Tracing of the sources of dissolved organic matter in coastal groundwater using fluorescence indices and end-member mixing analysis
-
摘要:
滨海地下水中溶解性有机质(DOM)长期受到陆源、海洋源等多种有机质混合,定量评估其来源对认识滨海地区碳迁移转化具有重要意义。选取了江苏连云港市为研究区,利用同位素示踪和光谱指数识别了地下水DOM来源,并通过光谱指数与端元混合模型(EMMA)定量评估了不同端元对滨海地下水DOM的贡献占比。结果表明:滨海地下水DOM主要由河水DOM、海水DOM和沉积物可溶性有机质混合影响,3个端元贡献占比分别为44%±22%、33%±10%和22%±13%。研究区北侧地下水受到海水混入和淡水补给共同影响,地下水DOM具有较高海水DOM贡献占比和自生源特征;而研究区南侧地下水咸化严重,高盐度地下水在径流过程中促进了沉积物可溶性有机质释放,地下水DOM具有较高的沉积物可溶性有机质贡献占比和腐殖化特征。研究成果为滨海地下水DOM来源的计算提供了评估方法。
Abstract:Objective Dissolved organic matter (DOM) in coastal groundwater is long-term mixed with from multiple sources, including terrestrial input, marine intrusion, and organic leachates from sediments. Quantitative estimation of the contributions of different sources is crucial for understanding carbon transport and transformation processes in coastal aquifers.
Methods In this study, coastal groundwater in Lianyungang City, Jiangsu Province was investigated using stable isotopic tracers, fluorescence indices, combined with end-member mixing analysis (EMMA) to identify and quantify DOM sources.
Results The results showed that DOM in coastal groundwater mainly derives from DOM in river water, seawater, and sediments, contributing 44% ±22%, 33% ± 10%, and 22% ± 13%, respectively. Groundwater in the northern part of the study area is affected by both seawater intrusion and freshwater recharge, exhibiting higher proportion of seawater DOM and stronger autochthonous characteristics. In contrast, groundwater in the southern part shows pronounced salinization, where elevated salinity enhances the mobilization of sediment-derived soluble organic matter, resulting in groundwater DOM with a higher proportion of sediment-derived sduble organic matter contribution and humification characteristics.
Conclusion This study highlights that DOM in coastal groundwater is jointly controlled by hydrodynamic and hydrogeochemical conditions. The integration of fluorescence indices with EMMA provides a reliable quantitative and efficient approach for source apportionment of DOM, offering new insights into the land-ocean continuum of the carbon cycle.
-
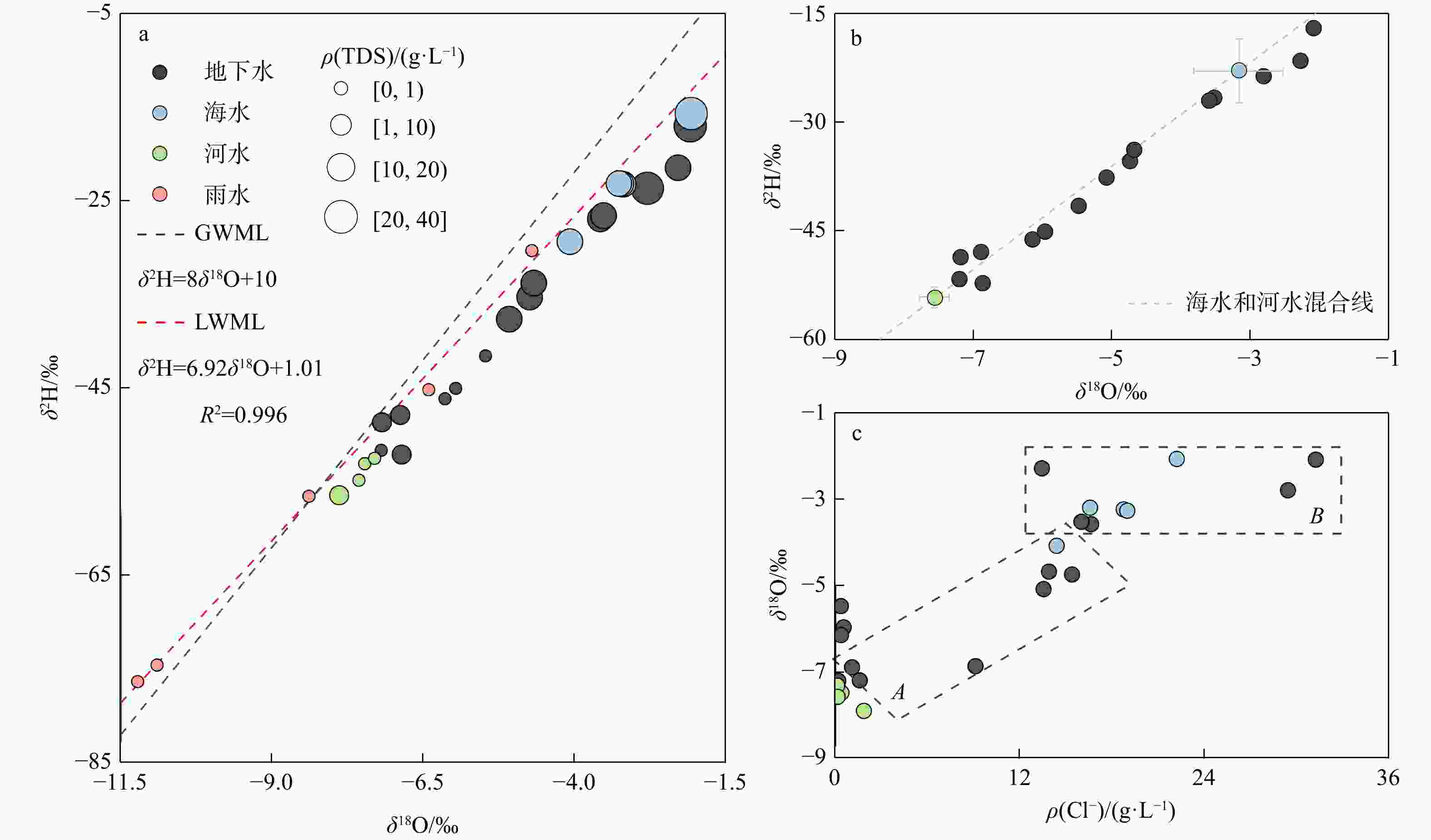
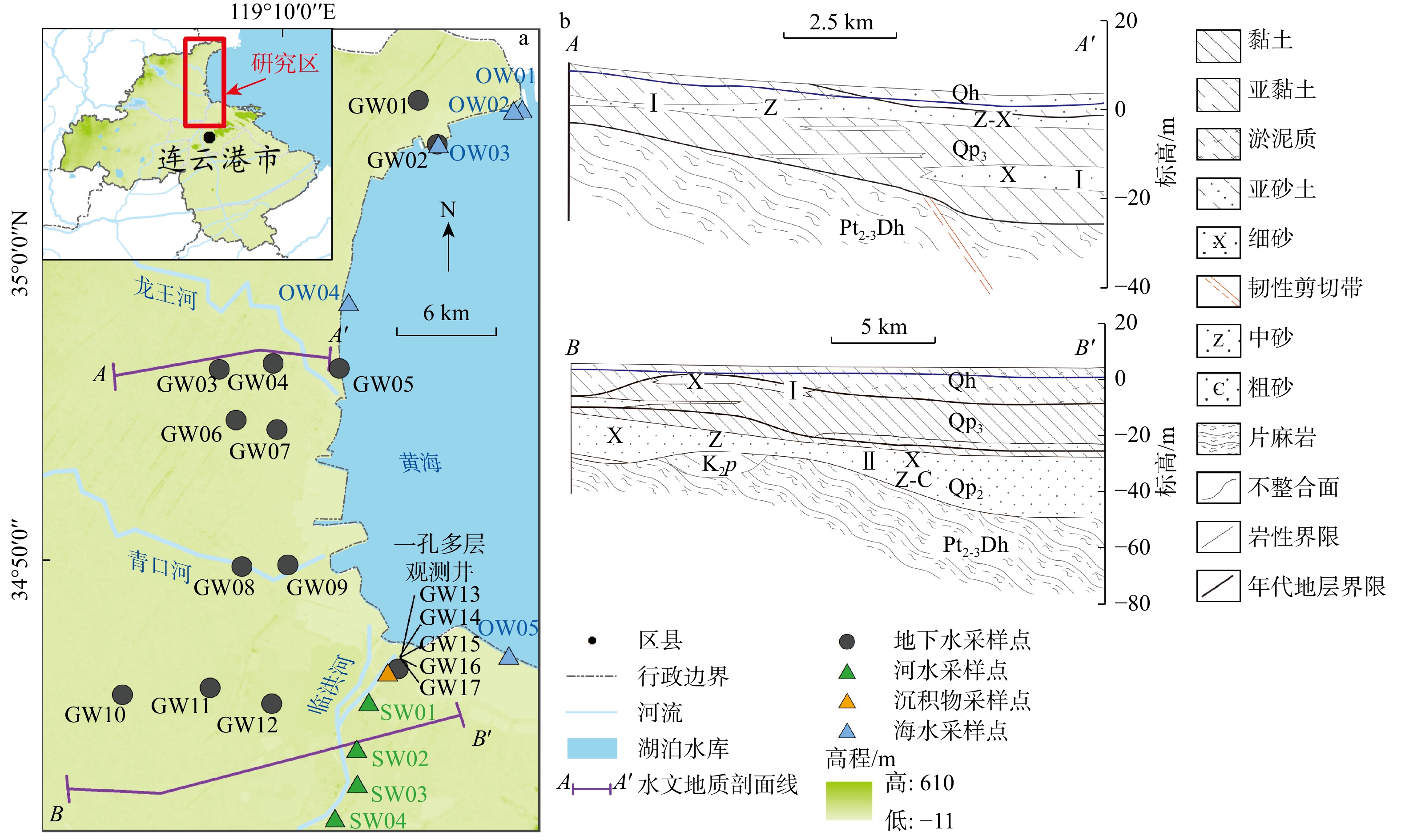
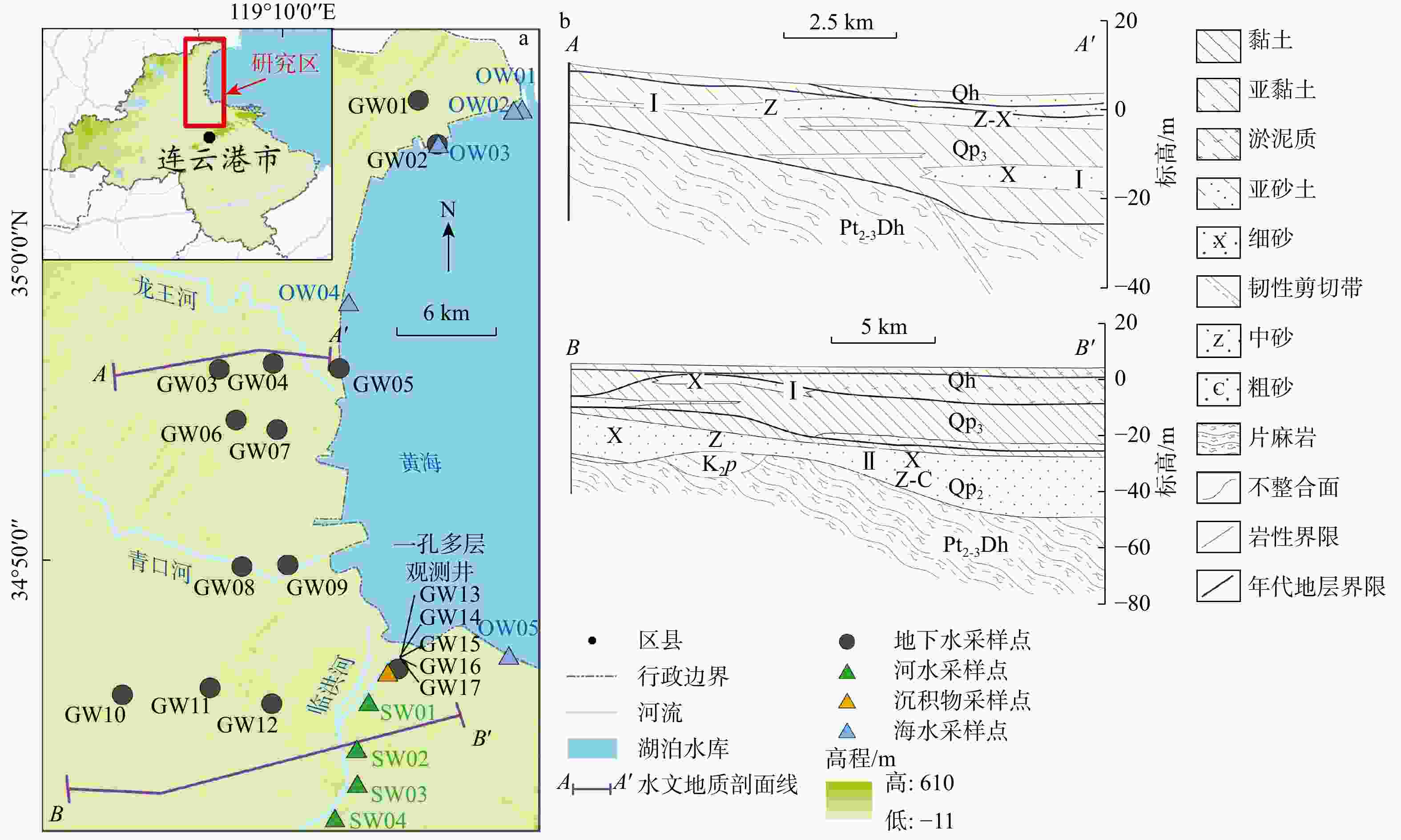
图 2 地下水、河水、海水和雨水的δ2H-δ18O关系(a),地下水与海水和河水混合线关系(b),以及地下水、河水和海水的δ18O-ρ(Cl−)关系(c)
GWML. 全球大气降水线;LMWL. 当地大气降水线;A. 低盐分区;B. 高盐分区
Figure 2. Relationships of δ2H and δ18O among groundwater, river water, sea water and precipitation (a), relationship between groundwater and the mixing line of sea water and river water (b), and relationships of δ18O and ρ(Cl−) among groundwater, river water and sea water (c)
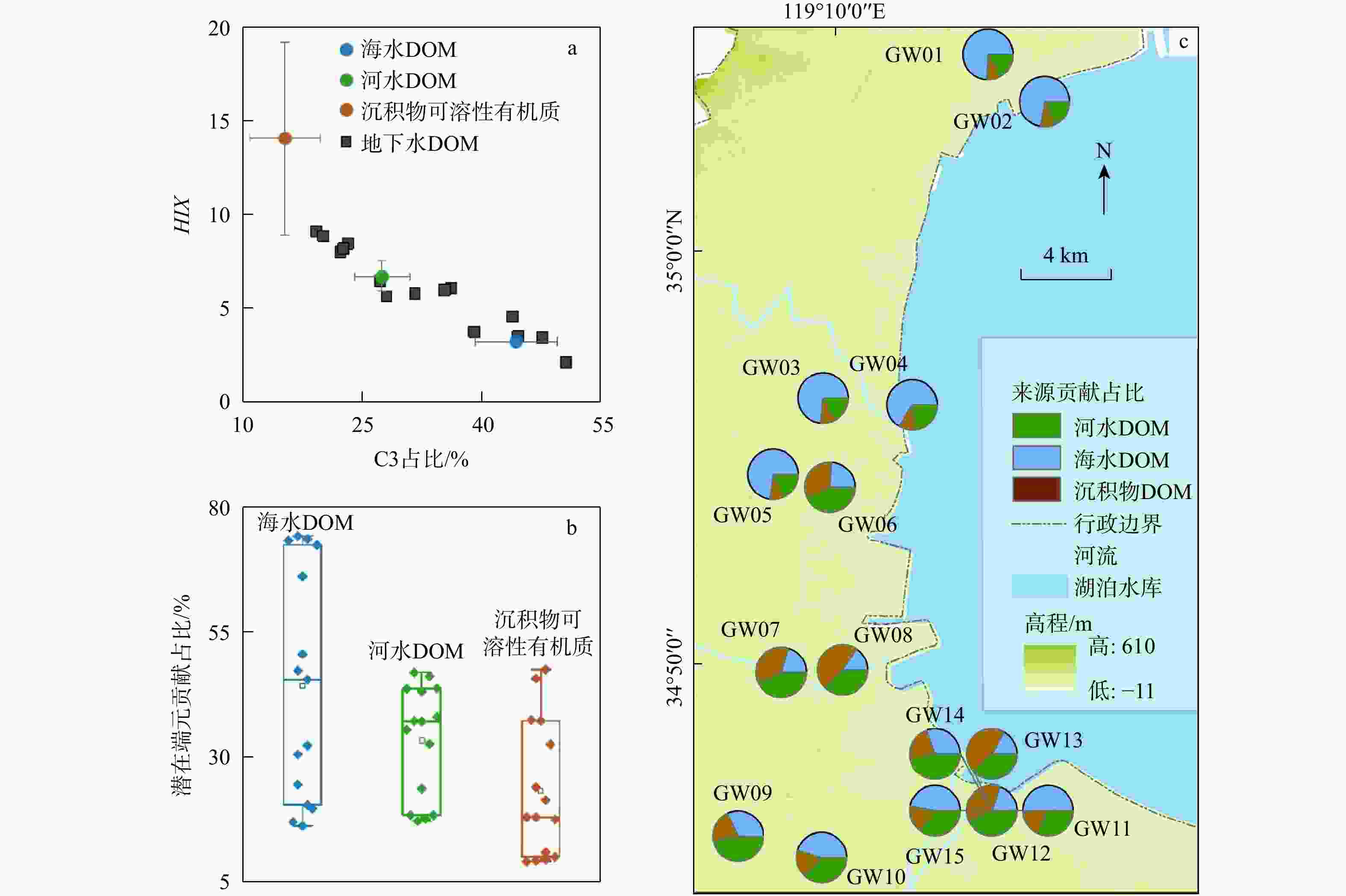
图 6 地下水中DOM和各端元的HIX-C3占比关系(a),地下水DOM各端元贡献占比(b)及端元贡献占比空间分布图(c)
Figure 6. Relationships between HIX and C3 ratio of DOM in groundwater and different endmembers (a), boxplot of the contribution proportions of endmembers to groundwater DOM (b), and spatial distribution of endmember contribution proportions (c)
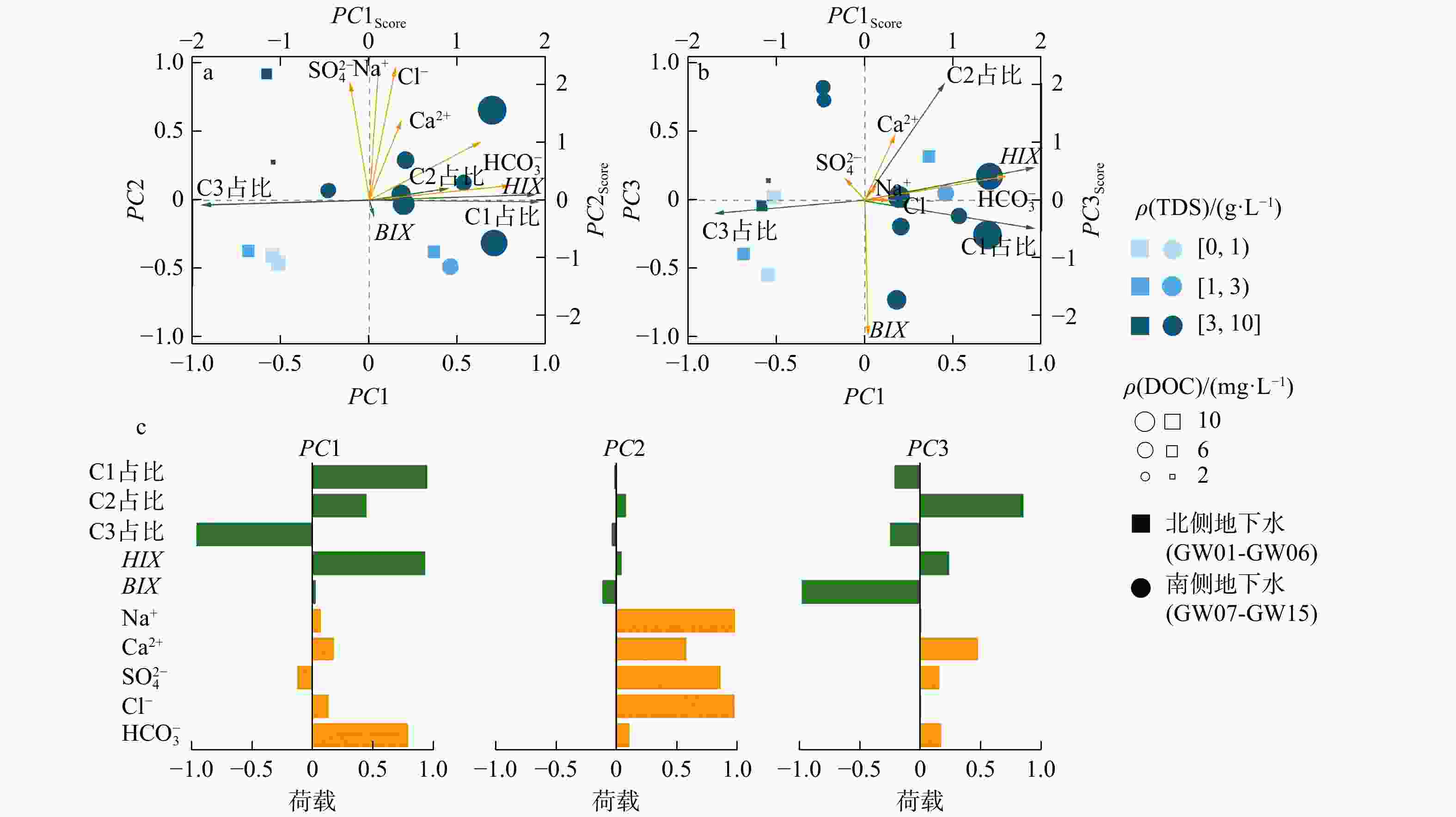
表 1 各双光谱指数端元混合模型对滨海地下水DOM来源占比分析的适用性
Table 1. Applicability of different dual fluorescence index combinations for endmember mixing analysis of DOM sources in coastal groundwater
双光谱指数端
元混合模型模型参数 G MRE/% RMSE C1占比-BIX C1占比 −0.238 10.223 0.119 BIX 0.227 11.439 0.069 C1占比-C3占比 C1占比 0.445 7.572 0.059 C3占比 0.678 9.491 0.058 C2占比-BIX C2占比 −0.239 8.701 0.119 BIX −1.079 13.688 0.068 C2占比-C3占比 C2占比 −0.559 21.193 0.059 C3占比 0.591 16.01 0.065 HIX−BIX HIX 0.0913 27.141 2.023 BIX 0.096 6.573 0.102 HIX−C3占比 HIX 0.715 9.589 1.132 C3占比 0.712 10.642 0.054 注:G. 预测优度;MRE. 相对误差;RMSE. 均方根误差;下同 -
[1] WARD N D, BIANCHI T S, MEDEIROS P M, et al. Where carbon goes when water flows: Carbon cycling across the aquatic continuum[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2017, 4: 7. [2] ZHANG Y, WANG X J, XUE Y, et al. Advances in the study of submarine groundwater discharge (SGD) in China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2022, 65(10): 1948-1960. doi: 10.1007/s11430-021-9946-x [3] 王焰新, 甘义群, 邓娅敏, 等. 海岸带海陆交互作用过程及其生态环境效应研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 1-10.WANG Y X, GAN Y Q, DENG Y M, et al. Land-ocean interactions and their eco-environmental effects in the coastal zone: Current progress and future perspectives[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] MOORE W S, SARMIENTO J L, KEY R M. Submarine groundwater discharge revealed by 228 Ra distribution in the upper Atlantic Ocean[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1(5): 309-311. doi: 10.1038/ngeo183 [5] SLOMP C, VAN C. Nutrient inputs to the coastal ocean through submarine groundwater discharge: Controls and potential impact[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2004, 295(1/2/3/4): 64-86. [6] MOORE W S, JOYE S B. Saltwater intrusion and submarine groundwater discharge: Acceleration of biogeochemical reactions in changing coastal aquifers[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 9: 600710. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.600710 [7] BECK M, RECKHARDT A, AMELSBERG J, et al. The drivers of biogeochemistry in beach ecosystems: A cross-shore transect from the dunes to the low-water line[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2017, 190: 35-50. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2017.01.001 [8] HUETTEL M, BERG P, KOSTKA J E. Benthic exchange and biogeochemical cycling in permeable sediments[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 2014, 6: 23-51. doi: 10.1146/annurev-marine-051413-012706 [9] WASKA H, SIMON H, AHMERKAMP S, et al. Molecular traits of dissolved organic matter in the subterranean estuary of a high-energy beach: Indications of sources and sinks[J]. Frontiers in Marine Science, 2021, 8: 607083. doi: 10.3389/fmars.2021.607083 [10] BECK A J, TSUKAMOTO Y, TOVAR-SANCHEZ A, et al. Importance of geochemical transformations in determining submarine groundwater discharge-derived trace metal and nutrient fluxes[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2007, 22(2): 477-490. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2006.10.005 [11] SEIDEL M, BECK M, GRESKOWIAK J, et al. Benthic-pelagic coupling of nutrients and dissolved organic matter composition in an intertidal sandy beach[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2015, 176: 150-163. doi: 10.1016/j.marchem.2015.08.011 [12] OSBURN C L, HANDSEL L T, PEIERLS B L, et al. Predicting sources of dissolved organic nitrogen to an estuary from an agro-urban coastal watershed[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016, 50(16): 8473-8484. [13] CHOI W J, RO H M, CHANG S X. Carbon isotope composition of Phragmites australis in a constructed saline wetland[J]. Aquatic Botany, 2005, 82(1): 27-38. doi: 10.1016/j.aquabot.2005.02.005 [14] KANG S J, KIM J H, KIM D, et al. Temporal variation in riverine organic carbon concentrations and fluxes in two contrasting estuary systems: Geum and Seomjin, South Korea[J]. Environment International, 2019, 133: 105126. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2019.105126 [15] LI Z W, WANG S L, NIE X D, et al. The application and potential non-conservatism of stable isotopes in organic matter source tracing[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 838: 155946. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155946 [16] APOSTOLOPOULOU M V, MONTEYNE E, KRIKONIS K, et al. n-Alkanes and stable C, N isotopic compositions as identifiers of organic matter sources in Posidonia oceanica meadows of Alexandroupolis Gulf, NE Greece[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2015, 99(1/2): 346-355. [17] LIU C, WU Z N, HU B X, et al. Linking recent changes in sediment yields and aggregate-associated organic matter sources from a typical catchment of the Loess Plateau, China[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2021, 321: 107606. [18] 李小倩, 刘鋆, 何宁洁, 等. 炼油污染场地地下水DOM三维荧光指纹特征及指示意义[J]. 地球科学, 2024, 49(6): 2199-2212.LI X Q, LIU Y, HE N J, et al. Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix characteristics and implication of dissolved organic matter in groundwater at a typical refinery-polluted site[J]. Earth Science, 2024, 49(6): 2199-2212. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 安洋, 周松, 苏春利, 等. 胶州湾北部表层沉积物重金属污染及DOM对其环境行为的影响[J]. 地球科学, 2024, 49(8): 2901-2913.AN Y, ZHOU S, SU C L, et al. Heavy metal pollution of sediments in northern Jiaozhou Bay and the influence of DOM on their environmental behavior[J]. Earth Science, 2024, 49(8): 2901-2913. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] 李琬钰, 周建伟, 贾晓岑, 等. 湖南锡矿山锑矿区水环境中DOM三维荧光特征及其对锑污染的指示意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(4): 215-224.LI W Y, ZHOU J W, JIA X C, et al. EEMs characteristics of dissolved organic matter in water environment and its implications for antimony contamination in antimony mine of Xikuangshan, Hunan Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(4): 215-224. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 许洁, 梁莹, 张振超, 等. 江汉平原地下水中有机质季节变化对氮反应迁移的影响[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(4): 228-240.XU J, LIANG Y, ZHANG Z C, et al. Effects of seasonal variation in organic matter in groundwater on reactive nitrogen transport in the Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(4): 228-240. (in Chinese with English abstract [22] STEDMON C A, BRO R. Characterizing dissolved organic matter fluorescence with parallel factor analysis: A tutorial[J]. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods, 2008, 6(11): 572-579. [23] LEE M H, LEE Y K, DERRIEN M, et al. Evaluating the contributions of different organic matter sources to urban river water during a storm event via optical indices and molecular composition[J]. Water Research, 2019, 165: 115006. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.115006 [24] CAO X, HE W, FAN M Q, et al. Novel insights into source apportionment of dissolved organic matter in aquifer affected by anthropogenic groundwater recharge: Applicability of end-member mixing analysis based optical indices[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2023, 863: 160885. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.160885 [25] YU X, ZHANG J L, KONG F L, et al. Identification of source apportionment and its spatial variability of dissolved organic matter in Dagu River-Jiaozhou Bay estuary based on the isotope and fluorescence spectroscopy analysis[J]. Ecological Indicators, 2019, 102: 528-537. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.03.004 [26] SMITH M A, KOMINOSKI J S, PRICE R M, et al. Linking seasonal changes in organic matter composition and nutrients to shifting hydraulic gradients in coastal urban canals[J]. Water Resources Research, 2023, 59(2): e2022WR033334. doi: 10.1029/2022WR033334 [27] DERRIEN M, SHIN K H, HUR J. Assessment on applicability of common source tracking tools for particulate organic matter in controlled end member mixing experiments[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 666: 187-196. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.258 [28] 杨磊, 龚绪龙, 陆徐荣, 等. 连云港北部地区高氟地下水分布特征及成因[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(4): 1161-1169.YANG L, GONG X L, LU X R, et al. Distribution and genesis of high-fluoride groundwater in northern Lianyungang area[J]. Geology in China, 2015, 42(4): 1161-1169. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 李进, 龚绪龙, 张岩, 等. 连云港地区地下咸水水化学特征及其成因分析[C]//曲久辉. 中国环境科学学会2021年科学技术年会: 环境工程技术创新与应用分会场论文集. 天津: 中国环境科学学会环境工程分会, 2021: 115-122.LI J, GONG X L, ZHANG Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and origins of salt groundwater in Lianyungang area[C]//QU J H. The 2021 Annual Meeting of Science and Technology of China Society for Environmental Sciences: Technical Innovation and Application of Environmental Engineering Sub-conference Proceedings. Tianjin: Chinese Society for Environmental Sciences, Environmental Engineering Branch, 2021: 115-122. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] WEI W H, NGHIEM A, MA R, et al. Factors controlling iodine enrichment in a coastal plain aquifer in the North Jiangsu Yishusi Plain, China[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2021, 243: 103894. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2021.103894 [31] LI J, HEAP A D. A review of comparative studies of spatial interpolation methods in environmental sciences: Performance and impact factors[J]. Ecological Informatics, 2011, 6(3/4): 228-241. [32] MCKNIGHT D M, BOYER E W, WESTERHOFF P K, et al. Spectrofluorometric characterization of dissolved organic matter for indication of precursor organic material and aromaticity[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2001, 46(1): 38-48. doi: 10.4319/lo.2001.46.1.0038 [33] HUGUET A, VACHER L, RELEXANS S, et al. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2009, 40(6): 706-719. doi: 10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.03.002 [34] TOOSI E R, CASTELLANO M J, SINGER J W, et al. Differences in soluble organic matter after 23 years of contrasting soil management[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 2012, 76(2): 628-637. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2011.0280 [35] WANG J, LU N, FU B J. Inter-comparison of stable isotope mixing models for determining plant water source partitioning[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 666: 685-693. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.02.262 [36] 赵鲁松, 孙自永, 马瑞, 等. 青藏高原季节冻土山区河流的溶解性碳输出特征及控制因素[J]. 地球科学, 2024, 49(3): 1177-1188.ZHAO L S, SUN Z Y, MA R, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of dissolved carbon export from an alpine catchment underlain by seasonal frost in the Qilian Mountains, Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Earth Science, 2024, 49(3): 1177-1188. (in Chinese with English abstract) (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 毛龙富, 付舒, 刘宏, 等. 基于氢氧稳定同位素的喀斯特泉水补给来源分析[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(9): 3480-3493.MAO L F, FU S, LIU H, et al. Analysis of recharge source of karst spring water based on stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(9): 3480-3493. (in Chinese with English abstract [38] 侯国华, 高茂生, 党显璋, 等. 江苏盐城滨海地区浅层地下咸水的水盐来源及咸化成因[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2021, 41(4): 48-59.HOU G H, GAO M S, DANG X Z, et al. Water and salt sources and salinization of shallow saline groundwater in the coastal area of Yancheng, Jiangsu[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2021, 41(4): 48-59. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] HAN D M, SONG X F, CURRELL M J, et al. Chemical and isotopic constraints on evolution of groundwater salinization in the coastal plain aquifer of Laizhou Bay, China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 508: 12-27. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.10.040 [40] 袁晓芳, 邓娅敏, 杜尧, 等. 江汉平原高砷地下水稳定碳同位素特征及其指示意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5): 156-163.YUAN X F, DENG Y M, DU Y, et al. Characteristics of stable carbon isotopes and its implications on arsenic enrichment in shallow groundwater of the Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(5): 156-163. (in Chinese with English abstract [41] HE B, DAI M, HUANG W, et al. Sources and accumulation of organic carbon in the Pearl River Estuary surface sediment as indicated by elemental, stable carbon isotopic, and carbohydrate compositions[J]. Biogeosciences, 2010, 7(10): 3343-3362. doi: 10.5194/bg-7-3343-2010 [42] LI S D, MENG L Z, ZHAO C, et al. Spatiotemporal response of dissolved organic matter diversity to natural and anthropogenic forces along the whole mainstream of the Yangtze River[J]. Water Research, 2023, 234: 119812. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2023.119812 [43] ISHII S K L, BOYER T H. Behavior of reoccurring PARAFAC components in fluorescent dissolved organic matter in natural and engineered systems: A critical review[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(4): 2006-2017. [44] COBLE P G, DEL CASTILLO C E, AVRIL B. Distribution and optical properties of CDOM in the Arabian Sea during the 1995 southwest monsoon[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 1998, 45(10/11): 2195-2223. [45] STEDMON C A, MARKAGER S. Tracing the production and degradation of autochthonous fractions of dissolved organic matter by fluorescence analysis[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2005, 50(5): 1415-1426. doi: 10.4319/lo.2005.50.5.1415 [46] COBLE P G. Characterization of marine and terrestrial DOM in seawater using excitation-emission matrix spectroscopy[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1996, 51(4): 325-346. doi: 10.1016/0304-4203(95)00062-3 [47] GUÉGUEN C, MOKHTAR M, PERROUD A, et al. Mixing and photoreactivity of dissolved organic matter in the Nelson/Hayes estuarine system (Hudson Bay, Canada)[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2016, 161: 42-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2016.05.005 [48] OH H, CHOI J H. Changes in the dissolved organic matter characteristics released from sediment according to precipitation in the namhan river with weirs: A laboratory experiment[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2022, 19(9): 4958. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19094958 [49] DERRIEN M, YANG L Y, HUR J. Lipid biomarkers and spectroscopic indices for identifying organic matter sources in aquatic environments: A review[J]. Water Research, 2017, 112: 58-71. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.023 [50] WANG S M, JIA Y F, LIU T, et al. Delineating the role of calcium in the large-scale distribution of metal-bound organic carbon in soils[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(10): e2021GL092391. doi: 10.1029/2021GL092391 [51] 侯国华, 高茂生, 叶思源, 等. 黄河三角洲浅层地下水盐分来源及咸化过程研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(3): 145-154.HOU G H, GAO M S, YE S Y, et al. Source of salt and the salinization process of shallow groundwater in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(3): 145-154. (in Chinese with English abstract [52] SANTOS I R, CHEN X G, LECHER A L, et al. Submarine groundwater discharge impacts on coastal nutrient biogeochemistry[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2021, 2(5): 307-323. [53] TIEMEYER B, PFAFFNER N, FRANK S, et al. Pore water velocity and ionic strength effects on DOC release from peat-sand mixtures: Results from laboratory and field experiments[J]. Geoderma, 2017, 296: 86-97. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.02.024 -




 下载:
下载: