Hydrogeochemical modeling of groundwater formation mechanism at the Beishan preselected site for high-level radioactive waste disposal
-
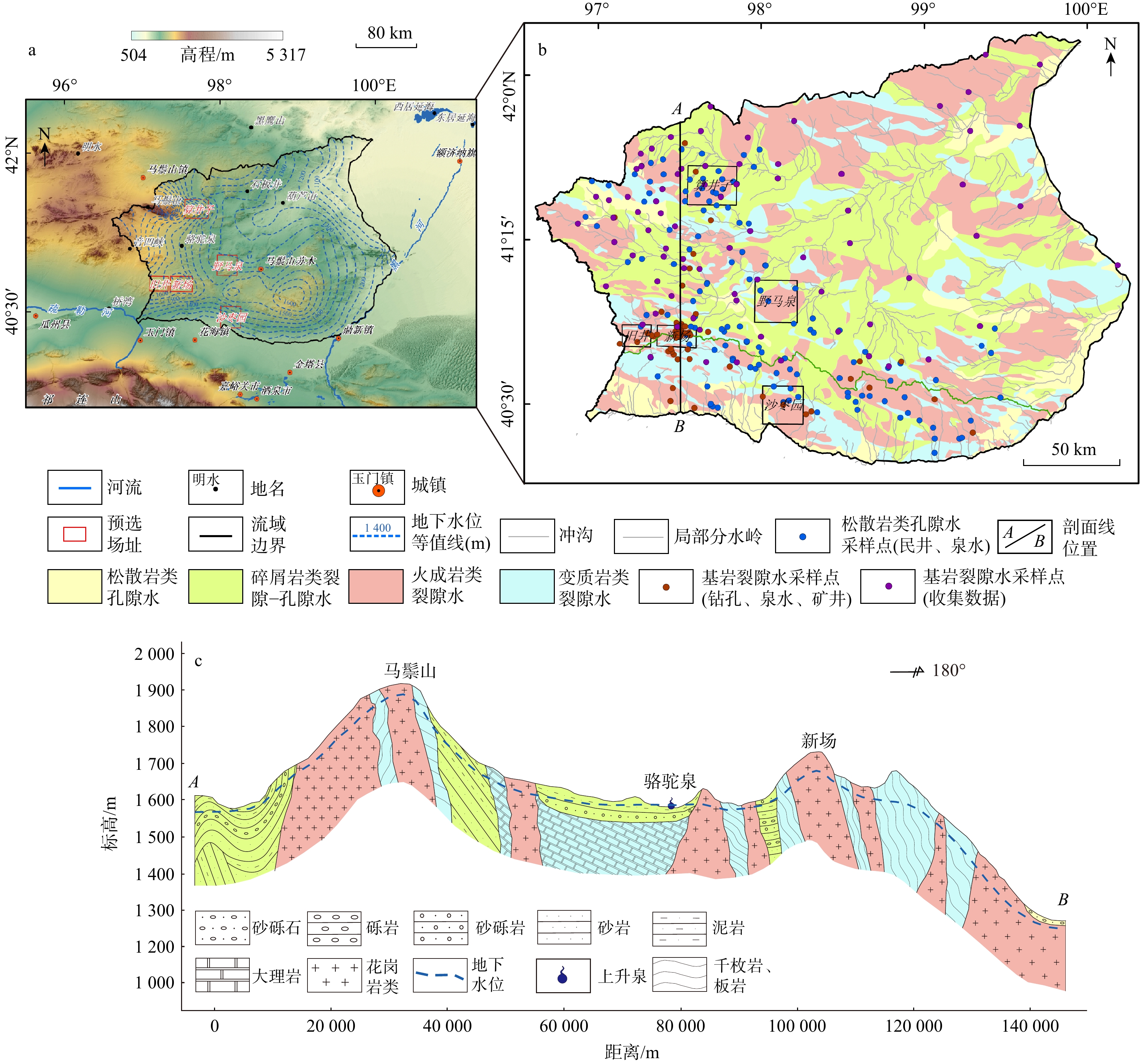
摘要:
研究地下水化学特性对于高放废物处置库选址和长期性能安全评价是十分必要的。采用水文地球化学综合分析和模拟方法,探讨了我国高放废物处置库预选区甘肃北山地区基岩裂隙水的基本化学特征、水平分带性以及不同水文地质区水化学形成机制。结果表明:区内地下水化学类型主要为Cl·SO4-Na型和SO4·Cl-Na型,pH值多在7.5~8.3之间。基岩裂隙水对岩盐、石膏、萤石、绿泥石以及长石类等矿物多处于未饱和状态,而对黏土类矿物则多处于过饱和状态。从补给区到排泄区,基岩裂隙水化学分布表现出较为明显的水平分带性。马鬃山一带是区域地下水主要补给区,地下水矿化度低,水化学组分形成主要受溶滤作用控制;沉积盆地是地下水主要排泄区,地下水矿化度高,水化学组分形成主要受蒸发作用控制;在径流区,地下水化学形成主要受岩盐、石膏等矿物的溶解控制,而碳酸盐类和硅酸盐类矿物的溶解或沉淀作用微弱。该区基岩裂隙水化学形成主要受蒸发浓缩作用及水−岩相互作用的影响和控制,该结果为高放废物处置库选址提供了地下水化学基础信息和数据。
Abstract:Objective Hydrogeochemical characteristics play a pivotal role in site selection and long-term safety assessment for high-level radioactive waste (HLW) disposal repositories.
Methods This study employs integrated hydrogeochemical analysis and modeling to investigate the basic hydrogeochemical characteristics, horizontal zoning, and formation mechanisms in different hydrogeological zones of the Beishan preselected site for HLW disposal in Gansu Province, China.
Results The results show that the predominant hydrogeochemical types were Cl·SO4-Na and SO4·Cl-Na, Province with pH values generally ranging from 7.5 to 8.3. Fractured bedrock groundwater is typically undersaturated with respect to halite, gypsum, fluorite, glauconite, and feldspar, and oversaturated with respect to clay minerals. A distinct horizontal zonation is observed in the hydrogeochemical composition from the recharge area to the discharge area. The Mazongshan region serves as the primary recharge zone, characterized by low mineralization, where hydrogeochemical composition is mainly controlled by leaching processes. The sedimentary basins act as the main discharge areas with high mineralization, where evaporation processes dominate. The water-rock interaction processes along the flow path are primarily driven by the dissolution of halite and gypsum, while the effect of carbonate and silicate dissolution or precipitation remains relatively weak.
Conclusion Overall, the hydrogeochemical formation of fractured bedrock groundwater in the Beishan area is predominantly governed by evaporation and water-rock interaction processes. This study provides fundamental hydrogeochemical data and insights to support the site selection of the HLW disposal repository.
-
表 1 各模拟路径上地下水取样信息和水化学参数分析
Table 1. Groundwater sampling information and hydrogeochemical parameter analysis along the simulation flow path
采样点 取样深度/m F− Cl− ${\mathrm{SO}}^{2-}_4 $ Na+ K+ Mg2+ Ca2+ $ {\mathrm{HCO}}^{-}_3 $ Si Al3+ pH值 温度/℃ 岩性 质量浓度ρB/(mg·L−1) 1073 -2井2.5~5.0 0.70 179.0 171.0 154 5.79 13.7 80.7 173.0 1.867 0.00289 7.75 13.09 砂砾石 1072 泉0 0.74 236.0 255.0 222 7.65 19.3 112.0 287.0 2.800 0.00365 7.95 13.90 花岗岩 头道泉 0 0.81 480.0 519.0 463 13.50 34.1 120.0 391.0 3.733 0.00416 8.32 13.27 花岗岩 N26 2.6~30 0.76 95.4 126.3 107 2.68 10.8 52.7 176.3 2.947 0.00368 7.90 12.38 花岗岩 滴石泉 0 1.35 696.0 1291.0 703 11.70 111.0 220.0 164.0 9.671 0.00661 7.53 12.18 变质岩 BET 50 1.90 836.0 828.0 820 7.20 19.6 121.0 226.0 4.542 0.01120 7.58 11.77 花岗岩 BSQ20 10~30 3.00 1209.0 1048.0 944 12.00 48.6 286.0 109.0 5.347 0.01530 7.68 9.66 花岗岩 BSQ05 6.5~30 0.82 446.0 401.0 403 8.03 22.4 106.0 236.0 4.309 0.00345 7.83 12.60 花岗岩 金钻孔 3.6~60 1.39 498.0 539.0 490 9.24 28.5 156.0 383.0 4.395 0.01300 7.80 11.83 变质岩 老王井 65~100 0.66 386.0 496.0 466 6.48 8.1 51.9 180.0 4.072 0.01070 7.83 10.80 花岗岩 BSQ34 15~30 1.72 448.0 601.0 496 8.53 18.4 106.0 157.0 5.019 0.02560 7.71 10.42 变质岩 BS60 59~70 1.04 176.0 170.0 232 2.83 4.3 30.0 169.0 3.875 0.00318 7.98 11.43 花岗岩 BSQ36 37~60 1.40 867.0 1426.0 884 9.28 57.4 296.0 100.0 10.200 0.00898 7.52 12.81 花岗岩 表 2 北山地区水化学指标统计
Table 2. Statistical summary of hydrogeochemical indicators in the Beishan area
地下水类型 水质指标 最大值 最小值 平均值 标准差 偏度 变异系数/% 基岩裂隙水
(样品数N=147)ρ(Na++K+)/(mg·L−1) 19870.50 61.62 1785.27 2811.68 4.02 157.49 ρ(Ca2+)/(mg·L−1) 3002.00 29.50 315.64 366.06 3.65 115.97 ρ(Mg2+)/(mg·L−1) 1952.90 5.40 126.59 227.10 4.77 179.40 ρ(Cl−)/(mg·L−1) 39175.60 65.50 2319.26 4586.38 5.08 197.75 $\rho ({\mathrm{SO}}^{2-}_4 )/({\mathrm{mg}}\cdot{\mathrm{L}}^{-1})$ 10213.80 84.50 1635.30 1670.44 2.19 102.15 $\rho ({\mathrm{HCO}}^{-}_3 )/({\mathrm{mg}}\cdot{\mathrm{L}}^{-1}) $ 1428.40 37.60 227.94 197.52 3.30 86.65 $\rho ({\mathrm{NO}}^{-}_3 )/({\mathrm{mg}}\cdot{\mathrm{L}}^{-1}) $ 250.00 < 0.08 15.02 26.30 5.56 175.10 pH值 8.35 6.80 7.74 0.30 −0.63 3.88 ρ(TDS)/(mg·L−1) 67383.45 387.11 6312.65 9075.08 3.81 143.76 松散岩类
孔隙水
(样品数N=158)ρ(Na++K+)/(mg·L−1) 36467.00 22.26 1734.24 4406.60 6.11 254.09 ρ(Ca2+)/(mg·L−1) 1040.00 16.70 210.74 199.02 2.13 94.44 ρ(Mg2+)/(mg·L−1) 490.00 2.50 41.20 48.71 5.59 118.23 ρ(Cl−)/(mg·L−1) 25667.00 41.20 1025.09 2188.66 9.28 213.51 $\rho ({\mathrm{SO}}^{2-}_4 )/({\mathrm{mg}}\cdot{\mathrm{L}}^{-1}) $ 7192.00 43.50 1045.87 946.63 2.79 90.51 $\rho ({\mathrm{HCO}}^{-}_3 )/({\mathrm{mg}}\cdot{\mathrm{L}}^{-1}) $ 859.00 11.30 224.68 122.61 2.31 54.57 $\rho ({\mathrm{NO}}^{-}_3 )/({\mathrm{mg}}\cdot{\mathrm{L}}^{-1}) $ 138.00 < 0.08 19.18 21.84 2.10 113.87 pH值 8.58 6.71 7.76 0.30 −0.17 3.87 ρ(TDS)/(mg·L−1) 53343.52 370.02 3408.98 4724.61 7.75 138.59 -
[1] WANG J,CHEN L,SU R,et al. The Beishan underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China:Planning,site selection,site characterization and in situ tests[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2018,10(3):411-435. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2018.03.002 [2] BIANCHI M,LIU H H,BIRKHOLZER J T. Radionuclide transport behavior in a generic geological radioactive waste repository[J]. Groundwater,2015,53(3):440-451. doi: 10.1111/gwat.12171 [3] 郭永海,王驹. 高放废物地质处置中的地质、水文地质、地球化学关键科学问题[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(增刊2):3926-3931.GUO Y H,WANG J. Key scientific issues of geology,hydrogeology and geochemistry in high-level radioactive waste geological disposal[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,26(S2):3926-3931. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] TSANG C F,NERETNIEKS I,TSANG Y. Hydrologic issues associated with nuclear waste repositories[J]. Water Resources Research,2015,51(9):6923-6972. doi: 10.1002/2015WR017641 [5] 王驹,陈伟明,苏锐,等. 高放废物地质处置及其若干关键科学问题[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2006,25(4):801-812. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.04.015WANG J,CHEN W M,SU R,et al. Geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste and its key scientific issues[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2006,25(4):801-812. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2006.04.015 [6] ZHANG H T,XU G Q,ZHAN H B,et al. Identification of hydrogeochemical processes and transport paths of a multi-aquifer system in closed mining regions[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2020,589:125344. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125344 [7] SHARIF M U,DAVIS R K,STEELE K F,et al. Inverse geochemical modeling of groundwater evolution with emphasis on arsenic in the Mississippi River Valley alluvial aquifer,Arkansas (USA)[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2008,350(1/2):41-55. [8] LIU P,HOTH N,DREBENSTEDT C,et al. Hydro-geochemical paths of multi-layer groundwater system in coal mining regions:Using multivariate statistics and geochemical modeling approaches[J]. Science of The Total Environment,2017,601:1-14. [9] DOMENICO P A,SCHWARTZ F W. Physical and chemical hydrogeology[M]. 2nd ed. [S. l. ]:John Wiley & Sons,1997. [10] 王丽,王金生,林学钰. 水文地球化学模型研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2003,30(6):105-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.06.024WANG L,WANG J S,LIN X Y. A review of hydrogeochemical modeling[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology,2003,30(6):105-109. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2003.06.024 [11] SUNG K Y,YUN S T,PARK M E,et al. Reaction path modeling of hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in granitic bedrocks,South Korea[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2012,118:90-97. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.05.004 [12] 范芷若. 再生水灌溉条件下的地下水水质分析及水文地球化学模拟[D]. 西安:长安大学,2024.FAN Z R. Groundwater quality analysis and hydrogeochemical simulation under reclaimed water irrigation[J]. Xi'an:Chang'an University,2024. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 袁昊辰,张幼宽,梁修雨. 广州某地下水污染场地监控自然衰减修复模拟[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(4):268-278.YUAN H C,ZHANG Y K,LIANG X Y. Modelling of groundwater remediation using monitored natural attenuation at a contamination site in Guangzhou[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(4):268-278. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] LIPSON D S,MCCRAY J E,THYNE G D. Using PHREEQC to simulate solute transport in fractured bedrock[J]. Groundwater,2007,45(4):468-472. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2007.00318.x [15] 李杰彪,梁修雨,周志超,等. 某地下核设施场址地下水化学特征及其对水循环的指示意义[J]. 地球科学,2024,49(3):965-977.LI J B,LIANG X Y,ZHOU Z C,et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and its significance to groundwater flow system at an underground nuclear facility site[J]. Earth Science,2024,49(3):965-977. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] CHAE G T,YUN S T,KIM K,et al. Hydrogeochemistry of sodium-bicarbonate type bedrock groundwater in the Pocheon spa area,South Korea:Water-rock interaction and hydrologic mixing[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2006,321(1/2/3/4):326-343. [17] MORÁN-RAMÍREZ J,LEDESMA-RUIZ R,MAHLKNECHT J,et al. Rock-water interactions and pollution processes in the volcanic aquifer system of Guadalajara,Mexico,using inverse geochemical modeling[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2016,68:79-94. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2016.03.008 [18] GASTMANS D,HUTCHEON I,MENEGÁRIO A A,et al. Geochemical evolution of groundwater in a basaltic aquifer based on chemical and stable isotopic data:Case study from the northeastern portion of Serra Geral Aquifer,São Paulo state (Brazil)[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2016,535:598-611. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.02.016 [19] GÜLER C,THYNE G D,TAĞA H,et al. Processes governing alkaline groundwater chemistry within a fractured rock (ophiolitic mélange) aquifer underlying a seasonally inhabited headwater area in the aladağlar range (Adana,Turkey)[J]. Geofluids,2017,2017:3153924. [20] CHRISTOFI C,BRUGGEMAN A,KUELLS C,et al. Hydrochemical evolution of groundwater in gabbro of the Troodos Fractured Aquifer:A comprehensive approach[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2020,114:104524. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104524 [21] LAAKSOHARJU M,GASCOYNE M,GURBAN I. Understanding groundwater chemistry using mixing models[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2008,23(7):1921-1940. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.02.018 [22] GIMENO M J,AUQUÉ L F,ACERO P,et al. Hydrogeochemical characterisation and modelling of groundwaters in a potential geological repository for spent nuclear fuel in crystalline rocks (Laxemar,Sweden)[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2014,45:50-71. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.03.003 [23] DAVID A,PETE A,STEVEN J. Modelling solute transport and water–rock interactions in discrete fracture networks [R]. Working Report 2020-01,Finland. Posiva Oy,2020. [24] 郭永海,王驹,吕川河,等. 高放废物处置库甘肃北山野马泉预选区地下水化学特征及水−岩作用模拟[J]. 地学前缘,2005,12(增刊1):117-123.GUO Y H,WANG J,LU C H et al. Chemical characteristics of groundwater and water-rock interaction:Modeling of the Yemaquan preselected area for China's high level radioactive waste repository[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2005,12(S1):117-123. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 王驹. 中国高放废物地质处置21世纪进展[J]. 原子能科学技术,2019,53(10):2072-2082. doi: 10.7538/yzk.2019.53.10.2072WANG J. Progress of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China in the 21st century[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology,2019,53(10):2072-2082. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7538/yzk.2019.53.10.2072 [26] 郭永海,王驹,肖丰,等. 高放废物处置库甘肃北山预选区地下水的形成[J]. 高校地质学报,2010,16(1):13-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2010.01.003GUO Y H,WANG J,XIAO F,et al. Groundwater formation in Beishan (Gansu) preselected area of high-level radioactive waste disposal repository[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2010,16(1):13-18. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2010.01.003 [27] 李杰彪,周志超,云龙,等. 基于土壤氡气测量识别甘肃北山南缘隐伏断裂[J]. 地质学报,2022,96(6):2240-2250. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.06.024LI J B,ZHOU Z C,YUN L,et al. Identification of hidden faults based on soil radon measurement in thesouthern margin of the Beishan area,Gansu Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2022,96(6):2240-2250. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2022.06.024 [28] 李仁海. 甘肃北山钻孔地下水流速流向测定及地下水流数值模拟[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2020.LI R H. Measuring velocity and direction of groundwater in borehole and numerical simulation of groundwater in Beishan area, Gansu Province[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] LI J B,ZHANG Y K,ZHOU Z C,et al. Using multiple isotopes to determine groundwater source,age,and renewal rate in the Beishan preselected area for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2024,629:130592. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2023.130592 [30] 郭永海,王海龙,董建楠,等. 高放废物处置库芨芨槽预选场址深部地下水同位素研究[J]. 地质学报,2013,87(9):1477-1485.GUO Y H,WANG H L,DONG J N,et al. Isotopic study of deep groundwater in Jijicao preselected site for China's high level radioactive waste disposal repository[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2013,87(9):1477-1485. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] FU Y M,DONG Y H,WANG L H,et al. Characteristics of hydraulic conductivity in mountain block systems and its effects on mountain block recharge:Insights from field investigation and numerical modeling[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2022,612:128184. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128184 [32] LI L L,ZHANG Q L,ZHOU Z C,et al. Groundwater circulation patterns in bedrock aquifers from a pre-selected area of high-level radioactive waste repository based on two-dimensional numerical simulation[J]. Journal of Hydrology,2022,610:127849. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127849 [33] 郭永海,沈照理,钟佐燊. 河北平原地下水化学环境演化的地球化学模拟[J]. 中国科学(D辑:地球科学),1997,27(4):360-365.GUO Y H,SHEN Z L,ZHONG Z S. Geochemical simulation of groundwater chemical environment evolution in Hebei Plain[J]. Science in China,Ser D,1997,27(4):360-365. (in Chinese). [34] WANG Z J,GUO X L,KUANG Y,et al. Recharge sources and hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a heterogeneous karst water system in Hubei Province,Central China[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2022,136:105165. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2021.105165 [35] JU Q D,HU Y B,LIU Q M,et al. Key hydrological process of a multiple aquifer flow system in the mining area of Huaibei Plain,Eastern China[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2022,140:105270. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2022.105270 [36] 郭永海,王驹,萧丰,等. 高放废物处置库北山预选区地下水同位素组成特征及其意义[J]. 地球学报,2008,29(6):735-739. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.06.012GUO Y H,WANG J,XIAO F,et al. Groundwater isotope characteristics of the pre-selected site of a high level radioactive waste repository in the Beishan area,Gansu Province and their implications[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2008,29(6):735-739. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.06.012 [37] LAAKSOHARJU M,SMELLIE J,TULLBORG E L,et al. Hydrogeochemical evaluation and modelling performed within the Swedish site investigation programme[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2008,23(7):1761-1795. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.02.015 [38] GÜLER C,THYNE G D,MCCRAY J E,et al. Evaluation of graphical and multivariate statistical methods for classification of water chemistry data[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2002,10(4):455-474. doi: 10.1007/s10040-002-0196-6 [39] GIBBS R J. Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science,1970,170:1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088 [40] MARANDI A,SHAND P. Groundwater chemistry and the Gibbs diagram[J]. Applied Geochemistry,2018,97:209-212. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.07.009 [41] TÓTH J. Groundwater as a geologic agent:An overview of the causes,processes,and manifestations[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,1999,7(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s100400050176 [42] 马文静,王文科,侯昕悦,等. 玛纳斯河流域河水−地下水转化驱动下的水文地球化学空间演化[J]. 地质科技通报,2025,44(2):378-388.MA W J,WANG W K,HOU X Y,et al. Spatial evolution of hydrogeochemistry driven by river water-groundwater transformations in the Manas River Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2025,44(2):378-388. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] GLYNN P D,PLUMMER L N. Geochemistry and the understanding of ground-water systems[J]. Hydrogeology Journal,2005,13(1):263-287. doi: 10.1007/s10040-004-0429-y -





 下载:
下载: