Provenance analysis of Benxi Formation in the Yanchang exploration area of the Ordos Basin
-
摘要:
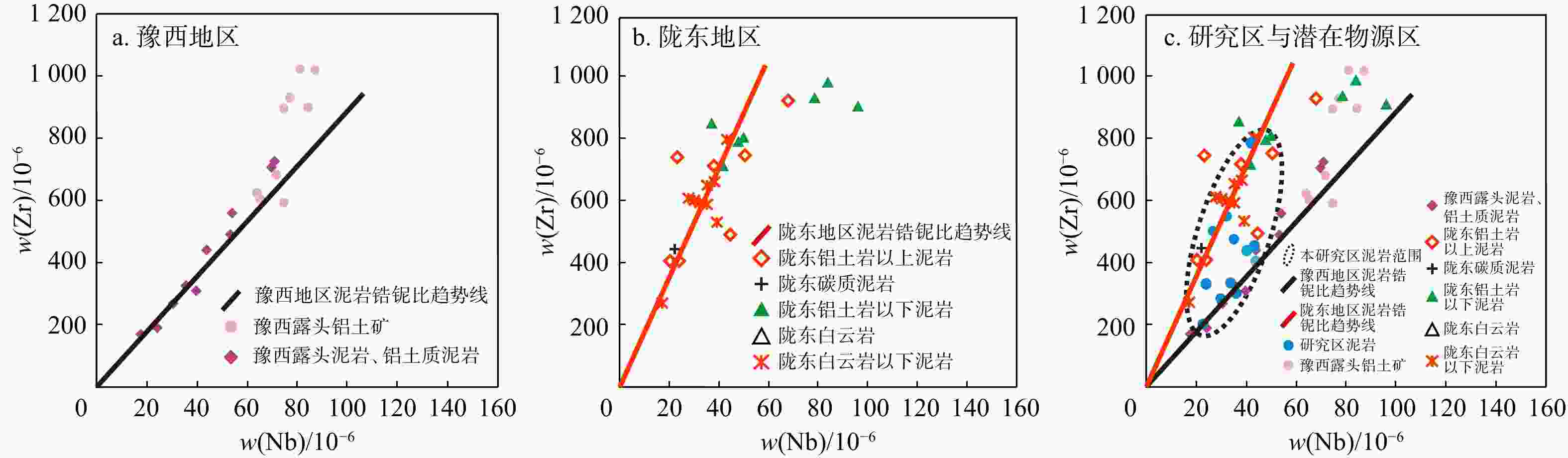
碎屑物质来源是控制鄂尔多斯盆地延长探区内本溪组砂岩储层发育和展布的重要因素之一。对延长探区内37口井砂岩和泥岩样品开展了碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄、重矿物组合、微量元素以及砂砾岩粒径统计等分析,揭示了本溪组碎屑物质的主要来源和搬运方向。研究表明探区内延528井的
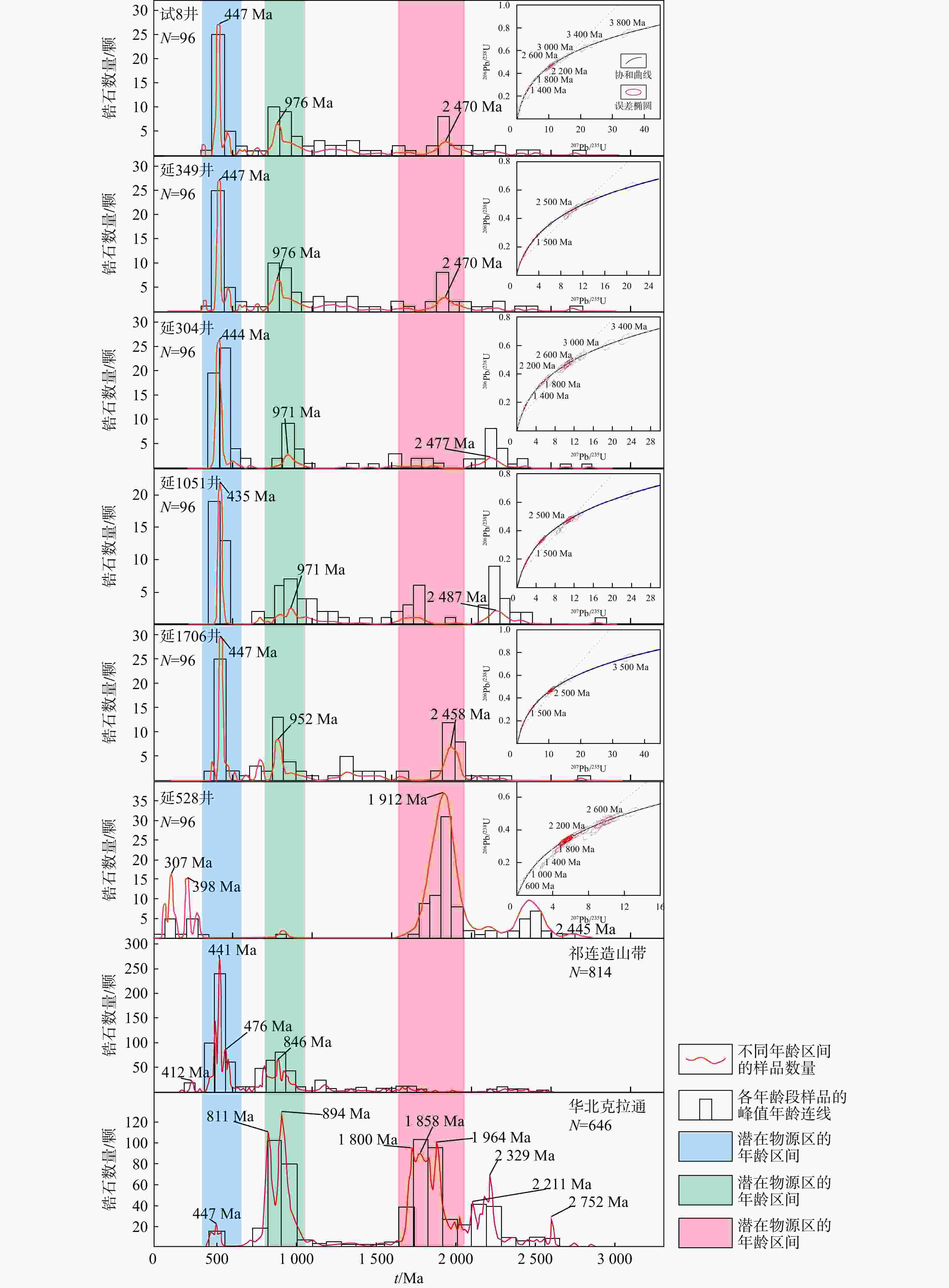
1912 Ma和2425 Ma 2个年龄峰值与华北克拉通北缘相对应,其他5口井的年龄峰值段435~447 Ma和952~976 Ma则与北秦岭的年龄峰值相对应,据此可将探区内物源划分为NE和S部2个方向。通过锆石、电气石和金红石等重矿物,可将S部物源进一步划分为WS和ES 2个方向;与重矿物分析结果相对应,在微量元素锆铌比分析中,存在WS陇东地区和ES豫西地区2个方向的物源;对砂砾岩粒径在平面上分布特征的显示,研究区存在来自ES方向的物源。综合分析可得,延长探区本溪组总体上可划分为NE、WS和ES 3个物源区,分别指示了盆地北缘阴山、盆地南缘祁连山和北秦岭东段剥蚀区,其中ES方向物源距延长探区最近,对探区影响较大。该成果探明了研究区内的3个物源方向以及其影响区域,对延长探区本溪组砂体分布预测和沉积相划分具有重要的参考意义。Abstract:Objective The provenance of detritus plays a vital role in controlling the development and spatial distribution of the Benxi Formation sandstone reservoir within the Yanchang exploration area.
Methods Based on previous research, this study employed four provenance analysis methods, including detrital zircon U-Pb ages, heavy mineral assemblages, trace elements, and statistical analysis of sandstone gravel size, applied to sand and mudstone samples from 37 wells in the Yanchang exploration area.
Results The zircon U-Pb age populations exhibited peaks at approximately
1912 Ma and2425 Ma, corresponding to the northern edge of the North China Craton. Additionally, peaks at 435−447 Ma and 952−976 Ma from five wells are linked to the North Qinling Mountains. Based on these findings, the provenance of sedimentary rocks can be divided into two primary directions: north and south. Furthermore, heavy mineral assemblage analysis showed higher zircon and tourmaline contents in the southwest region. At the same time, rutile was more abundant in the southeast, indicating that the southern source area can be subdivided into the southwest and southeast. Corresponding trace element analysis, notably the Zr/Nb values, supported these divisions, indicating two provenance directions of southwest Longdong and southeast Yuxi. Additionally, the spatial distribution of sandstone gravel diameters indicated a southeast source within the study area.Conclusion Comprehensive analysis reveals that the provenance of the Benxi Formation in the Yanchang exploration area stems from three main source regions: northeast (northern basin margin), southwest (Qilian Mountains), and southeast (North Qinling Mountains). The southeastern source is the closest and contributes the most sediments. This study illustrates the three provenance areas of the Benxi Formation and their influence zones, which are significant for predicting the distribution of sand bodies and delineating sedimentary facies in the Yanchang exploration area.
-
Key words:
- Benxi Formation /
- sediment provenance /
- zircon /
- heavy mineral /
- trace element /
- gravel size /
- Ordos Basin /
- Yanchang exploration area
-
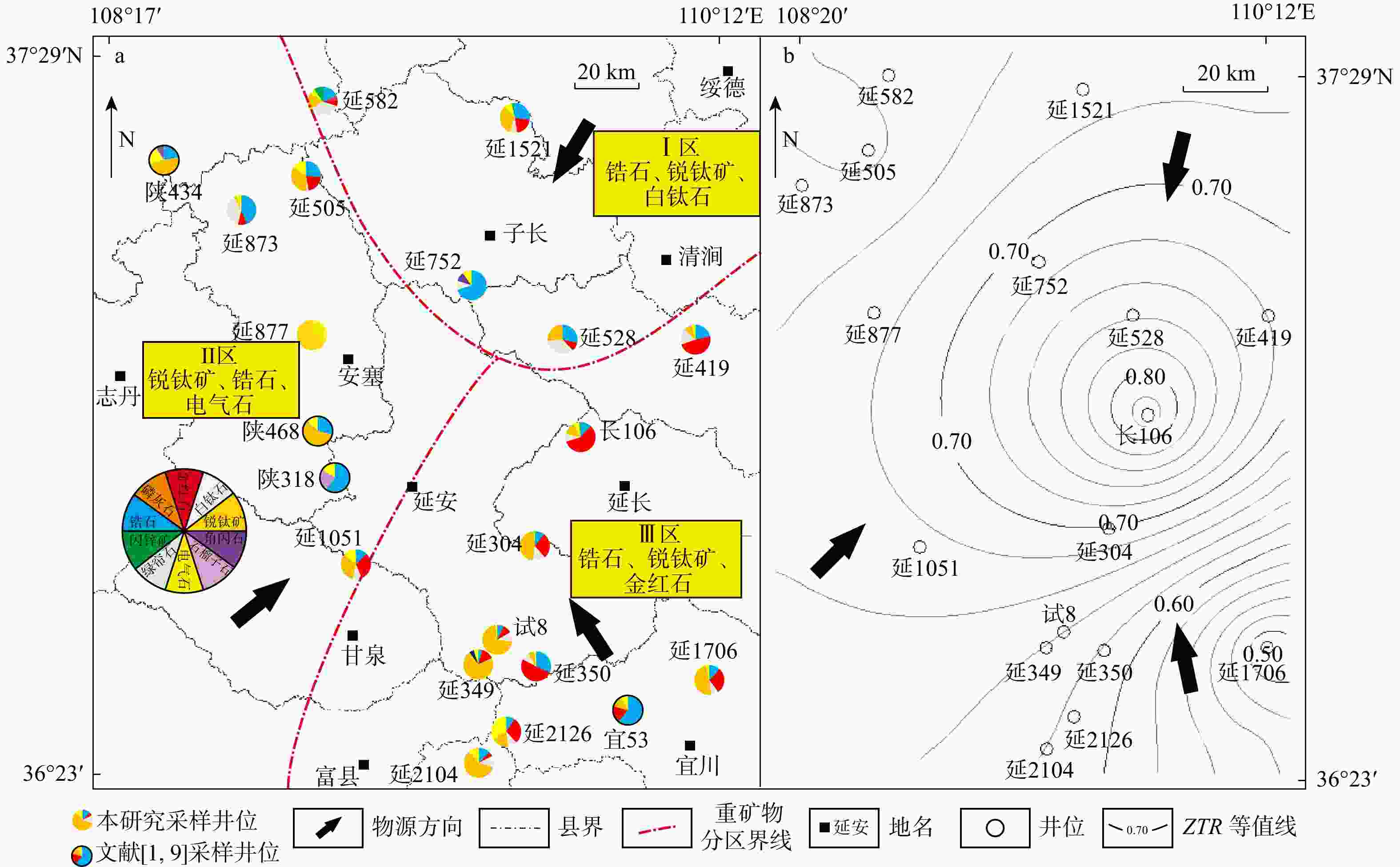
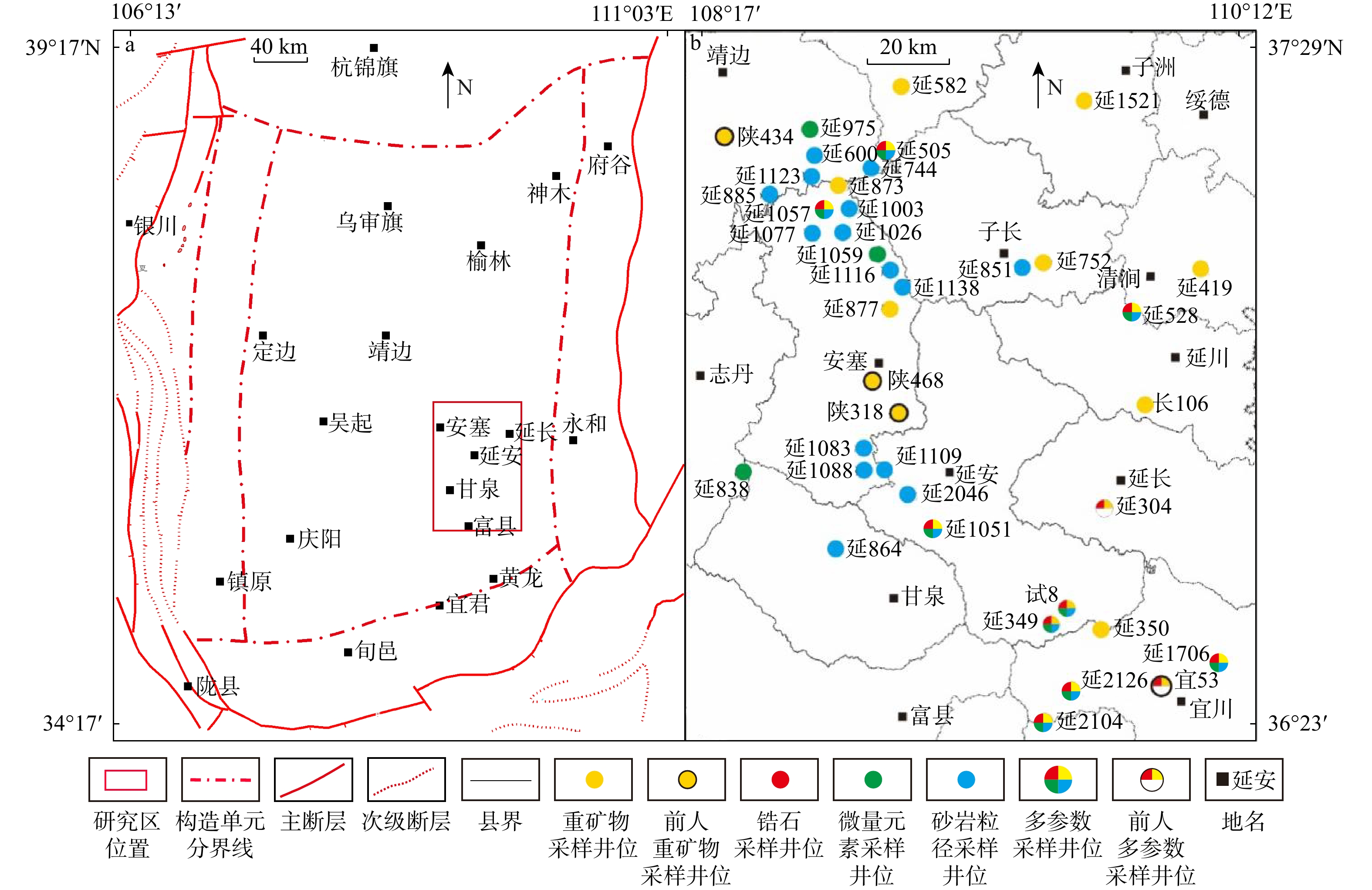
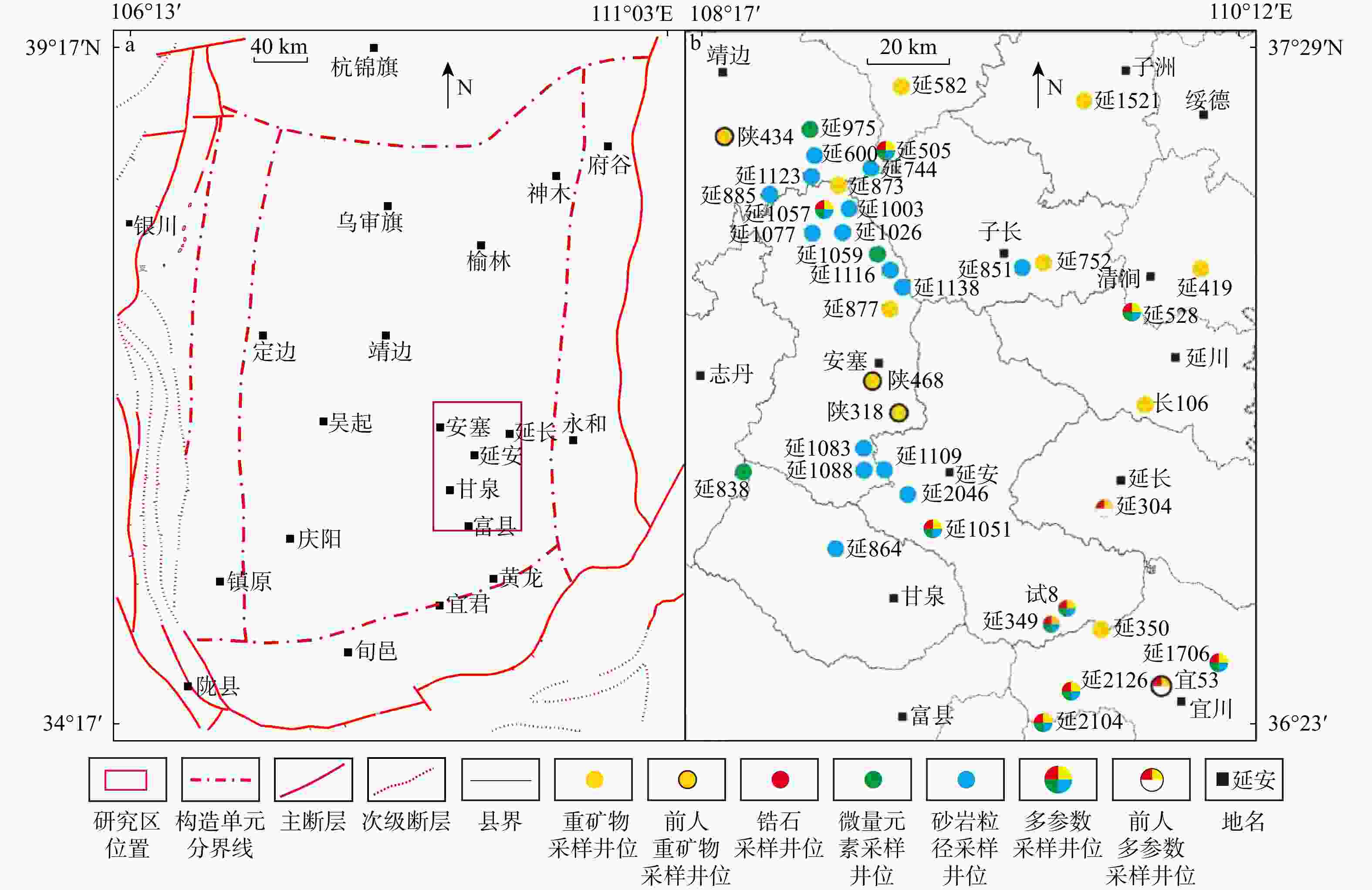
图 1 鄂尔多斯盆地延长探区的地理位置图(a)[7]及样品点位分布图(b)
Figure 1. Geographical location map of the Yanchang exploration area in the Ordos Basin(a) and sample point distribution map(b)
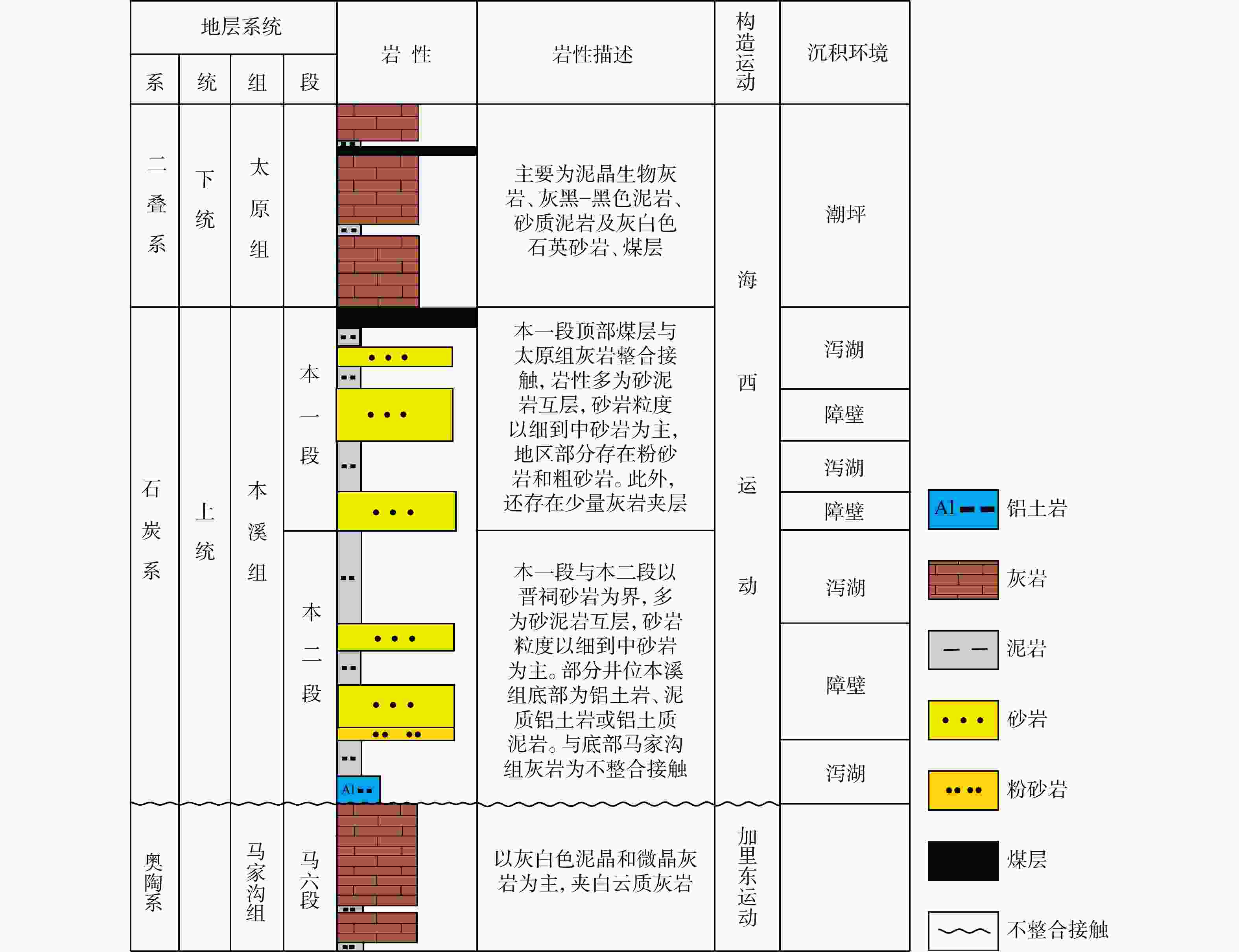
图 2 鄂尔多斯盆地延长探区地层综合柱状图[1]
Figure 2. Comprehensive stratigraphic bar chart of the Yanchang exploration area in the Ordos Basin
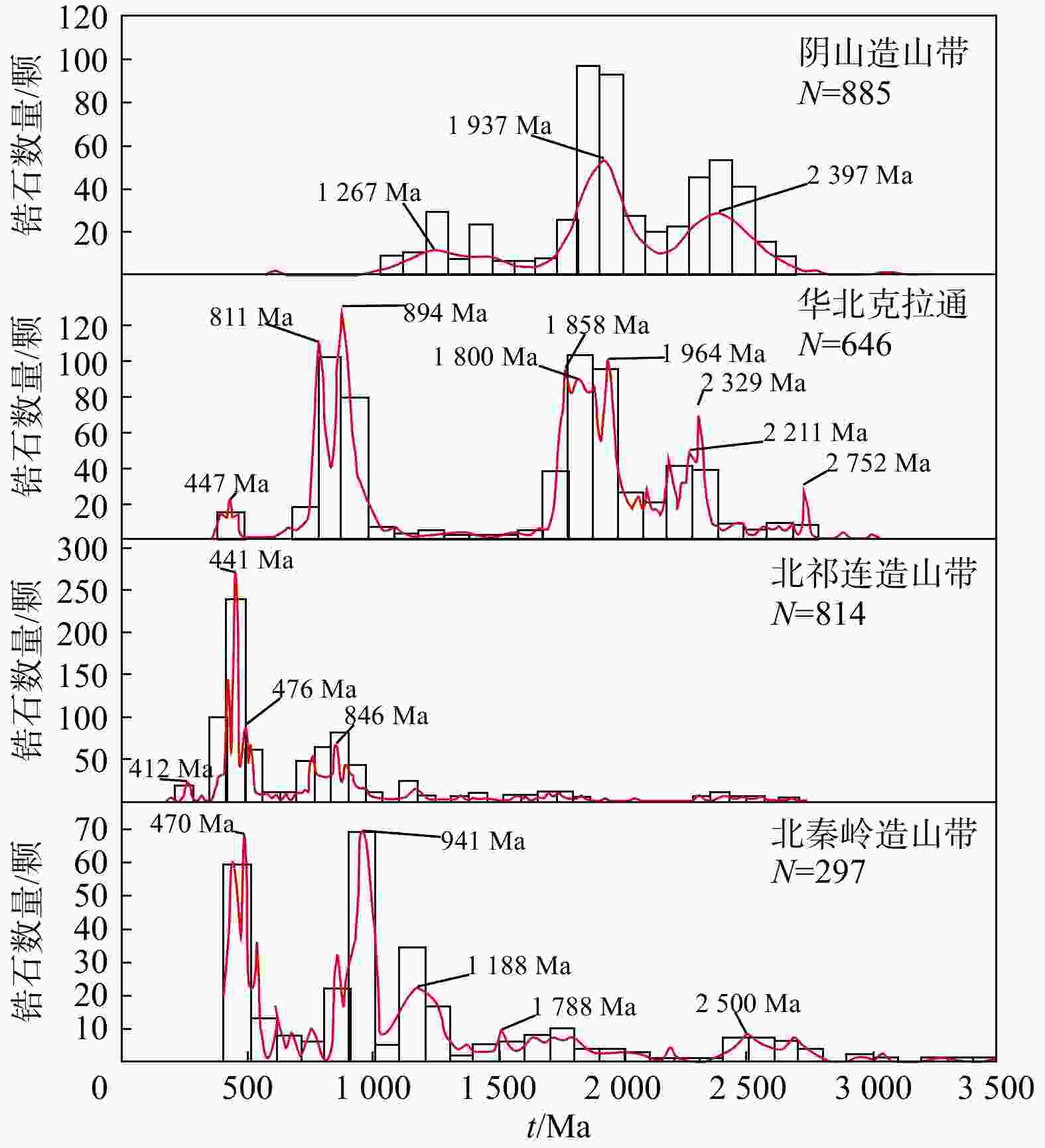
图 5 潜在物源年龄谱[18]
Figure 5. Potential source age spectrum
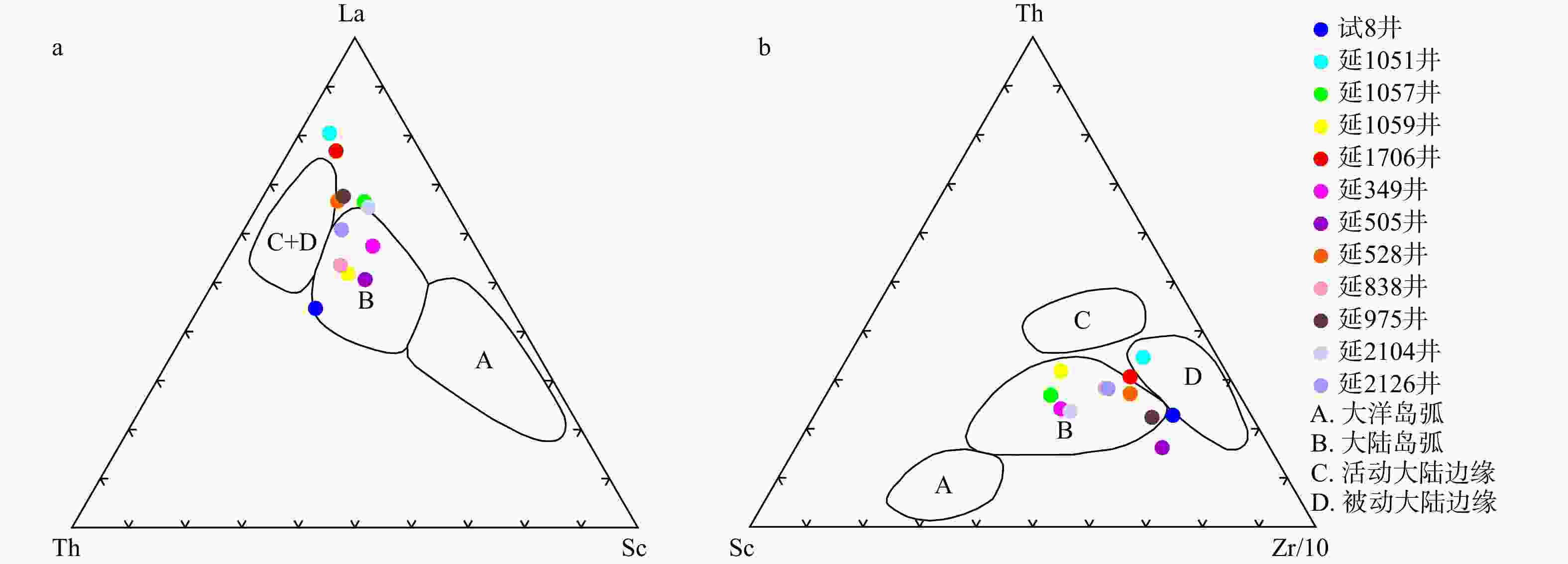
图 7 延长探区本溪组的La-Th-Sc (a)和Th-Sc-Zr/10图解(b)[22]
Figure 7. Diagram of La-Th-Sc (a) and Th-Sc-Zr/10 (b) in the Benxi Formation of the Yanchang exploration area
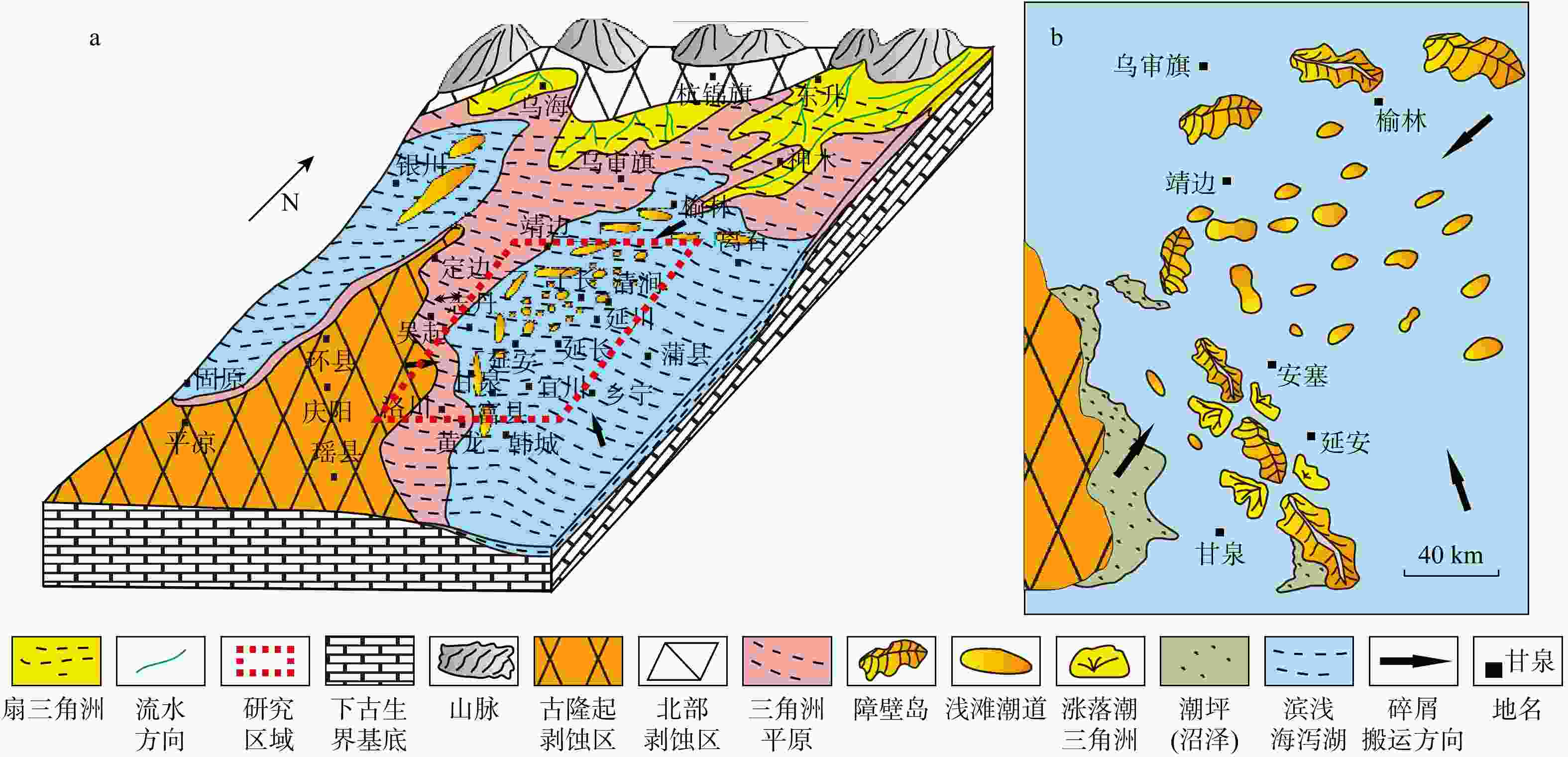
图 11 鄂尔多斯盆地本溪组沉积期古地理背景[32](a)与延长气田内的物源区分布示意图(b)
Figure 11. Paleogeographic background during the sedimentation of the Benxi Formation in the Ordos Basin (a) and distribution of source areas in the Yanchang Gas Field (b)
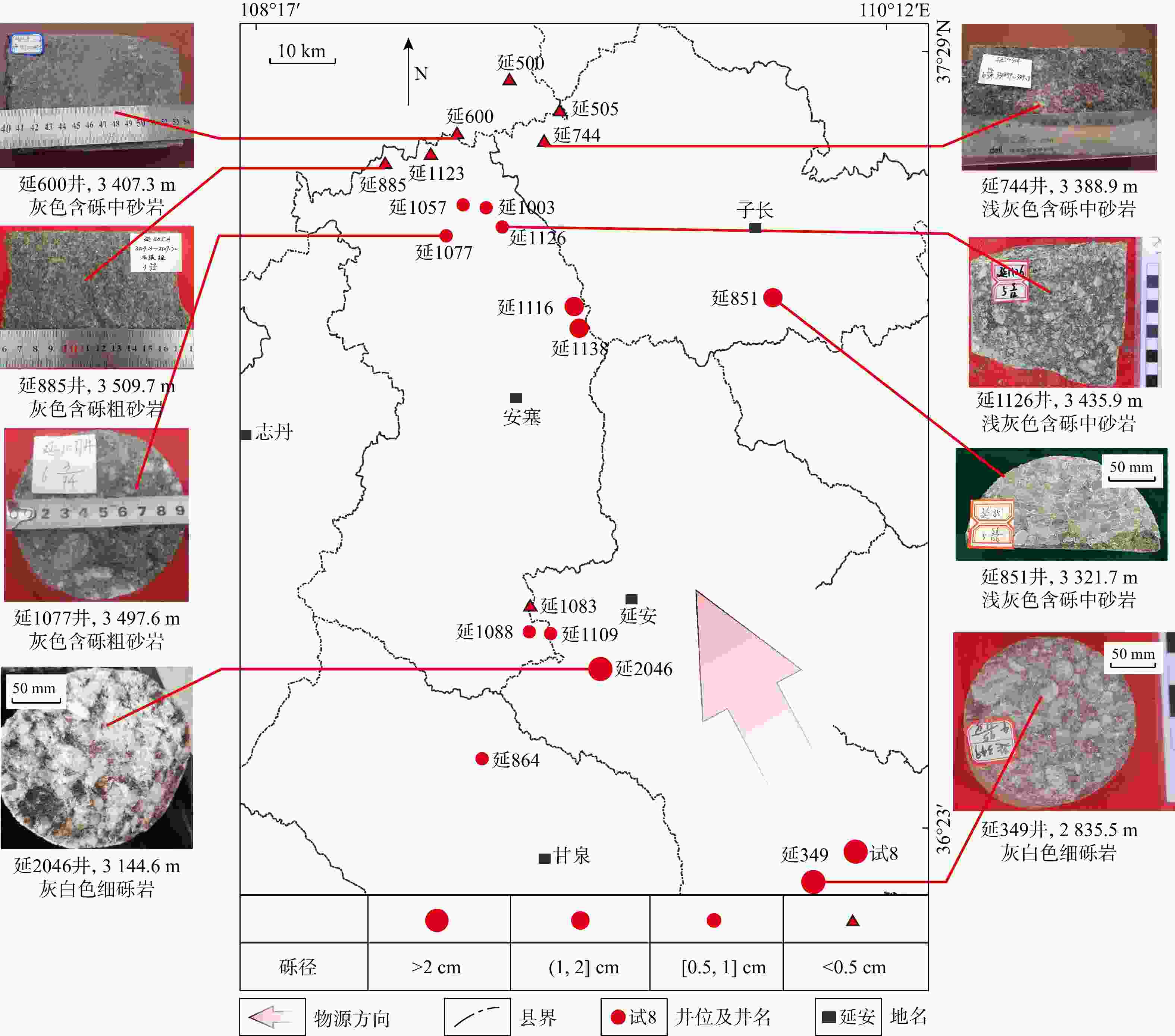
表 1 研究区采样井名、岩性和分析
Table 1. List of sampling well names, lithology, and analysis items in the study area
分析项目 岩性 样品数量/个 井名 重矿物 砂岩 17 延505,延873,延877,延2104,延2126,延582,延1521,延752,
延528,延419,长106,延1051,试8,延349,延1706,延304,延350碎屑锆石 砂岩 6 延349,延528,延1051,延1706,延304,试8 微量元素 泥岩 12 试8,延1051,延1057,延1059,延1706,延349,延505,延528,延838,延975,延2104,延2126 碎屑粒径 砂岩 20 延744,延500,延600,延505,延1123,延885,延1057,延1003,延1077,
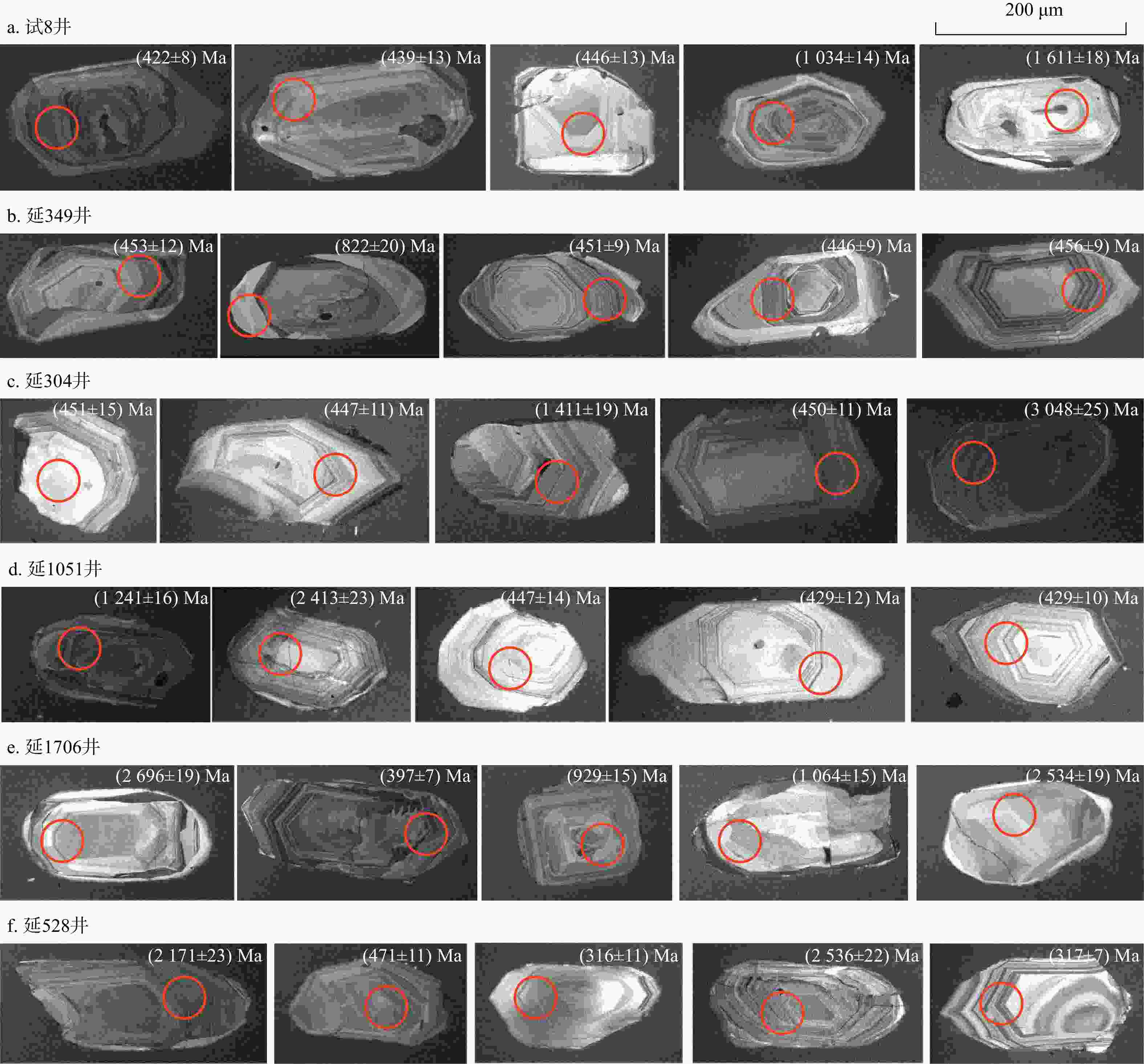
延1126,延1116,延1138,延851,延1083,延1088,延1109,延2046,延864,延349,试8表 2 研究区东部本溪组锆石年龄分析表
Table 2. Zircon age analysis in the Benxi Formation in the eastern part of the study area
取样井位 有效数据点/个 年龄变化范围/Ma 分组/Ma 峰值年龄/Ma 皓石数量/颗 百分比/% 试8井 96 422~ 3617 326~530 447 30 31.2 549~ 1462 976 35 36.5 1518 ~3615 2470 31 32.7 延349井 88 418~ 3120 414~496 447 33 34.4 502~ 1458 976 38 39.6 1589 ~3120 2470 23 26.0 延304井 96 424~ 3217 407~673 444 49 51.0 869~ 1595 971 18 18.8 1728 ~3204 2477 29 30.2 延1051井 96 422~ 3230 421~465 435 32 33.3 735~ 1932 971 42 43.8 2115 ~3210 2487 22 22.9 延1706井 96 390~ 3627 375~669 447 30 31.3 777~ 2042 952 39 40.6 2302 ~3621 2458 27 28.1 延528井 96 265~ 2651 265~467 307,398 13 13.5 1473 ~2651 1912 ,2425 77 80.2 963~ 1344 未形成年龄峰值 6 6.3 表 3 研究区本溪组重矿物质量对比
Table 3. Comparison of heavy mineral in the Benxi Formation the study area
样品
井位陆源重矿物质量/mg 锆石 电气石 石榴石 磷灰石 磁铁矿 白钛石 金红石 锐钛矿 延505井 54.39 31.84 — 1.03 0.61 4.11 42.08 72.87 延873井 66.79 8.26 — — 1.4 56.78 14.41 4.73 延877井 — 0.01 — — 0.02 — — — 延2104井 62.83 57.25 — — — 60.32 25.13 294.06 延2126井 26.65 93.53 — — — 26.65 79.96 53.3 延349井 0.59 0.79 — 0.1 — 0.1 2.23 11.39 延528井 17.34 — 21.97 — — 21.97 5.78 16.19 延1051井 7.69 7.69 — — — 6.18 18.09 19.45 延1706井 3.17 1.06 — — — 2.11 7.4 12.69 延304井 18.68 1.25 — — — 24.91 49.81 83.43 试8井 1.44 0.48 — — — 2.08 1.92 14.24 延752井 7.82 1.12 — — — 1.12 — — 延582井 3.79 1.19 — 0.96 — 7.45 1.37 3.79 延419井 17.82 3.56 — — — 14.25 39.2 7.13 延1521井 6.21 1.94 — — — 1.94 4.66 7.37 延350井 1.90 0.17 — — — 0.52 3.11 0.35 长106井 1.2 0.68 — — — 0.85 5.98 1.37 -
[1] 贾浪波,钟大康,孙海涛,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地本溪组沉积物物源探讨及其构造意义[J]. 沉积学报,2019,37(5):1087-1103.JIA L B,ZHONG D K,SUN H T,et al. Sediment provenance analysis and tectonic implication of the Benxi Formation,Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2019,37(5):1087-1103. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] 刘锐娥,黄月明,卫孝锋,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部晚古生代物源区分析及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石,2003,23(3):82-86.LIU R E,HUANG Y M,WEI X F,et al. Analysis of provenance of Late Paleozoic in the northern Ordos Basin and its geological significance[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology,2003,23(3):82-86. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 陈全红,李文厚,胡孝林,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地晚古生代沉积岩源区构造背景及物源分析[J]. 地质学报,2012,86(7):1150-1162.CHEN Q H,LI W H,HU X L,et al. Tectonic setting and provenance analysis of Late Paleozoic sedimentary rocks in the Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2012,86(7):1150-1162. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 张靖芪,虎建玲,谢远飞,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西北缘晚石炭世−中二叠世沉积背景特征与演化[J]. 沉积学报,2025,43(1):121-138.ZHANG J Q,HU J L,XIE Y F,et al. Depositional background and evolution of Late Carboniferous-Middle Permian,northwestern margin of the Ordos Basin,China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2025,43(1):121-138. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 刘贤. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长地区上古生界物源分析及意义[D]. 西安:西北大学,2010.LIU X. Provenance analysis and its significance of Upper Paleozoic in Yanchang area,Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an:Northwest University,2010. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 林进,李云,何剑. 鄂尔多斯延长探区本溪组物源及沉积体系分析[J]. 中国地质,2013,40(5):1542-1551.LIN J,LI Y,HE J. An analysis of the source and the sedimentary system of the Carboniferous Benxi Formation in Yanchang area of Ordos Basin[J]. Geology in China,2013,40(5):1542-1551. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 高志东. 鄂尔多斯盆地上石炭统本溪组物源分析及有利砂体发育规律[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2019.GAO Z D. Provenance analysis of Benxi Formation of Upper Carboniferous in Ordos Basin and distribution regularity of favorable sand bodies[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] YANG Y T,LI W,MA L. Tectonic and stratigraphic controls of hydrocarbon systems in the Ordos Basin:A multicycle cratonic basin in Central China[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2005,89(2):255-269. doi: 10.1306/10070404027 [9] ZHAO J F,LIU C Y,HUANG L,et al. Paleogeography reconstruction of a multi-stage modified intra-cratonic basin:A case study from the Jurassic Ordos Basin,western North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2020,190:104191. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104191 [10] SHEN Y L,GUO Y H,JING H X,et al. Study on sequence stratigraphy from Benxi to Taiyuan Formation in northeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science,2009,1(1):995-1001. doi: 10.1016/j.proeps.2009.09.154 [11] MORTON A C,WHITHAM A G,FANNING C M. Provenance of Late Cretaceous to Paleocene submarine fan sandstones in the Norwegian Sea:Integration of heavy mineral,mineral chemical and zircon age data[J]. Sedimentary Geology,2005,182(1/2/3/4):3-28. [12] ZHANG Z H,WANG H L. Comprehensive provenance analysis and its applications to Eocene clastic rocks in the Huimin Depression,Bohai Bay Basin,China[J]. Minerals,2019,9(9):517. doi: 10.3390/min9090517 [13] SAWAKUCHI A O,RODRIGUES F C G,MINELI T D,et al. Optically stimulated luminescence sensitivity of quartz for provenance analysis[J]. Methods and Protocols,2020,3(1):6. doi: 10.3390/mps3010006 [14] RAI P,BORGOHAIN B,CHETTRI N,et al. A comparative heavy mineral study of the Cenozoic sediments of Assam and Siwalik Foreland Basins,northeast Himalaya[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of India,2020,96(5):475-484. doi: 10.1007/s12594-020-1585-y [15] ZACHARIÁŠ J,KUCHAŘOVÁ A,KOTRLÝ M. Provenance analysis of marbles by combination of cathodoluminescence spectroscopy and electron microprobe analyses:Methodological comments[J]. Minerals,2023,13(2):244. doi: 10.3390/min13020244 [16] 龚胜利,闫琢玉,李百强,等. 琼东南盆地中中新统海底扇碎屑岩锆石U-Pb年龄特征及物源分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2024,43(5):45-54.GONG S L,YAN Z Y,LI B Q,et al. U-Pb age characteristics of detrital zircon and provenance analysis of a Middle Miocene submarine fan in the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2024,43(5):45-54. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 席胜利,王怀厂,秦伯平. 鄂尔多斯盆地北部山西组、下石盒子组物源分析[J]. 天然气工业,2002,22(2):21-24.XI S L,WANG H C,QIN B P. Analysis of the material sources of Shanxi Formation and Shihezi Formation in north Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry,2002,22(2):21-24. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] GUO P,LIU C Y,WANG J Q,et al. Detrital-zircon geochronology of the Jurassic coal-bearing strata in the western Ordos Basin,north China:Evidences for multi-cycle sedimentation[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2018,9(6):1725-1743. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2017.11.003 [19] ZHAO X C,LIU C Y,WANG J Q,et al. Provenance analyses of Lower Cretaceous strata in the Liupanshan Basin:From paleocurrents indicators,conglomerate clast compositions,and zircon U-Pb geochronology[J]. Journal of Earth Science,2020,31(4):757-771. doi: 10.1007/s12583-020-1324-8 [20] 潘双苹,胡光明,李积永,等. 柴达木盆地扎哈泉地区新近纪物源分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2023,42(3):201-209.PAN S P,HU G M,LI J Y,et al. Analysis of Neogene provenance in Zhahaquan area,Qaidam Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2023,42(3):201-209. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] BHATIA M R. Rare earth element geochemistry of Australian Paleozoic graywackes and mudrocks:Provenance and tectonic control[J]. Sedimentary Geology,1985,45(1/2):97-113. [22] BHATIA M R,CROOK K A W. Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary Basins[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1986,92(2):181-193. doi: 10.1007/BF00375292 [23] BOYNTON W V. Chapter 3-Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements:Meteorite Studies[A]//Anon. In Developments in Geochemistry[M]. edited by Henderson[S. l. ]:Elsevier,1984:63-114. [24] 刘江斌. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部三叠系延长组沉积体系研究[D]. 西安:西北大学,2017.LIU J B. Depositional system of the Triassic Yanchang Formation in southwestern Ordos Basin[D]. Xi'an:Northwest University,2017. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 魏方辉,裴先治,李瑞保,等. 甘肃天水地区早古生代黄门川花岗闪长岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及构造意义[J]. 地质通报,2012,31(9):1496-1509.WEI F H,PEI X Z,LI R B,et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of Early Paleozoic Huangmenchuan granodiorite in Tianshui area of Gansu Province and its tectonic significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2012,31(9):1496-1509. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 宋凯,吕剑文,杜金良,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中部上三叠统延长组物源方向分析与三角洲沉积体系[J]. 古地理学报,2002,4(3):59-66.SONG K,YU J W,DU J L,et al. Source direction analysis and delta depositional systems of Yanchang Formation of the Upper Triassic in the central Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography,2002,4(3):59-66. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 王廷印,高军平,王金荣,等. 内蒙古阿拉善北部地区碰撞期和后造山期岩浆作用[J]. 地质学报,1998,72(2):126-137.WANG T Y,GAO J P,WANG J R,et al. Magmatism of collisional and post-orogenic period in northern Alax region in Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,1998,72(2):126-137. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 耿元生,周喜文. 阿拉善地区新元古代早期花岗岩的地球化学和锆石Hf同位素特征[J]. 岩石学报,2011,27(4):897-908.GENG Y S,ZHOU X W. Characterastics of geochemistry and zircon Hf isotope of the Early Neoproterozoic granite in Alax area,Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2011,27(4):897-908. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 王晓霞,王涛,李伍平. 秦岭杂岩中花岗质片麻岩体的岩石地球化学特征及成因[J]. 矿物岩石,1997,17(3):76-82.WANG X X,WANG T,LI W P. The geochemistry characteristics and genesis of the granitic gneisses in Qinling complex[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology,1997,17(3):76-82. (in Chinese). [30] 林孝先. 陆源碎屑岩盆地综合物源分析:以鄂尔多斯盆地北部山西组为例[D]. 成都:成都理工大学,2011.LIN X X. A synthetic thought of provenance analysis in the terrigenous clastic rock basin:An example in the Lower Permian Shanxi Formation,northern Ordos Basin[D]. Chengdu:Chengdu University of Technology,2011. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] MENG X Z,PU R H,DOU T C,et al. Longshore changes in the microfacies and distribution of clastic barrier coastal sandbodies:A case from the Benxi Formation in the Ordos Basin,China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production Technology,2024,14(5):1129-1148. doi: 10.1007/s13202-024-01760-4 [32] 王若谷,周进松,杜永慧,等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部延安气田石炭系− 二叠系沉积演化模式[J]. 地质科学,2021,56(4):1088-1105.WANG R G,ZHOU J S,DU Y H,et al. Deposition evolution model of the Carboniferous-Permian in Yan'an gas field,the southeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica),2021,56(4):1088-1105. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] CHEN A Q,ZOU H,OGG J G,et al. Source-to-sink of Late Carboniferous Ordos Basin:Constraints on crustal accretion margins converting to orogenic belts bounding the North China Block[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2020,11(6):2031-2052. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.05.008 [34] CHEN R,WANG F,LI Z,et al. Late Paleozoic provenance shift in the east-central Ordos Basin:Implications for the tectonic evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2021,215:104799. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2021.104799 [35] FU C,YU X H,LI S L. Multiple sediment source infill in a low-accommodation basin:Implications for the Late Paleozoic sediment routing system in the southeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Magazine,2023,160(9):1649-1672. doi: 10.1017/S0016756823000572 -




 下载:
下载: