-
摘要:
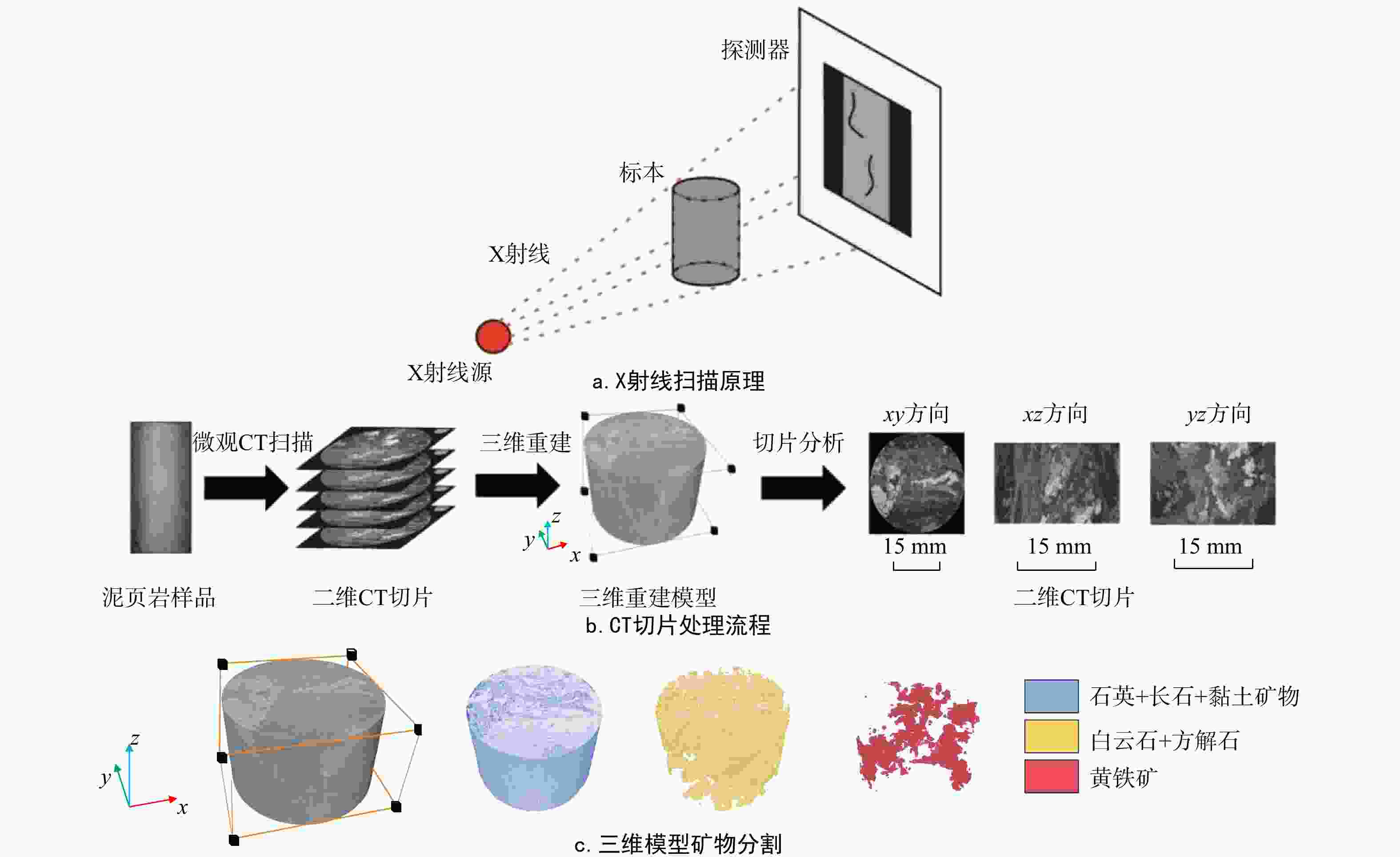
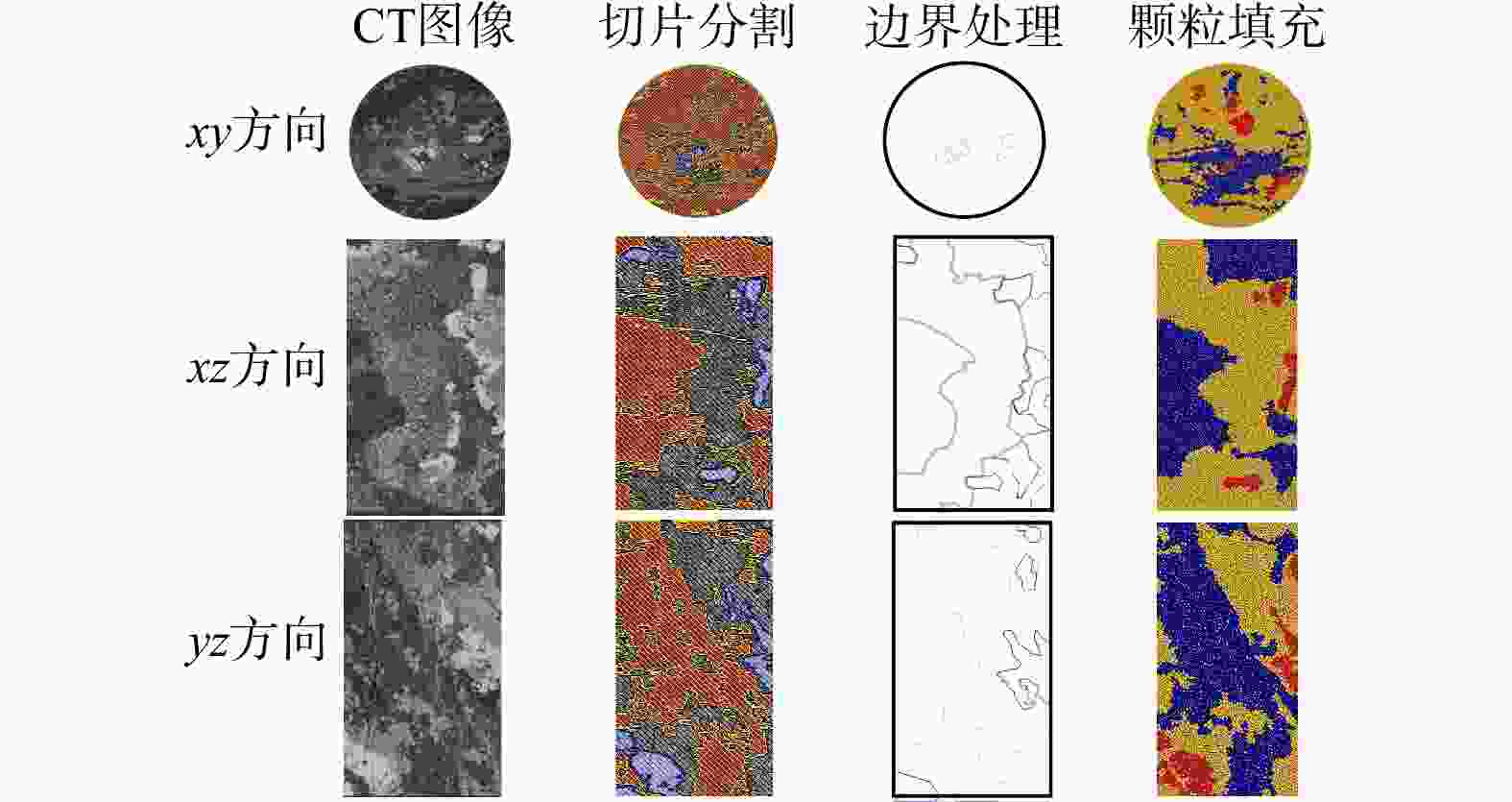
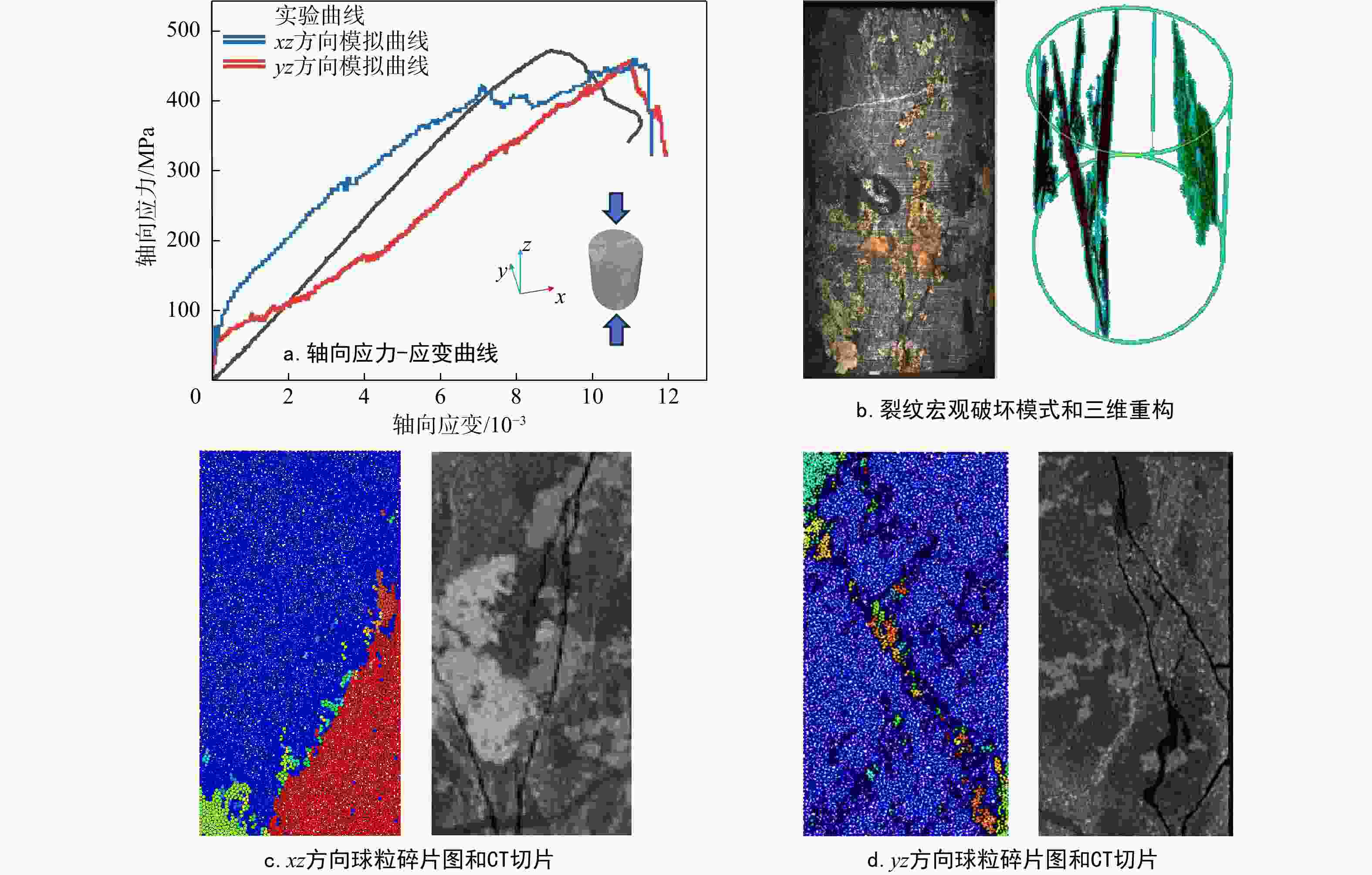
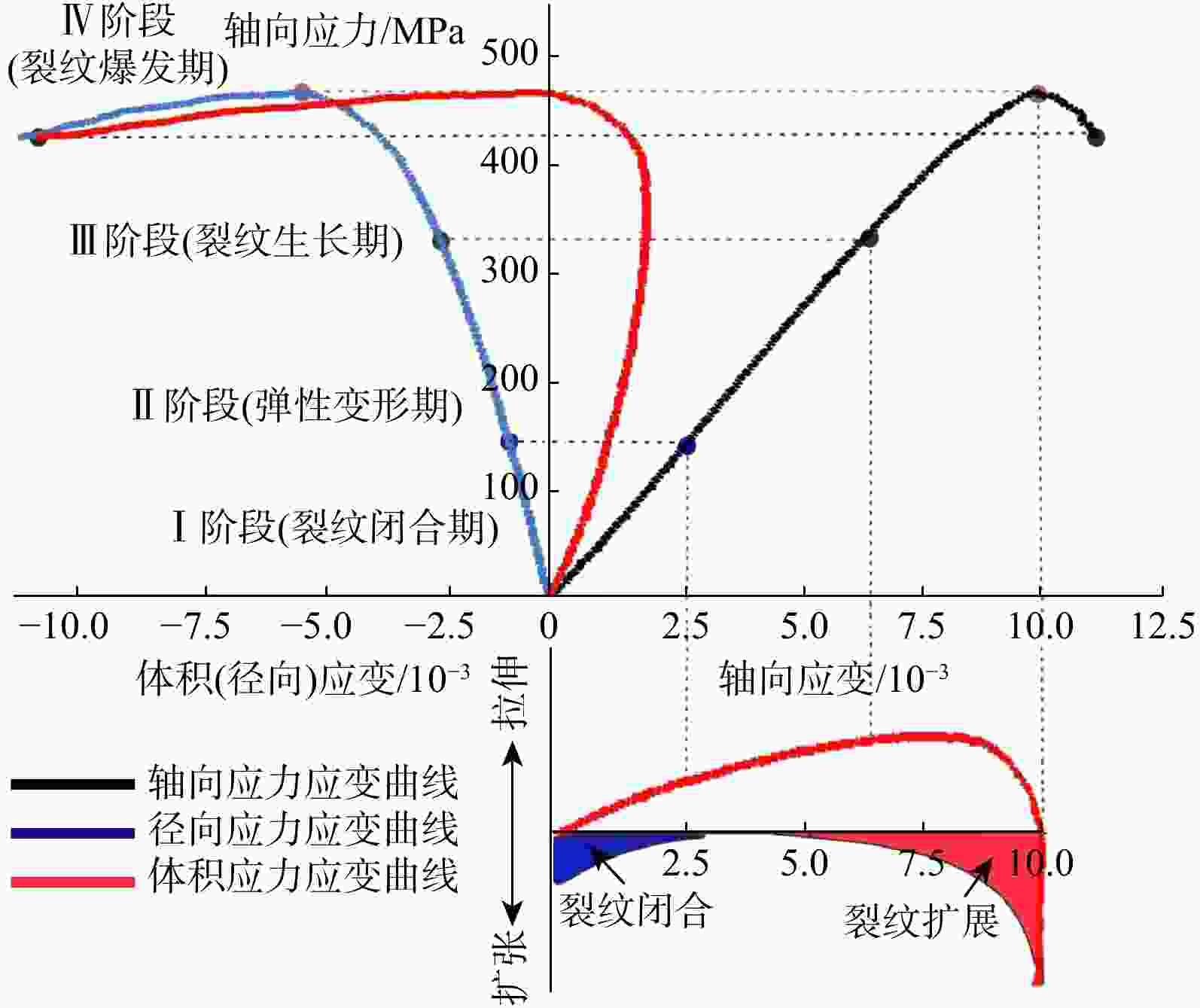
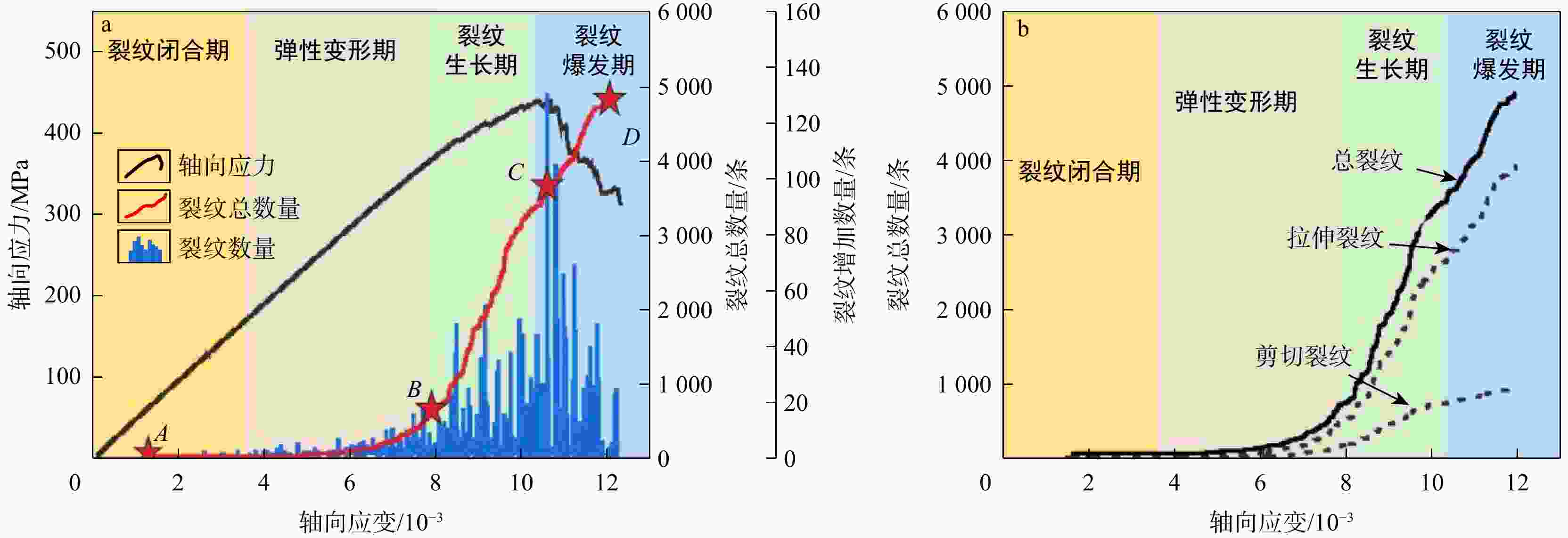
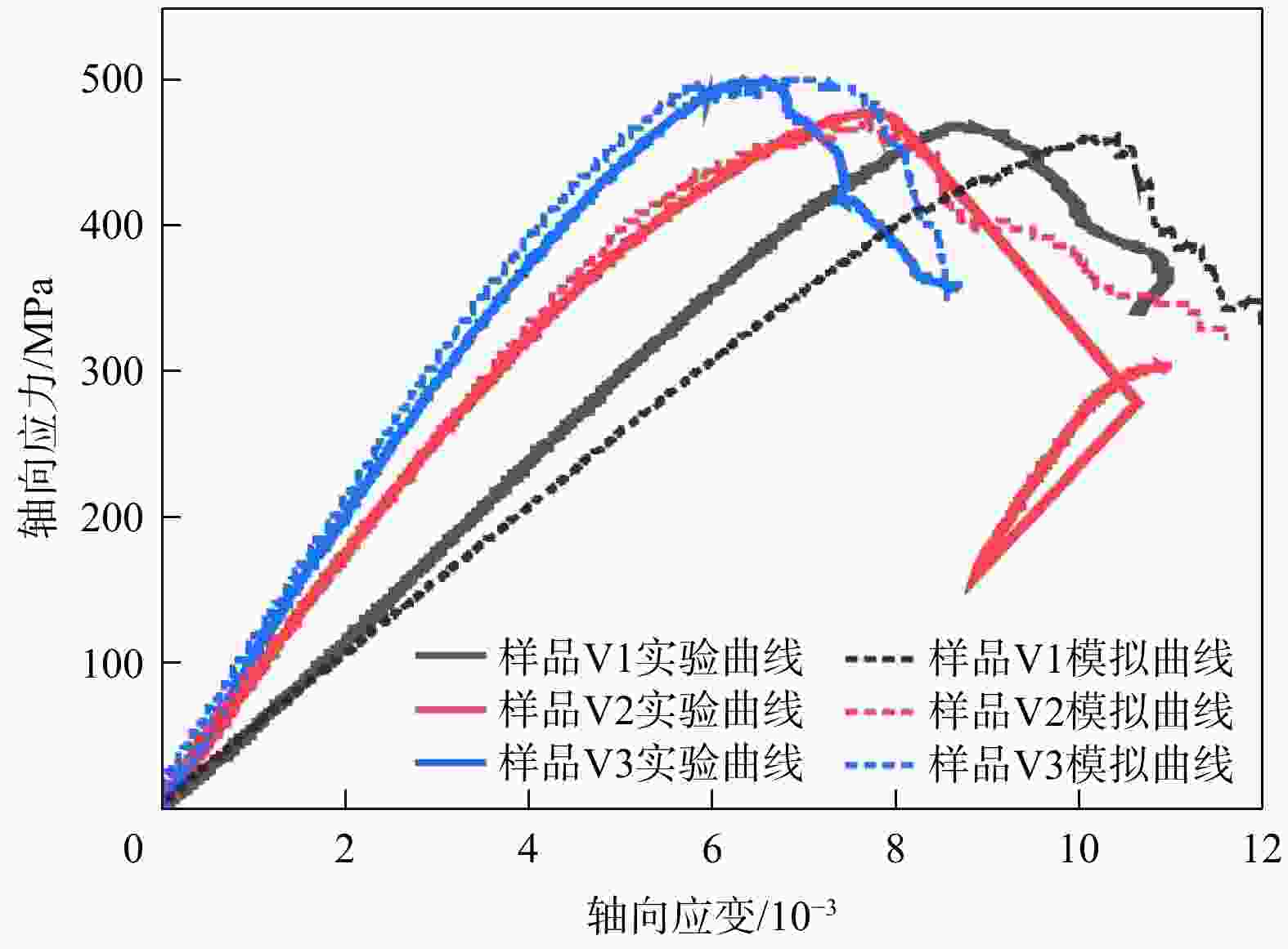
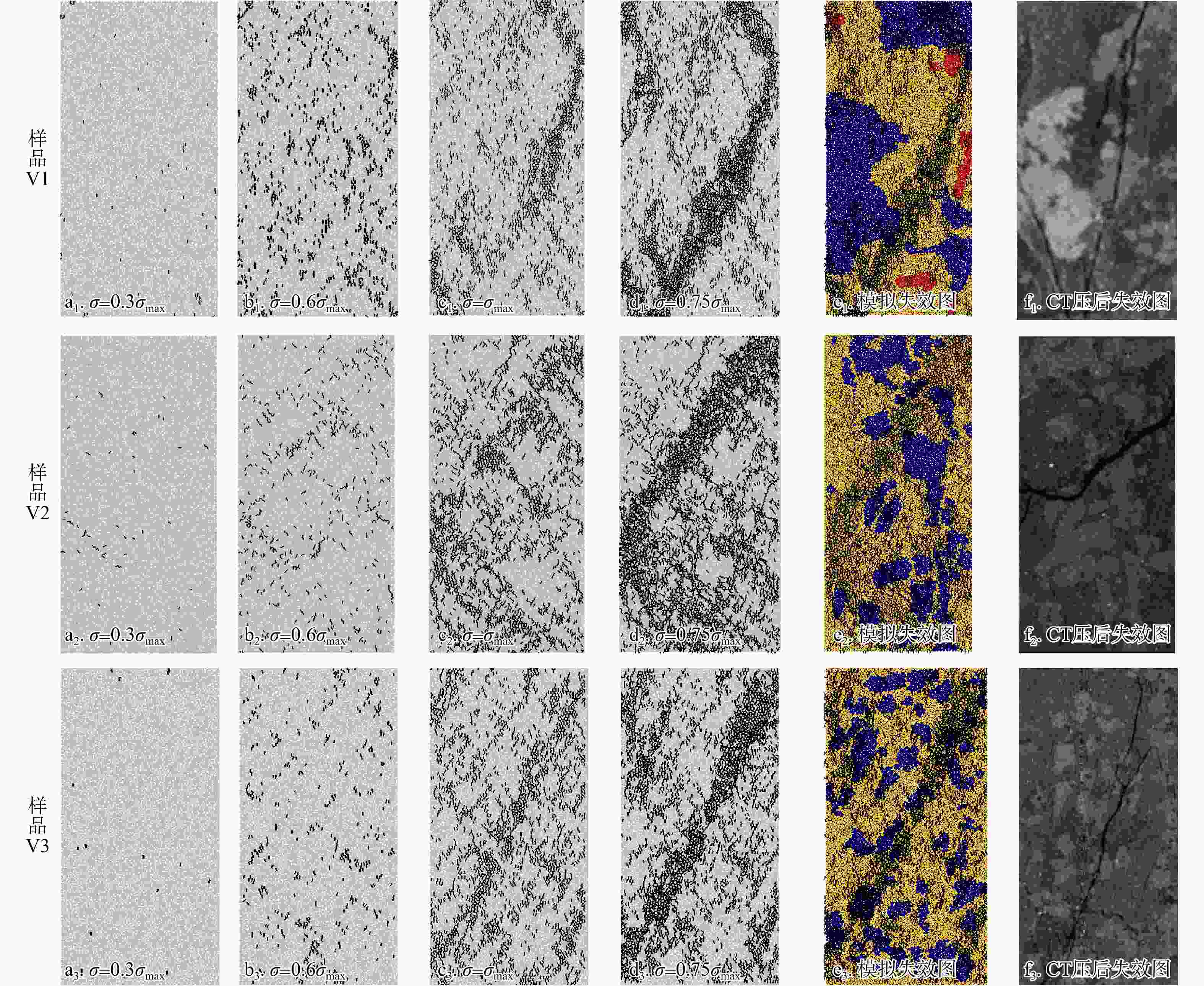
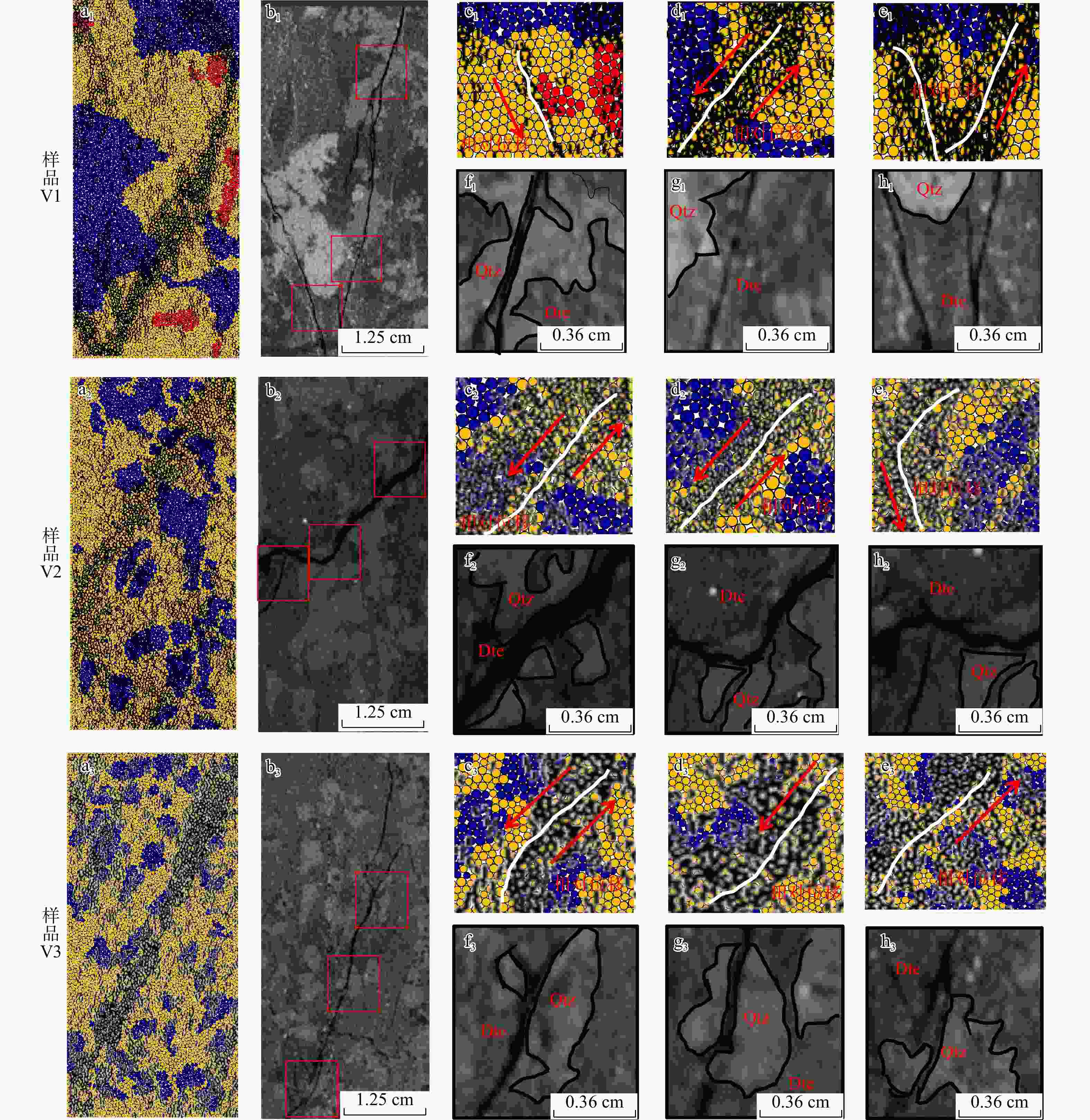
为探究细观尺度下岩石破坏机理,结合数字图像处理(DIP)技术和颗粒流代码(PFC)方法提出了一种带有表征矿物属性新的建模方法,利用常规三轴压缩实验条件下获取的宏观力学参数和破坏形态对建立的离散元数值模型进行了校正,分析了地应力条件下岩石矿物属性对岩石破坏演化的影响,探究了非均质性结构对微裂行为的影响。结果表明:常规三轴压缩实验加载过程主要分为裂纹闭合期、弹性变形期、裂纹生长期、裂纹爆发期;由选取的3块泥页岩样品计算机断层扫描(CT)切片模拟结果表明,岩石的非均质性对岩石微裂纹的产生和岩石物理力学参数均有一定的影响,非均质性越弱,峰值强度(
σ max)和弹性模量(E )越高;从岩石裂纹扩展分布来看,非均质性的增强使得微裂纹分布更加复杂;从岩石微裂纹空间分布来看,微裂纹更加倾向于产生在白云石类矿物和石英类矿物的边界之间。研究成果对油气地下深部开采、防灾工程具有重要的参考意义。Abstract:Objective To investigate the failure mechanism of rocks at the mesoscopic scale,
Methods this study proposes a novel modeling method that combines digital image processing (DIP) technology and particle flow code (PFC) to characterize mineral properties. The discrete element numerical model was calibrated using macroscopic mechanical parameters and failure modes obtained from conventional triaxial compression tests. Under geostress conditions, the influence of rock mineral properties on rock failure evolution and the effect of heterogeneous structures on microcracking behavior were analyzed.
Results The results show that the loading process of conventional triaxial compression tests can be divided into four stages: Crack closing stage, elastic deformation stage, crack growth stage, and crack explosion stage. Simulations based on computed tomography (CT) slices of three shale samples indicate that rock heterogeneity has a certain impact on the generation of rock microcracks and rock physical-mechanical parameters: Weaker heterogeneity corresponds to higher peak strength (
σ max) and elastic modulus (E ). In terms of crack propagation distribution, increased heterogeneity leads to a more complex microcrack distribution. From the perspective of the spatial distribution of rock microcracks, microcracks tend to occur preferentially at the interfaces between dolomite and quartz minerals.Conclusion The research findings provide important reference significance for deep underground oil and gas exploitation and disaster prevention engineering.
-
Key words:
- mud shale /
- image processing /
- rock mechanics /
- heterogeneity /
- microcracking behavior
-
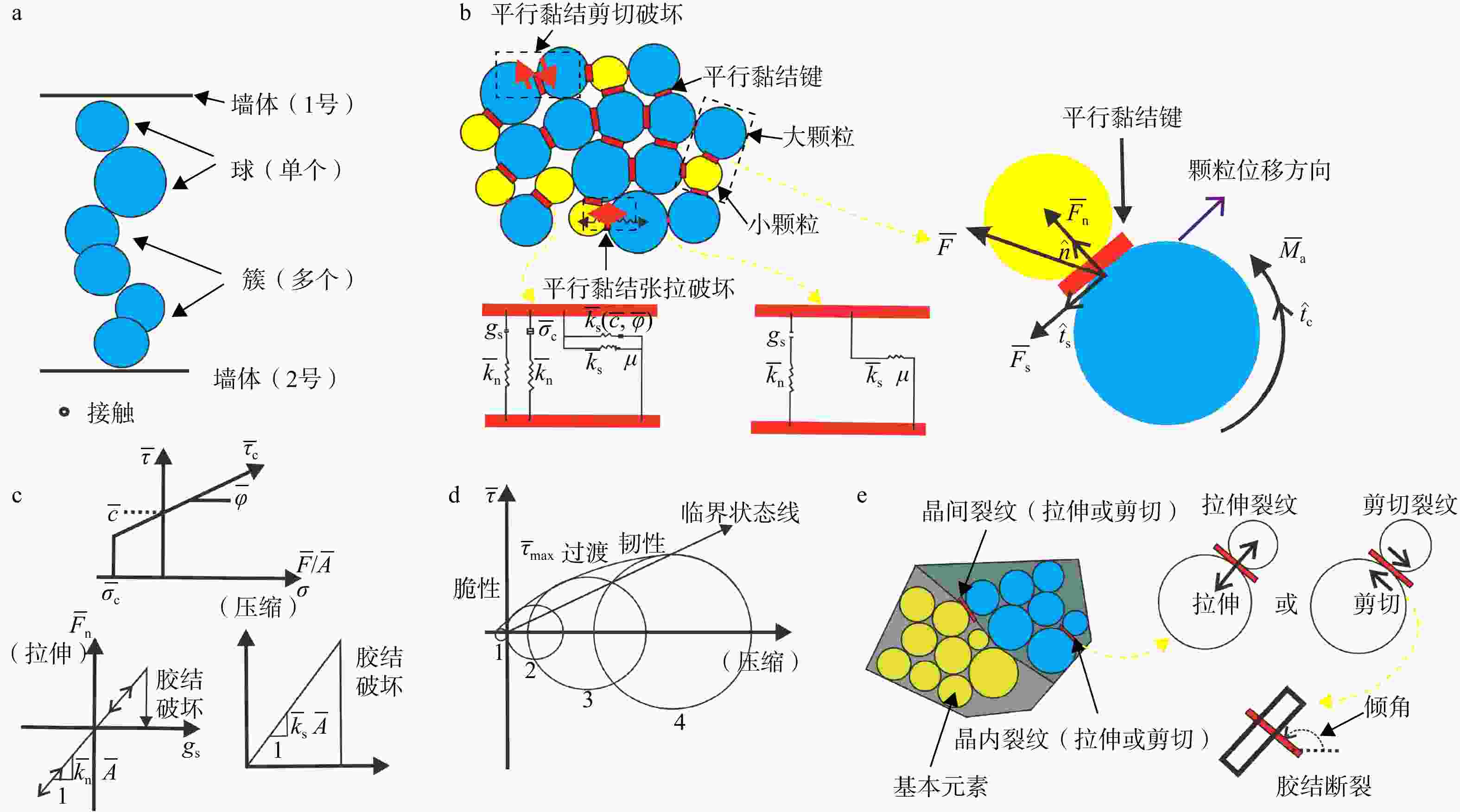
图 3 模型组成(a)、平行黏结模型本构关系(b)、平行黏结模型的力−位移规律和破坏包络线(c)、岩石的破坏包络线[32](d)、PFC颗粒破坏模式[33](e)
gs. 接触面积相关因子;$\bar{k}_{\mathrm{n}} $. 法向刚度;$\bar{k}_{\mathrm{s}} $. 切向刚度;$ \overline{\sigma}_{\mathrm{c}} $. 黏结强度;$\overline{c} $. 黏聚力;$ \overline{\varphi} $. 内摩擦角;μ. 摩擦系数;$ \overline{F}/\overline{A} $. 单位面积上受到的力(抗拉强度);$ \overline{\tau} $. 剪切强度;$\overline{\tau}_{\mathrm{max}} $为破坏时受到的剪切应力;$\overline{\tau}_{\mathrm{c}} $为岩石脆-塑到破坏变化过程中剪切强度的指向大小;σ为抗拉强度;$\overline{F}、{\overline{F}}_{\rm{n}}、{\overline{F}}_{\rm{s}}、{\overline{M}}_{\rm{a}} $分别为平行键力、平行键法向分力、平行键剪切分力、平行键合力矩的赋值;$\hat{n} $. 法向力方向;$ \hat{t}_{\mathrm{c}} $. 弯矩法向方向;$ \hat{t}_{\mathrm{s}} $. 剪切分量方向;1. 单轴拉伸;2. 单轴压缩;3. 脆塑转变;4.临界状态
Figure 3. Model composition (a), constitutive relation of parallel bond model (b), force-displacement law and failure envelope of the parallel bond model (c), rock failure envelope (d) and PFC particle failure pattern (e)
表 1 离散元细观参数标定值
Table 1. Calibration values of the discrete element mesoscopic parameters
元素 参数 石英类 白云石类 金属矿物 颗粒尺寸 最小粒径Rmin/mm 0.15 0.15 0.15 粒径比Rmax/Rmin 1.66 1.66 1.66 黏结模型参数 颗粒接触模量E*/GPa 62 58 80 颗粒刚度比k* 1.5 1.5 2.8 摩擦系数μ 0.5 0.5 0.5 平行黏结模量Ec/GPa 62 58 80 平行黏结刚度比kc 1.5 1.5 2.8 抗拉强度pb-ten/MPa 120 115 165 黏聚力pb-coh/MPa 135 130 182 光滑节理模型参数 法向刚度sj_kn/GPa 250000 切向刚度sj_ks/GPa 78000 摩擦系数sj_fric 0.45 抗拉强度sj-ten/MPa 50 黏聚力sj-coh/MPa 65 -
[1] JOSH M, ESTEBAN L, DELLE PIANE C, et al. Laboratory characterisation of shale properties[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2012, 88/89: 107-124. [2] WONG T F. Micromechanics of faulting in westerly granite[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1982, 19(2): 49-64. [3] ZHAO Y X, LIU S M, ZHAO G F, et al. Failure mechanisms in coal: Dependence on strain rate and microstructure[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research(Solid Earth), 2014, 119(9): 6924-6935. doi: 10.1002/2014JB011198 [4] JIANG T, SHAO J F, XU W Y, et al. Experimental investigation and micromechanical analysis of damage and permeability variation in brittle rocks[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2010, 47(5): 703-713. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.05.003 [5] ZHU Z N, TIAN H, CHEN J, et al. Experimental investigation of thermal cycling effect on physical and mechanical properties of heated granite after water cooling[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020, 79(5): 2457-2465. doi: 10.1007/s10064-019-01705-w [6] LI Y B, ZHAI Y, WANG C S, et al. Mechanical properties of Beishan granite under complex dynamic loads after thermal treatment[J]. Engineering Geology, 2020, 267: 105481. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105481 [7] ERARSLAN N. Microstructural investigation of subcritical crack propagation and fracture process zone (FPZ) by the reduction of rock fracture toughness under cyclic loading[J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 208: 181-190. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.04.035 [8] LIU X L, WANG F, NAWNIT K, et al. Experimental study on debris flow initiation[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020, 79(3): 1565-1580. doi: 10.1007/s10064-019-01618-8 [9] 郎颖娴, 梁正召, 段东, 等. 基于CT试验的岩石细观孔隙模型重构与并行模拟[J]. 岩土力学, 2019, 40(3): 1204-1212.LANG Y X, LIANG Z Z, DUAN D, et al. Three-dimensional parallel numerical simulation of porous rocks based on CT technology and digital image processing[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(3): 1204-1212. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] LIU C, LIU X L, WU C L, et al. Investigation of multiscale failure mechanism of red bed soft rock using grain-based finite-discrete element method combined with X-ray micro-computerized tomography[J]. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 2023, 27(3): 1350-1367. doi: 10.1007/s12205-023-1445-6 [11] ZHOU L, ZHU Z M, WANG M, et al. Dynamic propagation behavior of cracks emanating from tunnel edges under impact loads[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2018, 105: 119-126. doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2017.12.012 [12] HU L H, SU G S, LIANG X, et al. A distinct element based two-stage-structural model for investigation of the development process and failure mechanism of strainburst[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2020, 118: 103333. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.103333 [13] LI X B, ZOU Y, ZHOU Z L. Numerical simulation of the rock SHPB test with a special shape striker based on the discrete element method[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2014, 47(5): 1693-1709. doi: 10.1007/s00603-013-0484-6 [14] DU H B, DAI F, XU Y, et al. Numerical investigation on the dynamic strength and failure behavior of rocks under hydrostatic confinement in SHPB testing[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2018, 108: 43-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.05.008 [15] JU M H, XING H Z. Crack propagation in jointed rock and its effect on rock macrofracture resistance: Insights from discrete element analysis[J]. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources, 2021, 8(1): 21. [16] 闫欣宜, 胡新丽, 付茹. 橡胶纤维−砂混合料力学特性的离散元三轴试验研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 168-174.YAN X Y, HU X L, FU R. Triaxial shear test of mechanical characteristics on rubber fiber-sand mixtures based on particle flow code simulation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 168-174. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] CHUNG J, LEE H, KWON S. Numerical investigation of radial strain-controlled uniaxial compression test of Äspö diorite in grain-based model[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(10): 3659-3674. doi: 10.1007/s00603-019-01838-0 [18] GHAZVINIAN E, DIEDERICHS M S, QUEY R. 3D random Voronoi grain-based models for simulation of brittle rock damage and fabric-guided micro-fracturing[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 6(6): 506-521. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2014.09.001 [19] HOFMANN H, BABADAGLI T, ZIMMERMANN G. A grain based modeling study of fracture branching during compression tests in granites[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2015, 77: 152-162. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2015.04.008 [20] PENG J, WONG L N Y, TEH C I, et al. Modeling micro-cracking behavior of bukit timah granite using grain-based model[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2018, 51(1): 135-154. doi: 10.1007/s00603-017-1316-x [21] 张帆, 郭翰群, 赵建建, 等. 花岗岩微观力学性质试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(增刊2): 3864-3872.ZHANG F, GUO H Q, ZHAO J J, et al. Experimental study on micro-mechanical properties of granite[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(S2): 3864-3872. [22] ZHAO Z H, LIU Z N, PU H, et al. Effect of thermal treatment on Brazilian tensile strength of granites with different grain size distributions[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2018, 51(4): 1293-1303. doi: 10.1007/s00603-018-1404-6 [23] SUN H K, GAO Y, ZHENG X Y, et al. Meso-scale simulation of concrete uniaxial behavior based on numerical modeling of CT images[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(20): 3403. doi: 10.3390/ma12203403 [24] HU X J, XIE N, ZHU Q Z, et al. Modeling damage evolution in heterogeneous granite using digital image-based grain-based model[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2020, 53(11): 4925-4945. doi: 10.1007/s00603-020-02191-3 [25] 解经宇, 陆洪智, 陈磊, 等. 龙马溪组层状页岩微观非均质性及力学各向异性特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 67-77.XIE J Y, LU H Z, CHEN L, et al. Micro scopic heterogeneity and mechanical anisotropy of the laminated shale in Longmaxi Formation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 67-77. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 黄界海, 李小龙, 胡国庆, 等. 杨家岭页岩微宏观下物理力学特征研究[J]. 中国矿山工程, 2023, 52(6): 6-11.HUANG J H, LI X L, HU G Q, et al. Study on the micro macro physical and mechanical of properties of Yangjialing shale[J]. China Mine Engineering, 2023, 52(6): 6-11. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 胡训健, 卞康, 刘建, 等. 细观结构的非均质性对花岗岩蠕变特性影响的离散元模拟研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2019, 38(10): 2069-2083.HU X J, BIAN K, LIU J, et al. Discrete element simulation study on the influence of microstructure heterogeneity on the creep characteristics of granite[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2019, 38(10): 2069-2083. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 李博, 梁秦源, 周宇, 等. 基于CT-GBM重构法的花岗岩裂纹扩展规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(6): 1114-1125.LI B, LIANG Q Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Research on crack propagation law of granite based on CT-GBM reconstruction method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(6): 1114-1125. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] DING H F, FU X D, SHENG Q, et al. Study on macroscopic mechanical behavior and meso-failure evolution of gabbro of different particle sizes[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2023, 56(12): 8947-8963. doi: 10.1007/s00603-023-03531-9 [30] FAN L F, FAN Y D, XI Y, et al. Spatial failure mode analysis of frozen sandstone under uniaxial compression based on CT technology[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2022, 55(7): 4123-4138. doi: 10.1007/s00603-022-02859-y [31] 查明, 尹向烟, 姜林, 等. CT扫描技术在石油勘探开发中的应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(4): 228-235.ZHA M, YIN X Y, JIANG L, et al. Application of CT technology in petroleum exploration and development[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(4): 228-235. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] SINGH M, RAJ A, SINGH B. Modified Mohr-Coulomb criterion for non-linear triaxial and polyaxial strength of intact rocks[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2011, 48(4): 546-555. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2011.02.004 [33] GUO P Y, ZHANG P, BU M H, et al. Microcracking behavior and damage mechanism of granite subjected to high temperature based on CT-GBM numerical simulation[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2023, 159: 105385. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2023.105385 [34] LI H, MA H L, SHI X L, et al. A 3D grain-based model for simulating the micromechanical behavior of salt rock[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2020, 53(6): 2819-2837. doi: 10.1007/s00603-020-02085-4 [35] TIAN W L, YANG S Q, WANG J G, et al. Numerical simulation of permeability evolution in granite after thermal treatment[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2020, 126: 103705. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103705 [36] YIN T B, ZHUANG D D, LI M J, et al. Numerical simulation study on the thermal stress evolution and thermal cracking law of granite under heat conduction[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2022, 148: 104813. doi: 10.1016/j.compgeo.2022.104813 -




 下载:
下载: