Simulation of soil water transport considering the effects of soil structure and adsorption forces
-
摘要:
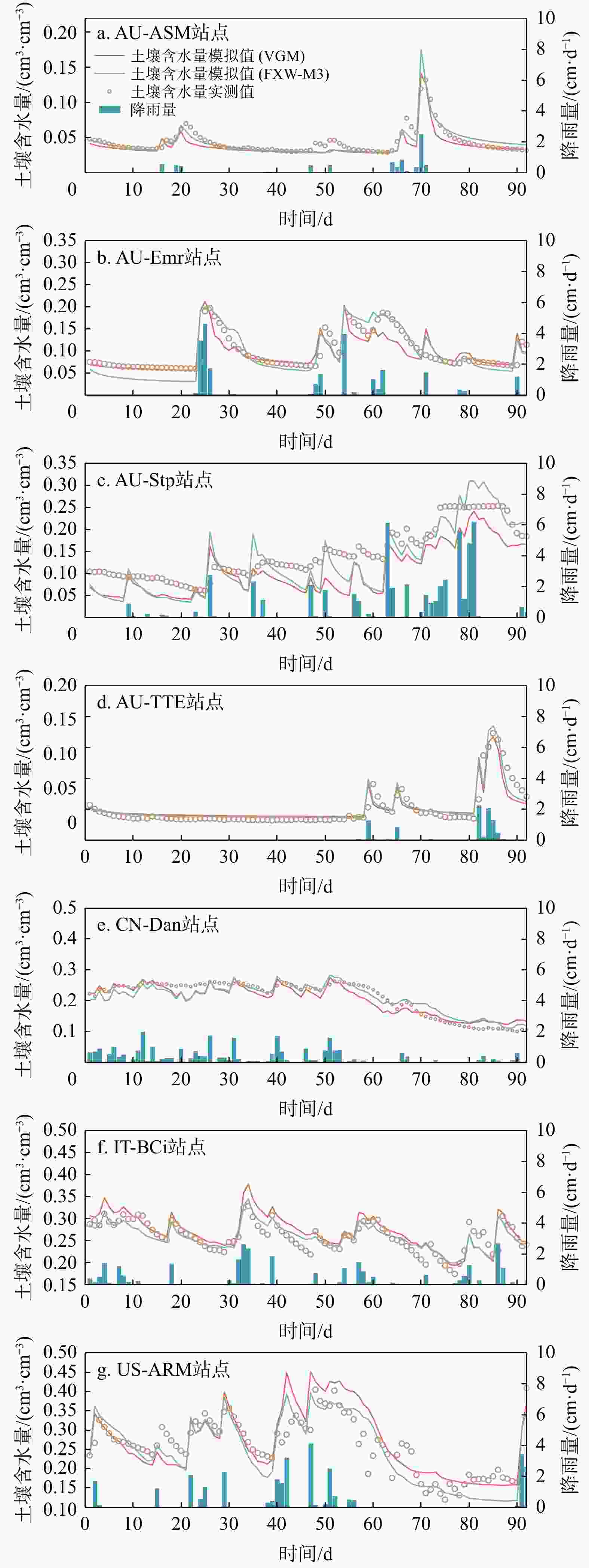
传统土壤水力模型基于毛细理论,对土壤结构(大孔隙)和土壤吸附作用的表征较差,不能准确刻画近饱和以及土壤含水量较低情形下的土壤水力特征,因而不能准确模拟土壤水分运移特征。为了对比不同土壤水力特征模型的表现,基于FLUXNET数据库7个站点土壤含水量的连续实测数据,分别使用考虑土壤结构、吸附力以及毛细作用的FXW-M3模型和仅考虑毛细力的VGM模型,通过改进的HYDRUS-1D软件对站点实测土壤含水量数据进行模拟分析。结果表明考虑土壤结构和吸附力影响的FXW-M3模型显著提高了土壤水分运移模拟的精度。7个站点FXW-M3模型的均方根误差
RMSE 的平均值为0.0048 cm3/cm3,低于VGM模型的0.0113 cm3/cm3;相关系数R 的平均值为0.80,高于VGM模型的0.75。模拟结果表明土壤结构和干吸附力对土壤水分运移有着显著影响。Abstract:Objective Traditional soil hydraulic models based on capillarity theory, poorly characterize soil structure (e.g., soil macropores) and adsorption forces, which limits their ability to accurately describe soil hydraulic properties under near-saturation and low soil water content conditions. Consequently, these models struggle to accurately simulate soil water movement.
Methods In this study, we evaluated the performance of different soil hydraulic characteristic models using continuous field-measured soil moisture data from seven FLUXNET sites. We employed the FXW-M3 model, which accounts for soil structure, adsorption, and capillary forces, and the VGM model, which considers only capillary forces. Using the improved HYDRUS-1D software, we simulated and analyzed site-specific soil moisture data.
Results The results indicated that the FXW-M3 model significantly improved the accuracy of soil water movement simulation. The average root mean square error (
RMSE ) for the FXW-M3 model was 0.0048 cm3/cm3, which was lower than the 0.0113 cm3/cm3 for the VGM model. The averageR for the FXW-M3 model was 0.80, which was higher than 0.75 for the VGM model.Conclusion These results highlighted the significant impact of soil structure and adsorption forces on soil water movement.
-
Key words:
- soil structure /
- adsorption forces /
- soil water transport /
- FXW-M3 model /
- VGM model /
- HYDRUS-1D software
-
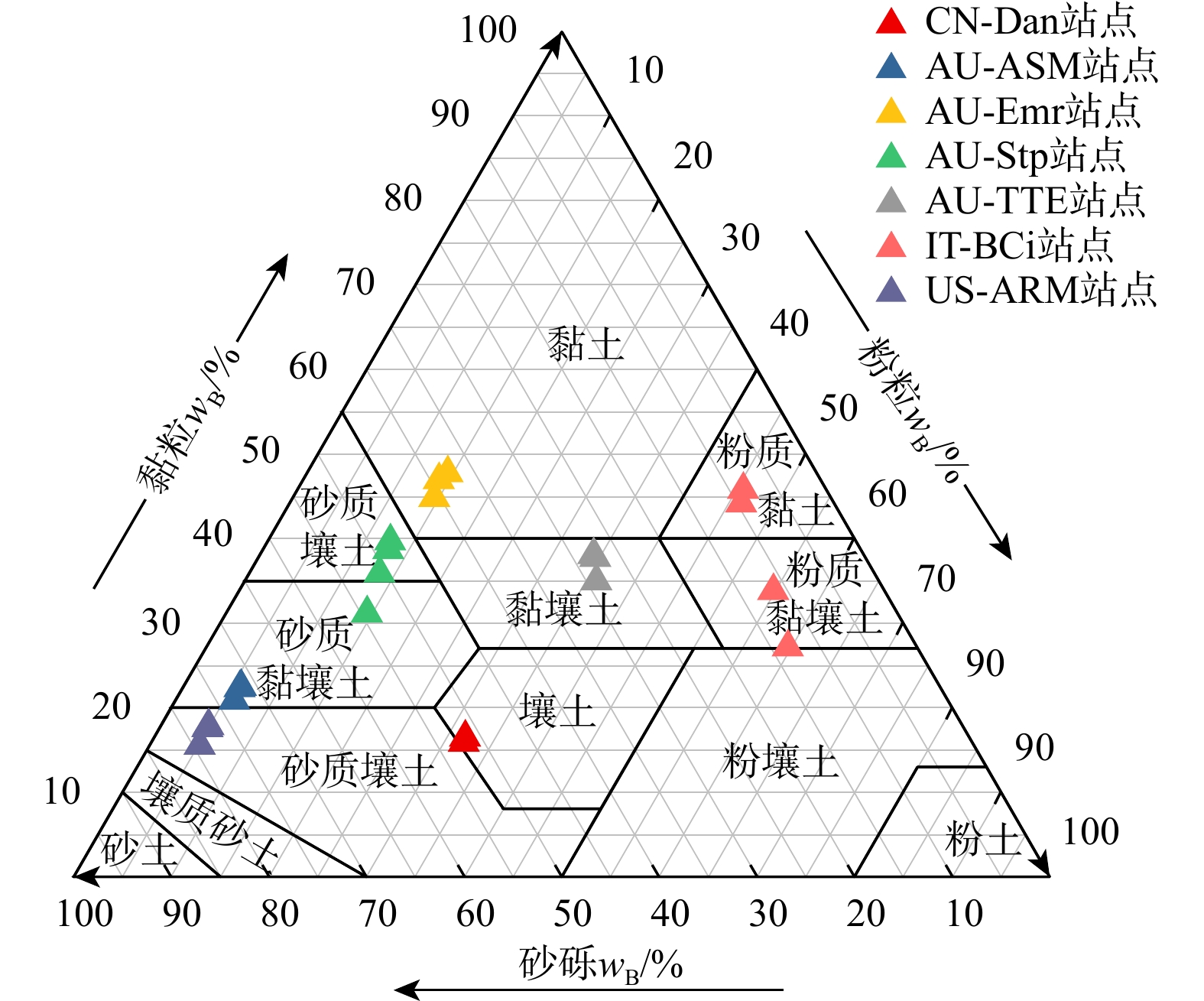
表 1 站点信息
Table 1. Site information
站点
名称纬度 经度 模拟开
始时间模拟
时间/d年降雨
量/cm年平均
温度/℃年潜在蒸
散发量/cmAU-ASM − 22.2830 133.2490 2011/11/01 92 41.16 25.26 36.49 AU-Emr − 23.8587 148.4746 2013/01/01 92 56.60 23.02 34.50 AU-Stp − 17.1507 133.3502 2010/11/01 92 112.19 27.46 72.97 AU-TTE − 22.2870 133.6400 2013/10/01 92 27.74 30.09 29.39 CN-Dan 30.4978 91.0664 2004/07/01 92 55.04 5.70 66.85 IT-BCi 40.5237 14.9574 2009/02/01 92 119.67 18.86 66.92 US-ARM 36.6058 − 97.4888 2004/05/12 92 90.13 16.39 63.39 表 2 土壤含水量的模拟误差
Table 2. Simulation error of soil water content
站点 AU-ASM AU-Emr AU-Stp AU-TTE CN-Dan IT-BCi US-ARM 平均值 相关系数R FXW-M3模型 0.81 0.80 0.80 0.81 0.89 0.76 0.75 0.80 VGM模型 0.80 0.68 0.76 0.76 0.87 0.71 0.67 0.75 均方根误差RMSE/(cm3·cm−3) FXW-M3模型 0.0004 0.0038 0.0179 0.0020 0.0007 0.0003 0.0089 0.0113 VGM模型 0.0054 0.0032 0.0393 0.0013 0.0065 0.0127 0.0112 0.0048 -
[1] VEREECKEN H, HUISMAN J A, PACHEPSKY Y, et al. On the spatio-temporal dynamics of soil moisture at the field scale[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 516: 76-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.11.061 [2] RICHARDS L A. Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums[J]. Physics, 1931, 1(5): 318-333. doi: 10.1063/1.1745010 [3] MUALEM Y. A new model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media[J]. Water Resources Research, 1976, 12(3): 513-522. doi: 10.1029/WR012i003p00513 [4] VAN GENUCHTEN M T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1980, 44(5): 892-898. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x [5] MILLINGTON R J, QUIRK J P. Permeability of porous solids[J]. Transactions of the Faraday Society, 1961, 57: 1200-1207. [6] ORR F M, SCRIVEN L E, RIVAS A P. Pendular rings between solids: Meniscus properties and capillary force[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1975, 67(4): 723-742. doi: 10.1017/S0022112075000572 [7] TOKUNAGA T K. Hydraulic properties of adsorbed water films in unsaturated porous media[J]. Water Resources Research, 2009, 45(6): 1-9. [8] ROSSI C, NIMMO J R. Modeling of soil water retention from saturation to oven dryness[J]. Water Resources Research, 1994, 30(3): 701-708. doi: 10.1029/93WR03238 [9] NIMMO J R. Comment on the treatment of residual water content in "a consistent set of parametric models for the two-phase flow of immiscible fluids in the subsurface" by L. Luckner et al[J]. Water Resources Research, 1991, 27(4): 661-662. doi: 10.1029/91WR00165 [10] TULLER M, OR D. Hydraulic conductivity of variably saturated porous media: Film and corner flow in angular pore space[J]. Water Resources Research, 2001, 37(5): 1257-1276. [11] LEBEAU M, KONRAD J M. A new capillary and thin film flow model for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated porous media[J]. Water Resources Research, 2010, 46(12): 1-15. [12] WANG Y Q, MA J Z, ZHANG Y L, et al. A new theoretical model accounting for film flow in unsaturated porous media[J]. Water Resources Research, 2013, 49(8): 5021-5028. doi: 10.1002/wrcr.20390 [13] ZHANG Z F. Soil water retention and relative permeability for conditions from oven-dry to full saturation[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 2011, 10(4): 1299-1308. doi: 10.2136/vzj2011.0019 [14] TULLER M, OR D, DUDLEY L M. Adsorption and capillary condensation in porous media: Liquid retention and interfacial configurations in angular pores[J]. Water Resources Research, 1999, 35(7): 1949-1964. doi: 10.1029/1999WR900098 [15] NIMMO J R. Modeling structural influences on soil water retention[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1997, 61(3): 712-719. [16] VAN GENUCHTEN M T, NIELSEN D R. On describing and predicting the hydraulic properties[C]//Anon. Annales Geophysicae. [S.l.]: [S.n.], 1985, 3(5): 615-628. [17] SCHAAP M G, LEIJ F J. Improved prediction of unsaturated hydraulic conductivity with the mualem-van genuchten model[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2000, 64(3): 843-851. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2000.643843x [18] SCHAAP M G, LEIJ F J, VAN GENUCHTEN M T. Rosetta: A computer program for estimating soil hydraulic parameters with hierarchical pedotransfer functions[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2001, 251(3/4): 163-176. [19] GERKE H H. Preferential flow descriptions for structured soils[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 2006, 169(3): 382-400. doi: 10.1002/jpln.200521955 [20] JARVIS N J. A review of non-equilibrium water flow and solute transport in soil macropores: Principles, controlling factors and consequences for water quality[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2007, 58(3): 523-546. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.2007.00915.x [21] SILVA O, GRIFOLL J. A soil-water retention function that includes the hyper-dry region through the BET adsorption isotherm[J]. Water Resources Research, 2007, 43(11): 1-13. [22] WANG Y Q, JIN M G, DENG Z J. Alternative model for predicting soil hydraulic conductivity over the complete moisture range[J]. Water Resources Research, 2018, 54(9): 6860-6876. doi: 10.1029/2018WR023037 [23] WANG Y Q, MA R, ZHU G F. Improved prediction of hydraulic conductivity with a soil water retention curve that accounts for both capillary and adsorption forces[J]. Water Resources Research, 2022, 58(4): 1-22. [24] LIAO K H, LAI X M, ZHOU Z W, et al. A simple and improved model for describing soil hydraulic properties from saturation to oven dryness[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 2018, 17(1): 180082. [25] YANG Z L, LI Z, TONG X, et al. Weibull distribution models for describing soil hydraulic properties over the entire matric suction range[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2023, 622: 129661. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129661 [26] PETERS A, HOHENBRINK T L, IDEN S C, et al. Prediction of the absolute hydraulic conductivity function from soil water retention data[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2023, 27(7): 1565-1582. doi: 10.5194/hess-27-1565-2023 [27] ZHANG Y G, WEIHERMÜLLER L, TOTH B, et al. Analyzing dual porosity in soil hydraulic properties using soil databases for pedotransfer function development[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 2022, 21(5): e20227. doi: 10.1002/vzj2.20227 [28] DURNER W, DIAMANTOPOULOS E, IDEN S C, et al. Hydraulic properties and non-equilibrium water flow in soils[M]. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2014: 403-434. [29] DEXTER A R. Advances in characterization of soil structure[J]. Soil and Tillage Research, 1988, 11(3/4): 199-238. [30] VAN GENUCHTEN M T, NIELSEN D R. On describing and predicting the hydraulic properties of unsaturated soils[J]. Annales Geophysicae, 1985, 3: 615-627. [31] FATICHI S, OR D, WALKO R, et al. Soil structure is an important omission in earth system models[J]. Nature Communications, 2020, 11: 522. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-14411-z [32] WANG Y Q, MA R, ZHU G F. Representation of the influence of soil structure on hydraulic conductivity prediction[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2023, 619: 129330. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.129330 [33] FREDLUND D G, XING A Q. Equations for the soil-water characteristic curve[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1994, 31(4): 521-532. doi: 10.1139/t94-061 [34] ŠIMŮNEK J, VAN GENUCHTEN M T, ŠEJNA M. Recent developments and applications of the HYDRUS computer software packages[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 2016, 15(7). [35] DUAN Q Y, SOROOSHIAN S, GUPTA V. Effective and efficient global optimization for conceptual rainfall-runoff models[J]. Water Resources Research, 1992, 28(4): 1015-1031. doi: 10.1029/91WR02985 [36] POLLACCO J A P, NASTA P, SORIA-UGALDE J M, et al. Reduction of feasible parameter space of the inverted soil hydraulic parameter sets for kosugi model[J]. Soil Science, 2013, 178(6): 267-280. doi: 10.1097/SS.0b013e3182a2da21 [37] 王兴华, 李小倩, 谢晓涵, 等. 土壤因子对三氯乙烯土−气分配系数的影响[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(5): 272-278. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240028WANG X H, LI X Q, XIE X H, et al. Impact of soil factors on soil-gas partition coefficient of trichloroethylene[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(5): 272-278. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240028 [38] 王铭森, 邓斌, 张晚祺, 等. 非均质包气带土壤含水率分布定量刻画及其模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(3): 296-308. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240256WANG M S, DENG B, ZHANG W Q, et al. Quantitative characterization and simulation of soil moisture distribution in heterogeneous vadose zone[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(3): 296-308. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240256 [39] 金玉, 陈文岭, 王铭森, 等. 基于露点水势仪与滤纸法的盐渍土蒸发过程中吸力动态规律[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(6): 270-280. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240065JIN Y, CHEN W L, WANG M S, et al. Dynamic law of suction during the evaporation process of saline soil based on dew point water potential meter and filter paper method[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(6): 270-280. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240065 [40] 李培月, 李佳慧, 吴健华, 等. 黄土−古土壤互层对土壤水分运移及土体微结构的影响[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2024, 51(3): 1-11.LI P Y, LI J H, WU J H, et al. Effects of loess-paleosol interbedding on soil moisture transport and soil microstructure[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(3): 1-11. -




 下载:
下载: