Information extraction of dangerous rock masses on high and steep slopes using multi-source remote sensing data fusion
-
摘要:
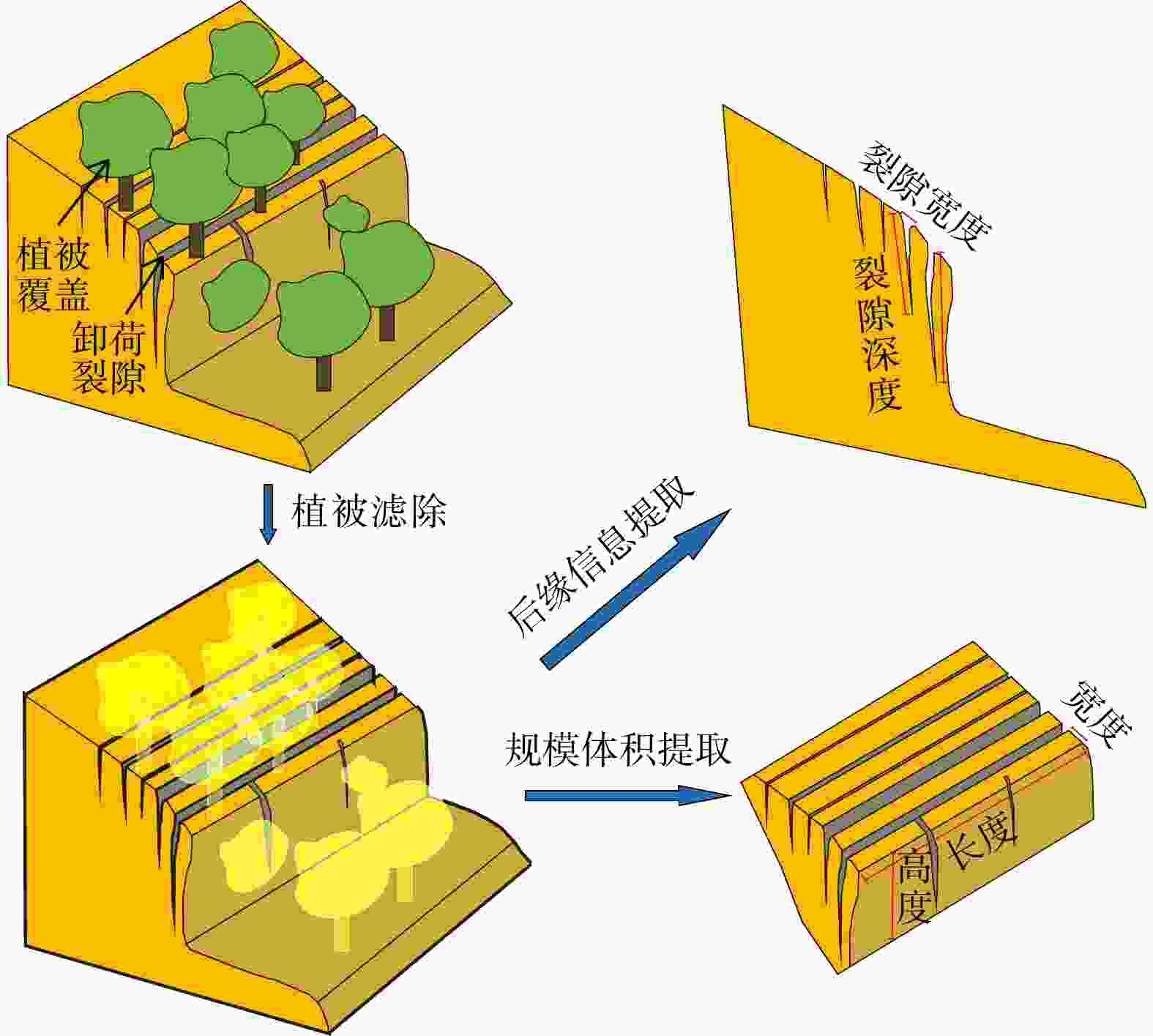
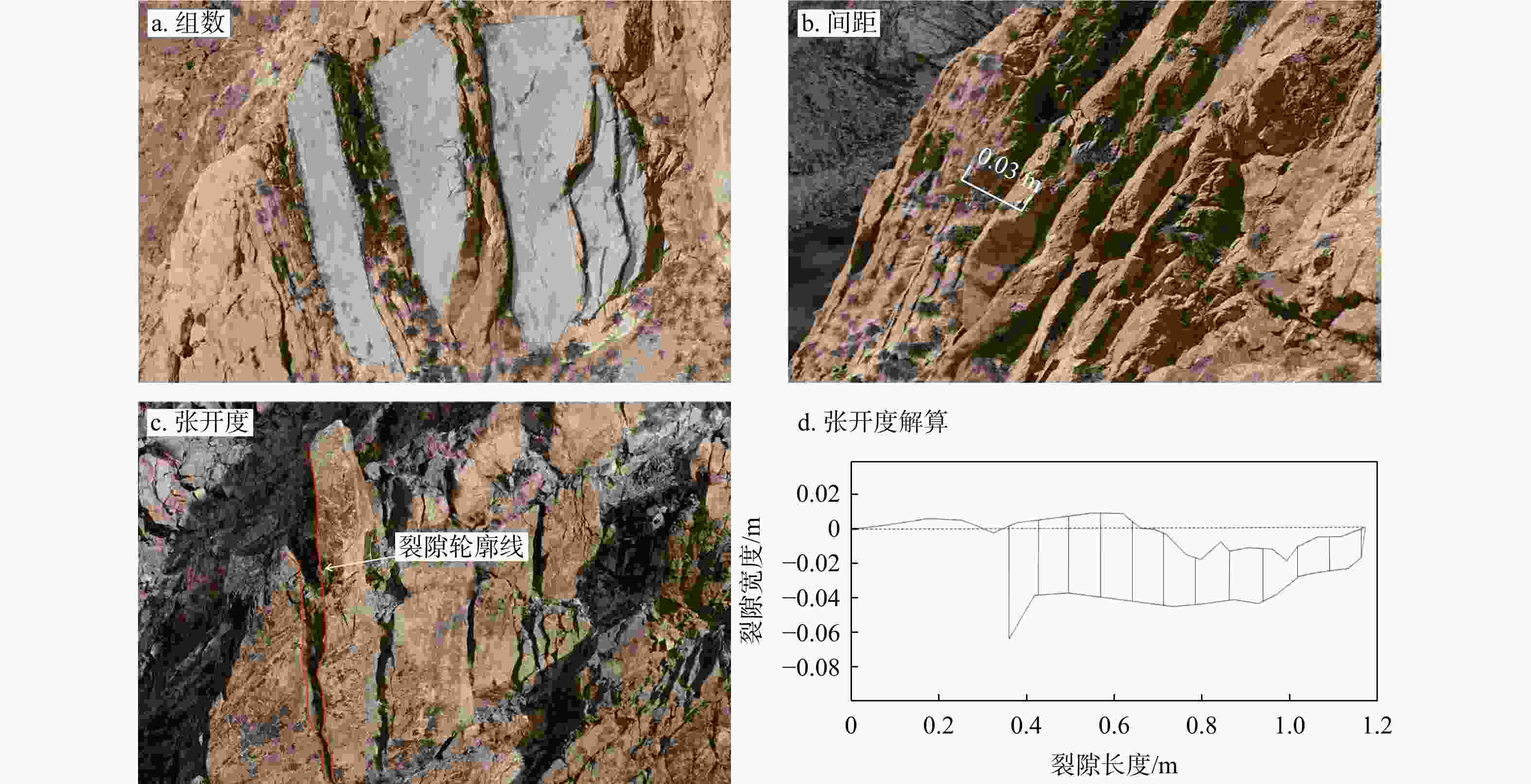
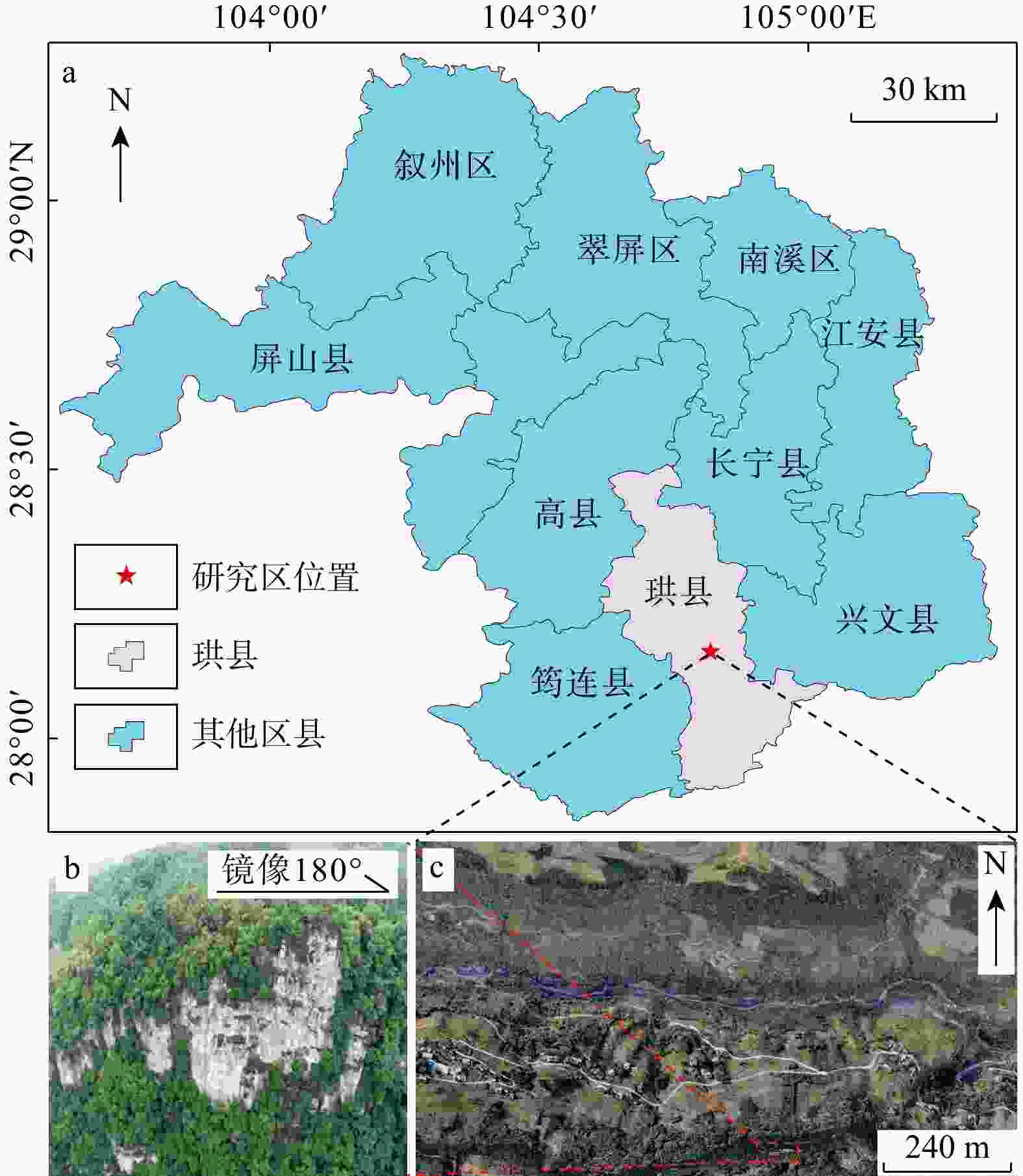
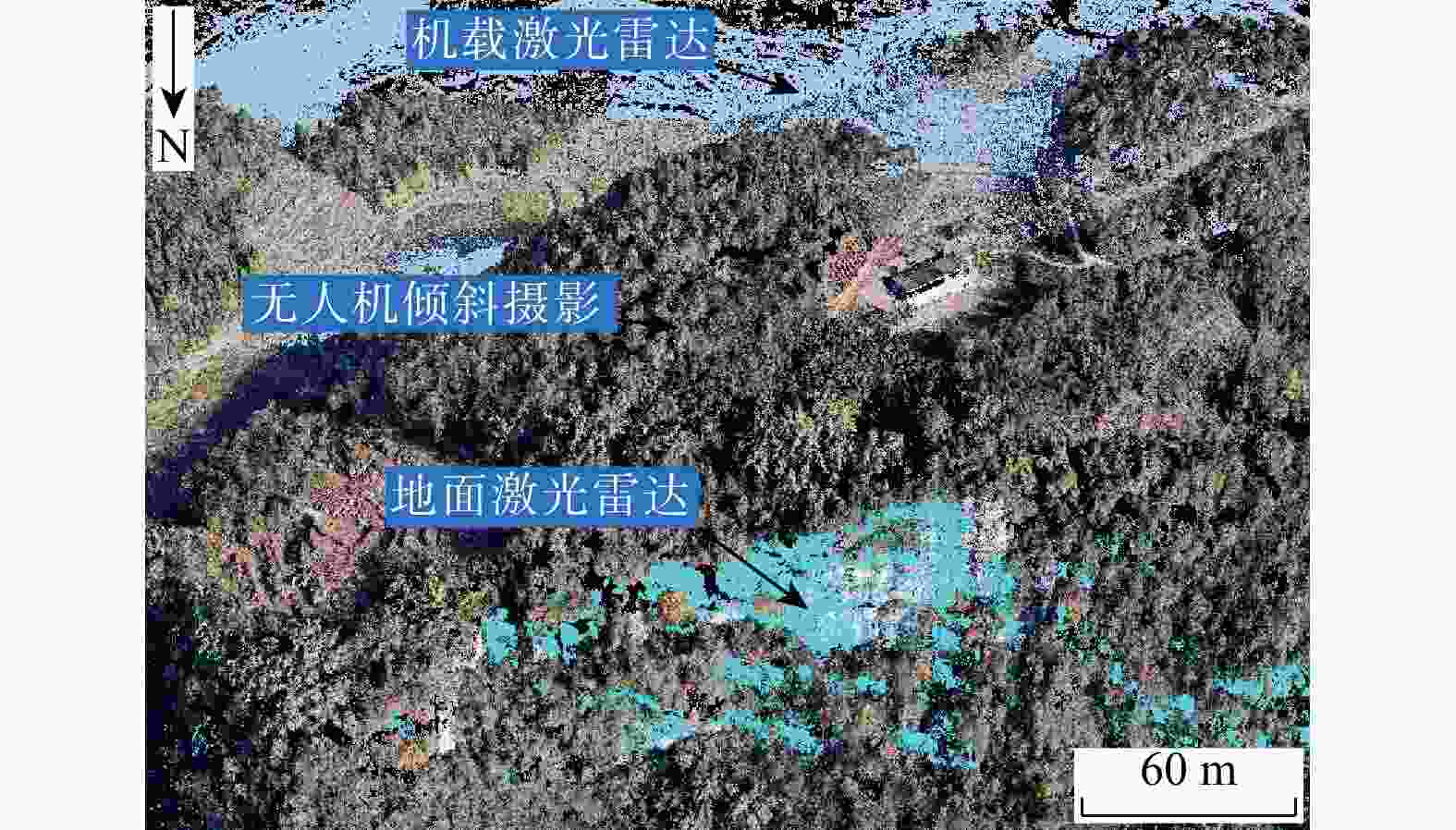
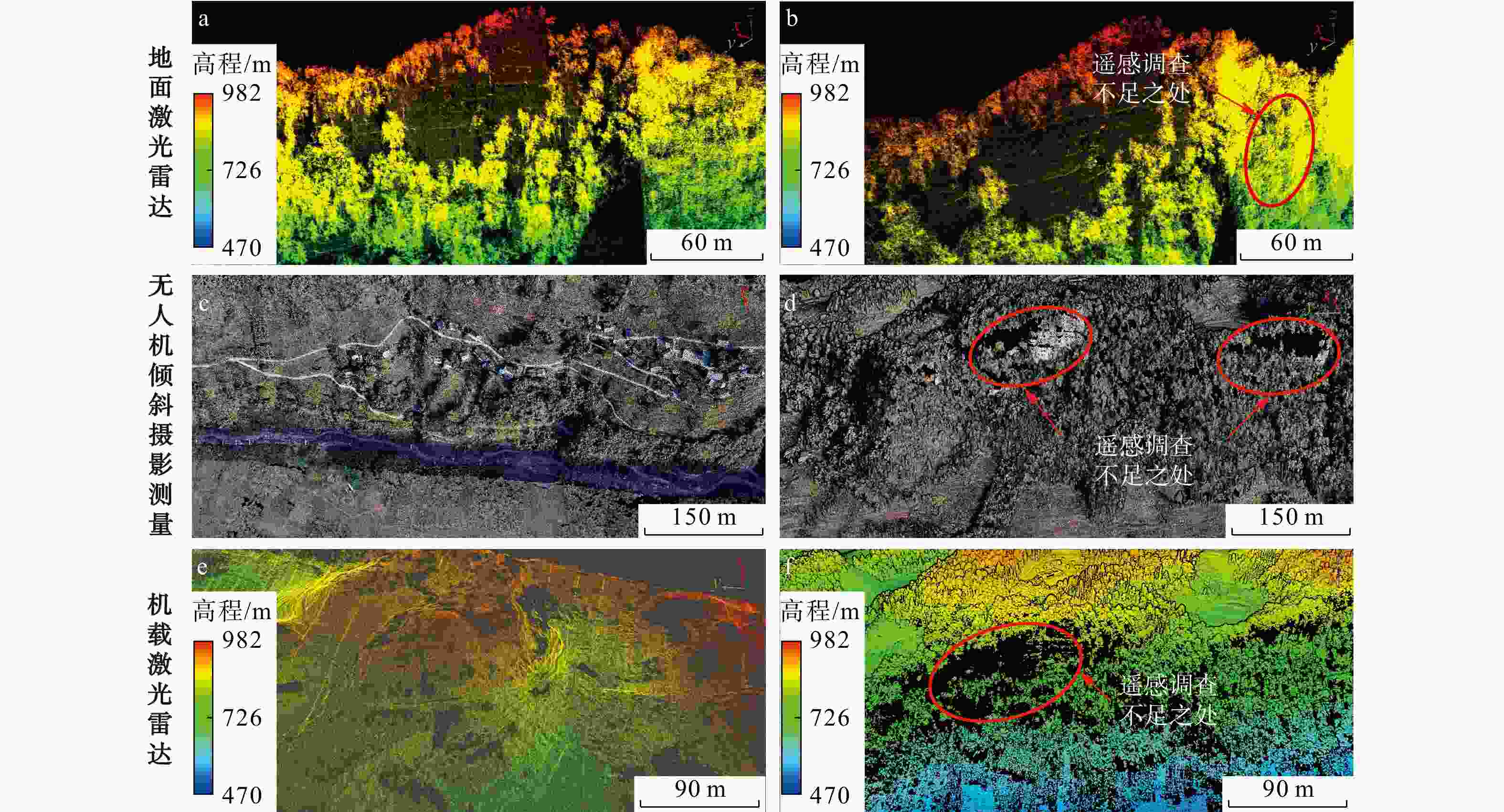
我国山区存在大量的高陡边坡,因其具有隐蔽性及危险性等特点,目前单一非接触式测量难以获取可用于高陡边坡危岩体几何参数及结构面信息提取分析的数据,而对于危岩体精细化调查,结构面特征参数信息又是重中之重。将机载激光雷达、地面激光雷达及无人机倾斜摄影测量获取的点云数据进行了多源数据融合,运用融合后点云对高陡边坡危岩的规模边界、后缘特征和产状信息等参数进行了信息提取。结果表明:多源数据融合方法有效互补了多种数据优势,运用融合后点云对高陡边坡危岩进行了规模边界、后缘信息及结构面特征参数信息提取,其数据提取值误差均在±5°以内,满足调查规范要求。研究成果为植被覆盖区域的危岩体详细调查提供了新的思路。
Abstract:Objective There are a large number of high and steep slopes in mountainous areas in China. Due to their concealed and hazardous nature, it is currently difficult to obtain usable data for extracting and analyzing geometric parameters and structural plane information of dangerous rock masses on high and steep slopes using a single non-contact measurement method. However, for the refined investigations of dangerous rock masses, the characteristic parameter information of structural planes is a top priority.
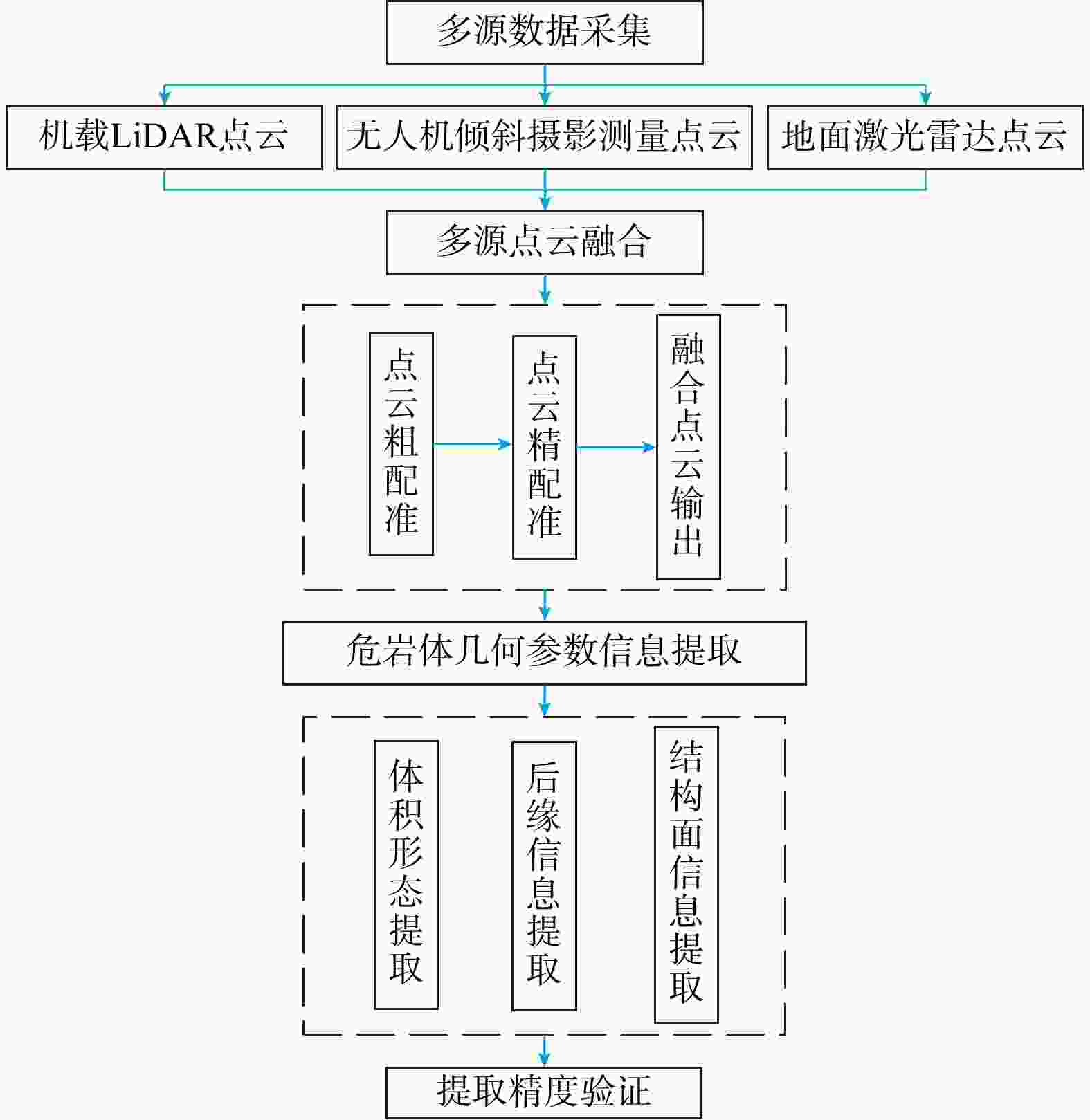
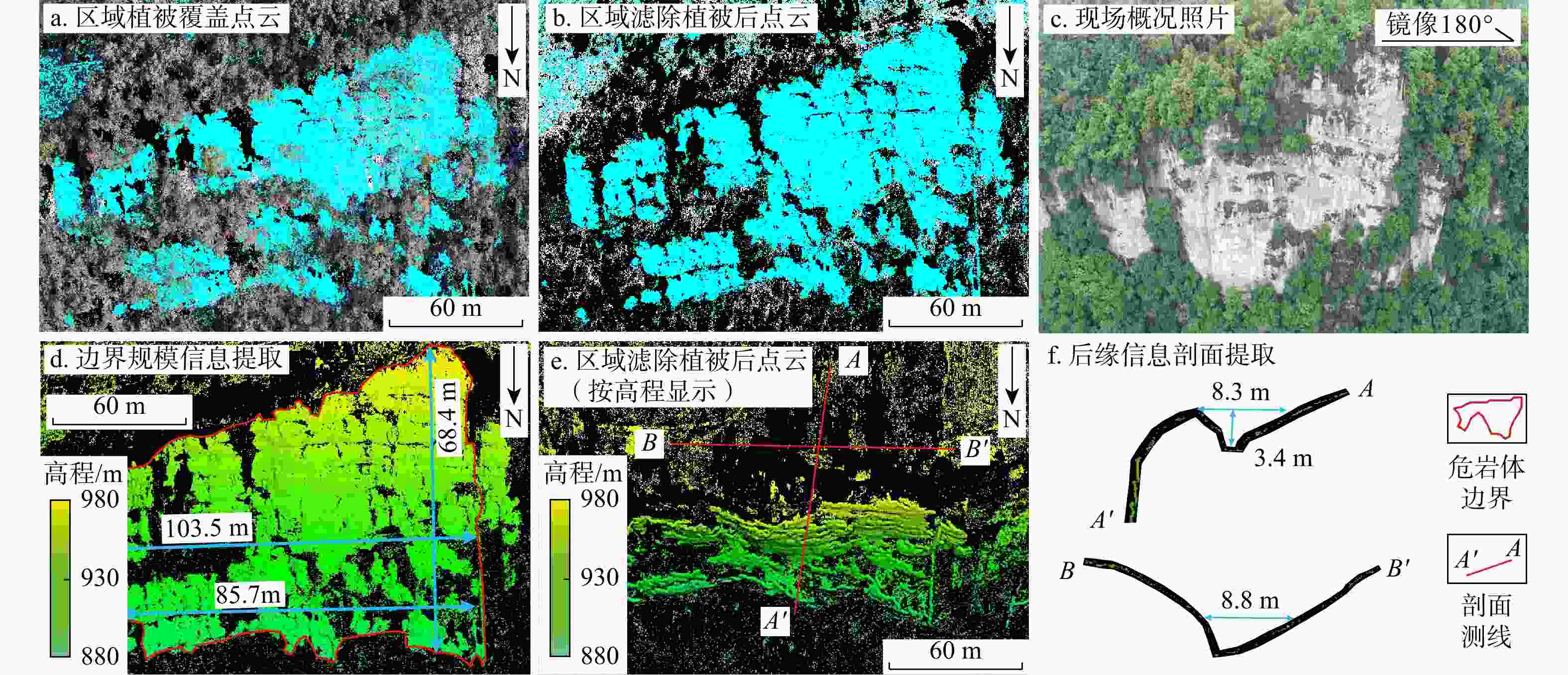
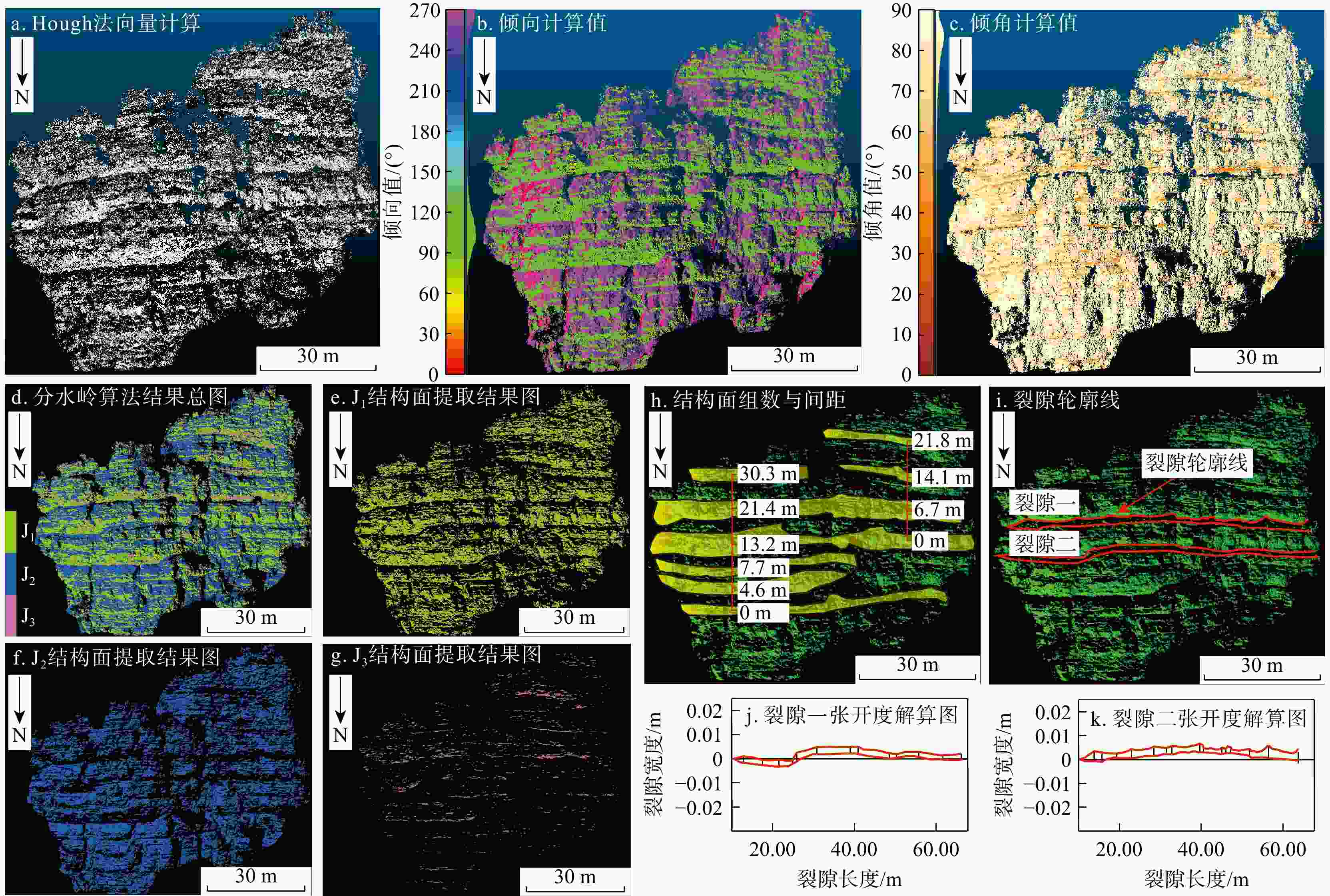
Methods Therefore, this paper fused the point cloud data obtained from airborne LiDAR, ground LiDAR and UAV oblique photogrammetry through multi-source data, integrated the advantages of the multi-source data, and used the fused point cloud to analyze dangerous rock masses on high and steep slopes. Parameters such as scale boundaries, back edge characteristics and occurrence information were extracted.
Results The results showed that the multi-source data fusion method adopted in this study effectively integrated the advantages of various data types. The values of extracted parameters, including scale boundaries, back edge features, and structural plane characteristics, all exhibited deviations within ±5°, meeting the requirements of the survey specifications.
Conclusion These research findings provide a new approach for detailed investigations of dangerous rock masses in vegetation-covered areas.
-
表 1 Hough空间法向量计算参数
Table 1. Hough space normal vector calculation parameters
领域尺寸
K平面数量
T累加器部署
nPhi累加器循环
次数nRot公差角
Tola/(°)领域估计密
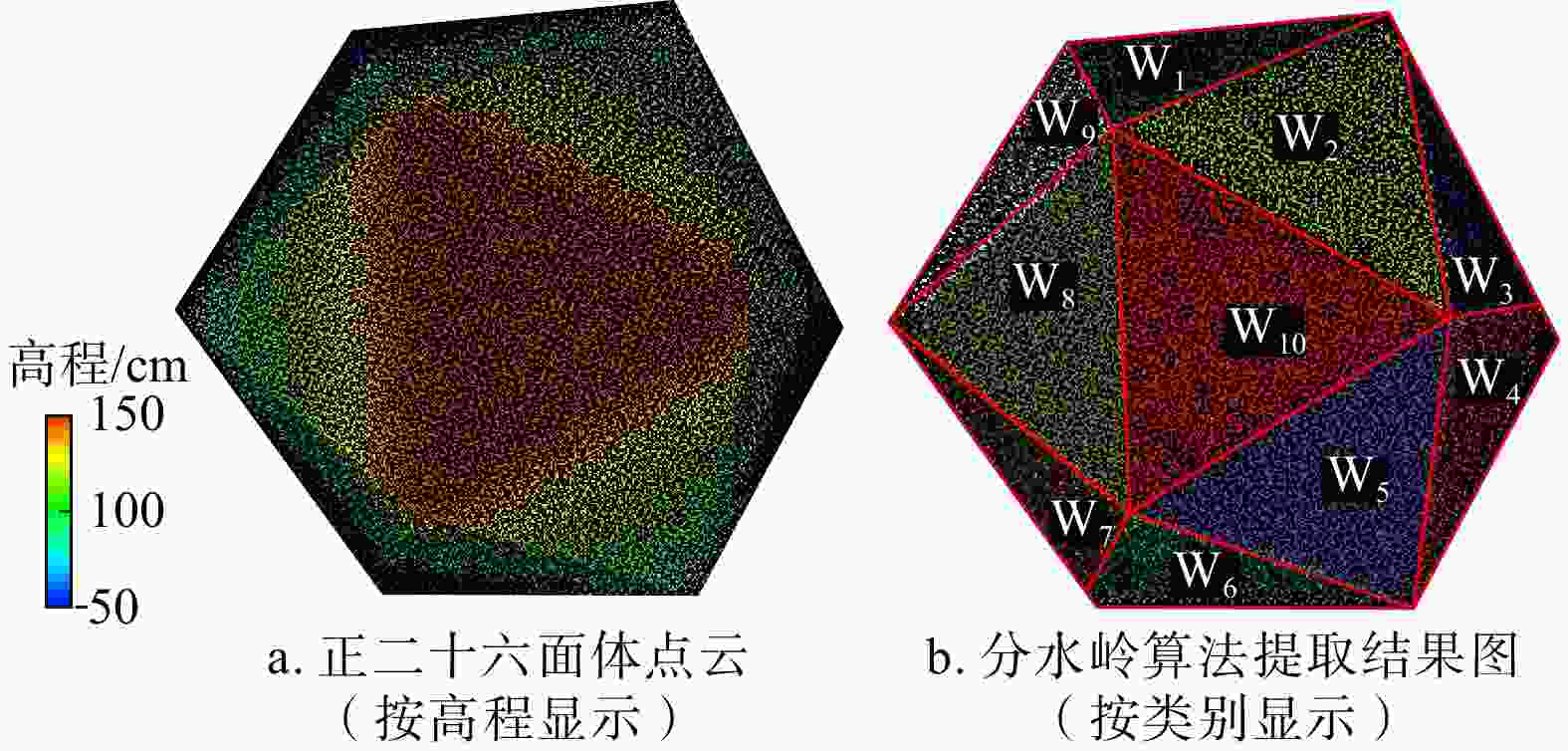
度大小Nsde100 700 15 5 90 5 表 2 正二十六面体自动聚类产状与已知结果产状对比
Table 2. Comparison between automatic clustering attitude of regular icosahedron and known results attitude
结构面
编号自动识别产状/(°) 已知结果产状/(°) 误差/(°) 倾向 倾角 倾向 倾角 倾向 倾角 W1 349 69 350 70 1 1 W2 28 42 27 41 1 1 W3 66 70 66 70 0 0 W4 109 71 109 70 0 1 W5 148 40 148 41 0 1 W6 185 69 186 70 1 1 W7 230 70 230 70 0 0 W8 266 40 268 41 2 1 W9 303 69 305 70 2 1 W10 / / / / / / 平均误差值 0.8 0.8 表 3 多源遥感数据质量参数
Table 3. Multi-source remote sensing data quality parameters
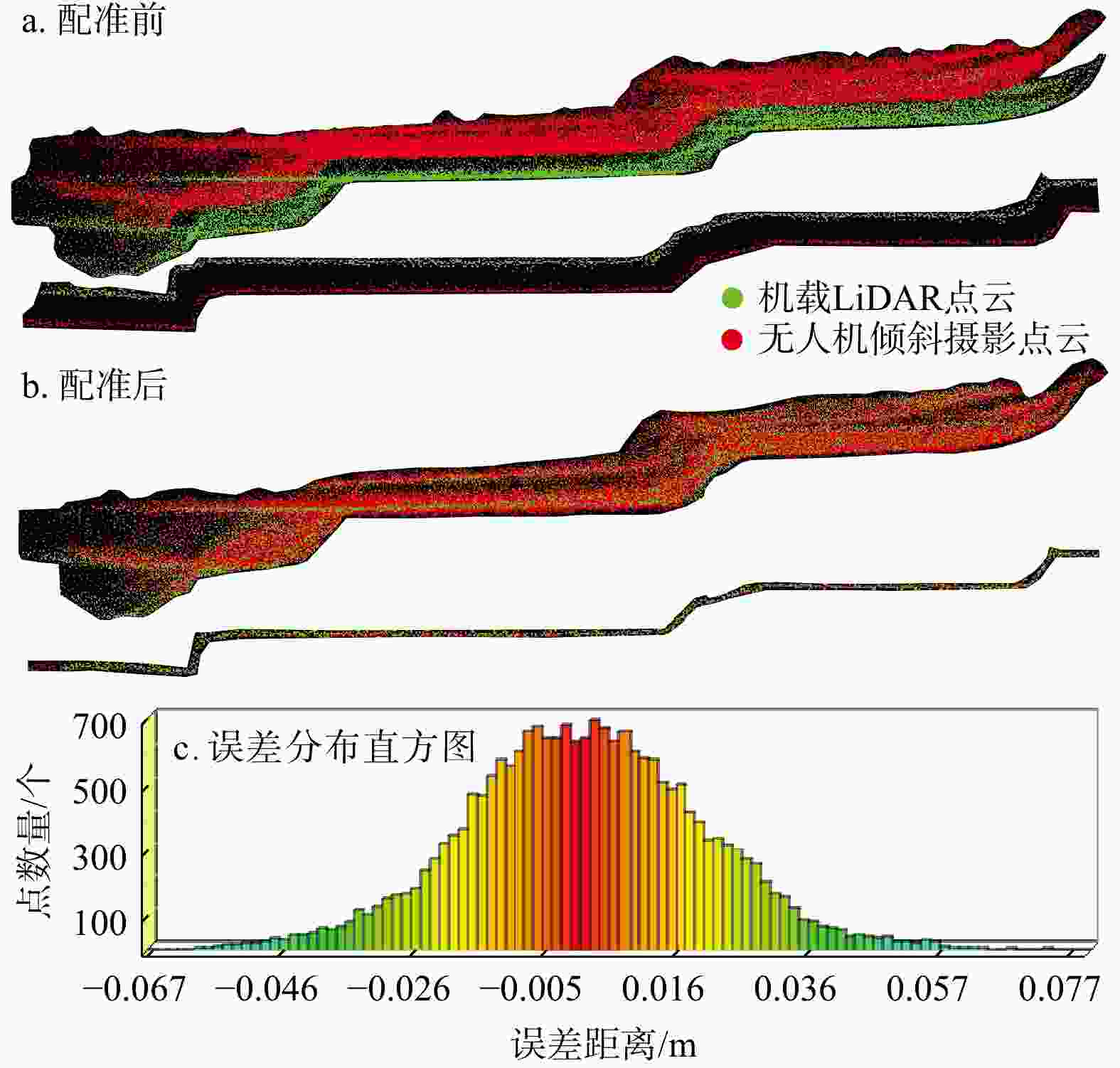
点云数据来源 点数量/个 覆盖面积/
km2最大点密度/
(点·m−2)平均点密度/
(点·m−2)无人机倾斜摄影测量 131225760 2.97 618 44.1 地面激光雷达 33980705 1.12 49584 30.4 机载LiDAR 69351093 1.85 387 37.4 表 4 分水岭算法自动聚类提取结构面产状与人工测量结构面产状对比
Table 4. Comparison between structural surface attitude extracted by the watershed algorithm automatic clustering and structural surface attitude obtained by manual measurement
结构面
组号人工测量产状/(°) 自动识别产状/(°) 误差/(°) 倾向 倾角 倾向 倾角 倾向 倾角 J1 312.8 78.7 316.4 78.4 2.6 0.3 J2 147.3 76.5 148.1 79.8 0.8 3.3 J3 306.9 47.8 309.4 46.1 2.5 1.7 平均误差值 2.0 1.8 -
[1] 刘卫华. 高陡边坡危岩体稳定性、运动特征及防治对策研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2008.LIU W H. Study on stability, movement characteristics and countermeasures of potential unstable rock mass in high-steep slope[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2008. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] WANG W, ZHAO W B, CHAI B, et al. Discontinuity interpretation and identification of potential rockfalls for high-steep slopes based on UAV nap-of-the-object photogrammetry[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2022, 166: 105191. [3] 董秀军. 三维激光扫描技术及其工程应用研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2007.DONG X J. The three-dimensional laser scanning technique and research on its engineering application[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract [4] 董秀军, 黄润秋. 三维激光扫描技术在高陡边坡地质调查中的应用[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(增刊2): 3629-3635.DONG X J, HUANG R Q. Application of 3D laser scanning technology to geologic survey of high and steep slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(S2): 3629-3635. (in Chinese with English abstract [5] KONG D H, SAROGLOU C, WU F Q, et al. Development and application of UAV-SfM photogrammetry for quantitative characterization of rock mass discontinuities[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2021, 141: 104729. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104729 [6] 梁欣廉, 张继贤, 李海涛, 等. 激光雷达数据特点[J]. 遥感信息, 2005, 20(3): 71-76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2005.03.019LIANG X L, ZHANG J X, LI H T, et al. The characteristics of LiDAR data[J]. Remote Sensing Information, 2005, 20(3): 71-76. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2005.03.019 [7] HUANG M, HONG C J, SHA P, et al. Method for visualizing the shear process of rock joints using 3D laser scanning and 3D printing techniques[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 15(1): 204-215. doi: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.02.013 [8] 崔溦, 谢恩发, 张贵科, 等. 利用无人机技术的高陡边坡孤立危岩体识别[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2021, 46(6): 836-843.CUI W, XIE E F, ZHANG G K, et al. Identification of isolated dangerous rock mass in high and steep slope using unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(6): 836-843. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 陈富强. 无人机倾斜摄影技术在高陡边坡危岩体识别及稳定性评价中的应用[J]. 测绘通报, 2024(10): 132-137.CHEN F Q. Application of drone tilt photography technology in identification and stability evaluation of high and steep slope dangerous rock bodies[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2024(10): 132-137. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 王凯. 无人机贴近摄影测量技术在高陡危岩体结构面调查中的应用[J]. 城市勘测, 2024(5): 160-163. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8262.2024.05.038WANG K. Application of UAV approach photogrammetry in the investigation of structural plane of high and steep dangerous rock mass[J]. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2024(5): 160-163. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8262.2024.05.038 [11] 成书楼, 张鹏, 黄波林, 等. 融合贴近摄影和LiDAR技术的危岩体三维模型构建及稳定性分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2024, 51(5): 172-181.CHENG S L, ZHANG P, HUANG B L, et al. Construction of three-dimensional model and stability analysis of dangerous rock mass based on nap-of-the-object photogrammetry and LiDAR technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(5): 172-181. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 吕权儒, 曾斌, 孟小军, 等. 基于无人机倾斜摄影技术的崩塌隐患早期识别及影响区划分方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 313-325.LYU Q R, ZENG B, MENG X J, et al. Early identification and influence range division method of collapse hazards based on UAV oblique photography technology[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 313-325. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] WANG L Q, YIN Y P, HUANG B L, et al. A study of the treatment of a dangerous thick submerged rock mass in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020, 79(5): 2579-2590. doi: 10.1007/s10064-020-01724-y [14] 李峰, 孟飙. 基于K4PCS与ICP算法在点云配准中的应用[J]. 智能计算机与应用, 2024, 14(11): 138-143.LI F, MENG B. Application of K4PCS and ICP algorithm in point cloud registration[J]. Intelligent Computer and Applications, 2024, 14(11): 138-143. (in Chinese with English abstract [15] 付德荃, 王珊珊, 吴彬, 等. 基于无人机摄影测量技术的高陡边坡危岩体特征构建与分析[J]. 地球学报, 2024, 45(1): 53-62.FU D Q, WANG S S, WU B, et al. Construction and analysis of dangerous rock mass characteristics of high and steep slope based on UAV photogrammetry technology[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2024, 45(1): 53-62. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] GUO X F, JIAO R, CAO Y, et al. Application of oblique photography in the investigation potential of rockfall[J]. Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(1): 65-69. [17] 康尘云. 基于倾斜摄影的高位危岩特征获取和稳定性评价: 以重庆万州观音山危岩带为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2022, 33(5): 66-75.KANG C Y. Feature acquisition and stability evaluation of high dangerous rock mass based on oblique photography: A case study at Guanyinshan in Wanzhou, Chongqing City[J]. Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(5): 66-75. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] 许哲, 董林啸, 吴家跃. 改进ICP算法的激光雷达点云配准[J]. 测绘通报, 2024(4): 1-5.XU Z, DONG L X, WU J Y. LiDAR point cloud registration with improved ICP algorithm[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2024(4): 1-5. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] LIU C J, ZHANG S F, DING L Q, et al. Identification of dangerous rock mass of high slope and study of anchoring method based on laser scanning[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(10): 2139-2146. [20] 王明辉, 曹熙平, 谯立家. 危岩体精细调查与崩塌过程三维场景模拟: 以西南某水电站高边坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2023, 34(6): 86-96.WANG M H, CAO X P, QIAO L J. Comprehensive analysis of hazardous rock mass and simulation of potential rockfall processes using 3D terrain model: A case study of the high cut slope near damsite of a hydropower station in southern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(6): 86-96. (in Chinese with English abstract [21] 夏雄彬, 谯立家, 许万忠. 基于机载LiDAR及无人机影像的高位危岩体调查和成因分析[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2023, 40(9): 188-194. doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20220394XIA X B, QIAO L J, XU W Z. Investigation and cause analysis of dangerous rock masses on high and steep slope based on airborne LiDAR and UAV imagery[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2023, 40(9): 188-194. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.11988/ckyyb.20220394 [22] 徐画, 陈建平, 张权平, 等. 无人机点云数据的危岩体结构信息提取[J]. 测绘科学, 2021, 46(7): 137-144.XU H, CHEN J P, ZHANG Q P, et al. Application of UAV photogrammetry in investigation of high and steep dangerous rock mass[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2021, 46(7): 137-144. (in Chinese with English abstract [23] 姚富潭, 吴明堂, 董秀军, 等. 基于贴近摄影测量技术的高陡危岩体结构面调查方法[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 50(2): 218-228.YAO F T, WU M T, DONG X J, et al. Investigation method of discontinuity in high and steep dangerous rock mass based on nap of the object photogrammetry[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science and Technology Edition), 2023, 50(2): 218-228. (in Chinese with English abstract [24] 马立广. 地面三维激光扫描测量技术研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2005.MA L G. The research of terrestrial laser scanning technology[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2005. (in Chinese with English abstract [25] 杨国东, 王民水. 倾斜摄影测量技术应用及展望[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2016, 39(1): 13-15.YANG G D, WANG M S. The tilt photographic measuration technique and expectation[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2016, 39(1): 13-15. (in Chinese with English abstract [26] 张航, 胡海瑞, 朱杰清, 等. 基于非接触测量楔形危岩体稳定性快速评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2025, 44(2): 67-77.ZHANG H, HU H R, ZHU J Q, et al. Rapid analysis of the stability of a wedge-shaped unstable rock mass on the basis of non-contact measurements[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2025, 44(2): 67-77. (in Chinese with English abstract [27] 梅文胜, 周燕芳, 周俊. 基于地面三维激光扫描的精细地形测绘[J]. 测绘通报, 2010(1): 53-56.MEI W S, ZHOU Y F, ZHOU J. Fine topographic mapping based on ground three-dimensional laser scanning[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2010(1): 53-56. (in Chinese with English abstract [28] 党杰, 董吉, 何松标, 等. 机载LiDAR与地面三维激光扫描在贵州水城独家寨崩塌地质灾害风险调查中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2022, 33(4): 106-113.DANG J, DONG J, HE S B, et al. Application of airborne LiDAR and ground 3D laser scanning in geological hazard risk investigation of Dujiazhai collapse in Shuicheng, Guizhou[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(4): 106-113. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] CHEN S W, WALSKE M L, DAVIES I J. Rapid mapping and analysing rock mass discontinuities with 3D terrestrial laser scanning in the underground excavation[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2018, 110: 28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.07.012 [30] 张林杰, 冯刚, 龙超, 等. 无人机倾斜摄影与贴近摄影融合建模在高位危岩体调查中的应用[J]. 水电与抽水蓄能, 2023, 9(增刊1): 85-90.ZHANG L J, FENG G, LONG C, et al. Application of UAV oblique photography and nap-of-theobject photography fusion modeling in the investigation of high unstable rock mass[J]. Hydropower and Pumped Storage, 2023, 9(S1): 85-90. [31] 杨俊斌, 张治平, 刘骏. 无人机摄影测量在超高陡危岩体整治工程中的应用[J]. 铁道建筑, 2022, 62(10): 147-150.YANG J B, ZHANG Z P, LIU J. Application of UAV-based photogrammetry in the treatment engineering of super-high and steep dangerous rock mass[J]. Railway Engineering, 2022, 62(10): 147-150. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 李斯, 杨自安, 李冬月, 等. 基于无人机倾斜摄影三维建模技术的赤马山铜矿地质环境调查及评价[J]. 地质与勘探, 2023, 59(6): 1271-1281. doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2023.06.012LI S, YANG Z A, LI D Y, et al. Geological environment investigation and evaluation of the Chimashan copper deposit based on 3D modeling technology of UAV tilt photography[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2023, 59(6): 1271-1281. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2023.06.012 [33] CHENG Z, GONG W P, TANG H M, et al. UAV photogrammetry-based remote sensing and preliminary assessment of the behavior of a landslide in Guizhou, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2021, 289: 106172. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106172 [34] 庞鑫, 袁明, 卢渊, 等. 基于无人机LiDAR仿地飞行技术的高陡边坡危岩体快速识别方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(6): 21-30.PANG X, YUAN M, LU Y, et al. Rapid identification method for the dangerous rock mass of a high-steep slope based on UAV LiDAR and ground imitation flight[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(6): 21-30. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] 杨力龙. 基于轻小型无人机的航空摄影测量技术在高陡边坡几何信息勘察中的应用研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017.YANG L L. Application of aerial photogrammetry based on light and small unmanned aerial vehicle in geometric information survey of high and steep slope[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract [36] 侯彬, 金尚忠, 王赟, 等. 点云配准方法在粗配准中的比较[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(8): 294-301.HOU B, JIN S Z, WANG Y, et al. Comparison of point cloud registration methods in coarse registration[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(8): 294-301. (in Chinese with English abstract [37] 周春艳, 李勇, 邹峥嵘. 三维点云ICP算法改进研究[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2011, 21(8): 75-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2011.08.019ZHOU C Y, LI Y, ZOU Z R. Three-dimensional cloud ICP algorithm improvement[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2011, 21(8): 75-77. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2011.08.019 [38] 宁悦. 三维点云配准方法研究[J]. 测绘与空间地理信息, 2022, 45(7): 188-191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2022.07.055NING Y. Research on 3D point cloud registration method[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2022, 45(7): 188-191. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5867.2022.07.055 [39] 任大伟. 联合地面激光雷达点云的无人机倾斜影像密集匹配及两类点云融合技术[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2022.REN D W. Dense matching of UAV oblique images combined with terrestrial laser scanning point cloud and point cloud fusion technology[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] VINCENT L, SOILLE P. Watersheds in digital spaces: An efficient algorithm based on immersion simulations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1991, 13(6): 583-598. doi: 10.1109/34.87344 -




 下载:
下载: