-
摘要:
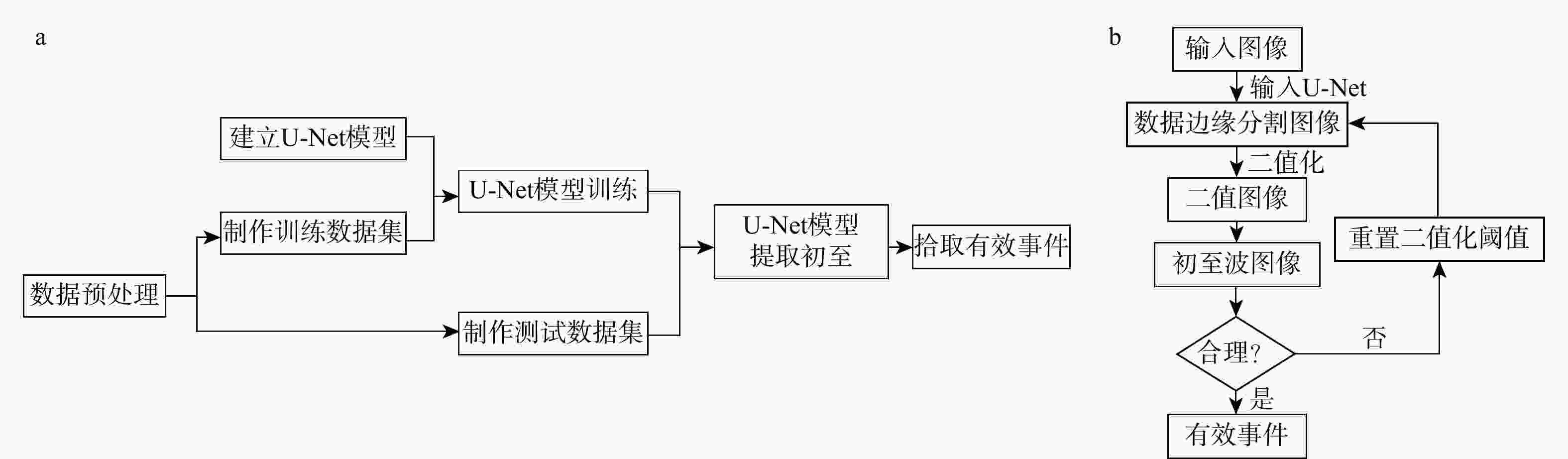
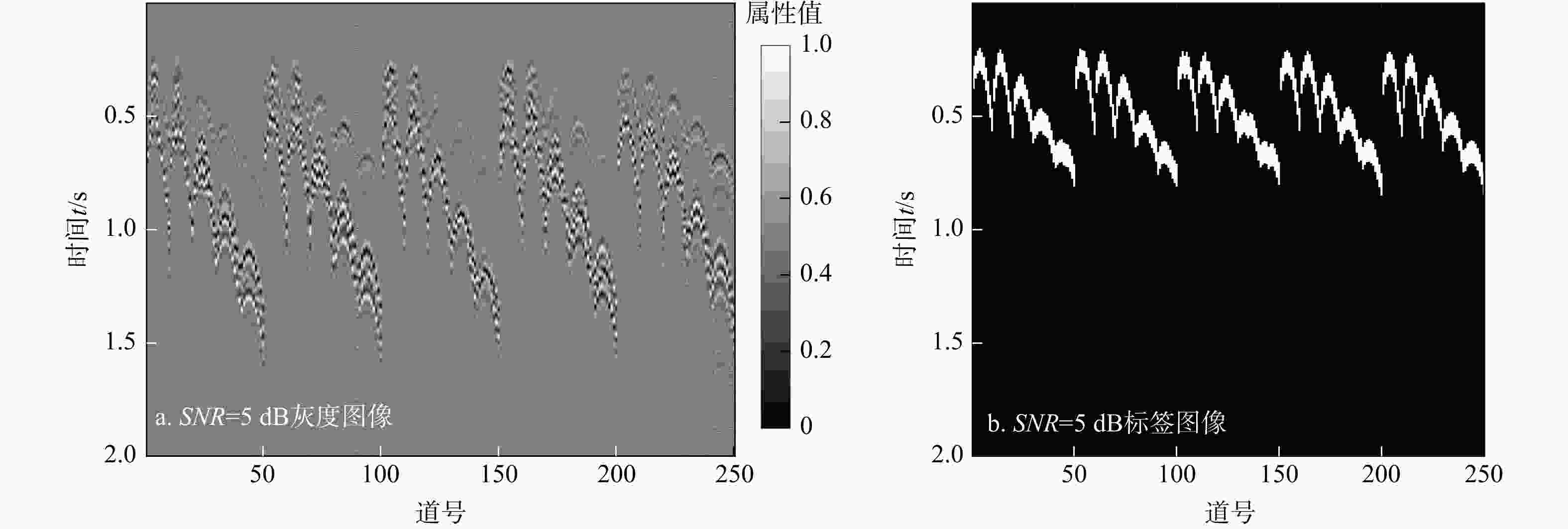
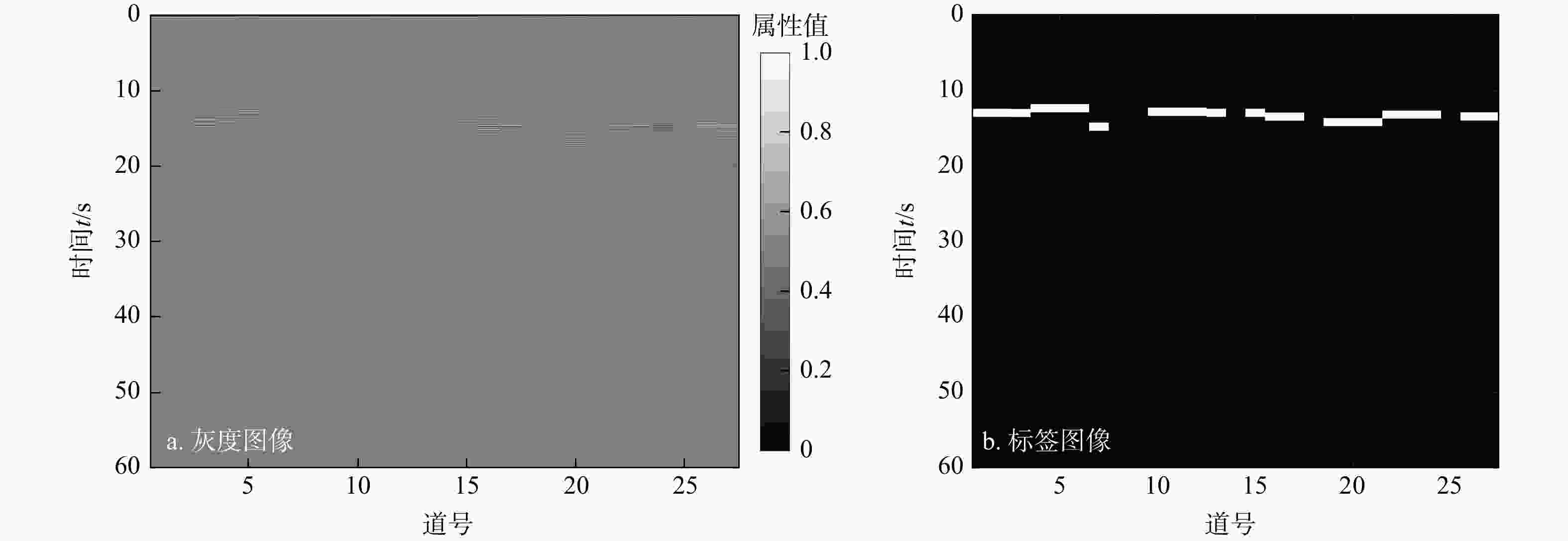
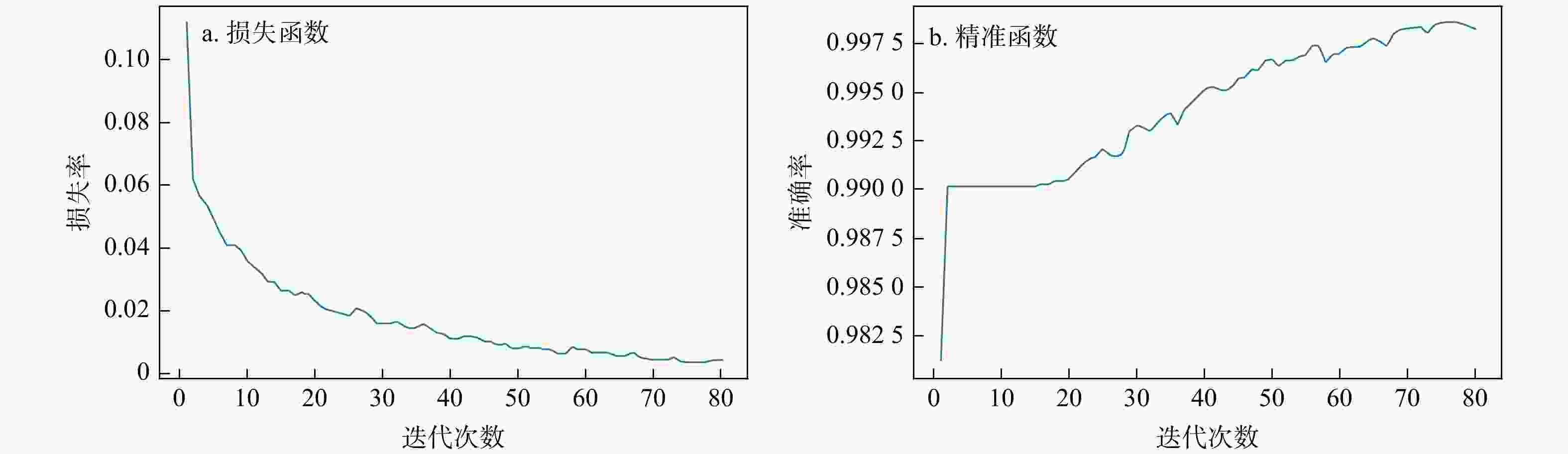
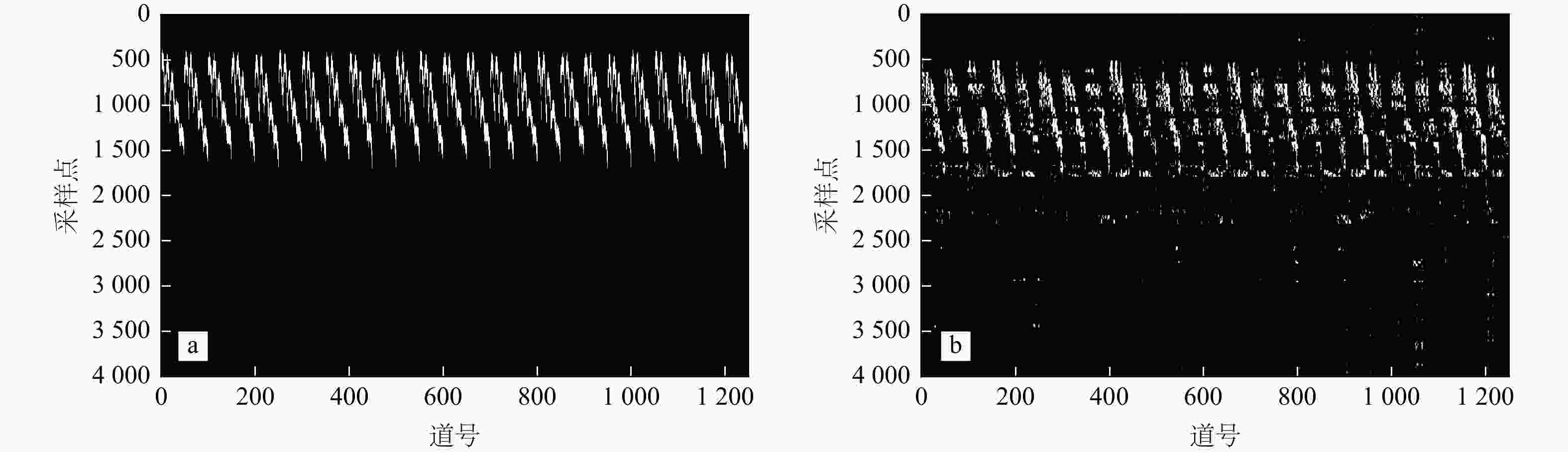
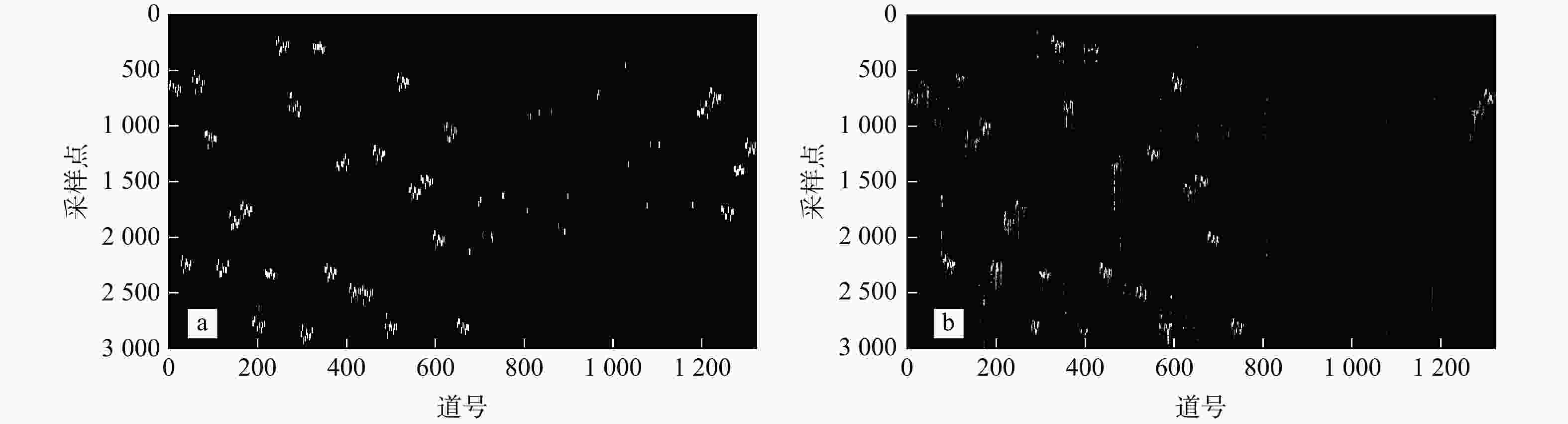
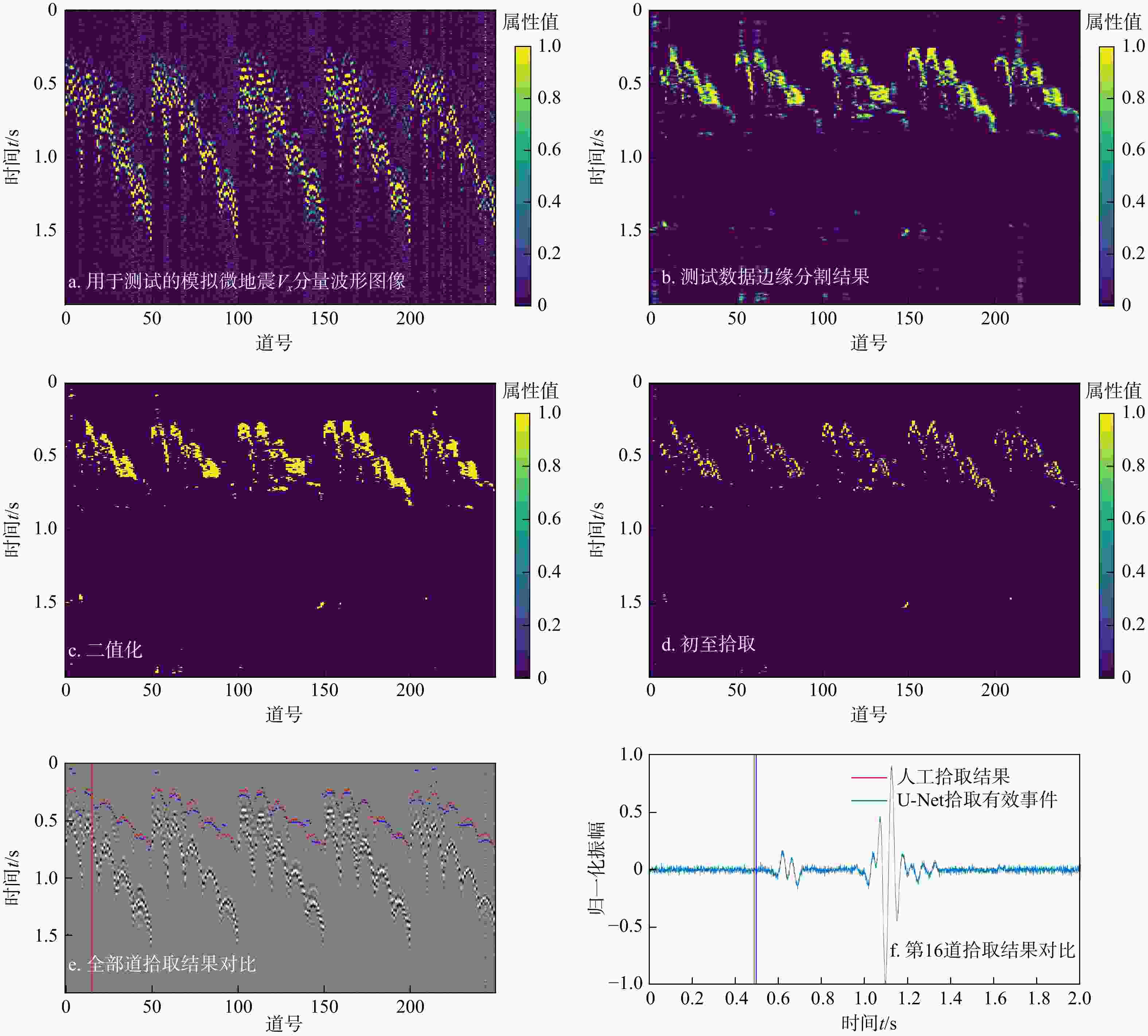
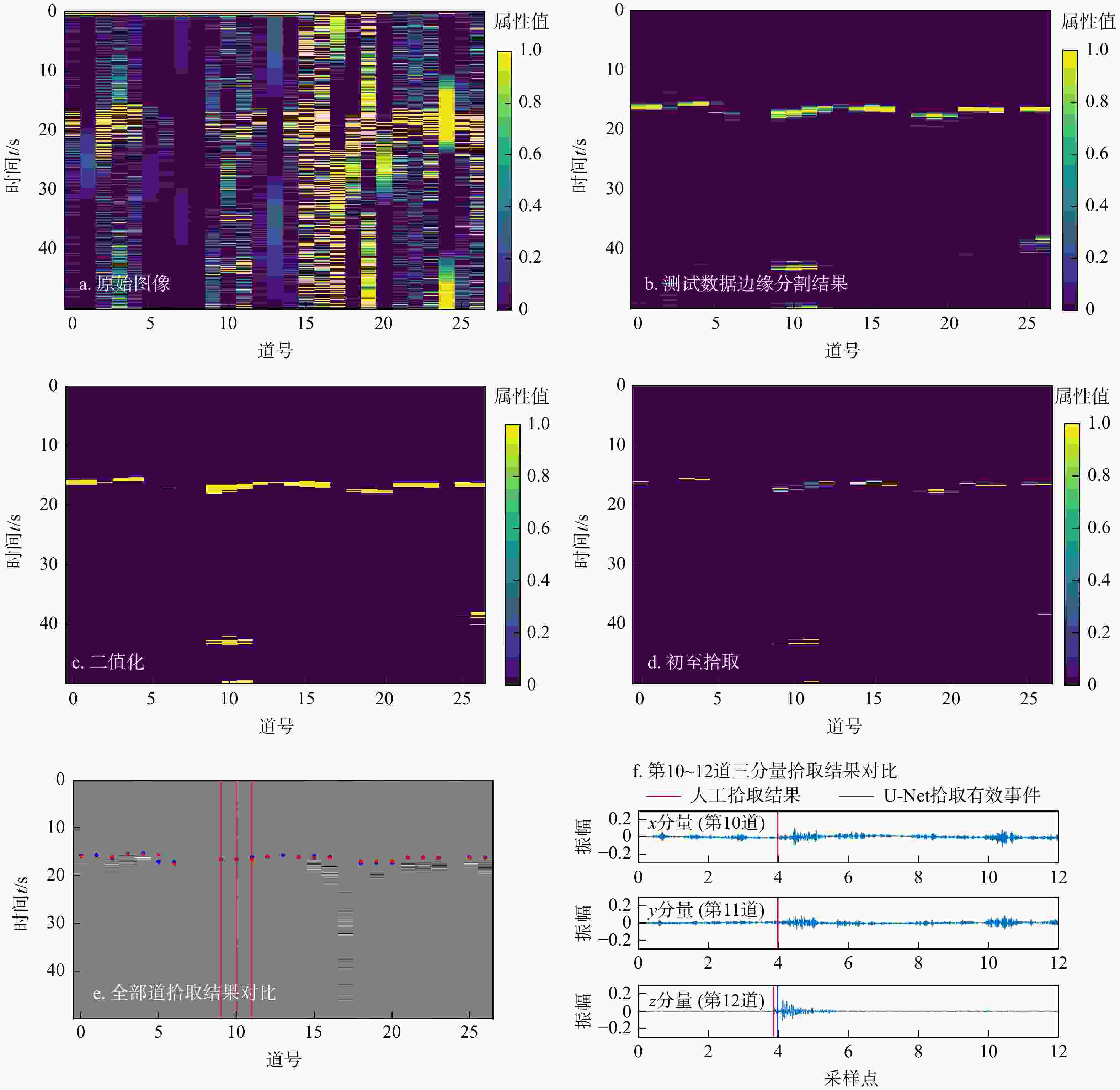
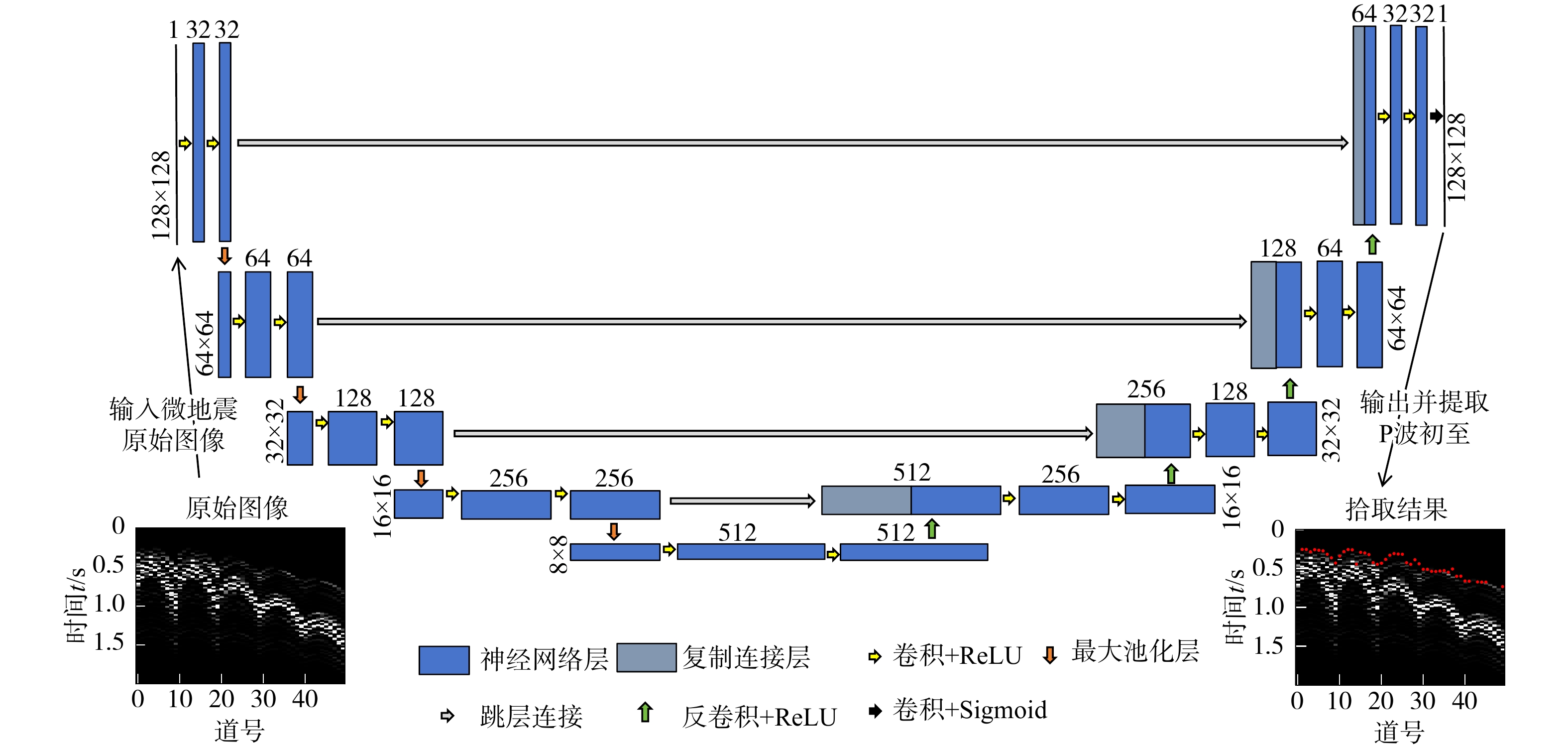
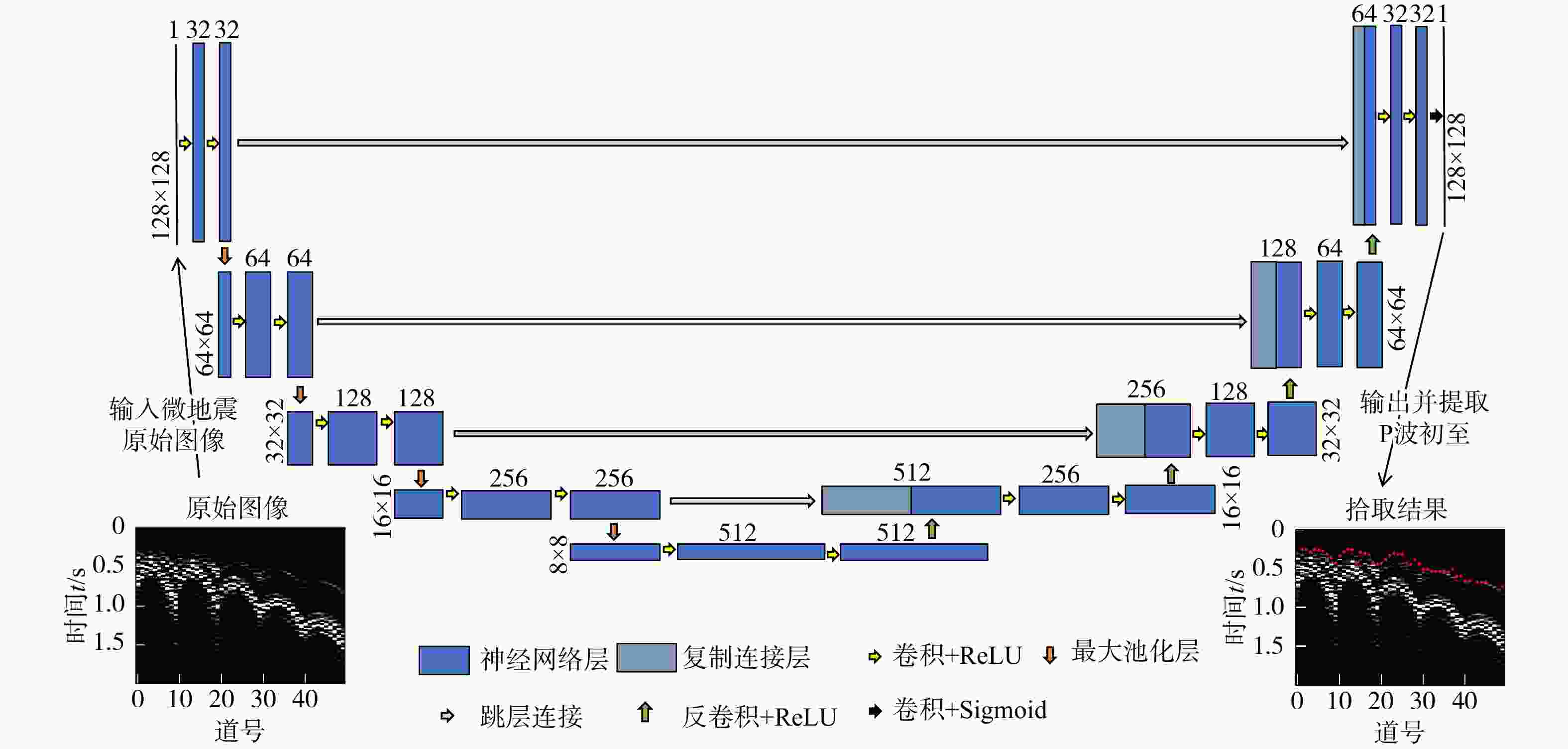
有效事件自动拾取是微地震监测的重要环节,拾取的准确性直接影响后续震源定位和震源机制反演的精度与可靠性。构建了10层U-Net神经网络模型框架,将三维有限差分模拟的原始微地震数据与实测储气库微地震原始数据制作为标签图像,将其切割为128×128大小切片并输入U-Net神经网络学习,输出预测后的切片并将其合并,再对预测后的图像进行二值化,最后提取微地震有效事件的P波初至,使得背景噪声与有效信号图像的边缘分割更加精细,提高了微地震有效事件的自动拾取效率与准确性。定量分析对比了U-Net与STA/LTA法的拾取率、错拾率和拾取误差,测试结果表明,U-Net的拾取效果优于STA/LTA法,而且U-Net也具有较强的抗干扰能力与泛化能力;评价不同标签宽度对初至拾取结果的影响,结果表明依据事件的主周期制作的标签拾取效果最佳。本研究建立的U-Net神经网络初至自动拾取算法是高效、高精度储气库完整性微地震智能监测系统的重要组成部分,对提高我国微地震监测技术水平具有重要意义。
Abstract:Objective Automatic picking of effective events is an important part of microseismic monitoring, and the accuracy of picking directly affects the precision and reliability of subsequent seismic source localization and seismic source mechanism inversion.
Methods In this study, a 10-layer U-Net neural network model framework was constructed. Labeled images were created using original microseismic data from 3D finite-difference simulations and raw microseismic data from measured gas storage reservoirs. These images were then sliced into 128×128-pixel patches and input into the U-Net neural network for training. The predicted slices were subsequently merged into complete images, binarized, and finally used to extract the P-wave first arrivals of effective microseismic events. This approach achieves more accurate edge segmentation between background noise and effective signal, thereby improving the efficiency and accuracy of automatic pickup of effective microseismic events.
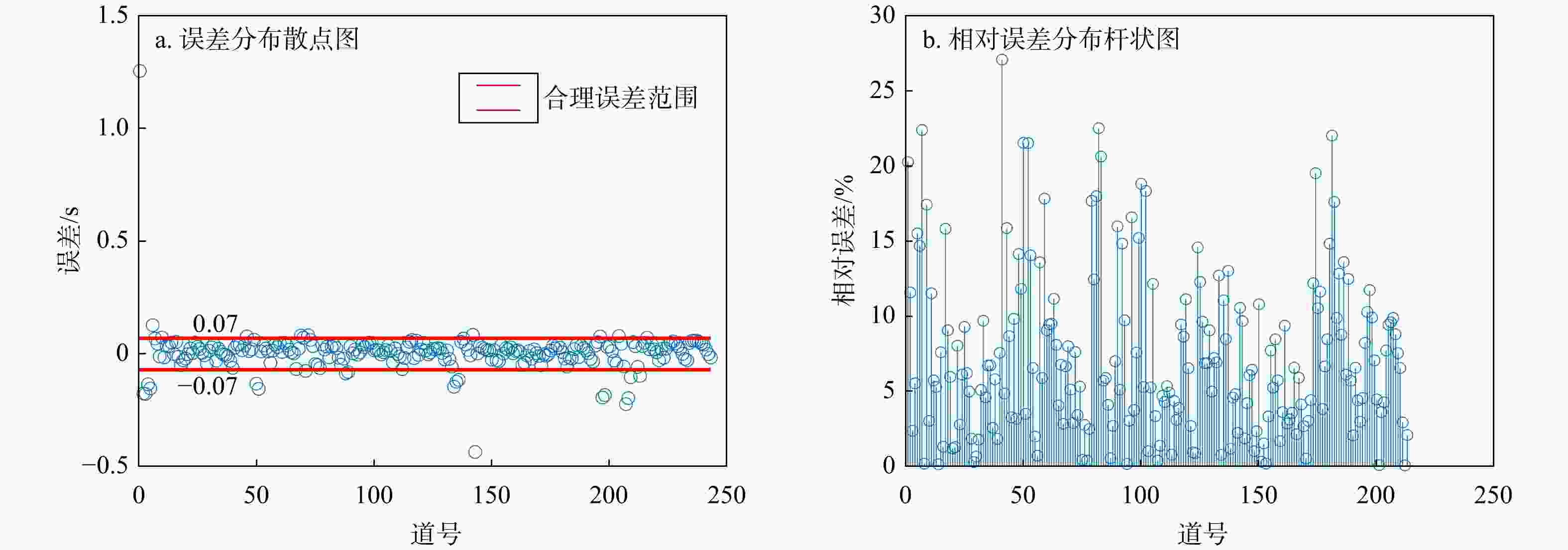
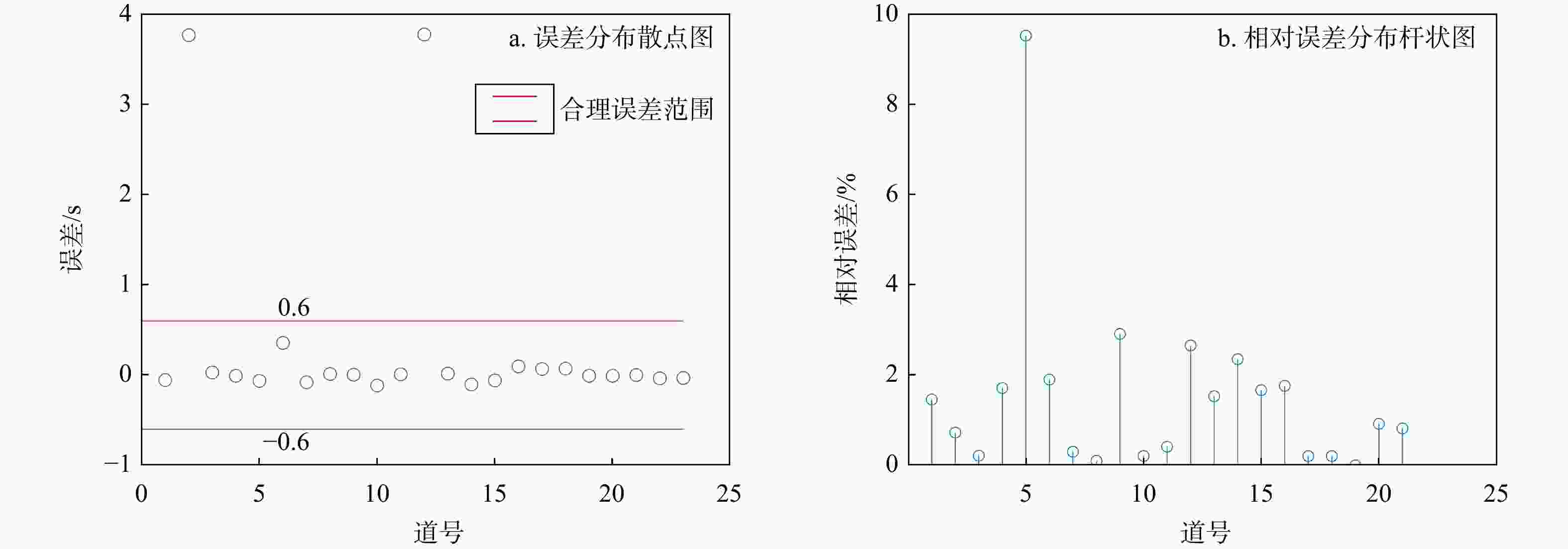
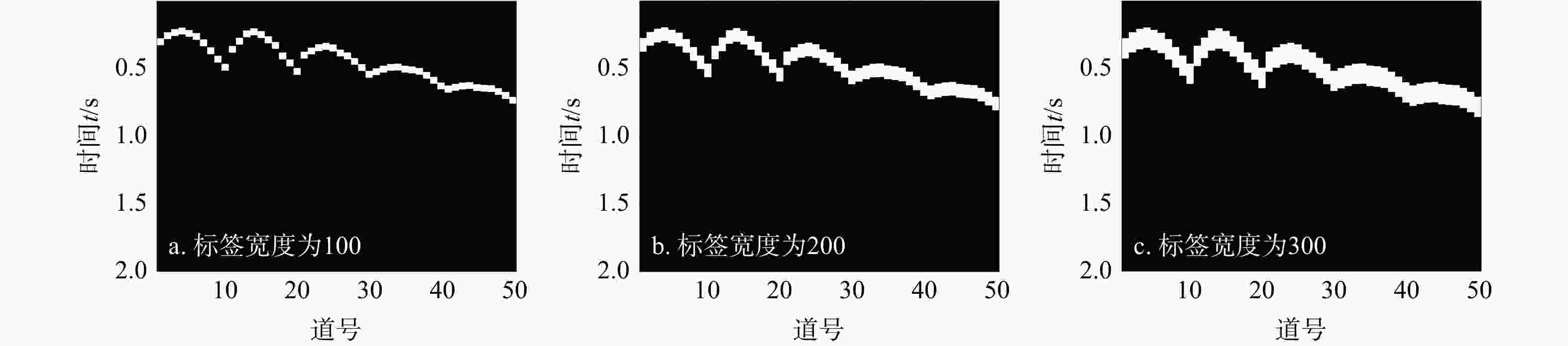
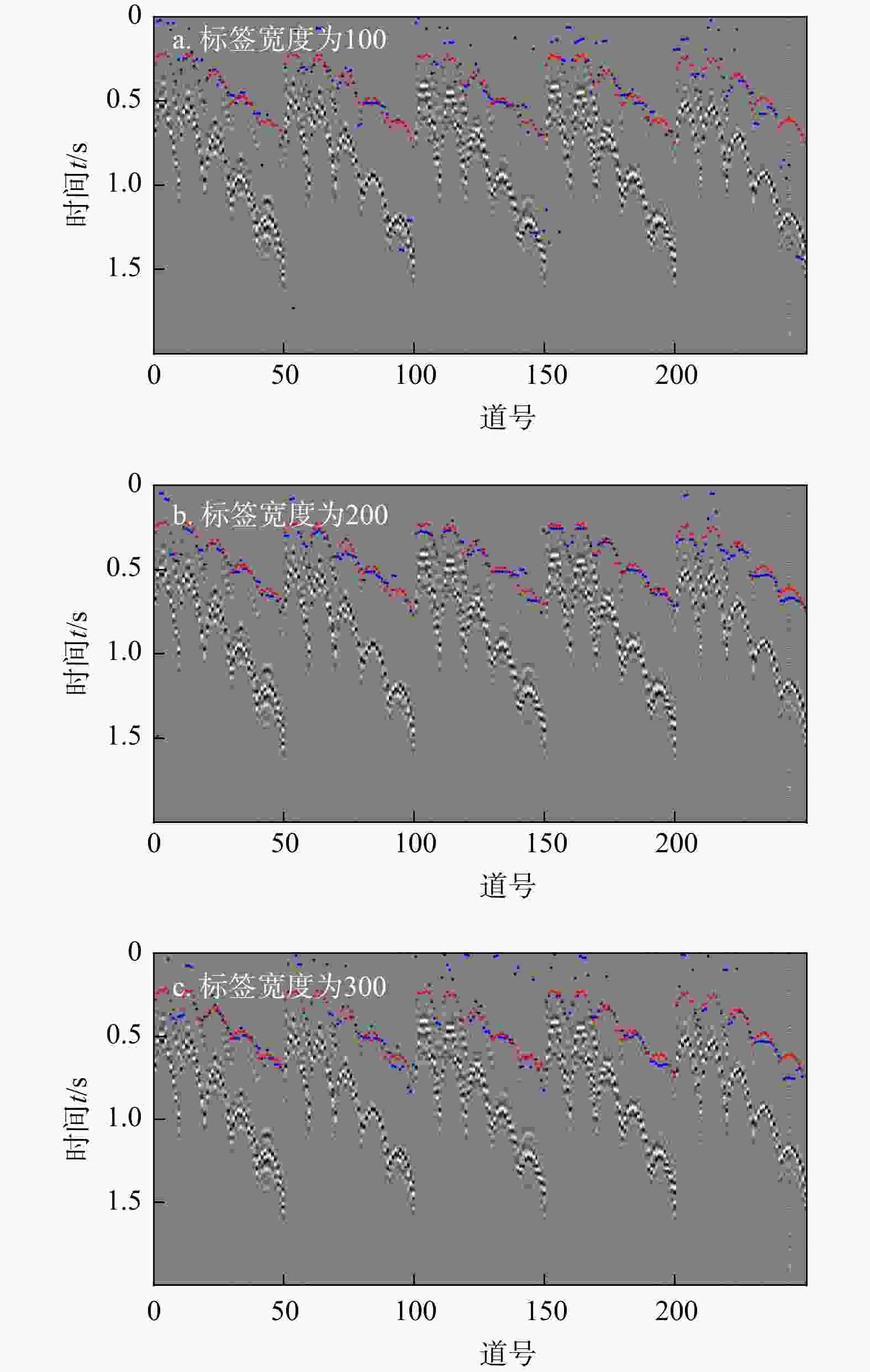
Results The study quantitatively analyzed and compared the picking rate, mispicking rate, picking error of U-Net method and STA/LTA method. The test results showed that the picking performance of U-Net was better than that of STA/LTA method, and U-Net also demonstrated stronger anti-jamming ability and generalization ability. The impact of different label widths on the picking results of first arrivals was evaluated, and the results showed that labels generated based on the dominant period of the events yielded the optimal picking performance.
Conclusion The U-Net-based first-arrival automatic pickup algorithm established in this study constitutes an important part of an efficient and high-precision intelligent microseismic monitoring system for gas storage integrity, providing significant support for advancing microseismic monitoring technology in China.
-
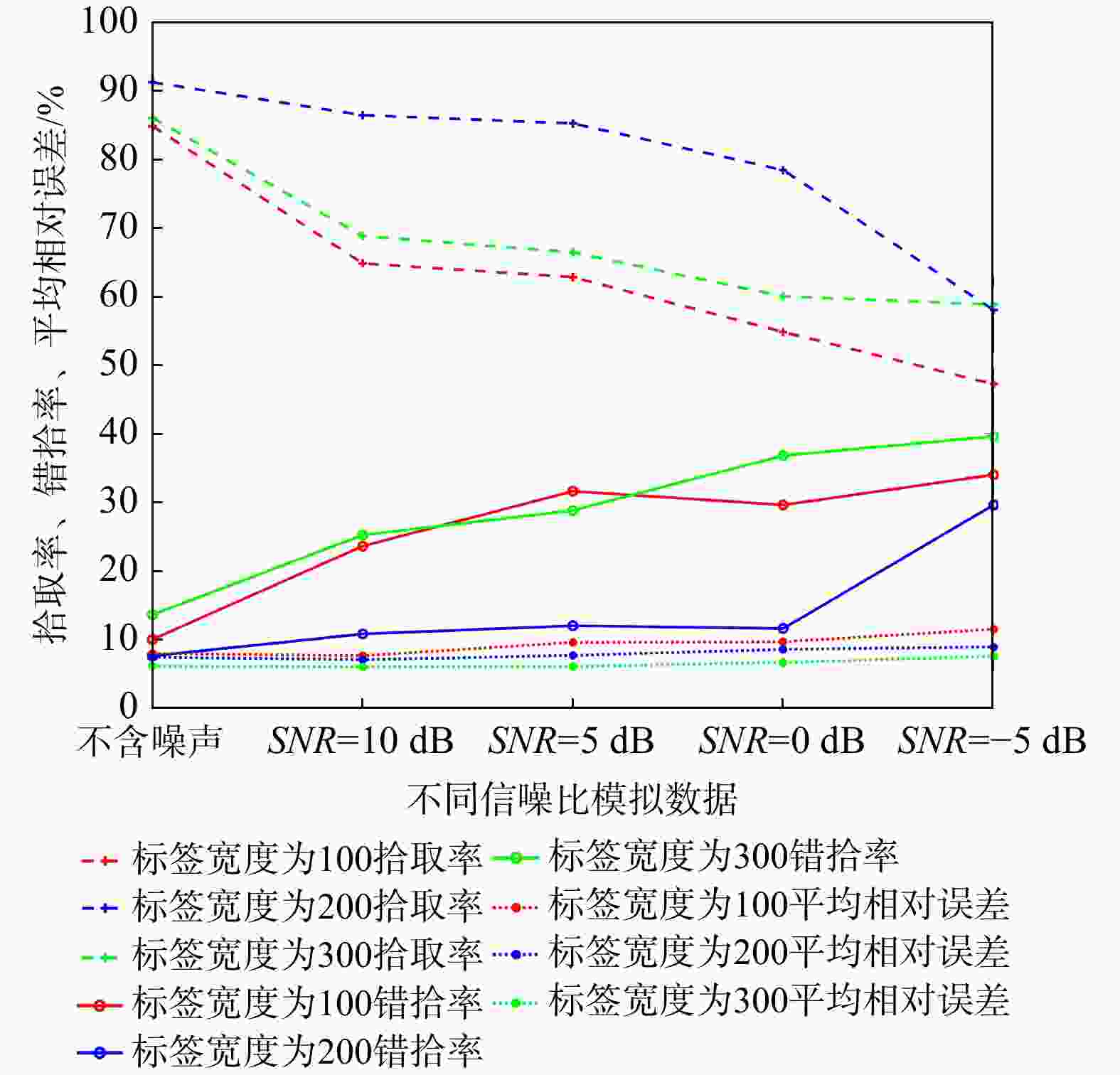
表 1 不同信噪比模拟数据拾取结果评价
Table 1. Evaluation of picking results for simulated data with different signal to noise ratios
方法 指标 不含
噪声SNR=
10 dBSNR=
5 dBSNR=
0 dBSNR=
−5 dBU-Net法 拾取率/% 91.2 86.4 85.2 78.4 58 错拾率/% 7.6 10.8 12.0 11.6 29.6 平均相对误差/% 6.12 5.68 7.27 7.9 9.79 STA/LTA法 拾取率/% 99 69.65 49.25 38.81 34.33 错拾率/% 0 30.35 50.75 61.19 65.67 平均相对误差/% 0.125 1.44 1.35 1.62 1.33 表 2 3个站点实测数据拾取结果评价
Table 2. Evaluation of picking results for three sites
方法 指标 站点1 站点2 站点3 平均值 U-Net法 拾取率/% 85 82.35 100 89.17 错拾率/% 20 29.41 9.52 19.64 平均相对误差/% 7.56 5.39 1.5 4.82 STA/LTA法 拾取率/% 55 64.71 66.67 62.13 错拾率/% 45 35.29 14.29 31.53 平均相对误差/% 7.72 3.26 3.05 4.68 表 3 模拟数据有效事件结果评价对比
Table 3. Comparison of picking results for simulated data
标签
宽度指标 不含
噪声SNR=10 dB SNR=5 dB SNR=0 dB SNR=−5 dB 100 拾取率/% 80.4 65.2 61.6 62 55.6 错拾率/% 10 23.6 31.6 29.6 34 平均相对误差/% 7.98 7.62 9.58 9.67 11.49 200 拾取率/% 91.2 86.4 85.2 78.4 58 错拾率/% 7.6 10.8 12 11.6 29.6 平均相对误差/% 6.12 5.68 7.27 7.9 9.79 300 拾取率/% 86 68.8 66.4 60 58.8 错拾率/% 13.6 25.2 28.8 36.8 39.6 平均相对误差/% 6.11 5.97 6.06 6.64 7.57 -
[1] 李萌. 微地震监测数据采集方案优化及正反演方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2017.LI M. Methods on acquisition optimization, wavefield simulation and inversion to improve microseismic monitoring[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract [2] LI M, WANG H, FANG Z L, et al. Imaging of annulus-formation interface using reverse time migration based on ultrasonic pitch-catch measurements: Case studies from an experimental well and a field well[J]. Ultrasonics, 2024, 141: 107323. doi: 10.1016/j.ultras.2024.107323 [3] LI M, SHEN H Y, GUO Y H, et al. Locating microseismic events using multiplicative time reversal imaging based on decoupled wavefields in 2D VTI media: Theoretical and synthetic cases studies[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 202: 108547. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2021.108547 [4] LI M, LI H F, TAO G, et al. Microseismic event location using multi-scale time reversed imaging[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 174: 144-160. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.11.015 [5] LI M, ALI M Y, TAO G, et al. Monitoring of induced microseismicity in an onshore oilfield from Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates: Implications for carbonate reservoir monitoring[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2017, 152: 33-48. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.02.012 [6] ALLEN R V. Automatic earthquake recognition and timing from single traces[J]. The Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 1978, 68(5): 1521-1532. doi: 10.1785/BSSA0680051521 [7] SLEEMAN R, VAN ECK T. Robust automatic P-phase picking: An on-line implementation in the analysis of broadband seismogram recordings[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 1999, 113(1/2/3/4): 265-275. [8] 宋维琪, 吕世超. 基于小波分解与Akaike信息准则的微地震初至拾取方法[J]. 石油物探, 2011, 50(1): 14-21.SONG W Q, LV S C. Automatic detection method of microseismic event based on wavelet decomposition and Akaike information criteria[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2011, 50(1): 14-21. (in Chinese with English abstract [9] 刘威, 朱鸿鹄, 王涛, 等. 基于分布式声波传感的大地探测技术研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(1): 29-41.LIU W, ZHU H H, WANG T, et al. Research progress of earth exploration technologies based on distributed acoustic sensing[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(1): 29-41. (in Chinese with English abstract [10] 张俊威. 深度学习在中低信噪比地震数据初至拾取中的应用研究[J]. 天然气与石油, 2024, 42(2): 81-89.ZHANG J W. Application research of deep learning in first-arrival pickup for seismic data with low to medium signal-to-noise ratio[J]. Natural Gas and Oil, 2024, 42(2): 81-89. (in Chinese with English abstract [11] 周创, 居兴国, 李子昂, 等. 基于深度卷积生成对抗网络的地震初至拾取[J]. 石油物探, 2020, 59(5): 795-803.ZHOU C, JU X G, LI Z A, et al. A deep convolutional generative adversarial network for first-arrival pickup from seismic data[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2020, 59(5): 795-803. (in Chinese with English abstract [12] 姜天琪. 基于深度学习的微地震数据处理与震源反演方法[D]. 北京: 中国矿业大学(北京), 2021.JIANG T Q. Processing and source inversion methods for microseismic monitoring based on deep learning[D]. Beijing: China University of Mining & Technology (Beijing), 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract [13] 郝鹏亮. 基于深度学习的复杂地表初至拾取及层析静校正应用研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2023.HAO P L. Application research of first-break picking and tomographic static correction based on deep learning on complex surface[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract [14] 李宇, 韩晓红, 张玲, 等. 融合时空注意力机制的P波到时拾取网络[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2023, 59(6): 113-124. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2109-0428LI Y, HAN X H, ZHANG L, et al. Seismic P-wave first-arrival picking model based on spatiotemporal attention mechanism[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2023, 59(6): 113-124. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2109-0428 [15] 赵扬锋, 王进铭, 潘一山, 等. 基于质量寻优与归一化STA/LTA方法的微震P波到时拾取技术研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2022, 41(8): 1610-1625.ZHAO Y F, WANG J M, PAN Y S, et al. Study on determining arrival times of microseismic P-wave based on quality optimization and normalized STA/LTA method[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2022, 41(8): 1610-1625. (in Chinese with English abstract [16] 罗浩, 彭代平, 黄鹏, 等. NARX神经网络微地震P波有效事件自动拾取方法研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2024, 39(6): 2345-2356.LUO H, PENG D P, HUANG P, et al. Research on automatic picking method of effective events of microseismic P-wave in NARX neural network[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2024, 39(6): 2345-2356. (in Chinese with English abstract [17] 吴治涛, 李仕雄. STA/LTA算法拾取微地震事件P波到时对比研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2010, 25(5): 1577-1582.WU Z T, LI S X. Comparison of STA/LTA P-pickers for micro seismic monitoring[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2010, 25(5): 1577-1582. (in Chinese with English abstract [18] 段建华, 程建远, 王云宏, 等. 基于STA/LTA方法的微地震事件自动识别技术[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2015, 43(1): 76-80.DUAN J H, CHENG J Y, WANG Y H, et al. Automatic identification technology of microseismic event based on STA/LTA algorithm[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2015, 43(1): 76-80. (in Chinese with English abstract [19] 李宇. 基于深度学习的地震P波到时拾取技术研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2022.LI Y. Research on the pickup of seismic P-wave arrival based on deep learning[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2022. (in Chinese with English abstract [20] AMINZADEH F, MAITY D, TAFTI T A, et al. Artificial neural network based autopicker for micro-earthquake data[C]//SEG. SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2011. Houston, Texas, USA: SEG, 2011: 1623-1626. [21] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Anon. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York, USA: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. [22] ZHENG J, LU J R, PENG S P, et al. An automatic microseismic or acoustic emission arrival identification scheme with deep recurrent neural networks[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2018, 212(2): 1389-1397. doi: 10.1093/gji/ggx487 [23] MOUSAVI S M, ZHU W Q, SHENG Y X, et al. CRED: A deep residual network of convolutional and recurrent units for earthquake signal detection[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9: 10267. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45748-1 [24] CHEN Y K, ZHANG G Y, BAI M, et al. Automatic waveform classification and arrival picking based on convolutional neural network[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2019, 6(7): 1244-1261. doi: 10.1029/2018EA000466 [25] ZHANG G Y, LIN C Y, CHEN Y K. Convolutional neural networks for microseismic waveform classification and arrival picking[J]. Geophysics, 2020, 85(4): WA227-WA240. doi: 10.1190/geo2019-0267.1 [26] BI X, ZHANG C, HE Y, et al. Explainable time-frequency convolutional neural network for microseismic waveform classification[J]. Information Sciences, 2021, 546: 883-896. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2020.08.109 [27] 李薇薇, 龚仁彬, 周相广, 等. 基于深度学习UNet++网络的初至波拾取方法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(1): 187-194. doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0152LI W W, GONG R B, ZHOU X G, et al. UNet++: A deep-neural-network-based seismic arrival time picking method[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(1): 187-194. (in Chinese with English abstract doi: 10.6038/pg2021EE0152 [28] 张逸伦, 喻志超, 胡天跃, 等. 基于U-Net的井中多道联合微地震震相识别和初至拾取方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2021, 64(6): 2073-2085.ZHANG Y L, YU Z C, HU T Y, et al. Multi-trace joint downhole microseismic phase detection and arrival picking method based on U-Net[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(6): 2073-2085. (in Chinese with English abstract [29] 李政超, 王维波, 高明, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的微地震初至拾取[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2022, 37(3): 1060-1069.LI Z C, WANG W B, GAO M, et al. Microseismic first arrival picking based on convolutional neural network[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37(3): 1060-1069. (in Chinese with English abstract [30] 胡婷, 徐彬, 王永发, 等. 基于U-Net的矿山微震初至拾取研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2023, 23(16): 6802-6809.HU T, XU B, WANG Y F, et al. Arrival picking of mine microseismic events using U-Net[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2023, 23(16): 6802-6809. (in Chinese with English abstract [31] 张野, 陈金桥, 李炎隆. 基于多深度模型的钻孔结构面智能识别与量化分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2023, 42(6): 31-41.ZHANG Y, CHEN J Q, LI Y L. Intelligent recognition and quantitative analysis of borehole hydraulic geological images utilizing multiple deep learning models[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2023, 42(6): 31-41. (in Chinese with English abstract [32] 冷泽男. 基于神经网络方法的微地震事件拾取及P波S波分类技术研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2024.LENG Z N. Research on microseismic event pickup and P-wave and S-wave classification technology based on neural network method[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2024. (in Chinese with English abstract [33] 封强. 深度学习框架下微地震信号识别与震源定位方法研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023.FENG Q. Research on microseismic signal identification and source localization methods based on deep learning framework[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract [34] 赵洪宝, 刘瑞, 顾涛, 等. 基于深度学习模式的微震信号P波自动拾取方法研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(增刊2): 3084-3097.ZHAO H B, LIU R, GU T, et al. Research on automatic picking method of microseismic signal P-wave based on deep learning mode[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(S2): 3084-3097. (in Chinese with English abstract [35] LI X B, SHANG X Y, WANG Z W, et al. Identifying P-phase arrivals with noise: An improved kurtosis method based on DWT and STA/LTA[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2016, 133: 50-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2016.07.022 [36] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//Anon. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York, USA: IEEE, 2014: 580-587. [37] LI M, TAO G, WANG H, et al. An improved multiscale and leaky P-wave removal analysis for shear-wave anisotropy inversion with crossed-dipole logs[J]. Petrophysics, 2016, 57(3): 270-293. [38] 赵驰, 李辉峰, 赵冲, 等. 三维自适应斜井井间地震高斯束正演数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2022, 37(3): 1228-1234.ZHAO C, LI H F, ZHAO C, et al. Adaptive Gaussian beam forward modeling of crosswell seismic in 3D deviated well[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37(3): 1228-1234. (in Chinese with English abstract [39] 罗浩, 杨飞龙, 李辉峰, 等. 黏弹VTI介质井间地震高斯束波场正演数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(4): 1431-1437.LUO H, YANG F L, LI H F, et al. Forward numerical modeling of cross-well seismic Gaussian beam wave field inviscoelastic VTI media[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2020, 35(4): 1431-1437. (in Chinese with English abstract [40] 徐光宪, 冯春, 马飞. 基于UNet的医学图像分割综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2023, 17(8): 1776-1792.XU G X, FENG C, MA F. Review of medical image segmentation based on UNet[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2023, 17(8): 1776-1792. (in Chinese with English abstract -




 下载:
下载: