Discussion on the spatiotemporal differences of Cenozoic rift formation and evolution and its genetic mechanism in the Pearl River Mouth Basin
-
摘要:
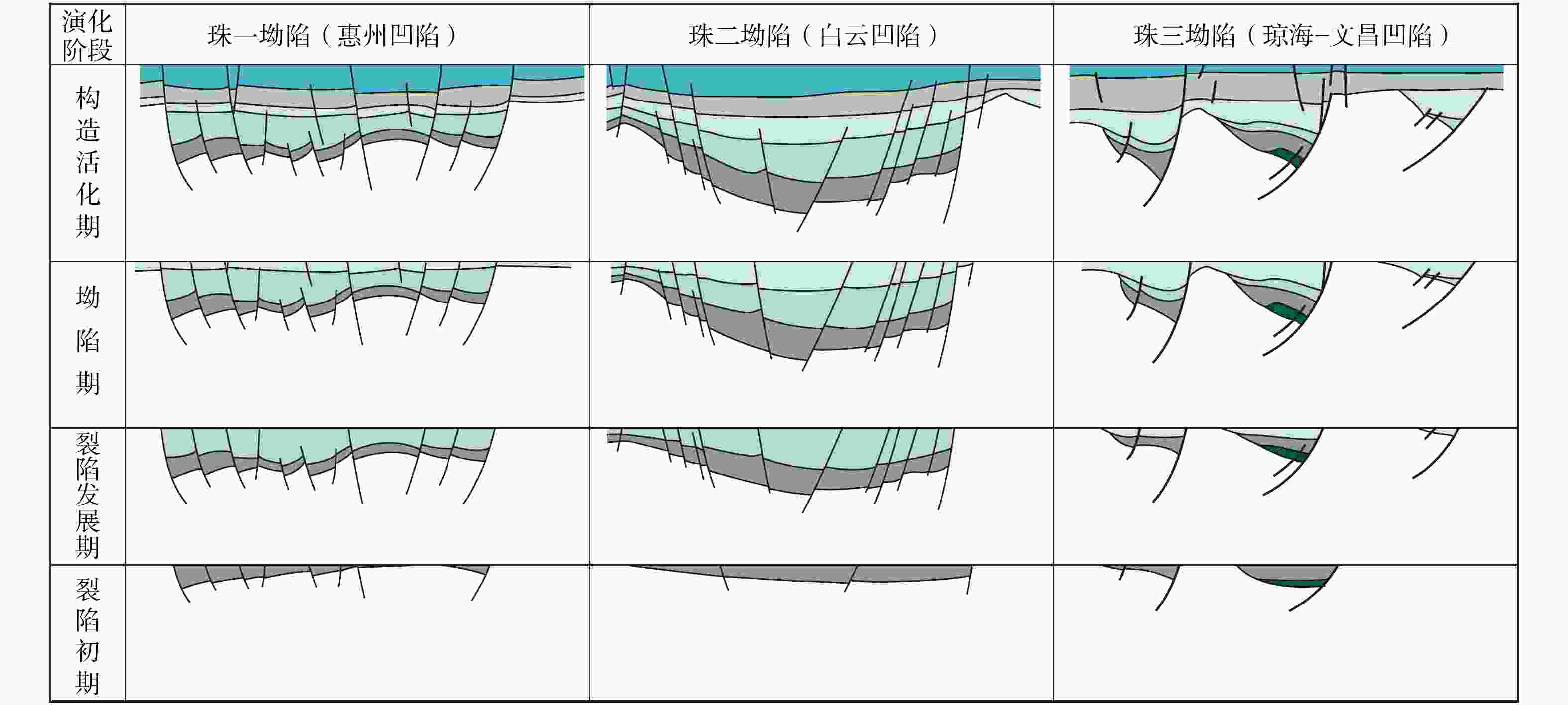
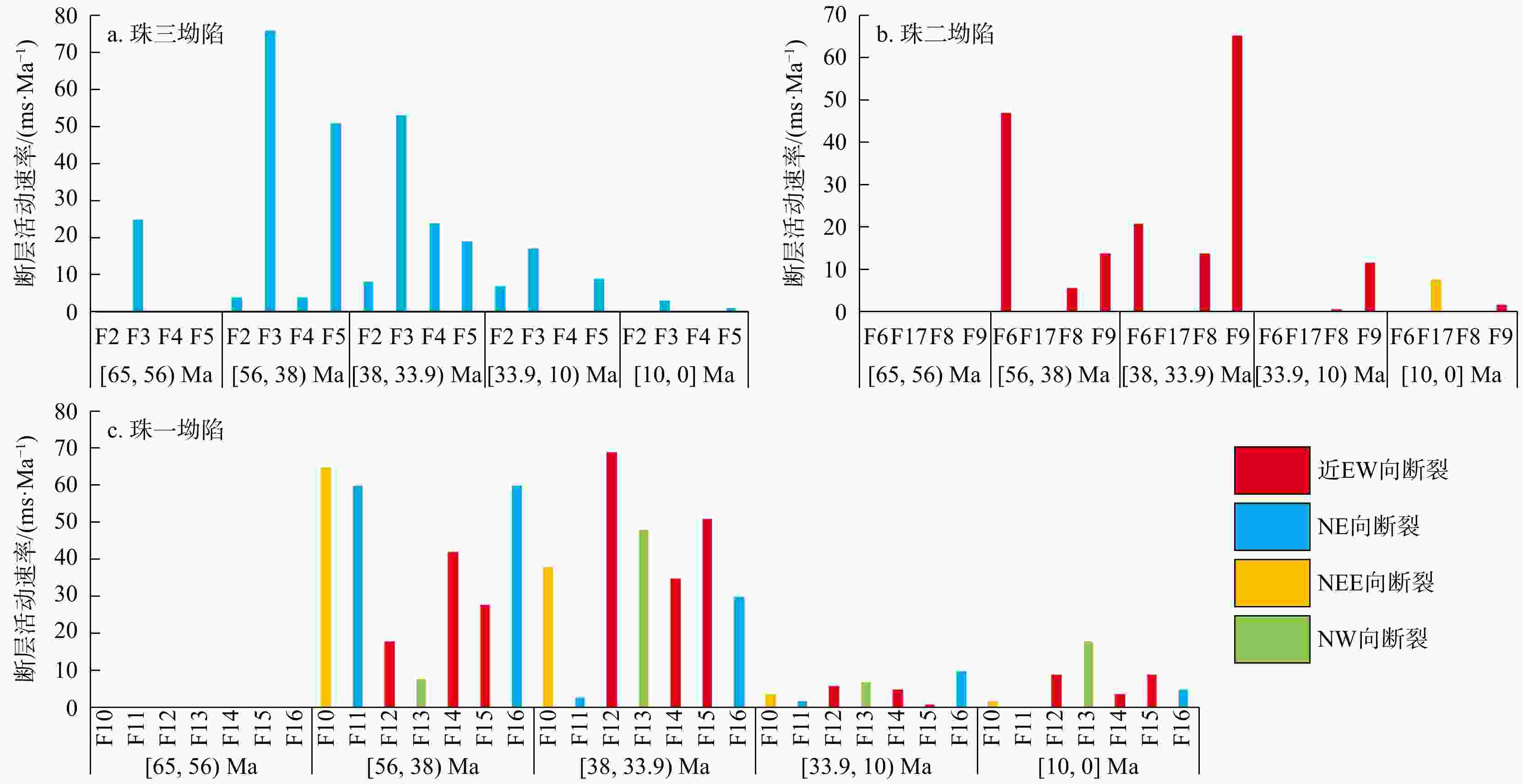
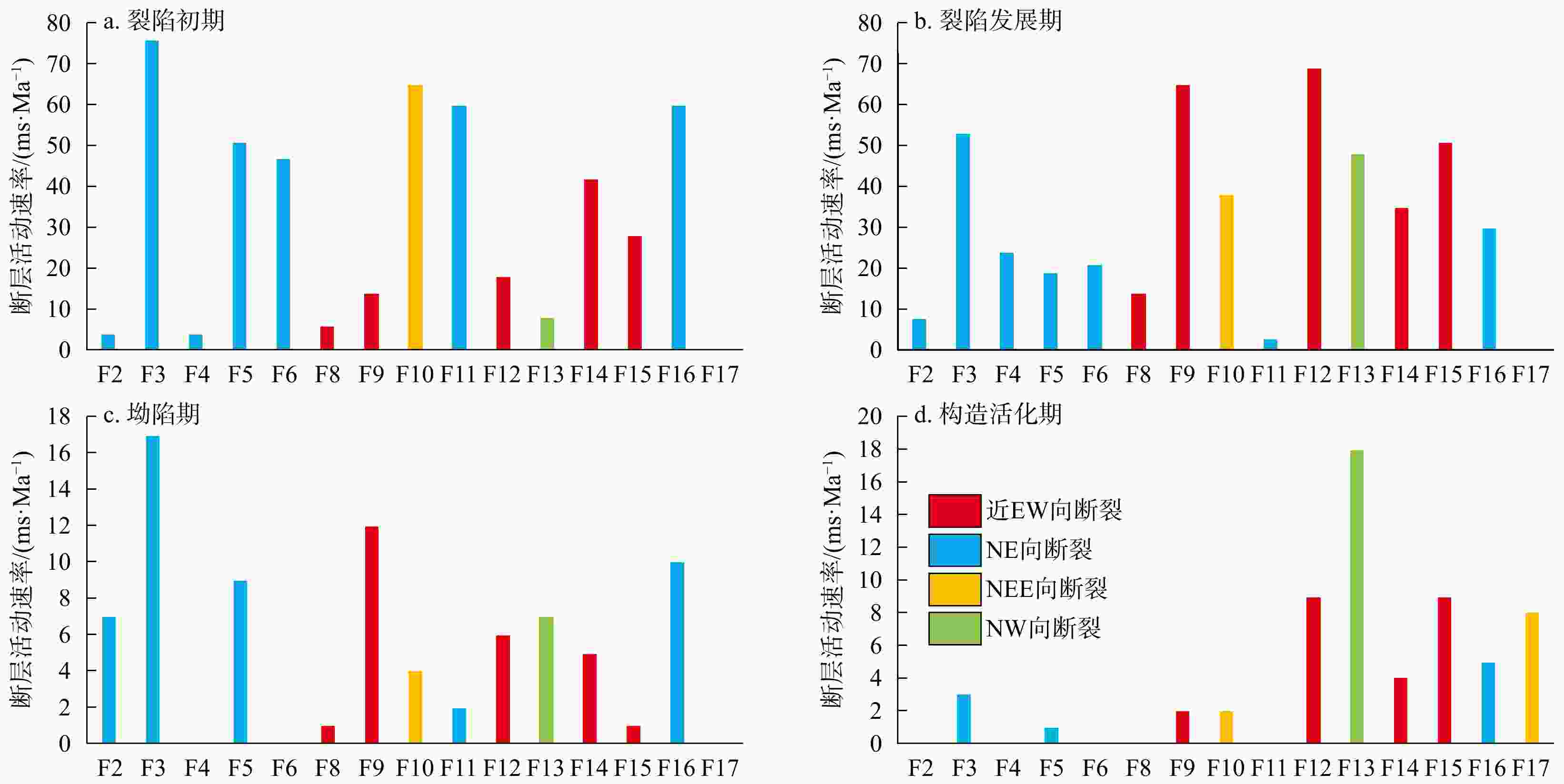
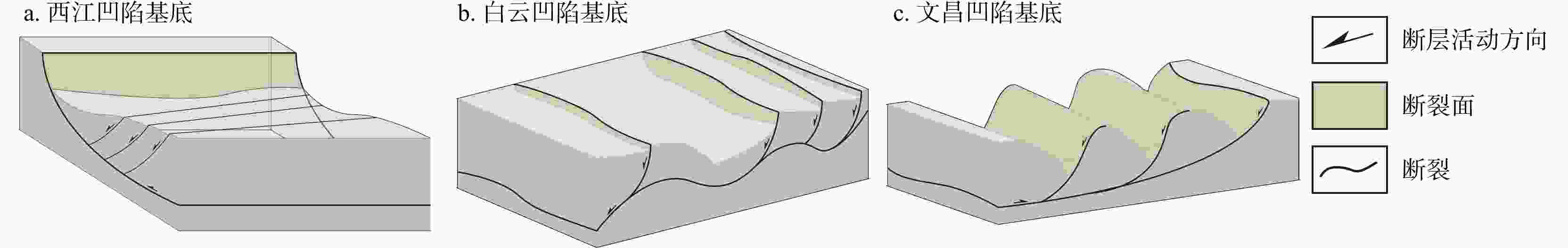
为加深对珠江口盆地内不同构造单元之间裂陷形成和演化时空差异性的认识,基于二维地震剖面资料,通过构造解析、平衡剖面恢复和断裂活动速率计算等方法,讨论了不同构造单元先存构造、基底岩性、断裂体系及构造演化的差异,并结合岩浆活动和动力学背景,探究了盆地内坳陷构造的成因。珠江口盆地基底先存构造主要发育了一系列NE向逆冲断裂和与之共轭的NW向先存逆冲断裂体系;珠三、珠二及珠一坳陷西部断裂以NE−NEE走向为主,珠一及珠二坳陷东部断裂以近EW−NWW走向为主,控制着盆地裂陷期的构造格局;裂陷作用自东向西逐渐减弱,珠一坳陷东部先存断裂更为活跃。裂陷期主要断裂是沿基底先存断裂继承发育,由于基底先存构造及岩性的差异具有不同的抗张和抗剪强度,同时受控于周缘板块运动、岩浆作用和区域应力场变化等,珠一和珠二坳陷内的同沉积主干断裂体系发生由NE−NEE向伸展性质顺时针转变为近EW−NW向伸展−走滑主导的变化过程;裂陷后期,受深度相关的伸展模式影响,裂陷结构由北向南为“下厚上薄”狭长型窄地堑、半地堑向“上厚下薄”宽缓型地堑、半地堑转变。
Abstract:Objective To deepen the understanding of spatial and temporal differences in rift formation and evolution among different tectonic units within the Pearl River Mouth Basin.
Methods Based on 2D seismic profile data, this study analyzes differences in pre-existing structures, basement lithology, fracture systems, and tectonic evolution across tectonic units using tectonic analysis, balanced cross-section restoration, and fracture activity rate calculation, combined with magmatic activities and dynamics background, the causes of depression tectonics in the basin are explored.
Results A series of NE-trending thrust faults and conjugate NW-trending pre-existing thrust faults developed on the basement tectonics of the Pearl River Mouth Basin. NE-NEE -trending faults dominate in the western parts of the Zhu Ⅲ, Zhu Ⅱ, and Zhu Ⅰ depressions, while near-EW- to NWW-trending faults dominate in the eastern Zhu Ⅰ and Zhu Ⅱ depressions, controlling the basin's tectonic pattern during the rifting period. Rifting intensity weakens from east to west, and the eastern part of Zhu Ⅰ Depression exhibits higher fault activity.
Conclusions During rifting, major faults during the rifting period inherited and developed along pre-existing basement faults. The main fault system within the same sedimentary trunk in the Zhu Ⅰ and Zhu Ⅱ depressions evolved clockwise from NW-NEE-trending to EW-NW-trending and strike-slip dominated, with tensile and shear strengths modulated by differences in basement structure and lithology, and influenced by surrounding plate movement, magmatic activities, and regional stress field changes. In the late stage, the rift architecture transitions from a narrow elongated graben/half-graben "thick lower part and thin upper part" in the north to a broad, gentle graben/half-graben with "thick upper part and thin lower part" in the south.
-
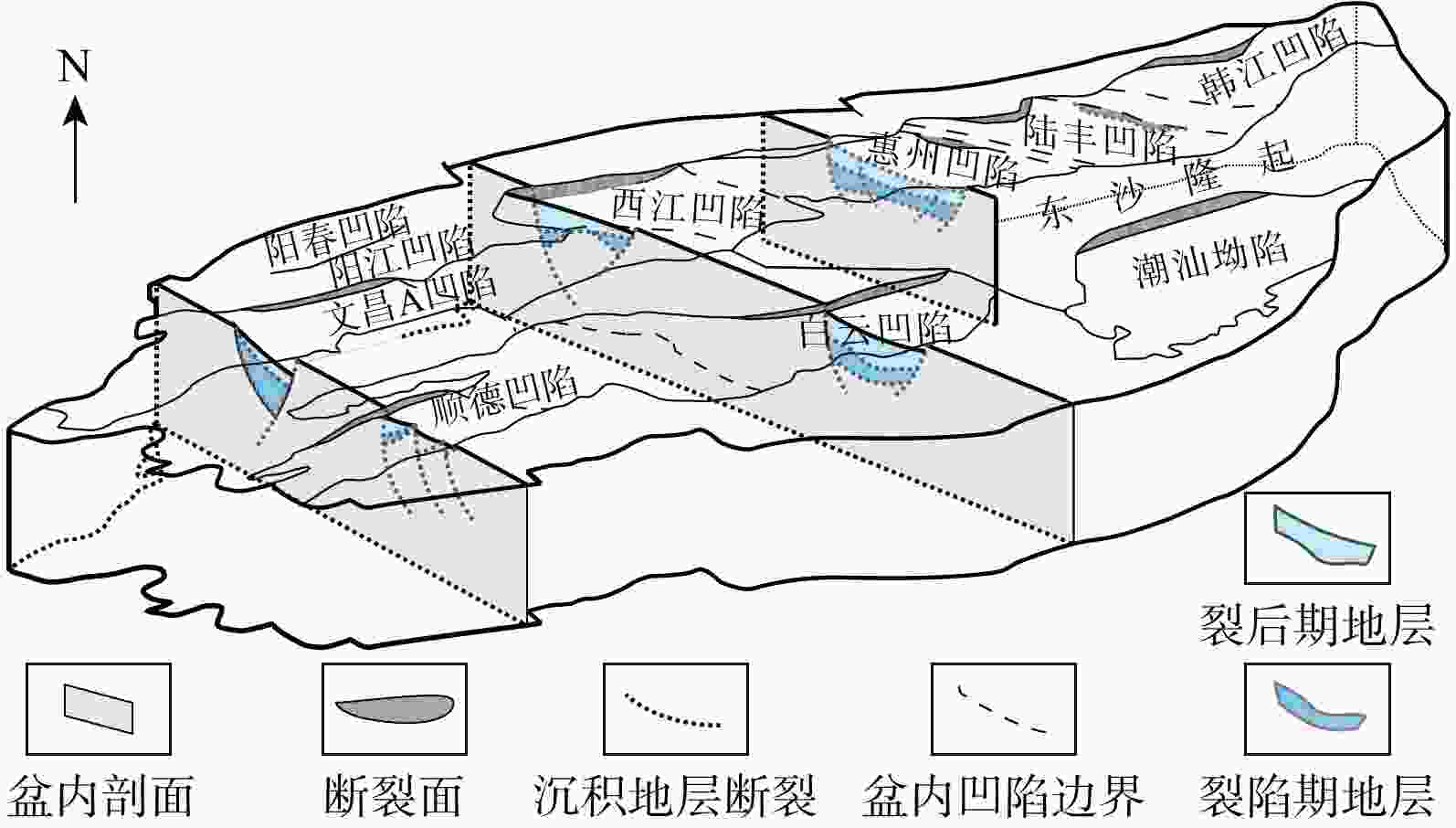
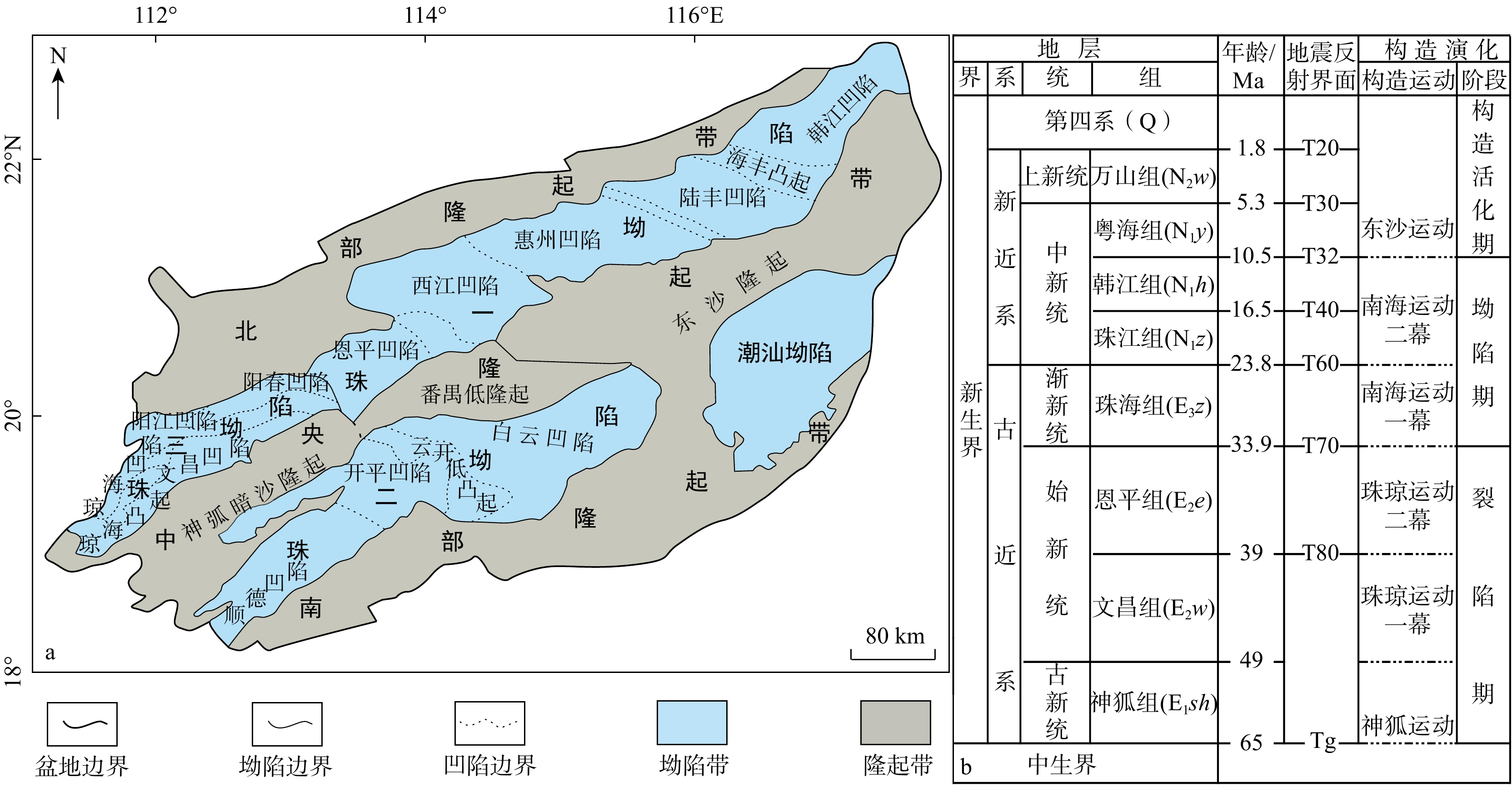
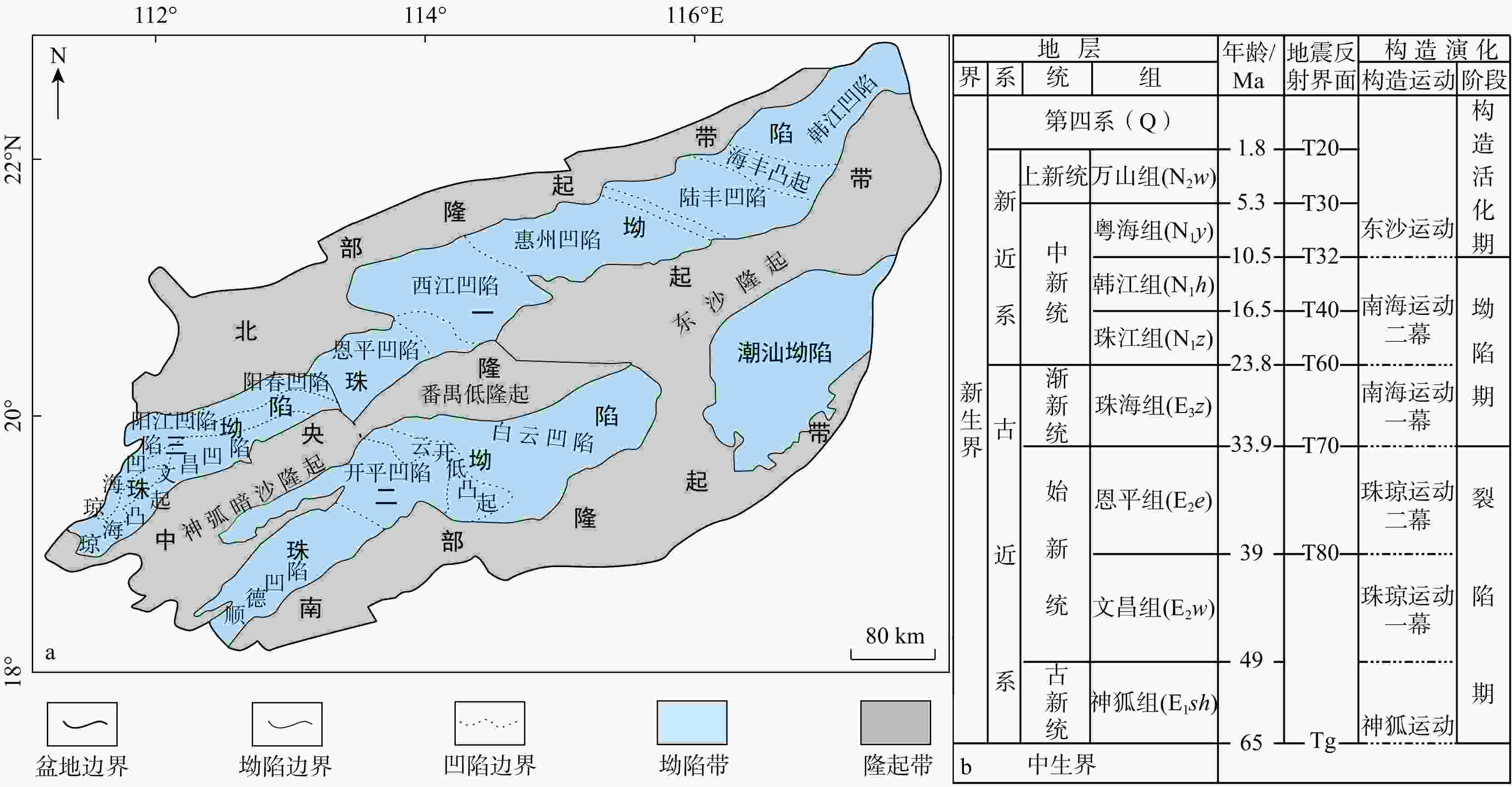
图 1 珠江口盆地区域构造单元划分(a)与地层综合图(b)(据文献[6]修改)
Figure 1. Structural units (a) and stratigraphic chart (b) in the Pearl River Mouth Basin
表 1 珠江口盆地构造单元结构特征
Table 1. Structural characteristics of the structural units in the Pearl River Mouth Basin
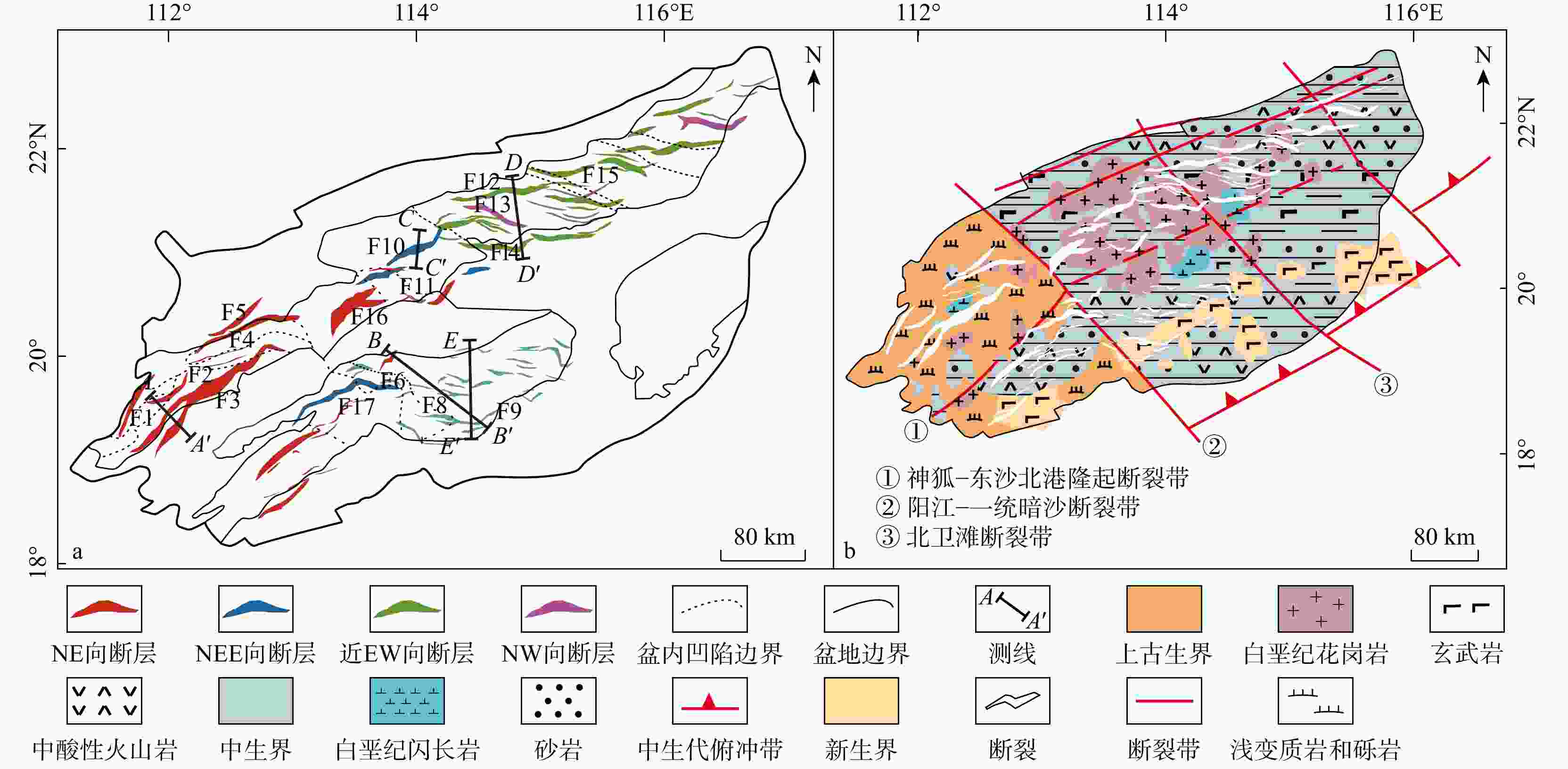
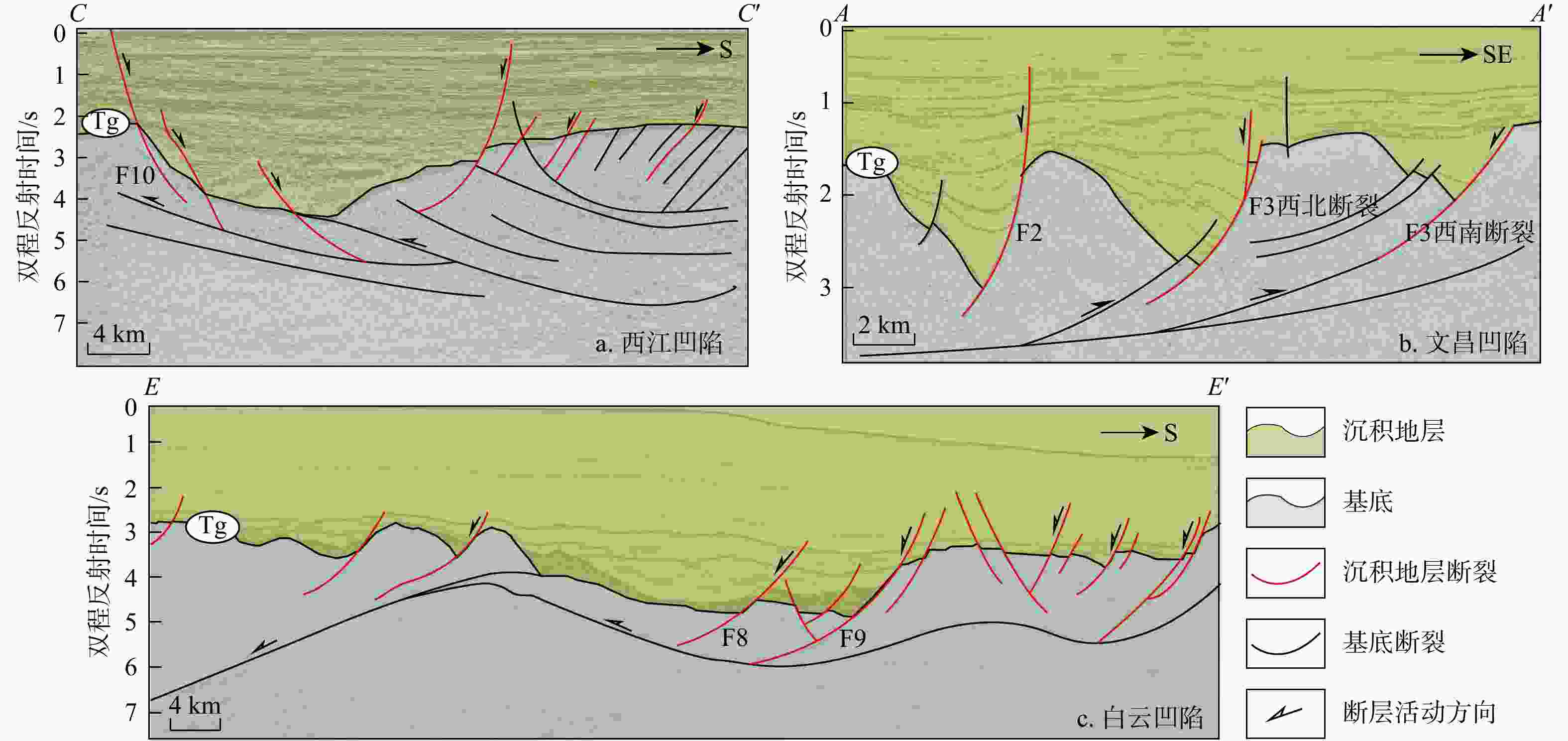
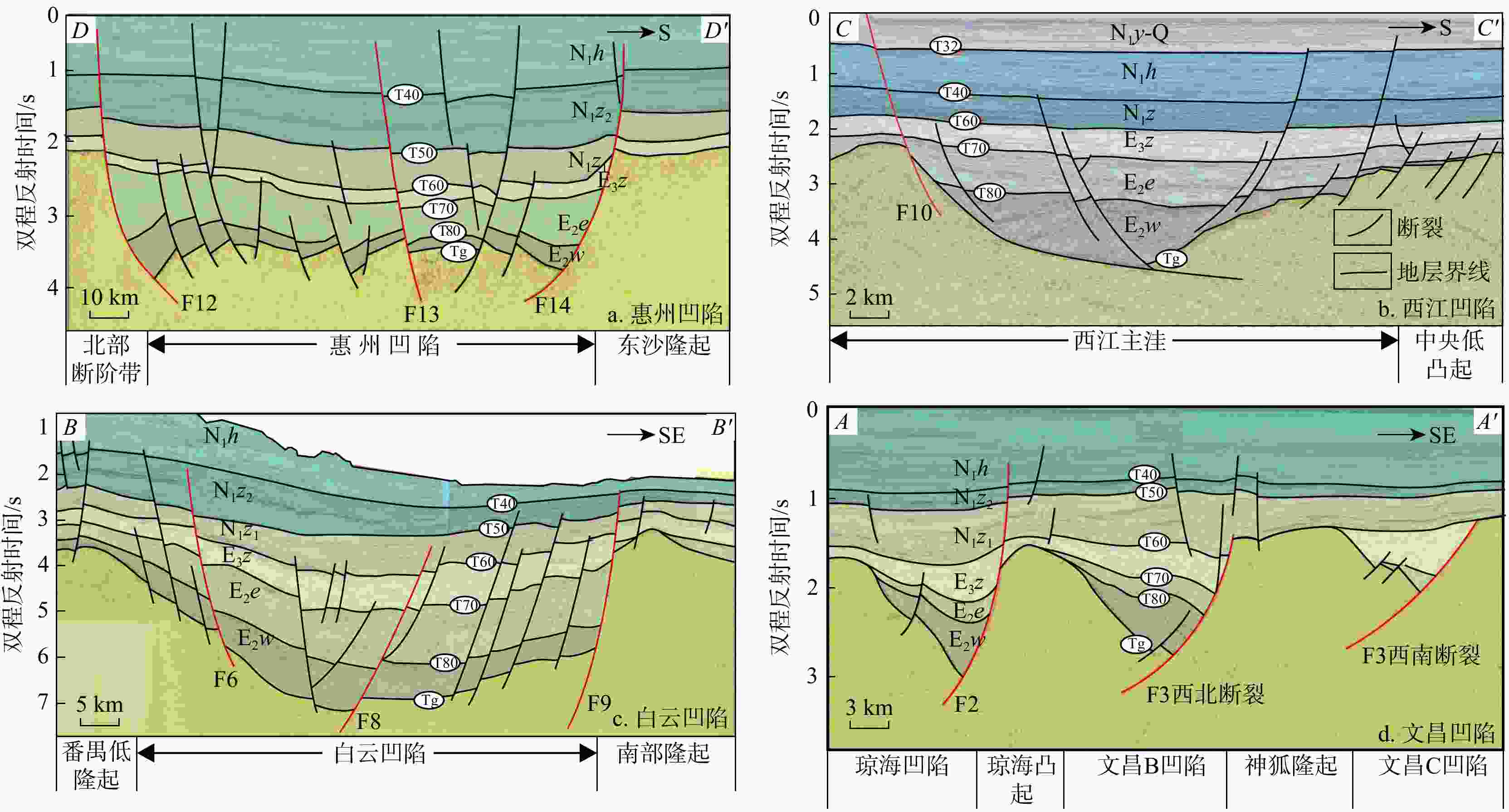
构造单元 走向 古近系断陷结构 先存构造 基地岩性 活动性特征 一级 二级 三级 珠江口盆地 珠一坳陷 恩平凹陷 NE 北断南超半地堑 逆冲断层 花岗岩为主、少量火山岩与沉积岩 裂陷期整体活动速率高,主控断层活动速率呈增大-减小-停止活动 西江凹陷 NE 北断南超半地堑 惠州凹陷 近EW 复式半地堑、地堑 陆丰凹陷 近EW 复式半地堑 韩江凹陷 近EW 复式半地堑、地堑 珠二坳陷 开平凹陷 NE 北断南超半地堑 拆离断层 变质岩、部分玄武岩 整体活动速率低,主控断层活动速率从古至今逐渐减小至停止活动 顺德凹陷 NE 地堑、半地堑 白云凹陷 近EW 地堑、半地堑 珠三坳陷 阳春凹陷 NE 南断北超半地堑 滑脱断坡
断坪变质砂岩、砾岩、少量闪长岩和沉积岩 整体活动速率较高,主控断层活动速率从古至今逐渐减弱 阳江凹陷 NE 复式半地堑、地堑 琼海凹陷 NE 南断北超半地堑 文昌凹陷 NE 南断北超半地堑 -
[1] 钟志洪, 施和生, 朱明, 等. 珠江口盆地构造-地层格架及成因机制探讨[J]. 中国海上油气, 2014, 26(5): 20-29.ZHONG Z H, SHI H S, ZHU M, et al. A discussion on the tectonic-stratigraphic framework and its origin mechanism in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2014, 26(5): 20-29. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] MA B S, QI J F, WU G H, et al. Structural variability and rifting process of the segmented Cenozoic Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern continental margin of the South China Sea[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 2022, 96(6): 2074-2092. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.14983 [3] DENG C, ZHU R X, HAN J H, et al. Impact of basement thrust faults on low-angle normal faults and rift basin evolution: A case study in the Enping Sag, Pearl River Basin[J]. Solid Earth, 2021, 12(10): 2327-2350. doi: 10.5194/se-12-2327-2021 [4] YE Q, MEI L F, SHI H S, et al. A low-angle normal fault and basement structures within the Enping Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin: Insights into Late Mesozoic to Early Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the South China Sea area[J]. Tectonophysics, 2018, 731/732: 1-16. [5] 叶青. 南海北部陆缘晚中生代构造体系: 动力学以及对珠江口盆地新生代构造的制约[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2019.YE Q. The Late Mesozoic structure systems in the northern South China Sea margin: Geodynamics and their influence on the Cenozoic structures in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [6] 刘雨晴. 南海周缘新生代盆地结构时空差异及其控制因素[D]. 山东青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2019.LIU Y Q. Temporal-spatial basin structure differences and their controlling factors of the Cenozoic basins around the South China Sea[D]. Qingdao Shandong: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [7] 刘雨晴, 吴智平, 程燕君, 等. 南海北缘古近纪裂陷结构时空差异及控制因素: 以珠江口盆地为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2019, 48(2): 367-376.LIU Y Q, WU Z P, CHENG Y J, et al. Spatial and temporal difference of Paleogene rift structure and its controlling factors in the northern South China Sea: A case study of Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2019, 48(2): 367-376. (in Chinese with English abstract [8] 余一欣, 张靖, 张忠涛, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷东北部断裂发育特征及其控油气作用[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2022, 42(3): 133-139.YU Y X, ZHANG J, ZHANG Z T, et al. Fault characteristics and its significances on hydrocarbon accumulation in northeastern Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2022, 42(3): 133-139. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 张功成, 贾庆军, 王万银, 等. 南海构造格局及其演化[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(10): 4194-4215. doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0698ZHANG G C, JIA Q J, WANG W Y, et al. On tectonic framework and evolution of the South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(10): 4194-4215. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0698 [10] 漆家福, 吴景富, 马兵山, 等. 南海北部珠江口盆地中段伸展构造模型及其动力学[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(2): 203-221.QI J F, WU J F, MA B S, et al. The structural model and dynamics concerning middle section, Pearl River Mouth Basin in north margin of South China Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(2): 203-221. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] MU D L, PENG G R, ZHU D W, et al. Structure and formation mechanism of the Pearl River Mouth Basin: Insights from multi-phase strike-slip motions in the Yangjiang Sag, SE China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2022, 226: 105081. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2022.105081 [12] 马兵山. 南海北部珠江口盆地新生代构造特征及其演化[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2020.MA B S. The Cenozoic structural characteristics and tectonic evolution of the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] ZHOU Z C, MEI L F, LIU J, et al. Continentward-dipping detachment fault system and asymmetric rift structure of the Baiyun Sag, northern South China Sea[J]. Tectonophysics, 2018, 726: 121-136. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2018.02.002 [14] LEYLA B H, ZHANG J X, YANG L L. Quantitative analysis of faults in Huizhou sub-basin, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2018, 29(1): 169-181. doi: 10.1007/s12583-018-0823-3 [15] 王福国, 张向涛, 梅廉夫, 等. 珠江口盆地白云东区古近纪挤压−伸展变形模式及勘探意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 246-252.WANG F G, ZHANG X T, MEI L F, et al. Characteristics of Paleogene compression-extension deformation and exploration significance in the Baiyun East area, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 246-252. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 赵萌. 珠江口盆地西江凹陷−白云凹陷构造对比研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2019.ZHAO M. Structural comparison between Xijiang Sag and Baiyun Sag in Pearl River Mouth Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 鲁宝亮, 王璞珺, 张功成, 等. 南海北部陆缘盆地基底结构及其油气勘探意义[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(4): 580-587.LU B L, WANG P J, ZHANG G C, et al. Basement structures of an epicontinental basin in the northern South China Sea and their significance in petroleum prospect[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(4): 580-587. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] 刘海伦. 珠江口盆地珠−坳陷裂陷结构: 基底属性与区域应力联合制约[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018.LIU H L. Rift style controlled by basement attribute and regional stress in Zhu Ⅰ Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 吴太霏, 王华, 刘恩涛, 等. 珠三坳陷珠江组一段沉积体系演化过程及其控制因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2024, 43(2): 111-122.WU T F, WANG H, LIU E T, et al. Evolutionary and controlling factors of sedimentary system in the First Member of the Zhujiang Formation in the Zhu Ⅲ Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2024, 43(2): 111-122. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 徐长贵, 高阳东, 刘军, 等. 珠江口盆地西江凹陷番禺4洼古近系勘探重大发现及其意义[J]. 石油学报, 2024, 45(7): 1031-1043. doi: 10.7623/syxb202407001XU C G, GAO Y D, LIU J, et al. Major discoveries and significance of hydrocarbon exploration in the Paleogene reservoirs of Panyu 4 subsag, Xijiang Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2024, 45(7): 1031-1043. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7623/syxb202407001 [21] 吴静. 珠江口盆地恩平凹陷北部隆起区油气远源富集与主控因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4): 117-124.WU J. Key factors of far-source hydrocarbon enrichment in the northern uplift area of Enping Sag in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 117-124. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] 杨海长, 陈莹, 纪沫, 等. 珠江口盆地深水区构造演化差异性与油气勘探意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2017, 22(6): 59-68. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2017.06.007YANG H Z, CHEN Y, JI M, et al. Structural evolution difference and the significance for oil and gas exploration in the deep water area of the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2017, 22(6): 59-68. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2017.06.007 [23] 庞雄, 郑金云, 梅廉夫, 等. 先存俯冲陆缘背景下南海北部陆缘断陷特征及成因[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(5): 1069-1080.PANG X, ZHENG J Y, MEI L F, et al. Characteristics and origin of continental marginal fault depressions under the background of preexisting subduction continental margin, northern South China Sea, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2021, 48(5): 1069-1080. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 葛家旺, 朱筱敏, 雷永昌, 等. 多幕裂陷盆地构造−沉积响应及陆丰凹陷实例分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(1): 77-89.GE J W, ZHU X M, LEI Y C, et al. Tectono-sedimentary development of multiphase rift basins: An example of the Lufeng Depression[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(1): 77-89. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 郭伟, 徐国强, 柳保军, 等. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷文昌组构造-沉积响应关系[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(7): 2433-2453.GUO W, XU G Q, LIU B J, et al. Structure-sedimentary response relationship of Wenchang Formation in Baiyun Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(7): 2433-2453. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 彭光荣, 郑金云, 蔡嵩, 等. 珠江口盆地珠二坳陷中部“对向拆离型复合洼陷” 结构特征及其成因探讨[J]. 地球科学, 2024, 49(4): 1385-1399.PENG G R, ZHENG J Y, CAI S, et al. Structural characteristics and genesis of opposite detachment type composite sag in middle of Zhu Ⅱ Depression, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2024, 49(4): 1385-1399. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 胡阳, 吴智平, 钟志洪, 等. 珠江口盆地珠一坳陷始新世中−晚期构造变革特征及成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(5): 779-785.HU Y, WU Z P, ZHONG Z H, et al. Characterization and genesis of the Middle and Late Eocene tectonic changes in Zhu 1 Depression of Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(5): 779-785. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] HUI G G, ZHANG P Z, LI Z G, et al. Opening of the South China Sea marginal basin: Insights from the tectonic evolution of the ENE-striking littoral fault zone[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2022, 145: 105854. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2022.105854 [29] HAN J H, XU G Q, LI Y Y, et al. Evolutionary history and controlling factors of the shelf breaks in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77: 179-189. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.06.009 [30] 杨海长, 曾清波, 纪沫, 等. 珠江口盆地深水区开平凹陷拆离型裂陷石油形成条件与勘探方向[J]. 石油学报, 2023, 44(6): 933-947. doi: 10.7623/syxb202306004YANG H Z, ZENG Q B, JI M, et al. Accumulation conditions and exploration direction of crude oil in detachment rift of Kaiping Sag in deep water area of Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2023, 44(6): 933-947. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.7623/syxb202306004 [31] 李博, 邓超, 周亮, 等. 珠江口盆地恩平凹陷与惠州凹陷断裂特征差异及构造演化[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2023, 39(7): 34-46.LI B, DENG C, ZHOU L, et al. Difference in fault characteristics and tectonic evolution between Enping Sag and Huizhou Sag in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2023, 39(7): 34-46. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 邓棚, 梅廉夫, 杜家元, 等. 珠江口盆地西江主洼低角度边界正断层特征及成因演化[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(3): 606-616. doi: 10.11743/ogg20200316DENG P, MEI L F, DU J Y, et al. Characteristics and genetic development of a low-angle boundary normal fault in Xijiang Main Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(3): 606-616. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11743/ogg20200316 [33] 施和生, 杜家元, 梅廉夫, 等. 珠江口盆地惠州运动及其意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(3): 447-461. doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.03.02SHI H S, DU J Y, MEI L F, et al. Huizhou movement and its significance in Pearl River Mouth Basin, China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(3): 447-461. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11698/PED.2020.03.02 [34] 能源, 吴景富, 漆家福, 等. 南海北部深水区新生代盆地三层结构及其构造演化[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(3): 403-414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.03.010NENG Y, WU J F, QI J F, et al. Three structural layers and its evolution of Cenozoic basins in deep water area of northern margin, South China Sea[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(3): 403-414. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.03.010 [35] 邓棚. 南海北部陆缘古近纪多幕裂陷作用属性及转换: 以珠江口盆地珠一坳陷为例[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018.DENG P. The nature and tectonic transition of the multiphase rifting in the northern margin of the South China Sea: Based on the study of the Zhu Ⅰ Depression in Pearl River Mouth Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] LI G, MEI L F, YE Q, et al. Post-rift faulting controlled by different geodynamics in the Pearl River Mouth Basin, northern South China Sea margin[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2023, 237: 104311. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.104311 [37] 丁巍伟. 南海大陆边缘动力学: 从陆缘破裂到海底扩张[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(3): 790-800.DING W W. Continental margin dynamics of South China Sea: From continental break-up to seafloor spreading[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(3): 790-800. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] WANG P C, SUO Y H, PENG G R, et al. Three-stage extension in the Cenozoic Pearl River Mouth Basin triggering onset of the South China Sea spreading[J]. Gondwana Research, 2023, 120: 31-46. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2022.05.023 [39] 詹诚, 卢绍平, 方鹏高. 汇聚背景下的多幕裂陷作用及其迁移机制: 以南海北部珠江口盆地为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(4): 307-318.ZHAN C, LU S P, FANG P G. Multiphase rift and migration mechanism in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(4): 307-318. [40] 唐旭, 张向涛, 余一欣, 等. 珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷南部古近系断裂发育特征与油气成藏[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2023, 43(3): 132-143.TANG X, ZHANG X T, YU Y X, et al. Fault characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation in the southern Lufeng Sag, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2023, 43(3): 132-143. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] 吕彩丽, 张功成, 杨东升. 珠江口盆地珠二坳陷文昌组构造差异性与动力学成因机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2017, 24(6): 333-341.LYU C L, ZHANG G C, YANG D S, et al. Differential structure and dynamic mechanism of Wenchang Formation in the Zhu Ⅱ Depression of the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2017, 24(6): 333-341. (in Chinese with English abstract [42] 李三忠, 索艳慧, 刘鑫, 等. 南海的盆地群与盆地动力学[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2012, 32(6): 55-78.LI S Z, SUO Y H, LIU X, et al. Basin dynamics and basin groups of the South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2012, 32(6): 55-78. (in Chinese with English abstract [43] 陈建军, 马艳萍, 陈建中, 等. 南海北部陆缘盆地形成的构造动力学背景[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(3): 38-47.CHEN J J, MA Y P, CHEN J Z, et al. Tectonic dynamics of northern continental margin basins in South China Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(3): 38-47. (in Chinese with English abstract [44] 李刚. 珠江口盆地裂后期断层和岩浆发育特征、时空差异及动力学含义[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2022.LI G. Post-rift faulting and magmatism within the Pearl River Mouth Basin: Spatial-temporal difference, and new insights into the geodynamics[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [45] 任建业. 中国近海海域新生代成盆动力机制分析[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(10): 3337-3361.REN J Y. Genetic dynamics of China offshore Cenozoic basins[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(10): 3337-3361. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: