Cyclostratigraphy and paleoclimate analysis of the Lingshui Formation in the Beijiao Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin
-
摘要:
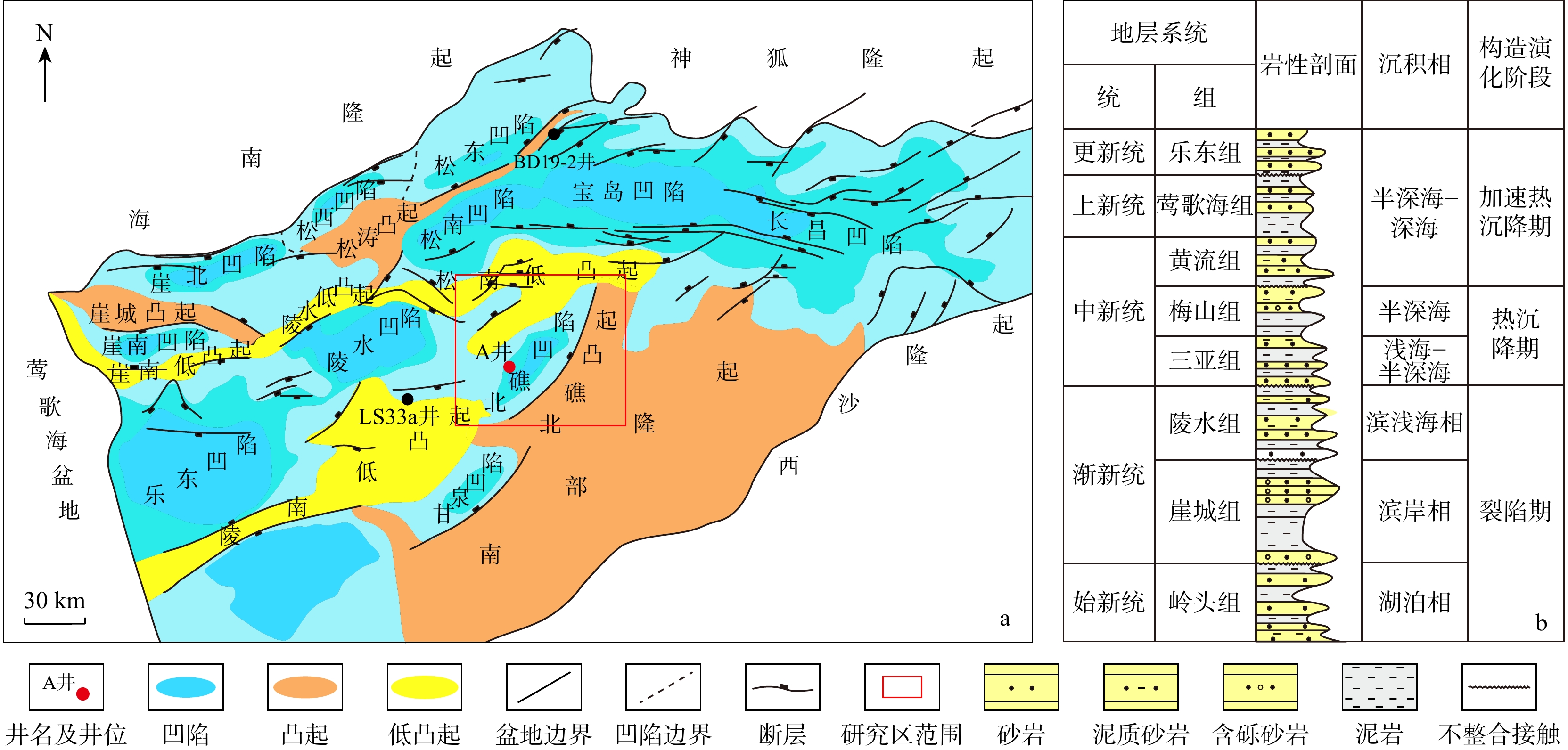
通过天文旋回研究,建立北礁凹陷渐新统陵水组的高精度且连续时间地层格架,并丰富该地区的古气候研究。采用时间序列分析方法,对北礁凹陷A井开展了旋回地层学分析研究;结合古生物多指标解释,开展了古气候演变分析。结果表明:在北礁凹陷陵水组沉积地层识别出了405 ka长偏心率周期、100 ka短偏心率周期、42.7 ka和43.2 ka斜率周期及20.5 ka岁差周期。通过天文调谐建立了持续时间约5.59 Ma的“浮动”天文年代标尺,以渐新世顶界面的地质年龄23.03 Ma作为时间锚点,最终建立陵水组(28.62~23.03 Ma)高精度的绝对天文年代框架。其中陵一段、陵二段和陵三段的底界面年龄分别为23.97,25.43,28.62 Ma,平均沉积速率分别为18.4,8.6,12.8 cm/ ka。利用有孔虫、有机碳质量分数、有机屑组分和碳氧同位素等古气候指标重建了陵水组沉积时期的古气候,其整体表现为暖−凉−暖的变化趋势。古气候分析和天文旋回分析对比显示,这一时期的气候演化受到偏心率、岁差等天文轨道力的控制。对北礁凹陷陵水组沉积地层进行天文旋回研究,探讨天文轨道参数对古气候的控制作用,建立了渐新统陵水组高精度且连续的时间地层格架。该方法为油气勘探中优质储集体层段预测提供了精细的年代框架,促进了北礁凹陷油气勘探的发展。
Abstract:Objective A high-resolution, continuous chronostratigraphic framework was established using the astronomical cycles, and the paleoclimatic characteristic was analyzed for the Oligocene Lingshui Formation of the Beijiao Sag.
Methods The cyclostratigraphy characteristics and the paleoclimatic evolution were determined by time series and multiple paleontological proxies analyses, respectively, in the Well A of the Beijiao Sag.
Results Cycles of 405 ka long eccentricity, 100 ka short eccentricity, 42.7 ka and 43.2 ka obliquity, and 20.5 ka precession were identified in the Lingshui Formation of the Beijiao Sag. Considering the time anchor of 23.03 at the top of Oligocene, the astronomical tuning revealed a "floating" astronomical chronology scale of 5.59 Ma. Within the high-precision absolute astronomical timeframe of the Lingshui Formation (28.62−23.03 Ma), the bottom boundary ages of Ling Ⅰ, Ling Ⅱ, and Ling Ⅲ members can be determined as 23.97 Ma, 25.43 Ma, and 28.62 Ma, respectively. These ages correspond to the average sedimentation rates of 18.4 cm/ka, 8.6 cm/ka, and 12.8 cm/ka, respectively. The palaeoclimatic indicators, including the foraminifera, organic carbon, organic detrital fractions, and carbon and oxygen isotopes, suggest an overall warm-cool-warm trend during the deposition of Lingshui Formation. The comparison of palaeoclimate evolution with astronomical rotation suggested that the climate evolution during this period was mainly controlled by astronomical orbital forces such as eccentricity and age difference. Astronomical cyclostratigraphic study on the Lingshui Formation of the Beijiao Sag explores the control of astronomical orbital parameters on paleoclimate and establishes a high-resolution and continuous chronostratigraphic framework.
Conclusion This method provides a refined chronological framework for predicting high-quality reservoir intervals in oil and gas exploration, promoting the development of oil and gas exploration in the Beijiao Sag.
-
Key words:
- Qiongdongnan Basin /
- Beijiao Sag /
- cyclostratigraphy /
- astronomical time scale /
- paleoclimate
-
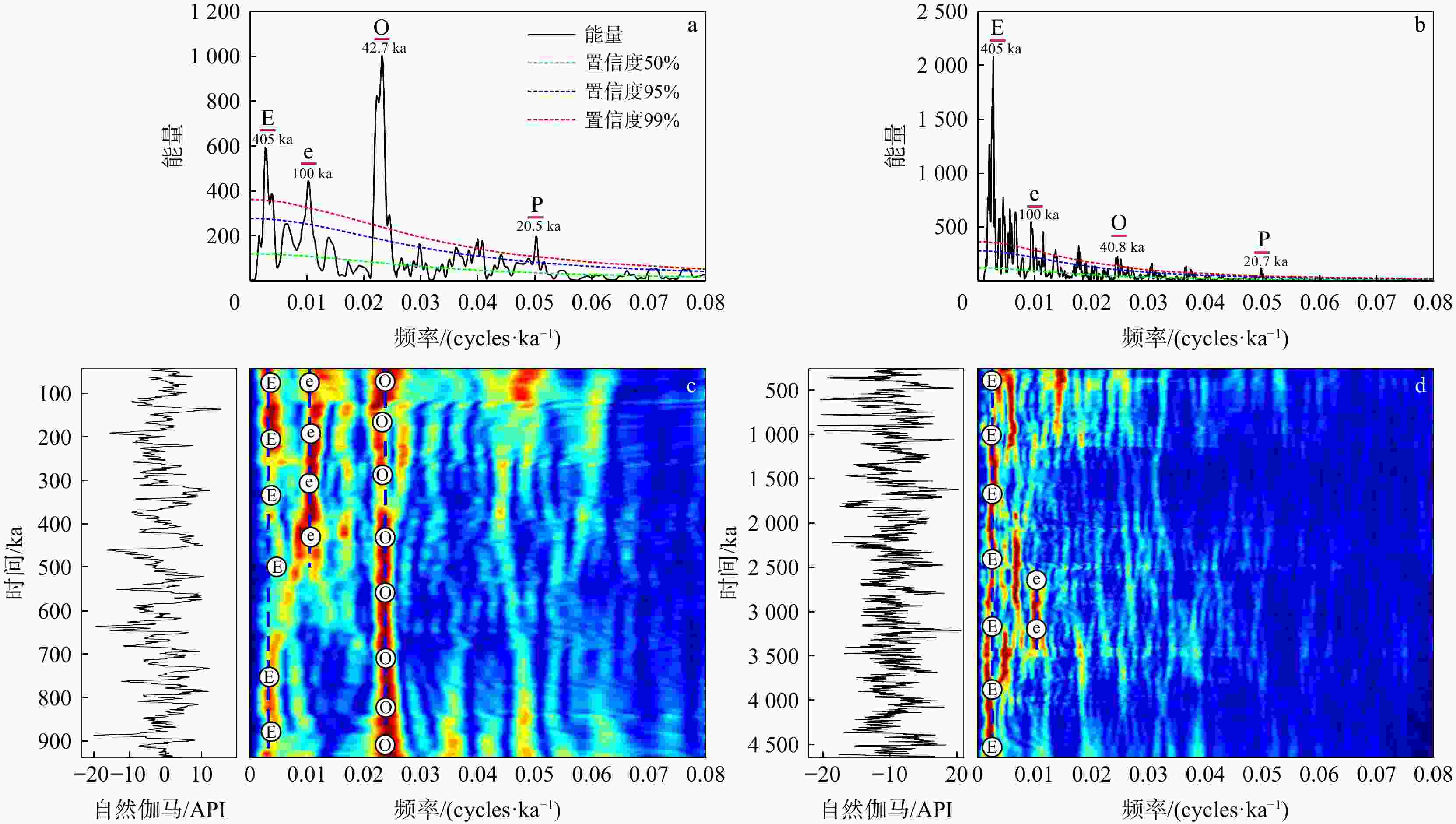
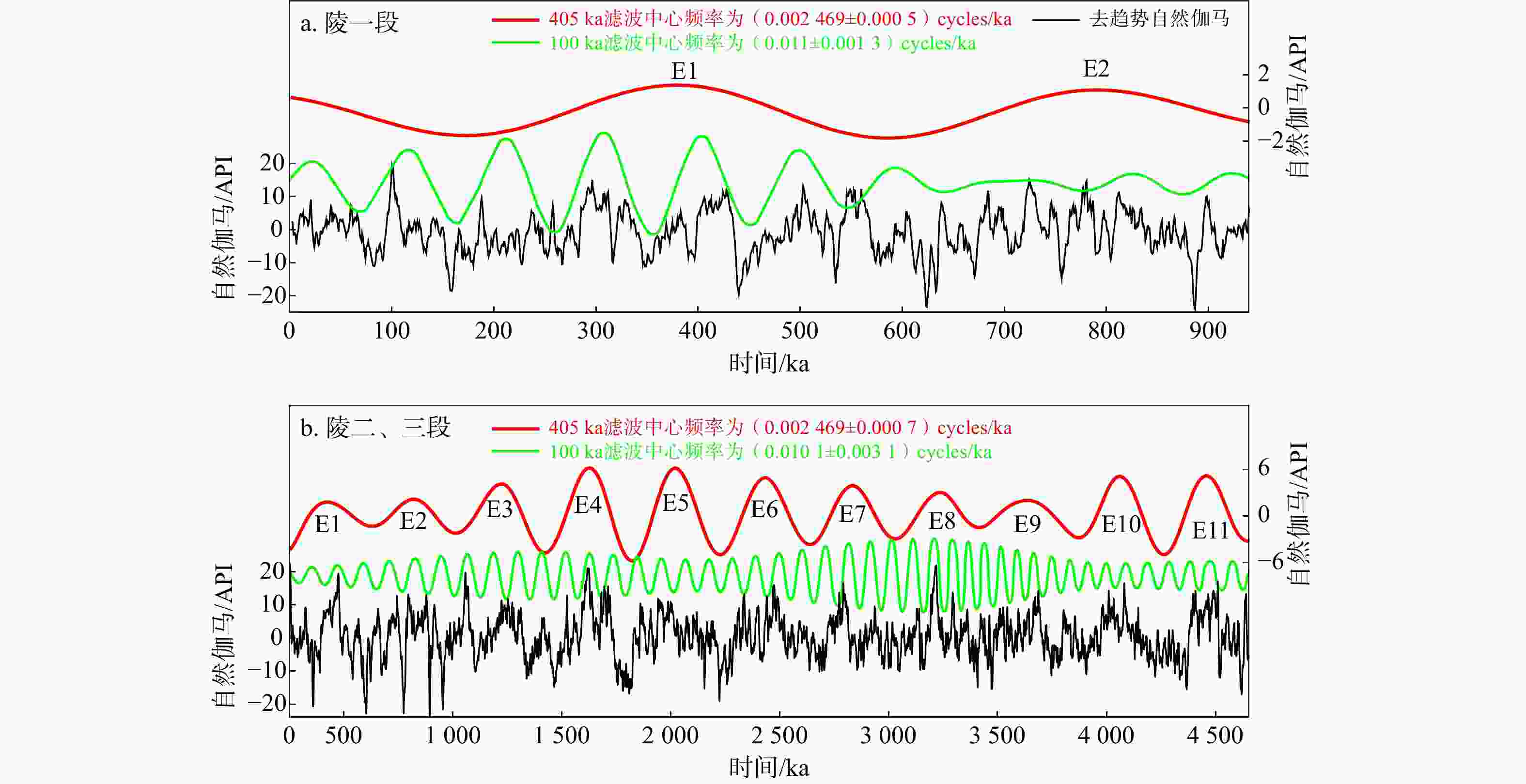
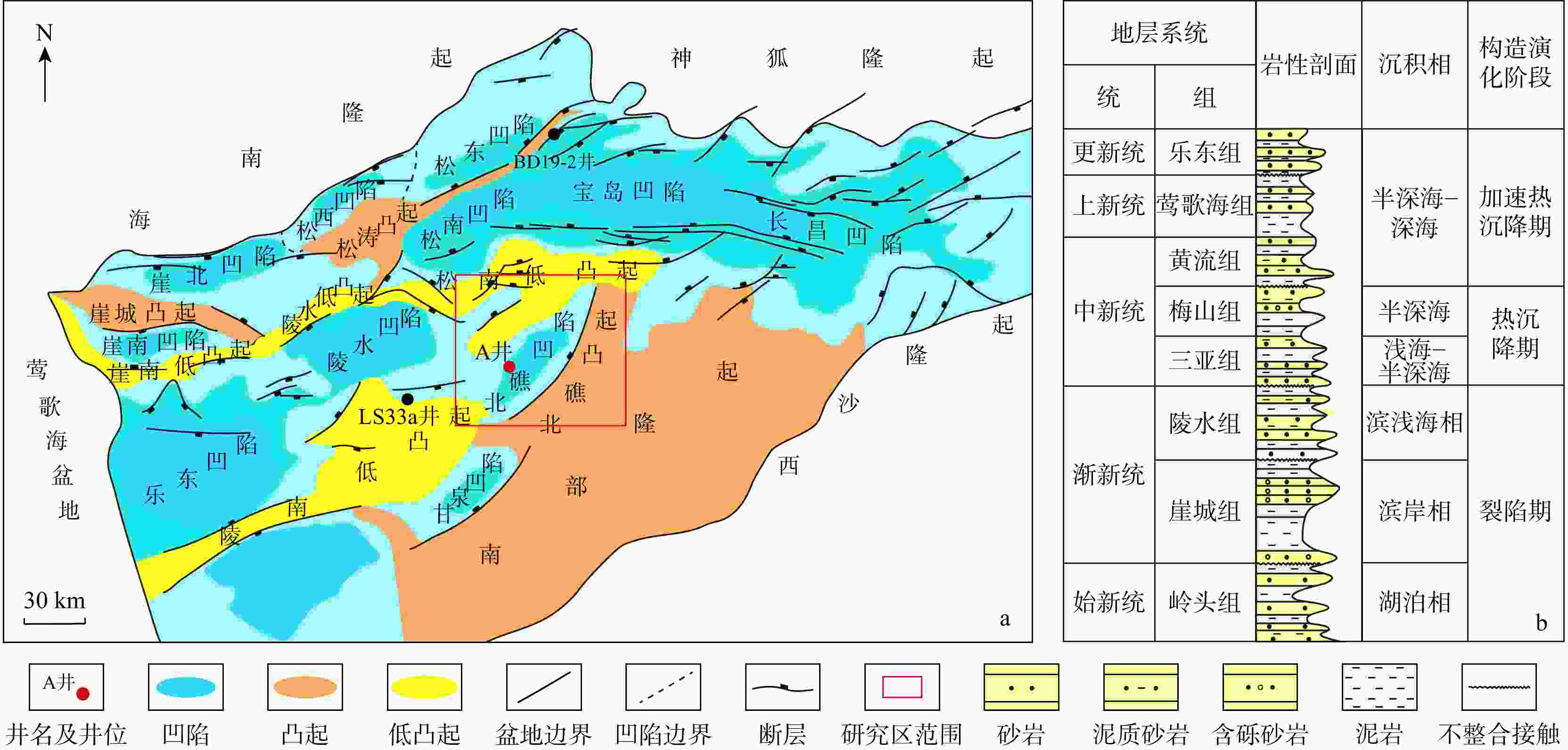
图 5 陵水组时间域频谱分析和演化功率谱分析
a. 陵一段时间域Lomb频谱分析结果,其中带有E、e、O、P标签的玫红色实线分别代表长偏心率、短偏心率、斜率和岁差旋回;b. 陵二、三段时间域Lomb频谱分析结果,其中带有E、e、O、P标签的玫红色实线分别代表长偏心率、短偏心率、斜率和岁差旋回;c. 陵一段时间域演化功率谱分析结果,其中带有E、e、O标签的蓝色虚线分别代表长偏心率、短偏心率和斜率旋回;d. 陵二、三段时间域演化功率谱分析结果,其中带有E、e标签的蓝色虚线分别代表长偏心率和短偏心率旋回
Figure 5. Spectrum analysis and evolutionary power spectrum in time of the Lingshui Formation
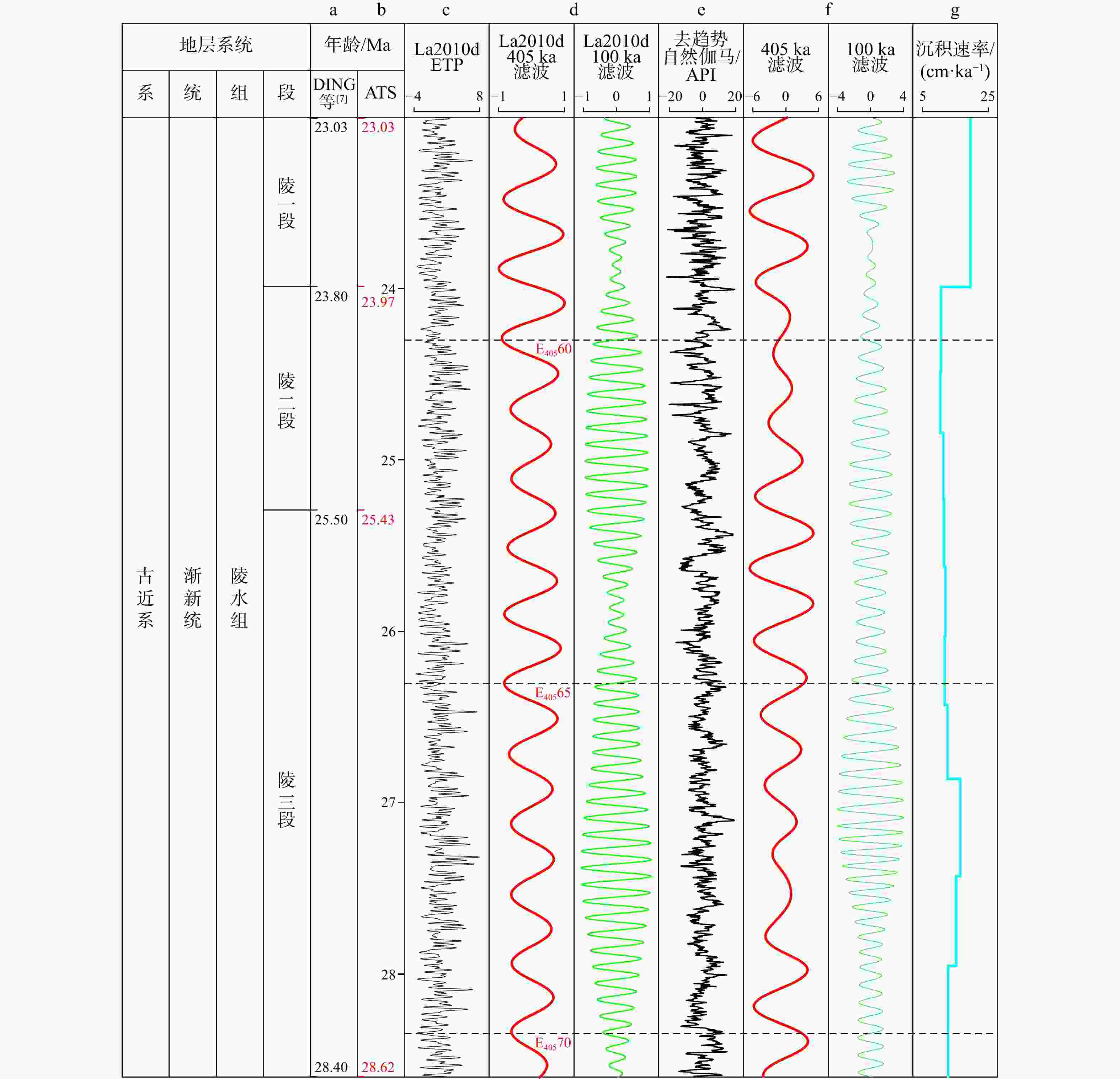
图 7 A井渐新统陵水组绝对天文年代标尺
a. DING等[7]的地层界面年龄;b. 天文年代标尺(ATS)校准的地层界面年龄;c. 根据 La2010d 模型,以理论轨道参数(ETP) 格式显示的 28.62~23.03 Ma 期间的地球轨道参数;d.La2010d 模型中ETP格式显示的405 ka长偏心率和100 ka短偏心率滤波曲线;f. A井去趋势后自然伽马曲线的405 ka长偏心率和100 ka短偏心率滤波曲线;g. 根据天文年代尺度结果计算出的沉积速率曲线
Figure 7. Absolute astronomical age scale for the Oligocence Lingshui Formation of the Well A
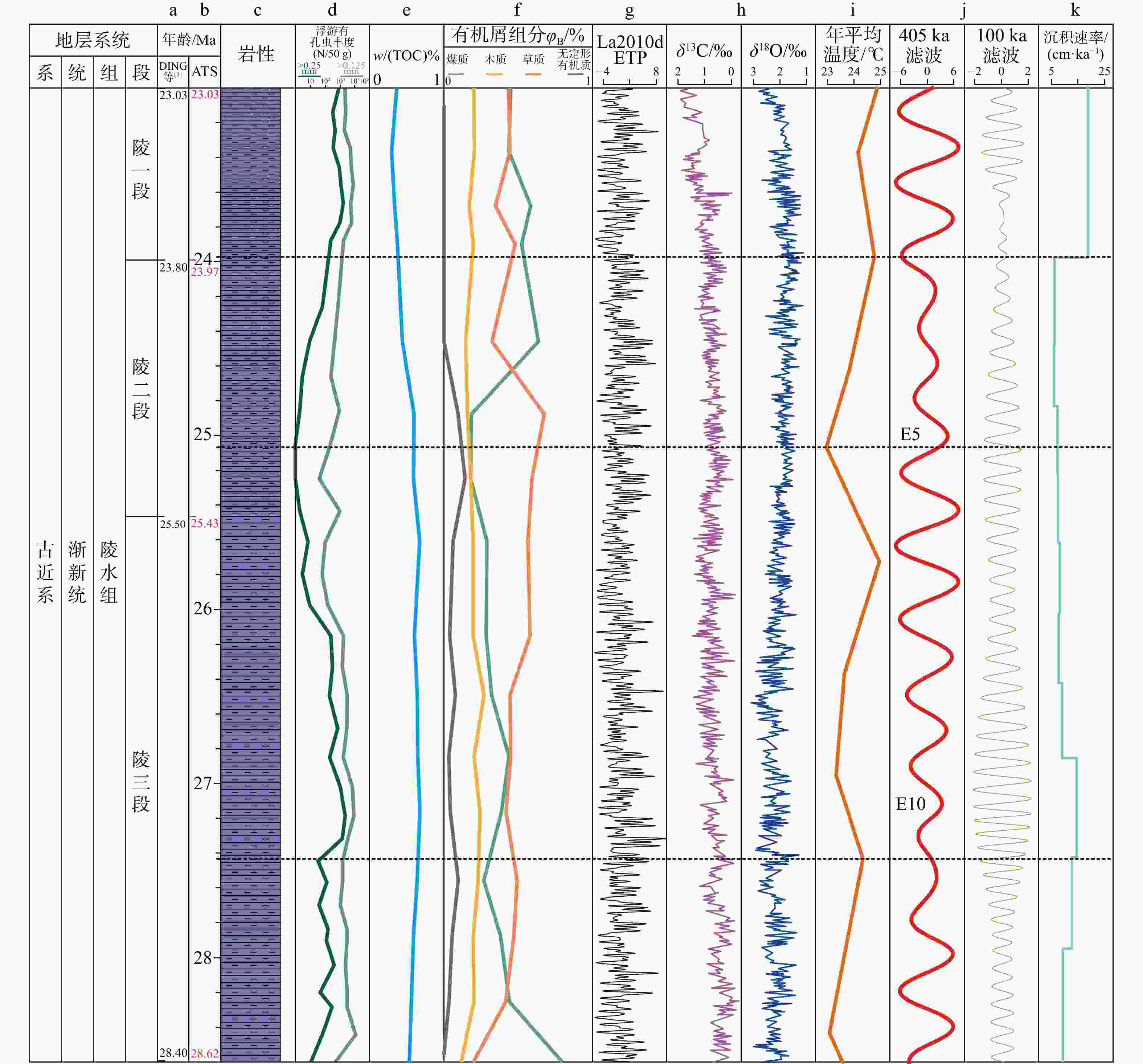
图 8 A井渐新统陵水组古气候替代指标对比
a. DING等[7]的地层界面年龄;b. 天文旋回(ATS)校准的地层界面年龄;g. 根据 La2010d 模型,以理论轨道参数( ETP) 格式显示的 28.62~ 23.03 Ma 期间的地球轨道参数;h. 来自 ODP1218站[38]的有孔虫碳和氧同位素;i. 年平均温度来自南海17490站有孔虫数据[39];j. A井去趋势后GR曲线的405 ka长偏心率和100 ka短偏心率滤波曲线;k. 根据天文时间尺度结果计算出的沉积速率曲线
Figure 8. Comparison of palaeoclimate proxies for the Oligocene Lingshui Formation of the Well A
-
[1] 朱继田, 杨希冰, 胡向阳, 等. 琼东南盆地北部中生代凹陷特征及油气成藏条件初探[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(2): 83-93.ZHU J T, YANG X B, HU X Y, et al. Characteristic and petroleum geology of the Mesozoic Sags of the northern Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(2): 83-93. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 徐长贵, 尤丽. 琼东南盆地松南−宝岛凹陷北坡转换带特征及其对大中型气田的控制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(6): 1061-1072. doi: 10.11698/PED.20220102XU C G, YOU L. North slope transition zone of Songnan–Baodao Sag in Qiongdongnan Basin and its control on medium and large gas fields, South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(6): 1061-1072. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.20220102 [3] 徐长贵, 邓勇, 吴克强, 等. 南海北部强活动型被动陆缘盆地宝岛21-1大气田的发现及地质意义[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(5): 713-729. doi: 10.7623/syxb202305001XU C G, DENG Y, WU K Q, et al. Discovery and geological significance of the large gas field Baodao 21-1 in a passive epicontinental basin with strong activity in the northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(5): 713-729. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7623/syxb202305001 [4] 吴克强, 解习农, 裴健翔, 等. 超伸展陆缘盆地深部结构及油气勘探意义: 以琼东南盆地为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(3): 651-661. doi: 10.11743/ogg20230310WU K Q, XIE X N, PEI J X, et al. Deep architecture of hyperextended marginal basin and implications for hydrocarbon exploration: A case study of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2023, 44(3): 651-661. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11743/ogg20230310 [5] 张功成, 纪沫, 陈莹, 等. 琼东南盆地“气聚集带” 的成藏特征与勘探潜力[J]. 石油学报, 2024, 45(1): 226-240. doi: 10.7623/syxb202401013ZHANG G C, JI M, CHEN Y, et al. Accumulation characteristics and exploration potentials of gas accumulation belt in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2024, 45(1): 226-240. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7623/syxb202401013 [6] 刘晓锋, 孙志鹏, 刘新宇, 等. 南海北部深水区LS33a钻井微体古生物年代地层格架[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(5): 890-902.LIU X F, SUN Z P, LIU X Y, et al. Chronostratigraphic framework based on micro-paleontological data from drilling LS33a in deep water area of northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(5): 890-902. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] DING W J, HOU D J, GAN J, et al. Palaeovegetation variation in response to the Late Oligocene-Early Miocene East Asian summer monsoon in the Ying-Qiong Basin, South China Sea[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 567: 110205. [8] 吴怀春, 房强. 旋回地层学和天文时间带[J]. 地层学杂志, 2020, 44(3): 227-238.WU H C, FANG Q. Cyclostratigraphy and astrochronozones[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2020, 44(3): 227-238. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 田军, 吴怀春, 黄春菊, 等. 从40万年长偏心率周期看米兰科维奇理论[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(10): 3543-3568.TIAN J, WU H C, HUANG C J, et al. Revisiting the Milankovitch theory from the perspective of the 405 ka long eccentricity cycle[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(10): 3543-3568. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] XU K, CHEN H H, HUANG C J, et al. Astronomical time scale of the Paleogene lacustrine paleoclimate record from the Nanxiang Basin, Central China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2019, 532: 109253. [11] 朱春霞, 张尚锋, 王雅宁, 等. 陆丰凹陷韩江组旋回地层学分析及天文年代标尺的建立[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2022, 38(4): 42-52.ZHU C X, ZHANG S F, WANG Y N, et al. Cyclical stratigraphic analysis and establishment of astronomical chronograph of Hanjiang Formation in Lufeng Sag[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2022, 38(4): 42-52. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 张念念, 范天来, 黄春菊, 等. 西沙群岛琛科2井珊瑚礁钻孔天文年代标尺的建立及天文周期记录[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(6): 436-450.ZHANG N N, FAN T L, HUANG C J, et al. Identification of orbital cycles in coral-reef core from Well CK-2, Xisha Islands and insights into coral reef evolution in the South China Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(6): 436-450. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] HILGEN F J, LANGEREIS C G. The age of the Miocene-Pliocene boundary in the Capo Rossello area (Sicily)[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1988, 91(1/2): 214-222. [14] HÜSING S K, CASCELLA A, HILGEN F J, et al. Astrochronology of the Mediterranean langhian between 15.29 and 14.17 Ma[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 290(3/4): 254-269. [15] 施和生, 杨计海, 张迎朝, 等. 琼东南盆地地质认识创新与深水领域天然气勘探重大突破[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(6): 691-698. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.06.001SHI H S, YANG J H, ZHANG Y Z, et al. Geological understanding innovation and major breakthrough to natural gas exploration in deep water in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(6): 691-698. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.06.001 [16] 王真真, 朱继田, 李安琪, 等. 琼东南盆地新生代东西分块差异构造演化及控藏意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(4): 157-169.WANG Z Z, ZHU J T, LI A Q, et al. Differential control of structures over reservoirs and its significance in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(4): 157-169. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 张功成. 南海渐进式边缘海构造旋回控制深水油气成藏理论[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(4): 569-582. doi: 10.7623/syxb202304001ZHANG G C. Theory of deepwater hydrocarbon accumulation controlled by progressive tectonic cycles of marginal sea in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(4): 569-582. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7623/syxb202304001 [18] 张功成, 刘震, 米立军, 等. 珠江口盆地−琼东南盆地深水区古近系沉积演化[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(4): 632-641.ZHANG G C, LIU Z, MI L J, et al. Sedimentary evolution of Paleogene series in deep water area of Zhujiangkou and Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(4): 632-641. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 龙根元, 吴世敏, 曾广东. 琼东南盆地北礁凹陷伸展构造的几何学分析[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(3): 71-77.LONG G Y, WU S M, ZENG G D. Structural geometry of the Beijiao Sag of the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2010, 30(3): 71-77. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 张义娜, 张功成, 何玉平, 等. 琼东南盆地北礁凹陷崖城组沉积与烃源岩发育特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(4): 725-732.ZHANG Y N, ZHANG G C, HE Y P, et al. Sedimentation and source rock characteristics of Yacheng Formation in Beijiao Sag of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(4): 725-732. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 李俞锋, 蒲仁海, 唐明, 等. 一种新型底流与浊流交互作用形成的储集砂体: 以北礁凹陷为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2018, 30(6): 55-66. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20180607LI Y F, PU R H, TANG M, et al. A new reservoir sand body resulted from interaction between turbidity flows and bottom currents: A case from Beijiao Sag of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2018, 30(6): 55-66. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20180607 [22] 张毅, 毛宁波, 何丽娟, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区新生代海底扇沉积演化: 以宝南断阶带为例[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019, 24(3): 48-54.ZHANG Y, MAO N B, HE L J, et al. Sedimentary evolution of submarine fan of Cenozoic in deep-water area of Qiongdongnan Basin: A case study in Baonan Fault Terrace Zone[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2019, 24(3): 48-54. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 谢辉, 周蒂, 石红才, 等. 珠江口盆地−琼东南盆地深水区新生代构造沉积演化对比分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2021, 43(3): 48-61.XIE H, ZHOU D, SHI H C, et al. Comparative study on the Cenozoic tectonic and sedimentary evolution in the deep water areas of the Zhujiang River Estuary Basin and the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2021, 43(3): 48-61. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 杜威, 纪友亮, 季梦瑶, 等. 渤海湾盆地饶阳凹陷早渐新世高精度年代地层格架建立及意义[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 44(4): 142-151. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2020.04.017DU W, JI Y L, JI M Y, et al. Establishment and significance of high-resolution Early Oligocene chronostratigraphic framework in Raoyang Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2020, 44(4): 142-151. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2020.04.017 [25] FALAHATKHAH O, KORDI M, FATEMI V, et al. Recognition of Milankovitch cycles during the Oligocene-Early Miocene in the Zagros Basin, SW Iran: Implications for paleoclimate and sequence stratigraphy[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2021, 421: 105957. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2021.105957 [26] 王嘉伟, 金思丁, 魏祥峰, 等. 黔西南下石炭统打屋坝组页岩的天文旋回识别及层序地层划分[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(4): 288-303.WANG J W, JIN S D, WEI X F, et al. Orbital cycle recognition and sequence stratigraphic division of the Lower Carboniferous Dawuba Formation shales in Southwest Guizhou[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(4): 288-303.(in Chinese with English abstract [27] 赵庆乐, 吴怀春, 李海燕, 等. 利用采样定理与沉积速率确定旋回分析最佳采样间隔[J]. 地球科学, 2011, 36(1): 12-16.ZHAO Q L, WU H C, LI H Y, et al. Determination of the optimal sampling interval for cyclostratigraphic analysis by using sampling theorem and accumulation rates[J]. Earth Science, 2011, 36(1): 12-16. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 赵韶华, 王雅宁, 张尚锋, 等. 南海北部中新世古气候分析: 基于天文旋回的冷却事件响应[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2022, 38(4): 53-62.ZHAO S H, WANG Y N, ZHANG S F, et al. Miocene paleoclimate analysis of the northern South China Sea: Response to cooling events based on astronomical cycles[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2022, 38(4): 53-62. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] LI M S, HINNOV L, KUMP L. Acycle: Time-series analysis software for paleoclimate research and education[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2019, 127: 12-22. [30] 宋翠玉, 吕大炜. 米兰科维奇旋回时间序列分析法研究进展[J]. 沉积学报, 2022, 40(2): 380-395.SONG C Y, LÜ D W. Advances in time series analysis methods for Milankovitch cycles[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2022, 40(2): 380-395. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] YANG H Z, TANG W, XU E Z, et al. Cyclostratigraphy and paleoclimate analysis of the Lingshui Formation in Changchang Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin, China[J]. Energy Geoscience, 2024, 5(1): 100224. doi: 10.1016/j.engeos.2023.100224 [32] LIU J, MA X D, LU Y C, et al. Astronomically forced Late Paleocene-Early Eocene climate variability in the Subei Basin, East China[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2024, 232: 104350. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2023.104350 [33] HUA X, YIN R S, KEMP D B, et al. Mercury isotope constraints on the timing and pattern of magmatism during the end-Triassic mass extinction[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2023, 624: 118438. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2023.118438 [34] LIU D Y, HUANG C J, KEMP D B, et al. Paleoclimate and sea level response to orbital forcing in the Middle Triassic of the eastern Tethys[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2021, 199: 103454. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2021.103454 [35] HUANG C J, OGG J G, KEMP D B. Cyclostratigraphy and astrochronology: Case studies from China[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 560: 110017. [36] LASKAR J, ROBUTEL P, JOUTEL F, et al. A long-term numerical solution for the insolation quantities of the Earth[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2004, 428(1): 261-285. [37] LASKAR J, FIENGA A, GASTINEAU M, et al. La2010: A new orbital solution for the long-term motion of the Earth[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2011, 532: A89. [38] PÄLIKE H, NORRIS R D, HERRLE J O, et al. The heartbeat of the Oligocene climate system[J]. Science, 2006, 314: 1894-1898. doi: 10.1126/science.1133822 [39] 刘磊, 管红香, 冯俊熙, 等. 南海北部31 ka以来GDGTs组成及其对古温度和季风变化的响应[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2020, 40(3): 144-159.LIU L, GUAN H X, FENG J X, et al. Composition of glycerol dibiphytanyl glycerol tetraethers(GDGTs) and its responses to paleotemperature and monsoon changes since 31 ka in northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2020, 40(3): 144-159. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 谭思哲, 高顺莉, 葛和平, 等. 南黄海盆地二叠系烃源岩孢粉相特征及其形成环境[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2015, 45(3): 691-700.TAN S Z, GAO S L, GE H P, et al. Palynofacies characteristics and formation environment of Permian source rock in South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2015, 45(3): 691-700. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 马博, 吉利明, 张明震, 等. 酒西盆地红柳峡地区下白垩统烃源岩孢粉相与沉积古环境特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(5): 22-33. doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210503MA B, JI L M, ZHANG M Z, et al. Palynofacies and sedimentary paleoenvironment of Lower Cretaceous source rocks in Hongliuxia area, Jiuxi Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(5): 22-33. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210503 [42] 马博, 吉利明, 张明震, 等. 酒西盆地下白垩统赤金堡组烃源岩孢粉相特征及其石油地质意义[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(11): 1376-1387. doi: 10.7623/syxb202011007MA B, JI L M, ZHANG M Z, et al. Palynofacies characteristics of source rocks of Lower Cretaceous Chijinbao Formation in Jiuxi Basin and their petroleum geological significance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(11): 1376-1387. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7623/syxb202011007 [43] 田军, 汪品先, 成鑫荣. 南沙ODP1143站有孔虫同位素变化对地球轨道驱动的响应[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2004, 34(5): 452-460.TIAN J, WANG P X, CHENG X R. Response of isotopic changes of foraminifera at ODP1143 station in Nansha to earth orbit drive[J]. Science in China(Ser. D), 2004, 34(5): 452-460. (in Chinese) [44] 汪品先, 田军, 黄恩清, 等. 地球系统与演变[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018.WANG P X, TIAN J, HUANG E Q, et al. Earth system and evolution[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018. (in Chinese) -




 下载:
下载: