Dynamic law of suction during the evaporation process of saline soil based on dew point water potential meter and filter paper method
-
摘要:
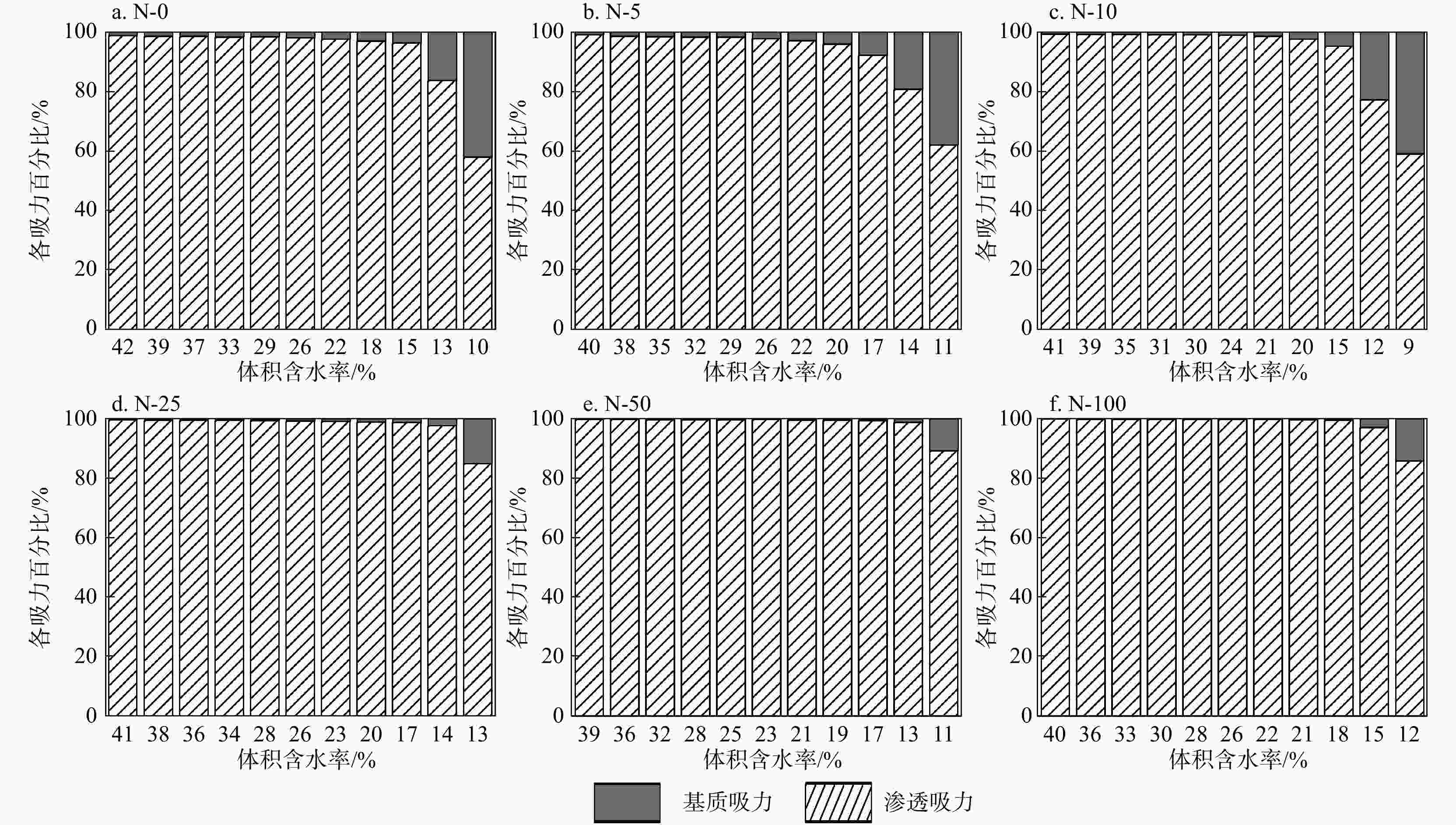
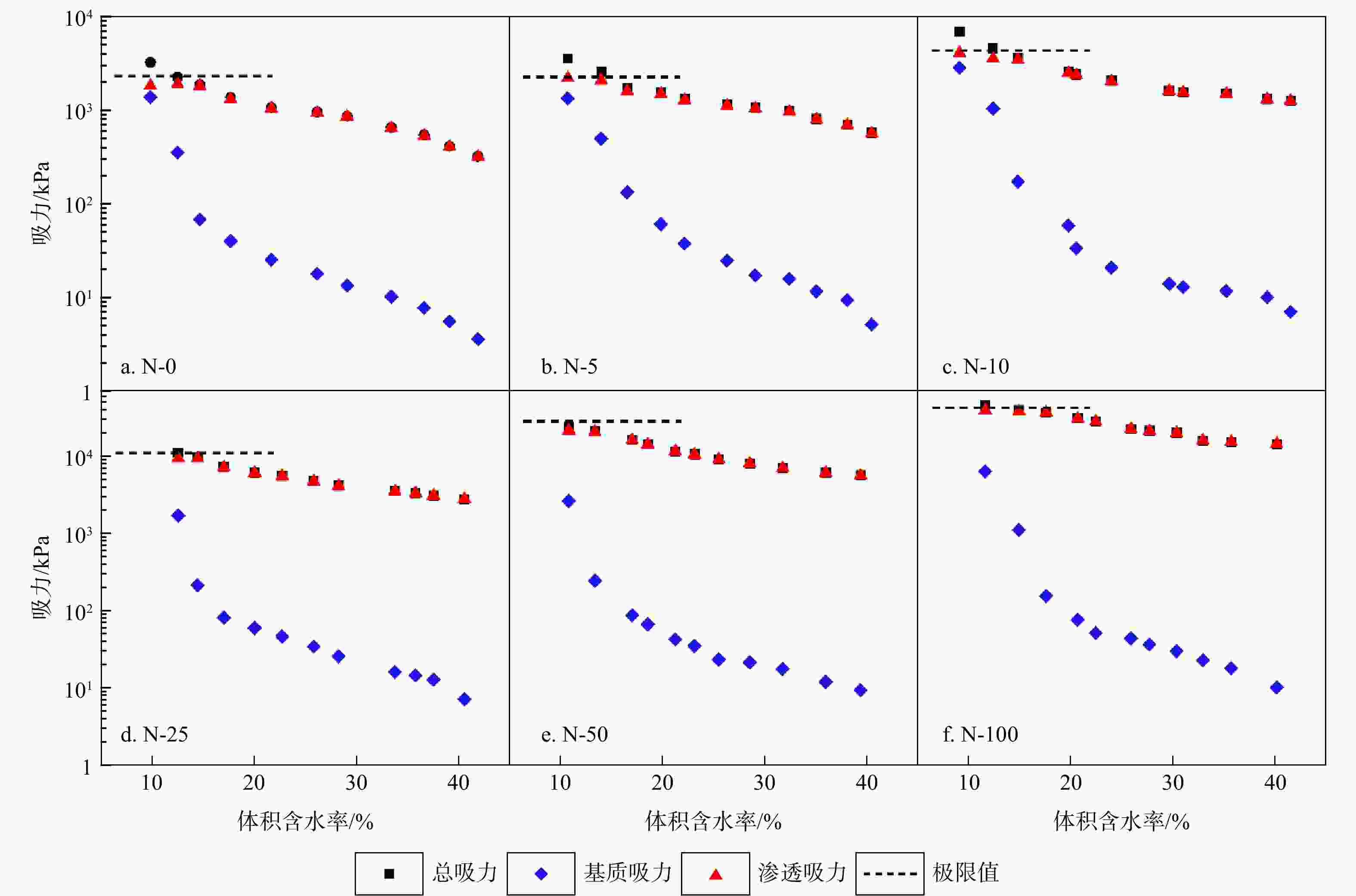
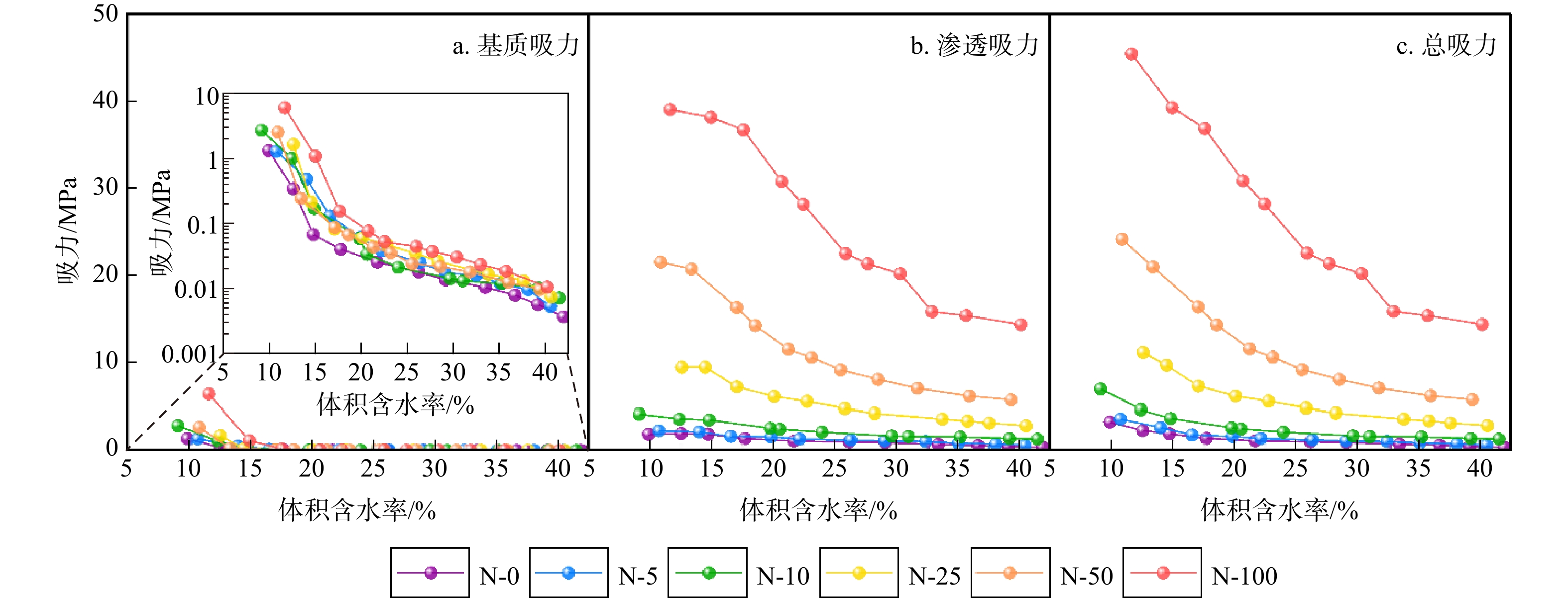
为获取盐渍土蒸发过程中总吸力、基质吸力及渗透吸力的大小,阐明不同水盐条件下各吸力动态变化特征及其对蒸发的影响,将冷镜露点水势仪(WP4C)和并行接触式滤纸法相结合,对不同含盐量土壤蒸发过程中总吸力、基质吸力与渗透吸力的动态过程及其对土壤蒸发的影响进行了分析;选取4种常用土壤水分特征曲线模型,利用SWRC-Fit对基质吸力与含水量之间的关系进行了拟合。结果表明:盐渍土在蒸发过程中基质吸力与渗透吸力占总吸力的比例不断发生变化,相同含水率下渗透吸力占比始终大于基质吸力;含水率与盐分均会影响土壤渗透吸力的大小,其中盐分的影响更显著。土壤蒸发强度及持续时间均会受到土壤盐分影响。通过WP4C与并行接触式滤纸法可以同时获取蒸发过程中非饱和土壤的总吸力、基质吸力与渗透吸力,Fredlund and Xing(FX)模型能够较好地拟合实验蒸发过程中的实测数据,在蒸发各阶段均有较好拟合精度,也进一步证明了实验方法与数据的可靠性。
Abstract:Objective In order to obtain total suction, matric suction and osmotic suction during the evaporation process of saline soil, the dynamic variation characteristics of each suction force under different water and salt conditions and its influence on evaporation were clarified.
Methods A combination of a cold mirror dew point water potential meter and a parallel contact filter paper method was employed to analyze the dynamic processes of total suction, matric suction, and osmotic suction during soil evaporation with different salt contents, as well as their effects on soil evaporation. Four commonly used soil water characteristic curve models were selected, and the relationship between matric suction and water content was fitted by SWRC-Fit package.
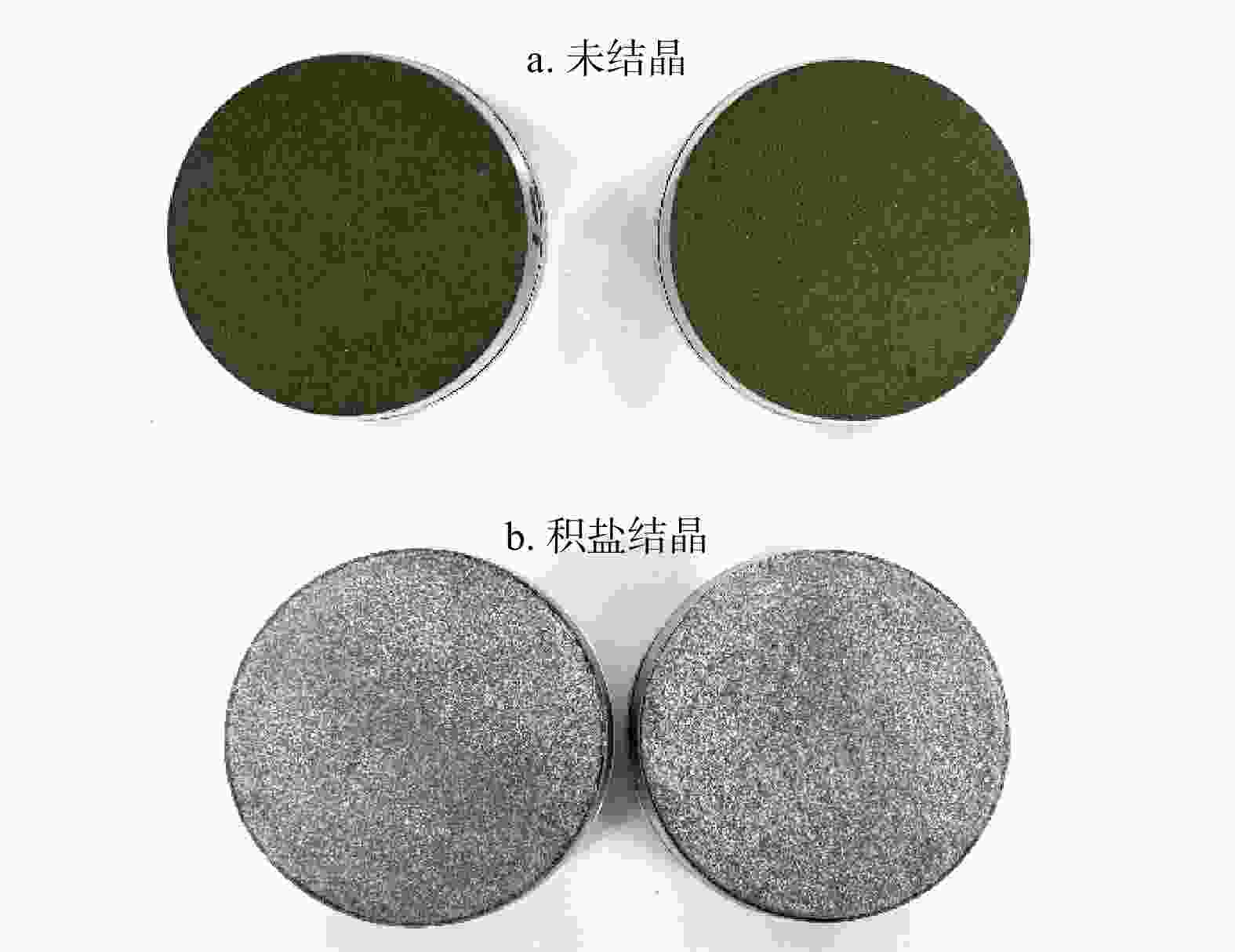
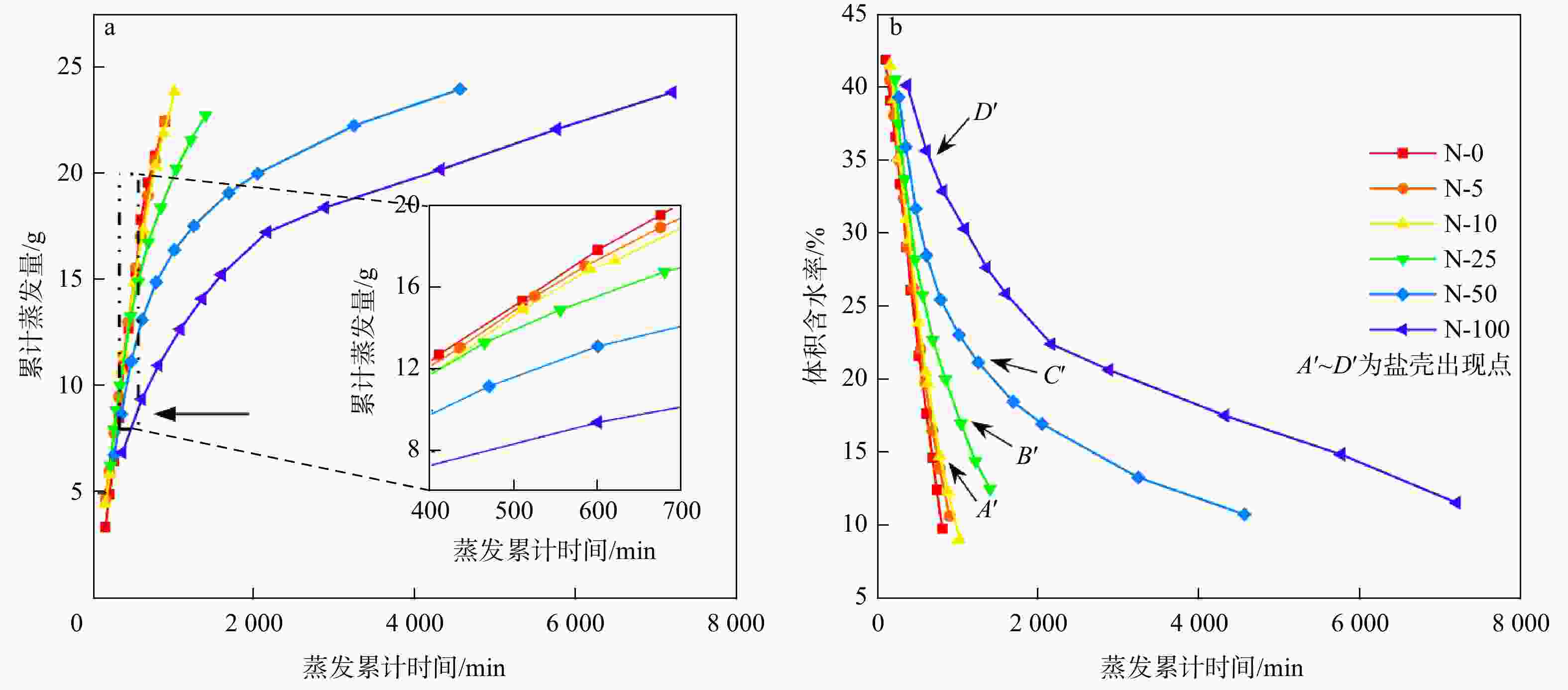
Results The results indicate that the proportion of matric suction and osmotic suction to total suction continuously changes during the evaporation process of saline soil, with the latter always being higher than the former. Both moisture content and salinity affect the magnitude of soil osmotic suction, with salinity showing a more significant impact. The intensity and duration of soil evaporation are both affected by soil salinity.
Conclusion Total suction, matric suction and osmotic suction in unsaturated soil during the evaporation process can be simultaneously obtained by WP4C and parallel contact filter paper method. The Fredlund and Xing model accurately fits the experimental data, maintaing good fitting accuracy throughout all evaporation stages, which further proves the reliability of the experimental method and data.
-
Key words:
- saline soil /
- evaporation /
- osmotic suction /
- matric suction /
- dew point water potential meter /
- filter paper method
-
表 1 实验土基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of test soil
砂粒 粉粒 黏粒 美国制
土壤定名干密度/
(g·cm−3)饱和含
水率/%电阻率(EC)/
(μS·cm−1)wB/% 50.77 49.04 0.19 砂质壤土 1.45 47.05 225 表 2 常用的土壤水分特征曲线(SWCC)模型
Table 2. Commonly used soil water characteristic curve models
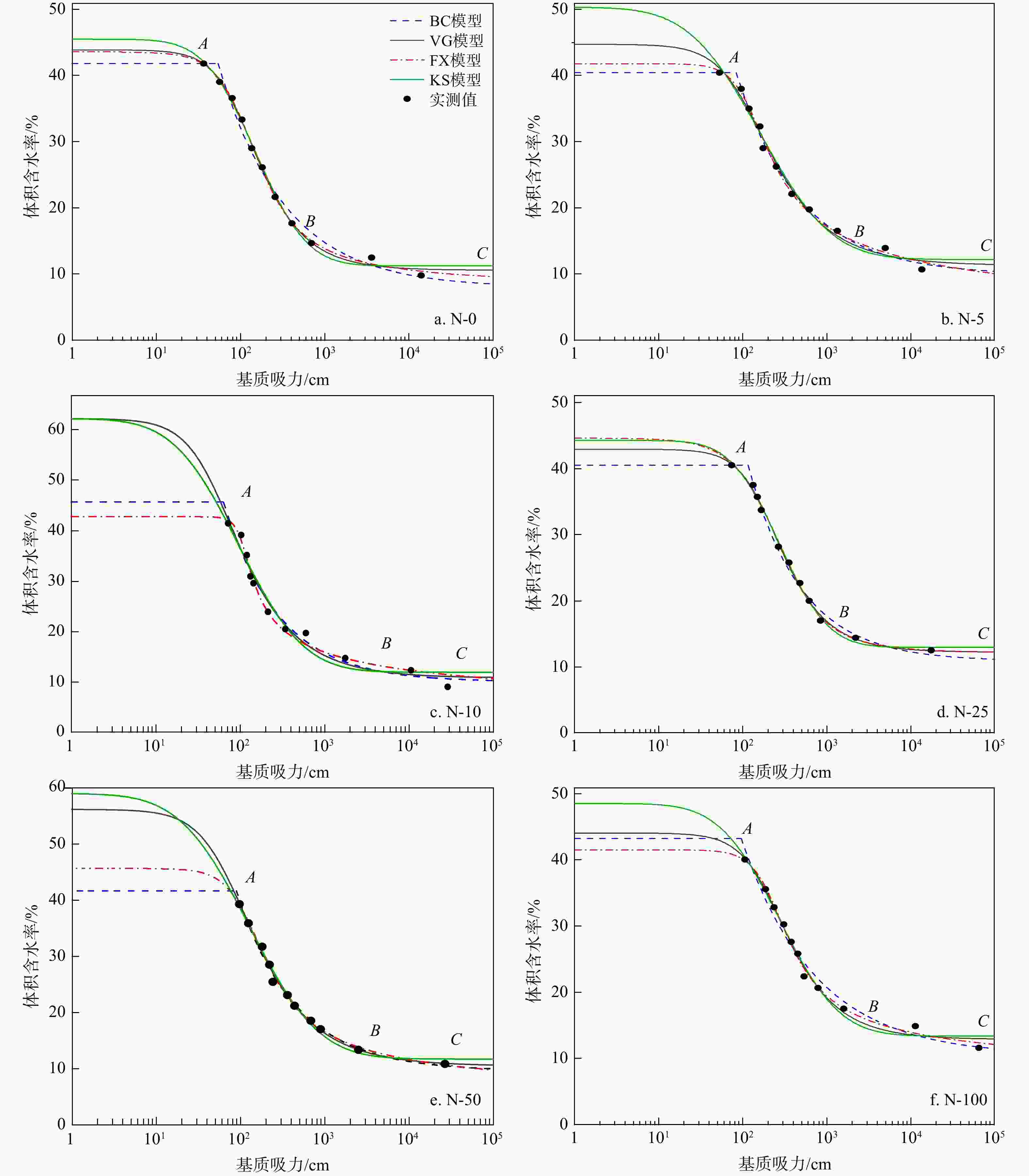
SWCC模型 年份 模型表达式 参数 参数含义 Brooks and Corey (BC) 1964 $ \displaystyle\frac{{\theta (h) - {\theta _{\mathrm{r}}}}}{{{\theta _{\mathrm{s}}} - {\theta _{\mathrm{r}}}}} = \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{{\left(\displaystyle\frac{{{h_b}}}{h}\right)}^{\lambda} },h > {h_{\mathrm{b}}}} \\ {1,h < {h_{\mathrm{b}}}} \end{array}} \right. $ hb,λ hb为进气吸力值,cm;λ为土壤孔隙尺寸分布参数,影响SWCC的斜率 Van Genuchten (VG) 1980 $ \displaystyle\frac{{\theta (h) - {\theta _{\mathrm{r}}}}}{{{\theta _{\mathrm{s}}} - {\theta _{\mathrm{r}}}}} = {\left[ {\displaystyle\frac{1}{{1 + {{(\alpha h)}^n}}}} \right]^m} $ α,n,m α为空气进气值的倒数,1/cm;n为与土壤的孔径分布有关参数;
m为与模型的不对称性有关参数,m=1−1/nFredlund and Xing (FX) 1994 $ \displaystyle\frac{{\theta (h)}}{{{\theta _{\mathrm{s}}}}} = C\left( h \right){\left[ {\displaystyle\frac{1}{{\ln [{\mathrm{e}} + {{\left( {h/a} \right)}^{n'}}]}}} \right]^{m'}} $ a,n',m' C(h)为修正因子;e为自然常数;a为与土壤进气值有关参数;n'为与SWCC的斜率有关参数,是表征土脱水速率相关的参数;m'为与残余含水率有关参数 Kosugi(KS) 1996 $ \displaystyle\frac{{\theta (h) - {\theta _{\mathrm{r}}}}}{{{\theta _{\mathrm{s}}} - {\theta _{\mathrm{r}}}}} = \displaystyle\frac{1}{2}erfc\left[\displaystyle\frac{{\ln (h/{h_{\mathrm{m}}})}}{{\sqrt 2 \sigma }}\right] $ hm,σ erfc为互补误差函数;hm 为中孔半径对应的吸力;σ为对数转换土壤孔隙半径和毛管压力正态分布的标准偏差。 注:θ(h)为土壤张力(h)下的体积含水率;θs为饱和含水率;θr为残余含水率;下同 表 3 土壤水分特征曲线(SWCC)模型决定系数(R2)
Table 3. Coefficient of determination of soil water characteristic curve models
SWCC模型 试样编号 平均值 N-0 N-5 N-10 N-25 N-50 N-100 BC模型 0.9875 0.9947 0.9745 0.9944 0.9936 0.9764 0.9869 VG模型 0.9977 0.9903 0.9743 0.9969 0.9952 0.9912 0.9909 FX模型 0.9983 0.9945 0.9877 0.9968 0.9956 0.9945 0.9946 KS模型 0.9961 0.9855 0.9639 0.9964 0.9914 0.9872 0.9868 表 4 土壤水分特征曲线(SWCC)模型参数
Table 4. Soil water characteristic curve model parameters
SWCC模型 参数 试样编号 N-0 N-5 N-10 N-25 N-50 N-100 BC模型 θs 0.4189 0.4047 0.4566 0.4054 0.4165 0.4331 θr 0.0798 0.0985 0.1005 0.1092 0.0956 0.1041 hb 54.29 84.00 63.69 115.74 89.82 96.29 λ 0.5494 0.5621 0.6614 0.6809 0.6220 0.4920 VG模型 θs 0.4394 0.4477 0.6221 0.4295 0.5617 0.4414 θr 0.1059 0.1131 0.1085 0.1229 0.1046 0.1289 α 0.0103 0.0095 0.0204 0.0056 0.0145 0.0052 n 2.0476 1.7855 1.8100 2.0860 1.7656 1.9598 m 0.5116 0.4399 0.4475 0.5206 0.4336 0.4897 FX模型 θs 0.4362 0.4185 0.4275 0.4461 0.4565 0.4159 θr 0.0796 1.00×10−10 1.13×10−23 0.1203 4.24×10−2 7.08×10−2 a 98.11 104.57 100.08 245.60 106.68 191.54 m' 1.1536 0.4860 0.3650 2.1934 0.7224 0.6819 n' 2.0338 2.7364 6.4658 1.5116 2.3887 2.6836 KS模型 θs 0.4554 0.5038 0.6221 0.4426 0.5898 0.4860 θr 0.1125 0.1222 0.1197 0.1301 0.1170 0.1340 hm 152.33 163.13 96.75 275.26 128.63 277.00 σ 1.1070 1.5433 1.3981 1.0572 1.4950 1.2944 注:参数含义见表2 表 5 不同初始 NaCl 溶液质量浓度(IC)试样分段拟合赤池信息量准则值(AIC)
Table 5. Akaike information criterion for segmented fitting of different initial NaCl solution mass concentration
试样分段 SWCC模型 试样编号 N-0 N-5 N-10 N-25 N-50 N-100 AB段 BC模型 − 47.2651 − 50.2044 − 44.2010 − 42.6631 − 47.7821 − 37.8055 VG模型 − 83.6666 − 48.8321 − 44.4647 − 40.4575 − 45.8076 − 34.5711 FX模型 − 85.3985 − 51.0529 − 46.8448 − 42.4888 − 47.8737 − 36.6249 KS模型 − 80.3509 − 50.3871 − 45.6695 − 42.3189 − 47.5579 − 36.3778 BC段 BC模型 − 18.6699 − 6.9495 − 16.1246 − 6.5038 − 8.7567 − 4.6833 VG模型 − 18.5223 − 5.6207 − 13.5710 − 5.1978 − 7.7703 − 4.0508 FX模型 − 21.7756 − 7.6994 − 16.3383 − 7.1818 − 10.0928 − 5.5888 KS模型 − 19.0465 − 7.7593 − 14.7271 − 7.1471 − 9.1259 − 6.5904 -
[1] 花圣卓, 蔡昕, 余新晓. 平坦下垫面植被蒸散特征及对气象因素的响应研究[J]. 水土保持学报, 2016, 30(3): 344-350.HUA S Z, CAI X, YU X X. Study on the evapotranspiration features of vegetation over flat underlying surface and response to meteorological factors[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2016, 30(3): 344-350. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] SHOKRI-KUEHNI S M S, RAAIJMAKERS B, KURZ T, et al. Water table depth and soil salinization: From pore-scale processes to field-scale responses[J]. Water Resources Research, 2020, 56(2): e2019WR026707. doi: 10.1029/2019WR026707 [3] DONG C Y, WANG N A, CHEN J S, et al. New observational and experimental evidence for the recharge mechanism of the lake group in the Alxa Desert, north-central China[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 2016, 124: 48-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2015.07.008 [4] 彭振阳, 郭会, 伍靖伟, 等. 溶质势对地表蒸发速率的影响[J]. 水科学进展, 2013, 24(2): 235-242.PENG Z Y, GUO H, WU J W, et al. Contribution of osmotic potential on bare soil evaporation rate[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2013, 24(2): 235-242. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] 宁卢, 威廉·力科思. 非饱和土力学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2012.NING L, LIKOS W J. Unsaturated soil mechanics[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2012. (in Chinese) [6] 邵明安, 王全九, 黄明斌. 土壤物理学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006.SHAO M A, WANG Q J, HUANG M B. Soil physics[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. (in Chinese) [7] 谢定义. 非饱和土土力学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2015.XIE D Y. Soil mechanics for unsaturated soils[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2015. (in Chinese) [8] 周凤玺, 王立业, 赖远明. 饱和盐渍土渗透吸力的回顾及研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(7): 1199-1210. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202007003ZHOU F X, WANG L Y, LAI Y M. Review and research on osmotic suction of saturated saline soils[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(7): 1199-1210. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11779/CJGE202007003 [9] CHEN H E, LI J F, YUAN X Q, et al. Influence of water and salt on suction characteristics of unsaturated clay: Variation, mechanism, and fitting[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2021, 80(11): 8535-8551. doi: 10.1007/s10064-021-02435-8 [10] ENGELHARDT W V, GAIDA K H. Concentration changes of pore solutions during compaction of clay sediments[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1963, 33(4): 919-930. doi: 10.1306/74D70F74-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D [11] 张爱军, 王毓国, 邢义川, 等. 伊犁黄土总吸力和基质吸力土水特征曲线拟合模型[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2019, 41(6): 1040-1049. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201906007ZHANG A J, WANG Y G, XING Y C, et al. Fitting models for soil-water characteristic curve of total and matrix suctions of Yili loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(6): 1040-1049. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11779/CJGE201906007 [12] LEONG E C, TRIPATHY S, RAHARDJO H. Total suction measurement of unsaturated soils with a device using the chilled-mirror dew-point technique[J]. Géotechnique, 2003, 53(2): 173-182. [13] AGUS S S, SCHANZ T. Comparison of four methods for measuring total suction[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 2005, 4(4): 1087-1095. doi: 10.2136/vzj2004.0133 [14] WANARE R, SHETTY R, JAYANTHI P N V, et al. Investigation to quantify suction characteristics of marine soil during drying and wetting cycles[J]. Geotechnical Testing Journal, 2021, 44(1): 112-129. doi: 10.1520/GTJ20190199 [15] HAGHVERDI A, NAJARCHI M, ÖZTÜRK H S, et al. Studying unimodal, bimodal, PDI and bimodal-PDI variants of multiple soil water retention models: I. direct model fit using the extended evaporation and dewpoint methods[J]. Water, 2020, 12(3): 900. doi: 10.3390/w12030900 [16] SAHA A, SEKHARAN S. Importance of volumetric shrinkage curve (VSC) for determination of soil-water retention curve (SWRC) for low plastic natural soils[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 596: 126113. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126113 [17] ROY S, RAJESH S. Influence of confining pressure on water retention characteristics of compacted soil[J]. Indian Geotechnical Journal, 2018, 48(2): 327-341. doi: 10.1007/s40098-017-0265-3 [18] 白福青, 刘斯宏, 袁骄. 滤纸法测定南阳中膨胀土土水特征曲线试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2011, 33(6): 928-933.BAI F Q, LIU S H, YUAN J. Measurement of SWCC of Nanyang expansive soil using the filter paper method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 33(6): 928-933. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 谷琪, 王家鼎, 仝云莉, 等. 滤纸法测非饱和黄土土水特征曲线试验及拟合研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2016, 47(3): 588-593.GU Q, WANG J D, TONG Y L, et al. Soil water characteristic curve test and simulation of unsaturated loess based on filter paper method[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 47(3): 588-593. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] ASTM Internation. Standard test method for measurement of soil potential (suction) using filter paper: ASTM D5298-16[S]. [S. 1.]: ASTM Internation, 2016. [21] 李旭, 刘阿强, 刘丽, 等. 全吸力范围内土−水特征曲线的快速测定方法[J]. 岩土力学, 2022, 43(2): 299-306.LI X, LIU A Q, LIU L, et al. A rapid method for determining the soil-water characteristic curves in the full suction range[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2022, 43(2): 299-306. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 许海楠, 谢强, 赵梦怡, 等. 冷镜露点技术在非饱和成都黏土吸力测试中的应用[J]. 工程地质学报, 2017, 25(4): 953-958.XU H N, XIE Q, ZHAO M Y, et al. Measurement of soil suction for remoulded Chengdu clay with chilled-mirror dew-point technology[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(4): 953-958. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 吴克宁, 赵瑞. 土壤质地分类及其在我国应用探讨[J]. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(1): 227-241.WU K N, ZHAO Y. Soil texture classification and its application in China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2019, 56(1): 227-241. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 朱赞成, 孙德安, 田进. 高吸力高温度下2种滤纸率定曲线及其应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2014, 36(6): 1020-1027.ZHU Z C, SUN D A, TIAN J. Calibration curves of two filter papers at high suction and temperature and their application[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 36(6): 1020-1027. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 晁建红. 基于滤纸法的黄土土−水特征曲线测试[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2017CHAO J H. Experimental study on soil-water characteristic curve of loess using filter paper method[D]. Xi'an: Changan University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] FAWCETT R G, COLLIS-GEORGE N. A filter-paper method for determining the moisture characteristics of soil[J]. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture, 1967, 7(25): 162. doi: 10.1071/EA9670162 [27] HAMBLIN A P. Filter-paper method for routine measurement of field water potential[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1981, 53(3/4): 355-360. [28] 唐栋, 李典庆, 金浩飞, 等. 国产“双圈” 牌滤纸吸力率定曲线研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2016, 49(1): 1-8.TANG D, LI D Q, JIN H F, et al. Research on calibration curves of home-made "Double Circle" filter papers[J]. Engineering Journal of Wuhan University, 2016, 49(1): 1-8. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] WANG Y G, ZHANG A J, REN W Y, et al. Study on the soil water characteristic curve and its fitting model of Ili loess with high level of soluble salts[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 578: 124067. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124067 [30] TOKUNAGA T K. Hydraulic properties of adsorbed water films in unsaturated porous media[J]. Water Resources Research, 2009, 45(6): W06415. [31] WANG Y Q, JIN M G, DENG Z J. Alternative model for predicting soil hydraulic conductivity over the complete moisture range[J]. Water Resources Research, 2018, 54(9): 6860-6876. doi: 10.1029/2018WR023037 [32] WANG Y Q, MA R, ZHU G F. Improved prediction of hydraulic conductivity with a soil water retention curve that accounts for both capillary and adsorption forces[J]. Water Resources Research, 2022, 58(4): e2021WR031297. doi: 10.1029/2021WR031297 [33] 孙德安, 张谨绎, 宋国森. 氯盐渍土土−水特征曲线的试验研究[J]. 岩土力学, 2013, 34(4): 955-960.SUN D A, ZHANG J Y, SONG G S. Experimental study of soil-water characteristic curve of chlorine saline soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(4): 955-960. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 唐洋, 李新虎, 郭敏, 等. 不同初始盐分浓度下土壤盐结皮的形成过程及其对蒸发的影响机理[J]. 干旱区地理, 2022, 45(4): 1137-1145. doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2021.438TANG Y, LI X H, GUO M, et al. Formation process of soil salt crust and its influence mechanism on evaporation under different initial salt concentrations[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2022, 45(4): 1137-1145. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12118/j.issn.1000-6060.2021.438 [35] 于沉香, 张虎元, 王志硕, 等. 盐渍土土水特征曲线测试及预测[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2013, 40(2): 113-118.YU C X, ZHANG H Y, WANG Z S, et al. Test and prediction of SWCC of saline soil[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2013, 40(2): 113-118. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 祁翠婷, 詹红兵, 郝永红. 包气带井回灌引起的非饱和−饱和流分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(4): 118-129.QI C T, ZHAN H B, HAO Y H. Analysis of unsaturated-saturated flow induced by a vadose zone well injection[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(4): 118-129. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] BROOKS R H, COREY A T. Hydraulic properties of porous media[M]. Fort Collins: Colorado State University, 1964. [38] VAN GENUCHTEN M T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 1980, 44(5): 892-898. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1980.03615995004400050002x [39] FREDLUND D G, XING A Q. Equations for the soil-water characteristic curve[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 1994, 31(4): 521-532. doi: 10.1139/t94-061 [40] KOSUGI K. Lognormal distribution model for unsaturated soil hydraulic properties[J]. Water Resources Research, 1996, 32(9): 2697-2703. doi: 10.1029/96WR01776 [41] SEKI K, TORIDE N, VAN GENUCHTEN M T. Evaluation of a general model for multimodal unsaturated soil hydraulic properties[J]. Journal of Hydrology and Hydromechanics, 2023, 71(1): 22-34. doi: 10.2478/johh-2022-0039 [42] BURNHAM K P, ANDERSON D R. Multimodel inference[J]. Sociological Methods & Research, 2004, 33(2): 261-304. [43] EYO E U, NG'AMBI S, ABBEY S J. An overview of soil-water characteristic curves of stabilised soils and their influential factors[J]. Journal of King Saud University (Engineering Sciences), 2022, 34(1): 31-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jksues.2020.07.013 [44] 向峥宇, 潘欢迎, 邓斌, 等. 基于蒸发法和联合测定仪测定土壤水分特征曲线和非饱和渗透系数的试验研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(4): 210-217.XIANG Z Y, PAN H Y, DENG B, et al. Experimental study of the soil water characteristic curve and unsaturated permeability coefficient based on the evaporation method and combined measuring instrument[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(4): 210-217. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: