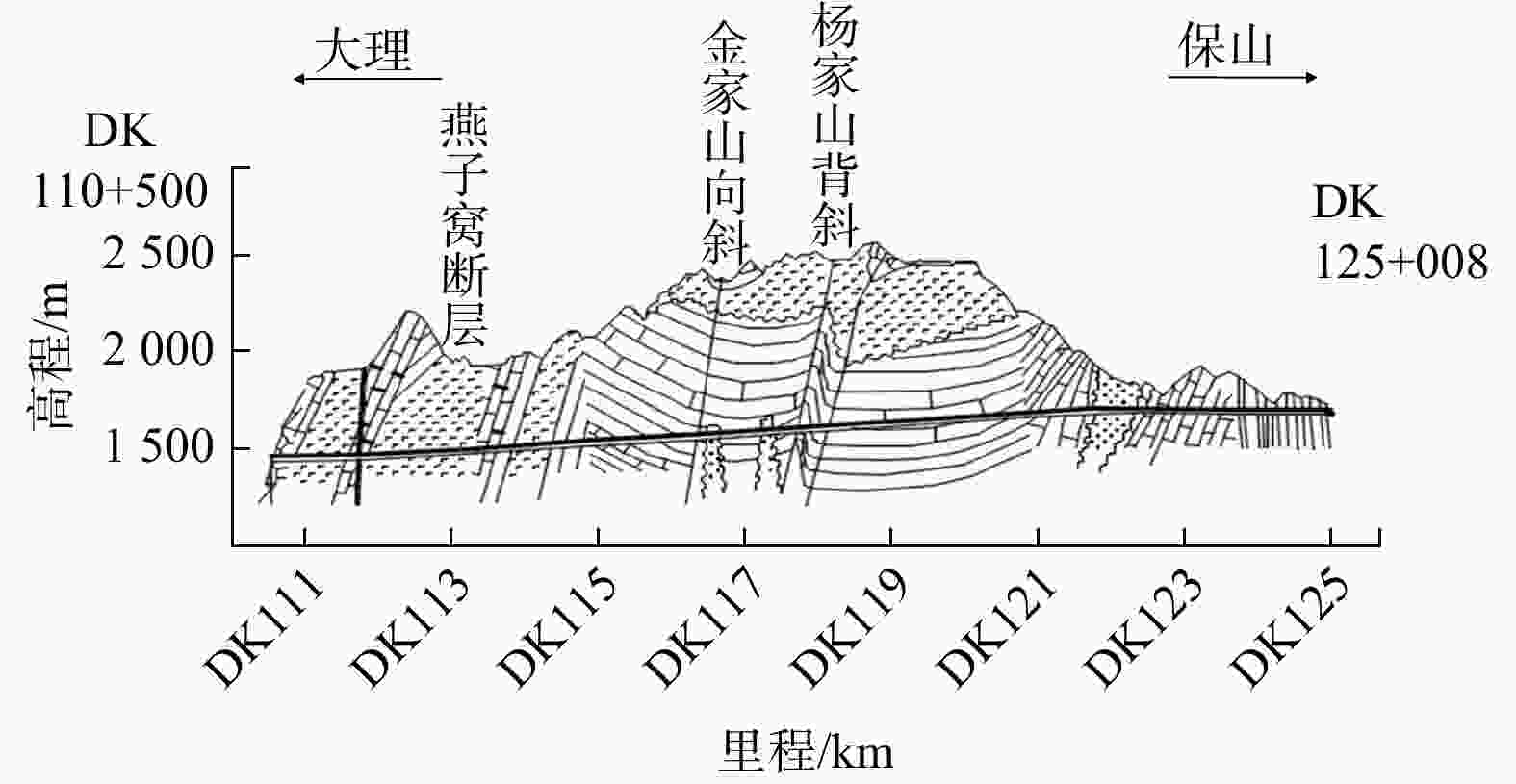
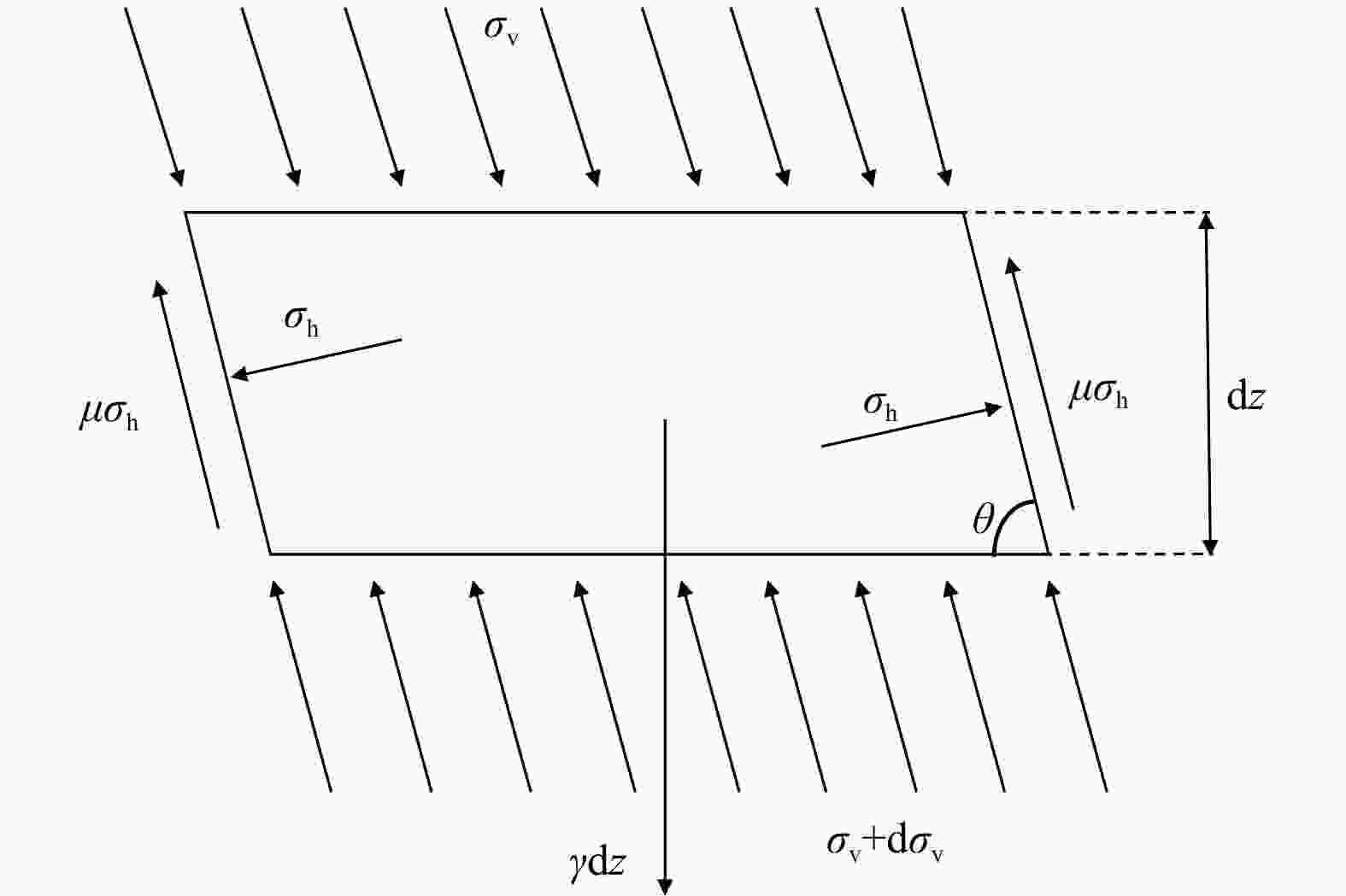
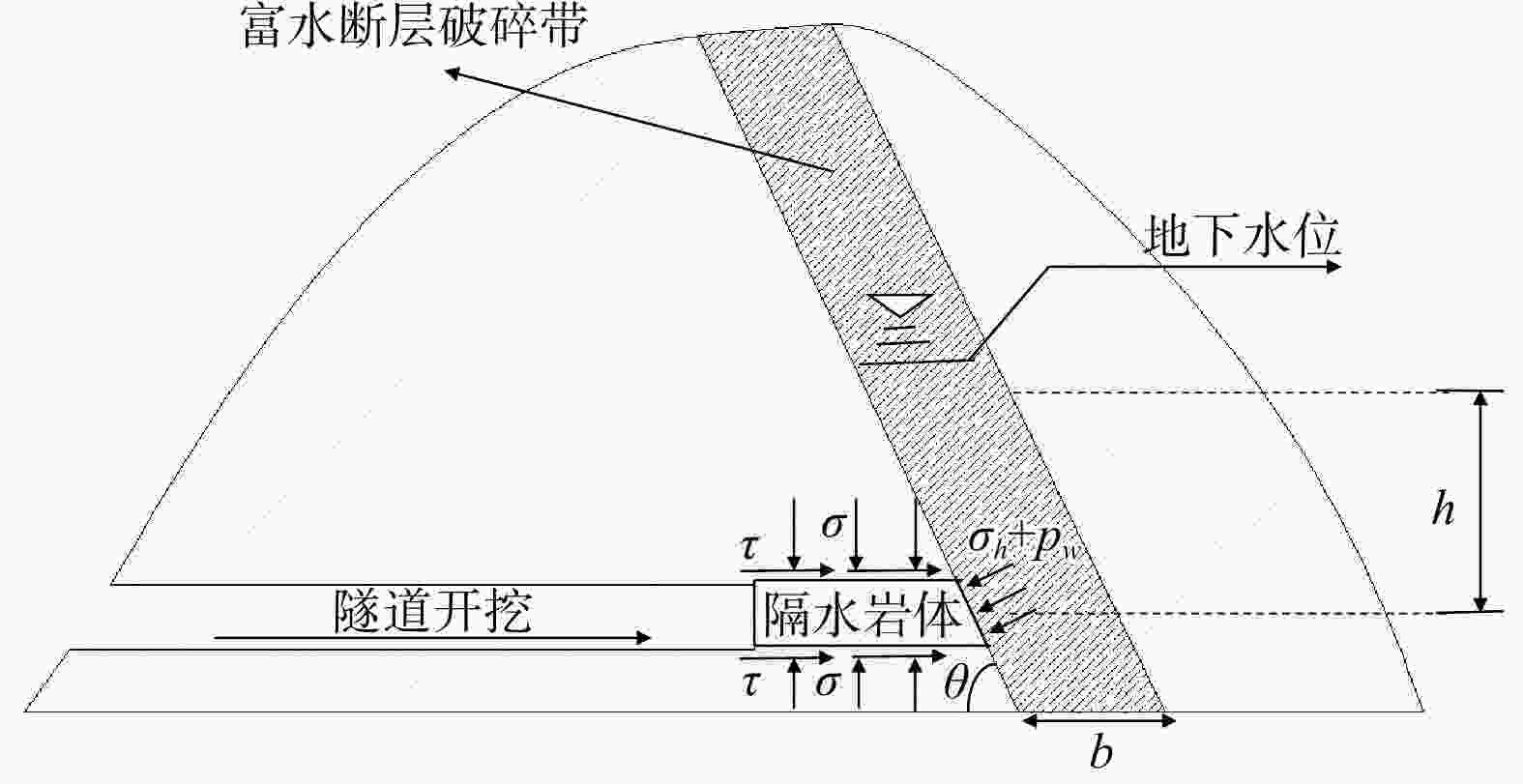
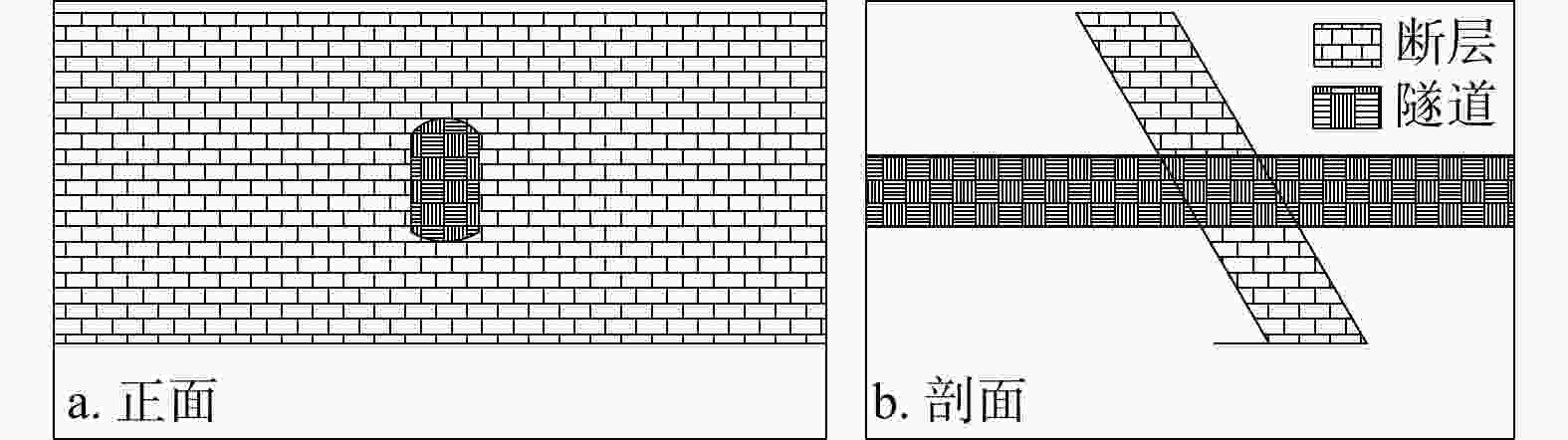
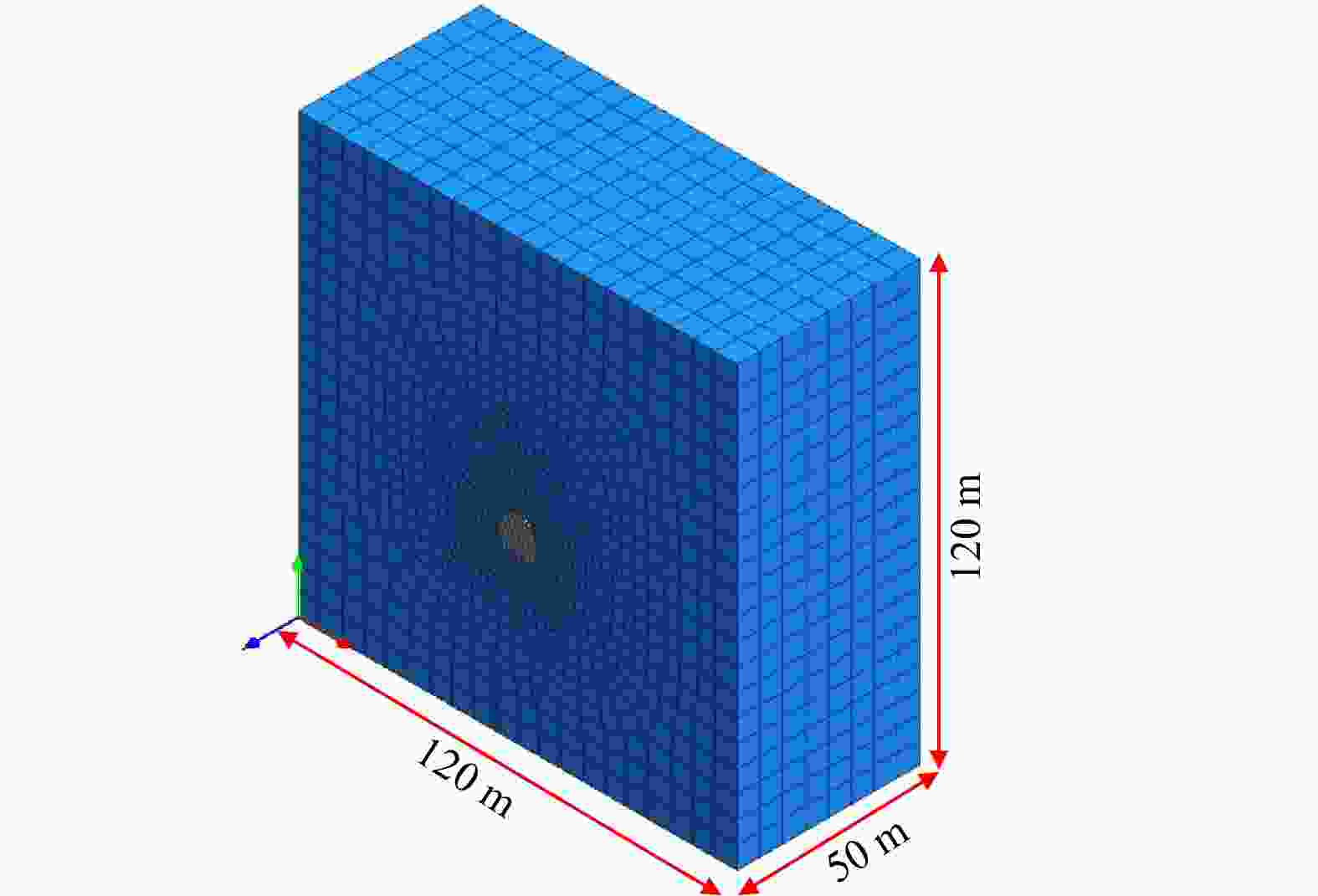
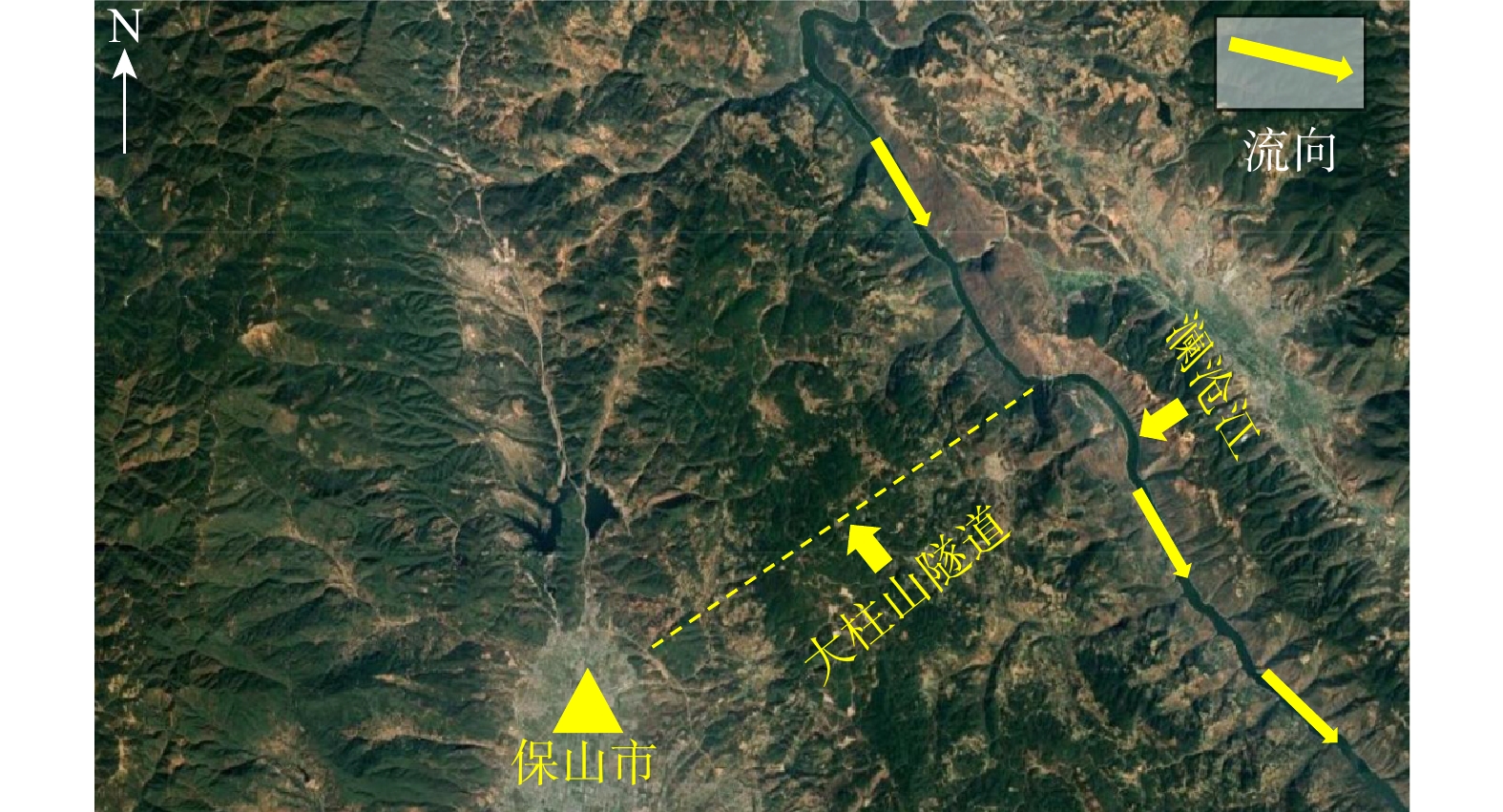
Evolution law of water and mud inrush disaster in deep-buried tunnel crossing water-rich fault fracture zone
-
摘要:
富水断层破碎带的存在对隧道突水突泥的发生有着较大的影响。为研究深埋隧道穿越富水断层破碎带时引起的突水突泥灾变演化规律,基于筒仓模型和极限平衡理论,考虑断层破碎带的宽度、长度和倾角,建立隧道穿越富水断层破碎带的隔水岩体力学模型,推导隔水岩体最小安全厚度的力学判据;通过MIDAS GTS NX数值模拟仿真,建立三维流固耦合数值模型,分析隧道开挖至断层破碎带内部时的位移、应力、孔隙水压力和渗流流速演化规律。结果表明:隔水岩体的最小安全厚度主要与断层破碎带长度、宽度、倾角、隧道埋深以及隔水岩体自身的力学性质有关;隧道开挖至断层后,其内部位移显著增大,最大主应力和最小主应力都存在明显的突变;低孔隙水压力区范围显著增大,孔隙水压力表现出先缓慢减小,后急剧减小,再逐渐趋于稳定的变化趋势;在断层内部出现了流速高值区,整个模型流速出现增大趋势,开挖过程中掌子面的最大流速整体呈现先增大后减小的变化趋势。该研究可为断层破碎带突水突泥灾害的预防提供相关参考。
-
关键词:
- 深埋隧道 /
- 突水突泥 /
- 断层破碎带 /
- 隔水岩体 /
- MIDAS GTS NX
Abstract:Objective The existence of water-rich fault fracture zones significantly influences the occurrence of water and mud inrush during tunnel construction. To study the disaster evolution mechanism during deep-buried tunnel excavation through water-rich fault fracture zones,
Methods this study establishes a mechanical model of the impermeable rock mass based on the silo model and limit equilibrium theory, considering the width, length, and inclination angle of the fault fracture zone. The mechanical criterion for the minimum safe thickness of the impermeable rock mass is derived. Using MIDAS GTS NX numerical simulation, a three-dimensional fluid-solid coupling numerical model is developed to analyze the evolution pattern of displacement, stress, pore water pressure, and seepage velocity when tunneling into the fault fracture zone.
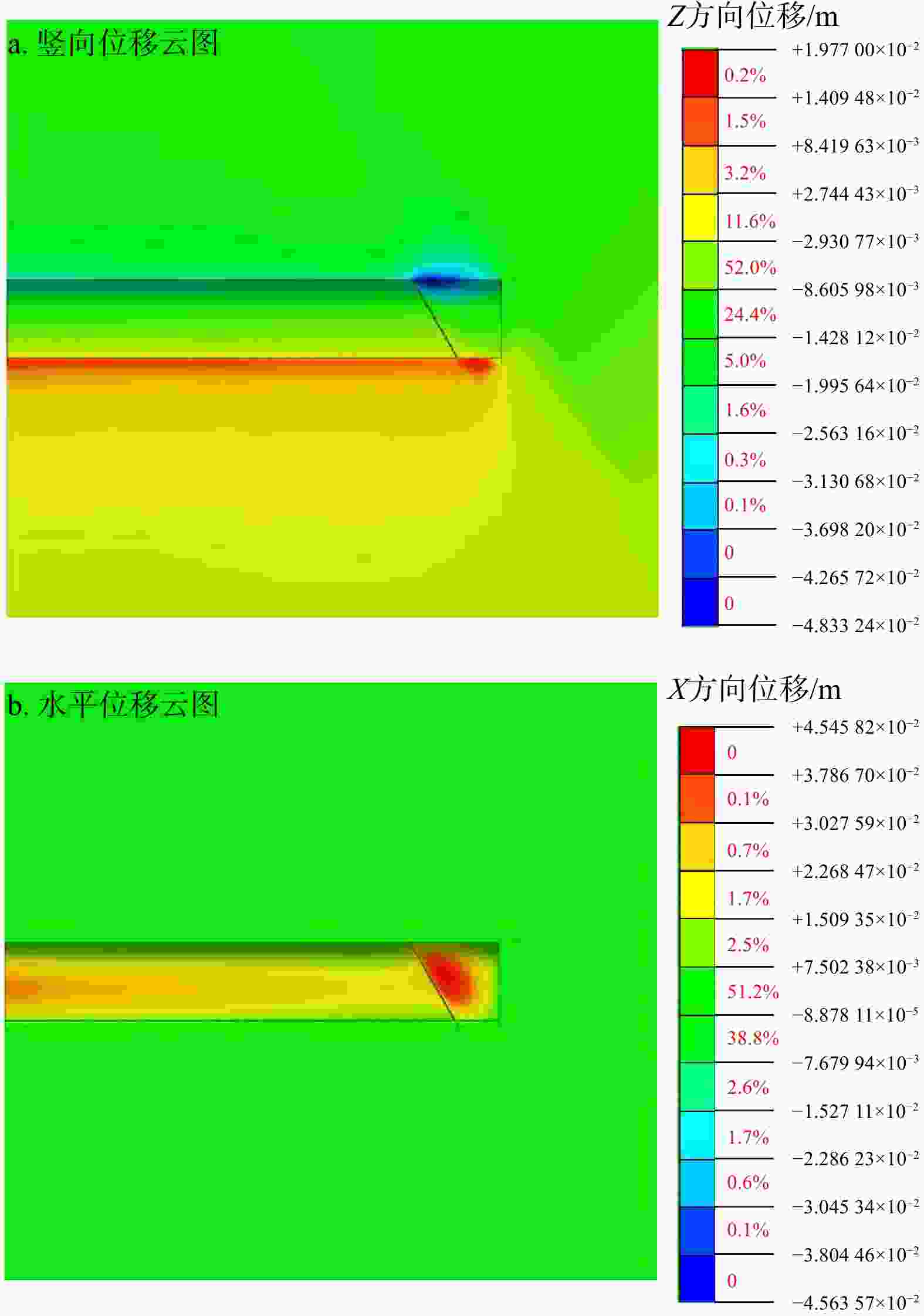
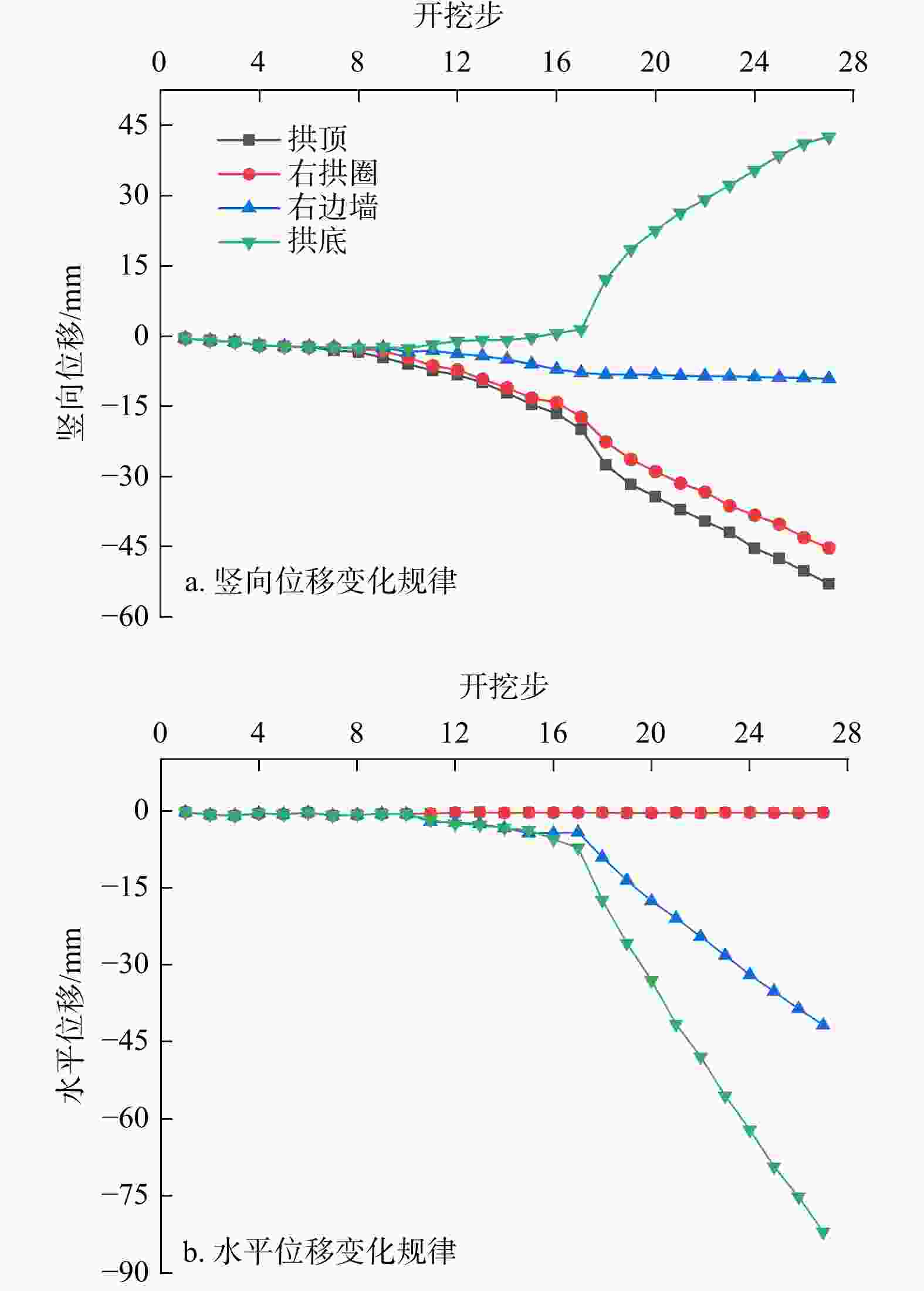
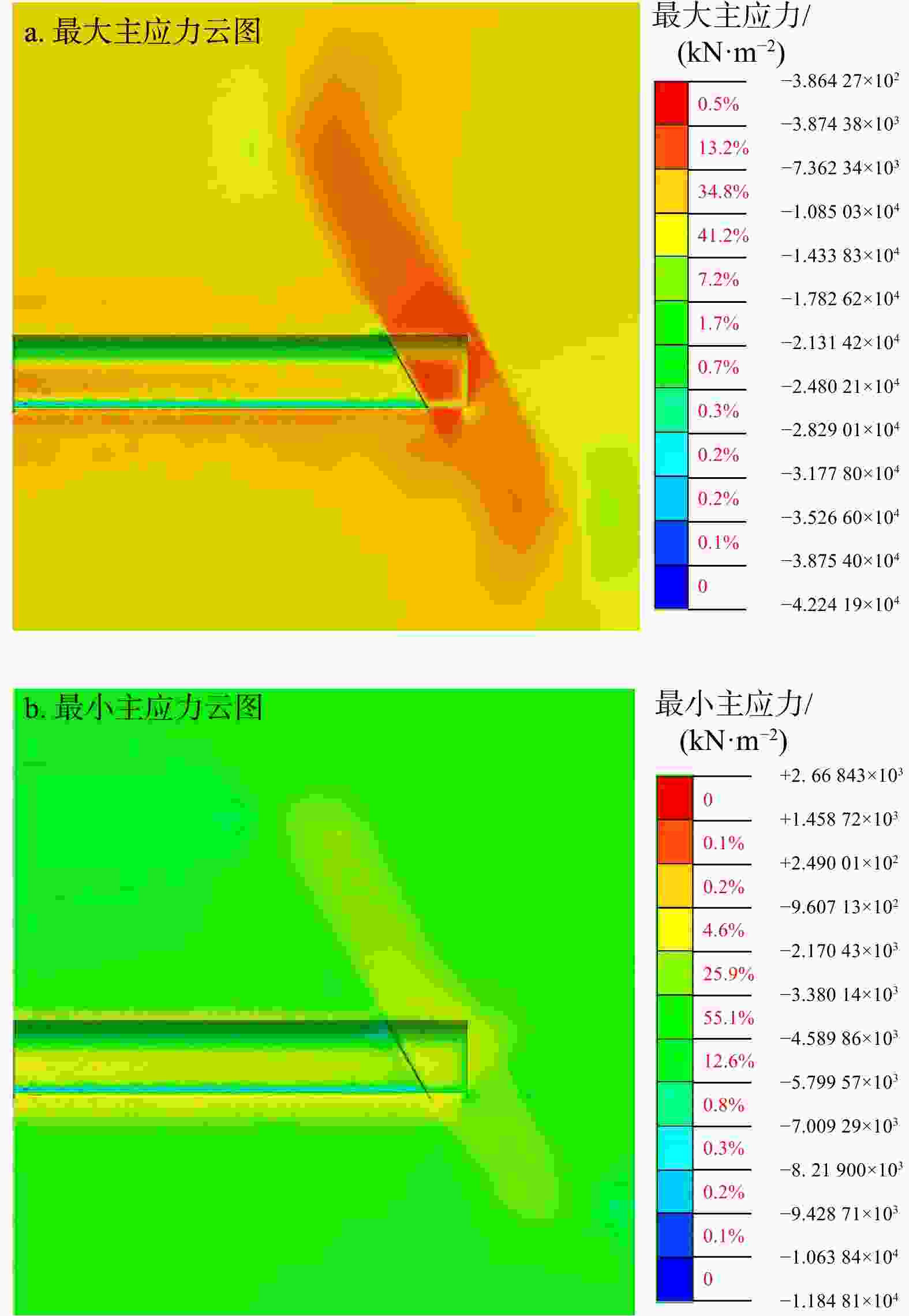
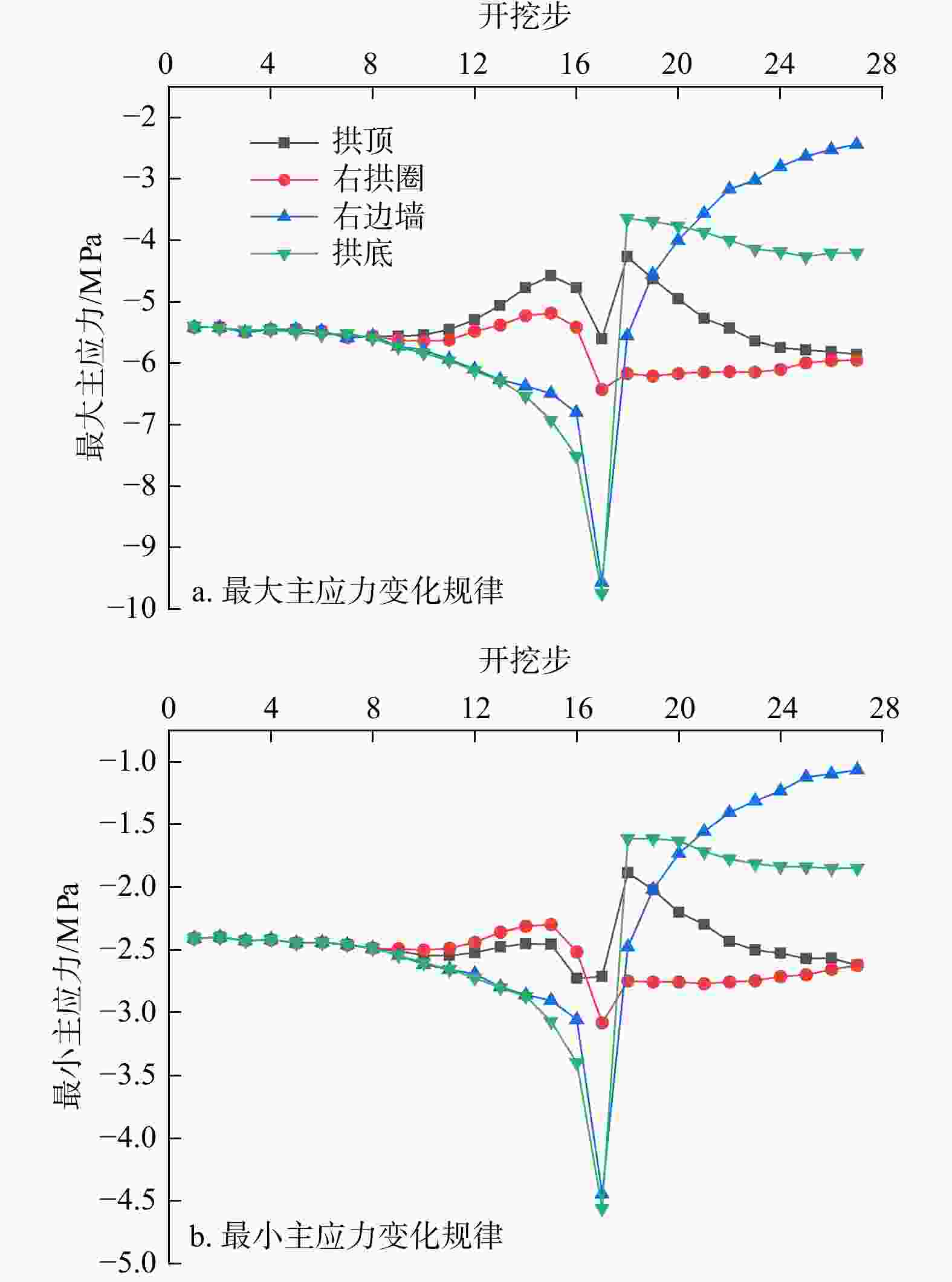
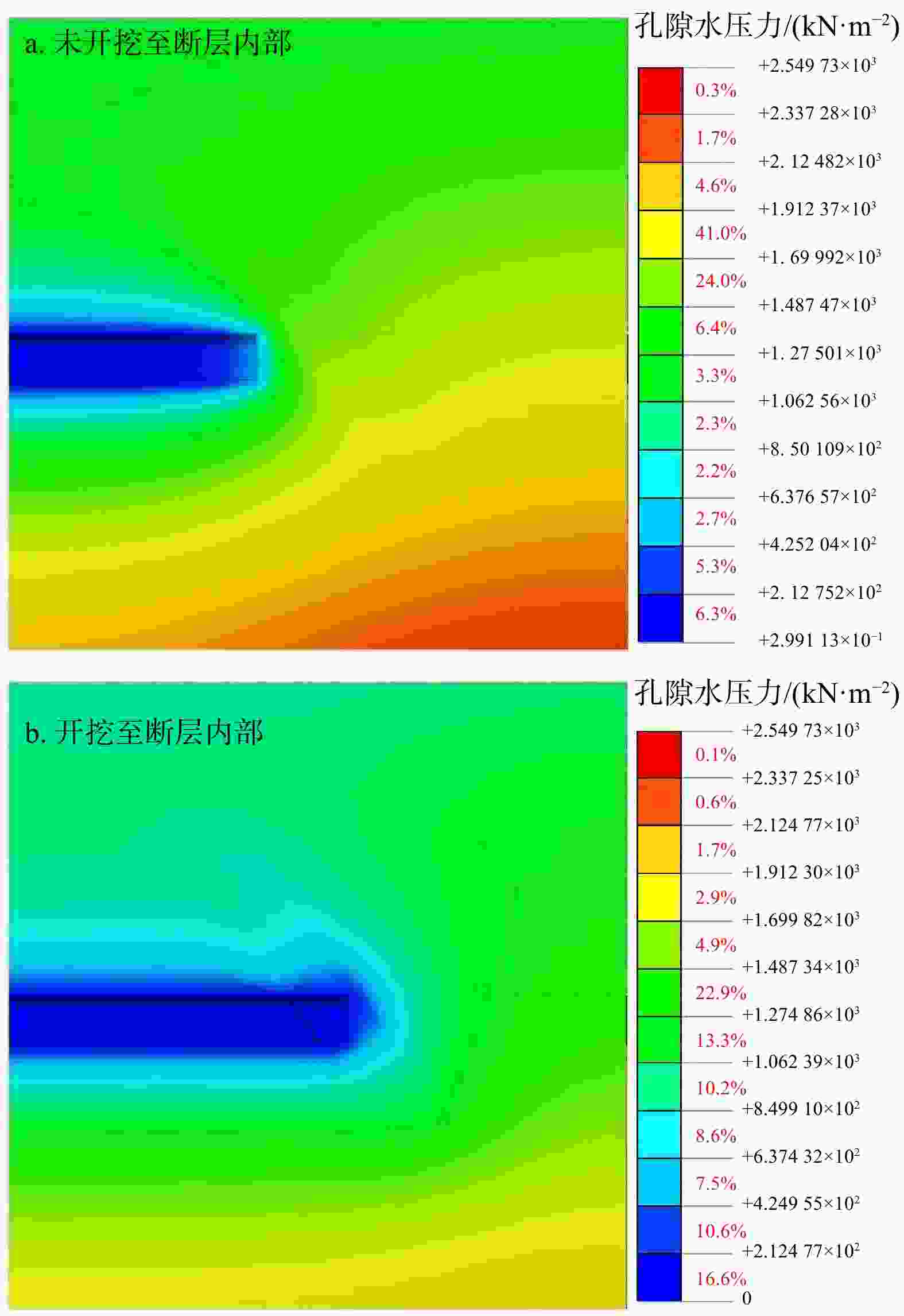
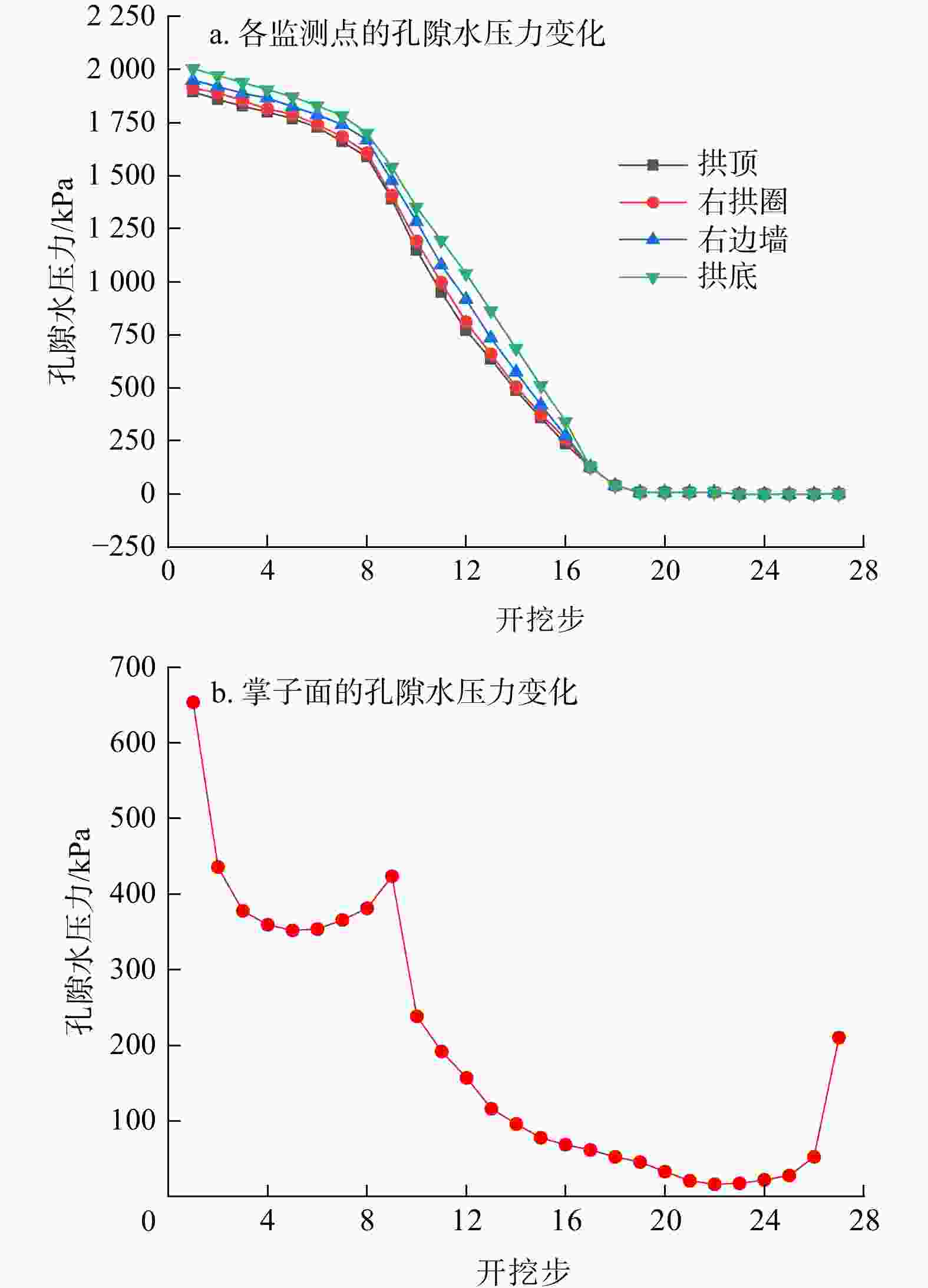
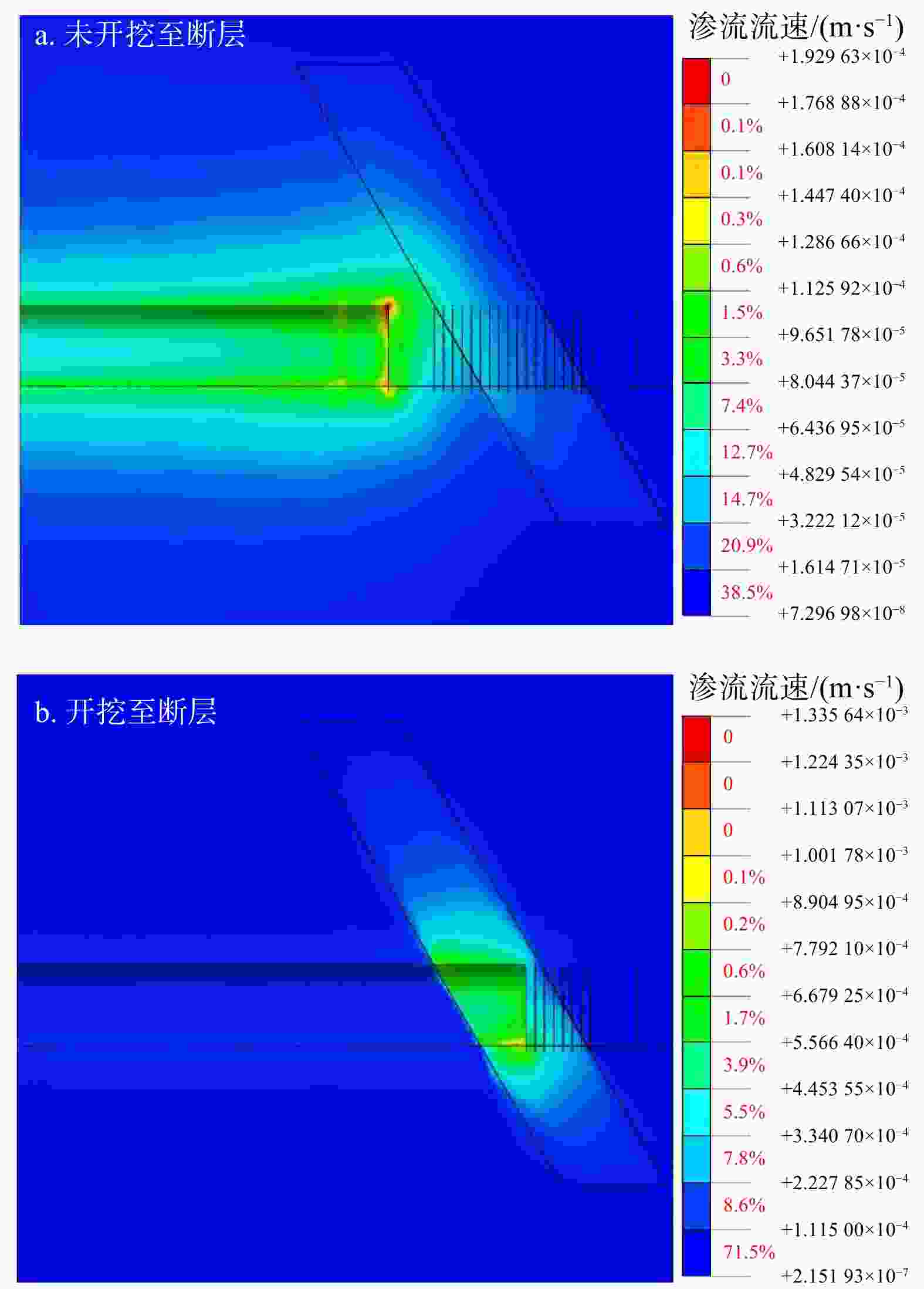
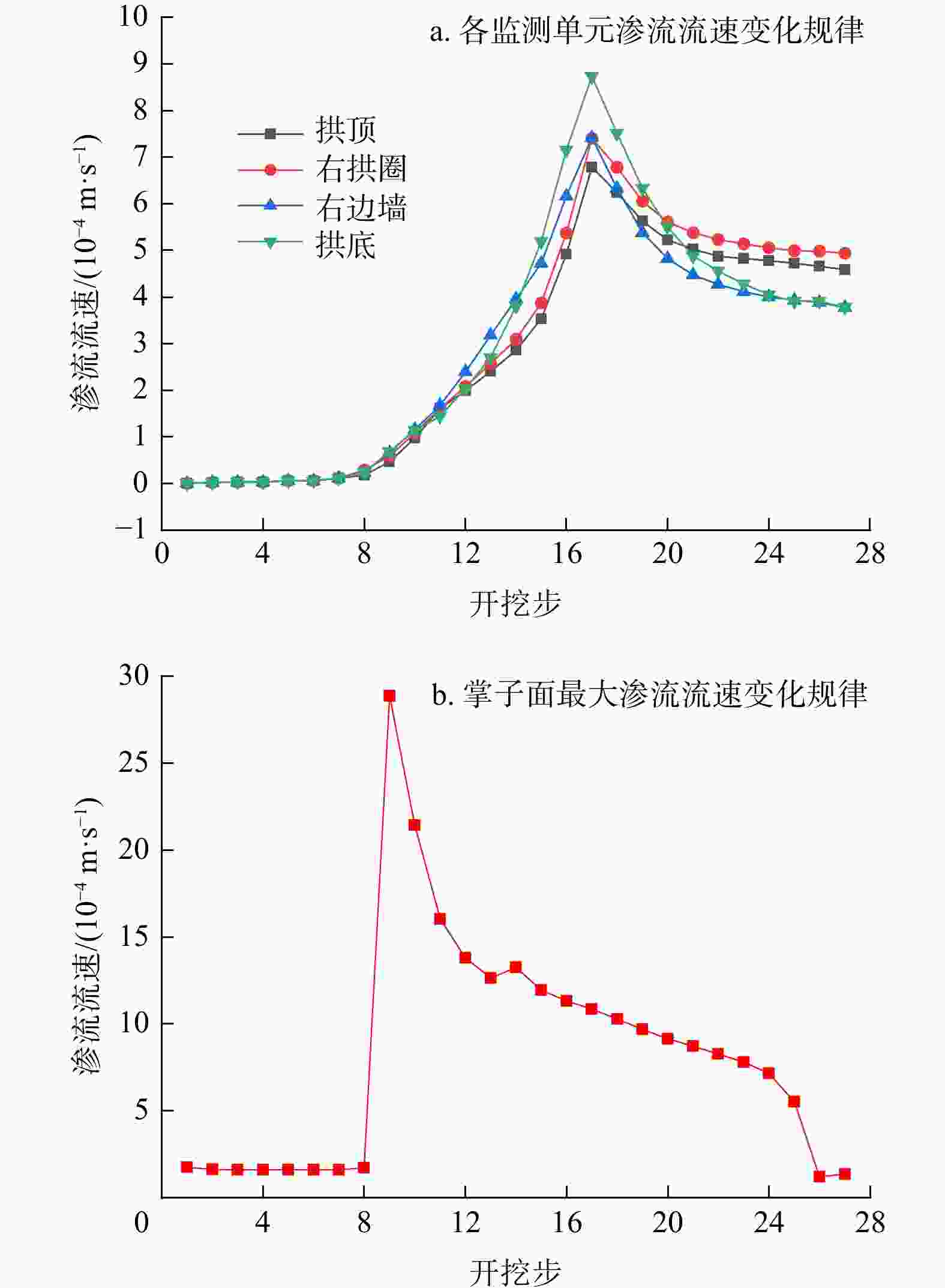
Results The results show that the minimum safe thickness of the impermeable rock mass is mainly influenced by the length, width, and inclination angle of the fault fracture zone, tunnel burial depth, and the mechanical properties of the impermeable rock mass. After tunnel excavation reaches the fault zone, internal displacement increases significantly, with abrupt changes in both the maximum and minimum principal stresses. The low pore water pressure zone expands considerably, showing a trend of initial slow decrease, followed by rapid decrease, and eventual stabilization. A high-velocity zone emerges within the fault, with overall model flow velocity increasing. During excavation, the maximum flow velocity at the tunnel face generally increases first and then decreases.
Conclusion This study provides important references for preventing water and mud inrush disasters in fault fracture zones.
-
Key words:
- deep-buried tunnel /
- water and mud inrush /
- fault fracture zone /
- impermeable rock mass /
- MIDAS GTS NX
-
表 1 模型计算参数
Table 1. Calculation parameters of the model
材料
类型容重/
(kN·m−3)饱和容重/
(kN·m−3)弹性模
量/GPa泊松
比内摩擦
角/(°)黏聚力/
MPa渗透系数/
(cm·s−1)Ⅳ级围岩 20.1 21.5 4.11 0.32 23.1 0.3 4.13×10-4 断层 19.5 18 0.9 0.3 19 0.05 4.02×10−3 -
[1] 钱七虎. 地下工程建设安全面临的挑战与对策[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(10): 1945-1956. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.10.001QIAN Q H. Challenges faced by underground projects construction safety and countermeasures[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(10): 1945-1956. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.10.001 [2] 王梦恕. 中国铁路、隧道与地下空间发展概况[J]. 隧道建设, 2010, 30(4): 351-364.WANG M S. An overview of development of railways, tunnels and underground works in China[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2010, 30(4): 351-364. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 李利平, 成帅, 张延欢, 等. 地下工程安全建设面临的机遇与挑战[J]. 山东科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 39(4): 1-13. doi: 10.16452/j.cnki.sdkjzk.2020.04.001LI L P, CHENG S, ZHANG Y H, et al. Opportunities and challenges of construction safety in underground engineering projects[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science), 2020, 39(4): 1-13. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.16452/j.cnki.sdkjzk.2020.04.001 [4] ZHONG Z L, SHEN Z, QIAO H Y, et al. Study on mechanism of water and mud inrush in deep-buried large-section tunnel crossing water-rich fault fracture zone[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2025, 58(1): 1147-1164. doi: 10.1007/s00603-024-04176-y [5] 李术才, 许振浩, 黄鑫, 等. 隧道突水突泥致灾构造分类、地质判识、孕灾模式与典型案例分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(5): 1041-1069. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.1332LI S C, XU Z H, HUANG X, et al. Classification, geological identification, hazard mode and typical case studies of hazard-causing structures for water and mud inrush in tunnels[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2018, 37(5): 1041-1069. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.1332 [6] XUE Y G, KONG F M, LI S C, et al. Water and mud inrush hazard in underground engineering: Genesis, evolution and prevention[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2021, 114: 103987. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2021.103987 [7] 郭如军, 何发亮. 隧道施工突水致灾构造及其分类[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2017, 54(1): 55-60. doi: 10.13807/j.cnki.mtt.2017.01.008GUO R J, HE F L. Geological structures inclined to hazards due to water burst in tunnel construction and their classifications[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2017, 54(1): 55-60. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.13807/j.cnki.mtt.2017.01.008 [8] 罗雄文, 何发亮. 深长隧道突水致灾构造及其突水模式研究[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2014, 51(1): 21-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6582.2014.01.004LUO X W, HE F L. A study of geological structures inclined to disaster and models of water burst in deep-buried long tunnels[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2014, 51(1): 21-25. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6582.2014.01.004 [9] 孟凡树, 王迎超, 焦庆磊, 等. 断层破碎带突水最小安全厚度的筒仓理论分析[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2020, 52(2): 89-95.MENG F S, WANG Y C, JIAO Q L, et al. Analysis of the minimum safe thickness of water inrush in fault fracture zone based on the silo theory[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020, 52(2): 89-95. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] FU H L, AN P T, CHENG G W, et al. Calculation of the safety thickness of water inrush with tunnel axis orthogonal to fault[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2021, 14(11): 931. doi: 10.1007/s12517-021-07297-8 [11] 袁东, 肖坤. 隧道穿越断层破碎带突水机制及岩墙最小安全厚度研究[J]. 地质力学学报, 2025, 31(1): 80-90. doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2024065YUAN D, XIAO K. Water inrush mechanism and the minimum safety thickness of the rock wall of a tunnel crossing a fault fracture zone[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2025, 31(1): 80-90. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2024065 [12] 张延杰, 董家兴, 周志强, 等. 近断层砂化白云岩隧洞突水涌砂演化过程及防突岩盘安全厚度研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2024, 43(3): 639-652.ZHANG Y J, DONG J X, ZHOU Z Q, et al. Water and sand inrush evolution and minimum safe thickness of waterproof resistant slab in sandy dolomite tunnels near the faults[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2024, 43(3): 639-652. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 张延杰, 浦仕江, 周辉, 等. 滇中引水工程安全建设与高效运行关键技术研究若干进展: 地下工程[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2024, 43(2): 333-357.ZHANG Y J, PU S J, ZHOU H, et al. Research progress on key technologies for safe construction and efficient operation of the Dianzhong water diversion project: Underground engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2024, 43(2): 333-357. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 张庆松, 王德明, 李术才, 等. 断层破碎带隧道突水突泥模型试验系统研制与应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(3): 417-426.ZHANG Q S, WANG D M, LI S C, et al. Development and application of model test system for inrush of water and mud of tunnel in fault rupture zone[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(3): 417-426. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] ZHANG Q S, JIANG Q C, ZHANG X, et al. Model test on development characteristics and displacement variation of water and mud inrush on tunnel in fault fracture zone[J]. Natural Hazards, 2019, 99(1): 467-492. doi: 10.1007/s11069-019-03753-7 [16] 王德明, 张庆松, 张霄, 等. 断层破碎带隧道突水突泥灾变演化模型试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2016, 37(10): 2851-2860. doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2016.10.016WANG D M, ZHANG Q S, ZHANG X, et al. Model experiment on inrush of water and mud and catastrophic evolution in a fault fracture zone tunnel[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2016, 37(10): 2851-2860. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.16285/j.rsm.2016.10.016 [17] GUO Y H, KONG Z J, HE J, et al. Development and application of the 3D model test system for water and mud inrush of water-rich fault fracture zone in deep tunnels[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021(1): 8549094. [18] 黄震, 李晓昭, 李仕杰, 等. 隧道突水模型试验流固耦合相似材料的研制及应用[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 49(12): 3029-3039. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2018.12.017HUANG Z, LI X Z, LI S J, et al. Research and development of similar material for liquid-solid coupling and its application in tunnel water-inrush model test[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2018, 49(12): 3029-3039. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2018.12.017 [19] WANG M X, YANG W M, ZHOU Z Q, et al. Experimental study on fractal characteristics of fault filling medium in the tunnel and relationship between fractal dimension and permeability coefficient[J]. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources, 2021, 8(1): 6. [20] 张振杰, 张强勇, 向文, 等. 复杂环境下新型流固耦合相似材料的研制及应用[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 52(11): 4168-4180. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.11.036ZHANG Z J, ZHANG Q Y, XIANG W, et al. Development and application of new-style hydro-mechanical coupling similar materials in complex environment[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2021, 52(11): 4168-4180. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7207.2021.11.036 [21] 杨建辉, 沈恺, 周杰, 等. 穿越富水断层破碎带隧道塌方机理分析与预防[J]. 工程地质学报, 2023, 31(1): 248-257.YANG J H, SHEN K, ZHOU J, et al. Mechanism and prevention of tunnel collapse through water-rich fault fracture zone[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2023, 31(1): 248-257. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] ZHONG Z L, WANG Z, ZHAO M, et al. Structural damage assessment of mountain tunnels in fault fracture zone subjected to multiple strike-slip fault movement[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2020, 104: 103527. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2020.103527 [23] ZHOU Z Q, JIN G H, LIU Y H, et al. A coarse-grained CFD-DEM method for efficient simulation of fluid-solid coupling failure process in geomaterials: Methodology and verification[J]. Powder Technology, 2026, 467: 121483. [24] 商成顺. 基于粗粒化理论的工程尺度DEM-CFD流固耦合模拟方法及应用[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2021.SHANG C S. A coarse-grained DEM-CFD coupling method for engineering-scale simulation and its application[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] ZHANG Z Q, CHEN Y L, ZHU X Y, et al. Investigating the evolution of debris flow disaster in tunnels: Model testing and numerical simulations[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2025, 186: 107420. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2025.107420 [26] XIE Q, CAO Z L, SUN W C, et al. Numerical simulation of the fluid-solid coupling mechanism of water and mud inrush in a water-rich fault tunnel[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2023, 131: 104796. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2022.104796 [27] 王美霞. 隧道断层破碎带渗透破坏演化机理与突水突泥防控决策方法及应用[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2022.WANG M X. Evolution mechanism of seepage failure and prevention and control method of water and mud inrush in tunnel fault and its application[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] JIANG A N, ZHENG S, WANG S Y. Stress-seepage-damage coupling modelling method for tunnel in rich water region[J]. Engineering Computations, 2020, 37(8): 2659-2683. doi: 10.1108/EC-10-2019-0465 [29] 柴琛, 周昌, 夏钊, 等. 新疆某千米埋深隧道断层控制地热成因及热害评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(4): 304-315.CHAI C, ZHOU C, XIA Z, et al. Geothermal genesis and hazard assessment for a fault-controlled kilometer-deep tunnel in Xinjiang[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(4): 304-315. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 肖竞, 万军伟, 成建梅, 等. MODFLOW-CFPv2 模型在岩溶隧道突涌水及对地下水环境影响中的应用: 以云南鹤庆锰矿沟岩溶水系统为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(3): 301-310.XIAO J, WAN J W, CHENG J M, et al. Application of MODFLOW-CFPv2 model in karst tunnel water inrush and its impact on groundwater environment: Example of the Mengkuanggou karst water system in Heqing County, Yunnan Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(3): 301-310.(in Chinese with English abstract [31] 陈迪, 闫海涛, 乔翔宇, 等. 巨厚非均质含水层中超深孔涌水量预测[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(4): 302-310.CHEN D, YAN H T, QIAO X Y, et al. Prediction of ultradeep pore water inflow in giant thick heterogeneous aquifers[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(4): 302-310.(in Chinese with English abstract [32] 石少帅. 深长隧道充填型致灾构造渗透失稳突涌水机理与风险控制及工程应用[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2014.SHI S S. Study on seepage failure mechanisim and risk control of water inrush induced by filled disaster structure in deep-long tunnel and engineering applications[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 罗雄文. 深长隧道突水突泥致灾构造及其致灾模式研究[D]. 北京: 中国铁道科学研究院, 2014.LUO X W. Study on disastrous structures and models of water-burst and mud-burst in deep and long tunnel[D]. Beijing: China Academy of Railway Sciences, 2014.(in Chinese with English abstract [34] 李鹏飞, 刘宏翔, 赵勇, 等. 隧道穿越断层破碎带防突水最小安全厚度及其影响因素[J]. 隧道与地下工程灾害防治, 2020, 2(3): 77-84.LI P F, LIU H X, ZHAO Y, et al. The minimum safe thickness of tunnel passing through fault fracture zone and its influencing factors[J]. Hazard Control in Tunnelling and Underground Engineering, 2020, 2(3): 77-84. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 郭佳奇. 岩溶隧道防突厚度及突水机制研究[D]. 北京: 北京交通大学, 2011.GUO J Q. Study on against-inrush thickness and waterburst mechanism of karst tunnel[D]. Beijing: Beijing Jiaotong University, 2011. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 中华人民共和国水利部. 水工隧洞设计规范: SL279-2016[S]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2016.Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. Specification for design of hydraulic tunnel: SL279-2016[S]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2016. (in Chinese) [37] 张金夫, 汶文钊. 大瑞铁路大柱山隧道高压富水断层处理技术[J]. 现代隧道技术, 2018, 55(3): 160-166. doi: 10.13807/j.cnki.mtt.2018.03.022ZHANG J F, WEN W Z. Construction technology for the Dazhushan tunnel in a high-pressure fault with abundant water[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology, 2018, 55(3): 160-166. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.13807/j.cnki.mtt.2018.03.022 [38] 李术才, 袁永才, 李利平, 等. 钻爆施工条件下岩溶隧道掌子面突水机制及最小安全厚度研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2015, 37(2): 313-320.LI S C, YUAN Y C, LI L P, et al. Water inrush mechanism and minimum safe thickness of rock wall of karst tunnel face under blast excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2015, 37(2): 313-320. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 陈志宇. 考虑动态泥膜的珠海大直径泥水盾构隧道掘进面稳定性分析[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2024.CHEN Z Y. Stability analysis of large-diameter slurry shield tunnel face in Zhuhai considering dynamic filter cake[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2024(in Chinese with English abstract [40] 臧东升, 裴书锋, 魏福泽, 等. 复合地层输水竖井围岩与支护稳定性分析[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 46(5): 60-67. doi: 10.19760/j.ncwu.zk.2025074ZANG D S, PEI S F, WEI F Z, et al. Stability analysis of surrounding rock and support of water conveyance shaft in composite formation[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition), 2025, 46(5): 60-67. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.19760/j.ncwu.zk.2025074 -




 下载:
下载: