Petrographic, geochemical characteristics and genesis of the siliceous rock in the Middle Permian Maokou Formation at the eastern Sichuan Basin
-
摘要:
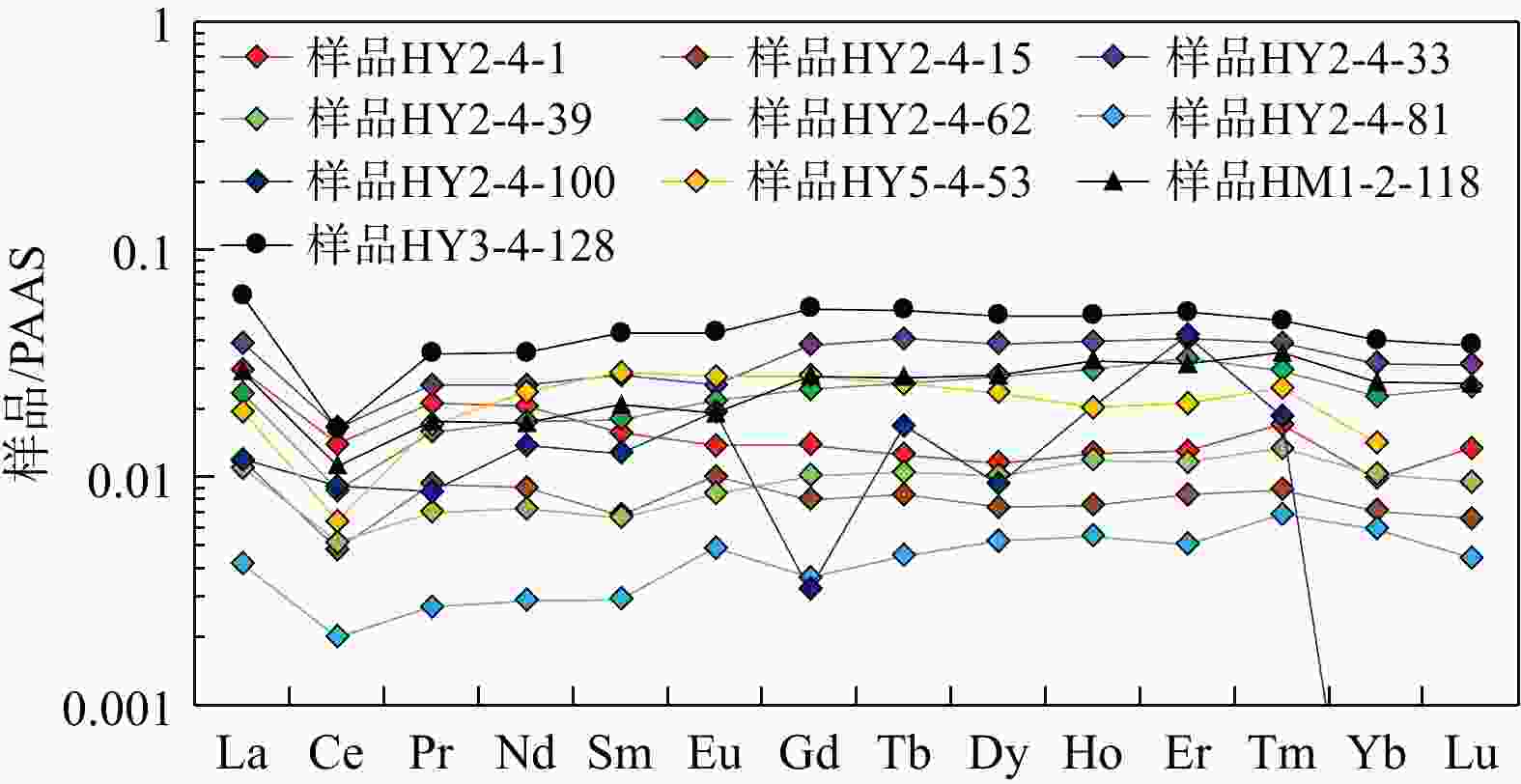
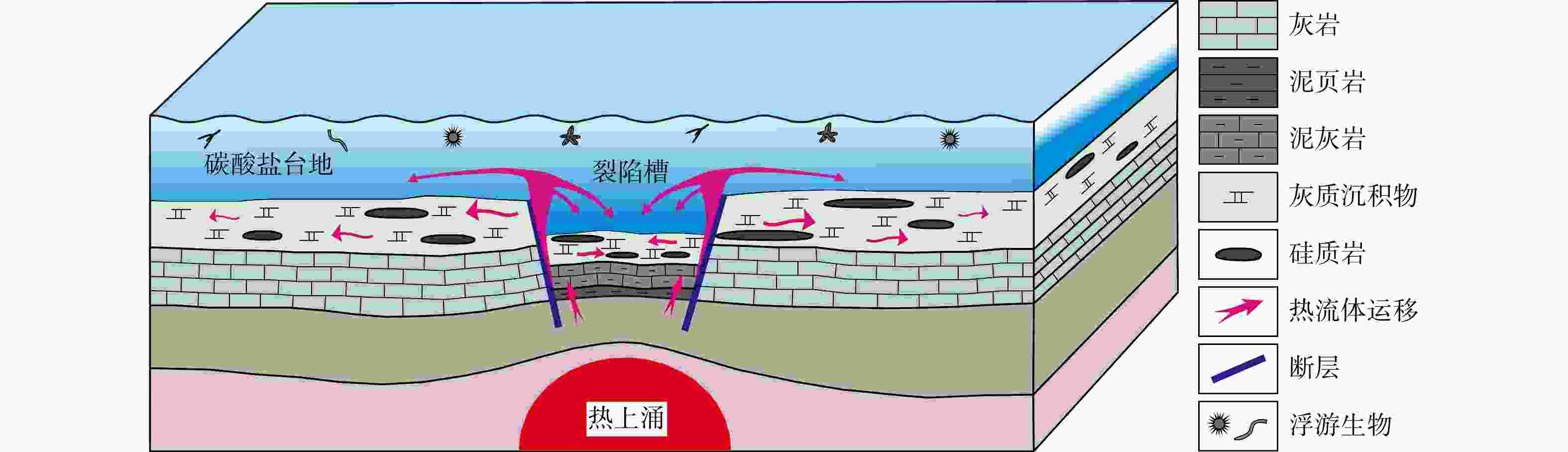
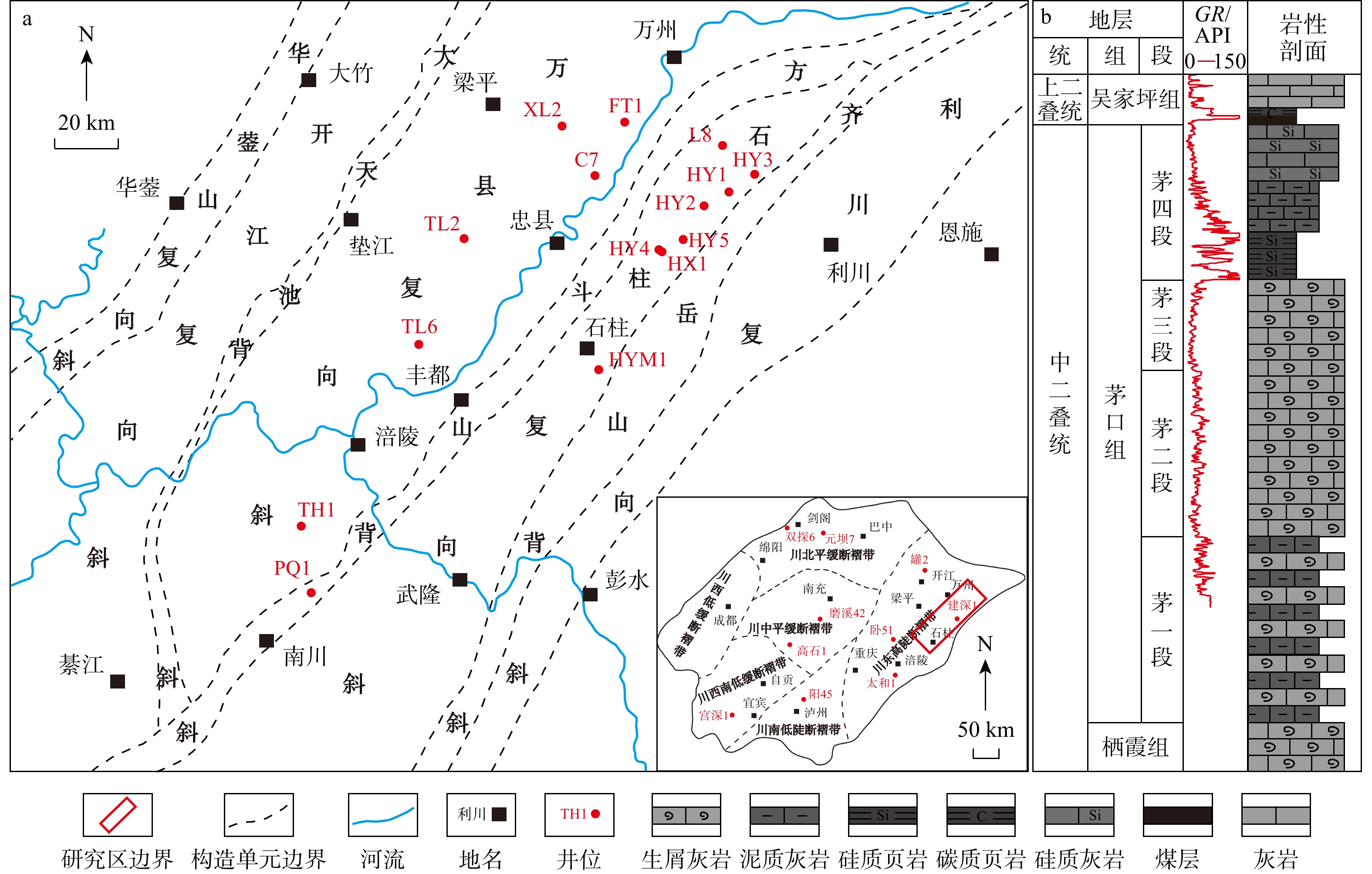
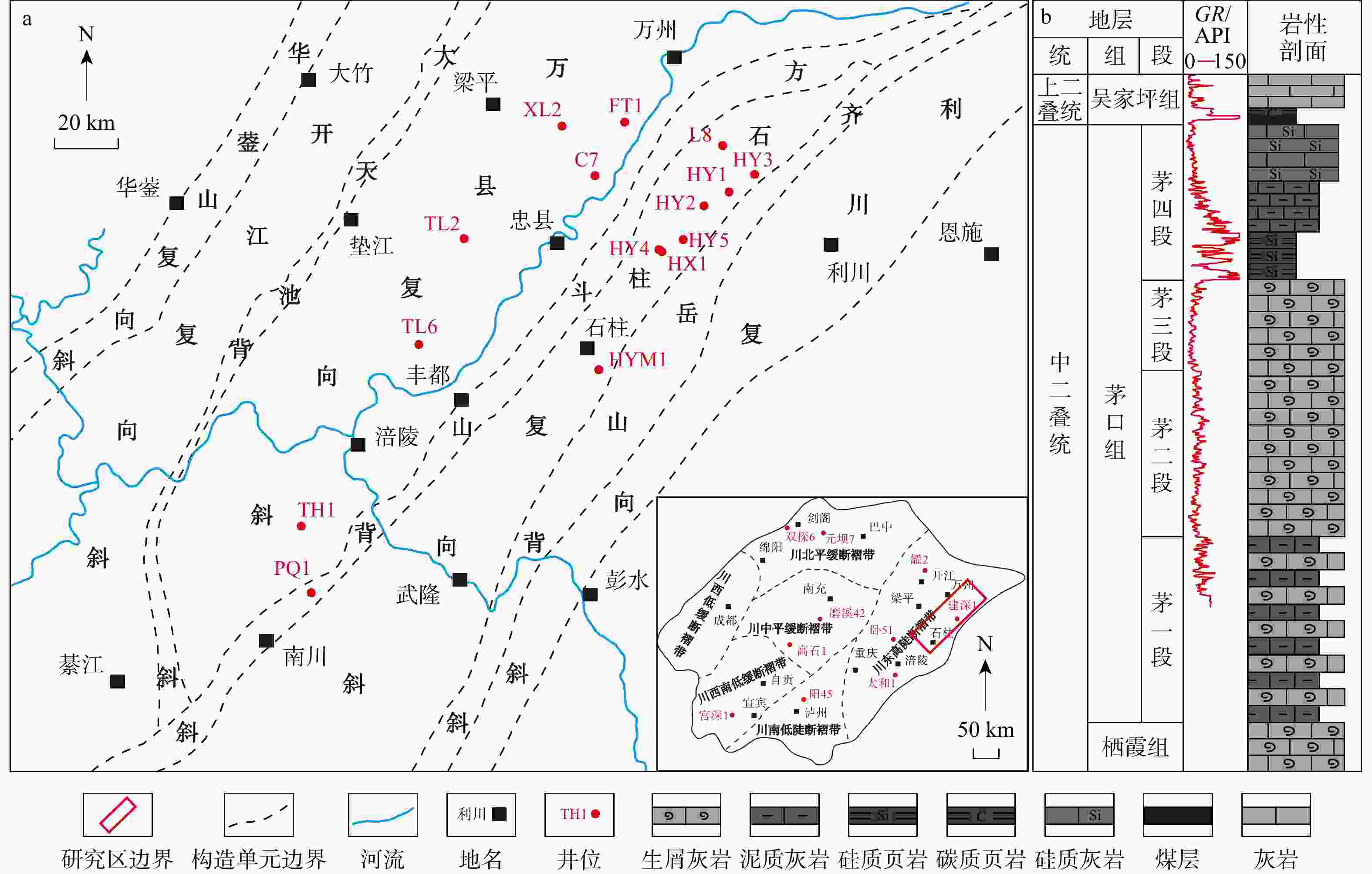
为明确上扬子东缘茅口组硅质岩的沉积环境、硅质来源及形成机理,以川东地区中二叠统茅口组硅质岩为研究对象,在详细的岩石学观察分析的基础上,开展硅质岩的主量元素、微量元素和稀土元素分析。结果表明:硅质岩的形成缺乏陆源物质的影响,其SiO2主要来源于与二叠纪岩浆活动相关的热液流体,同时生物作用参与了硅质岩的形成;硅质岩的形成环境主要为靠近大陆边缘的台盆相间背景下相对缺氧的深水裂陷槽内及周缘的浅水台地,峨眉地幔柱上拱导致的基底深大断裂活化以及新形成的同沉积断裂为热液流体的上升运移提供了主要通道,热液流体在运移过程中与地壳的相互作用导致其具有壳、幔混源的特征;硅质岩形成于同沉积期或沉积后不久,主要表现为通过交代碳酸盐质组分的方式而形成,疏松多孔的介质条件有利于热液流体在沉积物中的流动并发生顺层交代或沉淀,热液流体的间歇性作用则导致不均匀硅化作用的发生。该研究成果提出了上扬子川东地区茅口组硅质岩成因的新观点,深化了中晚二叠世之交的古构造沉积演化认识,对该地区的天然气勘探部署具有重要的指导意义。
Abstract:Objective To explore the sedimentary environment, sources, and formation mechanisms of siliceous rock from the Maokou Formation on the eastern edge of the Upper Yangtze Block.
Methods This study focuses on the siliceous rock in the Middle Permian Maokou Formation from the eastern Sichuan area. Based on detailed petrological observations and analyses, the major elements, trace elements, and rare earth elements of the siliceous rock were analyzed.
Results The results show that the formation of the siliceous rock was not influenced by terrigenous materials. The SiO2 primarily originated from hydrothermal fluids associated with Permian magmatism, with biological processes, which played a role in its formation. The siliceous rock formed in relatively hypoxic, deep-water rift troughs and surrounding shallow water platforms near the continental margin, under a background of alternating platforms and basins. The activation of deep basement faults caused by the Emei mantle plume and newly formed synsedimentary faults provided the main channels for the upward migration of hydrothermal fluids. The interaction between the hydrothermal fluids and the crust during migration resulted in characteristics indicative of crustal-mantle mixed sources. The siliceous rock was deposited during the synsedimentary period or shortly after deposition, mainly through the replacement of carbonate components. The loose and porous medium conditions facilitated the flow of hydrothermal fluids through the sediments, leading to bedding metasomatism or precipitation. The intermittent action of hydrothermal fluids caused uneven silicification.
Conclusion This research proposes a new perspective on the genesis of the Maokou Formation siliceous rock in the eastern Sichuan area of the Upper Yangtze Block, deepening the understanding of the paleotectonic sedimentary evolution at the Middle-Late Permian boundary, and providing important insights for natural gas exploration and development in this region.
-
Key words:
- eastern Sichuan Basin /
- Maokou Formation /
- siliceous rock /
- geochemistry /
- genesis
-
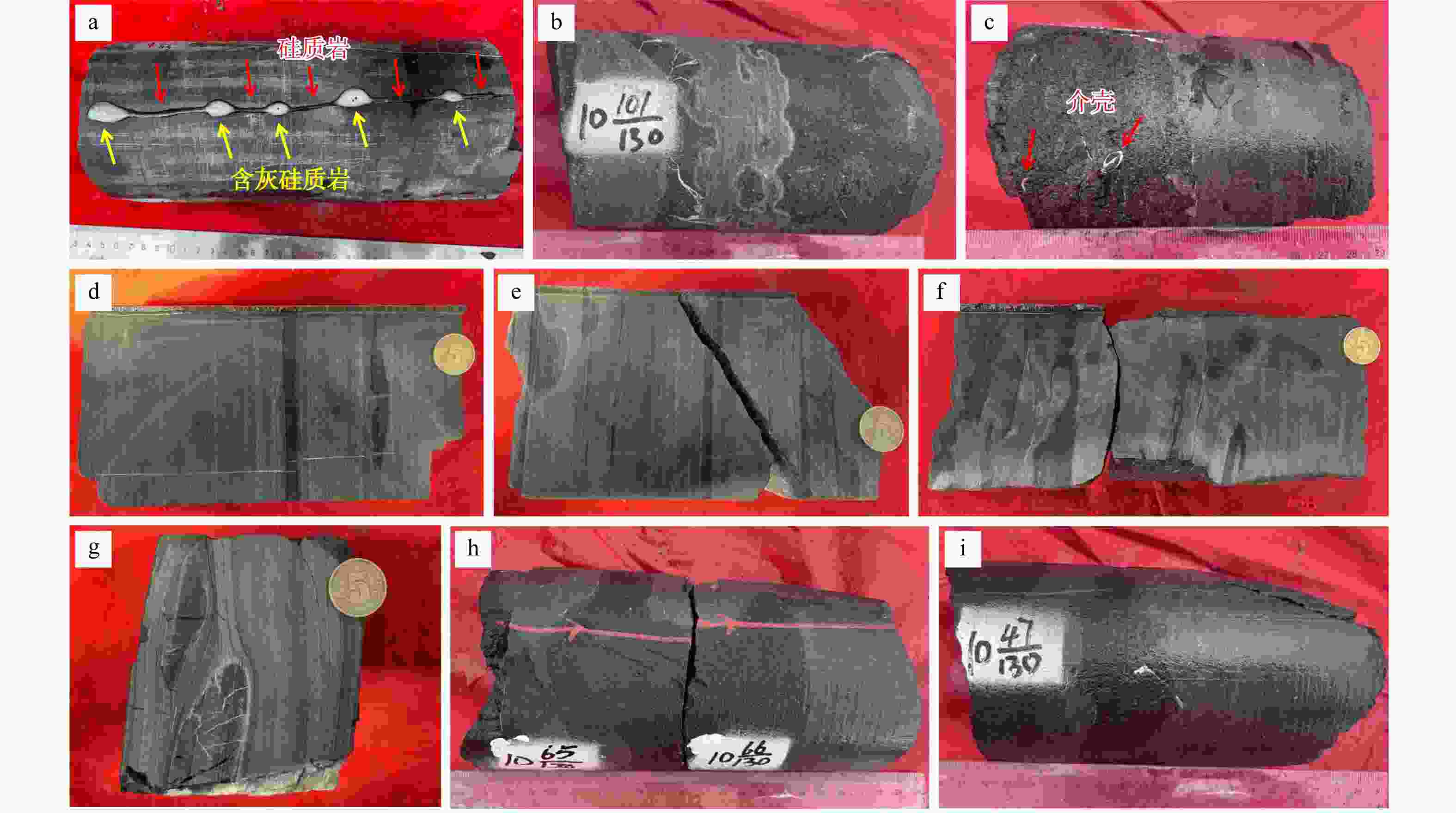
图 2 川东地区茅口组茅四段上亚段硅质岩宏观岩石学特征
a. 含灰硅质岩与硅质岩互层,滴15%浓度稀盐酸后,含灰硅质岩起泡剧烈,硅质岩不起泡,样品HY5-4-112/113(HY5为井号;4为取心回次;112/113为岩心块号,表示第4回次共取心113块,本研究采用第112块岩心进行试验;下同);b. 硅质岩中包裹的呈云朵状灰岩组分,样品HX1-10-101/130;c. 硅质岩中富含介壳类生物碎屑,样品HX1-10-34/130;d. 深灰色含硅灰岩中夹的黑色薄层条带状硅质岩,呈规则和不规则2种产状,样品HY2-5-27/27;e. 深灰色含硅灰岩中夹的黑色薄层条带状及结核状硅质岩,可见硅质岩中发育水平纹层,样品HY2-4-56/136;f. 深灰色含硅灰岩中夹的黑色薄层条带状硅质岩,呈不规则状,样品HY1-4-34/99;g. 深灰色含硅灰岩中夹的黑色硅质结核,结核中发育的水平纹层连续地延伸至两侧灰岩中,结核周缘灰岩中的纹层则绕过结核,样品HY2-4-133/136;h. 黑色团块状硅质结核,样品HX1-10-65-66/130;i. 黑色团块状硅质结核,样品HX1-10-47/130
Figure 2. Macroscopic petrographic characteristics of the siliceous rocks in the upper sub-member of the 4th member of the Maokou Formation in the eastern Sichuan area
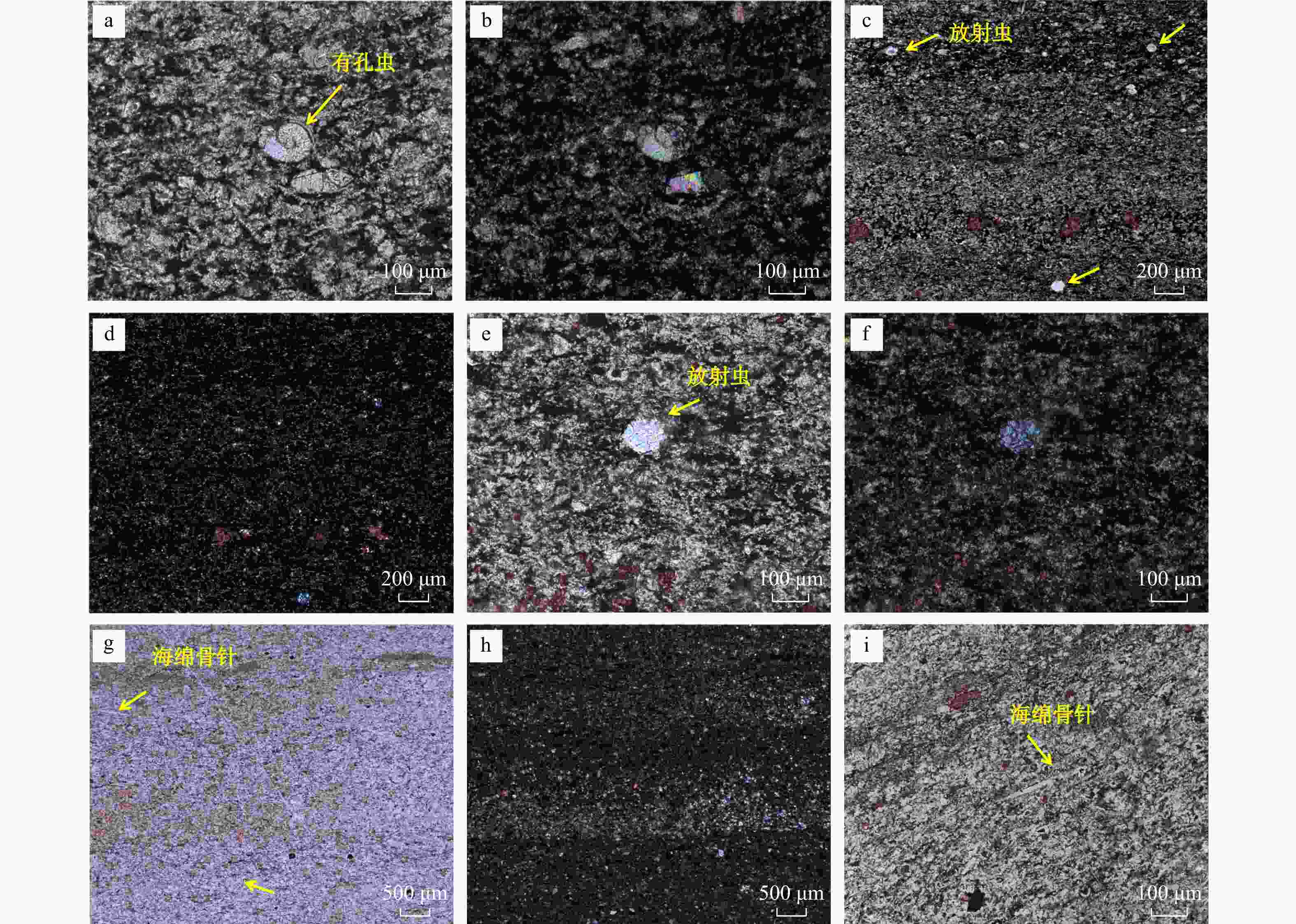
图 3 川东地区茅口组茅四段上亚段硅质岩微观岩石学特征
a. 硅质岩中的有孔虫等钙质生物碎屑被硅化,样品HY2-6-53/78,单偏光;b. a的正交偏光;c. 硅质岩中富含放射虫等硅质生物碎屑,茜素红染色,样品HY2-6-53/78,单偏光;d. c的正交偏光;e. c的局部放大;f. e的正交偏光;g. 硅质岩中残存的灰质组分,纵向上与硅质组分互层,茜素红染色,样品HY2-6-64/78,单偏光;h. g的正交偏光;i. g的局部放大
Figure 3. Microscopic petrographic characteristics of the siliceous rocks in the upper sub-member of the 4th member of the Maokou Formation in the eastern Sichuan area
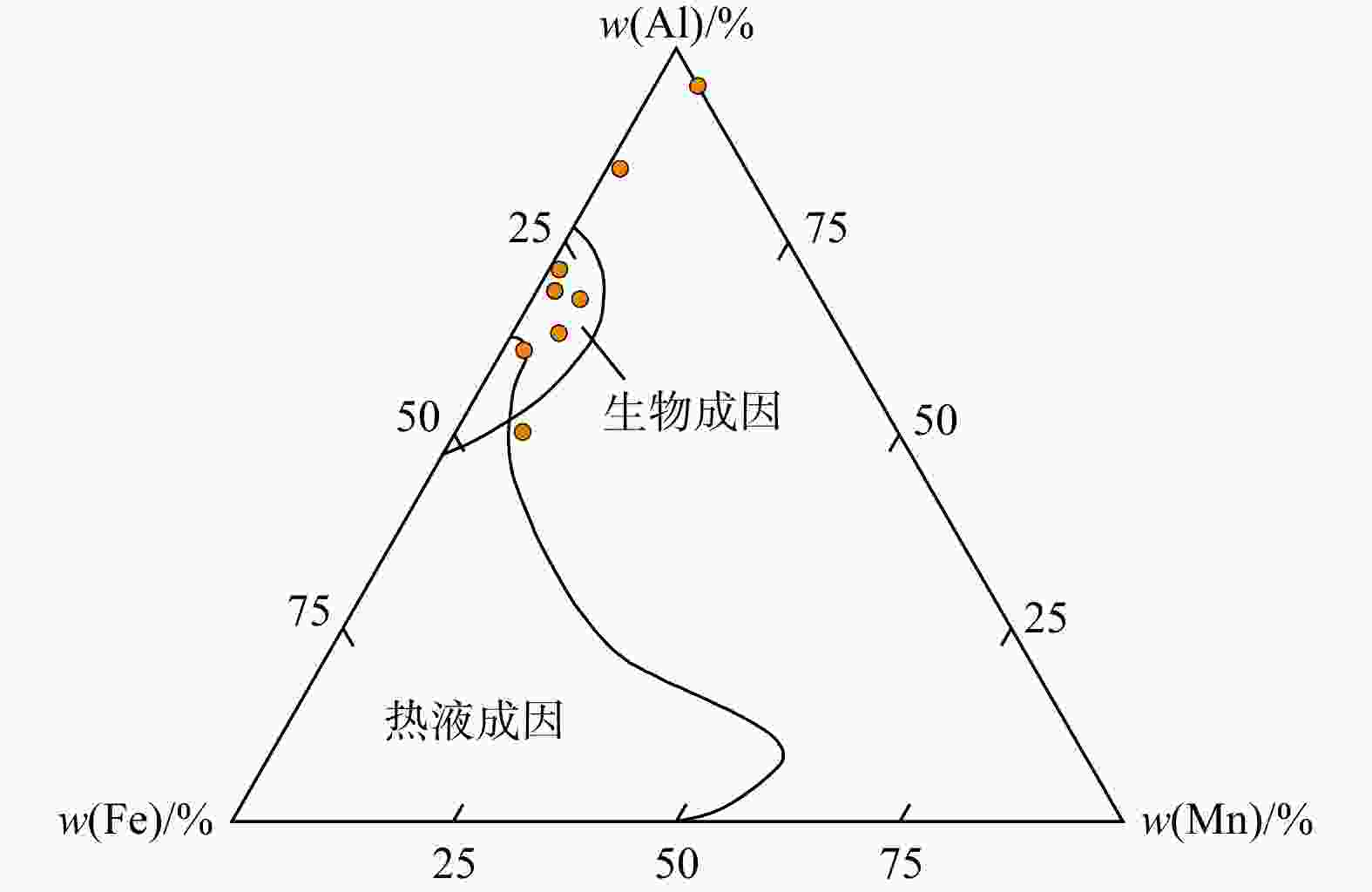
图 5 研究区茅口组茅四段上亚段硅质岩Al-Fe-Mn判别图解(底图据YAMAMOTO[34]修改)
Figure 5. Al-Fe-Mn diagram for the siliceous rocks in the upper sub-member of the 4th member of the Maokou Formation in the study area
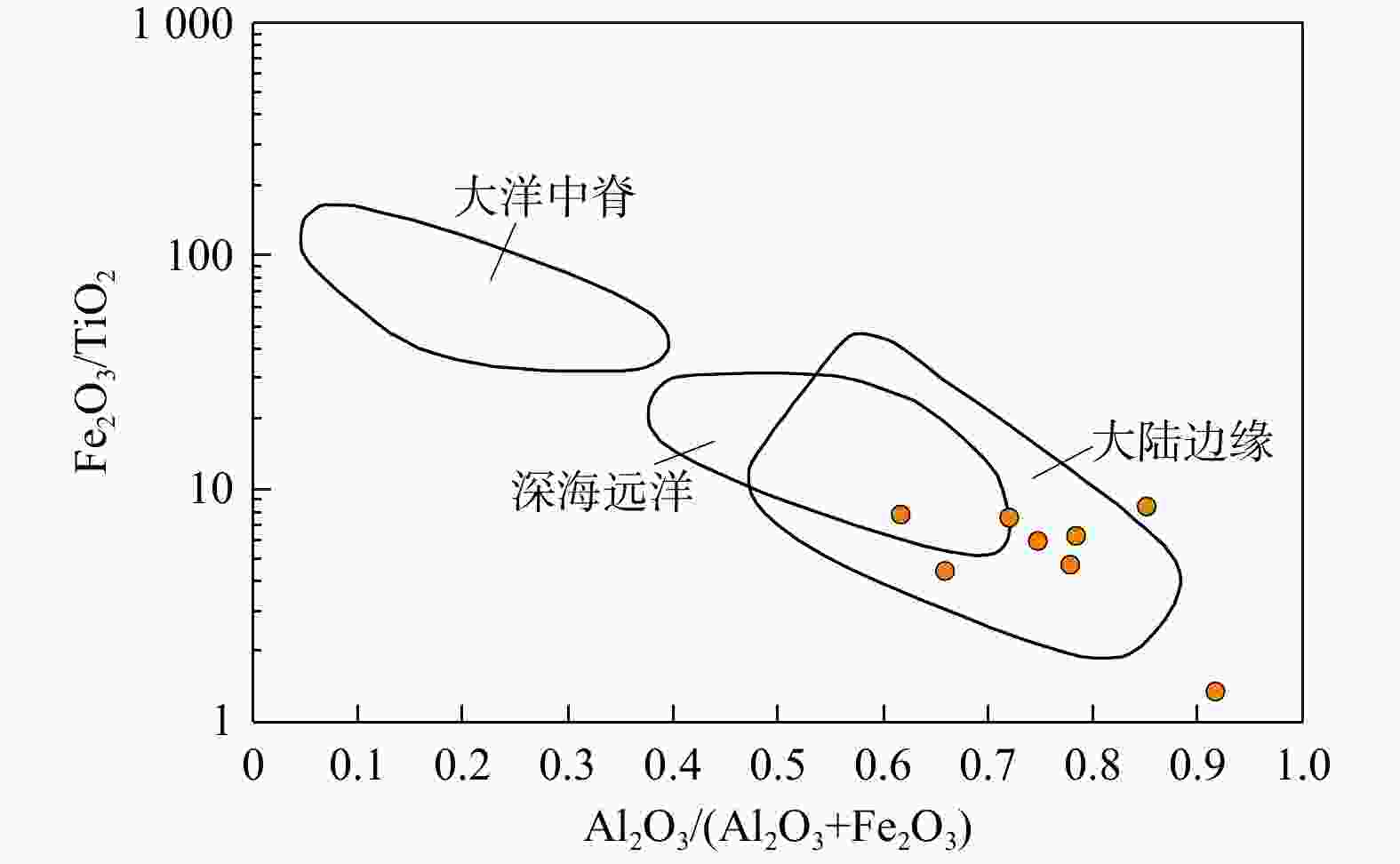
图 8 研究区茅口组茅四段上亚段硅质岩Fe2O3/TiO2与Al2O3/(Al2O3+Fe2O3)交汇图(底图据MURRAY[1]修改)
Figure 8. Plot of Fe2O3/TiO2 and Al2O3/(Al2O3+Fe2O3) for the siliceous rocks in the upper sub-member of the 4th member of the Maokou Formation in the study area
表 1 川东地区茅口组茅四段上亚段硅质岩主量元素、微量元素及稀土元素分析结果
Table 1. Analysis results of main, trace and rare earth elements of the siliceous rocks in the upper sub-member of the 4th member of the Maokou Formation in the eastern Sichuan area
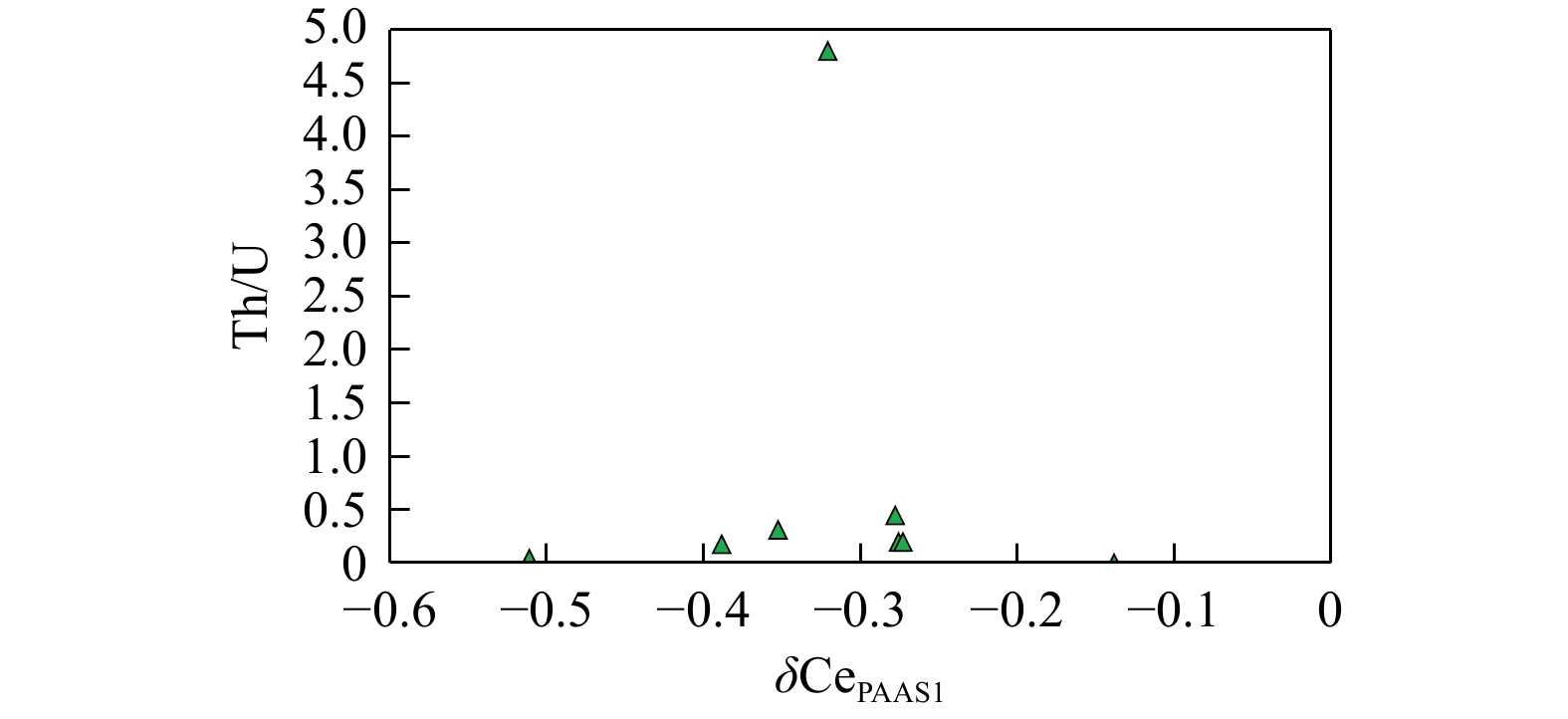
样品号 H2-4-33 H2-4-39 H2-4-100 H2-4-62 H2-4-81 H2-4-15 H2-4-1 HY5-4-53 HM1-2-118 HY3-4-128 岩性 硅质岩 灰岩 SiO2 wB/% 88.18 92.73 85.28 71.60 96.70 91.78 92.30 90.84 0.27 0.65 TiO2 0.011 0.010 0.005 0.007 0.002 0.006 0.009 0.006 0.005 0.004 Al2O3 0.24 0.09 0.08 0.13 0.11 0.12 0.11 0.09 0 0.02 CaO 5.04 2.42 6.93 11.38 1.03 4.40 2.57 3.92 54.79 54.44 Fe2O3 0.07 0.04 0.01 0.04 0.02 0.05 0.07 0.03 0 0.01 MgO 1.16 1.32 1.80 4.25 0.34 0.20 1.21 0.50 0.70 0.71 MnO 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.002 0.006 0.011 0.005 0.001 0.005 Na2O 0.07 0.07 0.05 0.07 0.08 0.07 0.06 0.07 0.03 0.04 K2O 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 P2O5 0.01 0.01 0 0.02 0 0.02 0.01 0.04 0.01 0.01 烧失量 5.41 3.69 6.24 12.12 1.87 3.71 4.05 4.09 43.97 43.85 总量 100.23 100.39 100.41 99.64 100.16 100.36 100.41 99.60 99.78 99.75 Al/(Al+Fe+Mn) 0.73 0.58 0.86 0.68 0.80 0.63 0.51 0.69 0.85 0.48 MnO/TiO2 0.21 0.21 0.38 0.26 0.65 0.92 1.24 0.84 0.52 1.14 Al2O3/(Al2O3+Fe2O3) 0.78 0.66 0.92 0.75 0.85 0.72 0.62 0.78 1.00 0.68 Ba wB/10−6 2.53 11.12 4.27 13.87 8.73 11.60 10.24 4.09 2.33 7.46 Th 0.16 0.07 0 0.12 0.04 0.04 0.15 0.06 0.08 0.08 U 0.03 0.32 0.28 0.67 0.22 0.12 0.32 1.46 3.00 2.90 Hf 0.08 0.05 0.07 0.05 0.07 0.05 0.07 0.06 0.09 0.06 Sc 0.53 0.79 2.29 0.95 0.61 0.22 0.38 0.57 0.20 0.15 Rb 0.07 0.17 1.65 0.33 0.33 0.19 0.25 0.15 0.62 0.44 Co 6.34 0.11 1.25 0.20 0.05 0.08 0.29 0.15 1.15 1.14 Cr 501.10 18.21 12.39 28.03 9.53 7.97 20.63 10.50 14.73 11.31 Zr 3.60 2.17 2.28 1.99 2.85 1.60 6.23 2.27 3.11 2.82 Mo 10.87 2.20 / 2.11 1.53 1.65 4.49 − 0.34 0.39 Sr 51.72 159.45 178.46 540.13 82.55 195.42 90.67 234.00 808.19 1012.71 Ni 307.89 5.01 3.65 6.08 3.34 2.94 6.31 9.21 16.70 8.92 Y 2.27 0.68 1.83 1.88 0.27 0.56 0.68 1.25 2.16 3.65 Th/U 4.80 0.20 0 0.17 0.20 0.32 0.45 0.04 0.03 0.03 Rb/Sr 0.001 0.001 0.009 0.001 0.004 0.001 0.003 0.001 0.001 0 La wB/10−6 1.49 0.42 0.46 0.89 0.16 0.45 1.13 0.74 1.11 2.40 Ce 1.31 0.41 0.73 0.70 0.16 0.38 1.11 0.51 0.90 1.29 Pr 0.22 0.06 0.08 0.14 0.02 0.08 0.19 0.15 0.16 0.31 Nd 0.86 0.25 0.47 0.59 0.10 0.31 0.70 0.80 0.59 1.19 Sm 0.16 0.04 0.07 0.10 0.02 0.04 0.09 0.16 0.12 0.24 Eu 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.05 Gd 0.18 0.05 0.02 0.11 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.13 0.13 0.26 Tb 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.02 0 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.04 Dy 0.18 0.05 0.04 0.13 0.02 0.03 0.05 0.11 0.13 0.24 Ho 0.04 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.03 0.05 Er 0.12 0.03 0.12 0.09 0.01 0.02 0.04 0.06 0.09 0.15 Tm 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0 0 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 Yb 0.09 0.03 0 0.06 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.04 0.07 0.11 Lu 0.01 0 0 0.01 0 0 0.01 0 0.01 0.02 $\Sigma $REE 4.73 1.38 2.04 2.92 0.55 1.41 3.45 2.78 3.39 6.37 LREE/HREE 6.13 6.36 8.30 5.16 5.33 9.33 14.74 6.13 5.73 6.14 δEuPAAS 0.77 1.01 2.43 1.03 1.49 1.36 0.94 0.98 0.79 0.88 δCePAAS1 −0.32 −0.28 −0.14 −0.39 −0.27 −0.35 −0.28 −0.51 −0.35 −0.52 δCePAAS2 0.51 0.57 0.89 0.45 0.58 0.46 0.55 0.35 0.48 0.33 (La/Ce)N 2.37 2.13 1.31 2.67 2.09 2.45 2.11 3.02 2.58 3.87 Sm/Nd 0.18 0.15 0.15 0.17 0.17 0.12 0.12 0.20 0.20 0.20 注:δEuPAAS=2×EuN/(SmN+GdN);δCePAAS1=lg[3CeN/(2LaN+NdN)];δCePAAS2=2CeN/(LaN+PrN);N. 澳大利亚后太古代平均页岩(PAAS)标准化比值[30];REE. 稀土元素;LREE. 轻稀土元素;HREE. 重稀土元素 -
[1] MURRAY R W. Chemical criteria to identify the depositional environment of chert: General principles and applications[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1994, 90(3/4): 213-232. [2] PACKARD J J, AL-AASM I, SAMSON I, et al. A devonian hydrothermal chert reservoir: The 225 bcf parkland field, British Columbia, Canada[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2001, 85(1): 51-84. [3] DELVIGNE C, CARDINAL D, HOFMANN A, et al. Stratigraphic changes of Ge/Si, REE+Y and silicon isotopes as insights into the deposition of a Mesoarchaean banded iron formation[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2012, 355: 109-118. [4] YOU D H, HAN J, HU W X, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanisms of silicified carbonate reservoirs in Well SN4 of the Tarim Basin[J]. Energy Exploration and Exploitation, 2018, 36(4): 820-849. doi: 10.1177/0144598718757515 [5] 吴建鑫. 四川盆地北缘−西南缘灯影组硅质岩特征及成因研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2019.WU J X. Characteristics and genesis of cherts from Dengying Formation in the northern and southwestern margins of Sichuan Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 郭世文, 徐争启, 李宝新, 等. 四川若尔盖地区寒武系硅质岩成因及其对铀成矿的意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2023, 43(4): 78-89. doi: 10.19719/j.cnki.1001-6872.2023.04.07GUO S W, XU Z Q, LI B X, et al. Genesis of Cambrian siliceous rocks in Zoige area of Sichuan Province and its significance for uranium mineralization[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2023, 43(4): 78-89. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19719/j.cnki.1001-6872.2023.04.07 [7] MURCHEY B L, JONES D L. A Mid-Permian chert event: Widespread deposition of biogenic siliceous sediments in coastal, island arc and oceanic basins[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 1992, 96(1/2): 161-174. [8] 张廷山, 陈晓慧, 刘治成, 等. 峨眉地幔柱构造对四川盆地栖霞期沉积格局的影响[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(8): 1251-1264.ZHANG T S, CHEN X H, LIU Z C, et al. Effect of Emeishan mantle plume over the sedimentary pattern of Mid-Permian Xixia period in Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(8): 1251-1264. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 赵宗举, 周慧, 陈轩, 等. 四川盆地及邻区二叠纪层序岩相古地理及有利勘探区带[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(增刊2): 35-51.ZHAO Z J, ZHOU H, CHEN X, et al. Sequence lithofacies paleogeography and favorable exploration zones of the Permian in Sichuan Basin and adjacent areas, China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(S2): 35-51. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 罗志立, 孙玮, 韩建辉, 等. 峨眉地幔柱对中上扬子区二叠纪成藏条件影响的探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(6): 144-154.LUO Z L, SUN W, HAN J H, et al. Effect of Emei mantle plume on the conditions of Permian accumulation in Middle-Upper Yangtze area[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(6): 144-154. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 杨跃明, 杨雨, 文龙, 等. 四川盆地中二叠统天然气勘探新进展与前景展望[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(7): 10-22.YANG Y M, YANG Y, WEN L, et al. New exploration progress and prospect of Middle Permian natural gas in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(7): 10-22. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 王惠君, 杨锐, 舒志国, 等. 川东南二叠系吴家坪组深层页岩气生排滞潜力评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(6): 96-109.WANG H J, YANG R, SHU Z G, et al. Quantitative evaluation of hydrocarbon generation, expulsion, and retention potential in deep Permian Wuchiaping shale gas reservoir, southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(6): 96-109. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 易雨昊, 包汉勇, 朱红涛, 等. 四川盆地东部上二叠统吴家坪组放射虫组合及其烃源意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(4): 167-180. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230721YI Y H, BAO H Y, ZHU H T, et al. Radiolarian assemblage from the Upper Permian Wujiaping Formation in the eastern Sichuan Basin and its hydrocarbon source significance[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(4): 167-180. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230721 [14] 方雪, 周瑶琪, 姚旭, 等. 四川广元上寺上二叠统硅质岩地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 矿物岩石, 2017, 37(1): 93-102.FANG X, ZHOU Y Q, YAO X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and petrogenesis of siliceous rocks from Shangsi section in Guangyuan, Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2017, 37(1): 93-102. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 赵振洋, 李双建, 王根厚. 中下扬子北缘中二叠统孤峰组层状硅质岩沉积环境、成因及硅质来源探讨[J]. 地球科学进展, 2020, 35(2): 137-153.ZHAO Z Y, LI S J, WANG G H. Discussion on sedimentary environments, origin and source of Middle Permian Gufeng Formation bedded cherts in the northern margin of the Middle-Lower Yangtze area[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2020, 35(2): 137-153. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 林良彪, 陈洪德, 朱利东. 川东茅口组硅质岩地球化学特征及成因[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(4): 500-507.LIN L B, CHEN H D, ZHU L D. The origin and geochemical characteristics of Maokou Formation silicalites in the eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(4): 500-507. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 徐锦龙, 沈仕豪, 汪雅菲, 等. 中二叠统热水沉积新证据: 以皖南“嵇亭岭砾岩” 为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(2): 284-296. doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2019.041XU J L, SHEN S H, WANG Y F, et al. New evidence of Middle Permian hydrothermal cherts deposition: A case study of Jitingling breccia, South Anhui Province[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(2): 284-296. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.14027/j.issn.1000-0550.2019.041 [18] LI J, CHEN L W, HAO C M, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of chert nodules in Qixia Formation, Pingding Mountain, Lower Yangtze Plate[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2021, 18(1): 88-100. doi: 10.1007/s11629-020-5982-x [19] 吕炳全, 王红罡, 胡望水, 等. 扬子地块东南古生代上升流沉积相及其与烃源岩的关系[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2004, 24(4): 29-35. doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2004.04.005LÜ B Q, WANG H G, HU W S, et al. Relationship between Paleozoic upwelling facies and hydrocarbon in southeastern marginal Yangtze block[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2004, 24(4): 29-35. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.16562/j.cnki.0256-1492.2004.04.005 [20] 肖传桃, 卢俊, 胡望水, 等. 安徽宿松地区中二叠统上升流沉积的发现及其岩相组合类型[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2008, 30(6): 19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2008.06.004XIAO C T, LU J, HU W S, et al. Discovery of upwelling deposits of Middle Permian in Susong area, Anhui Province and their lithofacies assemblage types[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2008, 30(6): 19-23. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9752.2008.06.004 [21] 程成, 李双应, 赵大千, 等. 扬子地台北缘中上二叠统层状硅质岩的地球化学特征及其对古地理、古海洋演化的响应[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(1): 155-166. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.01.018CHENG C, LI S Y, ZHAO D Q, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the Middle-Upper Permian bedded cherts in the northern margin of the Yangtze block and its response to the evolution of paleogeography and paleo-ocean[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(1): 155-166. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.01.018 [22] 杜小弟, 黄志诚, 陈智娜, 等. 下扬子区二叠纪主要岩石类型成因的地球化学信息[J]. 岩相古地理, 1998(1): 61-70.DU X D, HUANG Z C, CHEN Z N, et al. Geochemistry of the Permian sedimentary rocks in the Lower Yangtze area[J]. Sedimentary Facies and Palaeogeography, 1998(1): 61-70. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] CHEN H, XIE X N, HU C Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Late Permian sediments in the Dalong Formation of the Shangsi section, Northwest Sichuan Basin in South China: Implications for organic carbon-rich siliceous rocks formation[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 112: 35-53. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2011.06.011 [24] GAO P, HE Z L, LASH G G, et al. Mixed seawater and hydrothermal sources of nodular chert in Middle Permian limestone on the eastern Paleo-Tethys margin (South China)[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2020, 551: 109740. [25] 杨海生, 周永章, 杨志军, 等. 热水沉积硅质岩地球化学特征及意义: 以华南地区为例[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 42(6): 111-115. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2003.06.028YANG H S, ZHOU Y Z, YANG Z J, et al. Geochemical characteristics and significance of hydrothermal cherts: A case study of South China[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2003, 42(6): 111-115. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2003.06.028 [26] 王赞军, 王宏超, 董娣, 等. 华蓥山断裂带的物探成果综述[J]. 四川地震, 2018(3): 6-12. doi: 10.13716/j.cnki.1001-8115.2018.03.002WANG Z J, WANG H C, DONG D, et al. Review of geophysical results of Huayingshan fault zone[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan, 2018(3): 6-12. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.13716/j.cnki.1001-8115.2018.03.002 [27] 李让彬, 段金宝, 潘磊, 等. 川东地区中二叠统茅口组白云岩储层成因机理及主控因素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(9): 1347-1357. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2021.04.014LI R B, DUAN J B, PAN L, et al. Genetic mechanism and main controlling factors of the Middle Permian Maokou Formation dolomite reservoirs in the eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(9): 1347-1357. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2021.04.014 [28] 宋鸿彪, 罗志立. 四川盆地基底及深部地质结构研究的进展[J]. 地学前缘, 1995, 2(4): 231-237.SONG H B, LUO Z L. The study of the basement and deep geolo-gical structures of Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 1995, 2(4): 231-237. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 李红, 王良军, 柳益群, 等. 四川盆地东部中二叠统茅口组热液活动特征[J]. 古地理学报, 2021, 23(1): 153-174. doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2021.01.011LI H, WANG L J, LIU Y Q, et al. Hydrothermal activities in the Middle Permian Maokou Formation in eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2021, 23(1): 153-174. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2021.01.011 [30] MCLENNAN S M. Chapter 7. rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks: Influence of provenance and sedimentary processes[M]//Geochemistry and mineralogy of rare earth elements. Berlin, Germany: De Gruyter, 1989: 169-200. [31] ADACHI M, YAMAMOTO K, SUGISAKI R. Hydrothermal chert and associated siliceous rocks from the northern Pacific their geological significance as indication od ocean ridge activity[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1986, 47(1/2): 125-148. [32] GROMET L P, HASKIN L A, KOROTEV R L, et al. The "north American shale composite": Its compilation, major and trace element characteristics[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1984, 48(12): 2469-2482. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(84)90298-9 [33] KEMKIN I V, KEMKINA R A. Depositional environment of cherts of the Sikhote-Alin region (Russia far East): Evidence from major, trace and rare earth elements geochemistry[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2015, 26(2): 259-272. doi: 10.1007/s12583-015-0531-1 [34] YAMAMOTO K. Geochemical characteristics and depositional environments of cherts and associated rocks in the Franciscan and Shimanto Terranes[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 1987, 52(1/2): 65-108. [35] 邓空, 陆扬博, 张柏林, 等. 二叠纪中晚期地质事件对川东北富有机质页岩发育的控制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(2): 161-181. DENG K, LU Y B, ZHANG B L, et al. Controls of Middle and Late Permian major geological events on the development of the organic-rich shales in northeast Sichuan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(2): 161-181. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] FRIMMEL H E. Trace element distribution in Neoproterozoic carbonates as Palaeoenvironmental indicator[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 258(3/4): 338-353. [37] GUO L N, HOU L, LIU S S, et al. Rare earth elements geochemistry and C–O isotope characteristics of hydrothermal calcites: Implications for fluid-rock reaction and ore-forming processes in the phapon gold deposit, NW Laos[J]. Minerals, 2018, 8(10): 438. doi: 10.3390/min8100438 [38] MURRAY R W, JONES D L, TEN BRINK M R B. Diagenetic formation of bedded chert: Evidence from chemistry of the chert-shale couplet[J]. Geology, 1992, 20(3): 271-274. [39] FLEET A J. Hydrothermal and hydrogenous Ferro-manganese deposits: Do they from a continuum? the rare earth element evidence[M]. Hydrothermal processes at seafloor spreading centers. Boston, MA: Springer US, 1983: 535-555. [40] WANG J G, CHEN D Z, WANG D, et al. Petrology and geochemistry of chert on the marginal zone of Yangtze Platform, western Hunan, South China, during the Ediacaran-Cambrian transition[J]. Sedimentology, 2012, 59(3): 809-829. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2011.01280.x [41] GERMAN C R, HOLLIDAY B P, ELDERFIELD H. Redox cycling of rare earth elements in the suboxic zone of the Black Sea[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1991, 55(12): 3553-3558. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(91)90055-A [42] 黄思静. 碳酸盐岩的成岩作用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010.HUANG S J. Carbonate diagenesis[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2010. (in Chinese) [43] FAN H F, WEN H J, ZHU X K, et al. Hydrothermal activity during Ediacaran-Cambrian transition: Silicon isotopic evidence[J]. Precambrian Research, 2013, 224: 23-35. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.09.004 [44] HANS WEDEPOHL K. The composition of the continental crust[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(7): 1217-1232. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00038-2 [45] 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 喻学惠, 等. 青藏高原新生代碰撞−后碰撞火成岩[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009.MO X X, ZHAO Z D, YU X H, et al. Cenozoic collision-post collision igneous rocks in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2009. (in Chinese) [46] CARO G, BOURDON B. Non-chondritic Sm/Nd ratio in the terrestrial planets: Consequences for the geochemical evolution of the mantle–crust system[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(11): 3333-3349. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.02.025 [47] 李映涛, 叶宁, 袁晓宇, 等. 塔里木盆地顺南4井中硅化热液的地质与地球化学特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2015, 36(6): 934-944. doi: 10.11743/ogg20150608LI Y T, YE N, YUAN X Y, et al. Geological and geochemical characteristics of silicified hydrothermal fluids in Well Shunnan 4, Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2015, 36(6): 934-944. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11743/ogg20150608 [48] BOLHAR R, KAMBER B S, MOORBATH S, et al. Characterisation of early Archaean chemical sediments by trace element signatures[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 222(1): 43-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jpgl.2004.02.016 [49] HERZIG P M, BECKER K P, STOFFERS P, et al. Hydrothermal silica chimney fields in the Galapagos spreading center at 86°W[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1988, 89(3/4): 261-272. [50] MURRAY R W, BUCHHOLTZ TEN BRINK M R, JONES D L, et al. Rare earth elements as indicators of different marine depositional environments in chert and shale[J]. Geology, 1990, 18(3): 268-271. [51] 李长海, 董晓伟, 石倩茹, 等. 黄骅坳陷歧口主凹区东营组砂岩物源方向与沉积模式: 来自碎屑锆石U-Pb年代学的制约[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(5): 65-81. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240696LI C H, DONG X W, SHI Q R, et al. Source area and sedimentary model of the sandstone in the Third Member of Dongying Formation in main concave, Qikou Sag, Huanghua Depression: Constraints from detrital zircons U-Pb dating[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(5): 65-81. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20240696 [52] KIMURA H, WATANABE Y. Oceanic anoxia at the Precambrian-Cambrian boundary[J]. Geology, 2001, 29(11): 995. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0995:OAATPC>2.0.CO;2 [53] 张汉文. 秦岭泥盆系的热水沉积岩及其与矿产的关系: 概论秦岭泥盆纪的海底热水作用[J]. 西北地质科学, 1991(31): 15-39.ZHANG H W. On hydrothermal sedimentary rocks and their relationships with mineral resources in Devonian period of Qinling area, China[J]. Northwest Geoscience, 1991(31): 15-39. (in Chinese with English abstract [54] 杨康. 川东地区中二叠统茅口组硅质岩成因研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2022.YANG K. Research on genesis of the Middle Permian Maokou Formation siliceous rocks in the eastern Sichuan Basin[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [55] HUNT J D, MANNING C E. A thermodynamic model for the system SiO2-H2O near the upper critical end point based on quartz solubility experiments at 500– 1100 ℃ and 5–20 kbar[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 86: 196-213. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.03.006[56] 王立亭, 陆彦邦, 赵时久. 中国南方二叠纪岩相古地理与成矿作用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1994.WANG L T, LU Y B, ZHAO S J. Permian lithofacies Palaeogeography and mineralization in Southern China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1994. (in Chinese) [57] 刘嘉伟, 赵虎, 王轶, 等. 川东龙会场: 龙门地区二叠系火山岩分布特征及油气地质意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2022, 33(3): 381-395. doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2021.08.010LIU J W, ZHAO H, WANG Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and hydrocarbon geological significance of Permain volcanic rocks in Longhuichang-Longmen areas, eastern Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2022, 33(3): 381-395. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2021.08.010 [58] 胡明毅, 胡忠贵, 魏国齐, 等. 四川盆地茅口组层序岩相古地理特征及储集层预测[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(1): 45-55.HU M Y, HU Z G, WEI G Q, et al. Sequence lithofacies paleogeography and reservoir prediction of the Maokou Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2012, 39(1): 45-55. (in Chinese with English abstract [59] 冯增昭, 杨玉卿, 金振奎, 等. 中国南方二叠纪岩相古地理[J]. 沉积学报, 1996, 14(2): 1-11.FENG Z Z, YANG Y Q, JIN Z K, et al. Permian lithofacies Palaeogeography in Southern China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1996, 14(2): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract [60] 田景春, 林小兵, 郭维, 等. 四川盆地二叠纪玄武岩喷发事件的油气地质意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 44(1): 14-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2017.01.02TIAN J C, LIN X B, GUO W, et al. Geological significance of oil and gas in the Permian basalt eruption event in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2017, 44(1): 14-20. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2017.01.02 [61] 李军亮, 刘惠民, 王勇, 等. 济阳陆相断陷盆地页岩油研究进展[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(4): 60-72.LI J L, LIU H M, WANG Y, et al. Research progress of shale oil in Jiyang continental faulted basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(4): 60-72. -




 下载:
下载: