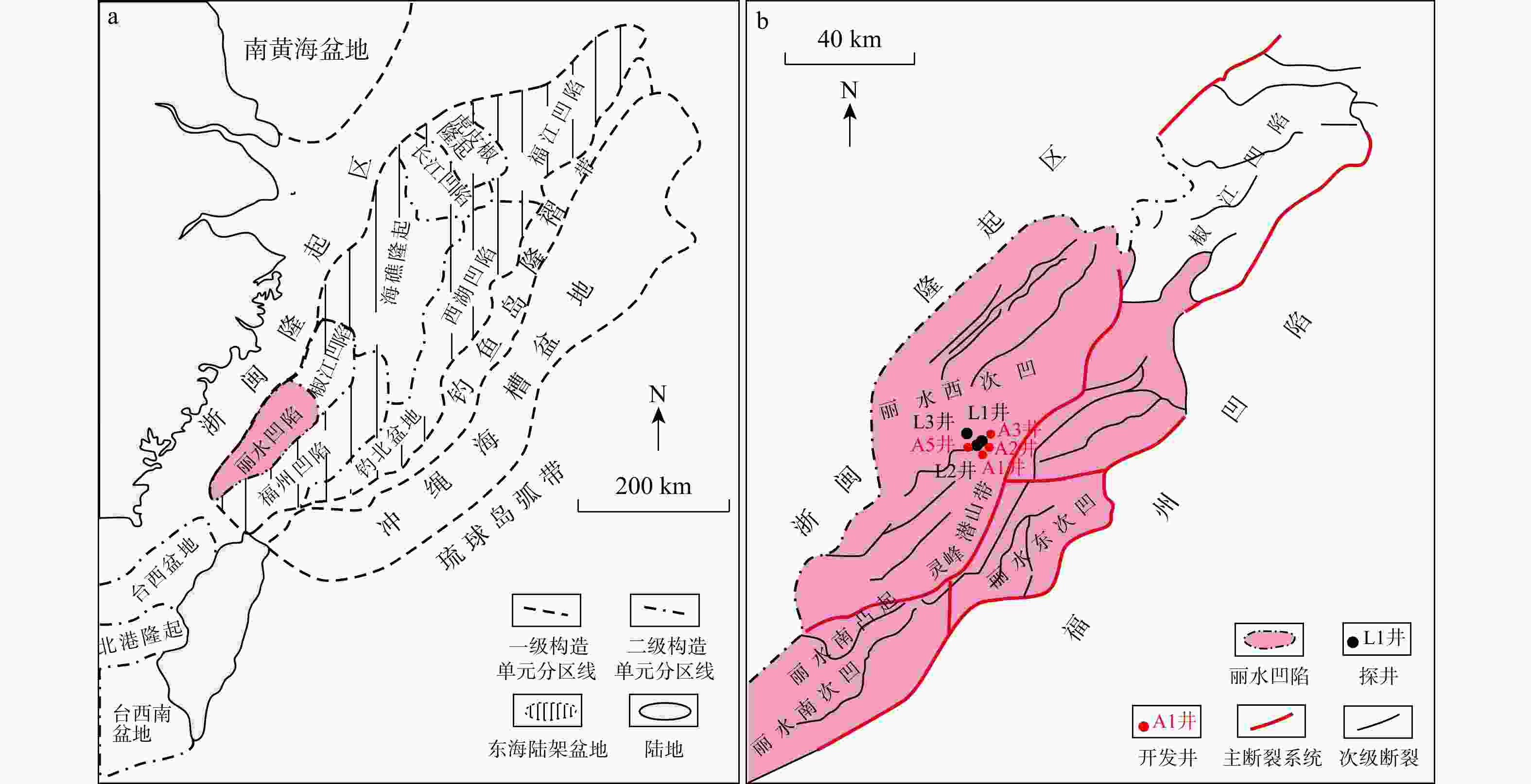
图 1 丽水凹陷构造位置及构造单元划分(据文献[24]修改)
Figure 1. Tectonic location and division of structural units of Lishui Sag
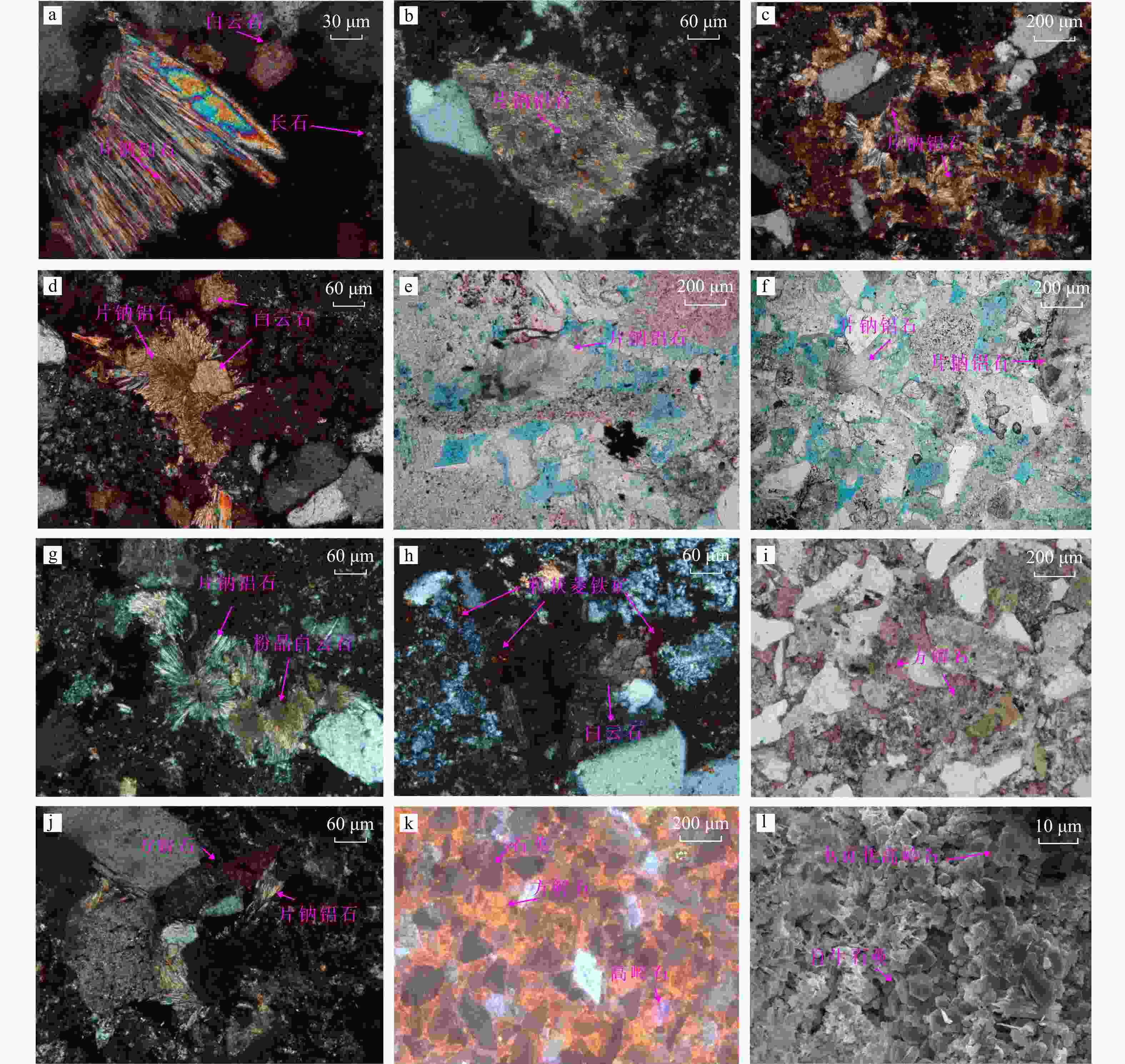
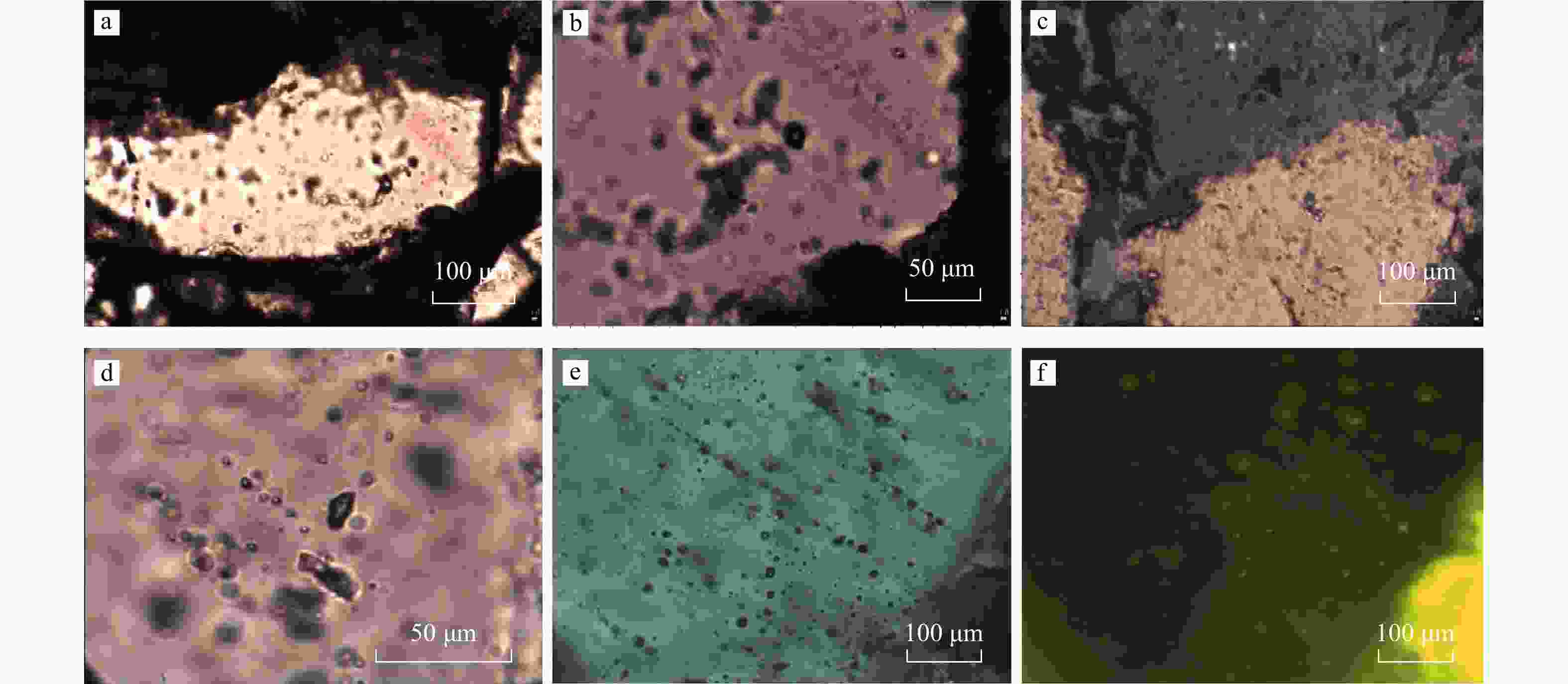
图 4 L气田储层镜下微观特征
a. L2井,
2235.82 m,明下段,片钠铝石交代长石,(+);b. L2井,2247.24 m,明下段,片钠铝石交代长石,(+);c. L2井,2293.63 m,明下段,片钠铝石交代石英及岩屑,(+);d. L2井,明下段,2235.82 m,放射束片钠铝石围绕铁白云石生长,(+);e. L2井,2235.30 m,明下段,纤维状片钠铝石,集合体呈放射状、花束状部分占据长石溶解孔隙,(−);f. L2井,2235.30 m,明下段,纤维状片钠铝石,集合体呈放射状、花束状部分占据长石溶解孔隙,(−);g. L2井,2293.63 m,明下段,片钠铝石、自形粉晶白云石,(+);h. L2井,2235.82 m,明下段,菱铁矿、白云石,(+);i. L1井,2575.83 m,明下段,方解石充填孔隙,(−);j. L1井,2583.97 m,明下段,方解石围绕片钠铝石生长,(+);k. L1井,2575.73 m,明下段,石英主要发蓝紫色光,粒间铁方解石胶结物主要发橙红−暗橙红色光,普遍交代碎屑颗粒边缘,粒间少量自生高岭石胶结物发靛蓝色光,阴极发光;l. L2井,2246.62 m,明下段,颗粒间充填书页状自生高岭石、自生石英等,扫描电镜Figure 4. Microscopic characteristics of reservoir of L gas field
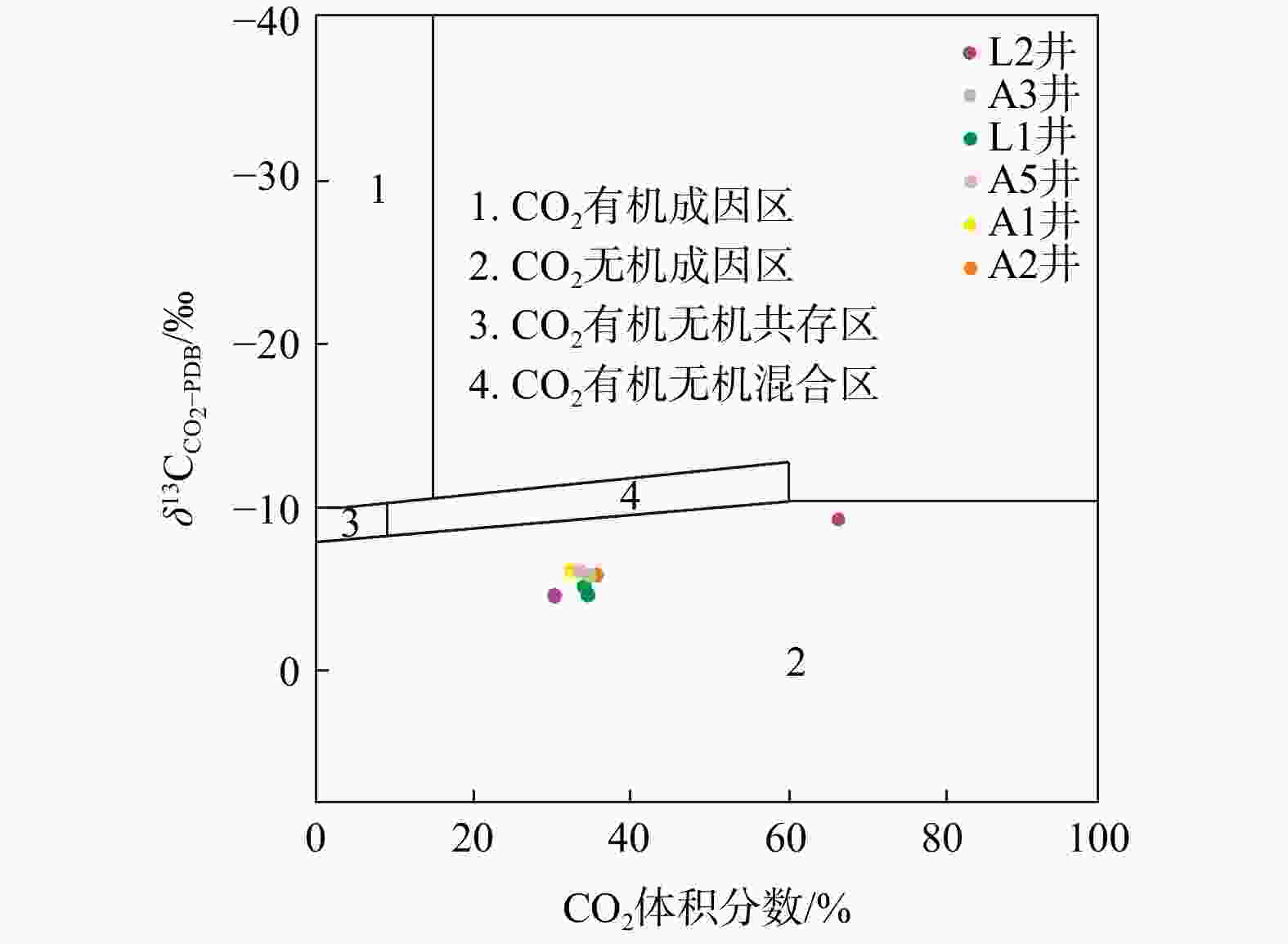
图 6 丽水凹陷L气田CO2有机与无机成因判别(据文献[30]修改)
Figure 6. Identification of organic or inorganic origin of CO2 of L gas field in Lishui Sag
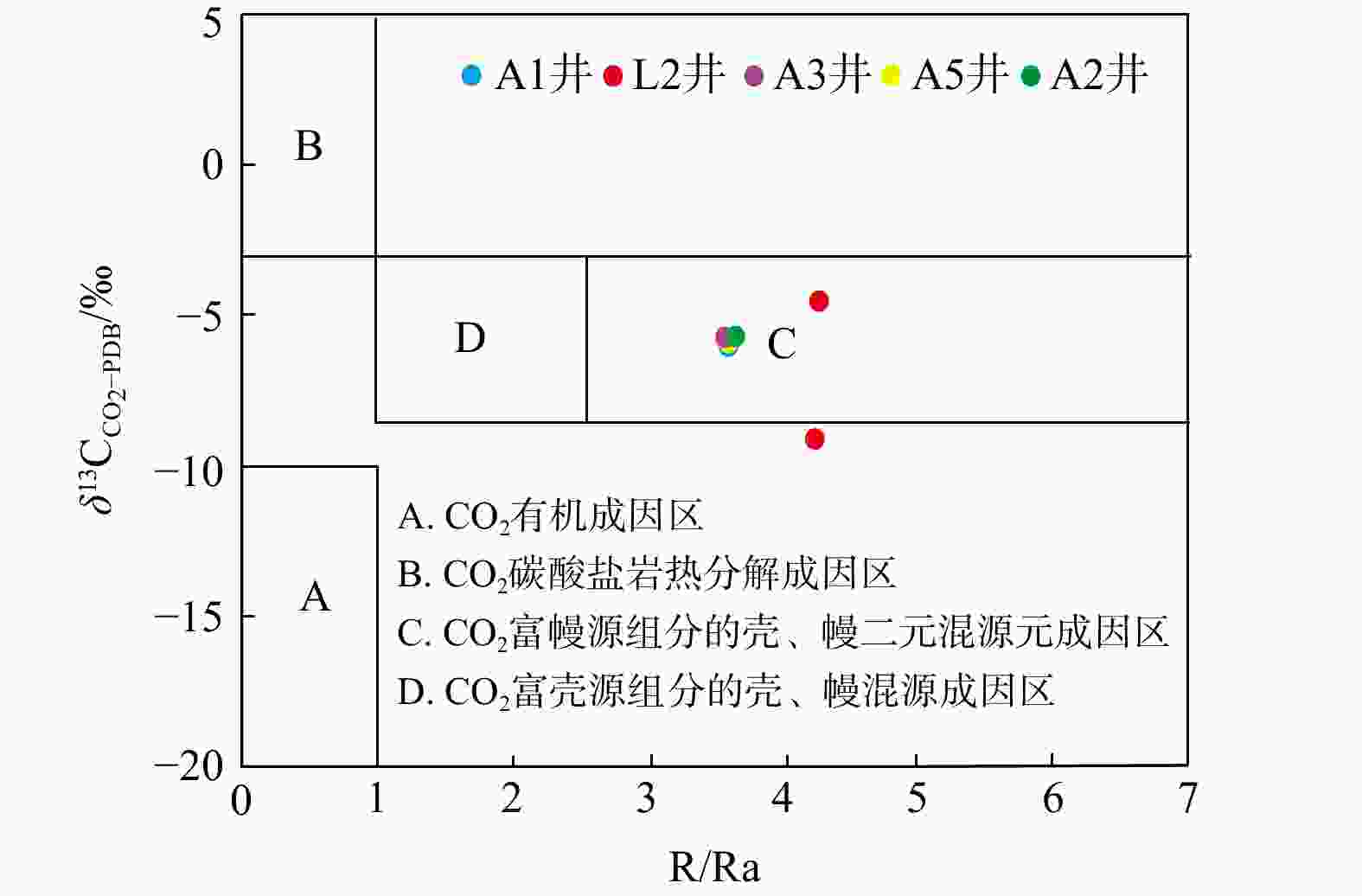
图 8 L气田$\delta^{13}{\mathrm{C}}_{{\mathrm{CO}}_2-{\mathrm{PDB}}} $−R/Ra关系图(据文献[36]修改)
Figure 8. Relationship between $\delta^{13}{\mathrm{C}}_{{\mathrm{CO}}_2\text{-}{\mathrm{PDB}}} $ and R/Ra in L gas field
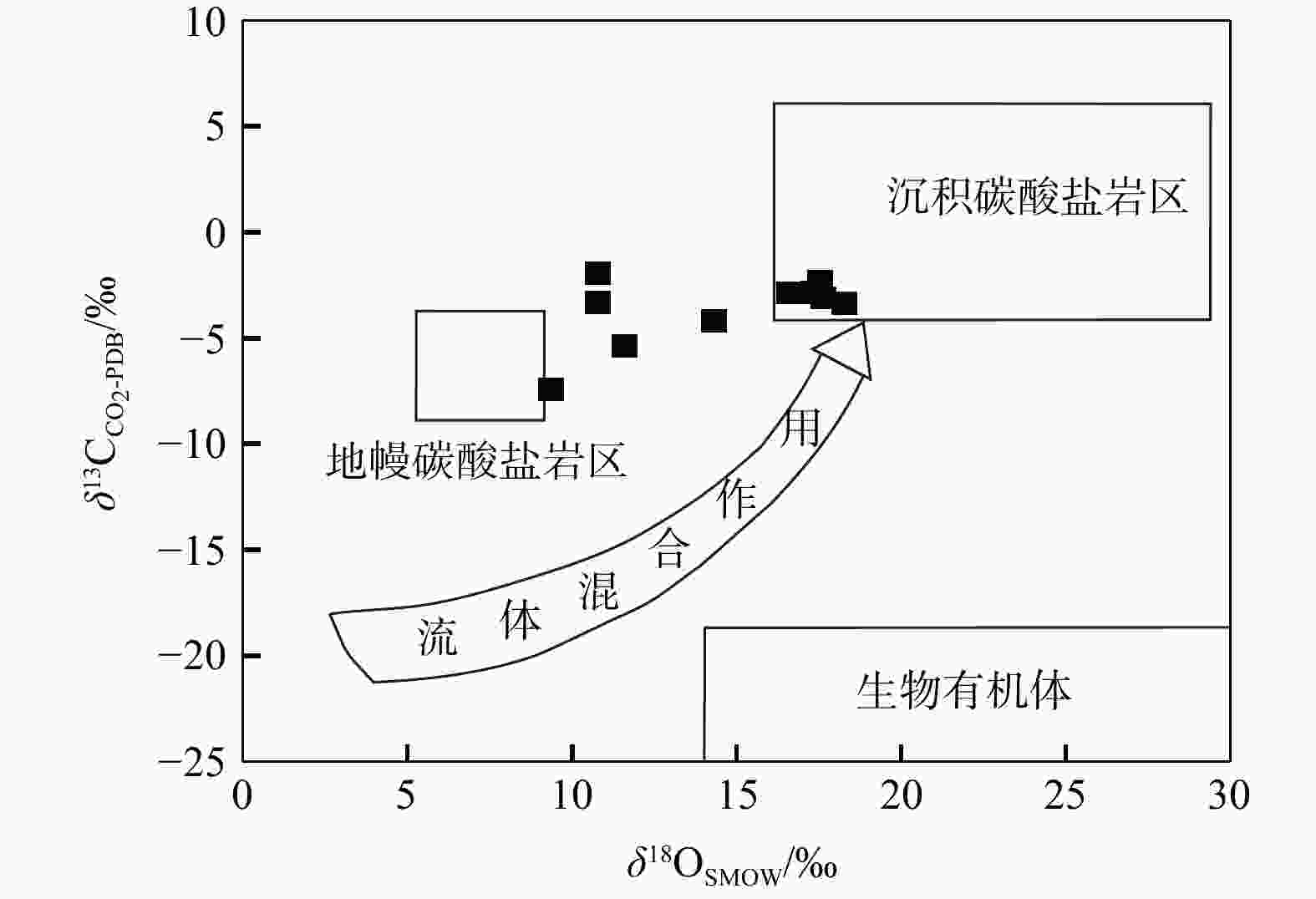
图 13 L气田碳酸盐胶结物$ \delta^{13}{\mathrm{C}}_{{\mathrm{CO}}_{2}\text{-}{\mathrm{PDB}}} $和δ18OSMOW相关图版(据文献[29]修改)
Figure 13. Correlogram of $ \delta^{13}{\mathrm{C}}_{{\mathrm{CO}}_{2}\text{-}{\mathrm{PDB}}} $ and δ18OSMOW of carbonate cements in L gas field
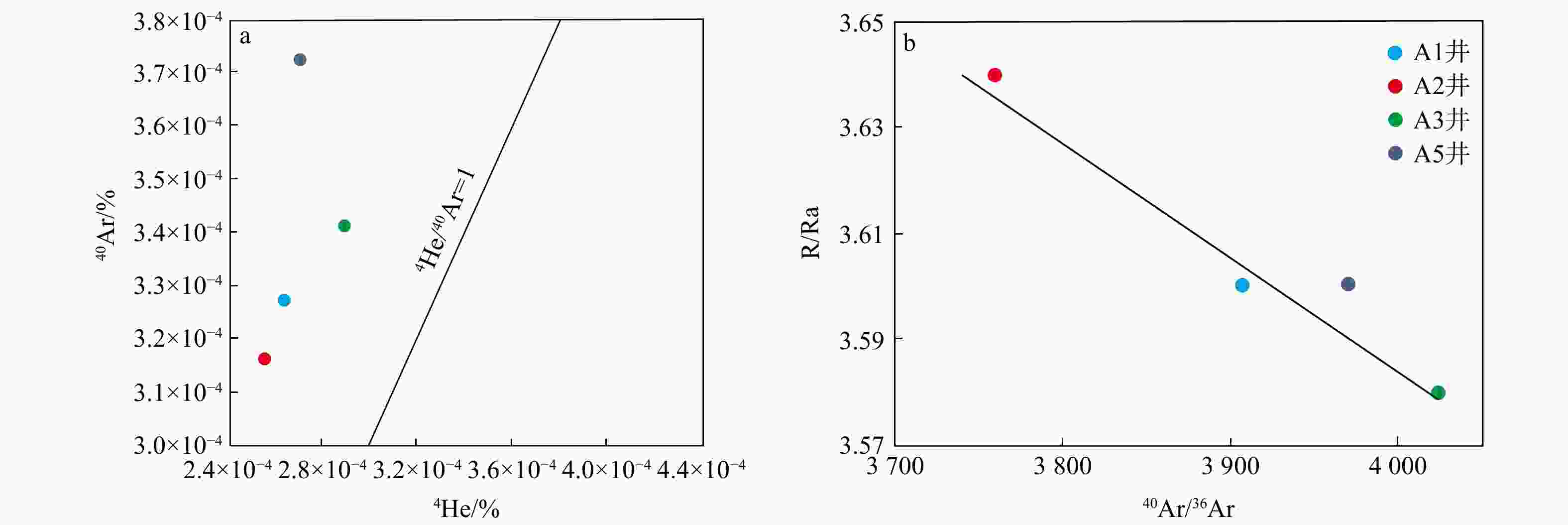
表 1 L气田CO2及稀有气体组分含量和同位素组成分析结果
Table 1. Analysis results of CO2 and rare gas component content and isotopic composition in L gas field
井位 深度/m $\delta^{13}{\mathrm{C}}_{{\mathrm{CO}}_2-{\mathrm{PDB}}} $/‰ 40Ar/% 4He/% R/Ra 3He/4He 40Ar/36Ar X/% Hme/% A1 3628 −5.9 3.27×10−4 2.64×10−4 3.60 5.041×10−6 3906.85 72.9 45.70 L1 2250 ~2265 85.3 2265 ~2283 90.4 L2 2315 ~2336 −9.2 4.24 5.93×10−6 25.7 53.80 2238 ~2260 −4.6 4.26 5.97×10−6 91.4 54.16 A2 3456 −5.7 3.16×10−4 2.55×10−4 3.64 5.1×10−6 3760.05 75.7 46.21 A3 2870 −5.7 3.41×10−4 2.90×10−4 3.58 5.012×10−6 4024.29 75.7 45.44 A5 3403 −5.9 3.72×10−4 2.71×10−4 3.60 5.041×10−6 3969.36 72.9 45.70 注:R/Ra. 样品氦R和大气氦Ra的同位素比值;X. 混合气体中无机CO2的体积分数;Hme. 气藏中幔源氦的比例 表 2 L气田含二氧化碳气包裹体分析结果
Table 2. Analysis results of CO2-bearing inclusions in L gas field
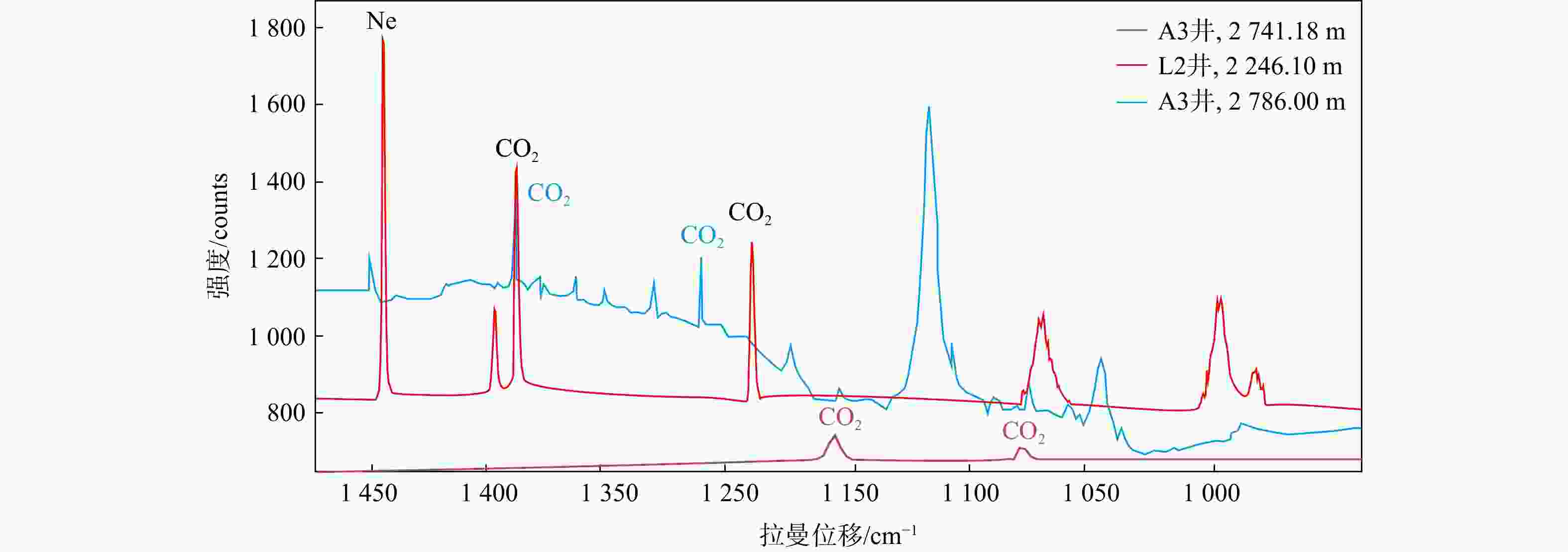
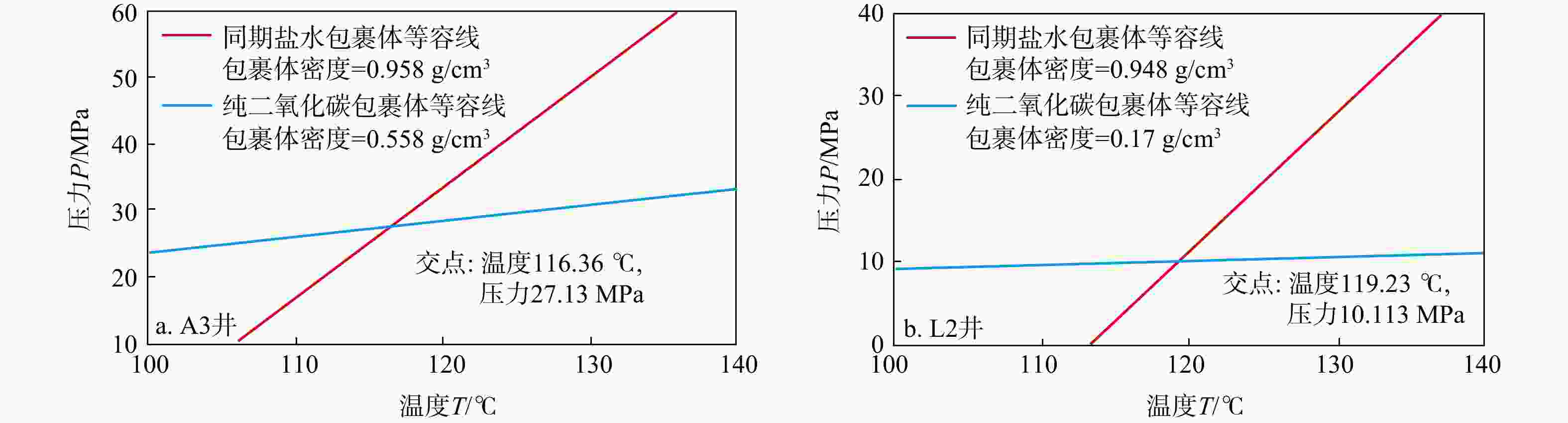
井号 深度/m 组名 测井解释 岩性 包裹体类型 包裹体总密度/(g·cm−3) 共生盐水包裹体均一温度/℃ A3 2741.18 灵下段 干层 细−中粒岩屑砂岩 纯二氧化碳气相 0.550 100~105 A3 2747.80 灵下段 干层 细−中粒岩屑砂岩 混合气 0.530 90~110 A3 2786.00 灵下段 气层 中粒岩屑砂岩 纯二氧化碳气相 0.460 100~110 L2 2246.10 明下段 气层 中粒岩屑砂岩 纯二氧化碳气相 0.167 113.2 L2 2291.00 明下段 气层 中粒岩屑砂岩 混合气 0.159 124 L2 2293.00 明下段 气层 细粒岩屑砂岩 油气 0.156 130~140 -
[1] 高玉巧,刘立. 自生片钠铝石的碳氧同位素特征及其成因意义[J]. 高校地质学报,2006,12(4):522-529. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2006.04.013GAO Y Q,LIU L. Carbon-oxygen isotopic characteristics of authigenic dawsonite and its genetic significance[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2006,12(4):522-529. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2006.04.013 [2] BAKER J C,BAI G P,HAMILTON P J,et al. Continental-scale magmatic carbon dioxide seepage recorded by dawsonite in the Bowen-Gunnedah-Sydney Basin system,eastern Australia[J]. 1995,65(3a):522-530. [3] MOORE J,ADAMS M,ALLIS R,et al. Mineralogical and geochemical consequences of the long-term presence of CO2 in natural reservoirs:An example from the Springerville-St. Johns Field,Arizona,and New Mexico,U. S. A. [J]. Chemical Geology,2005,217(3/4):365-385. [4] 刘妍鷨,陈红汉,王艳飞,等. 珠江口盆地白云−荔湾深水区幔源CO2充注的黏土矿物成岩响应[J]. 地质科技通报,2021,40(3):85-95.LIU Y H,CHEN H H,WANG Y F,et al. Diagenetic effect of mantle-derived CO2 charge to clay minerals in the Baiyun-Liwan deepwater area of the Pearl River Mouth Basin in South China Sea[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2021,40(3):85-95. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 黄善炳. 金湖凹陷阜宁组砂岩中片钠铝石特征及对物性的影响[J]. 石油勘探与开发,1996,23(2):32-34. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1996.02.009HUANG S B. The character of dawsonite in sandstone reservoirs of the Funing Formation in Jinhu Sag and its influence on reservoir properties[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,1996,23(2):32-34. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1996.02.009 [6] HELLEVANG H,AAGAARD P,OELKERS E H,et al. Can dawsonite permanently trap CO2?[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2005,39(21):8281-8287. [7] OKUYAMA Y,SASAKI M,NAKANISHI S,et al. Geochemical CO2 trapping in open aquifer storage:The Tokyo Bay model[J]. Energy Procedia,2009,1(1):3253-3258. doi: 10.1016/j.egypro.2009.02.110 [8] 刘娜,刘立,杨会东,等. 松辽盆地南部片钠铝石形成与碎屑长石的成因联系[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2011,41(1):54-63.LIU N,LIU L,YANG H D,et al. Genetic relationship between dawsonite and clastic feldspar in southern part of Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2011,41(1):54-63. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 董林森,刘立,张革,等. 火山碎屑岩对CO2的矿物捕获能力[J]. 沉积学报,2010,28(3):572-578.DONG L S,LIU L,ZHANG G,et al. The mineral trapping of CO2 for pyroclastic rocks[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2010,28(3):572-578. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] OELKERS E H,GISLASON S R,MATTER J. Mineral carbonation of CO2[J]. Elements,2008,4(5):333-337. doi: 10.2113/gselements.4.5.333 [11] CAO Z,LIN C Y,DONG C M,et al. Impact of CO2 influx on sandstone reservoir quality:A case study of the Quantou Formation,southern Songliao Basin,China[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2024,108(6):1149-1185. [12] 杨娇,戴建文,吴雪晴,等. 珠江口盆地恩平凹陷新近系储层菱铁矿胶结物成因及对物性的影响[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(2):127-136.YANG J,DAI J W,WU X Q,et al. Quantitative evaluation of the influence of siderite cements on middle-shallow reservoirs:A case study of the southern oil area in the Enping Sag,Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(2):127-136. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 高玉巧,刘立,曲希玉,等. 海拉尔盆地乌尔逊凹陷与松辽盆地孤店CO2气田含片钠铝石砂岩的岩石学特征[J]. 古地理学报,2008,10(2):111-123.GAO Y Q,LIU L,QU X Y,et al. Petrologic characteristics of dawsonite-bearing sandstones in Wuerxun Sag of Hailaer Basin and Gudian CO2 Gasfield in Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography,2008,10(2):111-123. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 刘立,朱德丰,曲希玉,等. 海拉尔盆地乌尔逊凹陷幔源CO2充注对下白垩统砂岩储层质量的影响[J]. 岩石学报,2009,25(10):2311-2319.LIU L,ZHU D F,QU X Y,et al. Impacts of mantle-genetic CO2,influx on the reservoir quality of Lower Cretaceous sandstone from Wuerxun Depression,Hailaer Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2009,25(10):2311-2319. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 黄俨然,张枝焕,王安龙,等. 黄桥地区深源CO2对二叠系−三叠系油气成藏的影响[J]. 天然气地球科学,2012,23(3):520-525.HUANG Y R,ZHANG Z H,WANG A L,et al. Deep-sourced CO2 influence on Permian and Triassic oil and gas accumulation in Huangqiao region[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2012,23(3):520-525. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 刘娜,吴克强,刘立,等. 莺歌海盆地乐东区片钠铝石特征及其对浅层CO2充注的指示[J]. 地球科学,2019,44(8):2695-2703.LIU N,WU K Q,LIU L,et al. Dawsonite characteristics and its implications on the CO2 in Yinggehai-Huangliu Formation of Ledong area,Yinggehai Basin[J]. Earth Science,2019,44(8):2695-2703. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 张月霞,胡文瑄,姚素平,等. 苏北盆地黄桥地区富CO2流体对二叠系龙潭组砂岩储层的改造与意义[J]. 地质通报,2018,37(10):1944-1955.ZHANG Y X,HU W X,YAO S P,et al. The interaction of CO2-rich fluid with sandstone and its significance for sandstone reservoirs of Permian Longtan Formation in Huangqiao area,Subei Basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2018,37(10):1944-1955. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] 许岩. 海拉尔盆地火山碎屑岩、含片钠铝石砂岩与普通砂岩的成岩作用及其比较研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2005.XU Y. Diagenesis and it's comparative study of pyroclastic rock,dowsonite-bearing sandstone and common sandstone in Hailaer Basin[D]. Changchun:Jilin University,2005. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] KASZUBA J P,JANECKY D R,SNOW M G. Carbon dioxide reaction processes in a model brine aquifer at 200 ℃ and 200 bars:Implications for geologic sequestration of carbon[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2003,18(7):1065-1080. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00239-1 [20] 曲希玉,刘立,胡大千,等. CO2流体对含片钠铝石砂岩改造作用的实验研究[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2007,37(4):690-697.QU X Y,LIU L,HU D Q,et al. Study on the dawsonite sandstones reformation with CO2 fluid[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2007,37(4):690-697. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 高玉巧,刘立,曲希玉. CO2与砂岩相互作用机理与形成的自生矿物组合[J]. 新疆石油地质,2007,28(5):579-584.GAO Y Q,LIU L,QU X Y. Mechanism of CO2-sandstone interaction and formative authigenic mineral assemblage[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology,2007,28(5):579-584. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 郭永华,于水,葛玲. 东海盆地丽水凹陷LS36-1构造成藏机理研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2003,30(6):29-31.GUO Y H,YU S,GE L. Formation of the LS36-1 oil and gas structure in the Lishui Sag,East China Sea Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2003,30(6):29-31. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 陈春峰,徐春明,周瑞华,等. 东海陆架盆地丽水凹陷岩性油气藏发育特征与成藏条件[J]. 中国海上油气,2013,25(2):30-35.CHEN C F,XU C M,ZHOU R H,et al. Development characteristics and accumulation conditions of lithologic reservoirs in Lishui Sag,East China Sea shelf basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas,2013,25(2):30-35. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 侯国伟,刘金水,蔡坤,等. 东海丽水凹陷古新统源−汇系统及控砂模式[J]. 地质科技情报,2019,38(2):65-74.HOU G W,LIU J S,CAI K,et al. Source-to-sink system and sand-controlling model of Paleocene in Lishui Sag,East China Sea Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information,2019,38(2):65-74. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 徐东浩,秦兰芝,李峻颉,等. 西湖凹陷平北斜坡带平湖组层序构型差异及控砂模式[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(4):154-166.XU D H,QIN L Z,LI J J,et al. Sequence stratigraphic architectures and sand-body distribution models of the Pinghu Formation in the Pingbei slope belt of the Xihu Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(4):154-166. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 中华人民共和国自然资源部. 海上石油天然气储量估算规范:DZ/T0252-2020[S]. 北京:地质出版社,2020.Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. Regulation of offshore petroleum reserves estimation:DZ/T0252-2020[S]. Beijing:Geological Press,2020. (in Chinese) [27] WATSON M N,ZWINGMANN N,LEMON N M. The Ladbroke Grove-Katnook carbon dioxide natural laboratory:A recent CO2 accumulation in a lithic sandstone reservoir[J]. Energy,2004,29(9/10):1457-1466. [28] 钱峥,黄先雄. 碳酸盐岩成岩作用及储层:以中国四川东部石炭系为例[M]. 北京:石油工业出版社,2000.QIAN Z,HUANG X X. Diagenesis and reservoir of carbonate rocks:A case study of Carboniferous in eastern Sichuan,China[M]. Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,2000. (in Chinese) [29] 肖晓光,秦兰芝,张武,等. 西湖凹陷平湖组碳酸盐胶结物形成机制及其对储层的影响[J]. 地质科学,2021,56(4):1062-1076. doi: 10.12017/dzkx.2021.056XIAO X G,QIN L Z,ZHANG W,et al. The origin of carbonate cements and the influence on reservoir quality of Pinghu Formation in Xihu Sag[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica),2021,56(4):1062-1076. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12017/dzkx.2021.056 [30] 戴金星,宋岩,戴春森,等. 中国东部无机成因气及其气藏形成条件[M]. 北京:科学出版社,1995.DAI J X,SONG Y,DAI C S,et al. Formation conditions of inorganic genetic gas and its gas reservoir in eastern China[M]. Beijing:Science Press,1995. (in Chinese) [31] 宋岩,徐永昌. 天然气成因类型及其鉴别[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2005,32(4):24-29. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.04.004SONG Y,XU Y C. Origin and identification of natural gases[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2005,32(4):24-29. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2005.04.004 [32] 党文龙,高岗,刘建平,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系马家沟组盐下天然气成因类型及来源[J]. 天然气地球科学,2022,33(2):207-217.DANG W L,GAO G,LIU J P,et al. Genetic types and sources of the subsalt natural gas in the Ordovician Majiagou Formation,Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2022,33(2):207-217. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 孙明良,陈践发,廖永胜. 济阳坳陷天然气氦同位素特征及二氧化碳成因与第三纪岩浆活动的关系[J]. 地球化学,1996,25(5):475-480.SUN M L,CHEN J F,LIAO Y S. Heliumisotopic characteristics,genesis of CO2 in natural gases and distribution of tertiary magamatite in the Jiyang Depression[J]. Geochimica,1996,25(5):475-480. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 仵宗涛,刘兴旺,李孝甫,等. 稀有气体同位素在四川盆地元坝气藏气源对比中的应用[J]. 天然气地球科学,2017,28(7):1072-1077.WU Z T,LIU X W,LI X F,et al. The application of noble gas isotope in gas-source correlation of Yuanba reservoir,Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience,2017,28(7):1072-1077. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 廖永胜,李钜源,李祥臣,等. 应用碳、氦、氩同位素探讨济阳坳陷二氧化碳气成因[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2001,20(4):351-353. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2001.04.040LIAO Y S,LI J Y,LI X C,et al. A discussion of CO2 genesis in Jiyang Depression by using C,He,Ar isotopes[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry,2001,20(4):351-353. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2001.04.040 [36] 陈红汉,米立军,刘妍鷨,等. 珠江口盆地深水区CO2成因、分布规律与风险带预测[J]. 石油学报,2017,38(2):119-134. doi: 10.7623/syxb201702001CHEN H H,MI L J,LIU Y H,et al. Genesis,distribution and risk belt prediction of CO2 in deep-water area in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica,2017,38(2):119-134. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7623/syxb201702001 [37] 刘立,侯启军,刘娜,等. 松辽盆地南部幔源CO2与油气充注时序:来自含片钠铝石砂岩的证据[J]. 石油与天然气地质,2011,32(6):873-881.LIU L,HOU Q J,LIU N,et al. Charging time sequence of mantle CO2 and hydrocarbon in southern Songliao Basin:An evidence from dawsonite-bearing sandstones[J]. Oil & Gas Geology,2011,32(6):873-881. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] ANDERSON D L. Theory of the earth[M]. Boston:Blackwell Scientific Publications,1989. [39] 胡宝群,王方正,孙占学,等. 岩石圈中的地压梯度[J]. 地学前缘,2003,10(3):129-133. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.03.012HU B Q,WANG F Z,SUN Z X,et al. The pressure gradient in the lithosphere[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2003,10(3):129-133. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.03.012 [40] 林松辉. 断裂及岩浆活动对幔源CO2气成藏的作用:以济阳坳陷为例[J]. 地球科学,2005,30(4):473-479. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2005.04.011LIN S H. Fault and magmatic activity as control of mantle source CO2 gas accumulation:A case study of Jiyang Depression[J]. Earth Science,2005,30(4):473-479. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2005.04.011 [41] 苏奥,陈红汉,曹来圣,等. 东海盆地丽水凹陷油气成因、来源及充注过程[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2014,41(5):523-532. doi: 10.11698/PED.2014.05.02SU A,CHEN H H,CAO L S,et al. Genesis,source and charging of oil and gas in Lishui Sag,East China Sea Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2014,41(5):523-532. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.2014.05.02 [42] 张敏强,黄思静,吴志轩,等. 东海盆地丽水凹陷古近系储层砂岩中碳酸盐胶结物及形成机制[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版),2007,34(3):259-266. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2007.03.007ZHANG M Q,HUANG S J,WU Z X,et al. Carbonate cements and their formation mechanism in Palaeogene sandstones of Lishui Sag,East China Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition),2007,34(3):259-266. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2007.03.007 [43] LIU L H,SUTO Y,BIGNALL G,et al. CO2 injection to granite and sandstone in experimental rock/hot water systems[J]. Energy Conversion and Management,2003,44(9):1399-1410. doi: 10.1016/S0196-8904(02)00160-7 [44] ZERAI B,SAYLOR B Z,MATISOFF G. Computer simulation of CO2 trapped through mineral precipitation in the Rose Run Sandstone,Ohio[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2006,21(2):223-240. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.11.002 -




 下载:
下载: