Logging identification and saturation estimation method for hydrate-bearing gas layers in the deep water and ultra-shallow strata of the South China Sea
-
摘要:
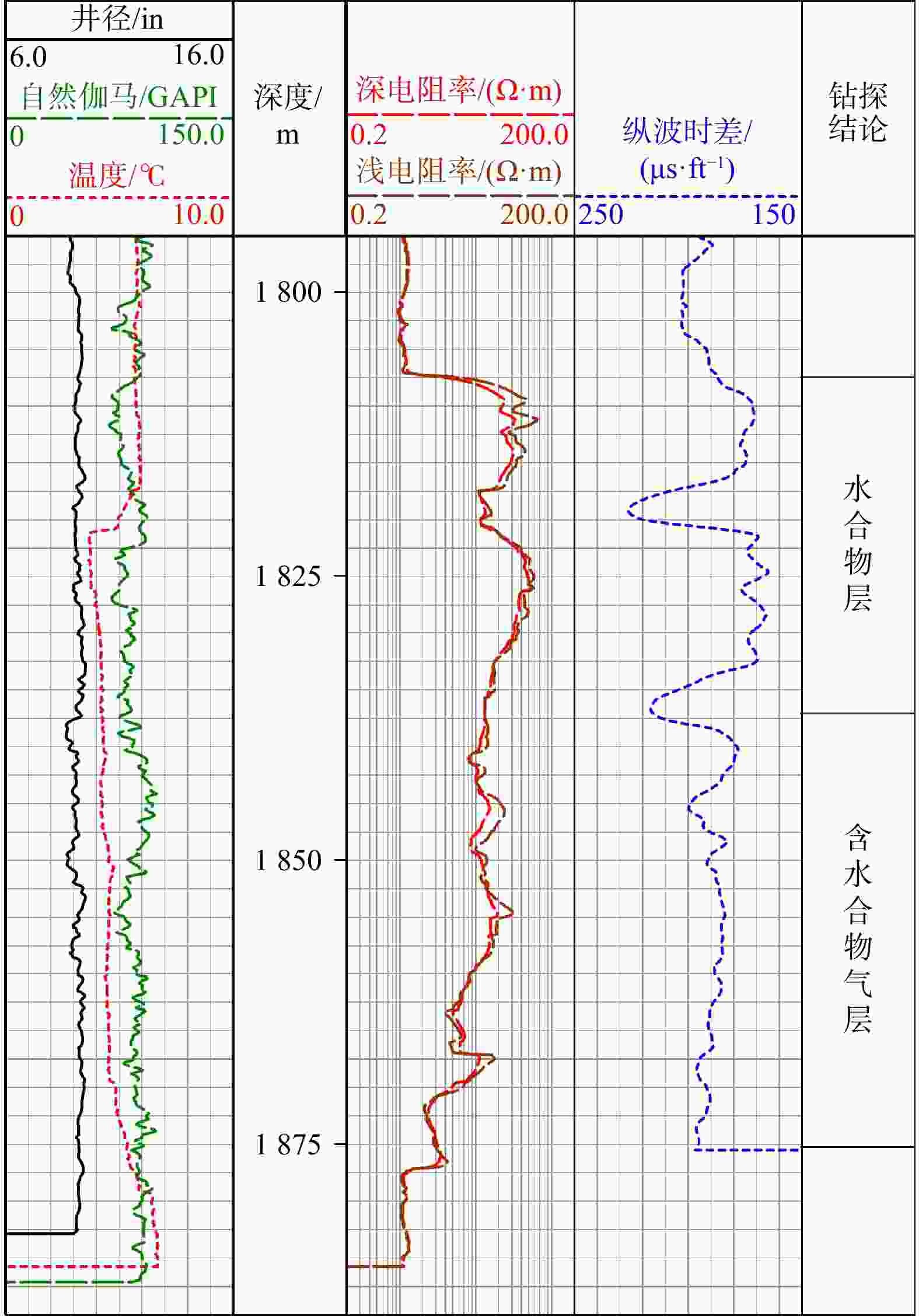
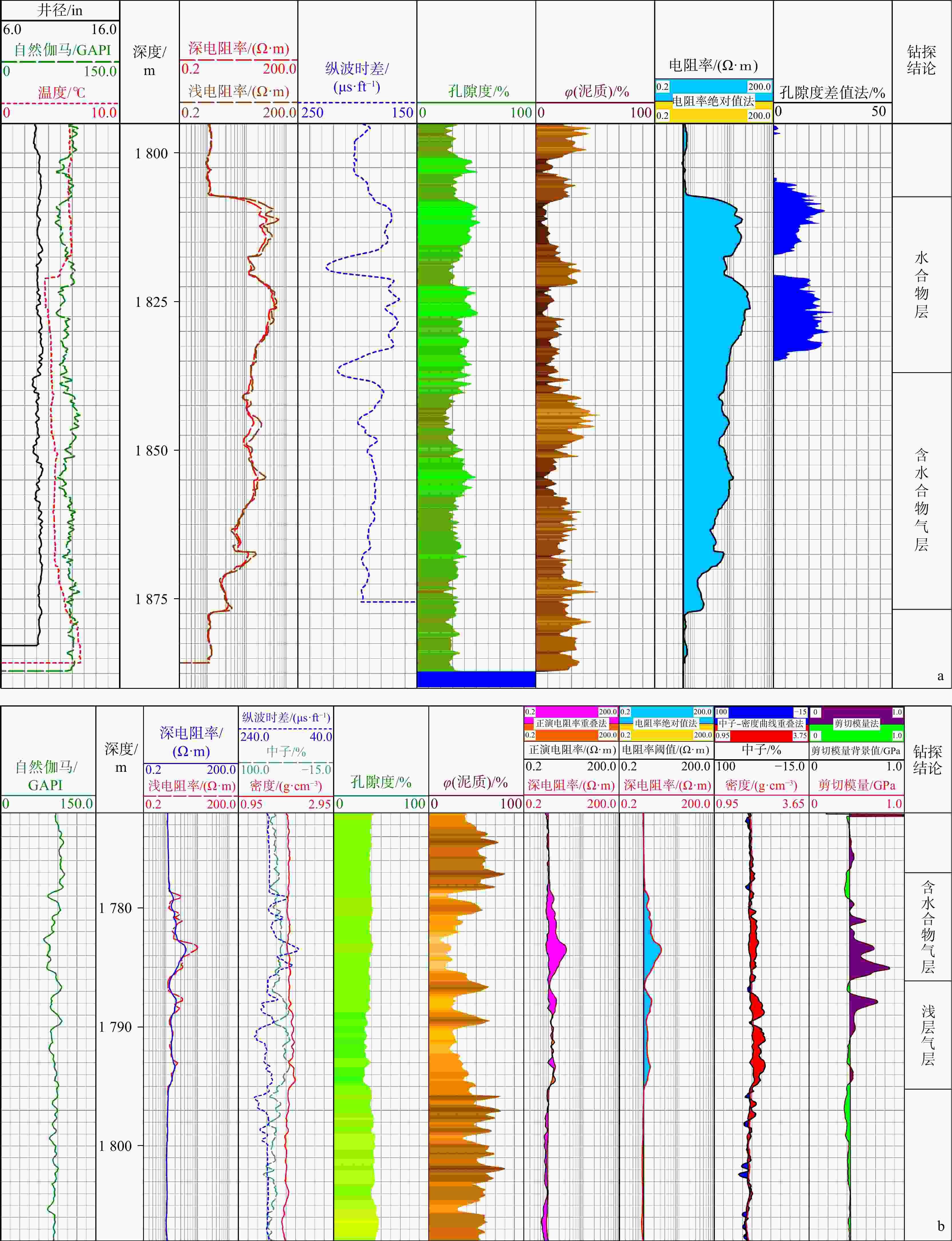
在海域天然气水合物的勘探过程中,含水合物气层因同时赋存天然气水合物与浅层气,电性测井响应特征异常复杂,导致其定性识别与定量评价面临较大挑战。为解决这一问题,本研究充分利用测井多物理场在水合物和浅层气中的差异响应,创新性地提出了基于纵波测井与电阻率测井多信息源的联合反演方法,以提高含水合物气层饱和度的计算精度。基于南海深水超浅层疏松砂岩含水合物气层“同增同减”的测井响应特征,综合筛选低自然伽马、低泥质含量、高孔隙度、稳定厚度的砂质层段作为储层,并结合孔隙度差值法、中子−密度曲线重叠法、剪切模量法等定性识别方法进行层位判定。随后,采用中子−密度联合法计算孔隙度,在三相Biot方程与阿尔奇公式均考虑含气饱和度的基础上,运用循环迭代法同步反演纵波速度与电阻率,优化联合误差,最终求解含水合物气层的饱和度。研究结果表明,在储层段内,通过综合运用含烃或水合物的测井指示方法,并结合流体性质判别表,可有效识别含水合物气层。含水合物气层的典型特征包括:电阻率绝对值法和正演电阻率曲线重叠法指示含烃或水合物,中子−密度曲线重叠法指示含浅层气,剪切模量高于背景值等。采用纵波与电阻率测井的联合反演方法计算含水合物气层饱和度,验证其可行性与可靠性。应用于L区块Z井的联合反演计算结果与岩心饱和度的吻合度达81.25%,L区块Y井的计算结果与单独使用水合物或浅层气计算模型的吻合度接近85%。研究成果可为现场含水合物气层的识别及饱和度计算提供重要参考,为深水区域水合物资源的精细化评价奠定技术基础。
Abstract:Objective In marine natural gas hydrate exploration, hydrate-bearing gas layers−simultaneously containing natural gas hydrates and shallow gas−exhibit extremely complex electrical logging responses. This complexity poses significant challenges for both qualitative identification and quantitative evaluation.
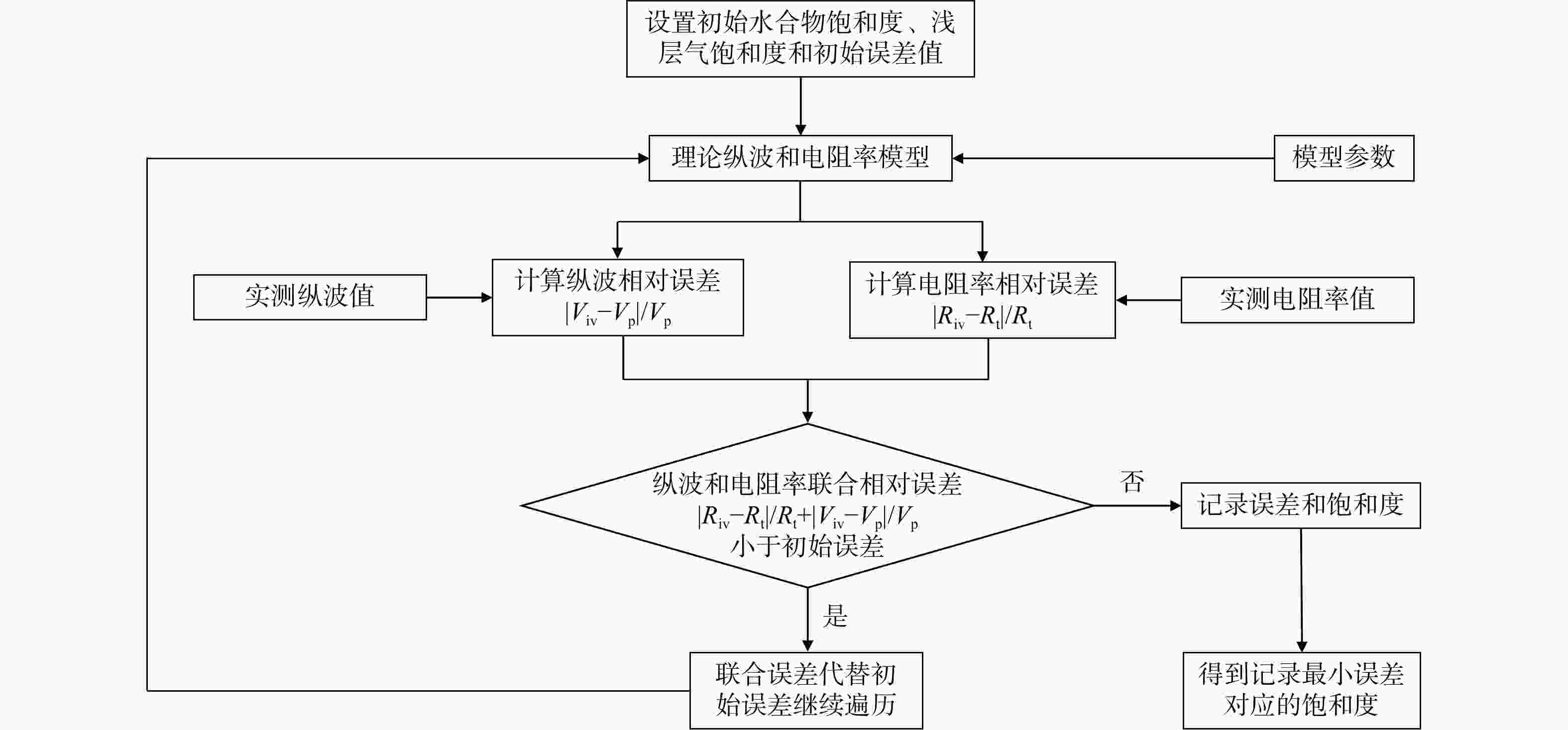
Methods To address this issue, this study fully leverages the differential responses of multi-physical logging in hydrates and shallow gas occurrences and proposes a novel joint inversion method based on multi-source information from P-wave logging and resistivity logging to improve the accuracy of hydrate-bearing gas layer saturation calculations. Guided by the "synchronous increase and decrease" logging response characteristics of hydrate-bearing gas layers in ultra-shallow unconsolidated sandstone reservoirs of the South China Sea, sandy intervals with low natural gamma, low shale content, high porosity, and stable thickness were comprehensively selected as reservoir layers. Qualitative identification was performed using porosity difference method, neutron-density curve overlap method, and shear modulus method. The neutron-density crossplot technique was employed to determine porosity, and by incorporating gas saturation into the three-phase Biot equation and Archie's formula, a cyclic iterative inversion method was used to simultaneously estimate P-wave velocity and resistivity, optimizing joint errors and ultimately solve for saturation of gas-hydrate-bearing layers.
Results Within the identified reservoir intervals, hydrate-bearing gas layers can be effectively distinguished by combining hydrocarbon or hydrate indicators from absolute resistivity method and the synthetic resistivity curve overlap method, neutron-density crossplots for shallow gas indications, and elevated shear-modulus values relative to the background. The joint inversion method integrating sonic and resistivity logging is feasible and reliable for calculating hydrate-bearing gas layer saturation. Applied to Well Z in Block L, the joint inversion yielded an 81.25% match with core-derived saturation. For Well Y in Block L, agreement between the joint inversion results and independent hydrate or shallow gas saturation models was approximately 85%.
Conclusion The study provides critical insights into the identification and estimation of the saturation of in-situ gas-hydrate-bearing layers, laying a technical foundation for the refined evaluation of hydrate resources in deepwater areas.
-
表 1 琼东南盆地L区块含水合物气层测井参数统计结果
Table 1. Statistical results of logging parameters for gas hydrate reservoir in Block L, Southeast Qiongdong Basin
流体性质 自然伽马/
GAPI电阻率/
(Ω·m)中子孔隙度/
%纵波时差/
(μs·ft−1)密度/
(g·cm−3)水
层83 1.5 57 175 2.02 85 1.6 56 178 2.02 81 1.7 49 176 2.04 84 1.6 56 175 2.09 85 1.6 52 178 2.07 83 1.6 61 177 2.12 83 1.8 61 172 2.05 水
合
物
层81 2.6 55 136 1.99 82 2.9 69 168 1.98 82 2.8 66 168 2.02 83 3.5 71 124 1.97 82 3.8 71 114 1.98 83 4.0 64 132 2.01 83 2.9 78 137 2.02 含
水
合
物
气
层78 1.8 55 164 1.91 90 1.9 52 187 1.91 85 2.1 49 192 1.92 78 4.1 48 202 1.93 78 4.4 49 206 1.97 74 2.6 50 196 1.87 73 2.3 50 179 1.9 浅
层
气
层81 2.2 46 179 1.83 78 2.0 42 180 1.76 81 1.9 40 172 1.77 79 1.9 40 178 1.69 80 1.9 39 182 1.69 81 2.0 39 181 1.67 85 1.9 38 181 1.69 注:1 ft=12 in= 0.3048 m,下同表 2 基于电阻率特征的流体性质判别
Table 2. Discrimination of fluid properties based on resistivity characteristics
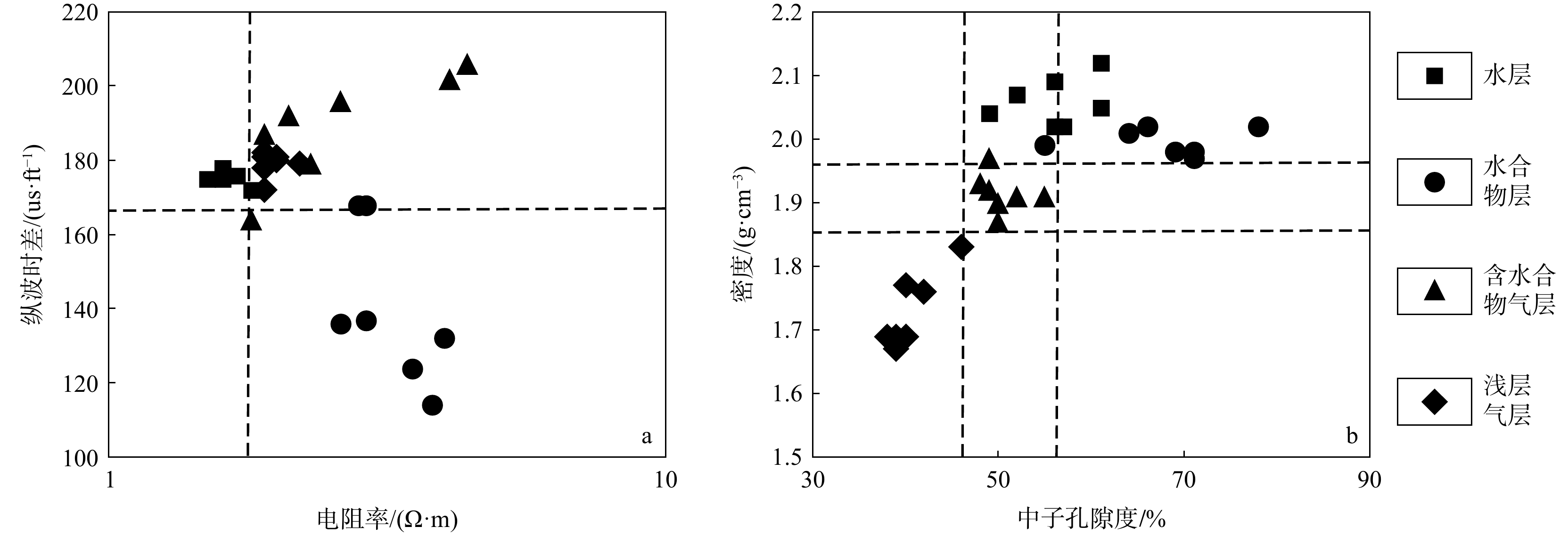
电阻率 $ {\mathbf{\varphi }}_{\rm{s}}-{\mathbf{\varphi }}_{\rm{w}} $ $ {\mathbf{\varphi }}_{\rm{D}}-{\mathbf{\varphi }}_{\rm{w}} $ TZ−TJ Gz−Gb 判别结果 不变 =0 =0 ≤0 =0 水层 增大 <0 ≈0 ≤0 >0 水合物层 增大 <0 >0 >0 >0 含水合物气层 水合物>浅层气 ≈0 >0 水合物≈浅层气 >0 >0 水合物<浅层气 增大 >>0 >>0 >0 =0 浅层气层 注:$\varphi_{\mathrm{s}} $. 纵波计算孔隙度;φw. 含水孔隙度;φD. 密度计算孔隙度;TZ. 中子孔隙度;TJ. 中子孔隙度基值;Gz. 剪切模量;Gb. 剪切模量背景值 表 3 井下泥砂样品信息
Table 3. Subsurface sand and mud samples information
序号 井深/m 黏土 石盐 石英 钾长石 斜长石 方解石 白云石 φB/% 1 1651.5 42.1 2.0 31.4 4.7 5.6 14.3 0 2 1653.6 30.2 0.9 23.5 29.2 4.7 11.5 0 3 1724.4 33.1 0 38.9 4.3 13.3 7.0 3.4 4 1728.4 41.0 0 33.6 3.2 11.4 7.6 3.1 表 4 琼东南盆地L区Z井含水合物气层饱和度预测结果对比
Table 4. Comparison of predicted saturation in the hydrate-bearing gas layer for Well Z, Block L, Qiongdongnan Basin
序号 深度/m 水合物饱和度预测值/% 岩心实测饱和度/% 误差值/% 1 1630.51 35.2 35.3 0.1 2 1632.34 33.4 33.6 0.2 3 1646.53 19.8 31.3 11.5 4 1647.35 21.2 22.1 0.1 5 1649.59 33.2 33.2 0 6 1650.82 42.2 32.6 9.6 7 1653.82 30.1 30.0 0.1 8 1654.62 22.4 22.3 0.1 9 1655.12 16.8 22.1 5.3 10 1668.92 31.3 30.9 0.4 11 1670.21 28.9 29.1 0.2 12 1671.59 25.9 25.8 0.1 13 1674.21 31.3 31.5 0.2 14 1675.11 29.9 30.2 0.3 15 1677.53 27.9 28.4 0.5 16 1707.26 18.2 18.5 0.3 -
[1] SLOAN E D. Fundamental principles and applications of natural gas hydrates[J]. Nature, 2003, 426: 353-359. doi: 10.1038/nature02135 [2] 李宁, 孙文杰, 李心童, 等. 天然气水合物饱和度测井解释模型及方程[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2022, 49(6): 1073-1079.LI N, SUN W J, LI X T, et al. Gas hydrate saturation model and equation for logging interpretation[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(6): 1073-1079. (in Chinese with English abstract [3] 马玲, 褚梦凡, 包锐. 浅谈南海水合物分解、甲烷转化及衍生碳的埋藏[J/OL]. 地质科技通报: 1-13[2024-04-03]. https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230591.MA L, CHU M F, BAO R. Hydrate decomposition, methane conversion and burial of methane-derived carbon in the South China Sea[J/OL]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology: 1-13[2024-04-03]. https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.tb20230591.(in Chinese with English abstract [4] 单文昊, 王琳, 吴祥恩, 等. 功能化多壁碳纳米管与L-亮氨酸复配体系中甲烷水合物动力学特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(5): 161-169.SHAN W H, WANG L, WU X E, et al. Kinetic characteristics of methane hydrate in functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and L-leucine compounding system[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(5): 161-169. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 郁桂刚, 欧文佳, 吴翔, 等. 天然气水合物分解动力学研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(3): 175-188.YU G G, OU W J, WU X, et al. Research advances on the dissociation dynamics of natural gas hydrates[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(3): 175-188. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 邓勇. 琼东南盆地天然气水合物地震识别与饱和度预测[J]. 地球科学, 2024, 49(5): 1865-1875.DENG Y. Seismic identification and saturation prediction of natural gas hydrate in the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2024, 49(5): 1865-1875. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 李丽松, 苗琦. 天然气水合物勘探开发技术发展综述[J]. 天然气与石油, 2014, 32(1): 67-71.LI L S, MIAO Q. Review on natural gas hydrate exploration and development technology[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2014, 32(1): 67-71. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] GUERIN G, GOLDBERG D, MELTSER A. Characterization of in situ elastic properties of gas hydrate-bearing sediments on the Blake Ridge[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth), 1999, 104(B8): 17781-17795. doi: 10.1029/1999JB900127 [9] LEE M W, COLLETT T S. Gas hydrate and free gas saturations estimated from velocity logs on hydrate ridge, offshore oregon, U. S. A[M]//TREHU A M, BOHRMANN G, TORRES M E, et al. Proceedings of the ocean drilling program, scientific results. [S. l.]: [s. n.], 2006: 1-25. [10] MILKOV A V, DICKENS G R, CLAYPOOL G E, et al. Co-existence of gas hydrate, free gas, and brine within the regional gas hydrate stability zone at Hydrate Ridge (oregon margin): Evidence from prolonged degassing of a pressurized core[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 222(3/4): 829-843. [11] KANG D J, LU J A, ZHANG Z J, et al. Fine-grained gas hydrate reservoir properties estimated from well logs and lab measurements at the Shenhu gas hydrate production test site, the northern slope of the South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 122: 104676. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104676 [12] LEE M W. Elastic velocities of partially gas-saturated unconsolidated sediments[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2004, 21(6): 641-650. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2003.12.004 [13] HUI G G, LI S Z, GUO L L, et al. Source and accumulation of gas hydrate in the northern margin of the South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 69: 127-145. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.10.009 [14] QIAN J, WANG X J, COLLETT T S, et al. Downhole log evidence for the coexistence of structure Ⅱ gas hydrate and free gas below the bottom simulating reflector in the South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 98: 662-674. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.09.024 [15] QIN X W, LU J G, LU H L, et al. Coexistence of natural gas hydrate, free gas and water in the gas hydrate system in the Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. China Geology, 2020, 3(2): 210-220. doi: 10.31035/cg2020038 [16] 谢莹峰, 陆敬安, 匡增桂, 等. 南海神狐海域水合物三相混合层测井评价方法研究[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(1): 182-192.XIE Y F, LU J A, KUANG Z G, et al. Well logging evaluation for three-phase zone with gas hydrate in the Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(1): 182-192. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] ZHAN L S, LU H L. Introducing realistic distributions of gas bubble size and inclusion aspect ratio to model the coexistence of gas hydrate and free gas[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2023, 213: 105023. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2023.105023 [18] 高兴军, 于兴河, 李胜利, 等. 地球物理测井在天然气水合物勘探中的应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2003, 18(2): 305-311.GAO X J, YU X H, LI S L, et al. Applicaton of geophysical well logging technology in exploration of gas hydrate[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2003, 18(2): 305-311. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 赵军, 武延亮, 周灿灿, 等. 天然气水合物的测井评价方法综述[J]. 测井技术, 2016, 40(4): 392-398.ZHAO J, WU Y L, ZHOU C C, et al. Review on logging technology evaluation methods of nature gas hydrate[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2016, 40(4): 392-398. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 王秀娟, 王吉亮, 李伟, 等. 基于声波阻抗估算印度安达曼海天然气水合物饱和度[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2013, 33(2): 163-168.WANG X J, WANG J L, LI W, et al. Gas hydrate saturation estimated from acoustic impedance in the Andaman Sea, India[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2013, 33(2): 163-168. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 康冬菊, 刘俊东, 李海燕, 等. 南海神狐海域天然气水合物储层参数定量评价方法[J]. 现代地质, 2024, 38(2): 385-397.KANG D J, LIU J D, LI H Y, et al. A quantitative evaluation method for the natural gas hydrate reservoir parameters in the Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. Geoscience, 2024, 38(2): 385-397. [22] 张磊. 改进的三相Biot模型在水合物地球物理测井评价中的研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.ZHANG L. Research on improved three-phase Biot model in gas hydrate geophysical logging evaluation [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 何彬, 匡邓晖, 王大魁. 海域天然气水合物测井响应的研究进展[J]. 科技信息, 2013(14): 3-4.HE B, KUANG D H, WANG D K. Research progress on logging response of natural gas hydrate in sea area[J]. Science & Technology Information, 2013(14): 3-4. (in Chinese) [24] 史謌, 杨东全. 岩石波速和孔隙度、泥质含量之间的关系研究[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 37(3): 379-384.SHI G, YANG D Q. The regression analysis study on velocity and porisity, and clay content of rocks[J]. Acta Scicentiarum Naturalum Universitis Pekinesis, 2001, 37(3): 379-384. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 谢莹峰, 任金锋, 邓炜, 等. 琼东南盆地渗漏型天然气水合物识别与差异成藏特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2024, 44(6): 1-11.XIE Y F, REN J F, DENG W, et al. Identification and the differential accumulation of leakage-typed gas hydrate in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2024, 44(6): 1-11. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 贾培文, 吕瑶瑶, 苏丕波, 等. 神狐海域天然气水合物测井-地震响应特征[J]. 地质学报, 2024, 98(9): 2654-2665.JIA P W, LYU Y Y, SU P B, et al. Logging-seismic response characteristics of natural gas hydrates in the Shenhu area, South China Sea[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2024, 98(9): 2654-2665. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 赵军, 郑超, 裴健翔, 等. 深水浅层松散沉积物水合物赋存状态识别与饱和度计算[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2024, 35(10): 1713-1723.ZHAO J, ZHENG C, PEI J X, et al. Hydrate occurrence identification of shallow loose sediments in deep water and its saturation calculation[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2024, 35(10): 1713-1723. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 周吉林. 天然气水合物和游离气储层的测井与地震响应特征研究[D]. 山东青岛: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所), 2022.ZHOU J L. The characteristics of gas hydrate-bearing and free gas-bearing sediments identified from well log and seismic data[D]. Qingdao Shandong: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 赵军, 刘仕鑫, 李元平, 等. 基于测井资料的南海天然气水合物储层识别与参数计算[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2022, 37(6): 2508-2517.ZHAO J, LIU S X, LI Y P, et al. Logging identification and evaluation of gas hydrate reservoirs in the South China Sea[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37(6): 2508-2517. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 王圣宜, 邹长春, 彭诚, 等. 海域孔隙型储层天然气水合物赋存模式定量化表征: 声波和电阻率测井的约束[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(1): 127-137.WANG S Y, ZOU C C, PENG C, et al. Quantitative characterization of hydrate occurrence mode in marine pore-filling gas hydrate reservoirs: Constraints from acoustic and resistivity log data[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(1): 127-137. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 肖昆, 邹长春, 卢振权, 等. 基于声波测井的冻土区孔隙型水合物储层水合物饱和度估算方法[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(5): 1664-1674.XIAO K, ZOU C C, LU Z Q, et al. The acoustic log method of estimating gas hydrate saturation in gas hydrate reservoirs[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(5): 1664-1674. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 孙建孟, 罗红, 焦滔, 等. 天然气水合物储层参数测井评价综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018, 33(2): 715-723.SUN J M, LUO H, JIAO T, et al. Review of the well logging assessment of natural gas hydrate reservoir parameters[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018, 33(2): 715-723. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 刘瑞文, 李春山, 管加强. 孔隙流体类型对地层声波速度的影响[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2007, 35(4): 32-34.LIU R W, LI C S, GUAN J Q. The impact of pore fluid types on formations acoustic velocity[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2007, 35(4): 32-34. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 高红艳, 钟广法, 梁金强, 等. 应用改进的Biot-Gassmann模型估算天然气水合物的饱和度[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(4): 83-89.GAO H Y, ZHONG G F, LIANG J Q, et al. Estimation of gas hydrate saturation with modified biotgassmann theory: A case from northern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(4): 83-89. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 周建, 宋延杰, 姜艳娇, 等. 海洋天然气水合物测井评价研究进展[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 42(2): 85-93.ZHOU J, SONG Y J, JIANG Y J, et al. The research progress of well logging evaluation of marine natural gas hydrate[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2020, 42(2): 85-93. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 杨克兵, 王竞飞, 马凤芹, 等. 阿尔奇公式的适用条件分析及对策[J]. 天然气与石油, 2018, 36(2): 58-63.YANG K B, WANG J F, MA F Q, et al. Analysis and countermeasures about applicable conditions of Archie's formula[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2018, 36(2): 58-63. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 赵军, 廖文海, 汤翟, 等. 深水浅层松散细粒水合物储层新型含水饱和度模型建立及应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2025, 36(2): 197-208.ZHAO J, LIAO W H, TANG Z, et al. Establishment and application of a new water saturation model for shallow and loose fine-grained hydrate reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2025, 36(2): 197-208. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 胡高伟, 业渝光, 张剑, 等. 南海沉积物中天然气水合物饱和度与声学特性的关系[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(6): 1112-1118.HU G W, YE Y G, ZHANG J, et al. Relationship between gas hydrate saturation and acoustic properties of sediments in the South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(6): 1112-1118. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 梁劲, 王明君, 王宏斌, 等. 南海神狐海域天然气水合物声波测井速度与饱和度关系分析[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(2): 217-223.LIANG J, WANG M J, WANG H B, et al. Relationship between the sonic logging velocity and saturation of gas hydrate in Shenhu area, northern slope of South China Sea[J]. Geoscience, 2009, 23(2): 217-223. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 孔秀, 李琦, 姜晓虹, 等. 印度克里希纳−戈达瓦里盆地天然气水合物饱和度特征[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2019, 38(3): 299-306.KONG X, LI Q, JIANG X H, et al. Characteristics of gas hydrate saturations in Krishna-Godavari Basin, India[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2019, 38(3): 299-306. (in Chinese with English abstract -




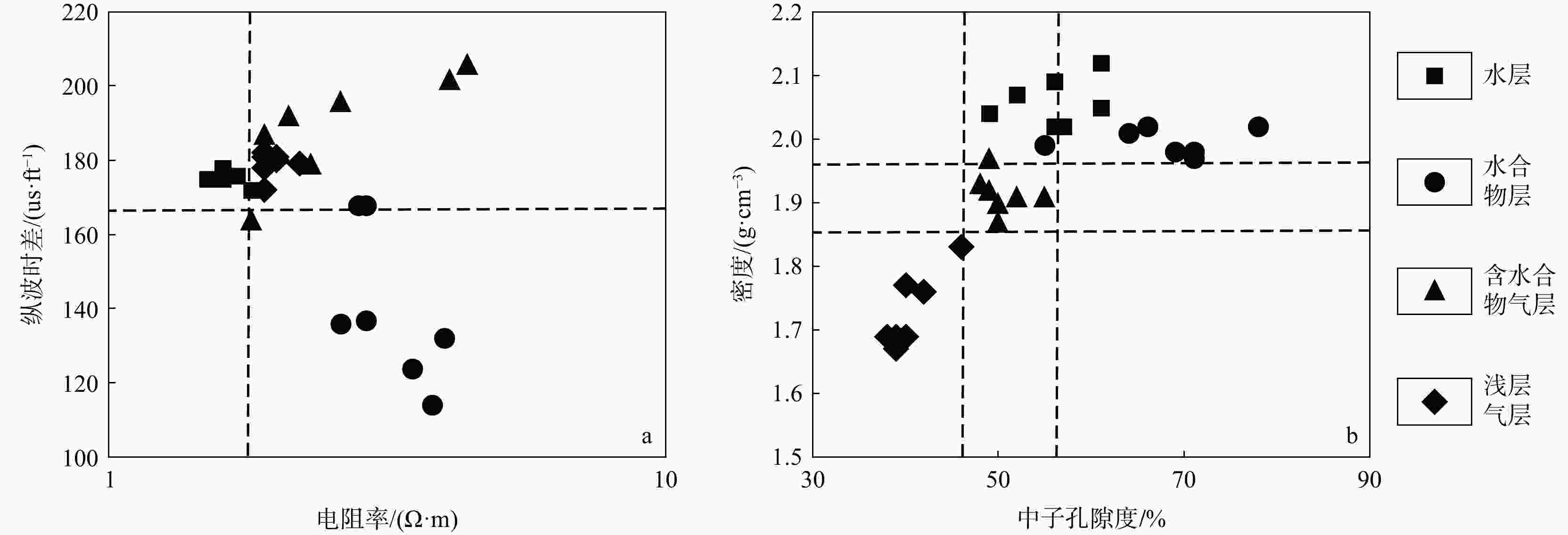
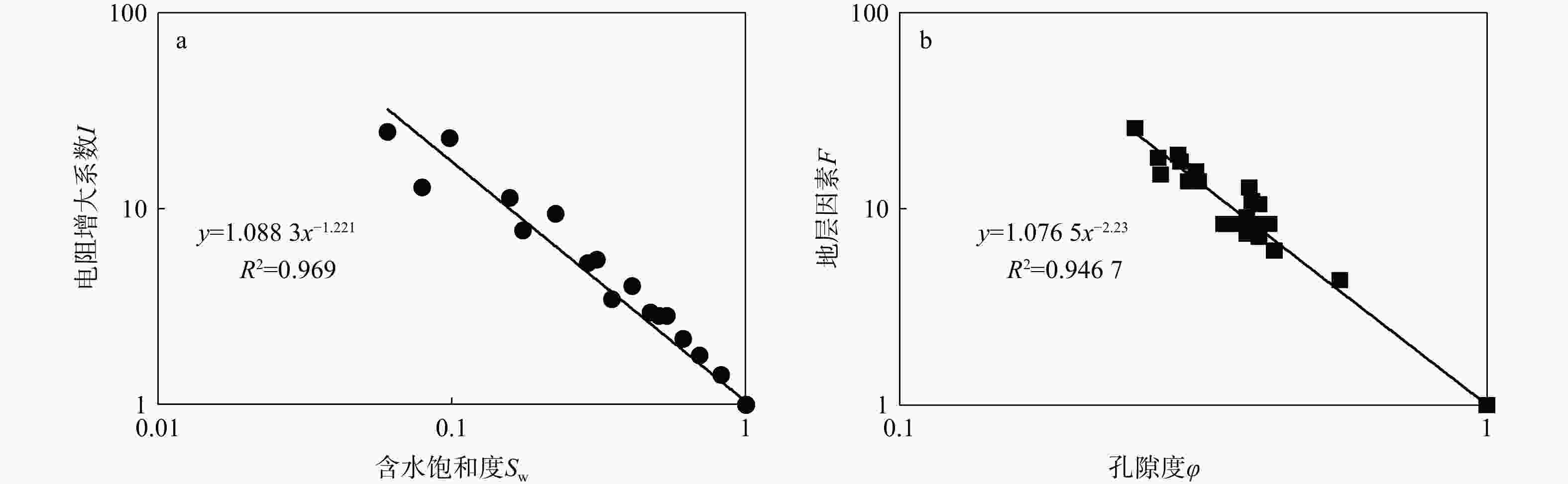
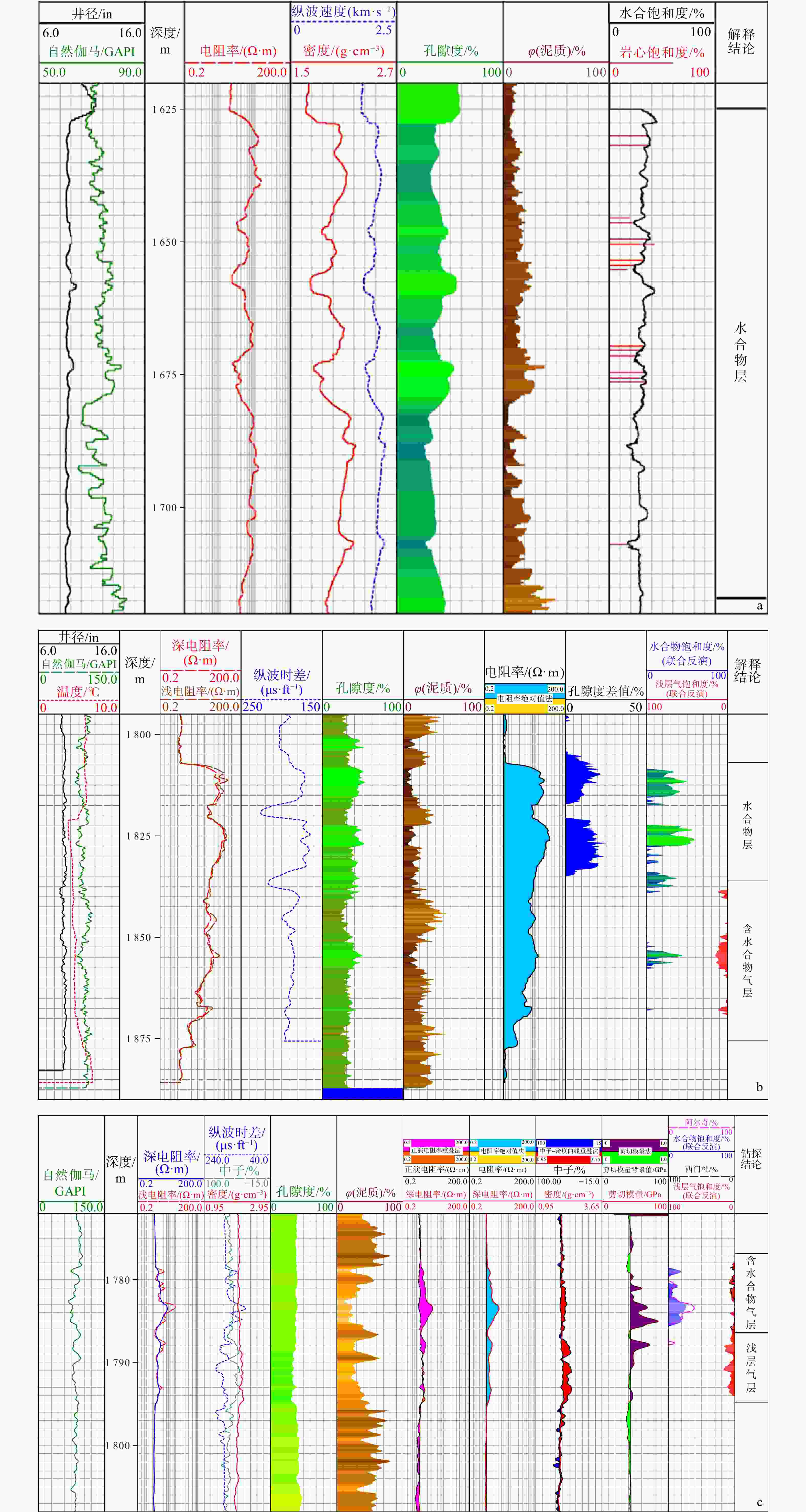
 下载:
下载: