Numerical simulation of conduit-type karst groundwater system based on TOPMODEL and MODFLOW-CFP
-
摘要:
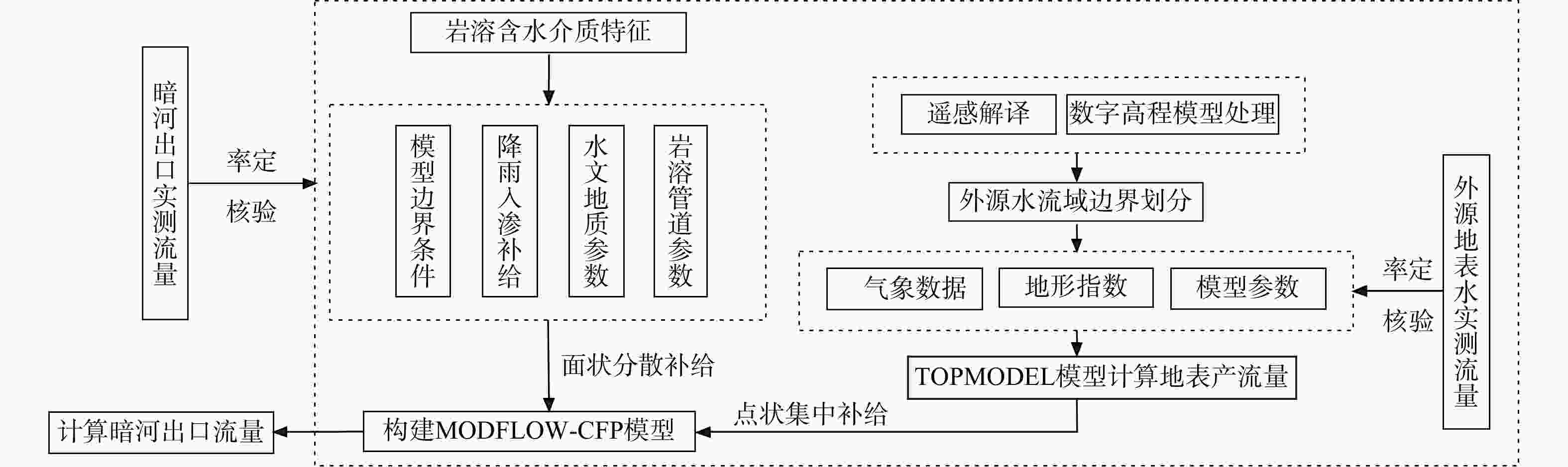
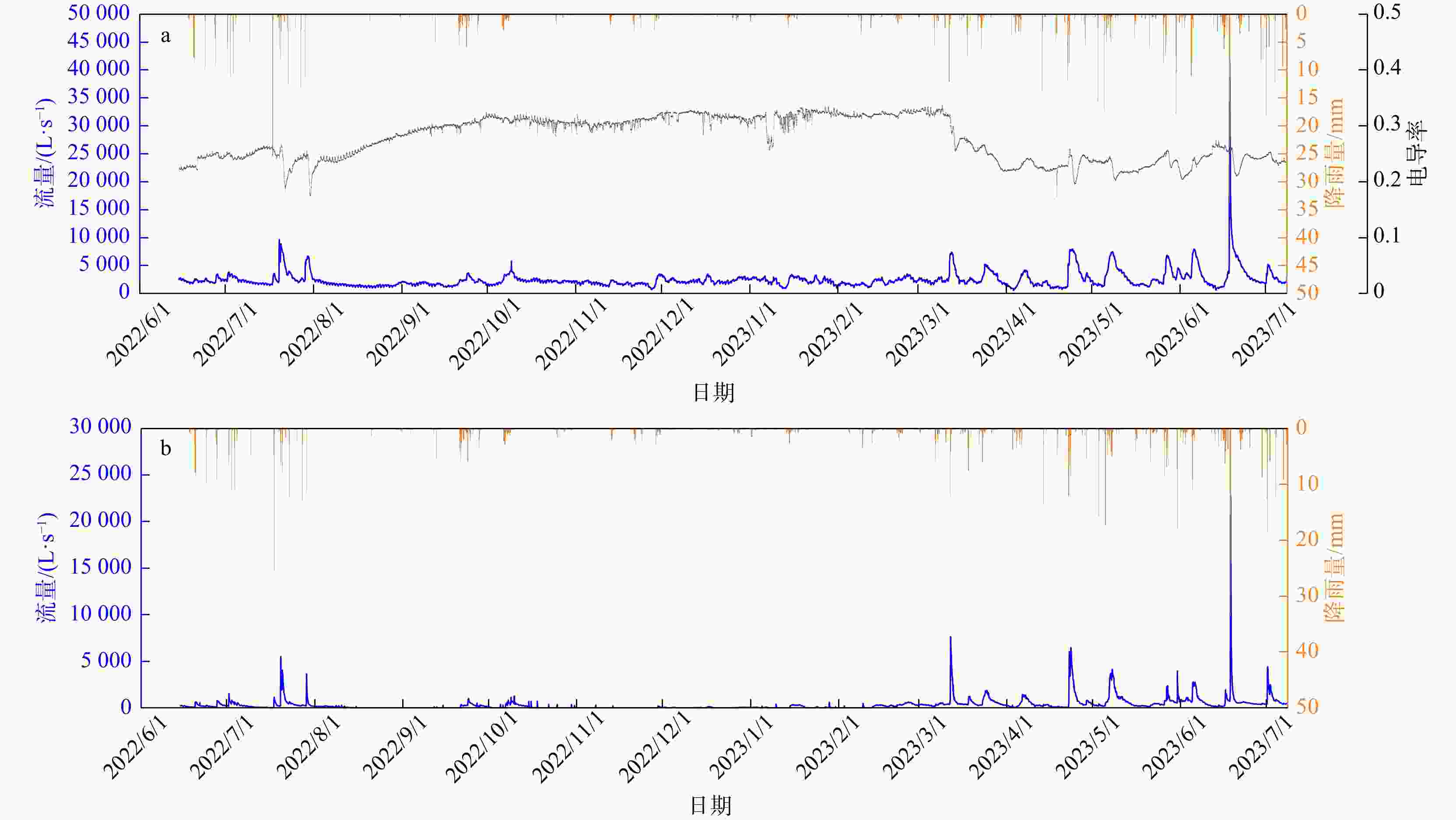
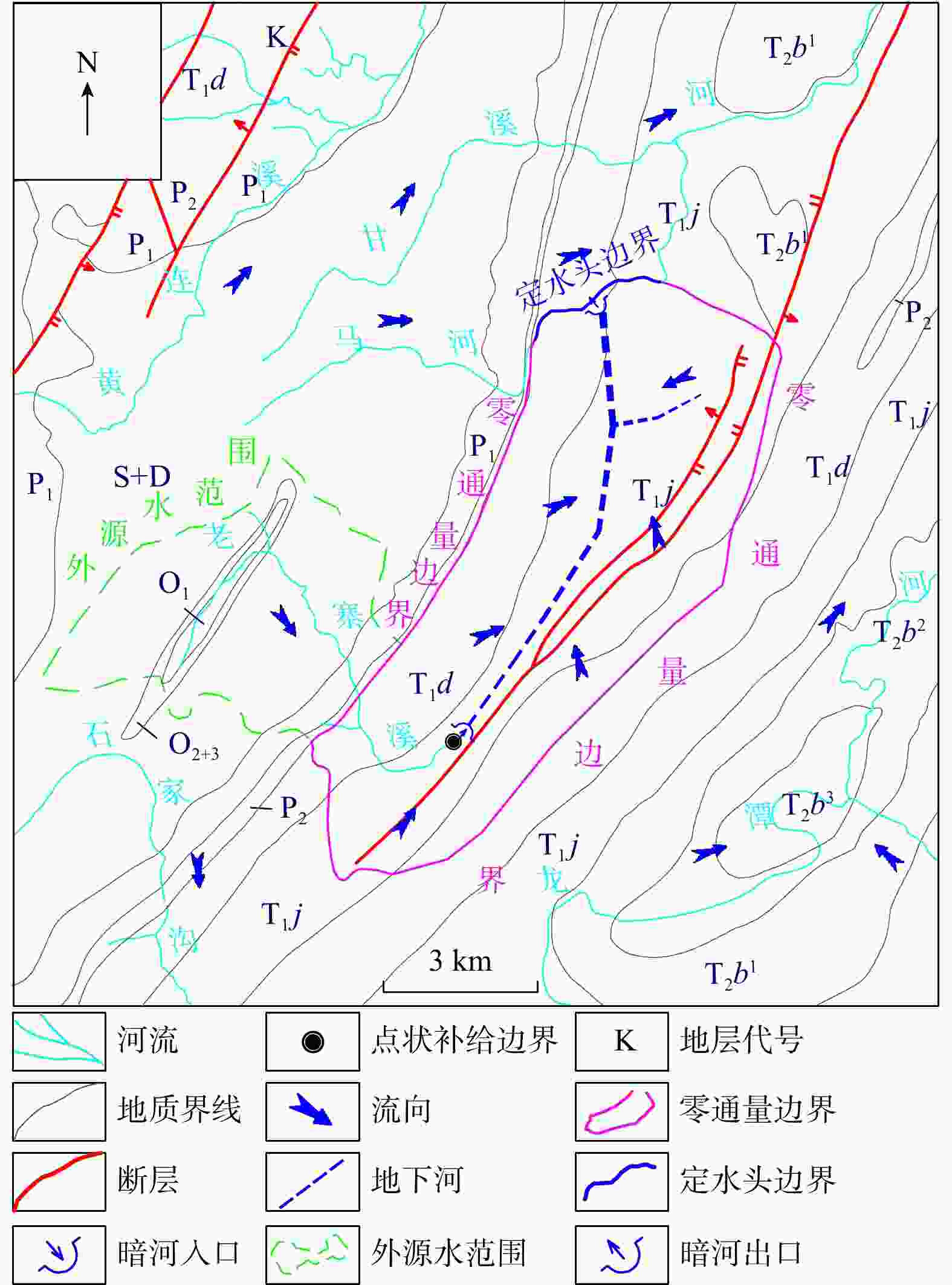
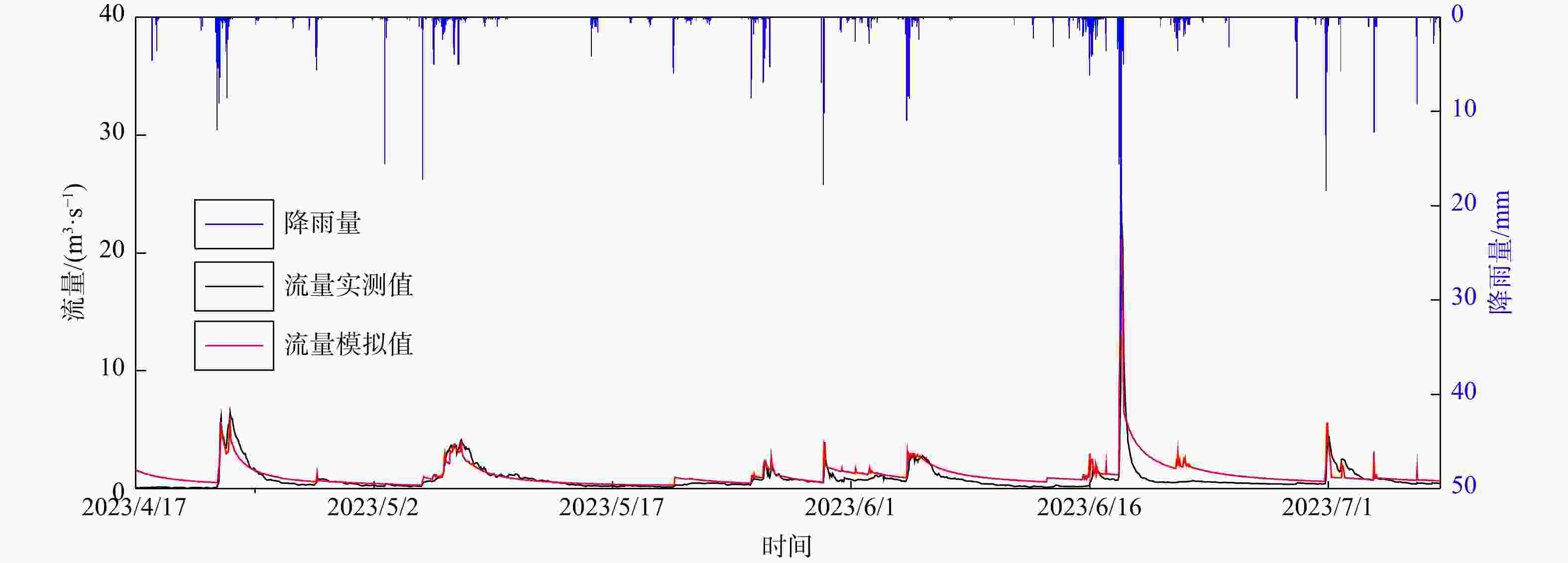
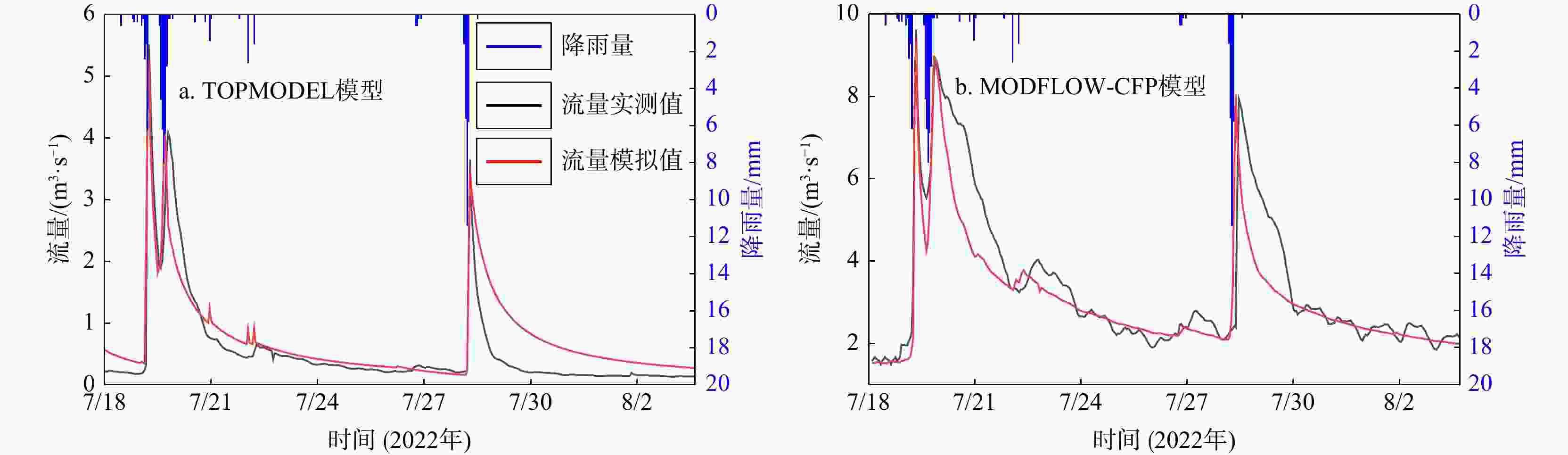
非岩溶区外源水是西南岩溶地下水系统较常见的补给来源,外源水的快速、集中补给方式使岩溶地下水系统的水循环表现出独特的响应,这种特殊补给方式的岩溶水系统调查、监测和数值模拟方法尚不够完善。为探究外源水补给型岩溶水系统数值模拟技术方法,以湖北省恩施市甘溪渔泉洞岩溶水系统为研究对象,在岩溶水系统含水介质特征、补给方式调查、地下水示踪试验以及高分辨率降雨−地表−地下径流的动态监测等工作基础上,采用MODFLOW-CFP数值模型刻画岩溶裂隙与管道双重介质特征,并针对岩溶管道入口处非岩溶区外源水集中灌入式补给的特点,采用地表水模型TOPMODEL来定量刻画非岩溶区外源水的产汇流过程,将其作为MODFLOW-CFP模型中岩溶管道入口的流量边界条件,实现地表−地下水模型的耦合,从而提高MODFLOW-CFP对外源水刻画的精度。研究结果表明:利用TOPMODEL和MODFLOW-CFP模型模拟甘溪渔泉洞暗河出口流量,与实测值对比峰值相对误差在0.7%~19.7%,峰现时差在3 h内,相关系数
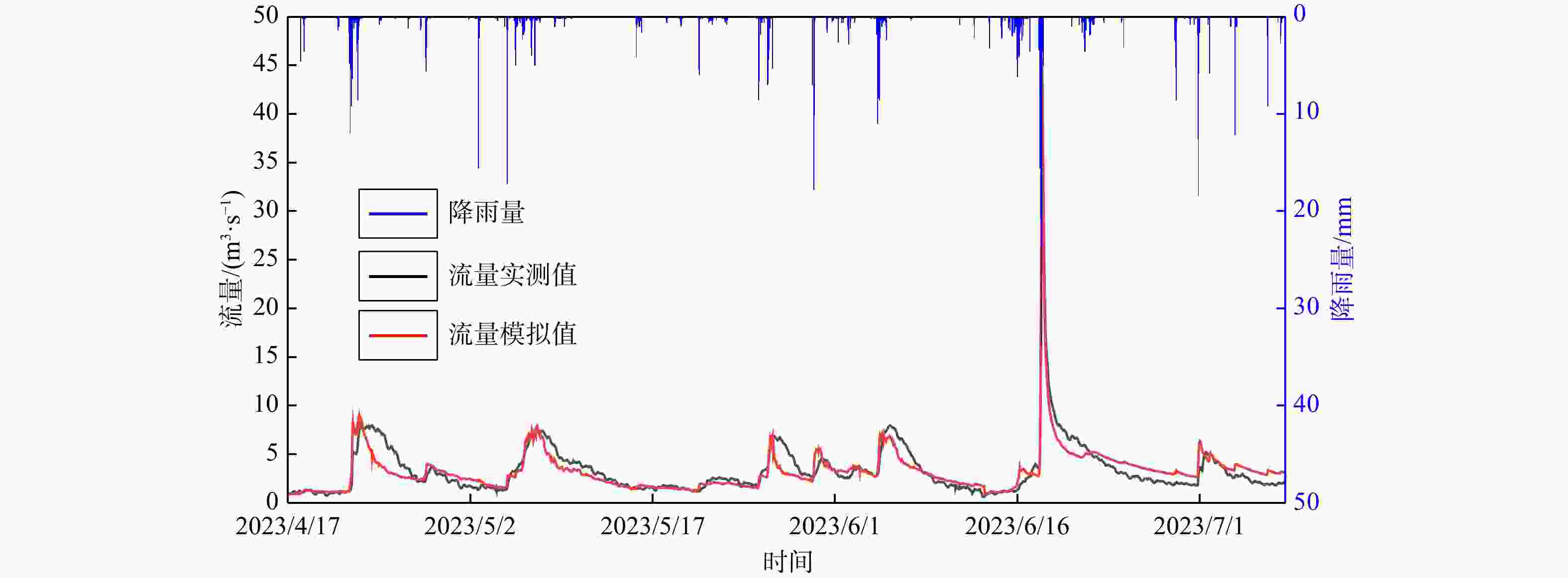
R 2为0.93,纳什效率系数NSE 为0.86。对模型的正确性进行检验,检验期模拟得到的暗河出口流量与实测值对比峰值相对误差在1.1%~2.5%,峰现时差在2 h内,相关系数R 2为0.91,纳什效率系数NSE 为0.77,有较好的拟合精度。本研究构建的TOPMODEL和MODFLOW-CFP耦合模型在外源水补给型岩溶水系统降雨−水文响应过程模拟上有着推广价值。Abstract:External water from non-karst areas is a common recharge source for karst groundwater system in Southwest China. The rapid and concentrated recharge of external water can lead to a unique hydrological response in the water-cycle processes of karst groundwater systems. Methods for investigation, monitoring, and numerically simulating for this special external-recharge process in karst groundwater systems remain insufficiently developed.
Objective This study aims to investigate the numerical simulation method for karst groundwater systems recharged by external water.
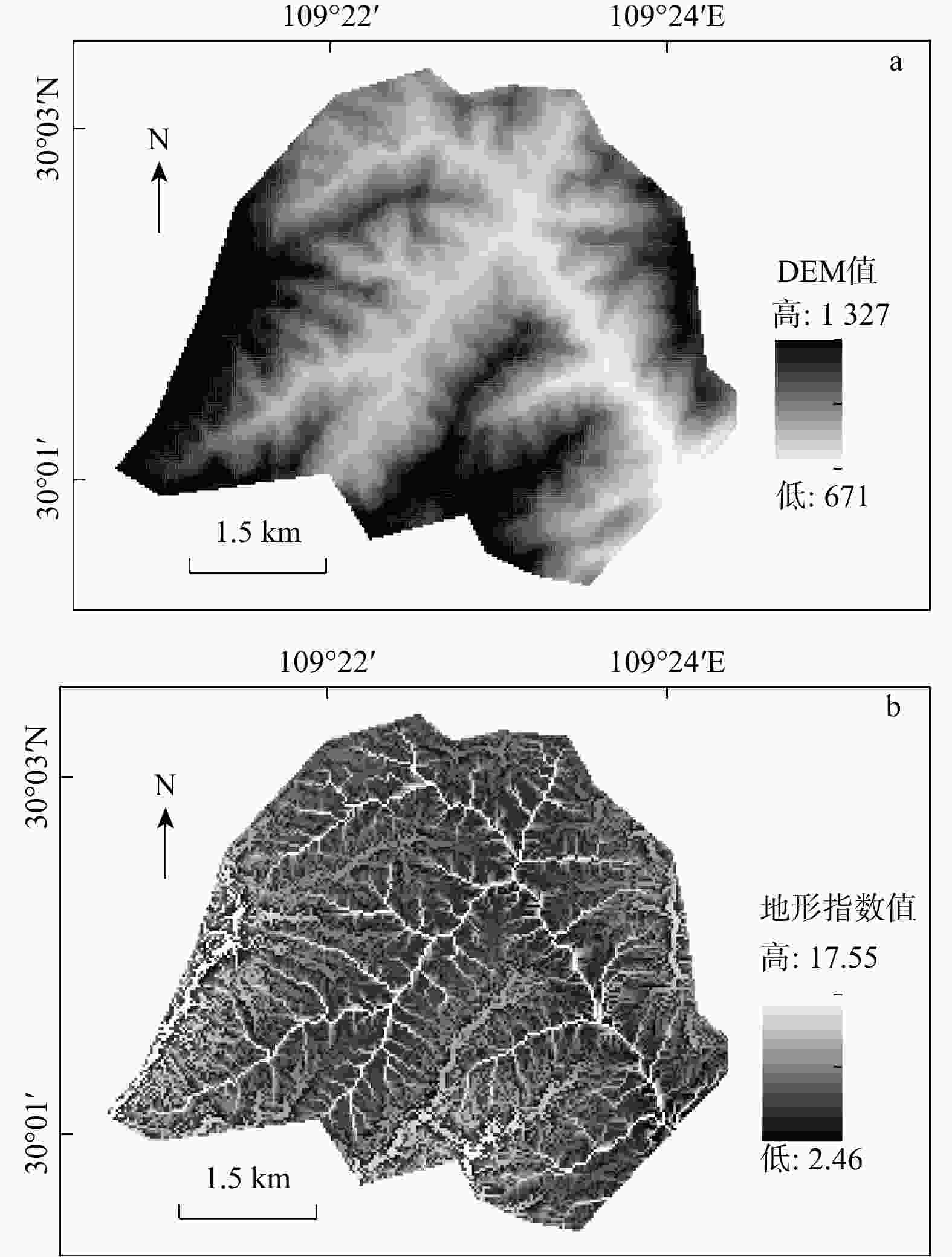
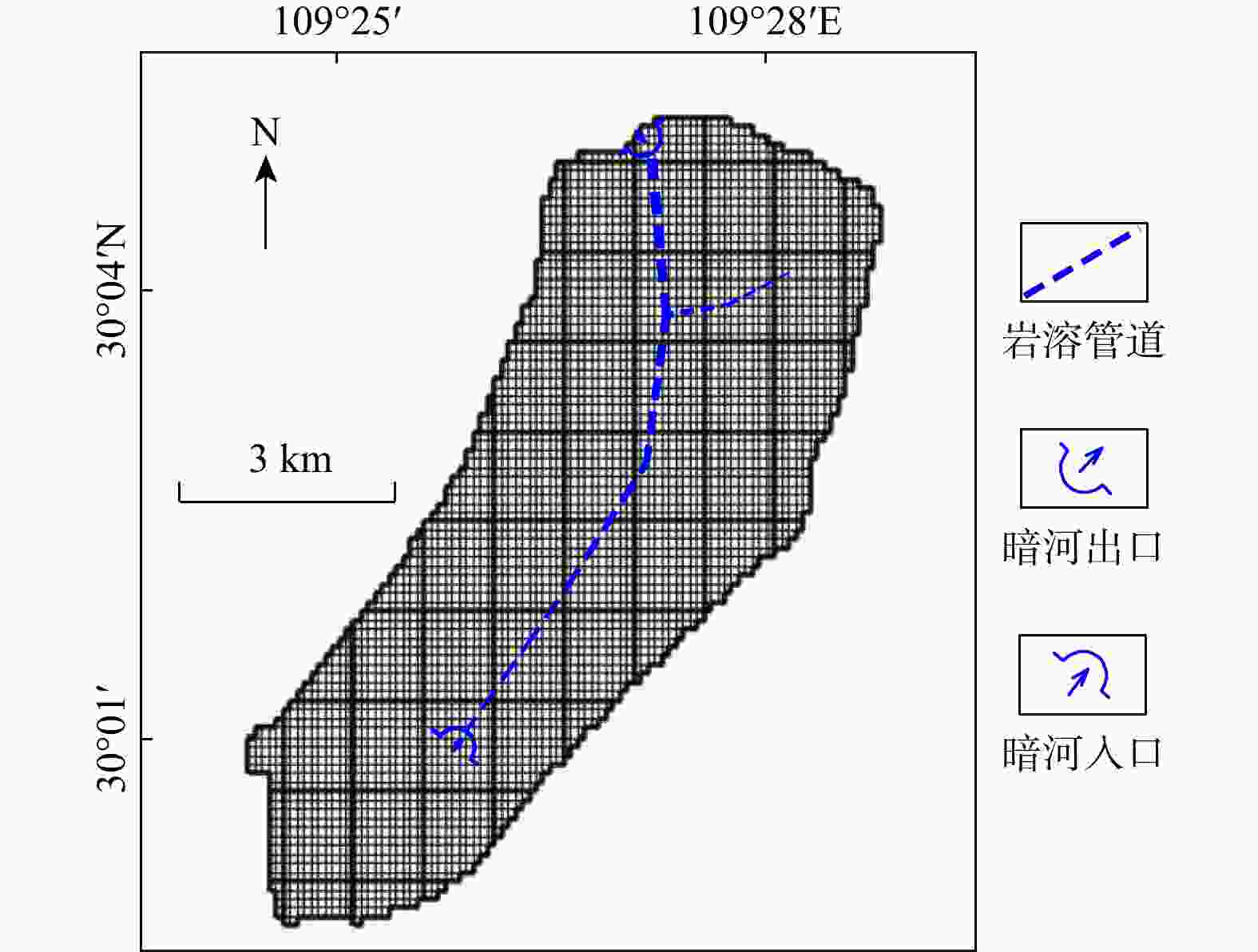
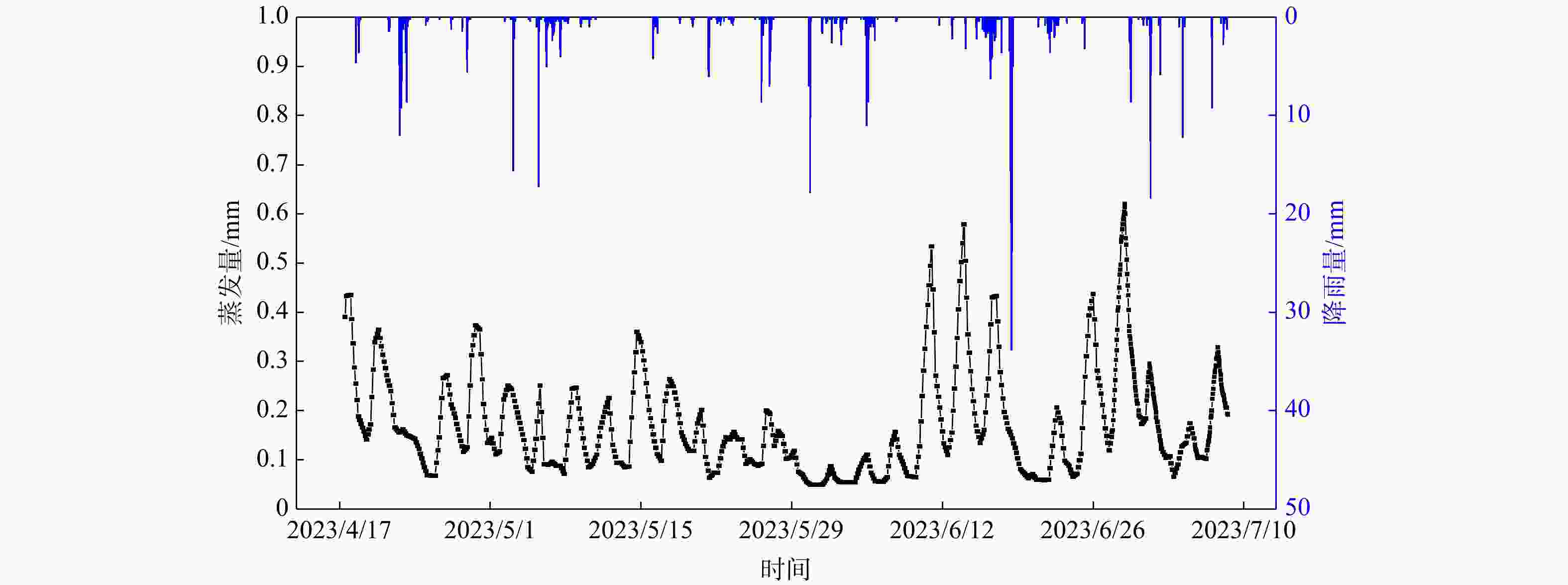
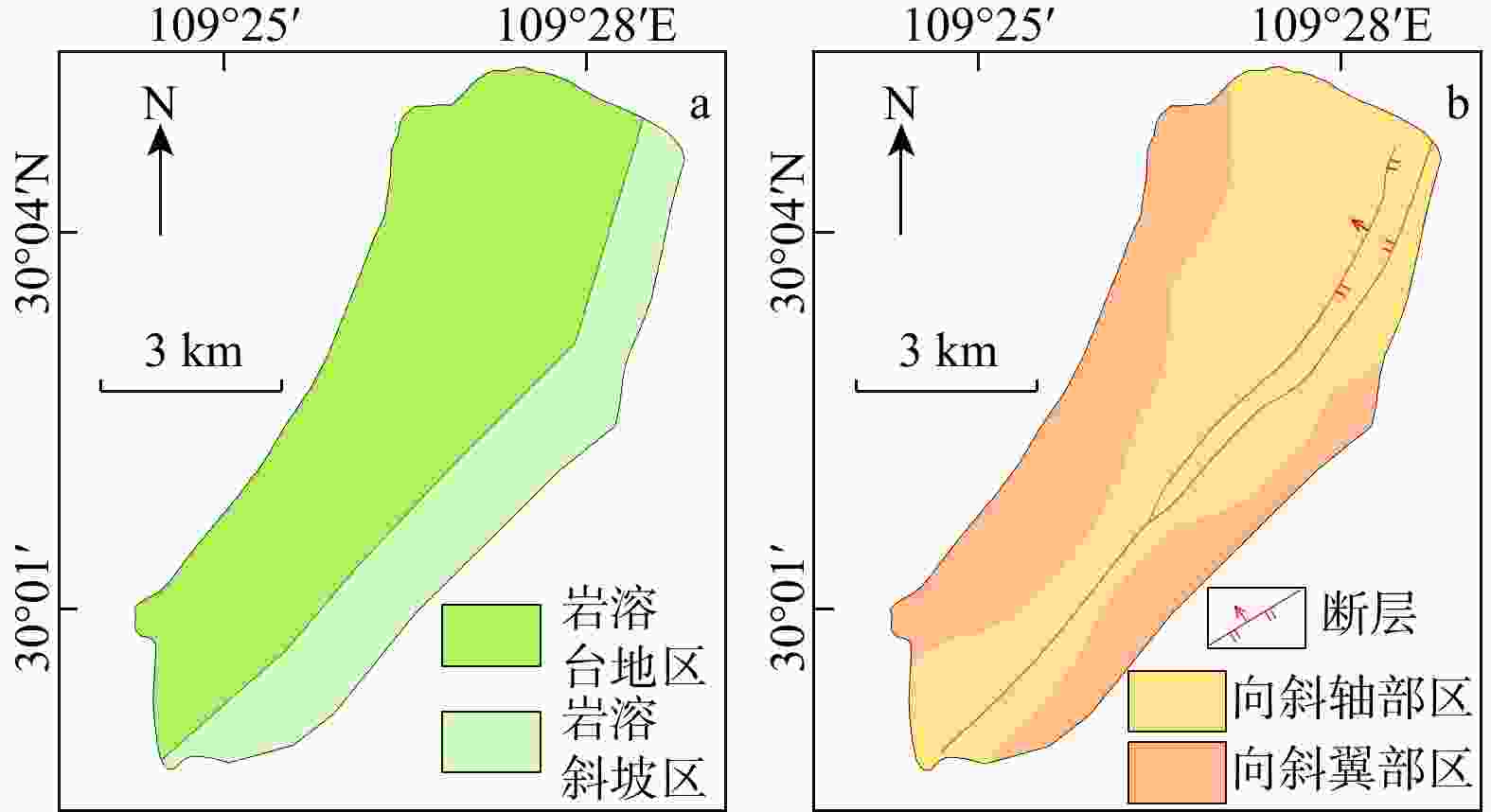
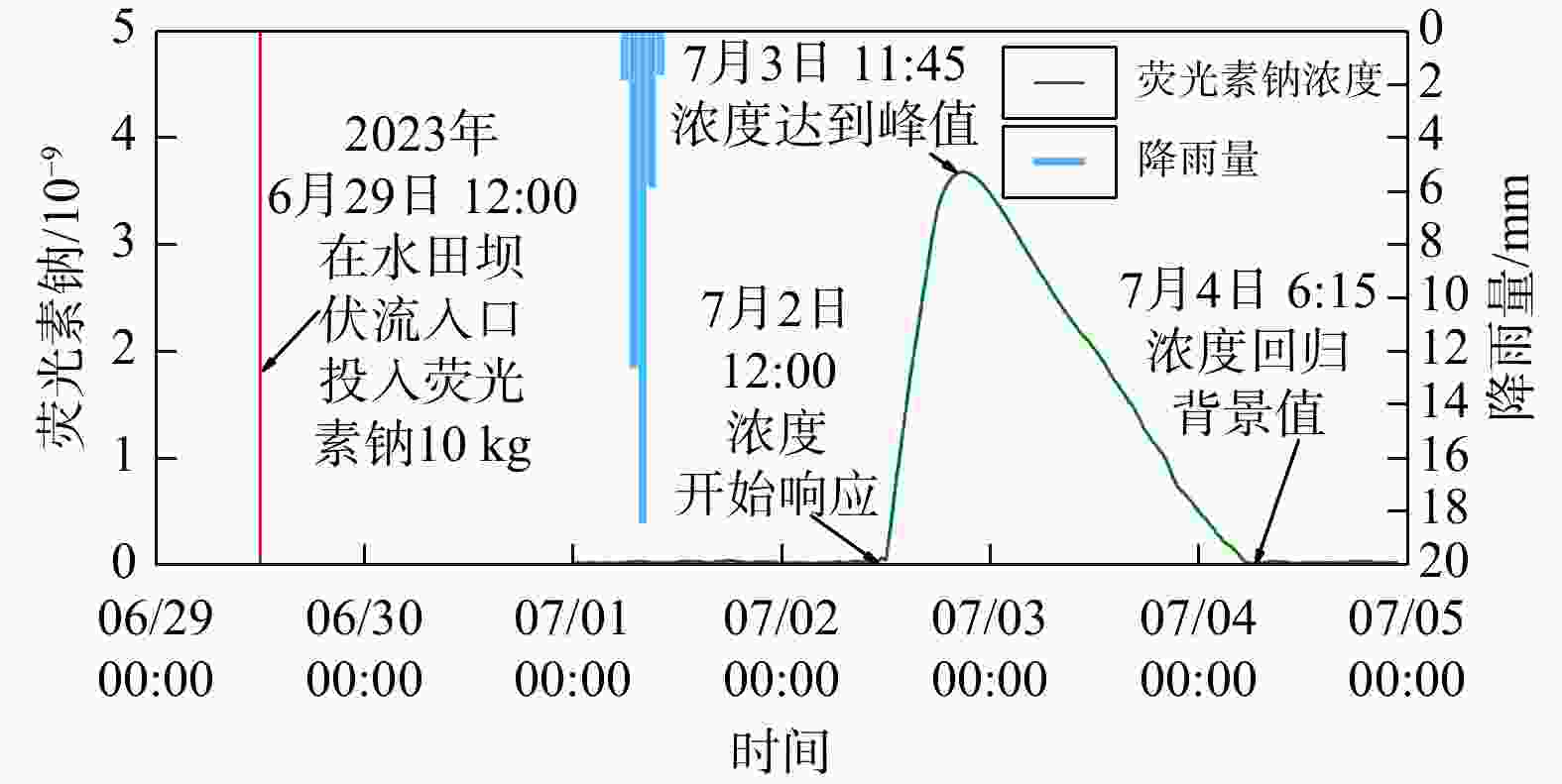
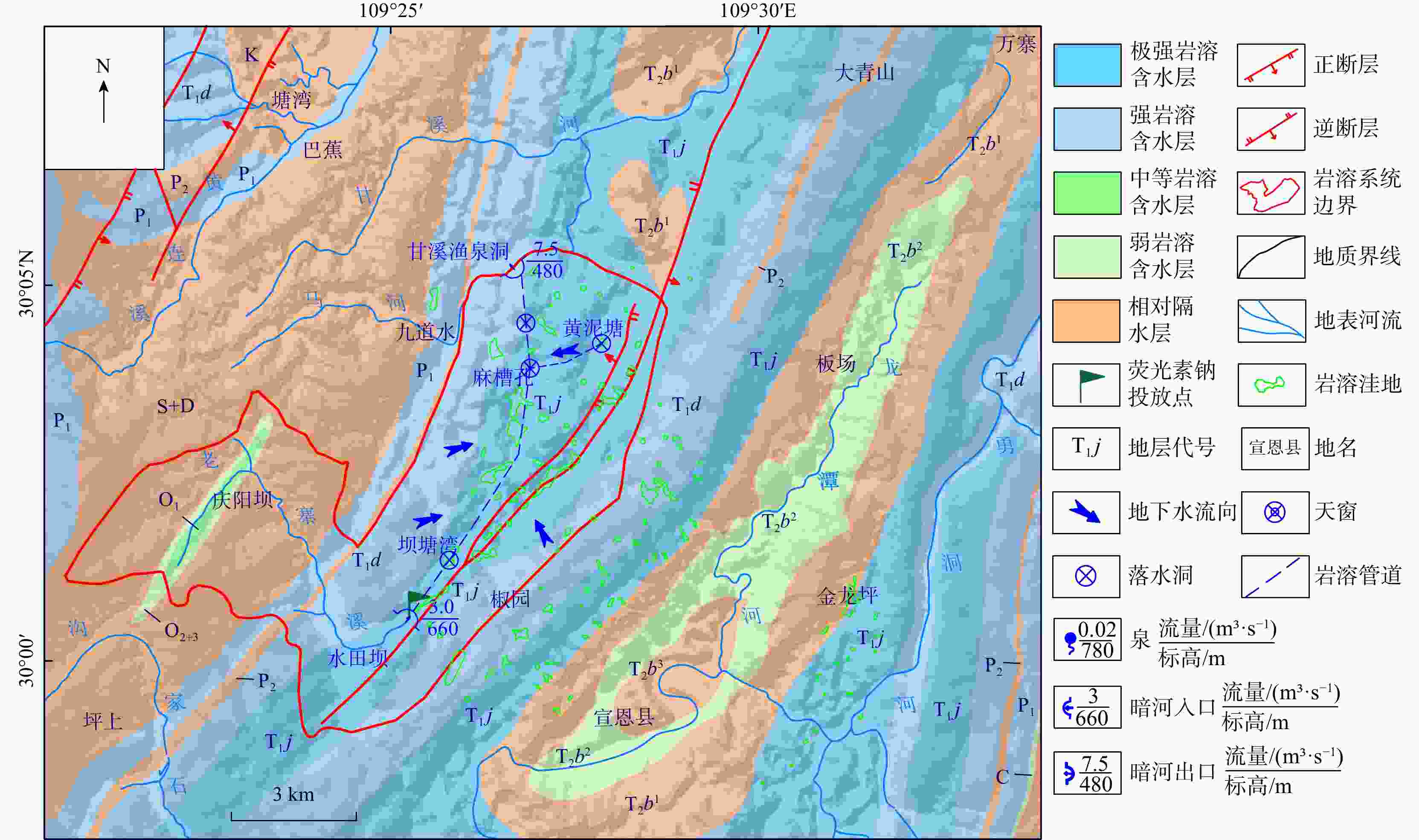
Methods Taking the Ganxi Yuquan Cave karst groundwater system in Enshi, Hubei as the study area, detailed investigation of the hydrogeological characteristics and recharge patterns of the karst groundwater system was conducted. Underground tracer tests and high-resolution monitoring of rainfall-surface-subsurface runoff dynamics were carried out. The MODFLOW-CFP numerical model was used to represent the dualmedium characteristics of karst fissures and conduits. Focusing on the concentrated inflow of external water from non-karst areas at the entrance of karst conduits, the surface water model TOPMODEL was used to quantitatively characterize the runoff generation and concentration processes of external water from non-karst catchment. This output was then set as the flow boundary condition at the conduit entrances in the MODFLOW-CFP model, achieving the coupling of surface water and groundwater models, and thereby improving the accuracy of representing external water recharge in the MODFLOW-CFP simulations.
Results The results show that when the coupled TOPMODEL and MODFLOW-CFP model is used to simulate the discharge at the outlet of the Ganxi Yuquan Cave karst groundwater system, the relative peak errors compared with the measured values range from 0.7% to 19.7%, the peak-time lag is within 3 hours, the correlation coefficient (
R 2) is 0.93, and the Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE ) is 0.86. During the validating period, the relative peak errors of the simulated outlet discharge of the Ganxi Yuquan Cave karst groundwater system compared with the measured values ranged from 1.1% to 2.5%, with peak-time lag within 2 hours,R 2 of 0.91, andNSE of 0.77, indicating good model performance.Conclusion These findings indicate that the coupled TOPMODEL and MODFLOW-CFP model developed in this study has practical value for simulating the rainfall-runoff and hydrological response processes of karst groundwater systems with external water recharge.
-
表 1 TOPMODEL模型参数
Table 1. Parameters of the TOPMODEL
参数 Q0 T0 M Td SR0 SRmax CHV RV XK0 HF DTH 单位 m/h m2/h m h m m m/h m/h m/h m % 取值 0.0002 1.5 0.04 1 0 0.05 3600 3600 1 0.1 10 注:参数含义见正文 -
[1] HARTMANN A, KRALIK M, HUMER F, et al. Identification of a karst system’s intrinsic hydrodynamic parameters: Upscaling from single springs to the whole aquifer[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2012, 65(8): 2377-2389. doi: 10.1007/s12665-011-1033-9 [2] JUKIĆ D, DENIĆ-JUKIĆ V. Groundwater balance estimation in karst by using a conceptual rainfall-runoff model[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2009, 373(3/4): 302-315. [3] ROZOS E, KOUTSOYIANNIS D. A multicell karstic aquifer model with alternative flow equations[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2006, 325(1/2/3/4): 340-355. [4] RONAYNE M J. Influence of conduit network geometry on solute transport in karst aquifers with a permeable matrix[J]. Advances in Water Resources, 2013, 56: 27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2013.03.002 [5] WORTHINGTON S R H. Diagnostic hydrogeologic characteristics of a karst aquifer (Kentucky, USA)[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2009, 17(7): 1665-1678. doi: 10.1007/s10040-009-0489-0 [6] 赵良杰, 夏日元, 杨杨, 等. 基于MODFLOW的岩溶管道水流模拟方法探讨与应用[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(3): 346-351.ZHAO L J, XIA R Y, YANG Y, et al. Discussion and application of simulation methods for karst conduit flow based on MODFLOW[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(3): 346-351. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 周志浩, 罗明明, 陈静, 等. 集中补给条件对岩溶地下河水文过程及污染响应的影响[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(3): 324-333.ZHOU Z H, LUO M M, CHEN J, et al. Effects of concentrated recharge conditions on hydrological processes and pollution responses of karst underground rivers[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(3): 324-333. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] LIEDL R, SAUTER M, HÜCKINGHAUS D, et al. Simulation of the development of karst aquifers using a coupled continuum pipe flow model[J]. Water Resources Research, 2003, 39(3): 1057. [9] 陈崇希. 岩溶管道−裂隙−孔隙三重空隙介质地下水流模型及模拟方法研究[J]. 地球科学, 1995, 20(4): 361-366.CHEN C X. Groundwater flow model and simulation method in triple media of karstic tube-fissure-pore[J]. Earth Science, 1995, 20(4): 361-366. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] SHOEMAKER W B, KUNIANSKY E L, BIRK S , et al . Documentation of a conduit flow process (CFP) for MODFLOW-2005 [M]. USGS : Techniques and Methods , 2007: 33-39. [11] REIMANN T, HILL M E. MODFLOW-CFP: A new conduit flow process for MODFLOW-2005[J]. Groundwater, 2009, 47(3): 321-325. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2009.00561.x [12] 谭家华. MODFLOW-CFP软件在岩溶水系统数值模拟应用中的若干关键问题[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(4): 636-647.TAN J H. Several key issues in the application of MODFLOW-CFP software to the numerical simulation of karst water systems[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(4): 636-647. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 刘道涵, 徐俊杰, 齐信, 等. 基于高密度电法的城市岩溶地下水通道三维电性成像[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(6): 1331-1338.LIU D H, XU J J, QI X, et al. Three-dimensional electrical imaging of urban karst groundwater channels based on electrical resistivity tomography[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(6): 1331-1338. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] XU Z X, HU B X, DAVIS H, et al. Numerical study of groundwater flow cycling controlled by seawater/freshwater interaction in a coastal karst aquifer through conduit network using CFPv2[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2015, 182: 131-145. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2015.09.003 [15] XU Z X, HU B X. Development of a discrete-continuum VDFST-CFP numerical model for simulating seawater intrusion to a coastal karst aquifer with a conduit system[J]. Water Resources Research, 2017, 53(1): 688-711. doi: 10.1002/2016WR018758 [16] 覃夏南, 姜光辉, 夏源. 考虑非饱和带作用及管道流的岩溶泉流量模拟[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2019, 39(3): 622-627.QIN X N, JIANG G H, XIA Y. Karst spring flow simulation considering the effects of unsaturated zone and pipe flow[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2019, 39(3): 622-627. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 焦友军, 潘晓东, 曾洁, 等. 岩溶管道结构影响泉流量变化的数值模拟研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 2017, 36(5): 736-742.JIAO Y J, PAN X D, ZENG J, et al. Numerical modeling of the influence of karst-conduit structure on variation of spring flow[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2017, 36(5): 736-742. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] 赵良杰, 夏日元, 杨杨, 等. 基于CFP的岩溶管道流数值模拟研究: 以桂林寨底地下河子系统为例[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(2): 225-232.ZHAO L J, XIA R Y, YANG Y, et al. Research on numerical simulation of karst conduit media based on CFP: A case study of Zhaidi karst underground river subsystem of Guilin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2018, 39(2): 225-232. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 杨杨, 赵良杰, 苏春田, 等. 基于CFP的岩溶管道流溶质运移数值模拟研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2019, 46(4): 51-57.YANG Y, ZHAO L J, SU C T, et al. A study of the solute transport model for karst conduits based on CFP[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(4): 51-57. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 党志文, 邵景力, 崔亚莉, 等. 基于MODFLOW-CFP的贵州大井流域岩溶地下水数值模拟[J]. 中国岩溶, 2023, 42(2): 266-276.DANG Z W, SHAO J L, CUI Y L, et al. Numerical simulation of karst groundwater in Dajing basin of Guizhou Province based on MODFLOW-CFP[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2023, 42(2): 266-276. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 常勇. 裂隙−管道二元结构的岩溶泉水文过程分析与模拟[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2015.CHANG Y. Analysis and simulation of the hydrological process of the karst aquifer with fracture-conduit dual structure[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 肖竞, 万军伟, 成建梅, 等. MODFLOW-CFPv2模型在岩溶隧道突涌水及对地下水环境影响中的应用: 以云南鹤庆锰矿沟岩溶水系统为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(3): 301-310.XIAO J, WAN J W, CHENG J M, et al. Application of MODFLOW-CFPv2 model in karst tunnel water inrush and its impact on groundwater environment: Example of the Mengkuanggou karst water system in Heqing County, Yunnan Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(3): 301-310. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 杨郑秋, 杨杨, 邵景力, 等. 基于MODFLOW-CFP的岩溶水模型降雨非线性入渗补给研究: 以湖南省香花岭地区为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2019, 38(5): 691-695.YANG Z Q, YANG Y, SHAO J L, et al. Study on non-linear rainfall infiltration recharge of numerical karst water model based on MODFLOW-CFP: A case study of Xianghualing area, Hunan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2019, 38(5): 691-695. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 常威. 复杂岩溶水系统识别及其在隧道涌水量预测的应用研究: 以张吉怀高铁大青山隧道为例[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2021.CHANG W. Study on the identification of complex karst water system and its application in tunnel water disaster prediction: Take the Daqing Mountain tunnel of the Zhangjiajie-Jishou-Huaihua High-Speed Railway as an example[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 杨晓洲. 基于TOPMODEL模型的安墩水流域洪水模拟研究[D]. 郑州: 华北水利水电大学, 2023.YANG X Z. TOPMODEL-based flood simulation study of Andun basin[D]. Zhengzhou: North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 李振亚, 黄国新, 肖凤林, 等. 基于TOPMODEL的分布式水文模型在中小流域的应用研究[J]. 江西水利科技, 2020, 46(5): 374-381.LI Z Y, HUANG G X, XIAO F L, et al. Application of distributed hydrological model based on TOPMODEL in small and medium-sized river basins[J]. Jiangxi Hydraulic Science & Technology, 2020, 46(5): 374-381. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 索立涛, 万军伟, 卢学伟. TOPMODEL模型在岩溶地区的改进与应用[J]. 中国岩溶, 2007, 26(1): 67-70.SUO L T, WAN J W, LU X W. Improvement and application of TOPMODEL in karst region[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2007, 26(1): 67-70. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 熊立华, 郭生练. 分布式流域水文模型[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2004.XIONG L H, GUO S L. Distributed watershed hydrological model[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2004. (in Chinese) [29] 罗明明, 尹德超, 张亮, 等. 南方岩溶含水系统结构识别方法初探[J]. 中国岩溶, 2015, 34(6): 543-550.LUO M M, YIN D C, ZHANG L, et al. Identifying methods of karst aquifer system structure in South China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2015, 34(6): 543-550. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 康凤新, 郑婷婷, 冯亚伟, 等. 北方岩溶区降水入渗补给系数及补给机制: 以羊庄岩溶水系统为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 268-282.KANG F X, ZHENG T T, FENG Y W, et al. Recharge coefficients and recharge mechanisms of precipitation to groundwater in karst areas of North China: A case study of Yangzhuang karst water system[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 268-282. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 尹德超, 罗明明, 张亮, 等. 基于流量衰减分析的次降水入渗补给系数计算方法[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2016, 43(3): 11-16.YIN D C, LUO M M, ZHANG L, et al. Methods of calculating recharge coefficient of precipitation event based on spring recession analyses[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(3): 11-16. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 杨闪. 基于放水试验和示踪试验的岩溶通道研究[J]. 现代矿业, 2023, 39(8): 47-50.YANG S. Study on karst channel based on water discharge test and tracer test[J]. Modern Mining, 2023, 39(8): 47-50. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 陈亚洲, 董维红. 利用示踪试验时间−浓度曲线分析岩溶管道结构特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2022, 49(1): 41-47.CHEN Y Z, DONG W H. Analysis of structural characteristics of karst conduit by timeconcentration curve of tracer test[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(1): 41-47. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 於开炳, 安祥龙, 汤罗圣, 等. 外源补给型岩溶管道系统特征及隧道涌水条件研究: 以利咸高速楼门隧道为例[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2023, 30(3): 100-108.YU K B, AN X L, TANG L S, et al. Characteristics of external recharge karst pipeline system and water inflow condition: Taking Loumen tunnel in Lixian expressway as an example[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2023, 30(3): 100-108. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 王泽君, 周宏, 齐凌轩, 等. 岩溶水系统结构和水文响应机制的定量识别方法: 以三峡鱼迷岩溶水系统为例[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(12): 4512-4523.WANG Z J, ZHOU H, QI L X, et al. Method for characterizing structure and hydrological response in karst water systems: A case study in Y-M system in Three Gorges area[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(12): 4512-4523. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 李兴男, 金江跃, 降亚楠. 地下水数值模型结构不确定性对模拟结果的影响分析[J]. 排灌机械工程学报, 2021, 39(2): 179-185.LI X N, JIN J Y, JIANG Y N. Analysis of groundwater numerical model structural uncertainty on simulation results[J]. Journal of Drainage and Irrigation Machinery Engineering, 2021, 39(2): 179-185. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 陆文, 陆垂裕, 何鑫, 等. 处理地下水模型单元疏干−湿润的两种算法对比研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2024, 51(5): 22-34.LU W, LU C Y, HE X, et al. Comparative study on two drying-rewetting algorithms of groundwater model cells[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(5): 22-34. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: